Quick Enquiry Form
Categories
- Agile and Scrum (225)
- BigData (36)
- Business Analysis (94)
- Cirtix Client Administration (54)
- Cisco (63)
- Cloud Technology (96)
- Cyber Security (56)
- Data Science and Business Intelligence (53)
- Developement Courses (53)
- DevOps (15)
- Digital Marketing (58)
- Emerging Technology (198)
- IT Service Management (76)
- Microsoft (54)
- Other (395)
- Project Management (502)
- Quality Management (142)
- salesforce (67)
Latest posts
AI Interview Questions You Need..
What Do Hypervisors Do in..
5 Practical Tips to Help..
Free Resources
Subscribe to Newsletter
Learn the basics of data classification for better security
Introduction to Data Classification
Data classification is a method of organizing data to determine how it can be used and interpreted. Data-assigned classification is more accessible and easier to use, but it also increases the possibility of misclassification. Classification can be accomplished in numerous ways. The most common type involves a hierarchical data organization in a database system. This article will introduce you to data classification.
What is Data Classification?
Data classification is assigning and managing data so it can be easily managed and understood. Data classification is used in business, government, and non-profit organizations to improve the quality of their data and make it easier to use.
Data classification is also used during the process of creating a structured database. The data classification system allows easy access to relevant information. This makes it easier for users to find what they are looking for without searching for a large amount of data.
Why is it Important?
Data classification is essential because it allows people to access the correct data. With data classification, all users would have access to all the same information, which could lead to information overload and clarity.
Data classification is an important part of data management. It is the process of determining how data should be stored, managed, and used to meet business needs.
Data classification enables you to organize your data into logical groups that are easy to understand and use. You can then access these groups using a single tool or application. This makes it easier for IT professionals, analysts, and business users to access information about the business in ways that are meaningful for them.
Purpose of Data Classification
Data classification is the process of grouping data into categories and assigning a unique identifier to each class. The purpose of data classification is to allow you to find information more easily and quickly.
For example, if you are looking for information about a specific product, one way to find it is by using keywords in the search engine. This will give you an answer to your question based on the words you used when searching.
However, if you were looking for information about all products in general, this method would not be very effective. The problem with this approach is that it would take too long and require too much effort if applied to every type of product.
The solution to this problem is data classification. Data classification allows you to identify specific categories related to your topic of interest and then use these categories as filters when searching for information related to that topic.
Types of Data Classification
There are three types of data classification:
Classification based on content: This is the most common type of classification. Variety based on content means that the data is classified based on its attributes and characteristics. For example, if a bank records account information about the customer's balances, it will be classified as an account.
Classification based on context: Context-based classification is a more complex method of classifying data because it requires knowledge of how the different attributes can be related to each other within specific contexts. For example, if we know that accounts in our bank are linked to customers, we may want to classify them as such.
Classification based on User: User-based data classification is a way of classifying the data relevant to a particular user. This kind of classification considers the type of user and the purpose for which the data will be used.
Determining Data Risk
Data risk is a generic term that covers the possibility that data may be compromised, altered, or lost. Data risk can occur through various means, including human error and malicious attacks.
Data loss occurs when the contents of a data store are corrupted or destroyed. Data loss can result from physical disasters such as fires and floods, accidental user deletion, or intentional data destruction by hackers.
Data alteration occurs when the integrity of stored data is altered without the consent of its owner. This attack may be carried out by malicious insiders within an organization (e.g., disgruntled employees) or by external agents (e.g., attackers).
Using a Data Classification Matrix
The Data Classification Matrix (DCLM) is a way of categorizing data into four main groups:
Sensitive data can be used to identify an individual and can only be accessed by specific individuals or groups. This is usually associated with personal information, such as medical records, bank details, and your income or savings. The DCLM can help you decide which data should be kept private or shared with specific people.
Non-sensitive data - this type of information is less likely to identify an individual but still contains sensitive information such as names, dates, and locations. Non-sensitive data could include research findings from a scientific study or results from an investigation into a particular problem area.
Sensitive non-personal data - this type of information can be used to identify an individual. Still, it could also include personal details irrelevant to their identity (for example, in a research study).
Personal non-personal data - this type of information does not identify an individual and includes household budgets or purchases made online using your account details and password.
The Data Classification Process
The data classification process involves some steps, which are as follows:
- Identify the type of data and its characteristics
The first step in data classification is identifying the data collection type and how it varies across sources. This information usually comes from an existing list of attributes or variables (see below). But sometimes, it may be challenging to determine which attribute or variable represents something specific about the collection process itself. In these cases, you'll need to make assumptions about the meaning of various attributes or variables based on their context (e.g., "customer name" might indicate whether they're male or female).
- Define classes based on the type of data.
It must be done carefully because it will determine how the data will be processed and stored. An excellent way to do this is by observing the information types found and then grouping them into different categories.
- Construct a model that can be used in classifying data.
After defining the classes, one must come up with a model to classify data. This could be a rule or algorithm that will classify each piece of information into one or more specific categories.
- Test models using the simulation method
This is done to test whether the model is working or not. For this, we need to make use of a model which has been created by the developer and then try it.
- Make final decisions on classifications.
At this stage, we need to make a final decision on which category each variable belongs to. This decision is based on the results received from testing models and making sure that they are valid, reliable, and helpful in making predictions.
Benefits of Data Classification
The benefits of data classification are:
- It helps you to focus on the most important things.
- It helps you to prioritize tasks, which makes it easier to manage your time.
- You can use classification schemes to set up project plan milestones and deadlines.
- You can use classification schemes for reporting purposes.
- It helps you to communicate information in a way that is easy for others to understand.
- By classifying your data, you can develop an understanding of how your data relates to each other in different ways; this will allow you to analyze relationships between variables and make better decisions based on research using statistics or other methods of analysis.
We hope you found this helpful resource and helped you understand the basics of data classification. But, more importantly, we hope it inspires you to use it in your job. By classifying your company's data, you can significantly benefit from greater control over that data, making all those processes much more accessible.
Read More
Introduction to Data Classification
Data classification is a method of organizing data to determine how it can be used and interpreted. Data-assigned classification is more accessible and easier to use, but it also increases the possibility of misclassification. Classification can be accomplished in numerous ways. The most common type involves a hierarchical data organization in a database system. This article will introduce you to data classification.
What is Data Classification?
Data classification is assigning and managing data so it can be easily managed and understood. Data classification is used in business, government, and non-profit organizations to improve the quality of their data and make it easier to use.
Data classification is also used during the process of creating a structured database. The data classification system allows easy access to relevant information. This makes it easier for users to find what they are looking for without searching for a large amount of data.
Why is it Important?
Data classification is essential because it allows people to access the correct data. With data classification, all users would have access to all the same information, which could lead to information overload and clarity.
Data classification is an important part of data management. It is the process of determining how data should be stored, managed, and used to meet business needs.
Data classification enables you to organize your data into logical groups that are easy to understand and use. You can then access these groups using a single tool or application. This makes it easier for IT professionals, analysts, and business users to access information about the business in ways that are meaningful for them.
Purpose of Data Classification
Data classification is the process of grouping data into categories and assigning a unique identifier to each class. The purpose of data classification is to allow you to find information more easily and quickly.
For example, if you are looking for information about a specific product, one way to find it is by using keywords in the search engine. This will give you an answer to your question based on the words you used when searching.
However, if you were looking for information about all products in general, this method would not be very effective. The problem with this approach is that it would take too long and require too much effort if applied to every type of product.
The solution to this problem is data classification. Data classification allows you to identify specific categories related to your topic of interest and then use these categories as filters when searching for information related to that topic.
Types of Data Classification
There are three types of data classification:
Classification based on content: This is the most common type of classification. Variety based on content means that the data is classified based on its attributes and characteristics. For example, if a bank records account information about the customer's balances, it will be classified as an account.
Classification based on context: Context-based classification is a more complex method of classifying data because it requires knowledge of how the different attributes can be related to each other within specific contexts. For example, if we know that accounts in our bank are linked to customers, we may want to classify them as such.
Classification based on User: User-based data classification is a way of classifying the data relevant to a particular user. This kind of classification considers the type of user and the purpose for which the data will be used.
Determining Data Risk
Data risk is a generic term that covers the possibility that data may be compromised, altered, or lost. Data risk can occur through various means, including human error and malicious attacks.
Data loss occurs when the contents of a data store are corrupted or destroyed. Data loss can result from physical disasters such as fires and floods, accidental user deletion, or intentional data destruction by hackers.
Data alteration occurs when the integrity of stored data is altered without the consent of its owner. This attack may be carried out by malicious insiders within an organization (e.g., disgruntled employees) or by external agents (e.g., attackers).
Using a Data Classification Matrix
The Data Classification Matrix (DCLM) is a way of categorizing data into four main groups:
Sensitive data can be used to identify an individual and can only be accessed by specific individuals or groups. This is usually associated with personal information, such as medical records, bank details, and your income or savings. The DCLM can help you decide which data should be kept private or shared with specific people.
Non-sensitive data - this type of information is less likely to identify an individual but still contains sensitive information such as names, dates, and locations. Non-sensitive data could include research findings from a scientific study or results from an investigation into a particular problem area.
Sensitive non-personal data - this type of information can be used to identify an individual. Still, it could also include personal details irrelevant to their identity (for example, in a research study).
Personal non-personal data - this type of information does not identify an individual and includes household budgets or purchases made online using your account details and password.
The Data Classification Process
The data classification process involves some steps, which are as follows:
- Identify the type of data and its characteristics
The first step in data classification is identifying the data collection type and how it varies across sources. This information usually comes from an existing list of attributes or variables (see below). But sometimes, it may be challenging to determine which attribute or variable represents something specific about the collection process itself. In these cases, you'll need to make assumptions about the meaning of various attributes or variables based on their context (e.g., "customer name" might indicate whether they're male or female).
- Define classes based on the type of data.
It must be done carefully because it will determine how the data will be processed and stored. An excellent way to do this is by observing the information types found and then grouping them into different categories.
- Construct a model that can be used in classifying data.
After defining the classes, one must come up with a model to classify data. This could be a rule or algorithm that will classify each piece of information into one or more specific categories.
- Test models using the simulation method
This is done to test whether the model is working or not. For this, we need to make use of a model which has been created by the developer and then try it.
- Make final decisions on classifications.
At this stage, we need to make a final decision on which category each variable belongs to. This decision is based on the results received from testing models and making sure that they are valid, reliable, and helpful in making predictions.
Benefits of Data Classification
The benefits of data classification are:
- It helps you to focus on the most important things.
- It helps you to prioritize tasks, which makes it easier to manage your time.
- You can use classification schemes to set up project plan milestones and deadlines.
- You can use classification schemes for reporting purposes.
- It helps you to communicate information in a way that is easy for others to understand.
- By classifying your data, you can develop an understanding of how your data relates to each other in different ways; this will allow you to analyze relationships between variables and make better decisions based on research using statistics or other methods of analysis.
We hope you found this helpful resource and helped you understand the basics of data classification. But, more importantly, we hope it inspires you to use it in your job. By classifying your company's data, you can significantly benefit from greater control over that data, making all those processes much more accessible.
PMP Exam Prep: Boost your ROI with strategic training!!
PMP Exam Prep: Return on Investment (ROI)
No matter what is at stake – money, time, relationships, customers – we all want to maximize the Return on Investment (ROI) of anything that we invest our time and energy into.
If you're reading this, you're probably someone who has recently taken a Project Management Professional (PMP) exam or is planning on taking one in the next few months.
What is Return on Investment (ROI)?
Return on investment (ROI) is a financial measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an asset or to compare the efficiency of a number of different investments. The ratio is the amount of money gained from the investment divided by the amount invested.
In project management, ROI determines whether a project should be completed or abandoned based on its expected return. The expected return is calculated by multiplying costs by benefits, then dividing it by time.
The formula for ROI is:
Profit / Cost = ROI
For example, if a company spends $10,000 on training and receives $11,000 in additional sales revenue due to the training, its ROI would be 110% ($11,000 - $10,000).
What is ROI used for?
ROI is an essential concept in project management. It stands for "return on investment" and measures the value of something compared to its cost.
You can use ROI to measure the value of a project, such as by comparing the cost of creating a new business process against the benefits it brings to your organization's bottom line.
You can also use ROI to measure a project's effectiveness, such as calculating the return on investment for one year of development work over two years.
Many think that ROI only applies to money spent on projects, but this isn't true. You can calculate an ROI for any resource that returns value to your organization — including time and effort spent on projects.
Benefits of ROI
There are many benefits to using ROI in project management. The most obvious benefit is the ability to measure a project's return on investment (ROI). This metric can be used to determine if a project should be approved or canceled, and it also helps you understand the potential impact of a project on its cost and duration.
Another benefit of using ROI is that it allows you to show that the help of a project outweighs its costs. For example, if you're trying to convince your boss that you need more people on your team, showing how much money your team will make can go a long way toward convincing them.
When used correctly, ROI can help organizations identify areas where they're spending money and resources without seeing results. It can also help identify areas where they're wasting resources but not realizing it until later when costs become too high, or productivity starts dropping off again.
Using ROI as part of your business strategy helps ensure that all projects are evaluated based on whether they provide value for the company rather than just being approved because they sound good at first glance or because someone wants them done quickly so they can move on something; else instead!
Limitations of ROI
The Return on Investment (ROI) is a financial ratio used to measure the efficiency of an investment. It is most often used in capital budgeting to evaluate whether or not a company should invest in a project or not. The calculation involves comparing the cost of an investment to its benefits, expressed as the ratio of benefits over costs.
There are many limitations to using ROI to evaluate projects:
- The calculation of ROI depends on accurate estimates and projections. If the company overestimates the benefits or underestimates the costs, it will get a lower ROI than expected.
- It does not consider future cash flows from the project or any other intangible benefits that may arise from it. For example, suppose your project increases customer satisfaction and loyalty. In that case, it can positively affect future sales and profits, but these won't be reflected in your ROI calculation.
- It doesn't consider risks associated with a project (e.g., technology obsolescence).
Conclusion
The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification is the most widely recognized credential awarded in project management and the only globally-recognized certificate in project management.
All told, it's a pretty good deal. While you should expect to invest time into studying for the exam—the most significant component of any Return on Investment (ROI)—the time required will vary based on your skill level and experience in project management.
You need not necessarily be an expert or an experienced PM, as long as you can demonstrate proficiency with the material. The secret to success is practice and discipline—lots of practice and lots of discipline.
Read More
PMP Exam Prep: Return on Investment (ROI)
No matter what is at stake – money, time, relationships, customers – we all want to maximize the Return on Investment (ROI) of anything that we invest our time and energy into.
If you're reading this, you're probably someone who has recently taken a Project Management Professional (PMP) exam or is planning on taking one in the next few months.
What is Return on Investment (ROI)?
Return on investment (ROI) is a financial measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an asset or to compare the efficiency of a number of different investments. The ratio is the amount of money gained from the investment divided by the amount invested.
In project management, ROI determines whether a project should be completed or abandoned based on its expected return. The expected return is calculated by multiplying costs by benefits, then dividing it by time.
The formula for ROI is:
Profit / Cost = ROI
For example, if a company spends $10,000 on training and receives $11,000 in additional sales revenue due to the training, its ROI would be 110% ($11,000 - $10,000).
What is ROI used for?
ROI is an essential concept in project management. It stands for "return on investment" and measures the value of something compared to its cost.
You can use ROI to measure the value of a project, such as by comparing the cost of creating a new business process against the benefits it brings to your organization's bottom line.
You can also use ROI to measure a project's effectiveness, such as calculating the return on investment for one year of development work over two years.
Many think that ROI only applies to money spent on projects, but this isn't true. You can calculate an ROI for any resource that returns value to your organization — including time and effort spent on projects.
Benefits of ROI
There are many benefits to using ROI in project management. The most obvious benefit is the ability to measure a project's return on investment (ROI). This metric can be used to determine if a project should be approved or canceled, and it also helps you understand the potential impact of a project on its cost and duration.
Another benefit of using ROI is that it allows you to show that the help of a project outweighs its costs. For example, if you're trying to convince your boss that you need more people on your team, showing how much money your team will make can go a long way toward convincing them.
When used correctly, ROI can help organizations identify areas where they're spending money and resources without seeing results. It can also help identify areas where they're wasting resources but not realizing it until later when costs become too high, or productivity starts dropping off again.
Using ROI as part of your business strategy helps ensure that all projects are evaluated based on whether they provide value for the company rather than just being approved because they sound good at first glance or because someone wants them done quickly so they can move on something; else instead!
Limitations of ROI
The Return on Investment (ROI) is a financial ratio used to measure the efficiency of an investment. It is most often used in capital budgeting to evaluate whether or not a company should invest in a project or not. The calculation involves comparing the cost of an investment to its benefits, expressed as the ratio of benefits over costs.
There are many limitations to using ROI to evaluate projects:
- The calculation of ROI depends on accurate estimates and projections. If the company overestimates the benefits or underestimates the costs, it will get a lower ROI than expected.
- It does not consider future cash flows from the project or any other intangible benefits that may arise from it. For example, suppose your project increases customer satisfaction and loyalty. In that case, it can positively affect future sales and profits, but these won't be reflected in your ROI calculation.
- It doesn't consider risks associated with a project (e.g., technology obsolescence).
Conclusion
The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification is the most widely recognized credential awarded in project management and the only globally-recognized certificate in project management.
All told, it's a pretty good deal. While you should expect to invest time into studying for the exam—the most significant component of any Return on Investment (ROI)—the time required will vary based on your skill level and experience in project management.
You need not necessarily be an expert or an experienced PM, as long as you can demonstrate proficiency with the material. The secret to success is practice and discipline—lots of practice and lots of discipline.
Top 15 Agile interview questions and answers for 2022!!
Top 15 Agile Interview Question and Answers 2022
Q1. What is Agile Methodology?
Agile is a project management methodology that involves breaking up a project into several phases. Teams cycle through planning, execution, and evaluation at every stage. Once the work begins, collaboration with stakeholders is constant.
Q2. How does agile work?
Agile is a software development methodology with many phases, with constant collaboration between stakeholders. It involves continuous improvement at every stage of the process, and team cycle through planning, executing, and evaluating.
Q3. What are the values of agile?
-
individuals and interactions over processes and tools
-
working software over comprehensive documentation
-
customer collaboration over contract negotiation
-
Responding to change over following a plan.
Q4. What are the best practices of Agile Methodology?
-
Visualizing Workflows.
-
Iterative Development
-
Using Professional Tools
-
Daily Meetings
-
Use Burndown Charts for Sprints
-
Creating Product Backlog and Product Vision Together
-
Practicing Stand-Ups
-
Setting communication guidelines for teams
Q5. Are agile and lean the same?
Lean management promotes the idea of work cells, where teams can complete projects in a more connected way, making them less prone to delay. Similarly, the agile methodology focuses on concepts such as cross-functional teams and flow-to-work pools.
Q6. Why is agile certification necessary?
Agile certifications give working professionals knowledge and authority over Agile practices. They can then use this expertise to implement Agile practices within their organization, leading to a higher pay package or salary.
Q7. How do you implement Agile?
-
Get the stakeholders to sign off on the plan.
-
Start with one thing you can do today.
-
Focus on inspiring and helping your team to succeed.
-
Choose a framework, and then stick with it.
-
Make changes to improve the work.
Q8. Are agile certifications worth it?
Getting Agile certification can help you get a promotion or change jobs. Certification often translates into higher salaries and is worth the time and money to obtain these certifications. In addition, many companies pay for the training of their employees, so they can get them certified.
Q9. What are the benefits of the agile process?
-
Customer satisfaction.
-
Superior quality product.
-
Reduced risks.
-
Better control.
-
Increased flexibility.
-
It improved project predictability.
-
Continuous improvement.
-
It improved team morale.
Q10. What are some of the biggest mistakes Agile teams make?
One of the most common mistakes when teams are forming new agile projects, is that managers tend to form groups in the same way they formed traditional projects. As a result, they have a really big team that includes many people who have minimal roles.
Q11. What is the difference between a project manager and a Scrum Master?
A Scrum Master is a person who ensures that their team is following Scrum principles. At the same time, a project manager oversees the entirety of a project, including logistics like budget and risk. A Scrum master may also be a project manager, but they are not the same thing.
Q12. How do Agile and DevOps interrelate?
While Agile controls software development, DevOps brings the code into production and enhances the process. Both approaches are critical characteristics of the software development life cycle.
Q13. What is Kanban?
Kanban is a popular Lean workflow management method for visualizing, managing and improving knowledge work. It helps you maximize efficiency, handle even the most complex projects in a single environment, and improve continuously.
Q14. What are the 12 Principles of Agile?
-
Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software.
-
Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer's competitive advantage.
-
Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference for the shorter timescale.
-
Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project.
-
Build projects around motivated individuals. Please give them the environment and support they need, and trust them to get the job done.
-
The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation.
-
Working software is the primary measure of progress.
-
Agile processes promote sustainable development. The sponsors, developers, and users should be able to maintain a constant pace indefinitely.
-
Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility.
-
Simplicity--the art of maximizing the amount of work not done--is essential.
-
The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.
-
At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
Q15. What are the three critical roles in a Scrum framework?
Scrum has three roles: product owner, scrum master, and development team members. For the most part, the job titles don't need to change when transitioning to Scrum. However, some organizations find it helpful to modify the tags slightly to reflect their new role in Scrum better.
Read More
Top 15 Agile Interview Question and Answers 2022
Q1. What is Agile Methodology?
Agile is a project management methodology that involves breaking up a project into several phases. Teams cycle through planning, execution, and evaluation at every stage. Once the work begins, collaboration with stakeholders is constant.
Q2. How does agile work?
Agile is a software development methodology with many phases, with constant collaboration between stakeholders. It involves continuous improvement at every stage of the process, and team cycle through planning, executing, and evaluating.
Q3. What are the values of agile?
-
individuals and interactions over processes and tools
-
working software over comprehensive documentation
-
customer collaboration over contract negotiation
-
Responding to change over following a plan.
Q4. What are the best practices of Agile Methodology?
-
Visualizing Workflows.
-
Iterative Development
-
Using Professional Tools
-
Daily Meetings
-
Use Burndown Charts for Sprints
-
Creating Product Backlog and Product Vision Together
-
Practicing Stand-Ups
-
Setting communication guidelines for teams
Q5. Are agile and lean the same?
Lean management promotes the idea of work cells, where teams can complete projects in a more connected way, making them less prone to delay. Similarly, the agile methodology focuses on concepts such as cross-functional teams and flow-to-work pools.
Q6. Why is agile certification necessary?
Agile certifications give working professionals knowledge and authority over Agile practices. They can then use this expertise to implement Agile practices within their organization, leading to a higher pay package or salary.
Q7. How do you implement Agile?
-
Get the stakeholders to sign off on the plan.
-
Start with one thing you can do today.
-
Focus on inspiring and helping your team to succeed.
-
Choose a framework, and then stick with it.
-
Make changes to improve the work.
Q8. Are agile certifications worth it?
Getting Agile certification can help you get a promotion or change jobs. Certification often translates into higher salaries and is worth the time and money to obtain these certifications. In addition, many companies pay for the training of their employees, so they can get them certified.
Q9. What are the benefits of the agile process?
-
Customer satisfaction.
-
Superior quality product.
-
Reduced risks.
-
Better control.
-
Increased flexibility.
-
It improved project predictability.
-
Continuous improvement.
-
It improved team morale.
Q10. What are some of the biggest mistakes Agile teams make?
One of the most common mistakes when teams are forming new agile projects, is that managers tend to form groups in the same way they formed traditional projects. As a result, they have a really big team that includes many people who have minimal roles.
Q11. What is the difference between a project manager and a Scrum Master?
A Scrum Master is a person who ensures that their team is following Scrum principles. At the same time, a project manager oversees the entirety of a project, including logistics like budget and risk. A Scrum master may also be a project manager, but they are not the same thing.
Q12. How do Agile and DevOps interrelate?
While Agile controls software development, DevOps brings the code into production and enhances the process. Both approaches are critical characteristics of the software development life cycle.
Q13. What is Kanban?
Kanban is a popular Lean workflow management method for visualizing, managing and improving knowledge work. It helps you maximize efficiency, handle even the most complex projects in a single environment, and improve continuously.
Q14. What are the 12 Principles of Agile?
-
Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software.
-
Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer's competitive advantage.
-
Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference for the shorter timescale.
-
Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project.
-
Build projects around motivated individuals. Please give them the environment and support they need, and trust them to get the job done.
-
The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation.
-
Working software is the primary measure of progress.
-
Agile processes promote sustainable development. The sponsors, developers, and users should be able to maintain a constant pace indefinitely.
-
Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility.
-
Simplicity--the art of maximizing the amount of work not done--is essential.
-
The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.
-
At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
Q15. What are the three critical roles in a Scrum framework?
Scrum has three roles: product owner, scrum master, and development team members. For the most part, the job titles don't need to change when transitioning to Scrum. However, some organizations find it helpful to modify the tags slightly to reflect their new role in Scrum better.
Feasibility Study and Its Importance in Project Management
Table of Content
What is a Feasibility Study?
Why is it important?
What do the results of a feasibility study show?
Benefits of a Feasibility Study
Phases of a Feasibility Study
When to Conduct a Feasibility Study?
What are the steps in a feasibility study?
Purpose of a Feasibility Study?
Conclusion
What is a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study is a business plan that describes how a new idea will be implemented, what resources are needed, and how much it will cost. The term "feasibility" means the study has been done, and the project is possible.
A feasibility study can evaluate an idea's viability before investing substantial time and money into developing it further.
For example, suppose a company has an idea for a new product or service but does not have enough information to make a business case for its development. In that case, it may need to conduct feasibility studies first.
A feasibility study will typically include:
- An evaluation of existing products and services in your market space
- A description of existing clientele and target audience
- Existing competition in your market space (if any)
- Current market conditions and trends (e.g., economic conditions)
- The results from previous feasibility studies on similar projects (if any)
Why is it important?
- A feasibility study is an essential part of project management. It helps in determining whether a project will be successful or not.
- A feasibility study also determines the cost and time element of the project, which are essential to determine whether a project is feasible.
- A feasibility study is essential to determine if a project can be completed on time, within budget, and within scope.
- It also helps determine the number of resources required to complete the project.
What do the results of a feasibility study show?
The results of a feasibility study can show project managers what the project will cost, how long it will take, and which products or services they should produce.
The results give you an idea of what it will take to produce the project, and whether it is worth doing it's not worth doing; There is no point in continuing with it.
If the company wants to build a new factory, it must consider cost, time, and quality before making any decisions. The feasibility study will give them the necessary information to make those decisions.
Benefits of a Feasibility Study
Feasibility studies are essential to project management because they help you evaluate your project against the criteria in your project plan.
A feasibility study is a process that involves evaluating your project against the criteria set out in your project plan. It helps you determine whether the risks and rewards of starting or continuing a project outweigh any potential benefits or costs.
Benefits of Using Feasibility Study in Project Management:
- Feasibility Studies help predict the results of a business, financial or operational activity.
- Feasibility studies help determine whether a business, financial or operational activity can be implemented successfully.
- The results from feasibility studies are used as inputs when making project decisions.
- A feasibility study helps determine whether there would be an increase in profits by implementing a new product line or service offered by an organization.
Phases of a Feasibility Study
The phases of a feasibility study are:
Pre-Feasibility Study
In this stage, you will need to establish the project objectives and determine if it is possible to achieve them. This is done by gathering information about the market, competitors, customers, and other relevant information. It would help if you also considered the financial implications of your project and how best to finance it.
Feasibility Study
The feasibility study phase looks at your proposed project's feasibility from an economic point of view, considering such things as investment costs, financing arrangements, technical specifications, and related costs. You can also conduct surveys with potential partners or suppliers for their opinions on whether or not they would participate in the project.
Scoping Study
The scoping study phase involves gathering information about your proposed project and identifying all its essential aspects. Then, it determines the scope and cost of each component of the project. The purpose of this phase is to provide you with a clear idea of how much time and effort you need to put into each component of the project so that you can ensure that everything fits into one schedule as far as possible.
Detailed Feasibility Study
A detailed feasibility study is a process that helps you to understand the pros and cons of your idea. In this study, you will be able to identify whether your idea is financially viable or not.
You can use this study as a guide for future projects. By doing this, you will be able to plan and avoid unnecessary expenses in the future.
When to Conduct a Feasibility Study?
It is essential to conduct feasibility studies, especially when starting a new project. This is because the availability of resources and the costs will determine whether the project can be completed successfully.
Projects that are too big, too high-risk, or too complex for the budget cannot be carried out successfully. A feasibility study will help you establish whether or not your project has been planned correctly and how it can be achieved based on available resources.
You should also conduct feasibility studies if you want to implement new technology, such as a new software application or web platform. In this case, you need to determine whether or not your business can adopt this new technology and if it meets your needs.
What are the steps in a feasibility study?
The steps in a feasibility study are:
Conduct a Preliminary Analysis
The purpose of this step is to identify the need for further investigation. You need to determine if the project will be profitable or if it will have a negative impact on your company's finances. The reason that you should conduct a preliminary analysis is that you want to make sure that any project will have a positive impact on your company's bottom line.
Prepare a Projected Income Statement
The projected income statement shows what you expect to earn from the completed project and how much of that you expect to spend on materials, labor, and other costs. If you're going to spend $10,000 on materials but only expect $6,000 in revenue from selling the completed product, then your projected income statement would look like this:
$10,000 - $6,000 = $4,000
You can use this projected income statement later in the planning process when it comes time to determine how much money is available for spending on additional projects.
Conduct a Market Survey
The first step in a feasibility study is to conduct market research. This will help you understand your customers, competitors, and the market as a whole. You can also use this information to determine how much of your business you can expect to generate and how much it will cost to produce.
Plan Business Organization and Operations
Once you have gathered all the information you need, you must decide on the business model for your new venture. This involves determining what type of organization will work best for your experience. Combining two or more models may be necessary to create a successful business plan.
Determine Marketing and Sales Strategies
Your next step is determining how much money you need for marketing and sales strategies. It would help if you also considered how much money will be required for advertising and other promotional activities. Once you have determined these numbers, it's time to develop marketing strategies that will help drive sales and maximize profits at launch time.
Review and Analyze All Data
The most important part of your feasibility study is to review and analyze all your data. You want to ensure that you have collected enough data, that the data are correct and that there are no missing or incorrect pieces of information in your information collection process. This can be done by using a checklist or by having someone else review the data with you and ensure that everything is accurate and up-to-date.
Make a Go/No-Go Decision
After reviewing all your data, it's time to decide whether or not this idea will work for your business plan. You may determine that this project does not fit your current schedule or budget. Still, you do want to keep it on file as an option for future consideration. For example, suppose this project does not fit your current schedule, budget, or timeline. In that case, you should move on with another idea (or ideas).
Purpose of a Feasibility Study
The purpose of a feasibility study is to analyze the business and technical requirements of an idea. In addition, the study helps determine if there is a market for the developed product or service.
A feasibility study also looks at all aspects of the project, including finances and management skills.
The feasibility study should be performed by someone who knows about the particular field and industry.
The person conducting the survey should be able to answer questions like "What are the advantages of this particular idea?" and "Is this something that people will want?"
Conclusion
A feasibility study is a preliminary assessment to determine if the project can succeed. This usually involves a thorough analysis of the objectives and requirements, examining the available resources and constraints, and some financial assessment or projection.
In most cases, a feasibility study will identify potential problems before they occur, saving valuable time and money in the long run. After all, with so many options on the table, it's always better to make an educated decision than risk a potentially poor or unsuccessful outcome.
Read More
Table of Content
What is a Feasibility Study?
Why is it important?
What do the results of a feasibility study show?
Benefits of a Feasibility Study
Phases of a Feasibility Study
When to Conduct a Feasibility Study?
What are the steps in a feasibility study?
Purpose of a Feasibility Study?
Conclusion
What is a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study is a business plan that describes how a new idea will be implemented, what resources are needed, and how much it will cost. The term "feasibility" means the study has been done, and the project is possible.
A feasibility study can evaluate an idea's viability before investing substantial time and money into developing it further.
For example, suppose a company has an idea for a new product or service but does not have enough information to make a business case for its development. In that case, it may need to conduct feasibility studies first.
A feasibility study will typically include:
- An evaluation of existing products and services in your market space
- A description of existing clientele and target audience
- Existing competition in your market space (if any)
- Current market conditions and trends (e.g., economic conditions)
- The results from previous feasibility studies on similar projects (if any)
Why is it important?
- A feasibility study is an essential part of project management. It helps in determining whether a project will be successful or not.
- A feasibility study also determines the cost and time element of the project, which are essential to determine whether a project is feasible.
- A feasibility study is essential to determine if a project can be completed on time, within budget, and within scope.
- It also helps determine the number of resources required to complete the project.
What do the results of a feasibility study show?
The results of a feasibility study can show project managers what the project will cost, how long it will take, and which products or services they should produce.
The results give you an idea of what it will take to produce the project, and whether it is worth doing it's not worth doing; There is no point in continuing with it.
If the company wants to build a new factory, it must consider cost, time, and quality before making any decisions. The feasibility study will give them the necessary information to make those decisions.
Benefits of a Feasibility Study
Feasibility studies are essential to project management because they help you evaluate your project against the criteria in your project plan.
A feasibility study is a process that involves evaluating your project against the criteria set out in your project plan. It helps you determine whether the risks and rewards of starting or continuing a project outweigh any potential benefits or costs.
Benefits of Using Feasibility Study in Project Management:
- Feasibility Studies help predict the results of a business, financial or operational activity.
- Feasibility studies help determine whether a business, financial or operational activity can be implemented successfully.
- The results from feasibility studies are used as inputs when making project decisions.
- A feasibility study helps determine whether there would be an increase in profits by implementing a new product line or service offered by an organization.
Phases of a Feasibility Study
The phases of a feasibility study are:
Pre-Feasibility Study
In this stage, you will need to establish the project objectives and determine if it is possible to achieve them. This is done by gathering information about the market, competitors, customers, and other relevant information. It would help if you also considered the financial implications of your project and how best to finance it.
Feasibility Study
The feasibility study phase looks at your proposed project's feasibility from an economic point of view, considering such things as investment costs, financing arrangements, technical specifications, and related costs. You can also conduct surveys with potential partners or suppliers for their opinions on whether or not they would participate in the project.
Scoping Study
The scoping study phase involves gathering information about your proposed project and identifying all its essential aspects. Then, it determines the scope and cost of each component of the project. The purpose of this phase is to provide you with a clear idea of how much time and effort you need to put into each component of the project so that you can ensure that everything fits into one schedule as far as possible.
Detailed Feasibility Study
A detailed feasibility study is a process that helps you to understand the pros and cons of your idea. In this study, you will be able to identify whether your idea is financially viable or not.
You can use this study as a guide for future projects. By doing this, you will be able to plan and avoid unnecessary expenses in the future.
When to Conduct a Feasibility Study?
It is essential to conduct feasibility studies, especially when starting a new project. This is because the availability of resources and the costs will determine whether the project can be completed successfully.
Projects that are too big, too high-risk, or too complex for the budget cannot be carried out successfully. A feasibility study will help you establish whether or not your project has been planned correctly and how it can be achieved based on available resources.
You should also conduct feasibility studies if you want to implement new technology, such as a new software application or web platform. In this case, you need to determine whether or not your business can adopt this new technology and if it meets your needs.
What are the steps in a feasibility study?
The steps in a feasibility study are:
Conduct a Preliminary Analysis
The purpose of this step is to identify the need for further investigation. You need to determine if the project will be profitable or if it will have a negative impact on your company's finances. The reason that you should conduct a preliminary analysis is that you want to make sure that any project will have a positive impact on your company's bottom line.
Prepare a Projected Income Statement
The projected income statement shows what you expect to earn from the completed project and how much of that you expect to spend on materials, labor, and other costs. If you're going to spend $10,000 on materials but only expect $6,000 in revenue from selling the completed product, then your projected income statement would look like this:
$10,000 - $6,000 = $4,000
You can use this projected income statement later in the planning process when it comes time to determine how much money is available for spending on additional projects.
Conduct a Market Survey
The first step in a feasibility study is to conduct market research. This will help you understand your customers, competitors, and the market as a whole. You can also use this information to determine how much of your business you can expect to generate and how much it will cost to produce.
Plan Business Organization and Operations
Once you have gathered all the information you need, you must decide on the business model for your new venture. This involves determining what type of organization will work best for your experience. Combining two or more models may be necessary to create a successful business plan.
Determine Marketing and Sales Strategies
Your next step is determining how much money you need for marketing and sales strategies. It would help if you also considered how much money will be required for advertising and other promotional activities. Once you have determined these numbers, it's time to develop marketing strategies that will help drive sales and maximize profits at launch time.
Review and Analyze All Data
The most important part of your feasibility study is to review and analyze all your data. You want to ensure that you have collected enough data, that the data are correct and that there are no missing or incorrect pieces of information in your information collection process. This can be done by using a checklist or by having someone else review the data with you and ensure that everything is accurate and up-to-date.
Make a Go/No-Go Decision
After reviewing all your data, it's time to decide whether or not this idea will work for your business plan. You may determine that this project does not fit your current schedule or budget. Still, you do want to keep it on file as an option for future consideration. For example, suppose this project does not fit your current schedule, budget, or timeline. In that case, you should move on with another idea (or ideas).
Purpose of a Feasibility Study
The purpose of a feasibility study is to analyze the business and technical requirements of an idea. In addition, the study helps determine if there is a market for the developed product or service.
A feasibility study also looks at all aspects of the project, including finances and management skills.
The feasibility study should be performed by someone who knows about the particular field and industry.
The person conducting the survey should be able to answer questions like "What are the advantages of this particular idea?" and "Is this something that people will want?"
Conclusion
A feasibility study is a preliminary assessment to determine if the project can succeed. This usually involves a thorough analysis of the objectives and requirements, examining the available resources and constraints, and some financial assessment or projection.
In most cases, a feasibility study will identify potential problems before they occur, saving valuable time and money in the long run. After all, with so many options on the table, it's always better to make an educated decision than risk a potentially poor or unsuccessful outcome.
Craft Your Project Management Plan Now: Step-by-Step Guide
How to Create Project Management Plan?
What is a Project Management Plan?
A project management plan (PMP) is a document that provides a high-level overview of the activities and deliverables required to complete a project. It is created before a project begins and provides an ordered list of tasks, milestones, and deliverables for the entire project duration.
This document aims to help you identify all the things that need to be done to complete your project successfully. In addition, it will give you an idea of how long it will take, who will be responsible for each task, and how much time each person needs to spend on it.
It can also help you identify risks associated with your project to plan for these potential problems ahead of time.
Use of Project Management Plan
The Project Management Plan (PMP) is an essential component of the project management process. The purpose of the PMP is to document and organize all necessary information related to a project's goals, objectives, tasks, and actions.
The PMP should be structured to facilitate communication between all parties involved in the project. It serves as a reference tool that can be used by everyone involved with the task at any point throughout its duration.
The PMP should contain relevant information about your company's capabilities, resources, and specific business goals for each project stage. The plan should also include detailed descriptions of each task or activity that needs to be completed by each team member on your team before moving on to another stage of work within your project timeline.
This plan should also include an estimate of how much time each item will take to complete based on your team members' experience levels and job responsibilities within your organization. This estimate will help you determine which tasks are most important first so that you can allocate more time towards these tasks while keeping other areas on track with their deadlines.
Components of a Project Management Plan
A PMP is a way for project managers to communicate with the project, define the project's scope and manage it. A PMP consists of five essential components:
Project Description: This is the primary document that describes the purpose and objective of your project to the stakeholders. Hence, they understand why you are undertaking it. It should include all relevant information about who you are working with and where you will be working from.
Planning Process: The planning process includes setting goals, identifying risks, identifying resources, and determining an approach to meet those goals. The plan should also include milestones along the way and contingency plans in case things don't go according to plan.
Organizational Structure: The organizational structure includes roles and responsibilities for each team member—whether employees or contractors — and how those roles will be divided among them.
Resources: The resources section details what kind of resources are required for each task to complete your project successfully. This includes people and equipment needed for specific tasks and funds allocated for certain tasks or projects (e.g., materials).
Milestones: These are specific targets or deadlines that must be met for the project to be completed successfully. Each milestone must have an established date and time frame and a corresponding budget for the resources needed to complete it.
The Importance of Project Management Planning
Project management planning is an essential project management skill. It helps the project manager to plan the execution of a project. In addition, it helps in determining the sequence of activities that need to be performed. The main benefits of this skill are:
- It gives an overview of all activities that need to be performed before starting any task or activity.
- It allows you to anticipate issues that may arise during the execution phase of your project.
- It also helps you to plan for dependencies that may arise between tasks and activities.
- It allows you to manage risks associated with your project using several tools and techniques such as a risk register, contingency plan, etc.
How to Make a Project Plan
A project plan is the cornerstone of your project. It is a document that explains how you will achieve your goals when you will do it, and what resources you need to get it done.
Project plans are written in a particular format and include several essential elements:
Executive summary: A one-sentence overview of the project, including its goals and objectives.
Background: A brief description of why this project is necessary or needed.
Scope statement: A detailed list that describes what the project will include (scope) and excludes (exclusions).
Requirements definition: How you'll figure out what's needed for the project to succeed.
Assumptions and constraints: The things that might prevent your success — such as assumptions about time frame or cost — along with any external limitations such as budget or regulatory compliance requirements.
Stakeholder analysis: Who needs to be involved for this project to succeed? How much influence do they have over its success? Who is most influential? What are their motivations — financial, political, and social— for getting involved in this project? What are their goals related to this project? What do they expect from it?
Work breakdown structure: The work breakdown structure is one of the essential elements of any project management system. It is a hierarchical list of all the major tasks needed to complete the project. It allows you to break down the larger tasks into smaller and more manageable pieces so they can be assigned to team members or individual contributors.
Conclusion
The project management plan is a crucial component of any project. This planning document details steps and resources needed, tasks to complete, timelines, and potential issues to prepare for. If you are working on a project for the first time, it can help to have an established template to guide you on what needs to be completed and when.
Read More
How to Create Project Management Plan?
What is a Project Management Plan?
A project management plan (PMP) is a document that provides a high-level overview of the activities and deliverables required to complete a project. It is created before a project begins and provides an ordered list of tasks, milestones, and deliverables for the entire project duration.
This document aims to help you identify all the things that need to be done to complete your project successfully. In addition, it will give you an idea of how long it will take, who will be responsible for each task, and how much time each person needs to spend on it.
It can also help you identify risks associated with your project to plan for these potential problems ahead of time.
Use of Project Management Plan
The Project Management Plan (PMP) is an essential component of the project management process. The purpose of the PMP is to document and organize all necessary information related to a project's goals, objectives, tasks, and actions.
The PMP should be structured to facilitate communication between all parties involved in the project. It serves as a reference tool that can be used by everyone involved with the task at any point throughout its duration.
The PMP should contain relevant information about your company's capabilities, resources, and specific business goals for each project stage. The plan should also include detailed descriptions of each task or activity that needs to be completed by each team member on your team before moving on to another stage of work within your project timeline.
This plan should also include an estimate of how much time each item will take to complete based on your team members' experience levels and job responsibilities within your organization. This estimate will help you determine which tasks are most important first so that you can allocate more time towards these tasks while keeping other areas on track with their deadlines.
Components of a Project Management Plan
A PMP is a way for project managers to communicate with the project, define the project's scope and manage it. A PMP consists of five essential components:
Project Description: This is the primary document that describes the purpose and objective of your project to the stakeholders. Hence, they understand why you are undertaking it. It should include all relevant information about who you are working with and where you will be working from.
Planning Process: The planning process includes setting goals, identifying risks, identifying resources, and determining an approach to meet those goals. The plan should also include milestones along the way and contingency plans in case things don't go according to plan.
Organizational Structure: The organizational structure includes roles and responsibilities for each team member—whether employees or contractors — and how those roles will be divided among them.
Resources: The resources section details what kind of resources are required for each task to complete your project successfully. This includes people and equipment needed for specific tasks and funds allocated for certain tasks or projects (e.g., materials).
Milestones: These are specific targets or deadlines that must be met for the project to be completed successfully. Each milestone must have an established date and time frame and a corresponding budget for the resources needed to complete it.
The Importance of Project Management Planning
Project management planning is an essential project management skill. It helps the project manager to plan the execution of a project. In addition, it helps in determining the sequence of activities that need to be performed. The main benefits of this skill are:
- It gives an overview of all activities that need to be performed before starting any task or activity.
- It allows you to anticipate issues that may arise during the execution phase of your project.
- It also helps you to plan for dependencies that may arise between tasks and activities.
- It allows you to manage risks associated with your project using several tools and techniques such as a risk register, contingency plan, etc.
How to Make a Project Plan
A project plan is the cornerstone of your project. It is a document that explains how you will achieve your goals when you will do it, and what resources you need to get it done.
Project plans are written in a particular format and include several essential elements:
Executive summary: A one-sentence overview of the project, including its goals and objectives.
Background: A brief description of why this project is necessary or needed.
Scope statement: A detailed list that describes what the project will include (scope) and excludes (exclusions).
Requirements definition: How you'll figure out what's needed for the project to succeed.
Assumptions and constraints: The things that might prevent your success — such as assumptions about time frame or cost — along with any external limitations such as budget or regulatory compliance requirements.
Stakeholder analysis: Who needs to be involved for this project to succeed? How much influence do they have over its success? Who is most influential? What are their motivations — financial, political, and social— for getting involved in this project? What are their goals related to this project? What do they expect from it?
Work breakdown structure: The work breakdown structure is one of the essential elements of any project management system. It is a hierarchical list of all the major tasks needed to complete the project. It allows you to break down the larger tasks into smaller and more manageable pieces so they can be assigned to team members or individual contributors.
Conclusion
The project management plan is a crucial component of any project. This planning document details steps and resources needed, tasks to complete, timelines, and potential issues to prepare for. If you are working on a project for the first time, it can help to have an established template to guide you on what needs to be completed and when.
High-Paying Careers in the USA for 2022: Top Lucrative Jobs
Highest Paying Jobs in USA in 2022
Nowadays, technology plays a significant role in human life. We can't imagine our life without technology. In recent years, the trend of learning IT skills has increased dramatically.
More and more people are working as web developers, software developers, etc. Technology is developing with innovations and discoveries every other day. We've pulled the data to bring you our list of the highest-paying tech jobs in 2022.
Data Scientist
A data scientist is a professional who uses statistics, predictive analytics, and other data-driven methods to create models that businesses can use. Data scientists often use programming languages like Python and SQL (structured query language) to analyze massive datasets and uncover patterns.
Full-Stack Developer
Full-stack developers have a broad range of technical skills that allow them to work on multiple parts of a web application simultaneously — from back-end coding using JavaScript or Ruby on Rails to front-end development using HTML5 or CSS3. This makes them an invaluable asset to organizations who need their websites rebuilt from scratch or want to start building mobile apps and desktop ones.
Software Engineering Manager
Software engineering managers typically plan, coordinate, and direct software engineering projects or systems within an organization. They develop strategies and plans to improve systems that are already in place or design new software based on current needs. These professionals must comprehensively understand technology, including programming languages and other tools used by developers.
Software engineering managers typically need a bachelor's degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field. Project management certification is also beneficial.
Data Security Analyst
Data security analysts use their knowledge of data administration, operating systems, and networking to ensure that companies' data is kept safe from outside sources.
In addition, they may work with firewalls and encryption systems to protect networks from unauthorized access by hackers or cybercriminals. These professionals generally work full time during regular business hours at an office location; however, some positions require availability during off-hours add weekends in case of emergencies or unexpected security systems issues.
DevOps Engineer
DevOps Engineers work in a collaborative environment to improve the development and release of software products. They work with software developers to troubleshoot problems and ensure that new releases are successful.
DevOps Engineers use automation tools to optimize the deployment of applications, which allows them to scale up quickly to meet growing demands on their projects. This role requires a high level of technical expertise, analytical skills, and strong interpersonal skills for working with clients and colleagues.
Blockchain Engineer
Block Chain Engineers design, build and maintain blockchain networks. They may also help organizations develop blockchain strategies and manage regulatory compliance issues related to cryptocurrencies. This role requires extensive knowledge of cryptography and computer science fundamentals and experience working with blockchain platforms such as Ethereum or Hyperledger Fabric.
Software Architect
A software architect is responsible for designing software systems that are both functional and easy to use. They must also manage all aspects of software development projects, including budgeting, testing, and implementation. Software architects usually need a bachelor's degree in computer science or a related field, along with several years of experience working on projects within the industry.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Engineer
Artificial intelligence is becoming more and more critical for the future of technology. While it currently exists in many forms and applications, it will only continue to grow and develop over the next decade.
AI engineers are professionals who work with artificial intelligence systems, creating new algorithms and improving existing ones. These professionals typically need a bachelor's degree in computer science or a related field and several years of experience working with computers.
Product Manager
Product managers are responsible for managing the development of a product or service from conception through its launch. They work in conjunction with other team members to ensure that all aspects of development are handled properly and efficiently.
Product managers are usually required to have at least a bachelor's degree in business administration or marketing and some experience in software development or design.
Cloud Architect
Cloud architects design cloud solutions based on client specifications and requirements while taking into consideration scalability, security, and performance factors related to the cloud platform being used by clients or organizations working with them on specific projects or initiatives involving cloud computing solutions
Big Data Engineer
A big data engineer is responsible for developing data warehouses, data lakes, and other analytical systems. Big data engineers are tasked with analyzing large amounts of unstructured information to make the correct decisions. They use various tools and techniques to manipulate large datasets and create new insights. They must be able to work in teams and independently on different projects.
IT Manager
An IT manager manages all aspects of an organization's information technology (IT). They are responsible for planning, implementing, and maintaining technology solutions that meet the needs of their company's goals and objectives. They are typically required to have a bachelor's degree in computer science or a related field.
Jobs
Average Salary
Data Scientist
$150,000
Full-Stack Developer
$106,000
Software Engineering Manager
$134,156
Data Security Analyst
$71,226
DevOps Engineer
$140,000
Block Chain Engineer
$150,000
Software Architect
$114,000
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Engineer
$110,000
Product Manager
$100,000
Cloud Architect
$107,000
Big Data Engineer
$140,000
IT Manager
$100,000
Technology professionals are in high demand and are making a lot of money. I hope this article helps you find the technology job that is best for you. The above-average salary is just indicative, and these numbers can vary hugely based on years of work experience.
Read More
Highest Paying Jobs in USA in 2022
Nowadays, technology plays a significant role in human life. We can't imagine our life without technology. In recent years, the trend of learning IT skills has increased dramatically.
More and more people are working as web developers, software developers, etc. Technology is developing with innovations and discoveries every other day. We've pulled the data to bring you our list of the highest-paying tech jobs in 2022.
Data Scientist
A data scientist is a professional who uses statistics, predictive analytics, and other data-driven methods to create models that businesses can use. Data scientists often use programming languages like Python and SQL (structured query language) to analyze massive datasets and uncover patterns.
Full-Stack Developer
Full-stack developers have a broad range of technical skills that allow them to work on multiple parts of a web application simultaneously — from back-end coding using JavaScript or Ruby on Rails to front-end development using HTML5 or CSS3. This makes them an invaluable asset to organizations who need their websites rebuilt from scratch or want to start building mobile apps and desktop ones.
Software Engineering Manager
Software engineering managers typically plan, coordinate, and direct software engineering projects or systems within an organization. They develop strategies and plans to improve systems that are already in place or design new software based on current needs. These professionals must comprehensively understand technology, including programming languages and other tools used by developers.
Software engineering managers typically need a bachelor's degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field. Project management certification is also beneficial.
Data Security Analyst
Data security analysts use their knowledge of data administration, operating systems, and networking to ensure that companies' data is kept safe from outside sources.
In addition, they may work with firewalls and encryption systems to protect networks from unauthorized access by hackers or cybercriminals. These professionals generally work full time during regular business hours at an office location; however, some positions require availability during off-hours add weekends in case of emergencies or unexpected security systems issues.
DevOps Engineer
DevOps Engineers work in a collaborative environment to improve the development and release of software products. They work with software developers to troubleshoot problems and ensure that new releases are successful.
DevOps Engineers use automation tools to optimize the deployment of applications, which allows them to scale up quickly to meet growing demands on their projects. This role requires a high level of technical expertise, analytical skills, and strong interpersonal skills for working with clients and colleagues.
Blockchain Engineer
Block Chain Engineers design, build and maintain blockchain networks. They may also help organizations develop blockchain strategies and manage regulatory compliance issues related to cryptocurrencies. This role requires extensive knowledge of cryptography and computer science fundamentals and experience working with blockchain platforms such as Ethereum or Hyperledger Fabric.
Software Architect
A software architect is responsible for designing software systems that are both functional and easy to use. They must also manage all aspects of software development projects, including budgeting, testing, and implementation. Software architects usually need a bachelor's degree in computer science or a related field, along with several years of experience working on projects within the industry.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Engineer
Artificial intelligence is becoming more and more critical for the future of technology. While it currently exists in many forms and applications, it will only continue to grow and develop over the next decade.
AI engineers are professionals who work with artificial intelligence systems, creating new algorithms and improving existing ones. These professionals typically need a bachelor's degree in computer science or a related field and several years of experience working with computers.
Product Manager
Product managers are responsible for managing the development of a product or service from conception through its launch. They work in conjunction with other team members to ensure that all aspects of development are handled properly and efficiently.
Product managers are usually required to have at least a bachelor's degree in business administration or marketing and some experience in software development or design.
Cloud Architect
Cloud architects design cloud solutions based on client specifications and requirements while taking into consideration scalability, security, and performance factors related to the cloud platform being used by clients or organizations working with them on specific projects or initiatives involving cloud computing solutions
Big Data Engineer
A big data engineer is responsible for developing data warehouses, data lakes, and other analytical systems. Big data engineers are tasked with analyzing large amounts of unstructured information to make the correct decisions. They use various tools and techniques to manipulate large datasets and create new insights. They must be able to work in teams and independently on different projects.
IT Manager
An IT manager manages all aspects of an organization's information technology (IT). They are responsible for planning, implementing, and maintaining technology solutions that meet the needs of their company's goals and objectives. They are typically required to have a bachelor's degree in computer science or a related field.
|
Jobs |
Average Salary |
|
Data Scientist |
$150,000 |
|
Full-Stack Developer |
$106,000 |
|
Software Engineering Manager |
$134,156 |
|
Data Security Analyst |
$71,226 |
|
DevOps Engineer |
$140,000 |
|
Block Chain Engineer |
$150,000 |
|
Software Architect |
$114,000 |
|
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Engineer |
$110,000 |
|
Product Manager |
$100,000 |
|
Cloud Architect |
$107,000 |
|
Big Data Engineer |
$140,000 |
|
IT Manager |
$100,000 |
Technology professionals are in high demand and are making a lot of money. I hope this article helps you find the technology job that is best for you. The above-average salary is just indicative, and these numbers can vary hugely based on years of work experience.
Security Risk Management: Safeguard Your Business & Data
Security Risk Management
Security risk management is identifying vulnerabilities, prioritizing and implementing procedures to defend against them, and maintaining constant awareness. Security risk management is more than just about electronic security. It is about managing the risks within your organization and how to mitigate them.
Understanding Security Risk Management
Security Risk Management is identifying and evaluating security risks in your business. It is a systematic way of analyzing, assessing, and prioritizing threats to your organization. It involves specifying your security infrastructure's "loose ends" and then implementing controls to address them.
Security risk management should be viewed as a continuous process involving a series of decisions about managing risk based on threat intelligence, available resources, and other factors. The key steps are:
- Identify vulnerabilities
- Assess impact
- Create an action plan
- Implement controls or mitigate vulnerabilities (if possible)
The Importance of Security Risk Management
Although security risk management is a relatively new concept and the field of risk management has a relatively short history, it has already become an essential aspect of any company's IT security strategy.
The importance of security risk management is closely related to the fact that it allows companies to protect themselves against cyberattacks and other vulnerabilities. Therefore, the main goal of this process is to reduce the likelihood of adverse events occurring in the future and thus help prevent them from happening.
In addition, companies that apply security risk management can develop measures for preventing damage caused by accidents, theft, or other events. Moreover, they can also use these methods to improve their overall security posture.
In addition, companies may choose to establish a dedicated team or department within their organization that focuses exclusively on this particular aspect of their business. This team will be responsible for developing policies and procedures that ensure compliance with all relevant regulations and standards and with other internal policies and procedures.
The role of security risk management specialists is vital for organizations because they have access to information about potential threats and vulnerabilities at all times. They can also provide recommendations on how best to address these issues.
Objectives of Security Risk Management
There are several objectives of security risk management.
The first is to protect your business from any potential cyber-attacks by ensuring that all systems are secured and up-to-date.
The second objective is to protect employees from potential threats, such as identity theft, data breaches, and fraud.
Finally, you want to ensure that your partners and customers are protected.
Why Security Risk Management?
Security risk management helps in the following ways:
- It ensures that the system complies with regulatory agencies and industry standards.
- It helps to protect your organization from data breaches.
- It ensures that your staff is not wasting time on low-priority tasks and instead working on high-priority issues.
- It helps to identify and understand the risks involved in a project and take steps to reduce them.
- It ensures that your resources are used more efficiently.
Risk Assessment
A risk assessment is a method of evaluating and quantifying the likelihood that a specific threat will occur and the potential impact if it does. If a threat is high, then appropriate steps can be taken to lower the risk through risk mitigation.
A risk assessment should consider various factors, such as the type and nature of the threat, vulnerability, and impact on the business if the threat is realized. Several steps should be taken when performing a risk assessment.
The first is to identify and list all existing threats. The next step is to assess the likelihood that each threat will occur, followed by an assessment of the threat's impact if it happens. Finally, risk mitigation strategies can be developed and implemented to reduce risk.
Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation reduces the risk associated with a specific threat, such as a cyberattack. There are several ways to mitigate risk.
The first is identifying and listing all existing threats and their potential severity. Once the threats are known, mitigation strategies can be developed to reduce the risk.
For example, several strategies can be implemented when it comes to mitigating the risk of cyberattacks. The first is to ensure that all software is up-to-date and patched and that firewalls are installed and properly configured. Other strategies include installing malware detection and prevention software and hiring a cyber-security firm to regularly test and scan your network.
Risk Monitoring
Risk monitoring is keeping track of potential threats to your organization and ensuring that they are managed and that a mitigation strategy is in place. This is not only useful for risk assessment but also all other elements of security risk management.
When monitoring risk, you want to ensure that you know everything happening within your organization. This includes new threats that may be emerging, changes in regulatory requirements, changes in technology, and changes in your organization's structure. If a threat is identified, the appropriate mitigation strategies can be implemented.
Conclusion
The security risk management process is vital to any organization's success, both in the digital and physical worlds. If you want to protect your business and your customers, then this is something that you need to be doing.
Additionally, it is essential to protect your employees as well. There are many different things to consider regarding security risk management. You may encounter many risks, and you need to be prepared to deal with them. If you want to be successful, then security risk management is something you need to do.
Read More
Security Risk Management
Security risk management is identifying vulnerabilities, prioritizing and implementing procedures to defend against them, and maintaining constant awareness. Security risk management is more than just about electronic security. It is about managing the risks within your organization and how to mitigate them.
Understanding Security Risk Management
Security Risk Management is identifying and evaluating security risks in your business. It is a systematic way of analyzing, assessing, and prioritizing threats to your organization. It involves specifying your security infrastructure's "loose ends" and then implementing controls to address them.
Security risk management should be viewed as a continuous process involving a series of decisions about managing risk based on threat intelligence, available resources, and other factors. The key steps are:
- Identify vulnerabilities
- Assess impact
- Create an action plan
- Implement controls or mitigate vulnerabilities (if possible)
The Importance of Security Risk Management
Although security risk management is a relatively new concept and the field of risk management has a relatively short history, it has already become an essential aspect of any company's IT security strategy.
The importance of security risk management is closely related to the fact that it allows companies to protect themselves against cyberattacks and other vulnerabilities. Therefore, the main goal of this process is to reduce the likelihood of adverse events occurring in the future and thus help prevent them from happening.
In addition, companies that apply security risk management can develop measures for preventing damage caused by accidents, theft, or other events. Moreover, they can also use these methods to improve their overall security posture.
In addition, companies may choose to establish a dedicated team or department within their organization that focuses exclusively on this particular aspect of their business. This team will be responsible for developing policies and procedures that ensure compliance with all relevant regulations and standards and with other internal policies and procedures.
The role of security risk management specialists is vital for organizations because they have access to information about potential threats and vulnerabilities at all times. They can also provide recommendations on how best to address these issues.
Objectives of Security Risk Management
There are several objectives of security risk management.
The first is to protect your business from any potential cyber-attacks by ensuring that all systems are secured and up-to-date.
The second objective is to protect employees from potential threats, such as identity theft, data breaches, and fraud.
Finally, you want to ensure that your partners and customers are protected.
Why Security Risk Management?
Security risk management helps in the following ways:
- It ensures that the system complies with regulatory agencies and industry standards.
- It helps to protect your organization from data breaches.
- It ensures that your staff is not wasting time on low-priority tasks and instead working on high-priority issues.
- It helps to identify and understand the risks involved in a project and take steps to reduce them.
- It ensures that your resources are used more efficiently.
Risk Assessment
A risk assessment is a method of evaluating and quantifying the likelihood that a specific threat will occur and the potential impact if it does. If a threat is high, then appropriate steps can be taken to lower the risk through risk mitigation.
A risk assessment should consider various factors, such as the type and nature of the threat, vulnerability, and impact on the business if the threat is realized. Several steps should be taken when performing a risk assessment.
The first is to identify and list all existing threats. The next step is to assess the likelihood that each threat will occur, followed by an assessment of the threat's impact if it happens. Finally, risk mitigation strategies can be developed and implemented to reduce risk.
Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation reduces the risk associated with a specific threat, such as a cyberattack. There are several ways to mitigate risk.
The first is identifying and listing all existing threats and their potential severity. Once the threats are known, mitigation strategies can be developed to reduce the risk.
For example, several strategies can be implemented when it comes to mitigating the risk of cyberattacks. The first is to ensure that all software is up-to-date and patched and that firewalls are installed and properly configured. Other strategies include installing malware detection and prevention software and hiring a cyber-security firm to regularly test and scan your network.
Risk Monitoring
Risk monitoring is keeping track of potential threats to your organization and ensuring that they are managed and that a mitigation strategy is in place. This is not only useful for risk assessment but also all other elements of security risk management.
When monitoring risk, you want to ensure that you know everything happening within your organization. This includes new threats that may be emerging, changes in regulatory requirements, changes in technology, and changes in your organization's structure. If a threat is identified, the appropriate mitigation strategies can be implemented.
Conclusion
The security risk management process is vital to any organization's success, both in the digital and physical worlds. If you want to protect your business and your customers, then this is something that you need to be doing.
Additionally, it is essential to protect your employees as well. There are many different things to consider regarding security risk management. You may encounter many risks, and you need to be prepared to deal with them. If you want to be successful, then security risk management is something you need to do.
Top 2022 Scrum Master Interview Questions for Agile Pros
Top Scrum Master Question for 2022
- Differentiate Between Agile and Scrum.
Agile is a software development method that focuses on the adaptive delivery of requirements in an iterative, incremental manner. It's a framework that enables teams to deliver working software frequently and with high quality.
Scrum is an agile framework that provides a set of principles and practices to help teams develop software more effectively.
- What do you mean by user stories in Scrum? What are the advantages of using them?
User stories describe a specific feature and its requirements without understanding how it should be implemented. They are used in Scrum to help focus on what the user is trying to achieve, and they help ensure that users build the product for users.
The advantage of using them is that they help to ensure that the right features get built and that features are developed in a way that allows users to understand what they do, why they do it, and how they do it.
- How are user stories, epics, and tasks different?
User stories are the smallest unit of work that a single team member can complete.
An epic describes a single feature or story.
Tasks are the smallest unit of work that only one person can complete.
- What do you mean by timeboxing in Scrum?
The timebox is a constraint that you place on the development team. The purpose of the timebox is to limit the amount of time spent on any given task and ensure that work is going to be used while waiting for other tasks to complete or considering other constraints. Timeboxing is a critical part of Scrum because it helps keep the development team focused on achieving their work as quickly as possible and helps them stay within their sprint goal.
- What are the tools used in Scrum projects?
- Microsoft Azure DevOps
- Asana
- Jira
- Trello
- What do you mean by 'Confidence Vote' in Scrum? Why is it important?
In Scrum, a team will have to release their product on time. If they don't meet the deadline, then they can be penalized. This is called a 'confidence vote. The team will vote on if they think they can meet the deadline or not. If they are confident they can reach the deadline, they can release their product and be confident in themselves.
The confidence vote is important because it helps teams know whether or not they have enough time to finish their project by the deadline. For example, suppose a team has a lot of work left to do. In that case, it is more likely that they won't make it in time for the next release date, and this could lead to them being penalized for not meeting their goal by missing deadlines which could lead to them losing money or even losing customers if someone else releases before them!
- What do you understand about Scope Creep? How can Scope Creep be managed?
Scope creep is a common problem in agile development. "scope creeps" refers to adding new functionality, features, and requirements to a project after it has started. This can be a costly problem, as it can increase the project's scope without adding any value.
In Scrum, scope creep is managed by allocating time for each task and ensuring the team stays within their sprints. If a team member can't complete their task within their sprint, they should be removed from the sprint, and they will have no impact.
- What is the role of a Scrum Master in a sprint retrospective?
A Scrum Master is a person who has the role of managing the Scrum project. They usually work in tandem with the Product Owner to help ensure that the project is successful and that everyone works together towards a common goal.
The Scrum Master has two prominent roles:
To help guide and coach the team through the Sprint review, helping them identify any issues they may have faced during their sprints and any improvements they want to make.
To help manage communication between stakeholders throughout the development process - is available to advise on how to deal with issues that may arise and step back and let others take control where appropriate.
- What exactly do you mean by Sprint in Scrum?
Sprint is the term for the period you are working on your product. It can be any period from a few hours to several months, depending on your needs and how much work you want to do in that time.
A sprint is a self-organizing event with no fixed start or end date but rather a focus on achieving specific goals within a sprint. Sprint starts with planning and ends with a review, so it can be considered a cycle of events.
Scrum sprints are typically 2 weeks (1 week each way) long and take place every 2 weeks or when specific events occur, such as when something hits an important milestone or some other special occasion that requires team attention.
- When should you use Waterfall over Scrum?
The reasons to use Waterfall over Scrum are :
First, Scrum is a framework, while Waterfall is a methodology. A waterfall can be applied to any project lifecycle, not just software development.
Second, the Agile Manifesto states that people and stakeholders should be involved early and often in the project lifecycle. But this is not possible when using Scrum because it needs an explicit process for communication between stakeholders and developers.
Third, Waterfall is better suited for large projects with clear goals, high-level planning, detailed specifications, and well-defined roles for all parties involved.
- What are the Scrum Process Artifacts?
The Product Backlog lists all items needed for the product or feature. In addition, it contains all user stories, acceptance criteria, and other requirements for that particular item in the product backlog.
The Sprint Backlog contains all tasks necessary to complete each sprint to meet its goal(s). These tasks may include analyzing the current status, creating designs and prototypes, developing code or tests needed to test completed functionality according to user stories in the product backlog, etc.
The product increment is the new functionality added to the product during each iteration, i.e., after each sprint. This is done so that all stakeholders can see how far along you are in your progress toward delivering functionality and making changes based on feedback from stakeholders or customers.
- Describe Scrumban?
Scrumban is a business management software that allows you to automate your daily tasks and give your employees more freedom.
With Scrumban, you can create simple or complex workflows to save time and increase efficiency. You can also use Scrumban to automate the most tedious parts of your business by creating scripts that will run on specific dates or times of the day.
This approach allows you to reuse scripts as much as possible without having to worry about constantly creating them from scratch each time you want to rerun them.
MCQ’s on Scrum
Who can be the best user proxy?
- Agile coach
- Scrum Master
- Customers
- Developer
When can a Sprint be canceled?
- The Sprint items are no longer needed
- Sprint can never be canceled
- Information required to start the development is not available
- Whenever the Product Owner say
How is Product Backlog Arranged?
- High priority items on top, followed low-priority items
- Large items at the top, small items at the bottom
- Items are randomly arranged
- Newer stories prioritized on top, followed by older stories
Who is responsible for ensuring that the scrum values and pillars are adhered to at all times?
- Product Owner
- Development Team
- Scrum Master
- None of above
Which one is not part of the Agile Manifesto?
- Maximize utilization
- Working Daily Together
- Continuous Attention
- Early & Continuous Delivery of Business Value
Should product backlog be ordered based on?
- The complexity of the items being delivered
- Size of the items being delivered
- Value of the items being delivered
- The risk associated with the items
Which of these is not a scrum pillar?
- Adaptation
- Focus
- Transparency
- Inspection
The Product Owner in a Scrum project?
- Collaborates with the developers over prioritization of product backlog items, but the product owner has the final say
- Creates a product backlog items but leaves prioritization to the business analyst
- Collaborates with the developers over prioritization of product backlog items, but the developers have the final say
- Has no control over the prioritization of product backlog items
Iterative development is NOT a good idea for?
- Back end development
- Front end development
- Software development
- Middleware development
What is the role of a tester in Scrum?
- In Scrum, there is no such thing as a tester.
- Bug hunting
- Create test scenarios and test cases as needed.
- Write scripts for automation
- What is conveyed by the BurnDown chart?
- The progress in the project.
- The team's rate of doing work.
- The team members' capabilities.
- The amount of work that needs to be completed in relation to the amount of time available.
Read More
Top Scrum Master Question for 2022
- Differentiate Between Agile and Scrum.
Agile is a software development method that focuses on the adaptive delivery of requirements in an iterative, incremental manner. It's a framework that enables teams to deliver working software frequently and with high quality.
Scrum is an agile framework that provides a set of principles and practices to help teams develop software more effectively.
- What do you mean by user stories in Scrum? What are the advantages of using them?
User stories describe a specific feature and its requirements without understanding how it should be implemented. They are used in Scrum to help focus on what the user is trying to achieve, and they help ensure that users build the product for users.
The advantage of using them is that they help to ensure that the right features get built and that features are developed in a way that allows users to understand what they do, why they do it, and how they do it.
- How are user stories, epics, and tasks different?
User stories are the smallest unit of work that a single team member can complete.
An epic describes a single feature or story.
Tasks are the smallest unit of work that only one person can complete.
- What do you mean by timeboxing in Scrum?
The timebox is a constraint that you place on the development team. The purpose of the timebox is to limit the amount of time spent on any given task and ensure that work is going to be used while waiting for other tasks to complete or considering other constraints. Timeboxing is a critical part of Scrum because it helps keep the development team focused on achieving their work as quickly as possible and helps them stay within their sprint goal.
- What are the tools used in Scrum projects?
- Microsoft Azure DevOps
- Asana
- Jira
- Trello
- What do you mean by 'Confidence Vote' in Scrum? Why is it important?
In Scrum, a team will have to release their product on time. If they don't meet the deadline, then they can be penalized. This is called a 'confidence vote. The team will vote on if they think they can meet the deadline or not. If they are confident they can reach the deadline, they can release their product and be confident in themselves.
The confidence vote is important because it helps teams know whether or not they have enough time to finish their project by the deadline. For example, suppose a team has a lot of work left to do. In that case, it is more likely that they won't make it in time for the next release date, and this could lead to them being penalized for not meeting their goal by missing deadlines which could lead to them losing money or even losing customers if someone else releases before them!
- What do you understand about Scope Creep? How can Scope Creep be managed?
Scope creep is a common problem in agile development. "scope creeps" refers to adding new functionality, features, and requirements to a project after it has started. This can be a costly problem, as it can increase the project's scope without adding any value.
In Scrum, scope creep is managed by allocating time for each task and ensuring the team stays within their sprints. If a team member can't complete their task within their sprint, they should be removed from the sprint, and they will have no impact.
- What is the role of a Scrum Master in a sprint retrospective?
A Scrum Master is a person who has the role of managing the Scrum project. They usually work in tandem with the Product Owner to help ensure that the project is successful and that everyone works together towards a common goal.
The Scrum Master has two prominent roles:
To help guide and coach the team through the Sprint review, helping them identify any issues they may have faced during their sprints and any improvements they want to make.
To help manage communication between stakeholders throughout the development process - is available to advise on how to deal with issues that may arise and step back and let others take control where appropriate.
- What exactly do you mean by Sprint in Scrum?
Sprint is the term for the period you are working on your product. It can be any period from a few hours to several months, depending on your needs and how much work you want to do in that time.
A sprint is a self-organizing event with no fixed start or end date but rather a focus on achieving specific goals within a sprint. Sprint starts with planning and ends with a review, so it can be considered a cycle of events.
Scrum sprints are typically 2 weeks (1 week each way) long and take place every 2 weeks or when specific events occur, such as when something hits an important milestone or some other special occasion that requires team attention.
- When should you use Waterfall over Scrum?
The reasons to use Waterfall over Scrum are :
First, Scrum is a framework, while Waterfall is a methodology. A waterfall can be applied to any project lifecycle, not just software development.
Second, the Agile Manifesto states that people and stakeholders should be involved early and often in the project lifecycle. But this is not possible when using Scrum because it needs an explicit process for communication between stakeholders and developers.
Third, Waterfall is better suited for large projects with clear goals, high-level planning, detailed specifications, and well-defined roles for all parties involved.
- What are the Scrum Process Artifacts?
The Product Backlog lists all items needed for the product or feature. In addition, it contains all user stories, acceptance criteria, and other requirements for that particular item in the product backlog.
The Sprint Backlog contains all tasks necessary to complete each sprint to meet its goal(s). These tasks may include analyzing the current status, creating designs and prototypes, developing code or tests needed to test completed functionality according to user stories in the product backlog, etc.
The product increment is the new functionality added to the product during each iteration, i.e., after each sprint. This is done so that all stakeholders can see how far along you are in your progress toward delivering functionality and making changes based on feedback from stakeholders or customers.
- Describe Scrumban?
Scrumban is a business management software that allows you to automate your daily tasks and give your employees more freedom.
With Scrumban, you can create simple or complex workflows to save time and increase efficiency. You can also use Scrumban to automate the most tedious parts of your business by creating scripts that will run on specific dates or times of the day.
This approach allows you to reuse scripts as much as possible without having to worry about constantly creating them from scratch each time you want to rerun them.
MCQ’s on Scrum
Who can be the best user proxy?
- Agile coach
- Scrum Master
- Customers
- Developer
When can a Sprint be canceled?
- The Sprint items are no longer needed
- Sprint can never be canceled
- Information required to start the development is not available
- Whenever the Product Owner say
How is Product Backlog Arranged?
- High priority items on top, followed low-priority items
- Large items at the top, small items at the bottom
- Items are randomly arranged
- Newer stories prioritized on top, followed by older stories
Who is responsible for ensuring that the scrum values and pillars are adhered to at all times?
- Product Owner
- Development Team
- Scrum Master
- None of above
Which one is not part of the Agile Manifesto?
- Maximize utilization
- Working Daily Together
- Continuous Attention
- Early & Continuous Delivery of Business Value
Should product backlog be ordered based on?
- The complexity of the items being delivered
- Size of the items being delivered
- Value of the items being delivered
- The risk associated with the items
Which of these is not a scrum pillar?
- Adaptation
- Focus
- Transparency
- Inspection
The Product Owner in a Scrum project?
- Collaborates with the developers over prioritization of product backlog items, but the product owner has the final say
- Creates a product backlog items but leaves prioritization to the business analyst
- Collaborates with the developers over prioritization of product backlog items, but the developers have the final say
- Has no control over the prioritization of product backlog items
Iterative development is NOT a good idea for?
- Back end development
- Front end development
- Software development
- Middleware development
What is the role of a tester in Scrum?
- In Scrum, there is no such thing as a tester.
- Bug hunting
- Create test scenarios and test cases as needed.
- Write scripts for automation
- What is conveyed by the BurnDown chart?
- The progress in the project.
- The team's rate of doing work.
- The team members' capabilities.
- The amount of work that needs to be completed in relation to the amount of time available.
Essential Insights About Agile Project Managers & Their Role
Things You Need To Know About Agile Project Manager
Agile project management is a structured planning method focusing on working software over comprehensive documentation. This means that the primary aim of agile project managers is to deliver software products, value-added services, or financial benefits within a fixed budget and timeframe. There are various approaches to agile project management, including Scrum, Lean and Extreme Programming.
Overview: Agile Project Manager
The Agile Project Manager is responsible for leading and managing an agile project. They must be able to take ownership of the project, ensuring that it is well-defined and moves forward as a team.
The Project Manager is also responsible for ensuring that all team members work towards the same goals, which can be difficult if multiple units work on different project parts.
The Project manager will need to manage conflict, which changes in priorities or other external factors can cause. In addition, they must be able to work with each team member and ensure that everyone clearly understands what needs to happen with their portion of the project. They should also be able to keep track of any issues that may arise during development and make sure that they are resolved before moving forward with work on another part of the project.
Job Description
An agile project manager is responsible for the following:
- First, create a roadmap that defines an agile project's goals, objectives, and tasks.
- Identifying missing skills or gaps in resources.
- Planning and managing sprints, typically two weeks, are time-boxed iterations that allow teams to deliver working software continuously (not in a waterfall model). The agile project manager also includes retrospectives to ensure that the team constantly learns from its work and adapts accordingly.
- Managing stakeholders so that they understand the status of their tasks and how to achieve them.
Responsibilities of APM
The role of an agile project manager is to ensure that the project is on track and within budget and time. The following are some responsibilities of an agile project manager:
- Planning is one of the most critical aspects of this role. This can be done by creating a plan based on what has already been done or creating a new plan based on what you want to do next.
- This person should monitor the progress of the project at all times. They should ensure that everything is going according to schedule and budget and identify any issues that may arise during a project.
- The agile project manager will regularly communicate with everyone involved in their project, whether with email updates or meetings between team members and management.
- Agile project managers should also be able to provide vision and guidance to help their teams reach their goals. In addition, they should be able to keep track of issues with each specific area of the project and make sure that they are resolved as soon as possible.
Skills Required For APM
The Agile Project Manager role combines the roles of Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Team Lead. The project manager is responsible for managing all the projects within an organization. Thus the skills required are:
- Excellent communication skills
- Good team-building skills
- Strong organizational skills
- Flexible and adaptable to change
- Leadership skills
- Understanding of the Agile Manifesto, principles, and values
- Ability to juggle multiple projects simultaneously
Traditional Project Manager vs. an APM
The traditional project manager is the person who organizes and plans the projects from A to Z. They are responsible for all aspects of a project, including identifying requirements, designing the solution, developing the software, and testing and documenting it.
The traditional project manager has multi-tasking skills and can manage multiple teams of people quickly. They also have excellent communication skills to manage all stakeholders involved in a project.
The agile project manager is different from the traditional project manager in several ways:
They are focused on delivering products at the highest quality possible. But unfortunately, this means they have less control over what happens in their organization. To be successful with this approach, they need to empower others and give them room to work autonomously.
Traditional managers often try to micromanage their employees by giving them unrealistic deadlines or requiring them to use specific tools or technologies (or both). This can lead to frustration among employees who feel they need more time or resources to succeed at their jobs.
Agile project managers allow their teams to make decisions without constant oversight from management or non-coders. This will enable them to help when needed but not get bogged down.
Conclusion
Despite what many think or would like to believe, project management is a challenging job. It may seem simple when you are in the middle of your project(s) and everything is running smoothly, but believe me, if it was that easy, then all of us could do it (and so many of us try).
Project management as a career brings new daily challenges that require a unique blend of skills from team leadership to technical knowledge and hands-on experience. So what makes being an Agile Project Manager different from any other type of project manager? Simply put, the agile approach requires some particular methodologies that have been proven time and time again to work in the design/development field. It also has some stringent rules on how you can and cannot manage.
Even though these restrictions may seem overly bureaucratic at first (and for the most part, they are), it is important to remember that there is a reason behind them. These rules help promote trust, good communication, quick decision-making, and much more, giving project leaders like yourself a clear vision of managing your projects effectively.
Read More
Things You Need To Know About Agile Project Manager
Agile project management is a structured planning method focusing on working software over comprehensive documentation. This means that the primary aim of agile project managers is to deliver software products, value-added services, or financial benefits within a fixed budget and timeframe. There are various approaches to agile project management, including Scrum, Lean and Extreme Programming.
Overview: Agile Project Manager
The Agile Project Manager is responsible for leading and managing an agile project. They must be able to take ownership of the project, ensuring that it is well-defined and moves forward as a team.
The Project Manager is also responsible for ensuring that all team members work towards the same goals, which can be difficult if multiple units work on different project parts.
The Project manager will need to manage conflict, which changes in priorities or other external factors can cause. In addition, they must be able to work with each team member and ensure that everyone clearly understands what needs to happen with their portion of the project. They should also be able to keep track of any issues that may arise during development and make sure that they are resolved before moving forward with work on another part of the project.
Job Description
An agile project manager is responsible for the following:
- First, create a roadmap that defines an agile project's goals, objectives, and tasks.
- Identifying missing skills or gaps in resources.
- Planning and managing sprints, typically two weeks, are time-boxed iterations that allow teams to deliver working software continuously (not in a waterfall model). The agile project manager also includes retrospectives to ensure that the team constantly learns from its work and adapts accordingly.
- Managing stakeholders so that they understand the status of their tasks and how to achieve them.
Responsibilities of APM
The role of an agile project manager is to ensure that the project is on track and within budget and time. The following are some responsibilities of an agile project manager:
- Planning is one of the most critical aspects of this role. This can be done by creating a plan based on what has already been done or creating a new plan based on what you want to do next.
- This person should monitor the progress of the project at all times. They should ensure that everything is going according to schedule and budget and identify any issues that may arise during a project.
- The agile project manager will regularly communicate with everyone involved in their project, whether with email updates or meetings between team members and management.
- Agile project managers should also be able to provide vision and guidance to help their teams reach their goals. In addition, they should be able to keep track of issues with each specific area of the project and make sure that they are resolved as soon as possible.
Skills Required For APM
The Agile Project Manager role combines the roles of Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Team Lead. The project manager is responsible for managing all the projects within an organization. Thus the skills required are:
- Excellent communication skills
- Good team-building skills
- Strong organizational skills
- Flexible and adaptable to change
- Leadership skills
- Understanding of the Agile Manifesto, principles, and values
- Ability to juggle multiple projects simultaneously
Traditional Project Manager vs. an APM
The traditional project manager is the person who organizes and plans the projects from A to Z. They are responsible for all aspects of a project, including identifying requirements, designing the solution, developing the software, and testing and documenting it.
The traditional project manager has multi-tasking skills and can manage multiple teams of people quickly. They also have excellent communication skills to manage all stakeholders involved in a project.
The agile project manager is different from the traditional project manager in several ways:
They are focused on delivering products at the highest quality possible. But unfortunately, this means they have less control over what happens in their organization. To be successful with this approach, they need to empower others and give them room to work autonomously.
Traditional managers often try to micromanage their employees by giving them unrealistic deadlines or requiring them to use specific tools or technologies (or both). This can lead to frustration among employees who feel they need more time or resources to succeed at their jobs.
Agile project managers allow their teams to make decisions without constant oversight from management or non-coders. This will enable them to help when needed but not get bogged down.
Conclusion
Despite what many think or would like to believe, project management is a challenging job. It may seem simple when you are in the middle of your project(s) and everything is running smoothly, but believe me, if it was that easy, then all of us could do it (and so many of us try).
Project management as a career brings new daily challenges that require a unique blend of skills from team leadership to technical knowledge and hands-on experience. So what makes being an Agile Project Manager different from any other type of project manager? Simply put, the agile approach requires some particular methodologies that have been proven time and time again to work in the design/development field. It also has some stringent rules on how you can and cannot manage.
Even though these restrictions may seem overly bureaucratic at first (and for the most part, they are), it is important to remember that there is a reason behind them. These rules help promote trust, good communication, quick decision-making, and much more, giving project leaders like yourself a clear vision of managing your projects effectively.
Inferential vs. Descriptive Statistics: Key Differences
Inferential vs. Descriptive Statistics
Statistics refers to collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data using the appropriate mathematical tools. Statistics is an essential tool that researchers in all fields use. Whether an undergraduate student struggling with advanced statistics problems or a professional statistician analyzing computer data, a basic understanding of descriptive statistics vs. inferential statistics can help your results be more precise and insightful.
What is Inferential Statistics?
Inferential statistics is drawing inferences from a set of observed data. Inferential statistics aims to generalize from the sample, or small unit, to a larger population. When conducting an assumption, we are interested in how the outcome of our study differs between groups. In other words, we want to know if our results would be different if we conducted the same experiment or survey with a diverse population.
Types of Inferential Statistics
Hypothesis tests, regression analysis, and confidence intervals are the main inferential statistical techniques used in research. They are different ways of testing whether a statistical relationship exists between two variables.
A hypothesis test is a way of testing whether one variable is related to another variable. For example, you may be interested in seeing if there is a relationship between age and income (a variable that can take values between 0 and 100). The null hypothesis is that there is no relationship between these two variables. However, if your data shows some connection, the alternative view is that there is a relationship.
Regression analysis tests whether a given variable affects another variable. This can be done by taking the square root of the sum of squared residuals and comparing it to zero (to determine if there is linearity). With linearity, it's possible to predict what will happen with this data set.
Confidence intervals are one of the essential types of inferential statistics. They are used to determine whether or not a sample mean statistically different from some reference value. The confidence interval tells us how large we can expect that difference to be, and it also tells us how accurate our estimate of the population parameter is.
What is Descriptive Statistics?
Descriptive statistics is the study of descriptive data, usually collected from observations made on a sample. Descriptive statistics include:
- Measures of central tendency (such as the mean).
- Measures of variability (such as the standard deviation).
- Information about how much each observation differs from the norm.
Descriptive statistics can be used to describe the characteristics of an entire population, or they can be used to describe specific groups in a population. Descriptive statistics are often used in conjunction with inferential statistics, which are used to make valid conclusions about large populations.
Types of Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics are used to describe the values of a particular variable along with its frequency. For example, you can use descriptive statistics to describe the height and weight of a group of people.
Central tendency measures how a group of data relates to the overall population. It is often used to determine where data fits within a distribution. The central tendency is usually determined by taking the average or median value of the data set.
Frequency distribution measures how often each value occurs in the given population. Frequency distributions can determine how many people have a particular characteristic (e.g., age).
The variability or dispersion of a variable is the measure of how widely it falls around a mean. Variability is measured in terms of standard deviation (SD).
The measure of variability is called the standard deviation. It is calculated from the mean and standard error. The standard deviation measures how much the values in a group are spread out from the mean. The larger the standard deviation, the greater the dispersion of points around their mean value.
A standard deviation is essential for determining whether a sample is representative of a population. For example, suppose you know that your data set has considerable variability and outliers. In that case, your sample may need to be more representative of the population as a whole. In this case, it would be best to look at another data set with similar characteristics to yours and see if they have much more variability than what you have found in yours.
Inferential vs. Descriptive Statistics
The difference between inferential and descriptive statistics is that inferential statistics are done to predict future data. In contrast, descriptive statistics are done to describe past data.
Inferential statistics are used to make predictions about future data based on historical data. For example, if a company has been in business for 10 years, it can predict its sales in the next year by using past sales as a reference point. This is an example of inferential statistics.
Descriptive statistics are used to describe past data and provide insight into how that past data compares to other similar situations. For example, suppose a company's sales have increased yearly for 10 years. In that case, their sales will likely continue to grow each year for another 10 years before finally plateauing at some point in time (which is also very likely). This is an example of descriptive statistics.
We have covered the fundamentals of inferential and descriptive statistics in this article. They both involve making assumptions about a population based on sample data collected. Inferential statistics are used for this purpose and are often conducted to make decisions about future data based on previous data that is already known. Descriptive statistics are for sharing your data with others.
Read More
Inferential vs. Descriptive Statistics
Statistics refers to collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data using the appropriate mathematical tools. Statistics is an essential tool that researchers in all fields use. Whether an undergraduate student struggling with advanced statistics problems or a professional statistician analyzing computer data, a basic understanding of descriptive statistics vs. inferential statistics can help your results be more precise and insightful.
What is Inferential Statistics?
Inferential statistics is drawing inferences from a set of observed data. Inferential statistics aims to generalize from the sample, or small unit, to a larger population. When conducting an assumption, we are interested in how the outcome of our study differs between groups. In other words, we want to know if our results would be different if we conducted the same experiment or survey with a diverse population.
Types of Inferential Statistics
Hypothesis tests, regression analysis, and confidence intervals are the main inferential statistical techniques used in research. They are different ways of testing whether a statistical relationship exists between two variables.
A hypothesis test is a way of testing whether one variable is related to another variable. For example, you may be interested in seeing if there is a relationship between age and income (a variable that can take values between 0 and 100). The null hypothesis is that there is no relationship between these two variables. However, if your data shows some connection, the alternative view is that there is a relationship.
Regression analysis tests whether a given variable affects another variable. This can be done by taking the square root of the sum of squared residuals and comparing it to zero (to determine if there is linearity). With linearity, it's possible to predict what will happen with this data set.
Confidence intervals are one of the essential types of inferential statistics. They are used to determine whether or not a sample mean statistically different from some reference value. The confidence interval tells us how large we can expect that difference to be, and it also tells us how accurate our estimate of the population parameter is.
What is Descriptive Statistics?
Descriptive statistics is the study of descriptive data, usually collected from observations made on a sample. Descriptive statistics include:
- Measures of central tendency (such as the mean).
- Measures of variability (such as the standard deviation).
- Information about how much each observation differs from the norm.
Descriptive statistics can be used to describe the characteristics of an entire population, or they can be used to describe specific groups in a population. Descriptive statistics are often used in conjunction with inferential statistics, which are used to make valid conclusions about large populations.
Types of Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics are used to describe the values of a particular variable along with its frequency. For example, you can use descriptive statistics to describe the height and weight of a group of people.
Central tendency measures how a group of data relates to the overall population. It is often used to determine where data fits within a distribution. The central tendency is usually determined by taking the average or median value of the data set.
Frequency distribution measures how often each value occurs in the given population. Frequency distributions can determine how many people have a particular characteristic (e.g., age).
The variability or dispersion of a variable is the measure of how widely it falls around a mean. Variability is measured in terms of standard deviation (SD).
The measure of variability is called the standard deviation. It is calculated from the mean and standard error. The standard deviation measures how much the values in a group are spread out from the mean. The larger the standard deviation, the greater the dispersion of points around their mean value.
A standard deviation is essential for determining whether a sample is representative of a population. For example, suppose you know that your data set has considerable variability and outliers. In that case, your sample may need to be more representative of the population as a whole. In this case, it would be best to look at another data set with similar characteristics to yours and see if they have much more variability than what you have found in yours.
Inferential vs. Descriptive Statistics
The difference between inferential and descriptive statistics is that inferential statistics are done to predict future data. In contrast, descriptive statistics are done to describe past data.
Inferential statistics are used to make predictions about future data based on historical data. For example, if a company has been in business for 10 years, it can predict its sales in the next year by using past sales as a reference point. This is an example of inferential statistics.
Descriptive statistics are used to describe past data and provide insight into how that past data compares to other similar situations. For example, suppose a company's sales have increased yearly for 10 years. In that case, their sales will likely continue to grow each year for another 10 years before finally plateauing at some point in time (which is also very likely). This is an example of descriptive statistics.
We have covered the fundamentals of inferential and descriptive statistics in this article. They both involve making assumptions about a population based on sample data collected. Inferential statistics are used for this purpose and are often conducted to make decisions about future data based on previous data that is already known. Descriptive statistics are for sharing your data with others.
Data Acquisition in Machine Learning: Fuel AI with Data now
Data Acquisition in Machine learning
Data acquisition in machine learning can significantly widen your knowledge of a particular topic. For example, suppose you are planning to analyze your website's data. In that case, it can help you find out what features and functions on your site work well and which ones don't appeal to the customers. During data collection, you might also be required to collect website domain names or page titles. Let’s know more about data acquisition.
What is Data Acquisition?
Data acquisition is one of the most important steps in a machine learning algorithm. It's used to collect data on how your model performs on new datasets.
Data acquisition is simply collecting new data and transforming it into a format your machine learning algorithm can use. Once you've acquired some training data, your model can learn from it and improve its performance on new tasks.
Why do we need Data Acquisition?
For most machine learning algorithms, you need to acquire training data before using them for prediction. This training data can be provided by humans or other machines (e.g., from web scraping). The goal is to have a large enough sample size that your model can learn from effectively but not so large that it takes too much time to train (and possibly overfit) the available data.
Components of Data Acquisition System
The Data Acquisition System (DAS) is a set of components that perform data acquisition. The components are:
Sensor: A sensor converts physical properties into electrical signals, which a DAS can use to acquire data. A sensor may be a simple device like an inductive proximity sensor or an expensive instrument with many channels and options.
Signal Conditioner: The signal conditioning system converts the analog signals from the sensor into digital form. It provides gain, offset, and trim controls for each channel on the DAS. It also filters out noise from external sources, such as motors or other electronics that generate electromagnetic interference.
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC): The ADC converts the analog signal from the signal conditioner into a digital format for processing by a computer or other processor.
Importance of Data Acquisition System
The most important aspect of data acquisition systems is the ability to record and analyze data. This includes both the hardware and software aspects. The hardware consists of the devices that collect data, including sensors and radio frequency identification (RFID) devices. The software aspect includes the software used to collect, store and process the data.
The purpose of a data acquisition system is to automate processes. Automating an approach means that it can be done without human intervention. This can reduce the time needed for a specific task or improve overall efficiency in performing tasks that require human intervention.
In addition to automating processes, a good data acquisition system will provide information about what went wrong when something does go wrong during an automated procedure. For example, suppose a computerized process fails several times in a row. In that case, something may be wrong with the program or one of its components. A good data acquisition system will alert users to potential problems before they cause severe damage to equipment (or humans).
Purposes of Data Acquisition
The most important purposes of data acquisition are:
First, data acquisition helps to understand the behavior of the system.
Data acquisition helps to develop a model for the system.
Finally, data acquisition helps to improve the performance of the system.
What Does a DAQ System Measure?
The DAQ system measures a variety of parameters, including:
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Voltage
- Current flow through an electrical circuit
- Power usage of a piece of equipment
A data acquisition system (DAS) measures various parameters that can be used to control and analyze equipment. The DAS is typically connected to the electrical system and can be programmed, via a web browser, for specific functions and tasks.
The following are some common uses for a DAQ system:
- Control of electronic devices such as motors, valves, and pumps
- Measuring variable parameters of temperature, pressure, or flow rate
- Monitoring vibration levels in air conditioning systems
- Providing feedback to users through visual displays or audible alarm tones
With that, we have finished our exploration of topics relevant to Data Acquisition in machine learning. I hope you learned a lot and enjoyed the read! Please leave any thoughts or questions you may have (along with any suggestions) in the comments section below.
Read More
Data Acquisition in Machine learning
Data acquisition in machine learning can significantly widen your knowledge of a particular topic. For example, suppose you are planning to analyze your website's data. In that case, it can help you find out what features and functions on your site work well and which ones don't appeal to the customers. During data collection, you might also be required to collect website domain names or page titles. Let’s know more about data acquisition.
What is Data Acquisition?
Data acquisition is one of the most important steps in a machine learning algorithm. It's used to collect data on how your model performs on new datasets.
Data acquisition is simply collecting new data and transforming it into a format your machine learning algorithm can use. Once you've acquired some training data, your model can learn from it and improve its performance on new tasks.
Why do we need Data Acquisition?
For most machine learning algorithms, you need to acquire training data before using them for prediction. This training data can be provided by humans or other machines (e.g., from web scraping). The goal is to have a large enough sample size that your model can learn from effectively but not so large that it takes too much time to train (and possibly overfit) the available data.
Components of Data Acquisition System
The Data Acquisition System (DAS) is a set of components that perform data acquisition. The components are:
Sensor: A sensor converts physical properties into electrical signals, which a DAS can use to acquire data. A sensor may be a simple device like an inductive proximity sensor or an expensive instrument with many channels and options.
Signal Conditioner: The signal conditioning system converts the analog signals from the sensor into digital form. It provides gain, offset, and trim controls for each channel on the DAS. It also filters out noise from external sources, such as motors or other electronics that generate electromagnetic interference.
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC): The ADC converts the analog signal from the signal conditioner into a digital format for processing by a computer or other processor.
Importance of Data Acquisition System
The most important aspect of data acquisition systems is the ability to record and analyze data. This includes both the hardware and software aspects. The hardware consists of the devices that collect data, including sensors and radio frequency identification (RFID) devices. The software aspect includes the software used to collect, store and process the data.
The purpose of a data acquisition system is to automate processes. Automating an approach means that it can be done without human intervention. This can reduce the time needed for a specific task or improve overall efficiency in performing tasks that require human intervention.
In addition to automating processes, a good data acquisition system will provide information about what went wrong when something does go wrong during an automated procedure. For example, suppose a computerized process fails several times in a row. In that case, something may be wrong with the program or one of its components. A good data acquisition system will alert users to potential problems before they cause severe damage to equipment (or humans).
Purposes of Data Acquisition
The most important purposes of data acquisition are:
First, data acquisition helps to understand the behavior of the system.
Data acquisition helps to develop a model for the system.
Finally, data acquisition helps to improve the performance of the system.
What Does a DAQ System Measure?
The DAQ system measures a variety of parameters, including:
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Voltage
- Current flow through an electrical circuit
- Power usage of a piece of equipment
A data acquisition system (DAS) measures various parameters that can be used to control and analyze equipment. The DAS is typically connected to the electrical system and can be programmed, via a web browser, for specific functions and tasks.
The following are some common uses for a DAQ system:
- Control of electronic devices such as motors, valves, and pumps
- Measuring variable parameters of temperature, pressure, or flow rate
- Monitoring vibration levels in air conditioning systems
- Providing feedback to users through visual displays or audible alarm tones
With that, we have finished our exploration of topics relevant to Data Acquisition in machine learning. I hope you learned a lot and enjoyed the read! Please leave any thoughts or questions you may have (along with any suggestions) in the comments section below.
Essential Key Terms and Core Concepts in Program Management
Everything You Need to Know About Program Management
The program management professional is a missing link in the software development process. These professionals are necessary for low-quality software to be produced. Program managers are responsible for many things in your organization — from initiating project plans to building the technical specifications to managing task lists and budgeting activities. It is essential that you have an understanding of what a program manager does and why it is important for your company's success.
What is Program Management?
Program management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling the work of a group or project to accomplish its objectives. Program management is a subset of project management that focuses on managing specific products and services produced by organizations. The processes involved in program management are modeled after those used in manufacturing industries.
- Program management is a structured approach to managing programs as they progress from inception through completion.
- A set of processes that provides for the effective delivery of projects within given resource constraints and timeframes.
- The process of identifying appropriate resources, developing plans and strategies, monitoring and controlling work within established limits, and evaluating results against stated goals and expectations.
Difference between Program Management and Project Management
Program management is a set of activities performed to achieve business objectives. The critical purpose of program management is to manage projects, programs, and services effectively. Program Managers are responsible for planning and executing programs. In addition, they work with other departments and stakeholders to ensure that projects are completed on schedule and within budget.
Project Management is the process of planning, organizing, and directing the efforts of resources to meet specific goals within a time frame. Project Management is performed by project team members who must coordinate their efforts with those of other departments or individuals involved in the project.
Program Manager and Responsibilities
A program manager is a person who is responsible for the management of a specific project or program. Program managers are responsible for planning, organizing, and coordinating all aspects of a project to complete it successfully. Therefore, they must be able to work effectively in a team environment and manage multiple tasks simultaneously.
Responsibilities of the Program Manager Include:
- The Program Manager is responsible for successfully implementing all programs, projects, and initiatives within their program or project area.
- Program Managers are responsible for ensuring that their unit's work is completed according to approved plans and budgets.
- Program Managers report directly to the Director of Human Resources, Risk Management, or Project Management.
- The program's overall direction and development, including the selection of courses, the design of courses, and the management of staff.
- Supervising and coordinating all aspects of a program's development, including course content, instructional strategies, delivery methods, and evaluation methods.
- The establishment of performance standards for program staff members at each level and in each area within the program shall be reviewed periodically by an appropriate committee or review body.
- Providing leadership in implementing a sound educational philosophy, management practices, and techniques by the approved policies and procedures governing programs under their supervision or guidance.
Benefits of Program Management
The benefits of program management are numerous. Some of the most critical include:
- Reduces risk: Program managers can improve the chances that projects will be completed on time and within budget.
- Increases accountability: When a program manager manages a project, someone is always responsible. This helps ensure the organization can handle a lack of accountability.
- Improves communications: As a program manager, you'll need to ensure that your team understands what needs to happen and when. A program manager can help with this process by providing everyone knows what's happening at all times.
- Resource Allocation: A program manager can allocate resources effectively to ensure that each project has the right amount of attention from all stakeholders. This saves time and money as well as helps improve overall efficiency in planning and execution.
- Project Affinity: A program manager can view project affinity by viewing all projects under their purview in one place instead of scrolling through dozens or hundreds of daily tasks. This helps them identify strengths and weaknesses concerning individual projects so they can take corrective action before it's too late!
Key Terms Related to Program Management
Program work breakdown structure (WBS) is the basis for defining a management program. It is a hierarchical, comprehensive list of all activities needed to complete the project. The WBS should be simple and easy to understand, but it should not be arbitrary or too detailed.
A programming portfolio is an organized set of programs that logically reflect the organization's strategies and goals. It includes long-term and short-term objectives and describes how they will be implemented.
A program management framework is a collection of processes that define how projects are managed through their entire lifecycle, from inception through termination or completion. It describes the roles and responsibilities of all stakeholders involved in managing a project, including project managers and team members who work on it daily.
Program Management Life Cycle (PMLC) is a structured approach for managing programs to meet program requirements within budget and time constraints.
Risk Management has a number of functions, including Risk Assessment, Identification & Monitoring, Risk Response & Mitigation Plans, and Risk Transfer from One Level to Another.
A Roadmap defines the activities that need to be completed to satisfy a project's requirements.
If you want to get started as a program manager and need help knowing where to begin, reading the list above will get you up to speed. It's not too hard to understand the basic principles of program management. You can always find out more later on in your career.
Read More
Everything You Need to Know About Program Management
The program management professional is a missing link in the software development process. These professionals are necessary for low-quality software to be produced. Program managers are responsible for many things in your organization — from initiating project plans to building the technical specifications to managing task lists and budgeting activities. It is essential that you have an understanding of what a program manager does and why it is important for your company's success.
What is Program Management?
Program management is the process of planning, organizing, and controlling the work of a group or project to accomplish its objectives. Program management is a subset of project management that focuses on managing specific products and services produced by organizations. The processes involved in program management are modeled after those used in manufacturing industries.
- Program management is a structured approach to managing programs as they progress from inception through completion.
- A set of processes that provides for the effective delivery of projects within given resource constraints and timeframes.
- The process of identifying appropriate resources, developing plans and strategies, monitoring and controlling work within established limits, and evaluating results against stated goals and expectations.
Difference between Program Management and Project Management
Program management is a set of activities performed to achieve business objectives. The critical purpose of program management is to manage projects, programs, and services effectively. Program Managers are responsible for planning and executing programs. In addition, they work with other departments and stakeholders to ensure that projects are completed on schedule and within budget.
Project Management is the process of planning, organizing, and directing the efforts of resources to meet specific goals within a time frame. Project Management is performed by project team members who must coordinate their efforts with those of other departments or individuals involved in the project.
Program Manager and Responsibilities
A program manager is a person who is responsible for the management of a specific project or program. Program managers are responsible for planning, organizing, and coordinating all aspects of a project to complete it successfully. Therefore, they must be able to work effectively in a team environment and manage multiple tasks simultaneously.
Responsibilities of the Program Manager Include:
- The Program Manager is responsible for successfully implementing all programs, projects, and initiatives within their program or project area.
- Program Managers are responsible for ensuring that their unit's work is completed according to approved plans and budgets.
- Program Managers report directly to the Director of Human Resources, Risk Management, or Project Management.
- The program's overall direction and development, including the selection of courses, the design of courses, and the management of staff.
- Supervising and coordinating all aspects of a program's development, including course content, instructional strategies, delivery methods, and evaluation methods.
- The establishment of performance standards for program staff members at each level and in each area within the program shall be reviewed periodically by an appropriate committee or review body.
- Providing leadership in implementing a sound educational philosophy, management practices, and techniques by the approved policies and procedures governing programs under their supervision or guidance.
Benefits of Program Management
The benefits of program management are numerous. Some of the most critical include:
- Reduces risk: Program managers can improve the chances that projects will be completed on time and within budget.
- Increases accountability: When a program manager manages a project, someone is always responsible. This helps ensure the organization can handle a lack of accountability.
- Improves communications: As a program manager, you'll need to ensure that your team understands what needs to happen and when. A program manager can help with this process by providing everyone knows what's happening at all times.
- Resource Allocation: A program manager can allocate resources effectively to ensure that each project has the right amount of attention from all stakeholders. This saves time and money as well as helps improve overall efficiency in planning and execution.
- Project Affinity: A program manager can view project affinity by viewing all projects under their purview in one place instead of scrolling through dozens or hundreds of daily tasks. This helps them identify strengths and weaknesses concerning individual projects so they can take corrective action before it's too late!
Key Terms Related to Program Management
Program work breakdown structure (WBS) is the basis for defining a management program. It is a hierarchical, comprehensive list of all activities needed to complete the project. The WBS should be simple and easy to understand, but it should not be arbitrary or too detailed.
A programming portfolio is an organized set of programs that logically reflect the organization's strategies and goals. It includes long-term and short-term objectives and describes how they will be implemented.
A program management framework is a collection of processes that define how projects are managed through their entire lifecycle, from inception through termination or completion. It describes the roles and responsibilities of all stakeholders involved in managing a project, including project managers and team members who work on it daily.
Program Management Life Cycle (PMLC) is a structured approach for managing programs to meet program requirements within budget and time constraints.
Risk Management has a number of functions, including Risk Assessment, Identification & Monitoring, Risk Response & Mitigation Plans, and Risk Transfer from One Level to Another.
A Roadmap defines the activities that need to be completed to satisfy a project's requirements.
If you want to get started as a program manager and need help knowing where to begin, reading the list above will get you up to speed. It's not too hard to understand the basic principles of program management. You can always find out more later on in your career.
Information Security Management: Guard Your Digital Assets!
Information Security Management
The wave of cyberattacks is increasing in number and complexity, with perpetrators taking advantage of the latest tools and technologies. The number of victims is growing exponentially, too, affecting a wide variety of organizations, from large corporations to small businesses, government agencies, and even individuals. These attacks are also getting more sophisticated by the day. A straightforward way to protect your network and information is mastering information security management, a core part of any comprehensive IT security strategy.
What is Information Security Management?
Information security management ensures that information assets are protected from loss, unauthorized access, misuse, and destruction. Information security management involves a systematic information security approach applied throughout an organization. This includes policies, procedures, and standards for safeguarding data; hiring qualified staff; establishing processes for detecting, reporting, responding to, and managing incidents involving information systems or when unauthorized users gain access to sensitive data, and maintaining a program that communicates information security expectations to employees.
Information security management is an ongoing process that begins with establishing policies and procedures but continues throughout the life cycle of an organization's information assets. The goal of information security management is not only to protect assets but also to help companies be more competitive in their markets by assisting them in understanding how their competitors are doing business.
Goal of ISM
Information security management aims to reduce the likelihood of a data breach or other security incident occurring by identifying vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. In addition, the aim is to prevent attackers from gaining access to sensitive data to steal money or information that could be used for illegal purposes.
Steps Involve in ISM
The steps involved in information security management are:
- First, identify the potential threats to your business or organization.
- Devise a plan to prevent and minimize these threats.
- Ensure compliance with security policies and procedures that address these risks.
- Implement monitoring systems to detect unauthorized access, use, and disclosure of information assets or activities that may adversely affect the confidentiality and integrity of information systems and data.
- Develop and implement measures to protect information assets through physical, technical, and administrative actions by the appropriate provisions of relevant laws and regulations.
Why Should You Care About Information Security Management?
If your organization is not concerned with information security management, you must do it right.
Information security is a critical function of any business. Therefore, it is essential to understand what makes your organization values and how to protect it from external threats.
As a senior leader, you should care about information security management because:
- It will help you understand your organization's risks and set goals for improving them over time.
- It will help you identify areas where your organization is at risk and give you the tools to mitigate them.
- It will help you build a culture of cybersecurity in your organization so that everyone understands how important it is to be vigilant about information security.
What are the Benefits of Information Security Management (ISM)?
Information Security Management (ISM) is a process that requires identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks to organizations from unauthorized access to or acquisition of their information systems.
The benefits of Information Security Management (ISM) include:
- Reduced risk of data breaches.
- Improved customer confidence in the organization.
- Enhanced reputation as an ethical business.
- Increased profitability and profitability.
- It helps to identify and manage risks effectively.
- It improves the security of information assets by ensuring that it is stored. securely and protected from unauthorized access or disclosure.
Difference Between Information Security, Computer Security, and Information Assurance
Information security protects information assets from threats and vulnerabilities. The goal is to keep information assets safe from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or modification. This means that your organization must have a comprehensive plan to protect your data from external threats and internal fraud/error.
Computer security refers to the protection of computers against external attacks. Computer attacks can come from human attackers or malicious software (malware) programs. Malware is a software developed by hackers and then distributed on the Internet for illegal purposes. Computer security aims to limit the damage caused by malware infections so that they do not impact productivity or compromise users' privacy.
Information assurance ensures the availability, integrity, and confidentiality of information and computer systems. Information assurance goals are to prevent and mitigate information-related risks, reduce impact when risks occur, and help ensure that business activities continue to be performed without interruption.
Conclusion
The threat of information security breaches is a growing concern for businesses and individuals alike. As technology advances, our information becomes more vulnerable, and we must take appropriate measures to protect ourselves from malicious threats. An excellent place to start is by educating yourself about the basics of Information Security Management and then adopting actions to protect your personal information.
Read More
Information Security Management
The wave of cyberattacks is increasing in number and complexity, with perpetrators taking advantage of the latest tools and technologies. The number of victims is growing exponentially, too, affecting a wide variety of organizations, from large corporations to small businesses, government agencies, and even individuals. These attacks are also getting more sophisticated by the day. A straightforward way to protect your network and information is mastering information security management, a core part of any comprehensive IT security strategy.
What is Information Security Management?
Information security management ensures that information assets are protected from loss, unauthorized access, misuse, and destruction. Information security management involves a systematic information security approach applied throughout an organization. This includes policies, procedures, and standards for safeguarding data; hiring qualified staff; establishing processes for detecting, reporting, responding to, and managing incidents involving information systems or when unauthorized users gain access to sensitive data, and maintaining a program that communicates information security expectations to employees.
Information security management is an ongoing process that begins with establishing policies and procedures but continues throughout the life cycle of an organization's information assets. The goal of information security management is not only to protect assets but also to help companies be more competitive in their markets by assisting them in understanding how their competitors are doing business.
Goal of ISM
Information security management aims to reduce the likelihood of a data breach or other security incident occurring by identifying vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. In addition, the aim is to prevent attackers from gaining access to sensitive data to steal money or information that could be used for illegal purposes.
Steps Involve in ISM
The steps involved in information security management are:
- First, identify the potential threats to your business or organization.
- Devise a plan to prevent and minimize these threats.
- Ensure compliance with security policies and procedures that address these risks.
- Implement monitoring systems to detect unauthorized access, use, and disclosure of information assets or activities that may adversely affect the confidentiality and integrity of information systems and data.
- Develop and implement measures to protect information assets through physical, technical, and administrative actions by the appropriate provisions of relevant laws and regulations.
Why Should You Care About Information Security Management?
If your organization is not concerned with information security management, you must do it right.
Information security is a critical function of any business. Therefore, it is essential to understand what makes your organization values and how to protect it from external threats.
As a senior leader, you should care about information security management because:
- It will help you understand your organization's risks and set goals for improving them over time.
- It will help you identify areas where your organization is at risk and give you the tools to mitigate them.
- It will help you build a culture of cybersecurity in your organization so that everyone understands how important it is to be vigilant about information security.
What are the Benefits of Information Security Management (ISM)?
Information Security Management (ISM) is a process that requires identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks to organizations from unauthorized access to or acquisition of their information systems.
The benefits of Information Security Management (ISM) include:
- Reduced risk of data breaches.
- Improved customer confidence in the organization.
- Enhanced reputation as an ethical business.
- Increased profitability and profitability.
- It helps to identify and manage risks effectively.
- It improves the security of information assets by ensuring that it is stored. securely and protected from unauthorized access or disclosure.
Difference Between Information Security, Computer Security, and Information Assurance
Information security protects information assets from threats and vulnerabilities. The goal is to keep information assets safe from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or modification. This means that your organization must have a comprehensive plan to protect your data from external threats and internal fraud/error.
Computer security refers to the protection of computers against external attacks. Computer attacks can come from human attackers or malicious software (malware) programs. Malware is a software developed by hackers and then distributed on the Internet for illegal purposes. Computer security aims to limit the damage caused by malware infections so that they do not impact productivity or compromise users' privacy.
Information assurance ensures the availability, integrity, and confidentiality of information and computer systems. Information assurance goals are to prevent and mitigate information-related risks, reduce impact when risks occur, and help ensure that business activities continue to be performed without interruption.
Conclusion
The threat of information security breaches is a growing concern for businesses and individuals alike. As technology advances, our information becomes more vulnerable, and we must take appropriate measures to protect ourselves from malicious threats. An excellent place to start is by educating yourself about the basics of Information Security Management and then adopting actions to protect your personal information.
Cloud: scalable, elastic, on-demand, multi-tenant, secure
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a development model where hardware, software, and data are hosted at remote and often public facilities. The traditional computing model has been based on a client-server architecture where the servers were dedicated to processing client requests. Instead, the cloud enables users to access applications, databases, and storage by Internet connection, all via a Web browser and web-based interfaces.
Cloud computing is a hot topic and one that is just getting started. Unfortunately, it’s also one of the most misunderstood. When you hear the word "cloud," most people think of hosting providers, virtual servers, and software as a service (SaaS). The reality is that when we talk about cloud computing, there are many different characteristics. Let's read about those characteristics.
- On-Demand Self-Service
Cloud computing allows customers to provision and pays for computing resources as needed without upfront commitments. This is called on-demand self-service. The customer can use the cloud as much or as little as required at any time. Customers are not tied to a set amount of time or number of usage cycles.
- Ubiquitous Network Access
A cloud service provider has a network that provides ubiquitous access to customers' applications and data throughout their enterprises, regardless of where they are located and what device they use. A client application may be accessed from anywhere worldwide, provided it is accessible via a network connection. The network may be a private cloud or an external (public) cloud.
- Sustainability & Resilience
Cloud computing provides sustainability and resilience due to its elasticity, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. In addition, it allows enterprises to deploy resources on demand, thus reducing the time it takes for them to react when business needs change.
- Rapid Elasticity
One of the key characteristics of cloud computing is the ability to quickly deploy servers and applications, either in a virtual environment or on physical hardware. This characteristic allows organizations to respond rapidly to market changes and customer demands without worrying about capital investment and maintenance. In addition, the ability to quickly move data from one location to another is also a significant benefit for businesses that need to scale up their operations.
- Resource Pooling
Resource pooling refers to allocating resources across multiple users, allowing each user access to as much technology as needed. As a result, resources are shared among all users instead of being allocated based on user status or usage levels. This reduces the cost per unit of IT infrastructure and makes it more accessible for all users at any time. In addition, resource pooling makes it easier for users who move between projects or departments because they do not have to worry about losing their current applications or data when they switch jobs or locations.
- Measured Service
Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimum management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model uses patterns to deliver an abstraction of virtualized hardware that allows developers to build applications without requiring a highly-specialized knowledge of the internal workings of a cloud service provider's hardware or software infrastructure.
- Pay-as-you-go model
Pay-as-you-go (PAYG) is an alternative payment scheme where users pay only for the actual resources they use or the time they use them. In the cloud computing environment, pay-as-you-go models allow users to pay only for their actual usage and not for any set amount of usage upfront. Thus in PAYG models, users are charged only for what they consume instead of being charged in advance for all services offered by the provider.
- Global Infrastructure
Cloud computing is based on the concept of geographic distribution. Therefore, data centers provide the service in different locations worldwide. This ensures you have access to high-performance servers and storage, regardless of location. It also provides redundancy, which means that if one data center becomes unavailable, another can take over its responsibilities, thus ensuring that your services continue uninterrupted.
- Reliability and Availability
The most important characteristic of cloud computing is its reliability and availability. Your applications are hosted by experts who monitor them 24/7 to ensure they run smoothly without any problems or disruptions. In addition, if you need support for any reason, someone is always available to help you resolve any issues.
- Security
Cloud computing provides vital security measures to help businesses keep their data safe. The cloud provider has access to all the necessary information, but only the user can access their information. In addition, there is no single point of failure, so if one part of the system fails, many others can take over. This means that even if a hacker gets into one part of the system and steals some data, they will not be able to find anything useful because it is deleted immediately and cannot be recovered.
- Privacy
Cloud computing offers businesses complete control over their data and its use. For example, companies can decide when and where employees or partners can access data and what information about customers is shared with external companies. Businesses also have complete control over who has access to their networks and systems so that no one else can see sensitive data without permission from the owner of that information.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is a radical shift that has brought about many changes. It has immense potential to change how we look at businesses and what makes them successful in the future. This innovation has brought many opportunities and innovations that have changed the way businesses get done. Progressive companies are gearing up with insights to use cloud computing better, while others are resting on their assets. It is high time to embrace the new technology-driven trends that the cloud offers and benefit from not being left behind.
Read More
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a development model where hardware, software, and data are hosted at remote and often public facilities. The traditional computing model has been based on a client-server architecture where the servers were dedicated to processing client requests. Instead, the cloud enables users to access applications, databases, and storage by Internet connection, all via a Web browser and web-based interfaces.
Cloud computing is a hot topic and one that is just getting started. Unfortunately, it’s also one of the most misunderstood. When you hear the word "cloud," most people think of hosting providers, virtual servers, and software as a service (SaaS). The reality is that when we talk about cloud computing, there are many different characteristics. Let's read about those characteristics.
- On-Demand Self-Service
Cloud computing allows customers to provision and pays for computing resources as needed without upfront commitments. This is called on-demand self-service. The customer can use the cloud as much or as little as required at any time. Customers are not tied to a set amount of time or number of usage cycles.
- Ubiquitous Network Access
A cloud service provider has a network that provides ubiquitous access to customers' applications and data throughout their enterprises, regardless of where they are located and what device they use. A client application may be accessed from anywhere worldwide, provided it is accessible via a network connection. The network may be a private cloud or an external (public) cloud.
- Sustainability & Resilience
Cloud computing provides sustainability and resilience due to its elasticity, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. In addition, it allows enterprises to deploy resources on demand, thus reducing the time it takes for them to react when business needs change.
- Rapid Elasticity
One of the key characteristics of cloud computing is the ability to quickly deploy servers and applications, either in a virtual environment or on physical hardware. This characteristic allows organizations to respond rapidly to market changes and customer demands without worrying about capital investment and maintenance. In addition, the ability to quickly move data from one location to another is also a significant benefit for businesses that need to scale up their operations.
- Resource Pooling
Resource pooling refers to allocating resources across multiple users, allowing each user access to as much technology as needed. As a result, resources are shared among all users instead of being allocated based on user status or usage levels. This reduces the cost per unit of IT infrastructure and makes it more accessible for all users at any time. In addition, resource pooling makes it easier for users who move between projects or departments because they do not have to worry about losing their current applications or data when they switch jobs or locations.
- Measured Service
Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimum management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model uses patterns to deliver an abstraction of virtualized hardware that allows developers to build applications without requiring a highly-specialized knowledge of the internal workings of a cloud service provider's hardware or software infrastructure.
- Pay-as-you-go model
Pay-as-you-go (PAYG) is an alternative payment scheme where users pay only for the actual resources they use or the time they use them. In the cloud computing environment, pay-as-you-go models allow users to pay only for their actual usage and not for any set amount of usage upfront. Thus in PAYG models, users are charged only for what they consume instead of being charged in advance for all services offered by the provider.
- Global Infrastructure
Cloud computing is based on the concept of geographic distribution. Therefore, data centers provide the service in different locations worldwide. This ensures you have access to high-performance servers and storage, regardless of location. It also provides redundancy, which means that if one data center becomes unavailable, another can take over its responsibilities, thus ensuring that your services continue uninterrupted.
- Reliability and Availability
The most important characteristic of cloud computing is its reliability and availability. Your applications are hosted by experts who monitor them 24/7 to ensure they run smoothly without any problems or disruptions. In addition, if you need support for any reason, someone is always available to help you resolve any issues.
- Security
Cloud computing provides vital security measures to help businesses keep their data safe. The cloud provider has access to all the necessary information, but only the user can access their information. In addition, there is no single point of failure, so if one part of the system fails, many others can take over. This means that even if a hacker gets into one part of the system and steals some data, they will not be able to find anything useful because it is deleted immediately and cannot be recovered.
- Privacy
Cloud computing offers businesses complete control over their data and its use. For example, companies can decide when and where employees or partners can access data and what information about customers is shared with external companies. Businesses also have complete control over who has access to their networks and systems so that no one else can see sensitive data without permission from the owner of that information.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is a radical shift that has brought about many changes. It has immense potential to change how we look at businesses and what makes them successful in the future. This innovation has brought many opportunities and innovations that have changed the way businesses get done. Progressive companies are gearing up with insights to use cloud computing better, while others are resting on their assets. It is high time to embrace the new technology-driven trends that the cloud offers and benefit from not being left behind.
Why Do Organizations Need DevOps for Growth and Efficiency?
Why Organizations Require DevOps?
DevOps has been a widely leveraged term in the software development domain over the last few years. DevOps is defined as a technique where IT professionals and developers work closely to share code, knowledge, and procedures across organizational space. The main aim of DevOps is to enhance collaboration and communication between teams to accelerate project deliveries.
In addition, DevOps can be compared to Agile practice, where teams collaborate with the customer - enhancing communication and unity across all developmental areas.
How DevOps Works
DevOps depends on having a system that allows automated code transfer from development to production. This system comprises various tools that help automate processes - container platforms, Version Control Systems (VCS), and build servers.
The systems also help accelerate software development by automating the procedures that can be done manually.
DevOps Benefits
a. Top Quality Products
Collaboration between DevOps team members makes it seamless for developers to work hand in hand to determine issues and prevent them from creeping into DevOps developed version. As a result, this alliance leads to top-quality products and is less likely to have errors that might impact performances.
b. Minimized Development Time
DevOps systems can help accelerate the developmental process by allowing developers to focus on writing code than configuring DevOps developing environments. This leads to the spending of minimum waiting time for DevOps tools to configure before coding, thus, helping the team to become productive.
c. Easy Upgrades
Since DevOps infrastructure automates several activities involved in maintaining and upgrading DevOps systems, it becomes easier for organizations to update their DevOps pipelines. This avoids compatibility issues and ensures the systems run at top-notch performance throughout.
d. Easier Team Collaboration
DevOps systems are developed on ideas of sharing knowledge between DevOps teammates. By automating its development, creators spend more time collaborating and developing better products with are shorter turnaround time.
The benefits of DevOps make it a valuable asset for any organization seeking to enhance its software development process. By leveraging DevOps, businesses can see the benefits of efficiency, time, and money.
In short, DevOps tools work together to develop a seamless automated process that helps enhance the pace and quality of software development projects. They also improve collaboration between team members, making the whole process productive.
Read More
Why Organizations Require DevOps?
DevOps has been a widely leveraged term in the software development domain over the last few years. DevOps is defined as a technique where IT professionals and developers work closely to share code, knowledge, and procedures across organizational space. The main aim of DevOps is to enhance collaboration and communication between teams to accelerate project deliveries.
In addition, DevOps can be compared to Agile practice, where teams collaborate with the customer - enhancing communication and unity across all developmental areas.
How DevOps Works
DevOps depends on having a system that allows automated code transfer from development to production. This system comprises various tools that help automate processes - container platforms, Version Control Systems (VCS), and build servers.
The systems also help accelerate software development by automating the procedures that can be done manually.
DevOps Benefits
a. Top Quality Products
Collaboration between DevOps team members makes it seamless for developers to work hand in hand to determine issues and prevent them from creeping into DevOps developed version. As a result, this alliance leads to top-quality products and is less likely to have errors that might impact performances.
b. Minimized Development Time
DevOps systems can help accelerate the developmental process by allowing developers to focus on writing code than configuring DevOps developing environments. This leads to the spending of minimum waiting time for DevOps tools to configure before coding, thus, helping the team to become productive.
c. Easy Upgrades
Since DevOps infrastructure automates several activities involved in maintaining and upgrading DevOps systems, it becomes easier for organizations to update their DevOps pipelines. This avoids compatibility issues and ensures the systems run at top-notch performance throughout.
d. Easier Team Collaboration
DevOps systems are developed on ideas of sharing knowledge between DevOps teammates. By automating its development, creators spend more time collaborating and developing better products with are shorter turnaround time.
The benefits of DevOps make it a valuable asset for any organization seeking to enhance its software development process. By leveraging DevOps, businesses can see the benefits of efficiency, time, and money.
In short, DevOps tools work together to develop a seamless automated process that helps enhance the pace and quality of software development projects. They also improve collaboration between team members, making the whole process productive.
Productivity Management: Key Strategies and Importance.
Productivity Management and Its Importance
Table of Content
Why Does Productivity Matter?
What is productivity management?
Why is productivity management important?
What Are Some Effective Ways to Manage Productivity?
Productivity is Essential for Today's Companies
Why Does Productivity Matter?
The productivity of a project is the amount of work that can be done in a given period. The productivity of a project will vary depending on many factors. Still, one of the most important is the quality of the team. A good team will provide better results, which means their productivity increases. Productivity matters in any project because it's a key driver for success. If you don't produce enough value, you won't be able to provide a good return on your investment.
What is Productivity Management?
Productivity management is a strategic management process that helps an organization achieve its goals by reducing waste and increasing the efficiency of business operations. Productivity management focuses on all aspects of the business, including sales, service, marketing, and financial results. Productivity management aims to create the highest level of value for the customer while minimizing costs or any other negative impact on the organization's bottom line.
Productivity management can be applied to any business or organization, whether a small business or a large corporation. Many companies use productivity management as one of their top priorities because it positively impacts their bottom line.
Why is Productivity Management Important?
The ability to manage productivity is an essential part of business success.
Productivity measures the amount of output produced by a worker over a specific period. In simple terms, it is the amount of work done per unit of time.
There are many reasons why productivity management is essential:
- It allows you to control costs.
- It helps you make better decisions about how you spend your money.
- It helps keep workloads down and staff happy.
- Setting goals for each employee so that they know what to work towards.
- Strategizing how to reach those goals.
- Measuring how well each employee is doing toward those goals.
- Maintaining consistent communication between all employees involved in the project or task.
What Are Some Effective Ways to Manage Productivity?
Productivity is the amount of work you get done in a day or week. The most effective way to manage productivity is by setting goals and keeping track of your progress toward those goals.
Here are some practical ways to manage productivity:
- Set realistic goals
Goals should be SMART (specific, measurable, action-oriented, realistic, and time-bound). You must set your goals based on your current level and what you are willing to do to achieve them.
- Track your progress
Once you have set your goals and recorded them in a place where you will constantly see them (such as a calendar), make sure that you keep track of how well you are doing each week or month.
- Take Advantage of Technology
Technology has become an integral part of our daily lives. It helps us stay connected and get things done faster. You can use technology to make managing your time easier by using app such as Google Calendar. This will help you keep track of the time you spend doing things and how much time it takes to complete them. For example, if you find that it takes 15 minutes to complete a task, to your calendar so they don't get forgotten about later on during the day when it would be too late to do anything about it!
- Create a Schedule
Creating a schedule for yourself is essential to get things done on time. It will help you organize your life around important tasks and juggle all the other stuff in between them. Schedule everything from work-related tasks like meetings, lunches with clients, or even just random errands.
- Set boundaries for yourself
When you have a lot of work, it can be easy to lose track of time. That's why it's important to set boundaries for yourself. If you know exactly when you will stop working on a project, you won't have any trouble staying focused until that time. Of course, you should also set these boundaries in advance so there are no surprises.
- Turn off distracting notifications.
It's easy to get distracted by notifications while working on something important. If you don't want to miss any important messages or alerts, turn them off while working on something else and then turn them back on when it's time for that project again. This way, all distractions will be behind closed doors and out of sight so that nothing distracts from what needs doing at that moment (and vice versa).
Productivity is Essential for Today's Companies
The world has become where we need to be productive to survive. The faster we can be effective, the more time we will have for ourselves and our loved ones.
Productivity is essential for today's companies because it allows them to operate at a higher efficiency level. However, suppose you are not able to produce your products or services at a quick rate. In that case, your company might not be able to stay competitive in the marketplace.
Productivity is also important because it allows us to get ahead and meet our financial obligations on time. However, when you cannot produce as much as possible within a given period, it can cause many problems with your finances and other aspects of your life.
Takeaway: How to Improve Productivity
There are many ways to improve productivity. Here are a few tips:
- Have a clear vision of what you want to achieve.
- Do not let yourself get distracted by other things in the project.
- Have a set of standards for what good looks like.
- Reward yourself for small victories along the way.
- Set deadlines and enforce them as necessary.
Conclusion
Productivity management is a broad term and can refer to several different things. However, the concept of "productivity" is simple to understand-it and deals with the quantity and quality of work output. That's not to say that it's easy to implement in the workplace. While it may seem like a simple issue on paper, getting employees to be productive at work can be far more complex than it looks. Nevertheless, here's hoping for a successful implementation for all!
Read More
Productivity Management and Its Importance
Table of Content
Why Does Productivity Matter?
What is productivity management?
Why is productivity management important?
What Are Some Effective Ways to Manage Productivity?
Productivity is Essential for Today's Companies
Why Does Productivity Matter?
The productivity of a project is the amount of work that can be done in a given period. The productivity of a project will vary depending on many factors. Still, one of the most important is the quality of the team. A good team will provide better results, which means their productivity increases. Productivity matters in any project because it's a key driver for success. If you don't produce enough value, you won't be able to provide a good return on your investment.
What is Productivity Management?
Productivity management is a strategic management process that helps an organization achieve its goals by reducing waste and increasing the efficiency of business operations. Productivity management focuses on all aspects of the business, including sales, service, marketing, and financial results. Productivity management aims to create the highest level of value for the customer while minimizing costs or any other negative impact on the organization's bottom line.
Productivity management can be applied to any business or organization, whether a small business or a large corporation. Many companies use productivity management as one of their top priorities because it positively impacts their bottom line.
Why is Productivity Management Important?
The ability to manage productivity is an essential part of business success.
Productivity measures the amount of output produced by a worker over a specific period. In simple terms, it is the amount of work done per unit of time.
There are many reasons why productivity management is essential:
- It allows you to control costs.
- It helps you make better decisions about how you spend your money.
- It helps keep workloads down and staff happy.
- Setting goals for each employee so that they know what to work towards.
- Strategizing how to reach those goals.
- Measuring how well each employee is doing toward those goals.
- Maintaining consistent communication between all employees involved in the project or task.
What Are Some Effective Ways to Manage Productivity?
Productivity is the amount of work you get done in a day or week. The most effective way to manage productivity is by setting goals and keeping track of your progress toward those goals.
Here are some practical ways to manage productivity:
- Set realistic goals
Goals should be SMART (specific, measurable, action-oriented, realistic, and time-bound). You must set your goals based on your current level and what you are willing to do to achieve them.
- Track your progress
Once you have set your goals and recorded them in a place where you will constantly see them (such as a calendar), make sure that you keep track of how well you are doing each week or month.
- Take Advantage of Technology
Technology has become an integral part of our daily lives. It helps us stay connected and get things done faster. You can use technology to make managing your time easier by using app such as Google Calendar. This will help you keep track of the time you spend doing things and how much time it takes to complete them. For example, if you find that it takes 15 minutes to complete a task, to your calendar so they don't get forgotten about later on during the day when it would be too late to do anything about it!
- Create a Schedule
Creating a schedule for yourself is essential to get things done on time. It will help you organize your life around important tasks and juggle all the other stuff in between them. Schedule everything from work-related tasks like meetings, lunches with clients, or even just random errands.
- Set boundaries for yourself
When you have a lot of work, it can be easy to lose track of time. That's why it's important to set boundaries for yourself. If you know exactly when you will stop working on a project, you won't have any trouble staying focused until that time. Of course, you should also set these boundaries in advance so there are no surprises.
- Turn off distracting notifications.
It's easy to get distracted by notifications while working on something important. If you don't want to miss any important messages or alerts, turn them off while working on something else and then turn them back on when it's time for that project again. This way, all distractions will be behind closed doors and out of sight so that nothing distracts from what needs doing at that moment (and vice versa).
Productivity is Essential for Today's Companies
The world has become where we need to be productive to survive. The faster we can be effective, the more time we will have for ourselves and our loved ones.
Productivity is essential for today's companies because it allows them to operate at a higher efficiency level. However, suppose you are not able to produce your products or services at a quick rate. In that case, your company might not be able to stay competitive in the marketplace.
Productivity is also important because it allows us to get ahead and meet our financial obligations on time. However, when you cannot produce as much as possible within a given period, it can cause many problems with your finances and other aspects of your life.
Takeaway: How to Improve Productivity
There are many ways to improve productivity. Here are a few tips:
- Have a clear vision of what you want to achieve.
- Do not let yourself get distracted by other things in the project.
- Have a set of standards for what good looks like.
- Reward yourself for small victories along the way.
- Set deadlines and enforce them as necessary.
Conclusion
Productivity management is a broad term and can refer to several different things. However, the concept of "productivity" is simple to understand-it and deals with the quantity and quality of work output. That's not to say that it's easy to implement in the workplace. While it may seem like a simple issue on paper, getting employees to be productive at work can be far more complex than it looks. Nevertheless, here's hoping for a successful implementation for all!
Introduction to Google Analytics: Track and Optimize Traffic
Introduction to Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a free online tool that tracks website traffic and traffic sources, which can help you measure your marketing campaign's success.
It's a great way to see how visitors engage with your site — where they came from and what they do while there. You can also use it to identify problems with your site so you can fix them before they affect visitors' experience.
Google Analytics tracks all the information about your site's visitors, including:
- Visitors' demographics: age, gender, and location
- How long do they spend on your pages
- How many times do they click through from search results or other websites to reach your site?
- What pages do they view when they visit, including keywords used in their search query (this is called "keyword tracking")
- How long it takes them to leave once they get there (called "exit intent")
Why Analytics is Important
Analytics is important for a website because it helps to understand its performance, which is essential for making changes to optimize performance and improve user experience. It also helps to understand how visitors use your site, which helps make decisions about where to allocate resources.
How Does Google Analytics Work
Google Analytics uses cookies to track website traffic. Cookies are small bits of information stored on your computer or mobile device by the web server that accesses your website. They contain non-personal information about how you interact with the website to help us improve the way we serve content and ads to you. The Google Analytics cookies collect pseudo-anonymous identifiers (i.e., something that is anonymous) that are stored on your device's hard drive so we can only read them. The Google Analytics cookies use a combination of JavaScript tracking code and cookies to identify and report on unique individuals and their behavior.
Types of Reports in Google Analytics
To understand the performance of the website, google analytics includes reports. These are:
Acquisition reports
This is a report about the traffic that has come to your website from other sources. As its name indicates, it's about who came to your site and why. You can use this report to see if any new visitors are coming to your website or if you have lost some existing visitors because they left the website or moved on to another site.
Monetization reports
These reports show how much money you made from advertising and how much you spent on ads. You can use this information to see what ads you should run to make more money and what kinds of ads don't work well since they might not generate enough revenue for you.
Engagement Reports
Engagement reports show how your audience is engaging with your content. This includes all forms of engagement, from clicks and page views to shares, comments, and more. You can use these reports to identify what content gets the most attention, what content performs well against competitors, and how you can improve your engagement metrics overall.
Demographics Reports
Demographics reports show you which demographics are most interested in your business. This can help you understand which areas of interest might be underserved by your company or website. It also allows you to target these people with specific ads and other marketing campaigns so that they know about your products and services before ever trying them out for themselves.
Advertising Reports
These reports show detailed data on your advertising performance. They include pages and clicks, cost per click, conversion rate, and more. Use these reports to help you optimize your advertising strategy and make decisions about your campaigns.
Technology Reports
These reports give information about what happens on your website when users access it. These reports include session duration (how long visitors spend on your site), bounce rate (the percentage of visitors who leave your site after visiting only once), average time on site (the number of time people spend browsing your site), page views per visit (how many people see at least one page on your location) and more.
Metrics in Google Analytics
Metrics are the key to making data-driven decisions. In Google Analytics, you can measure metrics like page views and time on page. Still, there are more advanced metrics that we use at the company to help us understand our business better. These metrics are –
Conversion Rate: The number of people who visit your website, complete a specific action, and purchase a product/service on your site.
Views: The total number of unique users who have viewed your website.
Traffic Sources: The volume of traffic each source provides to your website.
Event Tracking: A set of parameters that allows you to track specific events on your site, such as when someone views an article or purchases a product.
Sessions: how many times a person visited your website during a specified period (such as an hour)
Bounce rate: The percentage of users who leave your website before they complete their visit.
Acquisition: The acquisition metric is the number of users who have visited your site but did not convert into a lead.
Why Does the Company Use Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is used for a number of reasons. First, it gives your site owners an overview of how visitors interact with their website. This includes where they came from and what they did once they got on your site. If you have a page that has high traffic, you can see who the most popular pages are and determine which ones need more attention or improvement. You can also see how long people stay on each page, so you can ensure that all of your content is interesting enough to keep people coming back for more.
Google Analytics also offers reports on mobile analytics, which are helpful if you are trying to figure out how many people visit your website on their mobile devices.
Finally, it gives you information about how many users are dropping off at specific points on your site so that you can determine where they were lost and attempt to improve their experience.
Benefits of Google Analytics
Google Analytics is the most popular analytics platform in the world. It's free, easy to set up, and has many features.
Here are some of the benefits:
- It can track visitors from all over the web, not just your website.
- It offers custom reports for every aspect of your business (e.g., number of visitors by country or city)
- You can see how much traffic you have coming from social media.
- You can see which pages are the most popular.
- You can see where people go on your website when they interact with it (e.g., click on one of the links)
- Measure the performance of marketing campaigns (such as email marketing and e-commerce)
- Analyze search trends and traffic sources (search engine optimization)
- Access data in real-time (real-time bidding)
Conclusion
Although several tools are available for tracking your site's traffic and statistics, Google Analytics provides greater ease of use and access for free. If you aren't tracking your website's traffic and statistics now, it's well worth considering this tool.
Read More
Introduction to Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a free online tool that tracks website traffic and traffic sources, which can help you measure your marketing campaign's success.
It's a great way to see how visitors engage with your site — where they came from and what they do while there. You can also use it to identify problems with your site so you can fix them before they affect visitors' experience.
Google Analytics tracks all the information about your site's visitors, including:
- Visitors' demographics: age, gender, and location
- How long do they spend on your pages
- How many times do they click through from search results or other websites to reach your site?
- What pages do they view when they visit, including keywords used in their search query (this is called "keyword tracking")
- How long it takes them to leave once they get there (called "exit intent")
Why Analytics is Important
Analytics is important for a website because it helps to understand its performance, which is essential for making changes to optimize performance and improve user experience. It also helps to understand how visitors use your site, which helps make decisions about where to allocate resources.
How Does Google Analytics Work
Google Analytics uses cookies to track website traffic. Cookies are small bits of information stored on your computer or mobile device by the web server that accesses your website. They contain non-personal information about how you interact with the website to help us improve the way we serve content and ads to you. The Google Analytics cookies collect pseudo-anonymous identifiers (i.e., something that is anonymous) that are stored on your device's hard drive so we can only read them. The Google Analytics cookies use a combination of JavaScript tracking code and cookies to identify and report on unique individuals and their behavior.
Types of Reports in Google Analytics
To understand the performance of the website, google analytics includes reports. These are:
Acquisition reports
This is a report about the traffic that has come to your website from other sources. As its name indicates, it's about who came to your site and why. You can use this report to see if any new visitors are coming to your website or if you have lost some existing visitors because they left the website or moved on to another site.
Monetization reports
These reports show how much money you made from advertising and how much you spent on ads. You can use this information to see what ads you should run to make more money and what kinds of ads don't work well since they might not generate enough revenue for you.
Engagement Reports
Engagement reports show how your audience is engaging with your content. This includes all forms of engagement, from clicks and page views to shares, comments, and more. You can use these reports to identify what content gets the most attention, what content performs well against competitors, and how you can improve your engagement metrics overall.
Demographics Reports
Demographics reports show you which demographics are most interested in your business. This can help you understand which areas of interest might be underserved by your company or website. It also allows you to target these people with specific ads and other marketing campaigns so that they know about your products and services before ever trying them out for themselves.
Advertising Reports
These reports show detailed data on your advertising performance. They include pages and clicks, cost per click, conversion rate, and more. Use these reports to help you optimize your advertising strategy and make decisions about your campaigns.
Technology Reports
These reports give information about what happens on your website when users access it. These reports include session duration (how long visitors spend on your site), bounce rate (the percentage of visitors who leave your site after visiting only once), average time on site (the number of time people spend browsing your site), page views per visit (how many people see at least one page on your location) and more.
Metrics in Google Analytics
Metrics are the key to making data-driven decisions. In Google Analytics, you can measure metrics like page views and time on page. Still, there are more advanced metrics that we use at the company to help us understand our business better. These metrics are –
Conversion Rate: The number of people who visit your website, complete a specific action, and purchase a product/service on your site.
Views: The total number of unique users who have viewed your website.
Traffic Sources: The volume of traffic each source provides to your website.
Event Tracking: A set of parameters that allows you to track specific events on your site, such as when someone views an article or purchases a product.
Sessions: how many times a person visited your website during a specified period (such as an hour)
Bounce rate: The percentage of users who leave your website before they complete their visit.
Acquisition: The acquisition metric is the number of users who have visited your site but did not convert into a lead.
Why Does the Company Use Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is used for a number of reasons. First, it gives your site owners an overview of how visitors interact with their website. This includes where they came from and what they did once they got on your site. If you have a page that has high traffic, you can see who the most popular pages are and determine which ones need more attention or improvement. You can also see how long people stay on each page, so you can ensure that all of your content is interesting enough to keep people coming back for more.
Google Analytics also offers reports on mobile analytics, which are helpful if you are trying to figure out how many people visit your website on their mobile devices.
Finally, it gives you information about how many users are dropping off at specific points on your site so that you can determine where they were lost and attempt to improve their experience.
Benefits of Google Analytics
Google Analytics is the most popular analytics platform in the world. It's free, easy to set up, and has many features.
Here are some of the benefits:
- It can track visitors from all over the web, not just your website.
- It offers custom reports for every aspect of your business (e.g., number of visitors by country or city)
- You can see how much traffic you have coming from social media.
- You can see which pages are the most popular.
- You can see where people go on your website when they interact with it (e.g., click on one of the links)
- Measure the performance of marketing campaigns (such as email marketing and e-commerce)
- Analyze search trends and traffic sources (search engine optimization)
- Access data in real-time (real-time bidding)
Conclusion
Although several tools are available for tracking your site's traffic and statistics, Google Analytics provides greater ease of use and access for free. If you aren't tracking your website's traffic and statistics now, it's well worth considering this tool.
Cost of PMI - ACP Certification Exam and Details in 2023
Cost of PMI ACP Certification 2023
PMI ACP accreditation is one of the most globally renowned certifications, where the average salary of a certified individual is $123,000 annually. However, to attain this credential, professionals must have a precise understanding of the PMI Exam. Hence, before jumping onto the exam schedule, it's significant to know the basics of PMI ACP certification – definition, cost & payment methods.
PMI ACP Certification: Explained
A. Definition
Agile is a progressive technique of software delivery to the customers rather than dropping it as a whole to test. This software version lets you leverage and understands the software better. Hence, PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (ACP) accreditation equips an individual with Agile fundamentals to perform with top-notch integrity.
B. Cost
The cost of PMI ACP Certification depends entirely on the person's type of membership with PMI. If you're a PMI member, they offer a discounted price for the credential. On the other hand, if you're a non-member of PMI, you have to pay the full fee to attain the certification.
Exam
PMI Member
Non-PMI Member
PMI ACP Exam
INR 25,196
INR 38,299
PMI ACP Exam Retake
INR 19,404
INR 30,506
C. Eligibility Criteria
Let us see the prerequisites of PMI ACP Certification put forward by PMI:
- Secondary degree
- 21 contact hours in Agile practice training
- 12 months of general project experience within the last 5 years
- 8 months of Agile project experience within the last 3 years
D. Gain and Maintain
The PMI ACP Certification exam has 120 MCQs to be completed in 3 hours. To maintain PMI ACP Certification, professionals must earn 30 PDUs in Agile topics every three years.
E. Crack PMI ACP Exam
Let's look at some tips to crack the PMI ACP exam easily and in one go.
- Ensure you plan your study well and approach the certification exam like a project.
- Keep track of what you've learned and missed in PMBOK and Agile practice guides to keep yourself updated.
- Keep your study materials limited and strive to finish them before the exam
- Keep solving the practice questions.
Read More
Cost of PMI ACP Certification 2023
PMI ACP accreditation is one of the most globally renowned certifications, where the average salary of a certified individual is $123,000 annually. However, to attain this credential, professionals must have a precise understanding of the PMI Exam. Hence, before jumping onto the exam schedule, it's significant to know the basics of PMI ACP certification – definition, cost & payment methods.
PMI ACP Certification: Explained
A. Definition
Agile is a progressive technique of software delivery to the customers rather than dropping it as a whole to test. This software version lets you leverage and understands the software better. Hence, PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (ACP) accreditation equips an individual with Agile fundamentals to perform with top-notch integrity.
B. Cost
The cost of PMI ACP Certification depends entirely on the person's type of membership with PMI. If you're a PMI member, they offer a discounted price for the credential. On the other hand, if you're a non-member of PMI, you have to pay the full fee to attain the certification.
|
Exam |
PMI Member |
Non-PMI Member |
|
PMI ACP Exam |
INR 25,196 |
INR 38,299 |
|
PMI ACP Exam Retake |
INR 19,404 |
INR 30,506 |
C. Eligibility Criteria
Let us see the prerequisites of PMI ACP Certification put forward by PMI:
- Secondary degree
- 21 contact hours in Agile practice training
- 12 months of general project experience within the last 5 years
- 8 months of Agile project experience within the last 3 years
D. Gain and Maintain
The PMI ACP Certification exam has 120 MCQs to be completed in 3 hours. To maintain PMI ACP Certification, professionals must earn 30 PDUs in Agile topics every three years.
E. Crack PMI ACP Exam
Let's look at some tips to crack the PMI ACP exam easily and in one go.
- Ensure you plan your study well and approach the certification exam like a project.
- Keep track of what you've learned and missed in PMBOK and Agile practice guides to keep yourself updated.
- Keep your study materials limited and strive to finish them before the exam
- Keep solving the practice questions.
Become an Information Security Analyst in 2023: Start Now!
Become an Information Security Analyst 2023
With networked computing becoming a trend even in a small-scale company and the development of the internet and cloud solutions, accessing advanced data to solve business challenges has never been widespread.
As data systems are universal, data has become less secure, where more companies manage a colossal amount of data, making it an easier target for cybercriminals. Often smaller organizations need IT the experience to keep data safe. Over the last decade, more companies have dealt with high-profile data breaches.
As a result, the role of Information Security (IS) Analyst has advanced to a most sought-after position across industry verticals.
What is an IS Analyst?
An Information Security (IS) Analyst defends computer networks performed by private businesses, nonprofit organizations, and government organizations. However, there are a few domains where an IS Analyst can't find work relying on data security.
As ML and predictive modeling illustrate their investment returns, more enterprises need the skills of a competent IS Analyst. The sole responsibility of an Information Security Analyst is to develop scalable security apparatuses to address and prevent threats.
The job's criteria depend on the sector; however, an IS Analyst is often reserved in case of data breaches, hacking, or other crises based on tech asset security.
An analyst generates reports that IT admins and business professionals leverage to assess the practicality of their security systems. Depending on the Analyst's suggestions, organizations will modify security networks to ensure data is inaccessible to unauthorized people.
Developing and delivering educational courses is also a part of their work, as it's adequate to aid workforces in maintaining solid security practices.
Roles of Information Security Analysts
An IS Analyst is responsible for the following:
- Maintain data encryption and firewalls to safeguard sensitive data.
- Establish security standards
- Investigate security breaches on their company's networks.
- Ensure that senior IT staff is aware of security improvements
- Help users with learning and installation of new security products
- Staying updated on the latest advancements in IT security
Information Security Analysts: Job Prospects & Certification Requirement
According to BLS, IS Analyst job scope is projected to rise to 28% from 2016-2026, considerably more rapidly than other occupations' average growth. In addition, according to US News, IS Analyst is listed as the fourth best IT job in 2019, attributing to a wide variety of ventures looking for data security solutions.
According to Indeed, the average IS Analyst salary is $81,065 annually, which may increase as per expertise and knowledge.
An IS accreditation comprises a collection of credentials that set up foundational knowledge in different topics.
ICert Global helps people excel in the skills required for network security. Our security programs and certifications help participants to spot vulnerabilities, immediately respond to emergencies, and fend off attacks.
Some of the top-notch security certifications are as follows:
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Cyber Security Expert
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- CompTIA Security+
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Read More
Become an Information Security Analyst 2023
With networked computing becoming a trend even in a small-scale company and the development of the internet and cloud solutions, accessing advanced data to solve business challenges has never been widespread.
As data systems are universal, data has become less secure, where more companies manage a colossal amount of data, making it an easier target for cybercriminals. Often smaller organizations need IT the experience to keep data safe. Over the last decade, more companies have dealt with high-profile data breaches.
As a result, the role of Information Security (IS) Analyst has advanced to a most sought-after position across industry verticals.
What is an IS Analyst?
An Information Security (IS) Analyst defends computer networks performed by private businesses, nonprofit organizations, and government organizations. However, there are a few domains where an IS Analyst can't find work relying on data security.
As ML and predictive modeling illustrate their investment returns, more enterprises need the skills of a competent IS Analyst. The sole responsibility of an Information Security Analyst is to develop scalable security apparatuses to address and prevent threats.
The job's criteria depend on the sector; however, an IS Analyst is often reserved in case of data breaches, hacking, or other crises based on tech asset security.
An analyst generates reports that IT admins and business professionals leverage to assess the practicality of their security systems. Depending on the Analyst's suggestions, organizations will modify security networks to ensure data is inaccessible to unauthorized people.
Developing and delivering educational courses is also a part of their work, as it's adequate to aid workforces in maintaining solid security practices.
Roles of Information Security Analysts
An IS Analyst is responsible for the following:
- Maintain data encryption and firewalls to safeguard sensitive data.
- Establish security standards
- Investigate security breaches on their company's networks.
- Ensure that senior IT staff is aware of security improvements
- Help users with learning and installation of new security products
- Staying updated on the latest advancements in IT security
Information Security Analysts: Job Prospects & Certification Requirement
According to BLS, IS Analyst job scope is projected to rise to 28% from 2016-2026, considerably more rapidly than other occupations' average growth. In addition, according to US News, IS Analyst is listed as the fourth best IT job in 2019, attributing to a wide variety of ventures looking for data security solutions.
According to Indeed, the average IS Analyst salary is $81,065 annually, which may increase as per expertise and knowledge.
An IS accreditation comprises a collection of credentials that set up foundational knowledge in different topics.
ICert Global helps people excel in the skills required for network security. Our security programs and certifications help participants to spot vulnerabilities, immediately respond to emergencies, and fend off attacks.
Some of the top-notch security certifications are as follows:
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Cyber Security Expert
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- CompTIA Security+
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Boost your digital presence with proven SEO expertise today
Search Engine Optimization
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the art and science of ranking your website higher in search engines. You know, the best result in the list that usually contains thousands of similar searches. It's a very competitive field, and it's essential to use the right tools to give you a competitive advantage.
Definition: SEO
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of maximizing the visibility and volume of your website in search engines like Google. For example, suppose a visitor searches for a product and is directed to your website. In that case, this is called a "natural search result."
Search engine ranking is important when calculating how well a website ranks in a search engine. The higher you rank, the more opportunities you have to get visitors to your site and retain them for extended periods.
SEO Cycle

Business Analysis
Business analysis determines how a product or service fits into the market and how customers will use it. This is essential for any company seeking to develop its online reputation. It allows them to understand what people are searching for online and how they want to find its following product.
Keyword Analysis
A keyword analysis can help businesses identify the most popular keywords in their industry. It can then craft advertising campaigns that appeal to those customers.
Web Position Analysis
Web position analysis determines how a website ranks in Google and other search engines, including Yahoo and Bing. This can be done through keyword research, content analysis, and site audits.
On-Page Optimization
This is the stage where you focus on improving your website's ranking by increasing your page authority and keyword rankings. In addition, you can use backlink building, article marketing, and other SEO strategies to get better rankings in search engines. The steps involved in on-page optimization are:

Server-side Optimization
Server-side optimization goes a long way in helping your website rank on search engines. In addition, it helps to improve the responsiveness of your website, resulting in a better user experience. The process of server-side optimization includes the following:
- Scanning your website for broken links and other errors
- Fixing any errors found in the scanning step
- Redirecting old broken links to new ones
- Optimizing images for faster loading speeds
Search Engine (Website Submission)
This is the most important step in the SEO cycle. You need to submit your website to search engines as soon as possible after its creation or launch date. You can use any of the many free submission services available, such as Google Webmaster Tools, Yahoo! Site Explorer or Bing Webmaster Tools. These tools help you identify issues with your site and fix them as quickly as possible before they become a problem for you or your visitors.
Off-Page Optimization
This is where you create links between your site and other relevant websites to improve its ranking in search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo! etc. It also helps get natural links from other websites, which will boost your SEO rankings further due to Google being a real-time analyzer of data across the internet that uses algorithms based on human behavior patterns (or "algorithms"). It is also called Backlinking.
Report
The reports are the heart of the SEO process. You can see at a glance the status of your website to the various Search Engine Optimization (SEO) factors and how you compare to your competitors.
The report section is broken down into three major areas:
- Site Overview
- Keyword Analysis & Reporting
- Technical Analysis
Why SEO is Needed
SEO is the process of finding and creating content that is designed to draw people to your website. It can be a long, complicated process requiring much work and effort. But it can be challenging to know where or how to get started.
SEO is important because it helps search engines find your website. Once they find it, they see if there's anything on the site that would help them give you more traffic and make your site more visible in their database. If they find something valuable and relevant, they'll put it at the top of their search results page (SERPs).
So if you want people to visit your website, you need to make sure that when they search for something on Google, Bing, or Yahoo! they see your site first. They want to know what you have for sale or offer as an alternative because you will need other options to compete effectively.
Important Terms related to SEO
Keyword Density
Keyword density is the percentage of keywords in a particular piece of content. The higher the keyword density, the more competitive your page is. The lower it is, the less competitive it is.
Keyword proximity
Keyword proximity refers to how closely related two or more keywords are (in frequency). It's essential because it helps search engines understand which words in your content are most relevant to each other. Use different keywords from one another often in your content. You can improve your search engine rankings by ensuring they're close together.
Keyword stuffing
Keyword stuffing is when you add too many words that contribute little value to your content. Search engines penalize this practice because it makes your site look spammy and doesn't help users find what they're looking for.
Do-follow Links
A do-follow link is a link to a page with good-quality content and authority. This is because Google will consider your page high quality so that it will rank higher in search engine results than a page without such links. Do follow links are also known as organic or natural links.
No-follow Links
On the other hand, no-follow links do not pass PageRank or refer back to your website. This is because Google sees no reason to follow these links since they don't provide any value to its algorithm.
Domain Authority
Domain authority is a metric that indicates the overall quality of a website. Domain Authority is determined by analyzing the number of backlinks pointing to a website and specifying how many links are pointing to it from authoritative domains.
Page Authority
Page authority is a metric that reflects the quality of a page on your site. Page authority is determined by analyzing the number of links pointing to that specific page and determining how many links are from high-quality sites.
Regardless of your specific niche, SEO is a hugely important aspect of your website's success. It's the foundation on which all your other strategies will rest. Of course, numerous other techniques can help you increase traffic to your site, such as social media marketing. Still, none are as important as mastering SEO.
Read More
Search Engine Optimization
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the art and science of ranking your website higher in search engines. You know, the best result in the list that usually contains thousands of similar searches. It's a very competitive field, and it's essential to use the right tools to give you a competitive advantage.
Definition: SEO
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of maximizing the visibility and volume of your website in search engines like Google. For example, suppose a visitor searches for a product and is directed to your website. In that case, this is called a "natural search result."
Search engine ranking is important when calculating how well a website ranks in a search engine. The higher you rank, the more opportunities you have to get visitors to your site and retain them for extended periods.
SEO Cycle
Business Analysis
Business analysis determines how a product or service fits into the market and how customers will use it. This is essential for any company seeking to develop its online reputation. It allows them to understand what people are searching for online and how they want to find its following product.
Keyword Analysis
A keyword analysis can help businesses identify the most popular keywords in their industry. It can then craft advertising campaigns that appeal to those customers.
Web Position Analysis
Web position analysis determines how a website ranks in Google and other search engines, including Yahoo and Bing. This can be done through keyword research, content analysis, and site audits.
On-Page Optimization
This is the stage where you focus on improving your website's ranking by increasing your page authority and keyword rankings. In addition, you can use backlink building, article marketing, and other SEO strategies to get better rankings in search engines. The steps involved in on-page optimization are:
Server-side Optimization
Server-side optimization goes a long way in helping your website rank on search engines. In addition, it helps to improve the responsiveness of your website, resulting in a better user experience. The process of server-side optimization includes the following:
- Scanning your website for broken links and other errors
- Fixing any errors found in the scanning step
- Redirecting old broken links to new ones
- Optimizing images for faster loading speeds
Search Engine (Website Submission)
This is the most important step in the SEO cycle. You need to submit your website to search engines as soon as possible after its creation or launch date. You can use any of the many free submission services available, such as Google Webmaster Tools, Yahoo! Site Explorer or Bing Webmaster Tools. These tools help you identify issues with your site and fix them as quickly as possible before they become a problem for you or your visitors.
Off-Page Optimization
This is where you create links between your site and other relevant websites to improve its ranking in search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo! etc. It also helps get natural links from other websites, which will boost your SEO rankings further due to Google being a real-time analyzer of data across the internet that uses algorithms based on human behavior patterns (or "algorithms"). It is also called Backlinking.
Report
The reports are the heart of the SEO process. You can see at a glance the status of your website to the various Search Engine Optimization (SEO) factors and how you compare to your competitors.
The report section is broken down into three major areas:
- Site Overview
- Keyword Analysis & Reporting
- Technical Analysis
Why SEO is Needed
SEO is the process of finding and creating content that is designed to draw people to your website. It can be a long, complicated process requiring much work and effort. But it can be challenging to know where or how to get started.
SEO is important because it helps search engines find your website. Once they find it, they see if there's anything on the site that would help them give you more traffic and make your site more visible in their database. If they find something valuable and relevant, they'll put it at the top of their search results page (SERPs).
So if you want people to visit your website, you need to make sure that when they search for something on Google, Bing, or Yahoo! they see your site first. They want to know what you have for sale or offer as an alternative because you will need other options to compete effectively.
Important Terms related to SEO
Keyword Density
Keyword density is the percentage of keywords in a particular piece of content. The higher the keyword density, the more competitive your page is. The lower it is, the less competitive it is.
Keyword proximity
Keyword proximity refers to how closely related two or more keywords are (in frequency). It's essential because it helps search engines understand which words in your content are most relevant to each other. Use different keywords from one another often in your content. You can improve your search engine rankings by ensuring they're close together.
Keyword stuffing
Keyword stuffing is when you add too many words that contribute little value to your content. Search engines penalize this practice because it makes your site look spammy and doesn't help users find what they're looking for.
Do-follow Links
A do-follow link is a link to a page with good-quality content and authority. This is because Google will consider your page high quality so that it will rank higher in search engine results than a page without such links. Do follow links are also known as organic or natural links.
No-follow Links
On the other hand, no-follow links do not pass PageRank or refer back to your website. This is because Google sees no reason to follow these links since they don't provide any value to its algorithm.
Domain Authority
Domain authority is a metric that indicates the overall quality of a website. Domain Authority is determined by analyzing the number of backlinks pointing to a website and specifying how many links are pointing to it from authoritative domains.
Page Authority
Page authority is a metric that reflects the quality of a page on your site. Page authority is determined by analyzing the number of links pointing to that specific page and determining how many links are from high-quality sites.
Regardless of your specific niche, SEO is a hugely important aspect of your website's success. It's the foundation on which all your other strategies will rest. Of course, numerous other techniques can help you increase traffic to your site, such as social media marketing. Still, none are as important as mastering SEO.
Introduction to Digital Marketing: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction to Digital Marketing
In the past, digital marketing was something that only large companies could afford to do. However, today this is changing, as thousands of small business owners are adopting digital marketing into their businesses. And with the power of social media, word-of-mouth advertising, and data collection, you can see how concerned small business owners should be about using these resources to reach their targeted customers and build a profitable brand.
What is Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing uses digital technology and other strategies to address an organization's business objectives. It is a strategic approach that incorporates all aspects of a business, including branding, retailing, direct marketing, public relations, and advertising.
Digital marketing encompasses all technologies that can be used to deliver content to achieve these goals. These include web design, search engine optimization (SEO), online advertising (search ads, display ads), email marketing/remarketing, affiliate marketing/referral programs, paid search, and mobile apps.
Why is Digital Marketing Important?
Digital marketing is the most important way to reach your customers. It's often called 'marketing in a box' because it provides everything you need to run your business online.
Digital marketing is essential for any business owner who wants to connect with their audience, drive traffic and increase sales. Digital marketing helps you sell more products or services by building trust with your target audience and building an audience of loyal customers who come back again and again.
Types of Digital Marketing
There are many types of digital marketing, but each class can be broken down into a few core elements. Each element is designed to accomplish a specific task in driving online traffic and leads to your website.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO is optimizing your website for search engines like Google and Bing. Search engines use algorithms to determine which sites are most relevant to users based on their search terms, keywords, and other factors. The goal of SEO is to get your site listed as high up in the search results as possible.
Social Media Marketing (SMM)
Social media marketing involves using platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, or LinkedIn to promote your brand or business. It's also known as social media advertising or SMO. Content sharing and engagement are two important factors in this marketing strategy because they allow you to build relationships with people who might become customers. In addition, social media platforms enable businesses to collaborate with their customers to create content that can be shared with others in their network and across the web.
Content marketing
Content marketing is about producing valuable information for your audience relevant to their needs and interests. You can make this content yourself or hire writers specializing in content creation. The goal is to attract new audience members and build trust with existing ones through original, quality content available for free on websites like Medium or YouTube.
E-commerce
With e-commerce, you can sell products and services online. This includes shopping carts that allow consumers to buy online, websites that list products and services for sale, and sites where consumers can purchase items from third-party vendors (e.g., Amazon.com). In addition to selling products and services, e-commerce companies may provide other value-added services such as shipping and returns.
Mobile Marketing
Mobile marketing is using portable devices to deliver digital content, including advertisements. Mobile marketing began as a way for advertisers to reach potential customers on their phones. Still, it has now evolved into a full-fledged marketing channel with an entire ecosystem of apps, content, and services designed to help marketers reach potential customers through mobile devices and applications.
Email marketing
Email marketing is one part of digital marketing where you get paid directly by the company or company owner. You promote your service or product through email campaigns like newsletters or blasts. You can send notifications about new products or services available at certain time intervals or when there is some special event in the industry related to your niche if you are an expert in that area or have expertise in that industry.
Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is a method of marketing that pays website owners and publishers based on the performance of their advertisements and sales. Affiliate marketers use special links called affiliate codes to identify themselves and the products they are promoting. When potential customers click on those links, they are taken to the merchant's site, where they can purchase if they wish.
Digital Marketing Benefits
There are many benefits to digital marketing, which include:
- Leverage Search Engine Optimization (SEO) to attract traffic, leads, and sales.
- Create content that people will want to read and share on social media.
- Automate your email marketing campaigns so you can focus on growing your business.
- Measure the effectiveness of your digital marketing campaigns by tracking ROI, conversions, and other KPIs.
- It's easy to use.
- You don't risk getting sued by a customer or consumer who feels you have misled them or made a false claim about your product or service.
- You can target specific groups of people with digital marketing campaigns that will appeal to their interests, lifestyle, and even psychology (for example, they may be interested in products that are related to their interests).
- Digital marketing is effective because it reaches people when they are using their mobile devices (or computers) on the go - which means that they are more likely to see it than other forms of advertising, such as TV or billboard ads would be!
Future of Digital Marketing
In the last few years, digital marketing has become a significant part of businesses' growth strategies. In fact, according to Statista, digital marketing expenditure is expected to reach $1 trillion by 2020 and $5 trillion by 2025.
Digital marketing is not just about online advertising anymore. Nowadays, it's also about social media marketing, email marketing, content marketing, and many other channels integrated into a single package.
The future of digital marketing is bright because there are so many different aspects that can be used to reach your target audience and generate leads for you or your business.
Your job as a digital marketer is to create new and innovative ways for people to interact with your brand and purchase your products or services. So you have to get creative and think of new ways to deliver value so that your customers don't feel like they are just another number on someone's list.
This introduction to digital marketing has opened a few doors for you. You might not know much about it now, but at least you know what goes into digital marketing and why it's there.
Read More
Introduction to Digital Marketing
In the past, digital marketing was something that only large companies could afford to do. However, today this is changing, as thousands of small business owners are adopting digital marketing into their businesses. And with the power of social media, word-of-mouth advertising, and data collection, you can see how concerned small business owners should be about using these resources to reach their targeted customers and build a profitable brand.
What is Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing uses digital technology and other strategies to address an organization's business objectives. It is a strategic approach that incorporates all aspects of a business, including branding, retailing, direct marketing, public relations, and advertising.
Digital marketing encompasses all technologies that can be used to deliver content to achieve these goals. These include web design, search engine optimization (SEO), online advertising (search ads, display ads), email marketing/remarketing, affiliate marketing/referral programs, paid search, and mobile apps.
Why is Digital Marketing Important?
Digital marketing is the most important way to reach your customers. It's often called 'marketing in a box' because it provides everything you need to run your business online.
Digital marketing is essential for any business owner who wants to connect with their audience, drive traffic and increase sales. Digital marketing helps you sell more products or services by building trust with your target audience and building an audience of loyal customers who come back again and again.
Types of Digital Marketing
There are many types of digital marketing, but each class can be broken down into a few core elements. Each element is designed to accomplish a specific task in driving online traffic and leads to your website.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO is optimizing your website for search engines like Google and Bing. Search engines use algorithms to determine which sites are most relevant to users based on their search terms, keywords, and other factors. The goal of SEO is to get your site listed as high up in the search results as possible.
Social Media Marketing (SMM)
Social media marketing involves using platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, or LinkedIn to promote your brand or business. It's also known as social media advertising or SMO. Content sharing and engagement are two important factors in this marketing strategy because they allow you to build relationships with people who might become customers. In addition, social media platforms enable businesses to collaborate with their customers to create content that can be shared with others in their network and across the web.
Content marketing
Content marketing is about producing valuable information for your audience relevant to their needs and interests. You can make this content yourself or hire writers specializing in content creation. The goal is to attract new audience members and build trust with existing ones through original, quality content available for free on websites like Medium or YouTube.
E-commerce
With e-commerce, you can sell products and services online. This includes shopping carts that allow consumers to buy online, websites that list products and services for sale, and sites where consumers can purchase items from third-party vendors (e.g., Amazon.com). In addition to selling products and services, e-commerce companies may provide other value-added services such as shipping and returns.
Mobile Marketing
Mobile marketing is using portable devices to deliver digital content, including advertisements. Mobile marketing began as a way for advertisers to reach potential customers on their phones. Still, it has now evolved into a full-fledged marketing channel with an entire ecosystem of apps, content, and services designed to help marketers reach potential customers through mobile devices and applications.
Email marketing
Email marketing is one part of digital marketing where you get paid directly by the company or company owner. You promote your service or product through email campaigns like newsletters or blasts. You can send notifications about new products or services available at certain time intervals or when there is some special event in the industry related to your niche if you are an expert in that area or have expertise in that industry.
Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is a method of marketing that pays website owners and publishers based on the performance of their advertisements and sales. Affiliate marketers use special links called affiliate codes to identify themselves and the products they are promoting. When potential customers click on those links, they are taken to the merchant's site, where they can purchase if they wish.
Digital Marketing Benefits
There are many benefits to digital marketing, which include:
- Leverage Search Engine Optimization (SEO) to attract traffic, leads, and sales.
- Create content that people will want to read and share on social media.
- Automate your email marketing campaigns so you can focus on growing your business.
- Measure the effectiveness of your digital marketing campaigns by tracking ROI, conversions, and other KPIs.
- It's easy to use.
- You don't risk getting sued by a customer or consumer who feels you have misled them or made a false claim about your product or service.
- You can target specific groups of people with digital marketing campaigns that will appeal to their interests, lifestyle, and even psychology (for example, they may be interested in products that are related to their interests).
- Digital marketing is effective because it reaches people when they are using their mobile devices (or computers) on the go - which means that they are more likely to see it than other forms of advertising, such as TV or billboard ads would be!
Future of Digital Marketing
In the last few years, digital marketing has become a significant part of businesses' growth strategies. In fact, according to Statista, digital marketing expenditure is expected to reach $1 trillion by 2020 and $5 trillion by 2025.
Digital marketing is not just about online advertising anymore. Nowadays, it's also about social media marketing, email marketing, content marketing, and many other channels integrated into a single package.
The future of digital marketing is bright because there are so many different aspects that can be used to reach your target audience and generate leads for you or your business.
Your job as a digital marketer is to create new and innovative ways for people to interact with your brand and purchase your products or services. So you have to get creative and think of new ways to deliver value so that your customers don't feel like they are just another number on someone's list.
This introduction to digital marketing has opened a few doors for you. You might not know much about it now, but at least you know what goes into digital marketing and why it's there.
Explore top Power BI questions for expert-level insights.
Top Power BI Questions
- What is Power BI Desktop?
Power BI Desktop is a free, open-source tool for visualizing data. You can create dashboards and reports using the Power BI desktop app.
- What is DAX?
DAX stands for Data Analysis Expressions and is a standard query language for creating calculations in data analysis. It can be used with any dataset and is particularly useful for analytics queries. To create DAX queries, you need to use Excel as a working file and then use Power Query or Power Pivot to connect it with Power BI.
- What are Filters in Power BI?
Filters allow you to filter data from any field or table within a dataset to show only specific values or values based on other areas.
- What are the different views available in Power BI Desktop?
Power BI Desktop has two views:
Dashboard View. This is a simple way to view data inside a Power BI Desktop report. You can use this view to explore your data and make sense of it.
Report View. This is where most of your work will happen! Reports are interactive, allowing you to filter, sort, and analyze your data exactly how you want it using multiple dimensions and measures.
Model View. The user manages Complex Data in this view.
- What is row-level security?
Row-level security is a feature of Power BI that allows you to control who can see what data by specifying a user ID and report name. For example, you can use this feature to share only specific rows of data while hiding others from view.
- Where is data stored in Power BI?
Data are stored in Azure SQL Database and Azure Blob Storage.
- Name the critical component of Power BI.
The critical components are:
- Power Map
- Power Q&A
- Power Pivot
- Power Query
- Power View
- What do you mean by the content pack?
The Content Pack is a collection of data that can be used to create visualizations, reports, and dashboards or to analyze data. It has been designed to help you work with large volumes of structured and unstructured data in Power BI. The Content Pack is not limited to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database. Still, it can include any structured or unstructured data.
- Define bi-directional cross-filtering in Power BI
Bidirectional cross-filtering can perform a filter on two different columns in one query.
- What is query folding in Power BI?
Query folding is a feature in Power BI that allows you to group your data by a single dimension or multiple sizes. This is similar to how you group data in SQL Server and other relational databases. Many people often refer to this as SQL-style reporting because it works similarly to how SQL works when querying tables and grouping rows together.
- What do you mean by grouping?
When we talk about grouping in Power BI, we mean creating reports with multiple columns related to each other based on their values or conditions.
- What are the significant differences between Power BI's visual, page, and report-level filters?
In Power BI, you can create filters for visual-level, page-level, and report-level data.
- Visual-level filters are applied to the current view of your report. For example, use this filter if you want to filter by a specific measure in a report.
- Page-level filters are applied to the current page of your report. For example, use this filter to filter on a specific dimension or measure on a page.
- Report-level filters are applied to all reports in your dataset or dataset collection. For example, use this filter if you have multiple reports in your dataset and want them to be filtered at once.
- Explain responsive slicers in Power BI.
Responsive slicers are a new feature in Power BI that lets you present data in responsive formats, such as cards and tiles.
For example, if you have a dataset that shows the number of customers by region, you should show that data as a bar chart. But if your audience has different screen sizes, having smaller charts with more detail might be more beneficial. In addition, you can use responsive slicer controls to format your data visually.
- What are KPIs in Power BI?
KPIs (key performance indicators) are metrics that measure the success of your organization. KPIs can be used to track strategic initiatives and make informed decisions about allocating resources. The Power BI team has built powerful features around KPI creation, analysis, and reporting.
- Explain Power BI Designer.
Power BI Designer is a tool for creating and editing many types of KPIs. This tool can create basic or complex KPI tables, charts, maps, and dashboards.
- Different stages in the working of Power BI?
- Data integration is the process of combining data from multiple sources into a single destination.
- Data processing is the process of transforming raw data into meaningful information by applying specialized algorithms.
- Data presentation is displaying and visualizing the data, usually in a way that enables the audience to understand it easily.
- Application of PowerBI
- Power BI is a cloud service that lets you create interactive dashboards that help business users gain better insight into their data and make better decisions faster.
- To collaborate on reports and documents with others.
- To create visualizations that communicate complex information in an easy-to-understand way.
- What is the CALCULATE function in DAX?
The CALCULATE function in DAX allows you to calculate a sum, average, or count of values. It is typically used for calculations like calculating the total for a range or calculating the average values in a column.
- Different types of connections in Power BI
SQL Server Import
This mode allows you to import data from SQL Server. In this mode, you can select the data source and the name of your table. You also have the option to select all tables or individual tables as well.
Live connection
This is the most common mode used by Power BI users. In this mode, you can connect to your database directly through Azure or any other storage provider your organization may use. The data will then be pulled into Power BI and analyzed at scale, giving you a real-time visual representation of your data.
Direct query
A direct query is a potent tool that allows you to access any data source through an API call, making it possible to connect to third-party services such as Twitter or Facebook (if they support OAuth authentication). This gives you free access to third-party databases and other services that do not have an open API available yet.
- What is GetData?
GetData is a new feature in Power BI that allows you to get data from any source and bring it into your dashboard. It's like "scraping" the web for information - except instead of putting the data into Excel spreadsheets or text files, we're putting it into Power BI!
Read More
Top Power BI Questions
- What is Power BI Desktop?
Power BI Desktop is a free, open-source tool for visualizing data. You can create dashboards and reports using the Power BI desktop app.
- What is DAX?
DAX stands for Data Analysis Expressions and is a standard query language for creating calculations in data analysis. It can be used with any dataset and is particularly useful for analytics queries. To create DAX queries, you need to use Excel as a working file and then use Power Query or Power Pivot to connect it with Power BI.
- What are Filters in Power BI?
Filters allow you to filter data from any field or table within a dataset to show only specific values or values based on other areas.
- What are the different views available in Power BI Desktop?
Power BI Desktop has two views:
Dashboard View. This is a simple way to view data inside a Power BI Desktop report. You can use this view to explore your data and make sense of it.
Report View. This is where most of your work will happen! Reports are interactive, allowing you to filter, sort, and analyze your data exactly how you want it using multiple dimensions and measures.
Model View. The user manages Complex Data in this view.
- What is row-level security?
Row-level security is a feature of Power BI that allows you to control who can see what data by specifying a user ID and report name. For example, you can use this feature to share only specific rows of data while hiding others from view.
- Where is data stored in Power BI?
Data are stored in Azure SQL Database and Azure Blob Storage.
- Name the critical component of Power BI.
The critical components are:
- Power Map
- Power Q&A
- Power Pivot
- Power Query
- Power View
- What do you mean by the content pack?
The Content Pack is a collection of data that can be used to create visualizations, reports, and dashboards or to analyze data. It has been designed to help you work with large volumes of structured and unstructured data in Power BI. The Content Pack is not limited to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database. Still, it can include any structured or unstructured data.
- Define bi-directional cross-filtering in Power BI
Bidirectional cross-filtering can perform a filter on two different columns in one query.
- What is query folding in Power BI?
Query folding is a feature in Power BI that allows you to group your data by a single dimension or multiple sizes. This is similar to how you group data in SQL Server and other relational databases. Many people often refer to this as SQL-style reporting because it works similarly to how SQL works when querying tables and grouping rows together.
- What do you mean by grouping?
When we talk about grouping in Power BI, we mean creating reports with multiple columns related to each other based on their values or conditions.
- What are the significant differences between Power BI's visual, page, and report-level filters?
In Power BI, you can create filters for visual-level, page-level, and report-level data.
- Visual-level filters are applied to the current view of your report. For example, use this filter if you want to filter by a specific measure in a report.
- Page-level filters are applied to the current page of your report. For example, use this filter to filter on a specific dimension or measure on a page.
- Report-level filters are applied to all reports in your dataset or dataset collection. For example, use this filter if you have multiple reports in your dataset and want them to be filtered at once.
- Explain responsive slicers in Power BI.
Responsive slicers are a new feature in Power BI that lets you present data in responsive formats, such as cards and tiles.
For example, if you have a dataset that shows the number of customers by region, you should show that data as a bar chart. But if your audience has different screen sizes, having smaller charts with more detail might be more beneficial. In addition, you can use responsive slicer controls to format your data visually.
- What are KPIs in Power BI?
KPIs (key performance indicators) are metrics that measure the success of your organization. KPIs can be used to track strategic initiatives and make informed decisions about allocating resources. The Power BI team has built powerful features around KPI creation, analysis, and reporting.
- Explain Power BI Designer.
Power BI Designer is a tool for creating and editing many types of KPIs. This tool can create basic or complex KPI tables, charts, maps, and dashboards.
- Different stages in the working of Power BI?
- Data integration is the process of combining data from multiple sources into a single destination.
- Data processing is the process of transforming raw data into meaningful information by applying specialized algorithms.
- Data presentation is displaying and visualizing the data, usually in a way that enables the audience to understand it easily.
- Application of PowerBI
- Power BI is a cloud service that lets you create interactive dashboards that help business users gain better insight into their data and make better decisions faster.
- To collaborate on reports and documents with others.
- To create visualizations that communicate complex information in an easy-to-understand way.
- What is the CALCULATE function in DAX?
The CALCULATE function in DAX allows you to calculate a sum, average, or count of values. It is typically used for calculations like calculating the total for a range or calculating the average values in a column.
- Different types of connections in Power BI
SQL Server Import
This mode allows you to import data from SQL Server. In this mode, you can select the data source and the name of your table. You also have the option to select all tables or individual tables as well.
Live connection
This is the most common mode used by Power BI users. In this mode, you can connect to your database directly through Azure or any other storage provider your organization may use. The data will then be pulled into Power BI and analyzed at scale, giving you a real-time visual representation of your data.
Direct query
A direct query is a potent tool that allows you to access any data source through an API call, making it possible to connect to third-party services such as Twitter or Facebook (if they support OAuth authentication). This gives you free access to third-party databases and other services that do not have an open API available yet.
- What is GetData?
GetData is a new feature in Power BI that allows you to get data from any source and bring it into your dashboard. It's like "scraping" the web for information - except instead of putting the data into Excel spreadsheets or text files, we're putting it into Power BI!
Trends to Watch in Business Agility for 2023 and Beyond!
Trends to Look Forward in Business Agility 2023
Business Agility has taken a whole new round for organizations amid the pandemic forcing businesses to simplify development operations. As a result, enterprises seek to become dependent on Agile-based project management techniques to maintain their ventures' adaptability.
The Agile principle focuses on streamlining challenging operational procedures, enabling project professionals to deliver projects in operational phases, where modifications are made more quickly.
Agile allows project teams to utilize solutions and determine issues in the development phase, focusing on customer requirements. First, let us see how trends affect organizations the most.
Scaled Agile & Scrum Techniques
The Scrum development technique accredits project professionals to proficiently coordinate the activities of cross-functional teams and generate working code at the end of each sprint. Organizations these days are leaping onto scaling their Scrum activities to offer more excellent value and enhanced partnership.
According to a recent survey, the most popular framework, SAFe, is rated as the top-scaled agile technique. Leading SAFe practices are the most comprehensive for massive Agile projects and support a successful change of companies into Lean-Agile companies.
SAFe Scrum Masters are highly cherished as they're trained to plan and perform projects in the context of the business, not just individual sprints.
Business Agility and Design Thinking
The design thinking technique exposes customer requirements on a human level by creating solid user empathy and experimenting in stages to make a design right. Design thinking and agile have a lot in common. For instance, a project team can build additional time into sprint activities to better understand customer facts and enhance their overall satisfaction.
Taking the time upfront to establish user empathy and getting design feedback will help streamline modeling and testing, followed by visualizing a solution that can guide the team on the right path.
Within the Agile space, organizations should ponder staggered sprints that include user feedback loops, empathy, and ideation of the Agile process.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Supporting Agile
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence are the greatest booms in data analysis in the project and development environments. For instance, they offer real-time data and swift analytical capabilities to provide precise predictions of when project stages will be complete. That's significant when projects get close to the ending stage, and the eyes of various executive constituents are fixed on the schedules.
Additional benefits offered to Agile by ML and AI are:
- We offer accurate insights and transparent procedures for developing and testing programming code.
- Reviewing code with better precision to determine and eradicate bugs.
- Merging with innovative techs such as RPA, Quantum Computing, IoT devices, and intelligent techs to swift development time and get products to market faster.
Project management professionals leverage their resources to maintain their teams for optimum running, including Agile Scrums that scale to business criteria, design thinking techniques to merge customer requirements early on the lifecycle, and cutting-edge techs like ML and AI to fasten testing and market time.
Read More
Trends to Look Forward in Business Agility 2023
Business Agility has taken a whole new round for organizations amid the pandemic forcing businesses to simplify development operations. As a result, enterprises seek to become dependent on Agile-based project management techniques to maintain their ventures' adaptability.
The Agile principle focuses on streamlining challenging operational procedures, enabling project professionals to deliver projects in operational phases, where modifications are made more quickly.
Agile allows project teams to utilize solutions and determine issues in the development phase, focusing on customer requirements. First, let us see how trends affect organizations the most.
Scaled Agile & Scrum Techniques
The Scrum development technique accredits project professionals to proficiently coordinate the activities of cross-functional teams and generate working code at the end of each sprint. Organizations these days are leaping onto scaling their Scrum activities to offer more excellent value and enhanced partnership.
According to a recent survey, the most popular framework, SAFe, is rated as the top-scaled agile technique. Leading SAFe practices are the most comprehensive for massive Agile projects and support a successful change of companies into Lean-Agile companies.
SAFe Scrum Masters are highly cherished as they're trained to plan and perform projects in the context of the business, not just individual sprints.
Business Agility and Design Thinking
The design thinking technique exposes customer requirements on a human level by creating solid user empathy and experimenting in stages to make a design right. Design thinking and agile have a lot in common. For instance, a project team can build additional time into sprint activities to better understand customer facts and enhance their overall satisfaction.
Taking the time upfront to establish user empathy and getting design feedback will help streamline modeling and testing, followed by visualizing a solution that can guide the team on the right path.
Within the Agile space, organizations should ponder staggered sprints that include user feedback loops, empathy, and ideation of the Agile process.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Supporting Agile
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence are the greatest booms in data analysis in the project and development environments. For instance, they offer real-time data and swift analytical capabilities to provide precise predictions of when project stages will be complete. That's significant when projects get close to the ending stage, and the eyes of various executive constituents are fixed on the schedules.
Additional benefits offered to Agile by ML and AI are:
- We offer accurate insights and transparent procedures for developing and testing programming code.
- Reviewing code with better precision to determine and eradicate bugs.
- Merging with innovative techs such as RPA, Quantum Computing, IoT devices, and intelligent techs to swift development time and get products to market faster.
Project management professionals leverage their resources to maintain their teams for optimum running, including Agile Scrums that scale to business criteria, design thinking techniques to merge customer requirements early on the lifecycle, and cutting-edge techs like ML and AI to fasten testing and market time.
Top Data Science Interview Questions and Answers for 2023
Data Science Interview Questions 2023
- What is NumPy?
NumPy is a Python library for fast numerical computations. It provides high-performance, reliable, and scalable array functions. NumPy arrays can be used as an alternative to lists in many situations.
- What is the advantage of NumPy arrays over lists?
The advantage of using NumPy over lists is that they use less memory and are faster than lists.
They support multi-dimensional arrays, unlike lists which only help one-dimensional arrays.
They can be sliced or reshaped using the standard Python expression syntax for slicing and reshaping. In contrast, slices on lists must be done with special operators such as lambda or list comprehensions.
- Differentiate between univariate, bivariate, and multivariate analysis.
A univariate analysis is a data set that contains only one variable. The data set can be categorical or numerical.
The bivariate analysis combines two variables into one large dataset that allows you to make detailed comparisons between them (e.g., the difference in the mean response for each treatment group across all participants).
In multivariate analysis, there can be many more variables than in either univariate or bivariate analysis (usually, there is at least one variable per factor). The primary purpose of using multiple variables is to increase the accuracy of our statement about what we believe to be true about our dataset.
- What is the difference between the use of iloc and loc?
The difference between the use of iloc and loc is that iloc returns a row object that is a list of integer values. In contrast, loc returns a row object that has one column. In addition, the row object returned by iloc has a position set to 0, which means it starts at index 0. On the other hand, the row object returned by loc has no starting index, so there are no integers in the first column (the one containing the values).
- What is the difference between the Pandas series and Pandas Dataframe?
Pandas Dataframe is a data storage format for tabular data, which can be efficiently stored in memory. The Pandas library provides a high-level interface to manipulate and analyze tabular data. At the same time, the underlying data structure is stored in a data frame.
df = pd.DataFrame()
Pandas Series, On the other hand, Pandas Series is a multi-dimensional array that can store many different types of objects such as arrays, matrices, and lists. A pandas series is one dimensional with N rows and M columns where N can be any positive integer and M can be any positive integer or an empty list ([]). In other words, it is just like a list but without indexing.
s = pd.Series ()
- What are the ACID properties in SQL?
Atomicity: A transaction is defined as a set of operations that must be carried out without any partial effects or side effects. It means there should only be data updated in the database after the transaction has been committed.
Consistency: The database should be consistent at all times, i.e., all updates to the data must be visible to other users and processes.
Isolation: Each transaction in a database is isolated from other transactions so that they do not touch each other's data while running concurrently.
Durability: Each transaction should leave the database in a consistent state after its completion unless explicitly told otherwise by its owner.
- Difference between DDL and DML
DDL stands for Data Definition Language, while DML stands for Data Manipulation Language. The main difference between these two languages is that the first one is used to define the data. In contrast, the second one is used to manipulate it. In other words, DDL is used to create tables, whereas DML is used to modify existing records in a table.
DDL- CREATE, ALTER, DROP
DML- INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
- What are Constraints?
SQL constraints are used to limit the type of data that can go into a table, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data in the table. Constraints can be either column-level or table-level. Column-level constraints apply to a single column, while table-level constraints apply to the whole table.
- Difference between Join and Union
Join combines two different tables, each of which has a select list containing a single column. This can be done by using the join() function. It returns a view that combines all of the rows from both tables.
Union is used to combine multiple columns from a single table into one row. For example, the union() function does this by taking all of the selected columns from the first table and combining them into one row in the second table.
- What are Nested Triggers?
Nested Triggers are a feature of SQL Server that allows you to create a trigger that runs when the same statement is fired more than once. This can be useful in situations where you want to modify data based on an event but need only to process one row at a time.
- What is a Confusion Matrix?
The Confusion Matrix is a table that summarizes prediction results. It is used to describe the performance of a classification model. The Confusion Matrix is an n*n matrix that evaluates how well an algorithm predicts certain dataset features.
- What is the difference between long-format data and wide-format data?
A wide format is a data structure that allows for storing much more information than a long format. The main difference between the two is that wide format uses more bytes to keep the same amount of data as long format. This can make it harder to move around since you will be wasting more space on your hard drive or in memory if you use a wide format.
Long formats are generally used when you want to save space and speed up your computer, but wide formats are used when storing more data in your computer's memory or hard drive.
- Why is Python used for Data Cleaning in DS?
Python is used for Data Cleaning in data science because it can perform some of the essential cleaning and transformation operations without additional dependencies.
Python has excellent support for Pandas and NumPy library - a set of mathematical and statistical routines used for data manipulation and analysis. The extensive list of libraries available for Python also helps to achieve quick results when needed.
- What is a normal distribution?
The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that can be used to model various random variables. It is the most commonly used probability distribution and the most important in statistics, economics, and finance.
The normal distribution is a particular case of the Gaussian distribution: it has the same mean and variance, but the variance is twice as significant. The normal distribution functions as a bell curve when plotted along one axis and has an area under it equal to 1.
- What is logistic regression?
Logistic regression is a statistical technique to find the best-fitting model for a given set of observed data. For example, it can predict the probability of an event, such as whether a customer will buy your product.
The main idea behind logistic regression is to find the best-fitting model for your dataset, determining how many variables are needed to describe your data. The model you choose will depend on your dataset's complexity and how complex it needs to be for you to make reliable predictions.
Read More
Data Science Interview Questions 2023
- What is NumPy?
NumPy is a Python library for fast numerical computations. It provides high-performance, reliable, and scalable array functions. NumPy arrays can be used as an alternative to lists in many situations.
- What is the advantage of NumPy arrays over lists?
The advantage of using NumPy over lists is that they use less memory and are faster than lists.
They support multi-dimensional arrays, unlike lists which only help one-dimensional arrays.
They can be sliced or reshaped using the standard Python expression syntax for slicing and reshaping. In contrast, slices on lists must be done with special operators such as lambda or list comprehensions.
- Differentiate between univariate, bivariate, and multivariate analysis.
A univariate analysis is a data set that contains only one variable. The data set can be categorical or numerical.
The bivariate analysis combines two variables into one large dataset that allows you to make detailed comparisons between them (e.g., the difference in the mean response for each treatment group across all participants).
In multivariate analysis, there can be many more variables than in either univariate or bivariate analysis (usually, there is at least one variable per factor). The primary purpose of using multiple variables is to increase the accuracy of our statement about what we believe to be true about our dataset.
- What is the difference between the use of iloc and loc?
The difference between the use of iloc and loc is that iloc returns a row object that is a list of integer values. In contrast, loc returns a row object that has one column. In addition, the row object returned by iloc has a position set to 0, which means it starts at index 0. On the other hand, the row object returned by loc has no starting index, so there are no integers in the first column (the one containing the values).
- What is the difference between the Pandas series and Pandas Dataframe?
Pandas Dataframe is a data storage format for tabular data, which can be efficiently stored in memory. The Pandas library provides a high-level interface to manipulate and analyze tabular data. At the same time, the underlying data structure is stored in a data frame.
df = pd.DataFrame()
Pandas Series, On the other hand, Pandas Series is a multi-dimensional array that can store many different types of objects such as arrays, matrices, and lists. A pandas series is one dimensional with N rows and M columns where N can be any positive integer and M can be any positive integer or an empty list ([]). In other words, it is just like a list but without indexing.
s = pd.Series ()
- What are the ACID properties in SQL?
Atomicity: A transaction is defined as a set of operations that must be carried out without any partial effects or side effects. It means there should only be data updated in the database after the transaction has been committed.
Consistency: The database should be consistent at all times, i.e., all updates to the data must be visible to other users and processes.
Isolation: Each transaction in a database is isolated from other transactions so that they do not touch each other's data while running concurrently.
Durability: Each transaction should leave the database in a consistent state after its completion unless explicitly told otherwise by its owner.
- Difference between DDL and DML
DDL stands for Data Definition Language, while DML stands for Data Manipulation Language. The main difference between these two languages is that the first one is used to define the data. In contrast, the second one is used to manipulate it. In other words, DDL is used to create tables, whereas DML is used to modify existing records in a table.
DDL- CREATE, ALTER, DROP
DML- INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
- What are Constraints?
SQL constraints are used to limit the type of data that can go into a table, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data in the table. Constraints can be either column-level or table-level. Column-level constraints apply to a single column, while table-level constraints apply to the whole table.
- Difference between Join and Union
Join combines two different tables, each of which has a select list containing a single column. This can be done by using the join() function. It returns a view that combines all of the rows from both tables.
Union is used to combine multiple columns from a single table into one row. For example, the union() function does this by taking all of the selected columns from the first table and combining them into one row in the second table.
- What are Nested Triggers?
Nested Triggers are a feature of SQL Server that allows you to create a trigger that runs when the same statement is fired more than once. This can be useful in situations where you want to modify data based on an event but need only to process one row at a time.
- What is a Confusion Matrix?
The Confusion Matrix is a table that summarizes prediction results. It is used to describe the performance of a classification model. The Confusion Matrix is an n*n matrix that evaluates how well an algorithm predicts certain dataset features.
- What is the difference between long-format data and wide-format data?
A wide format is a data structure that allows for storing much more information than a long format. The main difference between the two is that wide format uses more bytes to keep the same amount of data as long format. This can make it harder to move around since you will be wasting more space on your hard drive or in memory if you use a wide format.
Long formats are generally used when you want to save space and speed up your computer, but wide formats are used when storing more data in your computer's memory or hard drive.
- Why is Python used for Data Cleaning in DS?
Python is used for Data Cleaning in data science because it can perform some of the essential cleaning and transformation operations without additional dependencies.
Python has excellent support for Pandas and NumPy library - a set of mathematical and statistical routines used for data manipulation and analysis. The extensive list of libraries available for Python also helps to achieve quick results when needed.
- What is a normal distribution?
The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that can be used to model various random variables. It is the most commonly used probability distribution and the most important in statistics, economics, and finance.
The normal distribution is a particular case of the Gaussian distribution: it has the same mean and variance, but the variance is twice as significant. The normal distribution functions as a bell curve when plotted along one axis and has an area under it equal to 1.
- What is logistic regression?
Logistic regression is a statistical technique to find the best-fitting model for a given set of observed data. For example, it can predict the probability of an event, such as whether a customer will buy your product.
The main idea behind logistic regression is to find the best-fitting model for your dataset, determining how many variables are needed to describe your data. The model you choose will depend on your dataset's complexity and how complex it needs to be for you to make reliable predictions.
Introduction to Cloud Computing: Overview and Benefits.
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a web-based, on-demand resource that allows people and organizations to share information and data. Cloud computing enables you to access applications, software, and data via the Internet from anywhere with an Internet connection. You can also use it to store your files online. The cloud offers many benefits over traditional on-premises solutions, such as scalability, flexibility, and security.
The cloud can be used for storing company data and applications, but it can be used for more than just storing data. For example, you can also use the cloud to host websites or deliver online services.
Two primary users of the cloud are:
End User: The end user is typically an individual or group of individuals who use computing resources such as processing power, memory, and storage.
Business management user: Business management users ensure that the cloud infrastructure operates at optimal performance levels to meet business requirements.
The three major cloud providers are:
- Google Cloud Platform
- Microsoft Azure
- Amazon Web Service (AWS)
Differences between on-premises computing and cloud computing
- On-premises refers to a physical location where the server hardware is located. In contrast, cloud computing refers to using a virtual machine or another hosted environment on a server or other device with access to computing resources.
- On-premises systems have their hardware and software infrastructure, whereas cloud systems rely on remote access via the Internet.
- On-premise users bear the cost of hardware and operating system, whereas, in cloud computing, users have to pay a subscription fee for hardware and operating system access.
- In on-premises, any failure means loss of the actual data. In contrast, in cloud computing, data are stored in the cloud, so if a failure occurs, there is still a copy of the data in the cloud.
Main Components of Cloud Platform
In the world of cloud computing, there are three main components: data center, Internet, and virtualization technology. These three technologies are what make up a cloud platform.
The data center is where servers and storage devices are stored.
The Internet is where applications run on those servers and storage devices.
Virtualization technology allows various software programs to run on top of those servers and storage devices.
Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud deployment models provide a way to separate a cloud computing environment's physical and virtual aspects. Three types of deployment models are:
Public Cloud
A public cloud is one where you can get your data, applications, and services from a provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform. A public cloud provides access to a shared pool of virtualized resources across multiple servers. The goal is to make it easier for you to use these resources as if they were in your own data center.
Advantage
- You can access your data from anywhere with an internet connection without worrying about storage capacity, as the vendor already provides it.
- There are no limits on bandwidth usage or the number of users accessing the same application at any given time. This means you will have more control over your resources than if you were running your server farm or cloud infrastructure.
- The pricing plans offered by public clouds are much cheaper than those provided by private cloud providers because there are fewer costs involved in maintaining such infrastructure and providing services to customers.
Disadvantage
- The security of your data is often better than if you had your hardware. If you have sensitive data or mission-critical applications, keep them in-house.
- You must pay for the service unless you host your hardware in-house.
- Public clouds don't have local storage for your applications. That means you have to move all of your data into the cloud before you can use it.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is one that an organization manages. It's not shared with anyone else, and it's often used for mission-critical tasks such as running large databases or complex applications.
Advantage
- Private clouds offer security and flexibility that's not possible with public cloud infrastructure, which is typically owned and managed by a third-party provider.
- The use of a private cloud environment enables the user to be in complete control over the data, applications, and services that they use. This gives them complete flexibility and freedom to make changes that are not possible in other environments.
- Private clouds allow users to test new operating systems, applications, and services without worrying about downtime or impact on their production environment.
Disadvantage
- Private clouds are often more expensive than public clouds. They require more infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking equipment. They may be more challenging to scale up or down than public clouds.
- Private clouds are that they provide a different level of scalability than the public cloud does. For example, suppose you have 100 users, and only 5% of them need extra resources in their virtual machines at any time. In that case, it makes sense to use a public cloud instead of a private one.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is between public and private clouds, where the services are hosted on multiple clouds. Organizations can manage the cloud infrastructure with different objectives, such as control, cost reduction, and security. A hybrid cloud offers the benefits of both public and private clouds at the same time.
Advantage
- It enables organizations to manage IT infrastructure more efficiently, reduce costs and maximize resources.
- It enables organizations to leverage existing hardware, software, and networking equipment investments to deliver their applications more quickly and cost-effectively.
- It allows organizations to become more agile and responsive by enabling them to deploy applications without waiting for new infrastructure or software upgrades.
Disadvantage
- A hybrid cloud is that it requires more management effort than using a single cloud provider. When you have multiple clouds and applications, you need to manage them individually.
- If one application becomes unavailable, other applications can also have problems.
Cloud Service Models
Cloud Services are mainly of three types:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
This is the most common model for hosting on the cloud. The provider will provide you with all the hardware, software, and support you need to run your application. In this model, you only pay for what you use. This is ideal for startups that need more capital to invest in their infrastructure. Many popular applications are hosted this way, including Salesforce, Google Apps, and Dropbox.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
In this model, you get access to an application but not the underlying infrastructure required to run it. SaaS apps can be hosted on dedicated servers or virtual machines (VMs). Famous examples include Slack, Trello, and GitHub Enterprise.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
In this model, you get access to an application that runs on top of an infrastructure provided by the provider (e.g., AWS). Famous examples include Windows Azure and AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Reduced Capital Expenditures
Businesses can reduce capital expenditures by providing services in-house or through third-party providers. They can also use cloud computing to expand their existing IT infrastructure without investing in new hardware or software.
Increased Flexibility
Cloud computing enables businesses to maintain their current IT infrastructure while expanding their operations with minimal effort. This means they can use new technologies without reworking existing systems or adopting them altogether.
Improved Security and Compliance
Cloud computing offers companies improved security and compliance features than on-premise solutions such as virtual machines or dedicated servers. The virtualization layer separates different data types into separate environments, making it easier for organizations to monitor and manage multiple domains simultaneously without compromising security or operational integrity.
Availability
The cloud is a convenient way to store and access files over the Internet. It enables companies to expand globally, giving them more options for increasing their business.
Data Storage
Customers can choose the amount of storage they need and pay only for what they use.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is the new wave in technology. With the three layers of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, developers and businesses can find a setup that works best for them based on their needs.
Through its rise to popularity, cloud computing has helped many startups get off the ground, big corporations save money on IT infrastructure, and it has driven many fields toward greater technological integration. It's not going anywhere anytime soon; it's growing fast.
Read More
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a web-based, on-demand resource that allows people and organizations to share information and data. Cloud computing enables you to access applications, software, and data via the Internet from anywhere with an Internet connection. You can also use it to store your files online. The cloud offers many benefits over traditional on-premises solutions, such as scalability, flexibility, and security.
The cloud can be used for storing company data and applications, but it can be used for more than just storing data. For example, you can also use the cloud to host websites or deliver online services.
Two primary users of the cloud are:
End User: The end user is typically an individual or group of individuals who use computing resources such as processing power, memory, and storage.
Business management user: Business management users ensure that the cloud infrastructure operates at optimal performance levels to meet business requirements.
The three major cloud providers are:
- Google Cloud Platform
- Microsoft Azure
- Amazon Web Service (AWS)
Differences between on-premises computing and cloud computing
- On-premises refers to a physical location where the server hardware is located. In contrast, cloud computing refers to using a virtual machine or another hosted environment on a server or other device with access to computing resources.
- On-premises systems have their hardware and software infrastructure, whereas cloud systems rely on remote access via the Internet.
- On-premise users bear the cost of hardware and operating system, whereas, in cloud computing, users have to pay a subscription fee for hardware and operating system access.
- In on-premises, any failure means loss of the actual data. In contrast, in cloud computing, data are stored in the cloud, so if a failure occurs, there is still a copy of the data in the cloud.
Main Components of Cloud Platform
In the world of cloud computing, there are three main components: data center, Internet, and virtualization technology. These three technologies are what make up a cloud platform.
The data center is where servers and storage devices are stored.
The Internet is where applications run on those servers and storage devices.
Virtualization technology allows various software programs to run on top of those servers and storage devices.
Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud deployment models provide a way to separate a cloud computing environment's physical and virtual aspects. Three types of deployment models are:
Public Cloud
A public cloud is one where you can get your data, applications, and services from a provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform. A public cloud provides access to a shared pool of virtualized resources across multiple servers. The goal is to make it easier for you to use these resources as if they were in your own data center.
Advantage
- You can access your data from anywhere with an internet connection without worrying about storage capacity, as the vendor already provides it.
- There are no limits on bandwidth usage or the number of users accessing the same application at any given time. This means you will have more control over your resources than if you were running your server farm or cloud infrastructure.
- The pricing plans offered by public clouds are much cheaper than those provided by private cloud providers because there are fewer costs involved in maintaining such infrastructure and providing services to customers.
Disadvantage
- The security of your data is often better than if you had your hardware. If you have sensitive data or mission-critical applications, keep them in-house.
- You must pay for the service unless you host your hardware in-house.
- Public clouds don't have local storage for your applications. That means you have to move all of your data into the cloud before you can use it.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is one that an organization manages. It's not shared with anyone else, and it's often used for mission-critical tasks such as running large databases or complex applications.
Advantage
- Private clouds offer security and flexibility that's not possible with public cloud infrastructure, which is typically owned and managed by a third-party provider.
- The use of a private cloud environment enables the user to be in complete control over the data, applications, and services that they use. This gives them complete flexibility and freedom to make changes that are not possible in other environments.
- Private clouds allow users to test new operating systems, applications, and services without worrying about downtime or impact on their production environment.
Disadvantage
- Private clouds are often more expensive than public clouds. They require more infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking equipment. They may be more challenging to scale up or down than public clouds.
- Private clouds are that they provide a different level of scalability than the public cloud does. For example, suppose you have 100 users, and only 5% of them need extra resources in their virtual machines at any time. In that case, it makes sense to use a public cloud instead of a private one.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is between public and private clouds, where the services are hosted on multiple clouds. Organizations can manage the cloud infrastructure with different objectives, such as control, cost reduction, and security. A hybrid cloud offers the benefits of both public and private clouds at the same time.
Advantage
- It enables organizations to manage IT infrastructure more efficiently, reduce costs and maximize resources.
- It enables organizations to leverage existing hardware, software, and networking equipment investments to deliver their applications more quickly and cost-effectively.
- It allows organizations to become more agile and responsive by enabling them to deploy applications without waiting for new infrastructure or software upgrades.
Disadvantage
- A hybrid cloud is that it requires more management effort than using a single cloud provider. When you have multiple clouds and applications, you need to manage them individually.
- If one application becomes unavailable, other applications can also have problems.
Cloud Service Models
Cloud Services are mainly of three types:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
This is the most common model for hosting on the cloud. The provider will provide you with all the hardware, software, and support you need to run your application. In this model, you only pay for what you use. This is ideal for startups that need more capital to invest in their infrastructure. Many popular applications are hosted this way, including Salesforce, Google Apps, and Dropbox.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
In this model, you get access to an application but not the underlying infrastructure required to run it. SaaS apps can be hosted on dedicated servers or virtual machines (VMs). Famous examples include Slack, Trello, and GitHub Enterprise.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
In this model, you get access to an application that runs on top of an infrastructure provided by the provider (e.g., AWS). Famous examples include Windows Azure and AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Reduced Capital Expenditures
Businesses can reduce capital expenditures by providing services in-house or through third-party providers. They can also use cloud computing to expand their existing IT infrastructure without investing in new hardware or software.
Increased Flexibility
Cloud computing enables businesses to maintain their current IT infrastructure while expanding their operations with minimal effort. This means they can use new technologies without reworking existing systems or adopting them altogether.
Improved Security and Compliance
Cloud computing offers companies improved security and compliance features than on-premise solutions such as virtual machines or dedicated servers. The virtualization layer separates different data types into separate environments, making it easier for organizations to monitor and manage multiple domains simultaneously without compromising security or operational integrity.
Availability
The cloud is a convenient way to store and access files over the Internet. It enables companies to expand globally, giving them more options for increasing their business.
Data Storage
Customers can choose the amount of storage they need and pay only for what they use.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is the new wave in technology. With the three layers of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, developers and businesses can find a setup that works best for them based on their needs.
Through its rise to popularity, cloud computing has helped many startups get off the ground, big corporations save money on IT infrastructure, and it has driven many fields toward greater technological integration. It's not going anywhere anytime soon; it's growing fast.
Boost Your Application with Project Management Certification
Strengthen Your Job Application with Project Management Certification
Today, Project Management is the most demanding professional accreditation, guaranteeing personal and professional achievements. As a result, we have often seen vacancy adverts for Project Management, where recruiters mention Project Management Certification as mandatory or preferred.
Over a decade, Project Management credentials have achieved global acceptance, with several companies recruiting candidates with certifications or pursuing the same.
Some of the popular Project Management Accreditations offering handsome remunerations are:
- Project Management Professional (PMP)
- Prince2
- Managing Successful Programmes (MSP)
- Risk Management Professional (RMP)
- PMI-ACP
- PgMP
- CAPM
Software Estimation Certification & Business Analysis (BA) Certification is also significant credential in Project Management.
Irrespective of large/small-scale companies, skilled and trained Project Management certification holders are in great demand. A globally-renowned credential highlights that a person fulfills the needs of being a great project manager. However, let's get the point clear: these certifications aren't only for project managers but for those associated with a project at any time.
Now, what counts is competency, and the days when someone got promoted to a project manager position for being loyal for years have long gone. What does an organization look for in a person for project manager position?
- Are you capable enough to take project charge?
- What are your necessary qualifications?
- Can you make use of all your given resources efficiently?
Let’s looks at some benefits of Project Management Certifications.
- Adds value to your resume
- Develops international recognition
- Increase customer satisfaction
- Successful completion of projects
- Handsome remunerations
- Validates your skills, knowledge and potential in project execution
- Client preferences
Here, we come to the conclusion that to have a distinct position in a competitive world, individuals must remain marketable. Project Management credentials act as a significant barrier in this regard. Being professionally certified after a particular age might be daunting; however, gaining an outstanding balance in your work career is always possible.
Read More
Strengthen Your Job Application with Project Management Certification
Today, Project Management is the most demanding professional accreditation, guaranteeing personal and professional achievements. As a result, we have often seen vacancy adverts for Project Management, where recruiters mention Project Management Certification as mandatory or preferred.
Over a decade, Project Management credentials have achieved global acceptance, with several companies recruiting candidates with certifications or pursuing the same.
Some of the popular Project Management Accreditations offering handsome remunerations are:
- Project Management Professional (PMP)
- Prince2
- Managing Successful Programmes (MSP)
- Risk Management Professional (RMP)
- PMI-ACP
- PgMP
- CAPM
Software Estimation Certification & Business Analysis (BA) Certification is also significant credential in Project Management.
Irrespective of large/small-scale companies, skilled and trained Project Management certification holders are in great demand. A globally-renowned credential highlights that a person fulfills the needs of being a great project manager. However, let's get the point clear: these certifications aren't only for project managers but for those associated with a project at any time.
Now, what counts is competency, and the days when someone got promoted to a project manager position for being loyal for years have long gone. What does an organization look for in a person for project manager position?
- Are you capable enough to take project charge?
- What are your necessary qualifications?
- Can you make use of all your given resources efficiently?
Let’s looks at some benefits of Project Management Certifications.
- Adds value to your resume
- Develops international recognition
- Increase customer satisfaction
- Successful completion of projects
- Handsome remunerations
- Validates your skills, knowledge and potential in project execution
- Client preferences
Here, we come to the conclusion that to have a distinct position in a competitive world, individuals must remain marketable. Project Management credentials act as a significant barrier in this regard. Being professionally certified after a particular age might be daunting; however, gaining an outstanding balance in your work career is always possible.
Cloud Computing Terminologies Every Professional Should Know
Cloud Computing Terminologies
When you work in cloud computing, it's easy to forget the vocabulary you need to know. It's also easy to forget which terminology is generic and which ones should be reserved for specific services. This can lead to confusion and frustration, the hallmarks of poor communication within a team or company. So let's get familiar with these terms.
- AWS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon.com Inc. It provides on-demand cloud computing services for developers and enterprises.
- Azure
Microsoft Azure is a cloud platform developed by Microsoft. It provides infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and Software as a service (SaaS).
- Big Data
Big Data refers to an extremely large amount of data that needs to be analyzed quickly to gain insights into how it affects business operations, customer behavior, and market trends.
- Cloud Provider
A cloud provider is a company that provides services to other companies through the Internet. These providers make their clients' IT infrastructure available securely and reliably via the Internet. In addition, the provider provides software, hardware, and connectivity to its clients.
- Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a cloud computing platform from Google, Inc., offering infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), application development platform, and enterprise software as a service (SaaS). It provides computing power, storage, databases, and other components for building applications across many industries.
- Data Migration
Data migration refers to moving data from one location to another. It is a critical step in cloud computing, especially for enterprises storing data in different locations.
- IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing service that allows users to rent virtualized computing resources over the Internet. It is one of the most common types of cloud computing, where users access applications and data stored in servers hosted by third-party providers.
- PaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS), is an application development platform that provides its users with access to a wide range of software design and development tools, such as databases, web servers, server administration tools, and so on.
- SaaS
SaaS (Software as a Service) is a cloud computing model that provides on-demand Software licensing and access to application software over the Internet. It's a perfect fit for companies that want to develop their applications but need help to create or maintain their infrastructure.
- User Interface
User interface refers to how a cloud application is designed and used by customers. It also refers to the tools for end users to interact with the system, such as dashboards and reports.
- Private Cloud
A private cloud is a cloud-based infrastructure that resides on a single company's premises, often in a data center or colocation facility but sometimes in an office setting. An organization's own IT team uses it to manage its workloads, applications, and data. Private clouds are often designed for specific applications such as backup and disaster recovery or specialized workloads such as healthcare or finance.
- Public Cloud
A public cloud is a type of cloud computing where resources are accessible over the Internet by anyone with an Internet connection and basic software skills. Public clouds are managed by third parties such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Salesforce.com, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These cloud providers provide computing resources for companies without having to build and maintain their data centers.
- Pay-As-You-Go
Pay-As-You-Go is where users pay only for what they use instead of being billed based on server usage. This is designed to encourage greater cloud service use by making it cheaper than traditional server options.
- On-Premise
The on-premises cloud is a private cloud consisting of hardware and Software owned by an organization. The cloud you can use to host your applications and services is on-premise. On-premise clouds are often used by companies that want to use their own internal IT resources to control the operating system, updates, applications, and other components.
- External Cloud
The external cloud hosts data and applications in a public cloud or third-party hosting services, such as IBM Cloud or Amazon Web Services (AWS). External clouds are typically managed by third parties who charge for their services and offer more choices than on-premises clouds. For example, these providers may provide additional features such as storage capacity or extra security measures, making them more attractive than traditional on-premises solutions.
- Internal Cloud
An internal cloud is simply a group of servers that are connected so that they can share information. This can be accomplished with any hardware or software solution. Still, most companies choose to go with an internal cloud because it allows them to save money on equipment costs by sharing resources across multiple locations instead of buying expensive new equipment for each location where they need it.
- Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is one where both private and public clouds exist simultaneously; this is often referred to as a "private-public" hybrid cloud due to its unique nature! Hybrid clouds allow businesses to take advantage of all aspects.
- Cloud storage
Cloud storage is a service that gives users access to data stored in the cloud. Examples include Dropbox and Google Drive.
- Middleware
Middleware refers to Software that sits between the application and database layers in a software stack. Examples include Oracle's database management system and Microsoft SQL Server.
- Elasticity
Elasticity refers to the ability of a cloud service to grow and shrink in size at any time. This is desirable as it allows you to quickly scale up or down your infrastructure when demand increases or decreases.
Read More
Cloud Computing Terminologies
When you work in cloud computing, it's easy to forget the vocabulary you need to know. It's also easy to forget which terminology is generic and which ones should be reserved for specific services. This can lead to confusion and frustration, the hallmarks of poor communication within a team or company. So let's get familiar with these terms.
- AWS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon.com Inc. It provides on-demand cloud computing services for developers and enterprises.
- Azure
Microsoft Azure is a cloud platform developed by Microsoft. It provides infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and Software as a service (SaaS).
- Big Data
Big Data refers to an extremely large amount of data that needs to be analyzed quickly to gain insights into how it affects business operations, customer behavior, and market trends.
- Cloud Provider
A cloud provider is a company that provides services to other companies through the Internet. These providers make their clients' IT infrastructure available securely and reliably via the Internet. In addition, the provider provides software, hardware, and connectivity to its clients.
- Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a cloud computing platform from Google, Inc., offering infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), application development platform, and enterprise software as a service (SaaS). It provides computing power, storage, databases, and other components for building applications across many industries.
- Data Migration
Data migration refers to moving data from one location to another. It is a critical step in cloud computing, especially for enterprises storing data in different locations.
- IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing service that allows users to rent virtualized computing resources over the Internet. It is one of the most common types of cloud computing, where users access applications and data stored in servers hosted by third-party providers.
- PaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS), is an application development platform that provides its users with access to a wide range of software design and development tools, such as databases, web servers, server administration tools, and so on.
- SaaS
SaaS (Software as a Service) is a cloud computing model that provides on-demand Software licensing and access to application software over the Internet. It's a perfect fit for companies that want to develop their applications but need help to create or maintain their infrastructure.
- User Interface
User interface refers to how a cloud application is designed and used by customers. It also refers to the tools for end users to interact with the system, such as dashboards and reports.
- Private Cloud
A private cloud is a cloud-based infrastructure that resides on a single company's premises, often in a data center or colocation facility but sometimes in an office setting. An organization's own IT team uses it to manage its workloads, applications, and data. Private clouds are often designed for specific applications such as backup and disaster recovery or specialized workloads such as healthcare or finance.
- Public Cloud
A public cloud is a type of cloud computing where resources are accessible over the Internet by anyone with an Internet connection and basic software skills. Public clouds are managed by third parties such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Salesforce.com, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These cloud providers provide computing resources for companies without having to build and maintain their data centers.
- Pay-As-You-Go
Pay-As-You-Go is where users pay only for what they use instead of being billed based on server usage. This is designed to encourage greater cloud service use by making it cheaper than traditional server options.
- On-Premise
The on-premises cloud is a private cloud consisting of hardware and Software owned by an organization. The cloud you can use to host your applications and services is on-premise. On-premise clouds are often used by companies that want to use their own internal IT resources to control the operating system, updates, applications, and other components.
- External Cloud
The external cloud hosts data and applications in a public cloud or third-party hosting services, such as IBM Cloud or Amazon Web Services (AWS). External clouds are typically managed by third parties who charge for their services and offer more choices than on-premises clouds. For example, these providers may provide additional features such as storage capacity or extra security measures, making them more attractive than traditional on-premises solutions.
- Internal Cloud
An internal cloud is simply a group of servers that are connected so that they can share information. This can be accomplished with any hardware or software solution. Still, most companies choose to go with an internal cloud because it allows them to save money on equipment costs by sharing resources across multiple locations instead of buying expensive new equipment for each location where they need it.
- Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is one where both private and public clouds exist simultaneously; this is often referred to as a "private-public" hybrid cloud due to its unique nature! Hybrid clouds allow businesses to take advantage of all aspects.
- Cloud storage
Cloud storage is a service that gives users access to data stored in the cloud. Examples include Dropbox and Google Drive.
- Middleware
Middleware refers to Software that sits between the application and database layers in a software stack. Examples include Oracle's database management system and Microsoft SQL Server.
- Elasticity
Elasticity refers to the ability of a cloud service to grow and shrink in size at any time. This is desirable as it allows you to quickly scale up or down your infrastructure when demand increases or decreases.
Certified Scrum Master Certification: Benefits in 2023!!
Certified Scrum Master Certification Benefits 2023
The Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) is a beginner’s certification to offer new Scrum enthusiasts an idea of project management techniques. The credential is a globally renowned course provided by the prestigious Scrum Alliance. This program is offered to individuals who prove their skills in Scrum techniques, principles, and terminologies in the CSM test.
Certified Scrum Master Certification: Explain
A Scrum Master credential pinpoints your competency in the principles of Scrum Project management. Scrum Masters are project managers who leverage Scrum as their project management practice.
People who achieve CSM credential shows tangible proof to the recruiter that they possess the accurate skills and training for the job. Moreover, accreditation is an excellent source, regardless of your chosen field.
When it comes to Scrum Masters, part of your credential procedure is achieving the knowledge required for the position. Scrum teams need leaders; else, the whole practice is a waste of energy and time.
In addition, Scrum Master is the most sought-after career today, making recruiters choose candidates with CSM certification.
Roles of Scrum Masters
In general, the roles of a Scrum Master include the following:
- Eradicate organizational challenges, remove outdated procedures, and train new Scrum leaders
- Schedule Scrum meetings more efficiently, aiding team members to focus on the concept driving Scrum.
- Resolve problems that stand in the way of project progress.
- Leverages daily challenges as a learning technique for the team to help them improve significantly.
- Helps team members to upskill self-organizing skills.
Benefits of CSM Certification
CSM credentials help you stand out, showcasing your leadership skills far beyond what a typical project manager could offer.
A significant benefit of a CSM credential is that it proves your potential to organizations looking for Scrum Masters. In addition, there's a drastic increase in demands for Scrum Masters as every team needs a committed person to perform different Agile projects.
Some benefits of CSM certification are:
- If you're a Scrum professional with prior experience, a credential in Scrum expands your knowledge and helps you overcome hardships. It's an added benefit when you manage massive cross-functional teams leveraging the same framework.
- Being a CSM professional can encourage and lead your teammates. You will direct them and help the team work efficiently. The CSM certification displays your potential to recruiters, thus having the edge over your counterparts.
- Becoming a CSM can drastically expand your career opportunities. This credential will make you more relevant in your field - leading to handsome remuneration compared to your counterparts. It also equips you with the accurate skills required to fulfill the enterprise's objectives.
The Certified Scrum Master Exam
Certified Scrum Master individuals must undergo CSM training by CST trainers and will have to CST trainers and will have to take and pass an online test after the training to get certified. Like Agile and Scrum, credential enables experts to improve their excellence in agile and Scrum techniques and gives them a chance to be a member of the Scrum Alliance for two years.
CSM exam syllabus includes:
- Scrum overview
- Scrum project overview
- The Scrum teams
- Product backlog
- The product owner
- Releases
- Sprints
- The Scrum Master
- Enterprise transformation
Read More
Certified Scrum Master Certification Benefits 2023
The Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) is a beginner’s certification to offer new Scrum enthusiasts an idea of project management techniques. The credential is a globally renowned course provided by the prestigious Scrum Alliance. This program is offered to individuals who prove their skills in Scrum techniques, principles, and terminologies in the CSM test.
Certified Scrum Master Certification: Explain
A Scrum Master credential pinpoints your competency in the principles of Scrum Project management. Scrum Masters are project managers who leverage Scrum as their project management practice.
People who achieve CSM credential shows tangible proof to the recruiter that they possess the accurate skills and training for the job. Moreover, accreditation is an excellent source, regardless of your chosen field.
When it comes to Scrum Masters, part of your credential procedure is achieving the knowledge required for the position. Scrum teams need leaders; else, the whole practice is a waste of energy and time.
In addition, Scrum Master is the most sought-after career today, making recruiters choose candidates with CSM certification.
Roles of Scrum Masters
In general, the roles of a Scrum Master include the following:
- Eradicate organizational challenges, remove outdated procedures, and train new Scrum leaders
- Schedule Scrum meetings more efficiently, aiding team members to focus on the concept driving Scrum.
- Resolve problems that stand in the way of project progress.
- Leverages daily challenges as a learning technique for the team to help them improve significantly.
- Helps team members to upskill self-organizing skills.
Benefits of CSM Certification
CSM credentials help you stand out, showcasing your leadership skills far beyond what a typical project manager could offer.
A significant benefit of a CSM credential is that it proves your potential to organizations looking for Scrum Masters. In addition, there's a drastic increase in demands for Scrum Masters as every team needs a committed person to perform different Agile projects.
Some benefits of CSM certification are:
- If you're a Scrum professional with prior experience, a credential in Scrum expands your knowledge and helps you overcome hardships. It's an added benefit when you manage massive cross-functional teams leveraging the same framework.
- Being a CSM professional can encourage and lead your teammates. You will direct them and help the team work efficiently. The CSM certification displays your potential to recruiters, thus having the edge over your counterparts.
- Becoming a CSM can drastically expand your career opportunities. This credential will make you more relevant in your field - leading to handsome remuneration compared to your counterparts. It also equips you with the accurate skills required to fulfill the enterprise's objectives.
The Certified Scrum Master Exam
Certified Scrum Master individuals must undergo CSM training by CST trainers and will have to CST trainers and will have to take and pass an online test after the training to get certified. Like Agile and Scrum, credential enables experts to improve their excellence in agile and Scrum techniques and gives them a chance to be a member of the Scrum Alliance for two years.
CSM exam syllabus includes:
- Scrum overview
- Scrum project overview
- The Scrum teams
- Product backlog
- The product owner
- Releases
- Sprints
- The Scrum Master
- Enterprise transformation
Cryptography: The science of securing data via encryption.
What Is Cryptography?
Do you know what cryptography is? Cryptography is the art of keeping secrets. It has its uses in protecting data and ensuring only trusted people have access. One of the most important topics for every network is cryptography. What does cryptography do, how does it work, and why is it necessary for security? This article will answer all these questions and more.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the science of protecting data by ensuring privacy and confidentiality. It's a method of securing data that ensures that only authorized parties can decrypt and read it.
Cryptography can be used to encrypt data, so only the sender and receiver can access it. Cryptography can also be used to verify the identity of an entity when communicating with them.
For example, some websites require users to enter personal information such as their name, email address, and bank account number before being granted access to their accounts. Cryptography then encrypts this information and sends it back to the website's servers, decrypted using a key only the site administrator can access. This prevents hackers from accessing the user's data without permission from their email provider or banking institution.
Importance of Cryptography
Cryptography is the science of making information secrets. It is used in many applications, including electronic commerce and computer security. The current focus of cryptography research is on designing secure algorithms against possible future attacks.
Cryptography is so important today because it provides an extra layer of protection against hackers who want to steal our personal information from our computers or other devices connected online, such as laptops or tablets. It also allows us to communicate securely.
Cryptography can be used for a variety of purposes:
Authentication: Verifying that the sender of a message is authorized to send it.
Confidentiality: Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access or misuse by third parties.
Data integrity: Ensuring that messages have been created without modification by an attacker or "man-in-the-middle" (MitM) attacker, who might otherwise try to change or add notes in transit.
Data origin authentication: Assuring that at least one party has originated a message, even if there is no assurance about whether it was altered in transit.
Key Terms in Cryptography
Key: A secret string of characters used to identify and verify a person or thing. A key is typically used to encrypt or decrypt messages or to authenticate communication.
Encryption: The process of converting information from a known plaintext form into an obscure coded form using an encryption algorithm.
Decryption: The process of transforming coded information into its original plaintext form using an appropriate decryption algorithm.
Authentication: The act of verifying the identity of a communication partner by determining that the sender and receiver are who they claim to be.
Message Authentication Code (MAC): A type of digital signature that uses a secret key to verify the origin of a message.
Key Exchange: Two parties exchange public keys, which are then used to encrypt messages.
Message Authentication: Verification of an electronic message's origin and integrity. Usually performed using a secret key, but may also use other methods such as digital signatures or hash functions.
Ciphertext: the result of encryption after an algorithm encrypts it. It can be decrypted with the same algorithm.
Symmetric Key Encryption: A symmetric key encryption scheme uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt the data. This differs from asymmetric key encryption, which uses two keys to encrypt and decrypt the data.
Asymmetric Key Encryption: Asymmetric key encryption uses two different keys (also called public and private keys) for encrypting and decrypting data. The public key can be shared widely with others and used to encrypt information, while the private key must be kept secret by its owner.
Cryptographic Hash Function: Cryptographic hash functions are one-way functions that take an arbitrary-length string as input and produce a fixed-length string as output. These hashes are often used to validate digital signatures and provide integrity services. Still, they can also be used to create pseudorandom numbers that can be used for a variety of other purposes.
Public key and Private Key in Cryptography
Public and private keys are used in cryptography, which refers to the pair of numbers that uniquely identify a given public key and its corresponding private key. The public key is published and made available to anyone, while its owner keeps the private key secret.
The public key can be shared with anyone who needs to encrypt a message to be sent to you, while the private key is known only to you. When you want to send someone else your message, you use their public address; when they want to send you theirs, they use your address. This way, both parties control messages sent back and forth between them.
A private key is kept secret, while a public key is shared with many people. The idea behind this scheme is that if someone wants to send an encrypted message to you, they will first type your public address into their computer and then type in their private address (which corresponds with their secret). Then, they will send it along with the message. When you receive the message and want to read it, you must type in your secret before decrypting it with your private key.
Conclusion
Learning about cryptography is becoming increasingly vital, especially with the growing focus on digital security and privacy. More people are beginning to appreciate how cryptography is used to protect their private information and are taking steps to learn more. Information is key to staying secure and safe in today's digital world. So the more you know, the better off you'll be.
This guide is for you if you're looking for cryptography but unsure where to start. With a bit of practice and practice, you can be well on your way to mastering the art of cryptography in no time.
Read More
What Is Cryptography?
Do you know what cryptography is? Cryptography is the art of keeping secrets. It has its uses in protecting data and ensuring only trusted people have access. One of the most important topics for every network is cryptography. What does cryptography do, how does it work, and why is it necessary for security? This article will answer all these questions and more.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the science of protecting data by ensuring privacy and confidentiality. It's a method of securing data that ensures that only authorized parties can decrypt and read it.
Cryptography can be used to encrypt data, so only the sender and receiver can access it. Cryptography can also be used to verify the identity of an entity when communicating with them.
For example, some websites require users to enter personal information such as their name, email address, and bank account number before being granted access to their accounts. Cryptography then encrypts this information and sends it back to the website's servers, decrypted using a key only the site administrator can access. This prevents hackers from accessing the user's data without permission from their email provider or banking institution.
Importance of Cryptography
Cryptography is the science of making information secrets. It is used in many applications, including electronic commerce and computer security. The current focus of cryptography research is on designing secure algorithms against possible future attacks.
Cryptography is so important today because it provides an extra layer of protection against hackers who want to steal our personal information from our computers or other devices connected online, such as laptops or tablets. It also allows us to communicate securely.
Cryptography can be used for a variety of purposes:
Authentication: Verifying that the sender of a message is authorized to send it.
Confidentiality: Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access or misuse by third parties.
Data integrity: Ensuring that messages have been created without modification by an attacker or "man-in-the-middle" (MitM) attacker, who might otherwise try to change or add notes in transit.
Data origin authentication: Assuring that at least one party has originated a message, even if there is no assurance about whether it was altered in transit.
Key Terms in Cryptography
Key: A secret string of characters used to identify and verify a person or thing. A key is typically used to encrypt or decrypt messages or to authenticate communication.
Encryption: The process of converting information from a known plaintext form into an obscure coded form using an encryption algorithm.
Decryption: The process of transforming coded information into its original plaintext form using an appropriate decryption algorithm.
Authentication: The act of verifying the identity of a communication partner by determining that the sender and receiver are who they claim to be.
Message Authentication Code (MAC): A type of digital signature that uses a secret key to verify the origin of a message.
Key Exchange: Two parties exchange public keys, which are then used to encrypt messages.
Message Authentication: Verification of an electronic message's origin and integrity. Usually performed using a secret key, but may also use other methods such as digital signatures or hash functions.
Ciphertext: the result of encryption after an algorithm encrypts it. It can be decrypted with the same algorithm.
Symmetric Key Encryption: A symmetric key encryption scheme uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt the data. This differs from asymmetric key encryption, which uses two keys to encrypt and decrypt the data.
Asymmetric Key Encryption: Asymmetric key encryption uses two different keys (also called public and private keys) for encrypting and decrypting data. The public key can be shared widely with others and used to encrypt information, while the private key must be kept secret by its owner.
Cryptographic Hash Function: Cryptographic hash functions are one-way functions that take an arbitrary-length string as input and produce a fixed-length string as output. These hashes are often used to validate digital signatures and provide integrity services. Still, they can also be used to create pseudorandom numbers that can be used for a variety of other purposes.
Public key and Private Key in Cryptography
Public and private keys are used in cryptography, which refers to the pair of numbers that uniquely identify a given public key and its corresponding private key. The public key is published and made available to anyone, while its owner keeps the private key secret.
The public key can be shared with anyone who needs to encrypt a message to be sent to you, while the private key is known only to you. When you want to send someone else your message, you use their public address; when they want to send you theirs, they use your address. This way, both parties control messages sent back and forth between them.
A private key is kept secret, while a public key is shared with many people. The idea behind this scheme is that if someone wants to send an encrypted message to you, they will first type your public address into their computer and then type in their private address (which corresponds with their secret). Then, they will send it along with the message. When you receive the message and want to read it, you must type in your secret before decrypting it with your private key.
Conclusion
Learning about cryptography is becoming increasingly vital, especially with the growing focus on digital security and privacy. More people are beginning to appreciate how cryptography is used to protect their private information and are taking steps to learn more. Information is key to staying secure and safe in today's digital world. So the more you know, the better off you'll be.
This guide is for you if you're looking for cryptography but unsure where to start. With a bit of practice and practice, you can be well on your way to mastering the art of cryptography in no time.
How Big Data Impacts Company Decision-Making Strategies
3 Ways Big Data Influences Company Decision-making
According to the latest research, we develop over 2.5 quintillion bytes of data every day. These days, companies have access to myriad data sources gathered from customer touchpoints like social media pages, documents, websites, archives, and more.
However, more than just collecting data is needed to develop a positive effect on your venture. First, you need to determine and change the collated data into segments of value-added data.
Let's discuss three ways companies use Big Data to drive crucial business decisions and improve their enterprise performance.
Improve Operational Efficiency
Most organizations use data to automate workflows, optimize selling techniques, and improve their overall business efficiency.
For instance, Elon Musk's Tesla vehicles are incorporated with sensors that gather data and send it to the core servers for analysis. This aids the enterprise in enhancing its car performance. The firm also informs individual car owners regarding priority repair.
Another beneficial aspect of Big Data is Tesla's autopilot technique. Tesla records more miles/day than the total miles the Google autonomous car program recorded. It has also generated roadmaps for autonomous vehicles by assembling all the data into the cloud.
These roadmaps are proven to be 100x more precise than conventional GPS. In addition, the improved autopilot software helps match your car's speed to traffic, direct lane changes, and self-parking.
No Additional Investment, Maximum Capacity
Have you ever wondered about an increased customer base without the need for additional resources/investment?
A telecommunication firm - Sprint, leveraged Big Data analytics to minimize network fallacies, enhance customer experience, and optimize resources by analyzing real-time data. This has helped the enterprise to achieve a 90% increase in its delivery rate.
Real-time Data: Enhance Customer Engagement & Retention
One of the most crucial domains of any sector is customer service, where enterprises must deliver metrics. Organizations leverage real-time data to provide individual personalized services to their customers.
The US retail company - Kroger leverage Big Data to offer personalized loyalty programs to its users. The enterprise uses the collected data to generate meaningful insights that help the brand to improve profitability and customer satisfaction.
Kroger claims that 95% of its sales rely on customer loyalty and has added 60% redemption rates and around $12Bn incremental revenue. This has helped the firm stay profitable even during a worldwide recession.
Why Prepare for Big Data Career?
Today, most sectors are enhanced with the application of Big Data. Likewise, every career domain is drastically improved when the potential to gather and analyze Big Data is added to an ongoing scenario.
Let's see why you must enroll in Big Data Analytics to expand your professional background.
- The first and foremost benefit of Big Data Analytics is its attractive salary pack, which is higher than its IT counterparts. According to a global recruitment company - Randstad, the rate of Big Data experts is 50% more than that of other IT professionals in India. Likewise, ITjobswatch highlights a 14% increase in average salary for Big Data consultants in the UK in 2016.
- There has been an increase in job opportunities in the Big Data management and analytics field over the last five years. A prediction report from the McKinsey Global Institute states a shortage of over 1.5Mn analysts in the US by the end of 2018.
- Various job titles like Big Data Engineer and Metrics & Analytics Specialist are some of the most demanding careers in the modern job market.
As more companies leap onto data-driven decision-making techniques, they must adopt learning and invest in their workforces to achieve value-added accreditations. Organizations must take the step to sponsor employees for significant training courses on analytical tools and techniques that will provide their teams with the skills needed to use data for informed decision-making.
Read More
3 Ways Big Data Influences Company Decision-making
According to the latest research, we develop over 2.5 quintillion bytes of data every day. These days, companies have access to myriad data sources gathered from customer touchpoints like social media pages, documents, websites, archives, and more.
However, more than just collecting data is needed to develop a positive effect on your venture. First, you need to determine and change the collated data into segments of value-added data.
Let's discuss three ways companies use Big Data to drive crucial business decisions and improve their enterprise performance.
Improve Operational Efficiency
Most organizations use data to automate workflows, optimize selling techniques, and improve their overall business efficiency.
For instance, Elon Musk's Tesla vehicles are incorporated with sensors that gather data and send it to the core servers for analysis. This aids the enterprise in enhancing its car performance. The firm also informs individual car owners regarding priority repair.
Another beneficial aspect of Big Data is Tesla's autopilot technique. Tesla records more miles/day than the total miles the Google autonomous car program recorded. It has also generated roadmaps for autonomous vehicles by assembling all the data into the cloud.
These roadmaps are proven to be 100x more precise than conventional GPS. In addition, the improved autopilot software helps match your car's speed to traffic, direct lane changes, and self-parking.
No Additional Investment, Maximum Capacity
Have you ever wondered about an increased customer base without the need for additional resources/investment?
A telecommunication firm - Sprint, leveraged Big Data analytics to minimize network fallacies, enhance customer experience, and optimize resources by analyzing real-time data. This has helped the enterprise to achieve a 90% increase in its delivery rate.
Real-time Data: Enhance Customer Engagement & Retention
One of the most crucial domains of any sector is customer service, where enterprises must deliver metrics. Organizations leverage real-time data to provide individual personalized services to their customers.
The US retail company - Kroger leverage Big Data to offer personalized loyalty programs to its users. The enterprise uses the collected data to generate meaningful insights that help the brand to improve profitability and customer satisfaction.
Kroger claims that 95% of its sales rely on customer loyalty and has added 60% redemption rates and around $12Bn incremental revenue. This has helped the firm stay profitable even during a worldwide recession.
Why Prepare for Big Data Career?
Today, most sectors are enhanced with the application of Big Data. Likewise, every career domain is drastically improved when the potential to gather and analyze Big Data is added to an ongoing scenario.
Let's see why you must enroll in Big Data Analytics to expand your professional background.
- The first and foremost benefit of Big Data Analytics is its attractive salary pack, which is higher than its IT counterparts. According to a global recruitment company - Randstad, the rate of Big Data experts is 50% more than that of other IT professionals in India. Likewise, ITjobswatch highlights a 14% increase in average salary for Big Data consultants in the UK in 2016.
- There has been an increase in job opportunities in the Big Data management and analytics field over the last five years. A prediction report from the McKinsey Global Institute states a shortage of over 1.5Mn analysts in the US by the end of 2018.
- Various job titles like Big Data Engineer and Metrics & Analytics Specialist are some of the most demanding careers in the modern job market.
As more companies leap onto data-driven decision-making techniques, they must adopt learning and invest in their workforces to achieve value-added accreditations. Organizations must take the step to sponsor employees for significant training courses on analytical tools and techniques that will provide their teams with the skills needed to use data for informed decision-making.
6 Significant Characteristics of Cloud Computing Must Know
6 Significant Characteristics of Cloud Computing You Must Know
Cloud involves an ever-growing list of techniques and tools; however, the significant aspects of cloud computing remain the same. The first alternative of the cloud to popularize was AWS, followed by Microsoft and Google
In the modern era, cloud computing extends from system to SaaS models, including Artificial Intelligence, IoT, serverless computing, and much more.
Though each subset has its advantages and disadvantages; however, numerous core cloud computing aspects underpin all of them.
This article will show you six main characteristics of cloud computing, explaining why it's the perfect solution for building and deploying innovative applications.
6 Essential Cloud Computing Characteristics
Resource Pooling
Public cloud providers depend on multi-tenant designs to accommodate more users simultaneously. Customers' workloads are preoccupied with the hardware and software, which serve numerous customers on the same host Cloud providers mainly depend on custom hardware and abstraction layers to enhance security and speed up user's resource access.
Security
Regarding security, Cloud services develop a stored copy of data to prevent data loss. If a server misses the data, the copied version is retrieved and restored from the other server. This characteristic comes in handy when several users work simultaneously on a particular file, and it suddenly gets corrupted.
On-demand Self-service
With data centers across the globe, Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and others have a colossal amount of computing and storage assets ready. This represents a radical departure for IT professionals customized to a procurement process that can take months.
Instead of waiting for a new server to be delivered to a private data center, creators can choose the tools they require via a cloud's self-service portal and setup the right way.
Wide Network Access
A significant part of the cloud's utility is its ubiquity. With internet connectivity, data can be uploaded and accessed from any part of the world. As a result, the cloud is an eye-alluring choice for most businesses with a combination of OS, platforms, and devices.
To preserve broad network access, cloud providers track and ensure various metrics that reflect how people access cloud data and resources.
Remote Working
Cloud Computing promotes remote working, where clients can function, work, or deliver services from anywhere. Hence, users can access organizational data even on their smart devices, thus, enabling them to connect swiftly.
Service Excellence
Cloud Computing ensures that customers receive the top-notch service possible. The benefits highlighted in Service Legal Agreements must have constant availability and comprehensive resources, capacity, and performance. Any compromise on these services leads to client loss and popularity.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
The following are the reasons why one must leverage Cloud Computing:
Deliver scalable business solutions
Reduce expenses in terms of procuring new hardware/software
Provide security and make easy access to Computing resources
It helps to maximize the capacity to adapt to the increasing enterprise demands of huge companies
Help enterprise clients to assess apps and services seamlessly.
Reliable as they offer backup and affordable methods for data recovery.
Read More
6 Significant Characteristics of Cloud Computing You Must Know
Cloud involves an ever-growing list of techniques and tools; however, the significant aspects of cloud computing remain the same. The first alternative of the cloud to popularize was AWS, followed by Microsoft and Google
In the modern era, cloud computing extends from system to SaaS models, including Artificial Intelligence, IoT, serverless computing, and much more.
Though each subset has its advantages and disadvantages; however, numerous core cloud computing aspects underpin all of them.
This article will show you six main characteristics of cloud computing, explaining why it's the perfect solution for building and deploying innovative applications.
6 Essential Cloud Computing Characteristics
Resource Pooling
Public cloud providers depend on multi-tenant designs to accommodate more users simultaneously. Customers' workloads are preoccupied with the hardware and software, which serve numerous customers on the same host Cloud providers mainly depend on custom hardware and abstraction layers to enhance security and speed up user's resource access.
Security
Regarding security, Cloud services develop a stored copy of data to prevent data loss. If a server misses the data, the copied version is retrieved and restored from the other server. This characteristic comes in handy when several users work simultaneously on a particular file, and it suddenly gets corrupted.
On-demand Self-service
With data centers across the globe, Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and others have a colossal amount of computing and storage assets ready. This represents a radical departure for IT professionals customized to a procurement process that can take months.
Instead of waiting for a new server to be delivered to a private data center, creators can choose the tools they require via a cloud's self-service portal and setup the right way.
Wide Network Access
A significant part of the cloud's utility is its ubiquity. With internet connectivity, data can be uploaded and accessed from any part of the world. As a result, the cloud is an eye-alluring choice for most businesses with a combination of OS, platforms, and devices.
To preserve broad network access, cloud providers track and ensure various metrics that reflect how people access cloud data and resources.
Remote Working
Cloud Computing promotes remote working, where clients can function, work, or deliver services from anywhere. Hence, users can access organizational data even on their smart devices, thus, enabling them to connect swiftly.
Service Excellence
Cloud Computing ensures that customers receive the top-notch service possible. The benefits highlighted in Service Legal Agreements must have constant availability and comprehensive resources, capacity, and performance. Any compromise on these services leads to client loss and popularity.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
The following are the reasons why one must leverage Cloud Computing:
Deliver scalable business solutions
Reduce expenses in terms of procuring new hardware/software
Provide security and make easy access to Computing resources
It helps to maximize the capacity to adapt to the increasing enterprise demands of huge companies
Help enterprise clients to assess apps and services seamlessly.
Reliable as they offer backup and affordable methods for data recovery.
Scrum Master Role & Responsibilities Explained Simply!!
Scrum Master Role and Responsibilities
Scrum Master is a multifaceted role. In fact, there are many different ways to define what it means to be a Scrum Master. However, regardless of how you define the role and responsibilities, everyone who plays a part in creating an agile project will be called upon to fill the Scrum Master shoes – regardless of their experience level or current project responsibilities.
What is a Scrum Master?
The Scrum Master is a person who helps the Product Owner, Development Team, and the Team to work together efficiently and effectively. The Scrum Master maintains a common understanding of the Scrum process and ensures that it is followed.
In addition, they act as a neutral facilitator for all meetings, remove impediments to progress, and provide coaching and training to help the team become more effective.
The Scrum Master guides how to adapt the Scrum process to their organization's specific needs. They also help teams improve their practices by providing feedback and education on best practices.
Scrum Master Roles and Responsibilities
- Facilitate the Scrum Teams in their work.
- Ensure that the teams understand all requirements and that they can meet them.
- Ensure that all communication between the teams is effective and efficient.
- Provide any additional training required for the team members to perform their work effectively.
- Understanding the teams' context and situation and their goals and objectives.
- Ensuring that each team member clearly understands who they are working with, their work roles, and any special requirements they may have (e.g., accessibility).
- Ensuring all team members understand how they can contribute to the product vision and strategy.
- Facilitating frequent interactions among all team members so that commitments are met, risks are shared, and progress is made (e.g., daily stand-up meetings).
Why Do Teams Need a Scrum Master?
There are many reasons why the Scrum Master needs to be a part of the Scrum team. The Scrum Master is not just another person on the team but an integral part.
The Scrum Master's role on a Scrum team is to help ensure that everyone on the team has access to information about what is going on at all times, as well as make sure that people are working together in a way that will help them achieve their goals. This role's goal is also to ensure whoever may need help has access to it as quickly as possible. This can be done by ensuring that everyone understands how they should interact with each other and how they should handle their tasks within their roles. It also means ensuring there are clear understandings and communication within the team.
This is important because there could be confusion over who should do what or how something should be done. As well as this, if you need someone who can participate in meetings and get everyone involved in discussions around what needs to happen next about your project or task, then it will take longer than necessary for things to get done.
Scrum Master vs. Product Manager
- Scrum master and product manager are two different titles. The main difference between the two is that one oversees the development activities of a team, and the other manages the overall business objectives of an organization.
- Scrum masters help teams deliver products, while product managers help organizations deliver products. Both roles involve collaborating with people from different departments to build and deliver software.
- Scrum masters create software, while product managers focus on its delivery.
- A scrum master guides a team through an iterative process that involves breaking down features into small increments and regularly testing them against user needs before releasing them to production. The product manager is responsible for managing this entire process, which involves coming up with business requirements and then helping teams develop software based on those requirements.
- The scrum master is responsible for the overall success of the project and the product. The product manager is responsible for the development of a specific product.
- A scrum master oversees the full sprint and ensures that all teams work together effectively. Finally, a product manager leads a particular team and oversees daily work.
- The main difference between these two roles is that a scrum master focuses more on long-term planning. In contrast, a product manager focuses more on short-term planning.
Scrum Master vs. Project Manager
- Scrum Master is a person who leads the Scrum process.
- He is responsible for ensuring that all scrum team members can work effectively together and that they clearly understand the roles they are required to perform.
- The Scrum Master also maintains a good working relationship with the product owner and stakeholders by acting as their agent during the development phase of an Agile project.
- In contrast, a Project Manager is responsible for managing projects within or between organizations.
- The manager’s job is to prepare the project plan, manage the resources (managers and staff) involved in implementing that plan, monitor progress toward completion of objectives and ensure that budgeted funds are available to fulfill tasks assigned to team members.
Qualities of a Successful Scrum Master
The qualities of a successful Scrum Master include:
- A good understanding of the Agile development process's principles, values, and practices.
- Understanding the individuals involved with the project and their roles and responsibilities.
- Knowledge of product management, design, development, and customer services.
- An ability to communicate effectively both verbally and in writing.
- The ability to influence change without being confrontational or confrontational; this includes dealing with difficult situations professionally and tactfully.
Conclusion
As for the future, Scrum Master is a profession just like every other programming job, and it might get fully independent shortly. However, lately, there has been an increased demand for Scrum Masters, and salaries are much higher than before.
Read More
Scrum Master Role and Responsibilities
Scrum Master is a multifaceted role. In fact, there are many different ways to define what it means to be a Scrum Master. However, regardless of how you define the role and responsibilities, everyone who plays a part in creating an agile project will be called upon to fill the Scrum Master shoes – regardless of their experience level or current project responsibilities.
What is a Scrum Master?
The Scrum Master is a person who helps the Product Owner, Development Team, and the Team to work together efficiently and effectively. The Scrum Master maintains a common understanding of the Scrum process and ensures that it is followed.
In addition, they act as a neutral facilitator for all meetings, remove impediments to progress, and provide coaching and training to help the team become more effective.
The Scrum Master guides how to adapt the Scrum process to their organization's specific needs. They also help teams improve their practices by providing feedback and education on best practices.
Scrum Master Roles and Responsibilities
- Facilitate the Scrum Teams in their work.
- Ensure that the teams understand all requirements and that they can meet them.
- Ensure that all communication between the teams is effective and efficient.
- Provide any additional training required for the team members to perform their work effectively.
- Understanding the teams' context and situation and their goals and objectives.
- Ensuring that each team member clearly understands who they are working with, their work roles, and any special requirements they may have (e.g., accessibility).
- Ensuring all team members understand how they can contribute to the product vision and strategy.
- Facilitating frequent interactions among all team members so that commitments are met, risks are shared, and progress is made (e.g., daily stand-up meetings).
Why Do Teams Need a Scrum Master?
There are many reasons why the Scrum Master needs to be a part of the Scrum team. The Scrum Master is not just another person on the team but an integral part.
The Scrum Master's role on a Scrum team is to help ensure that everyone on the team has access to information about what is going on at all times, as well as make sure that people are working together in a way that will help them achieve their goals. This role's goal is also to ensure whoever may need help has access to it as quickly as possible. This can be done by ensuring that everyone understands how they should interact with each other and how they should handle their tasks within their roles. It also means ensuring there are clear understandings and communication within the team.
This is important because there could be confusion over who should do what or how something should be done. As well as this, if you need someone who can participate in meetings and get everyone involved in discussions around what needs to happen next about your project or task, then it will take longer than necessary for things to get done.
Scrum Master vs. Product Manager
- Scrum master and product manager are two different titles. The main difference between the two is that one oversees the development activities of a team, and the other manages the overall business objectives of an organization.
- Scrum masters help teams deliver products, while product managers help organizations deliver products. Both roles involve collaborating with people from different departments to build and deliver software.
- Scrum masters create software, while product managers focus on its delivery.
- A scrum master guides a team through an iterative process that involves breaking down features into small increments and regularly testing them against user needs before releasing them to production. The product manager is responsible for managing this entire process, which involves coming up with business requirements and then helping teams develop software based on those requirements.
- The scrum master is responsible for the overall success of the project and the product. The product manager is responsible for the development of a specific product.
- A scrum master oversees the full sprint and ensures that all teams work together effectively. Finally, a product manager leads a particular team and oversees daily work.
- The main difference between these two roles is that a scrum master focuses more on long-term planning. In contrast, a product manager focuses more on short-term planning.
Scrum Master vs. Project Manager
- Scrum Master is a person who leads the Scrum process.
- He is responsible for ensuring that all scrum team members can work effectively together and that they clearly understand the roles they are required to perform.
- The Scrum Master also maintains a good working relationship with the product owner and stakeholders by acting as their agent during the development phase of an Agile project.
- In contrast, a Project Manager is responsible for managing projects within or between organizations.
- The manager’s job is to prepare the project plan, manage the resources (managers and staff) involved in implementing that plan, monitor progress toward completion of objectives and ensure that budgeted funds are available to fulfill tasks assigned to team members.
Qualities of a Successful Scrum Master
The qualities of a successful Scrum Master include:
- A good understanding of the Agile development process's principles, values, and practices.
- Understanding the individuals involved with the project and their roles and responsibilities.
- Knowledge of product management, design, development, and customer services.
- An ability to communicate effectively both verbally and in writing.
- The ability to influence change without being confrontational or confrontational; this includes dealing with difficult situations professionally and tactfully.
Conclusion
As for the future, Scrum Master is a profession just like every other programming job, and it might get fully independent shortly. However, lately, there has been an increased demand for Scrum Masters, and salaries are much higher than before.
Top 5 CompTIA Certifications You Should Pursue in 2023.
5 Best CompTIA Certifications to Pursue in 2023
One of the most appropriate methods to swiftly climb the career ladder is to gain accreditation in the right domain. For example, if you're working in the IT sector and focusing on fields like system admin, server environment, or computer security, there are numerous credentials, especially CompTIA courses, to help you display your skills and expertise.
CompTIA is a leading provider of vendor-neutral IT accreditations worldwide, helping IT experts become the next leaders in the digitally connected realm, where more than 2Mn IT credentials are globally issued.
Let's see the five best CompTIA certifications to pursue in 2023.
CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner (CASP)
CASP is one of the most demanding accreditations that several IT professionals desire to have in their toolkits. It covers the following domains - Risk analysis, Managing risk & forecasting, and Enterprise security.
Enterprise security is a crucial factor of CASP as it gives individuals practical skills to manage SME-sized organizations. The credential displays that an IT expert has in-depth knowledge and skills in computer security matters.
This is also a globally renowned credential and is vendor-neutral. It highlights that you're competent in enterprise security, communication, computing integration, and business disciplines.
CompTIA Security+ Certification
To have an alluring career in the network security field, a great place to start is to achieve the CompTIA Security+ accreditation Network security is among the significantly expanding domains in IT. Successfully passing the credential means you're competent in the network system, access control, security, and organization security.
Security+ is an excellent step to your Network+ credential, as it develops networking by focusing on the central security factors. Furthermore, there is an ever-growing demand for IT security professionals as threats to computer security are rising in severity. Hence, if you gain experience in networking and security, you will become a great fortune to any organization recruiting you.
CompTIA Network+ Certification
If you are an entry-level IT professional, then Network+ certification is for you. However, the credential is highly significant for those who wish to set their sights on becoming a great IT support expert. It's an excellent complement to the CompTIA A+ credential as it covers beyond the fundamental networking abilities only covered in the A+ accreditation.
Once you gain the credential, you'll have competence in the installation, management, troubleshooting, maintenance, and configuration of whole network systems.
Like an A+ credential, a Network+ certificate doesn't need a computer science degree to pass the test.
CompTIA A+ Certification
CompTIA A+ credential isn't just a globally renowned accreditation but a beginning course for a strong IT career. This course is a sign that an individual has computer technician skills. This encompasses numerous operating infrastructures such as IBM, Microsoft, Novell, and Apple and covers several technologies.
Several workforces regard this accreditation as the industry standard for support technicians, as certification indicates fundamental competency as a computer professional.
Moreover, it's a globally renowned certification and proves the holder is competent in security, networking, preventive maintenance, troubleshooting, and installation in various operating systems and technologies.
CompTIA Server+ Certification
Server+ accreditation is excellent for system admins as the knowledge and training in technical skills are required to build, maintain, troubleshoot, and support server hardware and software technologies.
The credential is a mid-level program covering advanced computing topics. Hence, it's aimed at professionals with a minimum of 18-24 months of experience working around the server environment.
According to CompTIA, it's best to achieve an A+ credential before jumping onto this program. Moreover, the A+ certification offers you a firm grounding for other CompTIA credentials like Server+, though you can get through with good computer experience.
To pass the CompTIA Server+ accreditation test, you'll have to pass a conventional format test that includes situations based on working with servers like disaster recovery, installation, upgrading, and more.
In addition, ensure that before appearing for the Server+ examination, you must have a solid working experience in the above domains.
Conclusion
CompTIA credentials are a trial and tested means of enhancing your career. As the credentials are vendor-neutral and globally renowned, you can get a job anywhere. In addition, the certification helps set your career to a greater extent as there is an ongoing shortage of computer experts, especially in the cybersecurity domain.
Moreover, merging A+, Server+, and Network+ is an excellent method to display your range of computer expertise to potential recruiters. All these 5 CompTIA certifications will give you a solid basis in IT and maximize your marketability, ultimately achieving Microsoft MCSA certification.
Read More
5 Best CompTIA Certifications to Pursue in 2023
One of the most appropriate methods to swiftly climb the career ladder is to gain accreditation in the right domain. For example, if you're working in the IT sector and focusing on fields like system admin, server environment, or computer security, there are numerous credentials, especially CompTIA courses, to help you display your skills and expertise.
CompTIA is a leading provider of vendor-neutral IT accreditations worldwide, helping IT experts become the next leaders in the digitally connected realm, where more than 2Mn IT credentials are globally issued.
Let's see the five best CompTIA certifications to pursue in 2023.
CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner (CASP)
CASP is one of the most demanding accreditations that several IT professionals desire to have in their toolkits. It covers the following domains - Risk analysis, Managing risk & forecasting, and Enterprise security.
Enterprise security is a crucial factor of CASP as it gives individuals practical skills to manage SME-sized organizations. The credential displays that an IT expert has in-depth knowledge and skills in computer security matters.
This is also a globally renowned credential and is vendor-neutral. It highlights that you're competent in enterprise security, communication, computing integration, and business disciplines.
CompTIA Security+ Certification
To have an alluring career in the network security field, a great place to start is to achieve the CompTIA Security+ accreditation Network security is among the significantly expanding domains in IT. Successfully passing the credential means you're competent in the network system, access control, security, and organization security.
Security+ is an excellent step to your Network+ credential, as it develops networking by focusing on the central security factors. Furthermore, there is an ever-growing demand for IT security professionals as threats to computer security are rising in severity. Hence, if you gain experience in networking and security, you will become a great fortune to any organization recruiting you.
CompTIA Network+ Certification
If you are an entry-level IT professional, then Network+ certification is for you. However, the credential is highly significant for those who wish to set their sights on becoming a great IT support expert. It's an excellent complement to the CompTIA A+ credential as it covers beyond the fundamental networking abilities only covered in the A+ accreditation.
Once you gain the credential, you'll have competence in the installation, management, troubleshooting, maintenance, and configuration of whole network systems.
Like an A+ credential, a Network+ certificate doesn't need a computer science degree to pass the test.
CompTIA A+ Certification
CompTIA A+ credential isn't just a globally renowned accreditation but a beginning course for a strong IT career. This course is a sign that an individual has computer technician skills. This encompasses numerous operating infrastructures such as IBM, Microsoft, Novell, and Apple and covers several technologies.
Several workforces regard this accreditation as the industry standard for support technicians, as certification indicates fundamental competency as a computer professional.
Moreover, it's a globally renowned certification and proves the holder is competent in security, networking, preventive maintenance, troubleshooting, and installation in various operating systems and technologies.
CompTIA Server+ Certification
Server+ accreditation is excellent for system admins as the knowledge and training in technical skills are required to build, maintain, troubleshoot, and support server hardware and software technologies.
The credential is a mid-level program covering advanced computing topics. Hence, it's aimed at professionals with a minimum of 18-24 months of experience working around the server environment.
According to CompTIA, it's best to achieve an A+ credential before jumping onto this program. Moreover, the A+ certification offers you a firm grounding for other CompTIA credentials like Server+, though you can get through with good computer experience.
To pass the CompTIA Server+ accreditation test, you'll have to pass a conventional format test that includes situations based on working with servers like disaster recovery, installation, upgrading, and more.
In addition, ensure that before appearing for the Server+ examination, you must have a solid working experience in the above domains.
Conclusion
CompTIA credentials are a trial and tested means of enhancing your career. As the credentials are vendor-neutral and globally renowned, you can get a job anywhere. In addition, the certification helps set your career to a greater extent as there is an ongoing shortage of computer experts, especially in the cybersecurity domain.
Moreover, merging A+, Server+, and Network+ is an excellent method to display your range of computer expertise to potential recruiters. All these 5 CompTIA certifications will give you a solid basis in IT and maximize your marketability, ultimately achieving Microsoft MCSA certification.
Data Science: 2022's Most-Sought After Career Choice Now
Is Data Science the Most-sought After Career in 2022?
As we dive deep into the year and can still see the role of Data Scientists booming, it's no doubt that data science is the most significant trend worldwide, with data-driven decision-making gaining massive popularity. Irrespective of how large or small the business is, every organization looks for master workforces who can understand and analyze the data precisely, making it the sexiest job and desirable career in any domain.
Data Science includes advanced analytics practices and scientific principles to extract valuable information from decision-making data. The technology leverages complex machine-learning algorithms to create predictive models. In addition, it leverages several statistical techniques ranging from data transformation to machine learning modeling.
The Data Science market is expected to expand from over $95Bn in 2021 to $322Bn by 2026. The role of data scientists combines mathematics, computer science, and statistics. They analyze, process, and model data and then interpret the outcomes to develop actionable insights for organizations.
The role was relatively less at the time; however, as more firms accepted big data, they realized they required an individual who could merge analytics, programming, and experimentation skills. Thus, Data Science will become the most sought-after career in the job market in 2022.
Data Science, the Hottest Buzzword in the Job Market
Data Science has drastically become a subject matter across various industry verticals. As a result, the data science job is more in demand than ever with recruiters. In addition, artificial Intelligence (AI) is significantly rising in ventures, and organizations globally feel the need for data scientists to create AI models.
According to the US BLS, the number of job opportunities needing data science skills is expected to rise by 27.9% by 2026. There are no automated techniques that can replace the skills of data scientists as long as we continuously learn and develop data-driven solutions. In the data science world, it's a top-notch professional ranking with the training to discover the world of big data. Many data professionals highlighted that they spend much of their time wrangling data, which is still the scenario despite a few developments in leveraging AI for data management.
Data experts understand that they face technical issues; however, they don't permit that to bog down their research for new solutions. Several other data scientists, especially from companies such as LinkedIn, Google, Walmart, and more, have added to and refined the toolkit. Over 80% of organizations globally are investing a large part of their investments into developing a skilled data analytics division, thus recruiting the most innovative talent pool in the industry.
Read More
Is Data Science the Most-sought After Career in 2022?
As we dive deep into the year and can still see the role of Data Scientists booming, it's no doubt that data science is the most significant trend worldwide, with data-driven decision-making gaining massive popularity. Irrespective of how large or small the business is, every organization looks for master workforces who can understand and analyze the data precisely, making it the sexiest job and desirable career in any domain.
Data Science includes advanced analytics practices and scientific principles to extract valuable information from decision-making data. The technology leverages complex machine-learning algorithms to create predictive models. In addition, it leverages several statistical techniques ranging from data transformation to machine learning modeling.
The Data Science market is expected to expand from over $95Bn in 2021 to $322Bn by 2026. The role of data scientists combines mathematics, computer science, and statistics. They analyze, process, and model data and then interpret the outcomes to develop actionable insights for organizations.
The role was relatively less at the time; however, as more firms accepted big data, they realized they required an individual who could merge analytics, programming, and experimentation skills. Thus, Data Science will become the most sought-after career in the job market in 2022.
Data Science, the Hottest Buzzword in the Job Market
Data Science has drastically become a subject matter across various industry verticals. As a result, the data science job is more in demand than ever with recruiters. In addition, artificial Intelligence (AI) is significantly rising in ventures, and organizations globally feel the need for data scientists to create AI models.
According to the US BLS, the number of job opportunities needing data science skills is expected to rise by 27.9% by 2026. There are no automated techniques that can replace the skills of data scientists as long as we continuously learn and develop data-driven solutions. In the data science world, it's a top-notch professional ranking with the training to discover the world of big data. Many data professionals highlighted that they spend much of their time wrangling data, which is still the scenario despite a few developments in leveraging AI for data management.
Data experts understand that they face technical issues; however, they don't permit that to bog down their research for new solutions. Several other data scientists, especially from companies such as LinkedIn, Google, Walmart, and more, have added to and refined the toolkit. Over 80% of organizations globally are investing a large part of their investments into developing a skilled data analytics division, thus recruiting the most innovative talent pool in the industry.
Business Analytics vs Data Science:Key Differences Explained
Business Analytics Vs Data Science
Understanding business analytics and data science is not a daunting query for just experts. The use of the internet has drastically increased to 70%, making the practical use of data essential. The industry verticals like entertainment, healthcare, banking, and manufacturing, and more accurately monitor data to make better business decisions.
Business Analytics and Data Science involve knowledge & information gathering, and modeling. However, the difference is that Analytics is linked to business-oriented issues like profit, cost, and more, while Science answers questions based on geographic influence, customer business demands, and seasonal factors.
In other words, Data Science combines data with algorithm technology & building to answer a wide array of questions. In contrast, Business Analytics is the company data analysis with the statistical concept to obtain insights and solutions.
Business Analytics: Explained
Business Analytics is the statistical study that bridges the gap between business and information technology by leveraging structured data to offer meaningful insights. Some of the top industries where business analytics are widely used are marketing, telecommunications, finance, supply chain, and healthcare.
According to LinkedIn Talent Solutions, a business analyst serves as a facilitator, communicator, and mediator - seeking the best techniques to enhance processes and maximize effectiveness via technology, analytical solutions, strategies, and more.
Some of the marketable skills of a business analyst are as follows:
• Data visualization and storytelling
• Mathematical and statistical skills
• Interpretations
• Analytical reasoning
• Proficiency in and written and communication skills.
Data Science: Explained
Data Science is the study of data leveraging technology, statistics, and algorithm, using both structured and unstructured data. It the process of leveraging data to determine solutions and predict results for a problem statement. Some of the top sectors leveraging data science are: e-commerce, manufacturing, and finance.
Data scientists apply Machine Learning algorithms to video, numbers, audio, text, and images to retrieve various insights from them. In addition, they create ML pipelines and customized data products to understand their customers and ventures to make meaningful decisions.
Some of core skills required in data science are:
- Machine Learning
- Statistical analysis
- Data visualization and storytelling
- Computer science and programming
- Multivariable calculus and linear algebra
Business Analytics Vs Data Science
BUSINESS ANALYTICS
DATA SCIENCE
Statistical study of business data to gain meaningful insights.
Study of data using technology, statistics, and algorithms
Leverage structured data
Leverage structured and unstructured data
Coding less as it's focused more on statistics.
Coding widely used
Whole analysis based on statistical concepts.
Statistics leveraged at the end of analysis followed by coding.
Studies trends and patterns related to business.
Studies almost every trend and pattern.
Average salary: $88,550 annually (As per ONET OnLine)
Average salary: $122,840 annually (As per ONET OnLine)
Read More
Business Analytics Vs Data Science
Understanding business analytics and data science is not a daunting query for just experts. The use of the internet has drastically increased to 70%, making the practical use of data essential. The industry verticals like entertainment, healthcare, banking, and manufacturing, and more accurately monitor data to make better business decisions.
Business Analytics and Data Science involve knowledge & information gathering, and modeling. However, the difference is that Analytics is linked to business-oriented issues like profit, cost, and more, while Science answers questions based on geographic influence, customer business demands, and seasonal factors.
In other words, Data Science combines data with algorithm technology & building to answer a wide array of questions. In contrast, Business Analytics is the company data analysis with the statistical concept to obtain insights and solutions.
Business Analytics: Explained
Business Analytics is the statistical study that bridges the gap between business and information technology by leveraging structured data to offer meaningful insights. Some of the top industries where business analytics are widely used are marketing, telecommunications, finance, supply chain, and healthcare.
According to LinkedIn Talent Solutions, a business analyst serves as a facilitator, communicator, and mediator - seeking the best techniques to enhance processes and maximize effectiveness via technology, analytical solutions, strategies, and more.
Some of the marketable skills of a business analyst are as follows:
• Data visualization and storytelling
• Mathematical and statistical skills
• Interpretations
• Analytical reasoning
• Proficiency in and written and communication skills.
Data Science: Explained
Data Science is the study of data leveraging technology, statistics, and algorithm, using both structured and unstructured data. It the process of leveraging data to determine solutions and predict results for a problem statement. Some of the top sectors leveraging data science are: e-commerce, manufacturing, and finance.
Data scientists apply Machine Learning algorithms to video, numbers, audio, text, and images to retrieve various insights from them. In addition, they create ML pipelines and customized data products to understand their customers and ventures to make meaningful decisions.
Some of core skills required in data science are:
- Machine Learning
- Statistical analysis
- Data visualization and storytelling
- Computer science and programming
- Multivariable calculus and linear algebra
Business Analytics Vs Data Science
|
BUSINESS ANALYTICS |
DATA SCIENCE |
|
Statistical study of business data to gain meaningful insights. |
Study of data using technology, statistics, and algorithms |
|
Leverage structured data |
Leverage structured and unstructured data |
|
Coding less as it's focused more on statistics. |
Coding widely used |
|
Whole analysis based on statistical concepts. |
Statistics leveraged at the end of analysis followed by coding. |
|
Studies trends and patterns related to business. |
Studies almost every trend and pattern. |
|
Average salary: $88,550 annually (As per ONET OnLine) |
Average salary: $122,840 annually (As per ONET OnLine) |
A Comprehensive Guide to Advanced Machine Learning in 2022!
A Guide to Machine Learning 2022
Machine Learning has changed our lives for the past few decades – taking pictures with a blurry background and focused face to virtual assistants answering our queries; we are drastically dependent on applications that execute ML at their core.
A data scientist will scrutinize the received data and extract actionable insights. And an ML engineer will create the self-running software that uses the extracted data and automates predictive models.
These engineers are experienced in fundamental data science skills such as quantitative analysis methods, statistics, data structures & modeling, and foundational software engineering skills.
With innovation around Machine Learning, it's no surprise that any enthusiast looking to advance their career in software technology would choose Machine Learning as a base to set their job.
As Machine Learning is a central factor of data science, algorithms are trained to make predictions through statistical methods, revealing crucial information within data mining projects.
Significance of Machine Learning
The main goal of ML technology is to help organizations enhance their overall productivity, decision-making process, and process flow. In addition, as machines start learning via algorithms, it will help ventures to resolve data patterns, helping the organization make better decisions without human support.
Some of the Machine Learning benefits are:
Business Transformation
Machine Learning has been changing businesses with the potential to offer valuable insights. For example, the insurance and finance sectors use the technology to create meaningful patterns within big data, prevent fraud, and provide personalized plans to several customers.
When considering the healthcare sector, fitness and wearable sensors powered by technology allow us to take charge of their health, minimizing the pressure on healthcare experts.
ML is also leveraged in the oil and gas industry to determine new energy sources, system failure predictions, analysis of ground minerals, and more.
As technologies evolve to new heights daily, Machine Learning has been augmenting business or organizational growth. This trend highlights how ML plays a vital role in business transformation.
Instantaneous Predictions
A feature that attracts the ML enthusiast is the swift processing of insightful data from myriad sources – helping to make spontaneous predictions that can be valuable for companies.
ML algorithms provide meaningful data on customers' buying and spending patterns, allowing businesses to devise procedures to minimize loss and maximize profits.
Moreover, it helps determine the backlogs of marketing campaigns and customer acquisition policies.
Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning is classified into three fields:
Supervised Learning
Here, labeled data is used for training the data. Then, the input goes through the Machine Learning algorithm and is used to train the model.
Once done, we can feed unknown data into the trained ML model and obtain a new desired response.
Prime algorithms that are used for supervised learning are:
- Naive Bayes
- Polynomial Regression
- Decision Trees, and more.
Unsupervised Learning
In this type of ML, the training data is unlabelled and unknown. However, labeled data is necessary for the input to be guided to the ML algorithm, where unsupervised learning occurs.
This data is used in the algorithm for training the model. Finally, the trained model searches for a pattern and generates the desired outcome. This case is similar to the Enigma machine trying to break code without human intervention.
Prime algorithms that are used for unsupervised learning are:
- Principal Component Analysis
- Fuzzy Means
- Apriori
- Partial Least Squares, and more.
Reinforcement Learning
The ML algorithm identifies data through a trial-and-error process in reinforcement learning and then decides what action yields higher benefits. Three significant components of this ML type are - the agent, the environment, and the steps.
The agent is the decision-maker, the environment consists of everything the agent interacts with, and the actions are what the agent does. This type of ML occurs when the decision-maker chooses activities that increase the expected profit over a given period.
Technical Skills of Machine Learning Engineers
We have learned how ML application operates, followed by various job offers in the IT domain for software engineers and data scientists. To be a part of Machine Learning technology, you need specific technical and soft skills.
Neural Network Architecture
Neural networks, called Simulated Neural Networks (SNN), are the predefined algorithm sets used for Machine Learning task implementation.
They offer models and play a vital role in this futuristic technology. Now, ML seekers must be skilled in neural networks because it provides an understanding of how our brain works and assist in model & simulating an artificial one.
Some of the neural network areas that are essential for ML are:
- Boltzmann machine network
- Convolutional neural networks
- Deep auto-encoders
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
It is a branch of linguistics, AI & computer science that, combined with Machine Learning, Deep Learning (DL), and statistical models, enables computers to process human language in the form of spoken words and text and understand its whole meaning with the writer's intent.
Some techniques and libraries of NLP technology used in ML are:
- Word2vec
- Summarization
- Genism & NLTK
- Sentiment analysis
Applied Mathematics
Machine Learning is all about developing algorithms that can learn data to predict. Hence, mathematics is significant for solving data science projects' DL use cases. Therefore, to be an ML engineer, you must be an expert in the following math specializations.
For instance, choosing appropriate algorithms to suit the outcomes, understanding & working with parameters, deciding validation approaches, and estimating the confidence intervals.
If you are wondering about the math proficiency level one must hold to be an ML engineer, it depends on the engineer's station.
Data Modeling & Evaluation
When Machine Learning has to work with extensive data and employ them in predictive analytics, data modeling & evaluation become essential to deal with these bulks and estimate the final model's good.
Hence, the following concepts are must-learn skills for an ML engineer:
- F1 Score
- Log loss
- Mean absolute error
- Confusion matrix
- Classification accuracy
- Area under curve
- Mean squared error
Soft Skills for Machine Learning Engineers
While ML engineering is a technical job, soft skills such as problem-solving, collaboration with others, communication, time management, etc., lead to the successful completion and delivery of the project.
Team Work
Machine Learning Engineers are often at the center of AI initiatives within a firm, so they naturally work with software engineers, product managers, data scientists, marketers, and testers. The potential to work closely with others and contribute to a supportive working environment is a skill many recruiters seek in ML engineers.
Problem-solving
The potential to solve an issue is a vital skill required for both software & Machine Learning engineers and data scientists. ML focuses on solving challenges in real time, so the potential to think creatively and critically about the problem and develop solutions accordingly is a fundamental skill.
Communication
Machine Learning Engineers must possess top-notch communication skills when communicating with shareholders regarding the project objectives, timeline, and expected delivery. In addition, we know that ML engineers collaborate with data scientists, marketing & product teams, research scientists, and more; hence, communication skill is crucial.
Domain Knowledge
To create self-running software and optimize solutions leveraged by end-users and businesses, Machine Learning Engineers should have an insight into the requirements of business demands and the type of issues the software is solving.
Without domain knowledge, an ML engineer's recommendation may lack accuracy, their task may overlook compelling aspects, and it might be strenuous to evaluate a model.
Programming Skills of Machine Learning Engineers
Machine learning is about coding and feeding the machines to carry out tasks. Therefore, ML engineers must have hands-on experience in software programming and related subjects to provide the code.
ML Algorithms & Libraries
Machine Learning engineers are expected to work with myriads algorithms, packages, and libraries as part of daily tasks.
ML engineers must be skilled with the following ML algorithms and libraries:
- Knowledge in packages & APIs - TensorFlow, Spark MLlib, sci-kit-learn, and more.
- Decide and choosing of hyperparameters that impact the learning model & the result.
- Algorithm selection provides the best performance from support vector machines, Naive Bayes Classifiers, and more.
Unix
Machine Learning Engineers require most servers and clusters to operate are Linux (Unix) variants. Though they can be performed on Mac & Windows, more than half of the time, they are required to run on Unix systems only. Therefore, having good knowledge of Linux & Unix is vital to being an ML engineer.
Computer Science Fundamentals & Programming
Engineers must apply the concepts of computer science and programming accurately as per the situation. The following ideas play a significant role in ML and are a must on the skillset list:
- Algorithms: search, sort, optimize, dynamic programming
- Computer architecture: memory, bandwidth, cache, distributed processing, and more.
- Data structures: queues, trees, stacks, graphs, and multi-dimensional arrays
- Complexity & computability: big-O notation, P vs. NP, approximate algorithm, and more.
System Design and Software Engineering
Machine Learning Engineers must have strong knowledge of the following areas of software programming & system design, as all they do is code:
- Top-notch measures to circumvent bottlenecks & develop user-friendly outcomes.
- Algorithm scaling with data size.
- Interacting with different working components and modules using library calls, REST APIs, and database queries.
- Fundamental software design methodologies and codings like testing, requirement analysis, and version management.
Read More
A Guide to Machine Learning 2022
Machine Learning has changed our lives for the past few decades – taking pictures with a blurry background and focused face to virtual assistants answering our queries; we are drastically dependent on applications that execute ML at their core.
A data scientist will scrutinize the received data and extract actionable insights. And an ML engineer will create the self-running software that uses the extracted data and automates predictive models.
These engineers are experienced in fundamental data science skills such as quantitative analysis methods, statistics, data structures & modeling, and foundational software engineering skills.
With innovation around Machine Learning, it's no surprise that any enthusiast looking to advance their career in software technology would choose Machine Learning as a base to set their job.
As Machine Learning is a central factor of data science, algorithms are trained to make predictions through statistical methods, revealing crucial information within data mining projects.
Significance of Machine Learning
The main goal of ML technology is to help organizations enhance their overall productivity, decision-making process, and process flow. In addition, as machines start learning via algorithms, it will help ventures to resolve data patterns, helping the organization make better decisions without human support.
Some of the Machine Learning benefits are:
Business Transformation
Machine Learning has been changing businesses with the potential to offer valuable insights. For example, the insurance and finance sectors use the technology to create meaningful patterns within big data, prevent fraud, and provide personalized plans to several customers.
When considering the healthcare sector, fitness and wearable sensors powered by technology allow us to take charge of their health, minimizing the pressure on healthcare experts.
ML is also leveraged in the oil and gas industry to determine new energy sources, system failure predictions, analysis of ground minerals, and more.
As technologies evolve to new heights daily, Machine Learning has been augmenting business or organizational growth. This trend highlights how ML plays a vital role in business transformation.
Instantaneous Predictions
A feature that attracts the ML enthusiast is the swift processing of insightful data from myriad sources – helping to make spontaneous predictions that can be valuable for companies.
ML algorithms provide meaningful data on customers' buying and spending patterns, allowing businesses to devise procedures to minimize loss and maximize profits.
Moreover, it helps determine the backlogs of marketing campaigns and customer acquisition policies.
Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning is classified into three fields:
Supervised Learning
Here, labeled data is used for training the data. Then, the input goes through the Machine Learning algorithm and is used to train the model.
Once done, we can feed unknown data into the trained ML model and obtain a new desired response.
Prime algorithms that are used for supervised learning are:
- Naive Bayes
- Polynomial Regression
- Decision Trees, and more.
Unsupervised Learning
In this type of ML, the training data is unlabelled and unknown. However, labeled data is necessary for the input to be guided to the ML algorithm, where unsupervised learning occurs.
This data is used in the algorithm for training the model. Finally, the trained model searches for a pattern and generates the desired outcome. This case is similar to the Enigma machine trying to break code without human intervention.
Prime algorithms that are used for unsupervised learning are:
- Principal Component Analysis
- Fuzzy Means
- Apriori
- Partial Least Squares, and more.
Reinforcement Learning
The ML algorithm identifies data through a trial-and-error process in reinforcement learning and then decides what action yields higher benefits. Three significant components of this ML type are - the agent, the environment, and the steps.
The agent is the decision-maker, the environment consists of everything the agent interacts with, and the actions are what the agent does. This type of ML occurs when the decision-maker chooses activities that increase the expected profit over a given period.
Technical Skills of Machine Learning Engineers
We have learned how ML application operates, followed by various job offers in the IT domain for software engineers and data scientists. To be a part of Machine Learning technology, you need specific technical and soft skills.
Neural Network Architecture
Neural networks, called Simulated Neural Networks (SNN), are the predefined algorithm sets used for Machine Learning task implementation.
They offer models and play a vital role in this futuristic technology. Now, ML seekers must be skilled in neural networks because it provides an understanding of how our brain works and assist in model & simulating an artificial one.
Some of the neural network areas that are essential for ML are:
- Boltzmann machine network
- Convolutional neural networks
- Deep auto-encoders
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
It is a branch of linguistics, AI & computer science that, combined with Machine Learning, Deep Learning (DL), and statistical models, enables computers to process human language in the form of spoken words and text and understand its whole meaning with the writer's intent.
Some techniques and libraries of NLP technology used in ML are:
- Word2vec
- Summarization
- Genism & NLTK
- Sentiment analysis
Applied Mathematics
Machine Learning is all about developing algorithms that can learn data to predict. Hence, mathematics is significant for solving data science projects' DL use cases. Therefore, to be an ML engineer, you must be an expert in the following math specializations.
For instance, choosing appropriate algorithms to suit the outcomes, understanding & working with parameters, deciding validation approaches, and estimating the confidence intervals.
If you are wondering about the math proficiency level one must hold to be an ML engineer, it depends on the engineer's station.
Data Modeling & Evaluation
When Machine Learning has to work with extensive data and employ them in predictive analytics, data modeling & evaluation become essential to deal with these bulks and estimate the final model's good.
Hence, the following concepts are must-learn skills for an ML engineer:
- F1 Score
- Log loss
- Mean absolute error
- Confusion matrix
- Classification accuracy
- Area under curve
- Mean squared error
Soft Skills for Machine Learning Engineers
While ML engineering is a technical job, soft skills such as problem-solving, collaboration with others, communication, time management, etc., lead to the successful completion and delivery of the project.
Team Work
Machine Learning Engineers are often at the center of AI initiatives within a firm, so they naturally work with software engineers, product managers, data scientists, marketers, and testers. The potential to work closely with others and contribute to a supportive working environment is a skill many recruiters seek in ML engineers.
Problem-solving
The potential to solve an issue is a vital skill required for both software & Machine Learning engineers and data scientists. ML focuses on solving challenges in real time, so the potential to think creatively and critically about the problem and develop solutions accordingly is a fundamental skill.
Communication
Machine Learning Engineers must possess top-notch communication skills when communicating with shareholders regarding the project objectives, timeline, and expected delivery. In addition, we know that ML engineers collaborate with data scientists, marketing & product teams, research scientists, and more; hence, communication skill is crucial.
Domain Knowledge
To create self-running software and optimize solutions leveraged by end-users and businesses, Machine Learning Engineers should have an insight into the requirements of business demands and the type of issues the software is solving.
Without domain knowledge, an ML engineer's recommendation may lack accuracy, their task may overlook compelling aspects, and it might be strenuous to evaluate a model.
Programming Skills of Machine Learning Engineers
Machine learning is about coding and feeding the machines to carry out tasks. Therefore, ML engineers must have hands-on experience in software programming and related subjects to provide the code.
ML Algorithms & Libraries
Machine Learning engineers are expected to work with myriads algorithms, packages, and libraries as part of daily tasks.
ML engineers must be skilled with the following ML algorithms and libraries:
- Knowledge in packages & APIs - TensorFlow, Spark MLlib, sci-kit-learn, and more.
- Decide and choosing of hyperparameters that impact the learning model & the result.
- Algorithm selection provides the best performance from support vector machines, Naive Bayes Classifiers, and more.
Unix
Machine Learning Engineers require most servers and clusters to operate are Linux (Unix) variants. Though they can be performed on Mac & Windows, more than half of the time, they are required to run on Unix systems only. Therefore, having good knowledge of Linux & Unix is vital to being an ML engineer.
Computer Science Fundamentals & Programming
Engineers must apply the concepts of computer science and programming accurately as per the situation. The following ideas play a significant role in ML and are a must on the skillset list:
- Algorithms: search, sort, optimize, dynamic programming
- Computer architecture: memory, bandwidth, cache, distributed processing, and more.
- Data structures: queues, trees, stacks, graphs, and multi-dimensional arrays
- Complexity & computability: big-O notation, P vs. NP, approximate algorithm, and more.
System Design and Software Engineering
Machine Learning Engineers must have strong knowledge of the following areas of software programming & system design, as all they do is code:
- Top-notch measures to circumvent bottlenecks & develop user-friendly outcomes.
- Algorithm scaling with data size.
- Interacting with different working components and modules using library calls, REST APIs, and database queries.
- Fundamental software design methodologies and codings like testing, requirement analysis, and version management.
Mastering Scrum Management:Essential Principles & Strategies
Scrum Project Management
These days, project management has become a crucial area of business. How you deal with it can determine the success of your upcoming projects. Scrum is a highly-popular method focused on stakeholder, team, and product management.
Scrum is a lean and flexible approach to project management that takes the best practices from other project management frameworks and distills them into core principles to help teams deliver high-quality software and avoid risks.
What is Scrum?
Scrum is a framework for project management, not a process for working on projects. Scrum's work has been refined over time, and there are many different ways to implement it, but all versions of it share some core ideas.
- The product owner owns the product backlog (the list of items needed) and sets priorities throughout the project.
- The development team creates a backlog item daily based on what they have accomplished during the previous day. They then use those items to create new work items if necessary.
- The team manages its work by assigning tasks to individual team members who report on their progress at daily stand-up meetings. The daily stand-ups also include a check-in with each member's progress against their assigned tasks or tasks from other team members.
- After each sprint, each team member goes through an evaluation meeting to discuss how well they did on their current sprint goal(s). This includes a retrospective, where they reflect on their actions and identify valuable lessons learned.
How is Scrum Different from Traditional Project Management?
Scrum is a framework for product development and management. It was designed to help organizations move from a series of projects to a continuous flow of products.
Traditional project management is a process that focuses on planning, scheduling, cost estimation, and risk management. Traditional project management has its roots in the aerospace industry, where the development cycle was very long, expensive, and time-consuming. Scrum leverages many of these same principles but adds more flexibility to adapt to changing requirements.
The Scrum framework helps teams manage their work through an iterative process of creating a product increment (typically called a sprint), testing it with users or customers, releasing it as code into test environments (typically called "user stories"), and then delivering it back to production as another increment (which can be delivered as another sprint).
Advantage
Scrum is one of the most practical ways to introduce agile practices into your organization. It implements many of the principles of Agile Software Development and can be implemented quickly with little training (although it does require some training).
These are the advantages of using Scrum:
- It helps you focus on delivering value instead of managing processes and documentation.
- It provides transparency across all teams.
- It helps you create a culture where people feel empowered.
- It encourages collaboration between all members of your team.
- It allows you to have more control over your project timeline.
- It allows you to improve the design quality of your software products by creating more stable requirements upfront (before coding).
- You can use the same methodology for large and smaller projects.
Disadvantage
There are some disadvantages of Scrum:
- There are no set time limits for the sprints. So if you need to deliver a vital feature quickly but only have a little time left in your last sprint, you can always extend it by adding more stories.
- You can't predict precisely how long it will take to complete a task; you'll have to find out as you go along (and hope your estimates are correct).
- The process of estimating task duration is entirely subjective and ambiguous because there's no clear definition of what "done" means in each case — one person may think they've finished. In contrast, another person thinks they're still working on it!
Steps of the Scrum Process
The following steps are used in the scrum process:
- First, define: the product owner, project manager, and developers define the project's scope and requirements. Next, the team works together to uncover what features need to be built, what tasks are required for those features, and how long lessons take.
- Gather: the team gathers requirements from stakeholders and gets an agreement on what needs to be built.
- Create: the team creates a plan for completing each task, breaking down work into subtasks and estimating how long each subtask will take.
- Plan: the team updates their goals as they complete tasks, adding new features as needed or making changes based on feedback from customers or other stakeholders.
- Do: each person completes their assigned task(s) until it's done right!
Scrum Tools
Jira is one of the most well-known agile management tools. Enterprises use it and software development firms and small and large businesses.
Trello is a task management tool popular with teams of all sizes, including software development teams and marketing efforts. It is easy to use but offers customizable options that allow you to organize processes differently.
Scrums is an easy-to-use, intelligent tool that helps you manage your Scrum projects. It allows you to organize tasks into checklists and monitor the percentage completion so that you always know where your project is.
Active Collab is an all-in-one agile project management application. In addition to standard Scrum tools, it comes with several extra features, such as adding and assigning tasks, creating a mobile app or software, managing a tech company, or simply beginning an internet business.
Zoho Sprints is a cloud-based project management tool designed for agile teams. It's easy to use and was created with agile methods in mind. Zoho Sprints helps you plan and track your projects, create dashboards and backlogs, assign tasks, schedule meetings, communicate with your team members, and more.
Conclusion
In the end, a project requires much more than just a website. It requires careful planning and the resources to carry out that plan. Scrum is thus an excellent framework for managing a complex project, as it helps teams manage their time and tasks effectively. In addition, Scrum provides a structure for ideation, implementation, and experimentation that wouldn't otherwise exist. And with clear goals in mind, teams can deliver more innovative websites and apps for clients in less time. It's a win-win situation for all involved.
Read More
Scrum Project Management
These days, project management has become a crucial area of business. How you deal with it can determine the success of your upcoming projects. Scrum is a highly-popular method focused on stakeholder, team, and product management.
Scrum is a lean and flexible approach to project management that takes the best practices from other project management frameworks and distills them into core principles to help teams deliver high-quality software and avoid risks.
What is Scrum?
Scrum is a framework for project management, not a process for working on projects. Scrum's work has been refined over time, and there are many different ways to implement it, but all versions of it share some core ideas.
- The product owner owns the product backlog (the list of items needed) and sets priorities throughout the project.
- The development team creates a backlog item daily based on what they have accomplished during the previous day. They then use those items to create new work items if necessary.
- The team manages its work by assigning tasks to individual team members who report on their progress at daily stand-up meetings. The daily stand-ups also include a check-in with each member's progress against their assigned tasks or tasks from other team members.
- After each sprint, each team member goes through an evaluation meeting to discuss how well they did on their current sprint goal(s). This includes a retrospective, where they reflect on their actions and identify valuable lessons learned.
How is Scrum Different from Traditional Project Management?
Scrum is a framework for product development and management. It was designed to help organizations move from a series of projects to a continuous flow of products.
Traditional project management is a process that focuses on planning, scheduling, cost estimation, and risk management. Traditional project management has its roots in the aerospace industry, where the development cycle was very long, expensive, and time-consuming. Scrum leverages many of these same principles but adds more flexibility to adapt to changing requirements.
The Scrum framework helps teams manage their work through an iterative process of creating a product increment (typically called a sprint), testing it with users or customers, releasing it as code into test environments (typically called "user stories"), and then delivering it back to production as another increment (which can be delivered as another sprint).
Advantage
Scrum is one of the most practical ways to introduce agile practices into your organization. It implements many of the principles of Agile Software Development and can be implemented quickly with little training (although it does require some training).
These are the advantages of using Scrum:
- It helps you focus on delivering value instead of managing processes and documentation.
- It provides transparency across all teams.
- It helps you create a culture where people feel empowered.
- It encourages collaboration between all members of your team.
- It allows you to have more control over your project timeline.
- It allows you to improve the design quality of your software products by creating more stable requirements upfront (before coding).
- You can use the same methodology for large and smaller projects.
Disadvantage
There are some disadvantages of Scrum:
- There are no set time limits for the sprints. So if you need to deliver a vital feature quickly but only have a little time left in your last sprint, you can always extend it by adding more stories.
- You can't predict precisely how long it will take to complete a task; you'll have to find out as you go along (and hope your estimates are correct).
- The process of estimating task duration is entirely subjective and ambiguous because there's no clear definition of what "done" means in each case — one person may think they've finished. In contrast, another person thinks they're still working on it!
Steps of the Scrum Process
The following steps are used in the scrum process:
- First, define: the product owner, project manager, and developers define the project's scope and requirements. Next, the team works together to uncover what features need to be built, what tasks are required for those features, and how long lessons take.
- Gather: the team gathers requirements from stakeholders and gets an agreement on what needs to be built.
- Create: the team creates a plan for completing each task, breaking down work into subtasks and estimating how long each subtask will take.
- Plan: the team updates their goals as they complete tasks, adding new features as needed or making changes based on feedback from customers or other stakeholders.
- Do: each person completes their assigned task(s) until it's done right!
Scrum Tools
Jira is one of the most well-known agile management tools. Enterprises use it and software development firms and small and large businesses.
Trello is a task management tool popular with teams of all sizes, including software development teams and marketing efforts. It is easy to use but offers customizable options that allow you to organize processes differently.
Scrums is an easy-to-use, intelligent tool that helps you manage your Scrum projects. It allows you to organize tasks into checklists and monitor the percentage completion so that you always know where your project is.
Active Collab is an all-in-one agile project management application. In addition to standard Scrum tools, it comes with several extra features, such as adding and assigning tasks, creating a mobile app or software, managing a tech company, or simply beginning an internet business.
Zoho Sprints is a cloud-based project management tool designed for agile teams. It's easy to use and was created with agile methods in mind. Zoho Sprints helps you plan and track your projects, create dashboards and backlogs, assign tasks, schedule meetings, communicate with your team members, and more.
Conclusion
In the end, a project requires much more than just a website. It requires careful planning and the resources to carry out that plan. Scrum is thus an excellent framework for managing a complex project, as it helps teams manage their time and tasks effectively. In addition, Scrum provides a structure for ideation, implementation, and experimentation that wouldn't otherwise exist. And with clear goals in mind, teams can deliver more innovative websites and apps for clients in less time. It's a win-win situation for all involved.
Top PMI Certifications for Project Management Professionals
Top PMI Project Management Certifications
The need for project managers in every sector is rising. In the coming years, global companies will need over 88Mn individuals to work in project management positions.
We see that recruiting companies look for individuals with project management certifications. However, which certificate to opt for depends on the type of project manager you desire to be.
From associate project management to professional accreditation, the Project Management Institute provides various certifications for project professionals and those who want to pursue a career.
Ensure that acquiring a certification is never a piece of cake. To pass the stringent credential test with flying colors, you must put much effort into attaining the same, including specialized formal training and several hours of experience.
Let's see PMI's top project management certification
PMI Certification and Top 6 Accreditations: Explained
Starting from entry-level to professional ground, PMI provides a variety of project management certifications that helps you in improving your career in the project management domain.
A PMI accreditation is handy as the human resource market demands project management skills.
The most prestigious PMI certification is the Project Management Professional (PMP) credential. However, other accreditations are suited for professionals in various career stages.
1. Project Management Professional (PMP)
It's a globally renowned and prestigious certificate that exposes you to benefits such as increased credibility, handsome remuneration, and high market value.
Acquiring PMP certification is difficult, as you will have to meet the eligibility prerequisites by PMI. However, there are other reasons PMP is known to be project managers' most challenging credential test. Instead, its examination pattern and validation are stringent.
The PMP examination tests your knowledge of People, Processes, and Business Environment.
According to the 2019 Exam Content Outline (ECO), the PMP examination has undergone a couple of changes and came into effect in 2021:
- Knowledge domain areas have been reduced from five to three.
- No. of questions will be 180 instead of 200.
- The duration of the PMP exam is 230 minutes (approx. 4 hours), which contains a combination type of questions.
The PMP credential is excellent for individuals who have experience managing projects and are keen on up-skilling their careers.
2. Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)
CAPM is an entry-level certification offered by PMI to individuals hoping to manage projects, take on advanced roles, or add project management skills to their resumes.
The CAPM credential is a stepping stone to PMP certification that helps you gain knowledge on project management terminologies and concepts. Moreover, individuals with a CAPM tag can rule out PMP eligibility prerequisites.
3. PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP)
PMI-ACP is an industry-recognized accreditation that proves your net worth as an Agile practitioner. It strengthens you with confidence in a framework obtaining traction and adoption by leading companies.
This certification is mainly pursued by project-managing individuals following Agile practices and trains them about the tool, techniques, and concepts employed in project management.
Who qualifies for the PMI-ACP credential?
- General Project Experience - 2,000 hours worked on project teams within the last five years or active PMP/PgMP certification.
- Agile Project Experience - 1,500 hours working on agile project teams or with agile methodologies in the last three years. This is in addition to 2,000 hours earned in General Project Experience.
- Agile Practice Training - 21 contact hours must be earned
4. Disciplined Agile
Disciplined Agile is a toolkit that targets the decisions you need to make, available options, and the trade-offs associated with the available options. It shows how you can effectively collaborate practices from Kanban, Scrum, SAFe, and other methodologies in a scalable manner.
PMI provides four certifications in this field - Disciplined Agile Coach (DAC), Disciplined Agile ScrumMaster (DASM), Disciplined Agile Value Stream Consultant (DAVSC), and Disciplined Agile Senior ScrumMaster (DASSM).
The certifications allow freshers to learn the fundamentals of the methodology and experienced Agile users to advance their skills.
Who qualifies for the Disciplined Agile credentials?
- Must have three years of experience working in an Agile leadership position.
- Each certification also requires training program completion from a qualifying Disciplined Agile training center.
5. Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA)
Business Analysis (BA) has become a competitive field of project management. However, becoming one can shift your career in a new direction while BA opportunities are rising.
The PMI-PBA certification tests you in assessment, planning, evaluation, monitoring, and other requirements related to BA aspects of project management.
Suppose you work with a project team and manage product development, or you are a project/program manager who performs BA. In that case, PMI-PBA certification is for these individuals.
Who qualifies for the PMI-PBA credential?
- Secondary degree (high school diploma, associate's degree)
- BA experience: 60 months
- BA educational training: 35 contact hours
OR
- Bachelor's degree or the global equivalent
- BA experience: 36 months
- BA educational training: 35 contact hours
6. Program Management Professional (PgMP)
The PgMP certification will help you develop a robust leadership approach to manage multiple projects and improve your efficiency in navigating complex activities.
You will learn to use the tools and techniques efficiently and understand business strategy and program processes.
The PgMP credential will take you through the PMI's five management performance domains and use a scalable framework to manage varying-sized programs.
PgMP accreditation is designed for the senior-level practitioner who manages multiple related projects in a coordinated way.
Who qualifies for the PgMP credential?
- Secondary degree (high school diploma, associate's degree, or the global equivalent)
- Project management experience: 6,000 hours
- Program management experience: 10,500 hours
OR
- Four-year degree
- Project management experience: 6,000 hours
- Program management experience: 6,000 hours
Read More
Top PMI Project Management Certifications
The need for project managers in every sector is rising. In the coming years, global companies will need over 88Mn individuals to work in project management positions.
We see that recruiting companies look for individuals with project management certifications. However, which certificate to opt for depends on the type of project manager you desire to be.
From associate project management to professional accreditation, the Project Management Institute provides various certifications for project professionals and those who want to pursue a career.
Ensure that acquiring a certification is never a piece of cake. To pass the stringent credential test with flying colors, you must put much effort into attaining the same, including specialized formal training and several hours of experience.
Let's see PMI's top project management certification
PMI Certification and Top 6 Accreditations: Explained
Starting from entry-level to professional ground, PMI provides a variety of project management certifications that helps you in improving your career in the project management domain.
A PMI accreditation is handy as the human resource market demands project management skills.
The most prestigious PMI certification is the Project Management Professional (PMP) credential. However, other accreditations are suited for professionals in various career stages.
1. Project Management Professional (PMP)
It's a globally renowned and prestigious certificate that exposes you to benefits such as increased credibility, handsome remuneration, and high market value.
Acquiring PMP certification is difficult, as you will have to meet the eligibility prerequisites by PMI. However, there are other reasons PMP is known to be project managers' most challenging credential test. Instead, its examination pattern and validation are stringent.
The PMP examination tests your knowledge of People, Processes, and Business Environment.
According to the 2019 Exam Content Outline (ECO), the PMP examination has undergone a couple of changes and came into effect in 2021:
- Knowledge domain areas have been reduced from five to three.
- No. of questions will be 180 instead of 200.
- The duration of the PMP exam is 230 minutes (approx. 4 hours), which contains a combination type of questions.
The PMP credential is excellent for individuals who have experience managing projects and are keen on up-skilling their careers.
2. Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)
CAPM is an entry-level certification offered by PMI to individuals hoping to manage projects, take on advanced roles, or add project management skills to their resumes.
The CAPM credential is a stepping stone to PMP certification that helps you gain knowledge on project management terminologies and concepts. Moreover, individuals with a CAPM tag can rule out PMP eligibility prerequisites.
3. PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP)
PMI-ACP is an industry-recognized accreditation that proves your net worth as an Agile practitioner. It strengthens you with confidence in a framework obtaining traction and adoption by leading companies.
This certification is mainly pursued by project-managing individuals following Agile practices and trains them about the tool, techniques, and concepts employed in project management.
Who qualifies for the PMI-ACP credential?
- General Project Experience - 2,000 hours worked on project teams within the last five years or active PMP/PgMP certification.
- Agile Project Experience - 1,500 hours working on agile project teams or with agile methodologies in the last three years. This is in addition to 2,000 hours earned in General Project Experience.
- Agile Practice Training - 21 contact hours must be earned
4. Disciplined Agile
Disciplined Agile is a toolkit that targets the decisions you need to make, available options, and the trade-offs associated with the available options. It shows how you can effectively collaborate practices from Kanban, Scrum, SAFe, and other methodologies in a scalable manner.
PMI provides four certifications in this field - Disciplined Agile Coach (DAC), Disciplined Agile ScrumMaster (DASM), Disciplined Agile Value Stream Consultant (DAVSC), and Disciplined Agile Senior ScrumMaster (DASSM).
The certifications allow freshers to learn the fundamentals of the methodology and experienced Agile users to advance their skills.
Who qualifies for the Disciplined Agile credentials?
- Must have three years of experience working in an Agile leadership position.
- Each certification also requires training program completion from a qualifying Disciplined Agile training center.
5. Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA)
Business Analysis (BA) has become a competitive field of project management. However, becoming one can shift your career in a new direction while BA opportunities are rising.
The PMI-PBA certification tests you in assessment, planning, evaluation, monitoring, and other requirements related to BA aspects of project management.
Suppose you work with a project team and manage product development, or you are a project/program manager who performs BA. In that case, PMI-PBA certification is for these individuals.
Who qualifies for the PMI-PBA credential?
- Secondary degree (high school diploma, associate's degree)
- BA experience: 60 months
- BA educational training: 35 contact hours
OR
- Bachelor's degree or the global equivalent
- BA experience: 36 months
- BA educational training: 35 contact hours
6. Program Management Professional (PgMP)
The PgMP certification will help you develop a robust leadership approach to manage multiple projects and improve your efficiency in navigating complex activities.
You will learn to use the tools and techniques efficiently and understand business strategy and program processes.
The PgMP credential will take you through the PMI's five management performance domains and use a scalable framework to manage varying-sized programs.
PgMP accreditation is designed for the senior-level practitioner who manages multiple related projects in a coordinated way.
Who qualifies for the PgMP credential?
- Secondary degree (high school diploma, associate's degree, or the global equivalent)
- Project management experience: 6,000 hours
- Program management experience: 10,500 hours
OR
- Four-year degree
- Project management experience: 6,000 hours
- Program management experience: 6,000 hours
Product Manager vs. Product Owner:Key Differences Explained
Product Manager Vs. Product Owner
There needs to be more clarity on the difference between a product owner and a product manager. Most companies start with a product owner who takes care of all the technical details and works closely with the developers to build features. However, there is more to the job of a product owner than that just coding new features. So let's figure out the difference and if it's necessary for your company.
The Product Owner and the Product Manager are two roles that may seem familiar. Still, they could be pretty different from each other. The differences between these two roles consider their purpose, how much authority they have over tasks and specific projects, and how much time they spend on development work.
Difference between Product Manager and Product Owner
A product manager is responsible for delivering a product to the market. The product manager knows what the development needs and needs to look like. The product manager then writes the requirements document, which details the product's features, benefits, and other requirements.
The product owner is responsible for defining the project's vision and goals. They are also responsible for communicating with the user community during design sessions, validating ideas, and ensuring that all stakeholders understand what will be delivered and why.
Product Manager
The Product Manager is a person who has the responsibility of managing the product development and marketing process of a company. The Product Manager should be able to identify and understand customer needs, develop new products, and manage the delivery of those products on time.
For example, suppose your product requires an update. In that case, you can predict how many people would benefit from it and then estimate how much time it will take to develop such an update.
This work involves gathering information about your customers, competitors, and other markets where your product might be sold. You also need to know what kind of service you want customers to get when they use your product.
Duties of Product Manager
The Product Manager is also accountable for the following:
- Ensure the product meets customer needs, solves problems, and satisfies customers.
- Identify new opportunities to create value for customers with new features or products.
- Providing regular updates on progress toward delivering value through features, functionality, and product performance.
- The product manager is also responsible for ensuring that all necessary tasks are completed before launch.
- The Product Manager also communicates with customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders to achieve product goals and manage the product portfolio.
Skills Required for Product Manager
- One of the essential skills required by a product manager is business acumen. A good product manager needs to understand every aspect of their business and how it relates to their products.
- They must also be able to identify problems before they become significant issues and decide if they can be fixed cost-effectively or if it would be better to delay the launch until another time.
- Another essential skill required for this role is leadership ability. This does not just mean being able to lead employees in the workplace; it also means getting things done within your team and helping others achieve their goals within your organization.
- Product managers are expected to have strong analytical skills, including identifying problems and opportunities for new products or services.
Product Owner
The product owner is responsible for the overall success of the product. They are a member of the product team and leads by example. The role of the product owner is to ensure that everyone on their team knows the goals for each sprint, what features should be built to meet those goals, and why those features are essential.
The product owner is not a "product manager," a "designer," an "engineer," or any other title that you see bandied about in business today. Instead, they are simply someone who owns what they build — and makes sure that others know it too.
Duties of Product Owner
- The Product Owner is accountable for the product vision, business strategy, and overall product success.
- The Product Owner has ultimate authority over the project and its management.
- The Product Owner is accountable for all decisions regarding executing the product vision and strategy.
- Establish a product-market fit strategy.
- Collaborate with stakeholders to build products.
- Manage the product backlog throughout the development.
Skills Required For Product Owner
- The Product Owner is responsible for understanding what customers want, building it, and making it valuable.
- The Product Owner needs to identify the customer problem and explain it through the product vision. Then, the product owner needs to be able to create an image for products that customers will love.
- The product owner must be able to articulate what makes a good product, why they chose the one they did, and why they believe it's better than another option.
- Product owners need to be able to listen carefully to truly understand their customers' needs. They should also be able to learn about any obstacles or problems that might hinder their product from being successful.
- Outstanding communication skills, able to influence and lead teams.
- Ability to work under pressure and manage multiple priorities at once.
Tips for product managers and product owners to work together better
The product manager and product owner are two critical roles in agile software development. They have different responsibilities but must work together to create a successful product. Here are five tips for creating synergy between the product manager and product owner:
Understand how each role works. For example, the PM is responsible for defining the vision and strategy of the product. In contrast, the PO brings a collaborative approach to developing features in small batches.
Agree on goals for each release before beginning work on a project. This gives everyone a clear view of what's expected from them over the next few weeks or months, making it much more likely that everyone will work towards a common goal.
Ensure that there is regular communication between team members about the progress being made on individual tasks. Make sure that if anyone has any concerns about what's being done or needs more information, they feel comfortable speaking up to address these issues as quickly as possible before they become problems.
Hold regular retrospectives at the end of each sprint to identify areas where your process could be improved and discuss how you can use this information to do things better next time.
Conclusion
One of the most significant differences between a Product Owner and a Product Manager is how they fit into an organization's structure. This can be difficult to manage because both roles are visible and often require them to work with several departments within their organization. In addition, the Product Owner or Product Manager must have strong communication skills to effectively liaise between the "development department" and other stakeholders in the business like sales, marketing, and HR. This ensures everyone is on the same page and has regular communication as updates are made for a product.
Read More
Product Manager Vs. Product Owner
There needs to be more clarity on the difference between a product owner and a product manager. Most companies start with a product owner who takes care of all the technical details and works closely with the developers to build features. However, there is more to the job of a product owner than that just coding new features. So let's figure out the difference and if it's necessary for your company.
The Product Owner and the Product Manager are two roles that may seem familiar. Still, they could be pretty different from each other. The differences between these two roles consider their purpose, how much authority they have over tasks and specific projects, and how much time they spend on development work.
Difference between Product Manager and Product Owner
A product manager is responsible for delivering a product to the market. The product manager knows what the development needs and needs to look like. The product manager then writes the requirements document, which details the product's features, benefits, and other requirements.
The product owner is responsible for defining the project's vision and goals. They are also responsible for communicating with the user community during design sessions, validating ideas, and ensuring that all stakeholders understand what will be delivered and why.
Product Manager
The Product Manager is a person who has the responsibility of managing the product development and marketing process of a company. The Product Manager should be able to identify and understand customer needs, develop new products, and manage the delivery of those products on time.
For example, suppose your product requires an update. In that case, you can predict how many people would benefit from it and then estimate how much time it will take to develop such an update.
This work involves gathering information about your customers, competitors, and other markets where your product might be sold. You also need to know what kind of service you want customers to get when they use your product.
Duties of Product Manager
The Product Manager is also accountable for the following:
- Ensure the product meets customer needs, solves problems, and satisfies customers.
- Identify new opportunities to create value for customers with new features or products.
- Providing regular updates on progress toward delivering value through features, functionality, and product performance.
- The product manager is also responsible for ensuring that all necessary tasks are completed before launch.
- The Product Manager also communicates with customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders to achieve product goals and manage the product portfolio.
Skills Required for Product Manager
- One of the essential skills required by a product manager is business acumen. A good product manager needs to understand every aspect of their business and how it relates to their products.
- They must also be able to identify problems before they become significant issues and decide if they can be fixed cost-effectively or if it would be better to delay the launch until another time.
- Another essential skill required for this role is leadership ability. This does not just mean being able to lead employees in the workplace; it also means getting things done within your team and helping others achieve their goals within your organization.
- Product managers are expected to have strong analytical skills, including identifying problems and opportunities for new products or services.
Product Owner
The product owner is responsible for the overall success of the product. They are a member of the product team and leads by example. The role of the product owner is to ensure that everyone on their team knows the goals for each sprint, what features should be built to meet those goals, and why those features are essential.
The product owner is not a "product manager," a "designer," an "engineer," or any other title that you see bandied about in business today. Instead, they are simply someone who owns what they build — and makes sure that others know it too.
Duties of Product Owner
- The Product Owner is accountable for the product vision, business strategy, and overall product success.
- The Product Owner has ultimate authority over the project and its management.
- The Product Owner is accountable for all decisions regarding executing the product vision and strategy.
- Establish a product-market fit strategy.
- Collaborate with stakeholders to build products.
- Manage the product backlog throughout the development.
Skills Required For Product Owner
- The Product Owner is responsible for understanding what customers want, building it, and making it valuable.
- The Product Owner needs to identify the customer problem and explain it through the product vision. Then, the product owner needs to be able to create an image for products that customers will love.
- The product owner must be able to articulate what makes a good product, why they chose the one they did, and why they believe it's better than another option.
- Product owners need to be able to listen carefully to truly understand their customers' needs. They should also be able to learn about any obstacles or problems that might hinder their product from being successful.
- Outstanding communication skills, able to influence and lead teams.
- Ability to work under pressure and manage multiple priorities at once.
Tips for product managers and product owners to work together better
The product manager and product owner are two critical roles in agile software development. They have different responsibilities but must work together to create a successful product. Here are five tips for creating synergy between the product manager and product owner:
Understand how each role works. For example, the PM is responsible for defining the vision and strategy of the product. In contrast, the PO brings a collaborative approach to developing features in small batches.
Agree on goals for each release before beginning work on a project. This gives everyone a clear view of what's expected from them over the next few weeks or months, making it much more likely that everyone will work towards a common goal.
Ensure that there is regular communication between team members about the progress being made on individual tasks. Make sure that if anyone has any concerns about what's being done or needs more information, they feel comfortable speaking up to address these issues as quickly as possible before they become problems.
Hold regular retrospectives at the end of each sprint to identify areas where your process could be improved and discuss how you can use this information to do things better next time.
Conclusion
One of the most significant differences between a Product Owner and a Product Manager is how they fit into an organization's structure. This can be difficult to manage because both roles are visible and often require them to work with several departments within their organization. In addition, the Product Owner or Product Manager must have strong communication skills to effectively liaise between the "development department" and other stakeholders in the business like sales, marketing, and HR. This ensures everyone is on the same page and has regular communication as updates are made for a product.
AI: A Promising Career Path with Growing Opportunities.
AI: A Future Career Option
Artificial intelligence is one of the crucial technologies behind the ever-growing tech revolution. It affects industry and society in numerous ways, and that effect will expand far into the future.
With the AI domain increasing, significant issues arise, i.e., too many jobs and not enough qualified candidates. However, this pinpoints an opportunity for professionals with the knowledge and skills to enter AI.
Why is AI a Future Career Goal?
AI is drastically expanding vertically, which provides several career opportunities. For example, the Bureau of Labour Statistics projects that computer science researchers will experience a growth of over 15 percent between 2022 and 2029, much more rapid than the national average for career growth. So, consider the initial step towards a phenomenal career in artificial intelligence.
Suppose you're looking to flourish your career or make your profile more competitive in the job market. In that case, AI is a perfect place to donate your energy and time. Moreover, as the domain grows, it will have a far-reaching impact on various sectors, opening new opportunities for those with the proper skill set.
Artificial Intelligence needs drastic training and commitment; however, the rewards of an AI career far outweigh the investment. And for those already employed and who would like a career change, supplemental programs can help make a smoother transition to the AI domain.
AI and Computer Science are the most exciting fields today. Research in these domains is focused on determining novel techniques to advance this technology, which means there are several opportunities for individuals in ML and AI-based careers.
Those looking to work in AI should consider a Master of Science in Artificial Intelligence, which offers students the skills, knowledge, and experience to build a successful career.
AI has different practical applications. For instance, it aids medical professionals in detecting diseases and illnesses. It's also used in transportation (self-driving cars and tracking trucks) for efficient deliveries.
Ventures use AI to identify performance figures, and manufacturers use it to assemble devices.
The jobs pay handsome remuneration; the average base salary is $125,000 annually. And as AI is a central part of several advancements, a career in this field will remain constant for years.
Concluding Facts
AI is simply a branch of computer science, which is, in turn, a branch of technology. So those are three fields that will see plenty of growth in the coming years.
And so long as you continue to develop your expertise and skillset, you'll be well-poised to enter any technological branch after learning about artificial intelligence—or before, for that matter.
Technology is growing by the day. And in a few years, Artificial Intelligence will be an integral part of our lives. Suppose you're interested in helping develop AI. In that case, there are many different ways to study and work towards becoming a data scientist.
Use the resources we've provided above as your launching-off point for your journey toward becoming a data scientist!
Learning artificial intelligence can be tricky, especially if unfamiliar with technical jargon. But I promise it's easier than you think.
As technology continues to grow in the future, it will undoubtedly directly impact our lives. In the coming years, people will need to keep up with advancements. Fortunately, there will be plenty of options for those looking to get involved with AI.
Read More
AI: A Future Career Option
Artificial intelligence is one of the crucial technologies behind the ever-growing tech revolution. It affects industry and society in numerous ways, and that effect will expand far into the future.
With the AI domain increasing, significant issues arise, i.e., too many jobs and not enough qualified candidates. However, this pinpoints an opportunity for professionals with the knowledge and skills to enter AI.
Why is AI a Future Career Goal?
AI is drastically expanding vertically, which provides several career opportunities. For example, the Bureau of Labour Statistics projects that computer science researchers will experience a growth of over 15 percent between 2022 and 2029, much more rapid than the national average for career growth. So, consider the initial step towards a phenomenal career in artificial intelligence.
Suppose you're looking to flourish your career or make your profile more competitive in the job market. In that case, AI is a perfect place to donate your energy and time. Moreover, as the domain grows, it will have a far-reaching impact on various sectors, opening new opportunities for those with the proper skill set.
Artificial Intelligence needs drastic training and commitment; however, the rewards of an AI career far outweigh the investment. And for those already employed and who would like a career change, supplemental programs can help make a smoother transition to the AI domain.
AI and Computer Science are the most exciting fields today. Research in these domains is focused on determining novel techniques to advance this technology, which means there are several opportunities for individuals in ML and AI-based careers.
Those looking to work in AI should consider a Master of Science in Artificial Intelligence, which offers students the skills, knowledge, and experience to build a successful career.
AI has different practical applications. For instance, it aids medical professionals in detecting diseases and illnesses. It's also used in transportation (self-driving cars and tracking trucks) for efficient deliveries.
Ventures use AI to identify performance figures, and manufacturers use it to assemble devices.
The jobs pay handsome remuneration; the average base salary is $125,000 annually. And as AI is a central part of several advancements, a career in this field will remain constant for years.
Concluding Facts
AI is simply a branch of computer science, which is, in turn, a branch of technology. So those are three fields that will see plenty of growth in the coming years.
And so long as you continue to develop your expertise and skillset, you'll be well-poised to enter any technological branch after learning about artificial intelligence—or before, for that matter.
Technology is growing by the day. And in a few years, Artificial Intelligence will be an integral part of our lives. Suppose you're interested in helping develop AI. In that case, there are many different ways to study and work towards becoming a data scientist.
Use the resources we've provided above as your launching-off point for your journey toward becoming a data scientist!
Learning artificial intelligence can be tricky, especially if unfamiliar with technical jargon. But I promise it's easier than you think.
As technology continues to grow in the future, it will undoubtedly directly impact our lives. In the coming years, people will need to keep up with advancements. Fortunately, there will be plenty of options for those looking to get involved with AI.
Capacity Planning: Allocating resources, tasks, and budgets
What is Capacity Planning?
If you want to manage your tasks most efficiently, it's essential to have a clear plan for how much capacity your project requires. Capacity planning is of utmost importance if you want to implement project management on a large scale. It helps you evaluate the resources necessary for the successful completion of the project and calculate various project management metrics such as Projected Cost and Schedule, Startup Time, and the Critical Path Method.
Definition: Capacity Planning
Capacity planning is determining all the resources, activities, and costs required to complete a project. The goal of capacity planning is to ensure that the required resources for a project are available at the start of the project and throughout its life cycle.
Capacity planning should be performed when a new project starts or when an existing project needs to be modified to meet new requirements or challenges. It can also be performed at any point to determine how much work is completed and how much remains before completion.
Capacity planning is essential because it informs management about the effort required to complete projects on time and within budget. It allows managers to better allocate their resources and ensures that they have adequate financial controls to stay within budget constraints.
Types of Capacity Planning
Capacity planning is an essential step in project management as it helps determine the effort required to complete tasks or projects. The purpose of capacity planning is to identify all critical systems, personnel, equipment, and services needed by a project at various stages throughout the life cycle.
Capacity planning helps ensure that all resources are available when needed by the project team, preventing delays due to unforeseen circumstances or equipment failures. Capacity planning also ensures that the correct amount of money has been allocated for each task within a particular budget.
There are three significant types of capacity planning:
Business case analysis
This is the essential type of capacity planning because it determines whether or not a project is worthwhile and should be undertaken. In addition, it determines the resources required and prepares a plan for those resources.
Capacity planning for management
This analysis determines what skills, tools, and equipment are available within a project's organization. It also determines whether or not these resources are adequate to support the project, especially if there are unforeseen delays or problems along the way.
Capacity planning for human resources
This type of analysis determines how many people will be needed to complete a project and the skills they need to have to do so successfully. It also helps determine how much training will be required to become proficient with new technology or procedures that may be introduced during a project."
Technical Capacity Planning
This extends organizational capacity planning, where organizations identify the skills required to perform a specific task or project.
Financial Capacity Planning
This involves identifying how much money will be needed for a particular task or project so that you can plan your budget accordingly.
Benefits of Capacity Planning
Capacity plans are created using a simple formula that determines the required resources, such as employees, equipment, materials, and time spent on each task. This information is then used to calculate how many people or items will be needed for each job. For example, if you have 10 employees working on your project, you would need 1 person who can handle every task and another responsible for scheduling meetings with other team members.
There are many benefits of capacity planning in project management. Some of the significant benefits include the following:
- It can be used for project risk assessment and risk mitigation.
- The capacity planning results can estimate future demand, which can help reduce costs and increase profits.
- It helps identify problem areas before they become critical by informing them about their current capacities and future needs so that they can take action to address them.
- Capacity planning helps stakeholders to understand their specific roles in providing services or products that are required by the company or organization, thus helping them to understand their responsibilities towards it.
- Providing an accurate estimate of costs
- Ensuring that all tasks are completed before the deadlines
- Identifying any potential risks associated with larger projects
When Capacity Planning is required
Capacity planning is a continuous process throughout the project life cycle. This means that it is vital that all project managers and senior management keep their staff informed of any changes in their workloads, as well as any new requirements or constraints that might affect their ability to deliver the project successfully.
The size of your team will have a significant impact on how you manage your capacity planning process. For example, suppose you have a small group. In that case, they may only be able to handle some of the work required by the project with additional resources. If this is the case, then it is likely that you will need to outsource some work or consider hiring other staff who can help support your team on this particular project.
Even with larger teams, however, there must be no bottlenecks in your delivery processes or areas where there are delays due to poor communication or mismanagement. This could lead to problems such as missed deadlines and delayed payments from clients, resulting in lost revenue and damage to reputation - both financially and publicly!
Capacity planning is a skill that we, as project managers, need to have to complete our projects ahead of the deadline and under budget. Unfortunately, we could only meet all deadlines with proper capacity planning, causing costly delays and missed opportunities.
Read More
What is Capacity Planning?
If you want to manage your tasks most efficiently, it's essential to have a clear plan for how much capacity your project requires. Capacity planning is of utmost importance if you want to implement project management on a large scale. It helps you evaluate the resources necessary for the successful completion of the project and calculate various project management metrics such as Projected Cost and Schedule, Startup Time, and the Critical Path Method.
Definition: Capacity Planning
Capacity planning is determining all the resources, activities, and costs required to complete a project. The goal of capacity planning is to ensure that the required resources for a project are available at the start of the project and throughout its life cycle.
Capacity planning should be performed when a new project starts or when an existing project needs to be modified to meet new requirements or challenges. It can also be performed at any point to determine how much work is completed and how much remains before completion.
Capacity planning is essential because it informs management about the effort required to complete projects on time and within budget. It allows managers to better allocate their resources and ensures that they have adequate financial controls to stay within budget constraints.
Types of Capacity Planning
Capacity planning is an essential step in project management as it helps determine the effort required to complete tasks or projects. The purpose of capacity planning is to identify all critical systems, personnel, equipment, and services needed by a project at various stages throughout the life cycle.
Capacity planning helps ensure that all resources are available when needed by the project team, preventing delays due to unforeseen circumstances or equipment failures. Capacity planning also ensures that the correct amount of money has been allocated for each task within a particular budget.
There are three significant types of capacity planning:
Business case analysis
This is the essential type of capacity planning because it determines whether or not a project is worthwhile and should be undertaken. In addition, it determines the resources required and prepares a plan for those resources.
Capacity planning for management
This analysis determines what skills, tools, and equipment are available within a project's organization. It also determines whether or not these resources are adequate to support the project, especially if there are unforeseen delays or problems along the way.
Capacity planning for human resources
This type of analysis determines how many people will be needed to complete a project and the skills they need to have to do so successfully. It also helps determine how much training will be required to become proficient with new technology or procedures that may be introduced during a project."
Technical Capacity Planning
This extends organizational capacity planning, where organizations identify the skills required to perform a specific task or project.
Financial Capacity Planning
This involves identifying how much money will be needed for a particular task or project so that you can plan your budget accordingly.
Benefits of Capacity Planning
Capacity plans are created using a simple formula that determines the required resources, such as employees, equipment, materials, and time spent on each task. This information is then used to calculate how many people or items will be needed for each job. For example, if you have 10 employees working on your project, you would need 1 person who can handle every task and another responsible for scheduling meetings with other team members.
There are many benefits of capacity planning in project management. Some of the significant benefits include the following:
- It can be used for project risk assessment and risk mitigation.
- The capacity planning results can estimate future demand, which can help reduce costs and increase profits.
- It helps identify problem areas before they become critical by informing them about their current capacities and future needs so that they can take action to address them.
- Capacity planning helps stakeholders to understand their specific roles in providing services or products that are required by the company or organization, thus helping them to understand their responsibilities towards it.
- Providing an accurate estimate of costs
- Ensuring that all tasks are completed before the deadlines
- Identifying any potential risks associated with larger projects
When Capacity Planning is required
Capacity planning is a continuous process throughout the project life cycle. This means that it is vital that all project managers and senior management keep their staff informed of any changes in their workloads, as well as any new requirements or constraints that might affect their ability to deliver the project successfully.
The size of your team will have a significant impact on how you manage your capacity planning process. For example, suppose you have a small group. In that case, they may only be able to handle some of the work required by the project with additional resources. If this is the case, then it is likely that you will need to outsource some work or consider hiring other staff who can help support your team on this particular project.
Even with larger teams, however, there must be no bottlenecks in your delivery processes or areas where there are delays due to poor communication or mismanagement. This could lead to problems such as missed deadlines and delayed payments from clients, resulting in lost revenue and damage to reputation - both financially and publicly!
Capacity planning is a skill that we, as project managers, need to have to complete our projects ahead of the deadline and under budget. Unfortunately, we could only meet all deadlines with proper capacity planning, causing costly delays and missed opportunities.
Top Reasons for Project Failure: Uncover Hidden Pitfalls!
Top Reasons for Project Failure
Project failure is an inevitable consequence of any project, and we've all been there. However, we can learn a lot from failed projects, particularly when they're at the early stages of their life cycle. Failure is expected, and learning from it is essential – so let's take a look at some of the top reasons for project failure . . .
Inadequate planning and analysis
The first step toward preventing project failure is to analyze the risks that could impact your project. This includes internal and external factors, such as delays from suppliers or competitors, market changes, weather conditions, and natural disasters.
No clear vision
With a clear vision for your project, it will be easier to keep the team focused on the goal. A good idea only means a little if you don't know where you want to end up. Planning your project's goals ahead of time will help ensure that everyone is on the same page to avoid confusion during implementation.
Lack of sponsorship from senior management members.
Sponsorship from senior management members is vital for the success of any project. However, it isn't easy to get support from senior managers as they do not want to share power with their juniors. In most cases, they are too busy with their projects and do not want to take on something new. This can lead to project failure if your project needs senior management support.
Insufficient resources
You must have enough resources before starting a new project. For example, if you have five members in your team, it would be better to have more than that number because you may need more people during this period. Also, having the right equipment and other resources, such as a software development kit (SDK). It would help if you also considered hiring experts from outside who are well-experienced in their field so that they can help your team succeed in this task.
Poor communication and cooperation
The biggest reason for project failure is poor communication. This is the biggest problem in any project, especially in software development. The reason behind this is that developers are not used to working with people outside their team, and they often need to understand how good vital communication is to building a successful product.
Lack of skilled professionals
Skilled professionals are needed for every step of the development process. It's necessary that you have enough workforce to do all the tasks that need to be done during the project lifecycle and after its completion. So ensure you've hired enough skilled professionals before starting your project so you will avoid any problems during its development process.
Monitoring and Controlling
To make sure that the project is going according to plan, you need to be able to monitor and control it. You need to know when things are happening and why they are happening so that you can take action. This will help you keep on track with all the tasks that need doing, as well as manage any unforeseen problems that might arise. If there are any problems with a particular part of the project, it should be easy for you to find out what has happened and how these things can be fixed.
Bad Stakeholder Management
If your stakeholders aren't happy with something, they will likely voice their concerns. However, if they aren't being listened to or if they feel like they're being ignored, then they may stop contributing. This can lead to a situation where nothing gets done because no one wants to work with each other anymore! Therefore, it's important that everyone remains happy and works together for things to get done correctly.
How to Avoid Project Failure
It's easy to get caught up in the excitement of a new project and lose focus on the details. Here are some things you can do to keep your project on track and avoid project failure:
Do a reality check. Take time to think through the pros and cons of each decision, as well as its impact on other aspects of the business. For example, if you're planning to hire new employees, be sure you have the budget for training them, or else you'll spend money on something that doesn't matter.
Identify risk factors early on. Risks can be minimized or avoided if they're identified at an early stage in a project's life cycle. If you see potential risks early enough, you can change course or reschedule them altogether — rather than waiting until it's too late and having to deal with them when they become a reality.
Avoid the common pitfalls. Only start if you clearly know what needs to be done. Make sure everyone on your team knows what they're expected to do and how they contribute. Give them a handbook or checklist that walks them through their tasks. Create a "to-do" list for each person and make sure everyone has a copy of it.
Get to know your team. The people you work with are your partners in creating a successful project. Therefore, you should have a good, trusting relationship with them. This means you should get to know their personalities, strengths, and weaknesses. You should also be able to communicate with them quickly and without any problems. If something makes you uncomfortable, you can discuss it with your colleagues.
The most important thing you can do to avoid project failure is to define a realistic scope in the first place. Know what you're getting into, and if there's anything you think might be out of grasp, leave it out. Nothing hurts more than working on a project you know will never get finished in advance. So, before you even begin your project, ensure you have a clear idea of what success would look like for you—and don't lose sight of that goal.
Read More
Top Reasons for Project Failure
Project failure is an inevitable consequence of any project, and we've all been there. However, we can learn a lot from failed projects, particularly when they're at the early stages of their life cycle. Failure is expected, and learning from it is essential – so let's take a look at some of the top reasons for project failure . . .
Inadequate planning and analysis
The first step toward preventing project failure is to analyze the risks that could impact your project. This includes internal and external factors, such as delays from suppliers or competitors, market changes, weather conditions, and natural disasters.
No clear vision
With a clear vision for your project, it will be easier to keep the team focused on the goal. A good idea only means a little if you don't know where you want to end up. Planning your project's goals ahead of time will help ensure that everyone is on the same page to avoid confusion during implementation.
Lack of sponsorship from senior management members.
Sponsorship from senior management members is vital for the success of any project. However, it isn't easy to get support from senior managers as they do not want to share power with their juniors. In most cases, they are too busy with their projects and do not want to take on something new. This can lead to project failure if your project needs senior management support.
Insufficient resources
You must have enough resources before starting a new project. For example, if you have five members in your team, it would be better to have more than that number because you may need more people during this period. Also, having the right equipment and other resources, such as a software development kit (SDK). It would help if you also considered hiring experts from outside who are well-experienced in their field so that they can help your team succeed in this task.
Poor communication and cooperation
The biggest reason for project failure is poor communication. This is the biggest problem in any project, especially in software development. The reason behind this is that developers are not used to working with people outside their team, and they often need to understand how good vital communication is to building a successful product.
Lack of skilled professionals
Skilled professionals are needed for every step of the development process. It's necessary that you have enough workforce to do all the tasks that need to be done during the project lifecycle and after its completion. So ensure you've hired enough skilled professionals before starting your project so you will avoid any problems during its development process.
Monitoring and Controlling
To make sure that the project is going according to plan, you need to be able to monitor and control it. You need to know when things are happening and why they are happening so that you can take action. This will help you keep on track with all the tasks that need doing, as well as manage any unforeseen problems that might arise. If there are any problems with a particular part of the project, it should be easy for you to find out what has happened and how these things can be fixed.
Bad Stakeholder Management
If your stakeholders aren't happy with something, they will likely voice their concerns. However, if they aren't being listened to or if they feel like they're being ignored, then they may stop contributing. This can lead to a situation where nothing gets done because no one wants to work with each other anymore! Therefore, it's important that everyone remains happy and works together for things to get done correctly.
How to Avoid Project Failure
It's easy to get caught up in the excitement of a new project and lose focus on the details. Here are some things you can do to keep your project on track and avoid project failure:
Do a reality check. Take time to think through the pros and cons of each decision, as well as its impact on other aspects of the business. For example, if you're planning to hire new employees, be sure you have the budget for training them, or else you'll spend money on something that doesn't matter.
Identify risk factors early on. Risks can be minimized or avoided if they're identified at an early stage in a project's life cycle. If you see potential risks early enough, you can change course or reschedule them altogether — rather than waiting until it's too late and having to deal with them when they become a reality.
Avoid the common pitfalls. Only start if you clearly know what needs to be done. Make sure everyone on your team knows what they're expected to do and how they contribute. Give them a handbook or checklist that walks them through their tasks. Create a "to-do" list for each person and make sure everyone has a copy of it.
Get to know your team. The people you work with are your partners in creating a successful project. Therefore, you should have a good, trusting relationship with them. This means you should get to know their personalities, strengths, and weaknesses. You should also be able to communicate with them quickly and without any problems. If something makes you uncomfortable, you can discuss it with your colleagues.
The most important thing you can do to avoid project failure is to define a realistic scope in the first place. Know what you're getting into, and if there's anything you think might be out of grasp, leave it out. Nothing hurts more than working on a project you know will never get finished in advance. So, before you even begin your project, ensure you have a clear idea of what success would look like for you—and don't lose sight of that goal.
Probabilistic Models in Machine Learning
The probabilistic Model in Machine Learning is a popular algorithm used for machine learning. It is a combination of Discriminant Analysis and a Multinomial Bayes classifier. The probabilistic Model in Machine Learning learns from data more efficiently than traditional statistical techniques. This article will explain it with an example.
What Is Probabilistic Modeling?
The probabilistic model is a machine learning method in which the decision-making is done by using the probability of the possible outcome of the independent variable and an assumption that the likelihood of certain events is constant. It may be used, for example, to make the best choice among several alternatives. The main advantage of this model lies in its reliance on an underlying learning algorithm, which uses simple rules like taking action if its expected value is positive or taking action if its expected value exceeds some threshold.
In Machine Learning, a probability model is used when we want to predict a new variable value based on previous variables or events. For example, in machine learning, we can use a Bayesian inference algorithm to find the best possible value for our prediction based on past data.
Importance of Probabilistic Models
Probabilistic models are fundamental in machine learning. They are used to represent the relationship between variables, and they help us make predictions about future data. Probabilistic models also help us understand the uncertainty in our data, which is essential because it helps us make more informed decisions. For example, suppose we know there is some probability of a problem occurring in our system. In that case, we can take steps to reduce the risk of failure.
The importance of probabilistic models has led to the creation of new fields, such as Bayesian Statistics, which helps us make better predictions about how certain events will affect our systems.
Probabilistic models are extensively used in machine learning applications. They help us to make predictions and learn from experience. Probabilistic models can be classified into two types:
Soft-soft Classification: In the soft-soft classifier, we use a probability distribution that is a function of the input variables and a soft linear function of the output variable. For example, suppose we have three inputs and one output. Then, we can use a Gaussian distribution to model the inputs and a soft linear function to model the output.
Hard-soft Classification: In the hard-soft classifier, we use complex linear functions for both the inputs and outputs. For example, suppose we have three inputs and two outputs. In that case, we can use an exponential function to model the input variables and a linear function to model the output variable.
Probabilistic Models
Discriminative and Generative Model
Discriminative models are used for classification, where the output is a binary (either true or false) prediction. Generative models are used for predicting novel outputs from a set of samples. Discriminative models are often trained using supervised learning techniques, while generative models are often trained using unsupervised learning techniques.
Discriminative models have been applied successfully in many machine learning applications, such as spam filtering, document classification, and voice recognition. They have also been used successfully to predict the outcomes of events such as earthquakes and natural disasters.
Generative models attempt to produce novel data by modeling the properties of their underlying distribution. Generative models have been used successfully to create artworks, generate poetry and music, simulate the evolution of biological species, and even create artificial life.
Straight Line Modeling
The straight-line model is a type of continuous probability distribution that models continuous data using discrete variables. For example, the straight line model is used to model the relationship between consecutive values of a continuous random variable, such as temperature and time. In this case, we assume that each point in time is a random sample from an underlying continuous distribution.
Generalized Linear Models
In Machine Learning, the general linear model is a statistical model used to describe conditional probabilities. It is a particular generalized linear model (GLM) case and can be used to model non-Gaussian data.
The general linear model can be used to model any distribution with a binomial distribution, Poisson distribution, or negative binomial distribution. The logistic and gamma distributions are also available as exceptional cases of this model.
The general linear model helps continuous model variables that have non-normal distributions. This is because it has an error term that can be modeled using coefficients specific to each type of distribution you are modeling.
Naive Bayes Algorithm
Naive Bayes is a popular probabilistic classification algorithm in machine learning. It is used to make predictions about new observations, given past observations and a set of parameters that describe the data distribution. The Naive Bayes algorithm works well for non-binary classifiers and can be easily understood with an example.
The Naive Bayes algorithm makes predictions about new observations, given past observations and a set of parameters that describe the data distribution. The Naive Bayes algorithm works well for non-binary classifiers.
Advantages of the Probabilistic Model
Probabilistic models are a widely used approach to machine learning and are particularly suited for modeling uncertainty. The probabilistic model is a good fit for many applications because it can handle both deterministic and random variables and provides a way to represent observed data as a sequence of samples drawn from a probability distribution.
The advantages of the probabilistic model include:
- First, it is flexible, allowing users to define their probability distributions or use existing ones such as Gaussian or Poisson.
- It provides a way to represent observed data as a sequence of samples drawn from the underlying distribution, which makes it easy to analyze data from real-world applications such as medical imaging and financial fraud detection.
- It allows users to specify how these probabilities change over time, which helps model phenomena that occur on time scales other than those we typically encounter daily (e.g., stock market prices).
- It is a well-understood statistical technique applied successfully in many engineering, physics, and biology areas.
- The models used by machine learning are based on probability theory, so they are mathematically tractable. In addition, the mathematical simplicity makes it possible to write down exact formulas for calculating a model's performance.
- The probabilistic model gives an unbiased estimate of a probability distribution over the data points, which can be interpreted as estimating how likely any given observation would occur under any given distribution. This allows us to use the same models for all observations and not worry about whether or not we're dealing with different data sets.
- The probabilistic model provides a reasonable estimate of variance because it assigns equal probabilities to all possible outcomes; this makes it easy to calculate variances from data points.
Conclusion
Probabilistic models are a great way to understand the trends that can be derived from data to make predictions for the future. In general, you will learn about probabilistic models early on in your study of machine learning.
Read More
The probabilistic Model in Machine Learning is a popular algorithm used for machine learning. It is a combination of Discriminant Analysis and a Multinomial Bayes classifier. The probabilistic Model in Machine Learning learns from data more efficiently than traditional statistical techniques. This article will explain it with an example.
What Is Probabilistic Modeling?
The probabilistic model is a machine learning method in which the decision-making is done by using the probability of the possible outcome of the independent variable and an assumption that the likelihood of certain events is constant. It may be used, for example, to make the best choice among several alternatives. The main advantage of this model lies in its reliance on an underlying learning algorithm, which uses simple rules like taking action if its expected value is positive or taking action if its expected value exceeds some threshold.
In Machine Learning, a probability model is used when we want to predict a new variable value based on previous variables or events. For example, in machine learning, we can use a Bayesian inference algorithm to find the best possible value for our prediction based on past data.
Importance of Probabilistic Models
Probabilistic models are fundamental in machine learning. They are used to represent the relationship between variables, and they help us make predictions about future data. Probabilistic models also help us understand the uncertainty in our data, which is essential because it helps us make more informed decisions. For example, suppose we know there is some probability of a problem occurring in our system. In that case, we can take steps to reduce the risk of failure.
The importance of probabilistic models has led to the creation of new fields, such as Bayesian Statistics, which helps us make better predictions about how certain events will affect our systems.
Probabilistic models are extensively used in machine learning applications. They help us to make predictions and learn from experience. Probabilistic models can be classified into two types:
Soft-soft Classification: In the soft-soft classifier, we use a probability distribution that is a function of the input variables and a soft linear function of the output variable. For example, suppose we have three inputs and one output. Then, we can use a Gaussian distribution to model the inputs and a soft linear function to model the output.
Hard-soft Classification: In the hard-soft classifier, we use complex linear functions for both the inputs and outputs. For example, suppose we have three inputs and two outputs. In that case, we can use an exponential function to model the input variables and a linear function to model the output variable.
Probabilistic Models
Discriminative and Generative Model
Discriminative models are used for classification, where the output is a binary (either true or false) prediction. Generative models are used for predicting novel outputs from a set of samples. Discriminative models are often trained using supervised learning techniques, while generative models are often trained using unsupervised learning techniques.
Discriminative models have been applied successfully in many machine learning applications, such as spam filtering, document classification, and voice recognition. They have also been used successfully to predict the outcomes of events such as earthquakes and natural disasters.
Generative models attempt to produce novel data by modeling the properties of their underlying distribution. Generative models have been used successfully to create artworks, generate poetry and music, simulate the evolution of biological species, and even create artificial life.
Straight Line Modeling
The straight-line model is a type of continuous probability distribution that models continuous data using discrete variables. For example, the straight line model is used to model the relationship between consecutive values of a continuous random variable, such as temperature and time. In this case, we assume that each point in time is a random sample from an underlying continuous distribution.
Generalized Linear Models
In Machine Learning, the general linear model is a statistical model used to describe conditional probabilities. It is a particular generalized linear model (GLM) case and can be used to model non-Gaussian data.
The general linear model can be used to model any distribution with a binomial distribution, Poisson distribution, or negative binomial distribution. The logistic and gamma distributions are also available as exceptional cases of this model.
The general linear model helps continuous model variables that have non-normal distributions. This is because it has an error term that can be modeled using coefficients specific to each type of distribution you are modeling.
Naive Bayes Algorithm
Naive Bayes is a popular probabilistic classification algorithm in machine learning. It is used to make predictions about new observations, given past observations and a set of parameters that describe the data distribution. The Naive Bayes algorithm works well for non-binary classifiers and can be easily understood with an example.
The Naive Bayes algorithm makes predictions about new observations, given past observations and a set of parameters that describe the data distribution. The Naive Bayes algorithm works well for non-binary classifiers.
Advantages of the Probabilistic Model
Probabilistic models are a widely used approach to machine learning and are particularly suited for modeling uncertainty. The probabilistic model is a good fit for many applications because it can handle both deterministic and random variables and provides a way to represent observed data as a sequence of samples drawn from a probability distribution.
The advantages of the probabilistic model include:
- First, it is flexible, allowing users to define their probability distributions or use existing ones such as Gaussian or Poisson.
- It provides a way to represent observed data as a sequence of samples drawn from the underlying distribution, which makes it easy to analyze data from real-world applications such as medical imaging and financial fraud detection.
- It allows users to specify how these probabilities change over time, which helps model phenomena that occur on time scales other than those we typically encounter daily (e.g., stock market prices).
- It is a well-understood statistical technique applied successfully in many engineering, physics, and biology areas.
- The models used by machine learning are based on probability theory, so they are mathematically tractable. In addition, the mathematical simplicity makes it possible to write down exact formulas for calculating a model's performance.
- The probabilistic model gives an unbiased estimate of a probability distribution over the data points, which can be interpreted as estimating how likely any given observation would occur under any given distribution. This allows us to use the same models for all observations and not worry about whether or not we're dealing with different data sets.
- The probabilistic model provides a reasonable estimate of variance because it assigns equal probabilities to all possible outcomes; this makes it easy to calculate variances from data points.
Conclusion
Probabilistic models are a great way to understand the trends that can be derived from data to make predictions for the future. In general, you will learn about probabilistic models early on in your study of machine learning.
How AI is Changing Everyday Work Across Industries and Jobs
How AI Changing Everyday Work
It's been palpable over the past few years that artificial intelligence is changing the world around us. From self-driving cars, drones, and robots performing tedious work in factories to teaching computers to understand human speech, artificial intelligence is being applied in ways we could only dream of decades ago.
But AI isn't just making life easier for businesses and their owners. AI has a hand in almost every industry today, with automated systems taking over the job of some humans – one day, even driving trucks!
How AI Changing Everyday Work
Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing everyday work. But it's not just about replacing humans — it's also about giving them new capabilities.
The most significant change is that AI is no longer a tool for solving specific problems; it's now a platform for creating applications and services that can solve many different issues. This shift towards AI as a service means that companies don't have to build their own AI infrastructure from scratch. Instead, they can leverage open-source software libraries and already available frameworks.
Companies are using AI as an engine for building apps and services that make their products or services more valuable to customers.
For example, Amazon uses machine learning to suggest items based on your previous purchases (Amazon Echo), predict which books will sell well (Amazon Publishing), or recommend restaurants for you to try (Amazon Restaurants).
In addition to essential AI technologies like chatbots and speech recognition, companies are also using more advanced forms of artificial intelligence, such as deep learning neural networks in which the network learns itself rather than being preprogrammed by an engineer.
Future of AI in the Global Marketplace
Artificial intelligence was once a faraway, futuristic thing. But research has made huge leaps in the past decade, and AI is now all around us. AI could be worth $15 trillion to the global economy by 2030. Moreover, AI will affect every industry, including sectors we don't often associate with technology. The supply chain, for instance, is an ideal environment for AI, which can track and trace products from the manufacturer to the end user.
AI Creates New Jobs
AI is a huge opportunity for job creation. In addition to the apparent opportunities for workers in the field, AI can generate new jobs in several other ways.
New industries will be created: AI's most obvious way to create new jobs is by creating new initiatives. Many examples are happening in the healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing sectors.
New products will be developed: Many companies are already developing products based on artificial intelligence technology. These products include self-driving cars and robots that perform repetitive tasks like cooking or cleaning. In addition to creating new jobs, these products could also save businesses money by increasing efficiency or improving quality control over time.
AI and Every Business
Artificial intelligence is a buzzword that has been making waves in the business world. AI uses computers to solve problems by making decisions based on user input and experience.
The usefulness of AI in various industries has led to an increase in research and development, which will help businesses innovate and improve their products.
For example, IBM Watson was developed to answer complex questions posed by physicians or health professionals. It can read medical records, recommend patient treatment plans, and even order supplies for doctors' offices.
Artificial intelligence is also being used in developing safer vehicles. For example, Nissan's autonomous vehicle technology uses artificial intelligence algorithms to predict how drivers will interact with the car, allowing it to decide how to respond based on what it knows about its driver. This technology could ultimately lead to self-driving cars that can drive themselves without human intervention.
Advantage of AI
- AI can be used for various tasks, including finding patterns in data and executing complex math problems. It can do this faster than human beings can, and it's cheaper, too.
- AI can help with customer service, data analysis, logistics, and cybersecurity. AI is used in one-third of all sales calls. AI can predict supply and demand, which helps businesses plan and save on inventory.
- AI can also help companies to reduce emissions, water, and energy use. AI can help people with disabilities, too.
- It can read, understand and talk in a human language.
- AI can detect patterns, identify risks and offer recommendations.
- Intelligent machines can read medical scans, such as x-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, and diagnose diseases.
- AI can help with everyday tasks, like scheduling appointments, answering simple questions, and helping people navigate public transportation.
- It can also help with creative endeavors, like writing poetry and designing websites.
Disadvantage of AI
AI is not a cure-all. It does have drawbacks. AI can't understand context, for example. This is important for specific jobs, such as reading and understanding contracts. If there is one thing that AI can't do, its creativity. AI cannot generate new ideas, concepts, or solutions. A technology that can do this is still a long way off.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is changing the way we do many things, from business to education to entertainment. It's changing the very nature of work, too. But AI won't displace all jobs. Machines are taking over the tedious parts of work, like data entry. Humans have strengths that computers don't have, such as creativity and critical thinking. AI will change the global economy and the way we work. But people will remain a crucial part of the picture.
Read More
How AI Changing Everyday Work
It's been palpable over the past few years that artificial intelligence is changing the world around us. From self-driving cars, drones, and robots performing tedious work in factories to teaching computers to understand human speech, artificial intelligence is being applied in ways we could only dream of decades ago.
But AI isn't just making life easier for businesses and their owners. AI has a hand in almost every industry today, with automated systems taking over the job of some humans – one day, even driving trucks!
How AI Changing Everyday Work
Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing everyday work. But it's not just about replacing humans — it's also about giving them new capabilities.
The most significant change is that AI is no longer a tool for solving specific problems; it's now a platform for creating applications and services that can solve many different issues. This shift towards AI as a service means that companies don't have to build their own AI infrastructure from scratch. Instead, they can leverage open-source software libraries and already available frameworks.
Companies are using AI as an engine for building apps and services that make their products or services more valuable to customers.
For example, Amazon uses machine learning to suggest items based on your previous purchases (Amazon Echo), predict which books will sell well (Amazon Publishing), or recommend restaurants for you to try (Amazon Restaurants).
In addition to essential AI technologies like chatbots and speech recognition, companies are also using more advanced forms of artificial intelligence, such as deep learning neural networks in which the network learns itself rather than being preprogrammed by an engineer.
Future of AI in the Global Marketplace
Artificial intelligence was once a faraway, futuristic thing. But research has made huge leaps in the past decade, and AI is now all around us. AI could be worth $15 trillion to the global economy by 2030. Moreover, AI will affect every industry, including sectors we don't often associate with technology. The supply chain, for instance, is an ideal environment for AI, which can track and trace products from the manufacturer to the end user.
AI Creates New Jobs
AI is a huge opportunity for job creation. In addition to the apparent opportunities for workers in the field, AI can generate new jobs in several other ways.
New industries will be created: AI's most obvious way to create new jobs is by creating new initiatives. Many examples are happening in the healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing sectors.
New products will be developed: Many companies are already developing products based on artificial intelligence technology. These products include self-driving cars and robots that perform repetitive tasks like cooking or cleaning. In addition to creating new jobs, these products could also save businesses money by increasing efficiency or improving quality control over time.
AI and Every Business
Artificial intelligence is a buzzword that has been making waves in the business world. AI uses computers to solve problems by making decisions based on user input and experience.
The usefulness of AI in various industries has led to an increase in research and development, which will help businesses innovate and improve their products.
For example, IBM Watson was developed to answer complex questions posed by physicians or health professionals. It can read medical records, recommend patient treatment plans, and even order supplies for doctors' offices.
Artificial intelligence is also being used in developing safer vehicles. For example, Nissan's autonomous vehicle technology uses artificial intelligence algorithms to predict how drivers will interact with the car, allowing it to decide how to respond based on what it knows about its driver. This technology could ultimately lead to self-driving cars that can drive themselves without human intervention.
Advantage of AI
- AI can be used for various tasks, including finding patterns in data and executing complex math problems. It can do this faster than human beings can, and it's cheaper, too.
- AI can help with customer service, data analysis, logistics, and cybersecurity. AI is used in one-third of all sales calls. AI can predict supply and demand, which helps businesses plan and save on inventory.
- AI can also help companies to reduce emissions, water, and energy use. AI can help people with disabilities, too.
- It can read, understand and talk in a human language.
- AI can detect patterns, identify risks and offer recommendations.
- Intelligent machines can read medical scans, such as x-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, and diagnose diseases.
- AI can help with everyday tasks, like scheduling appointments, answering simple questions, and helping people navigate public transportation.
- It can also help with creative endeavors, like writing poetry and designing websites.
Disadvantage of AI
AI is not a cure-all. It does have drawbacks. AI can't understand context, for example. This is important for specific jobs, such as reading and understanding contracts. If there is one thing that AI can't do, its creativity. AI cannot generate new ideas, concepts, or solutions. A technology that can do this is still a long way off.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is changing the way we do many things, from business to education to entertainment. It's changing the very nature of work, too. But AI won't displace all jobs. Machines are taking over the tedious parts of work, like data entry. Humans have strengths that computers don't have, such as creativity and critical thinking. AI will change the global economy and the way we work. But people will remain a crucial part of the picture.
Top 10 Essential Machine Learning Algorithms You Should Know
Top Machine Learning Algorithms
Finding a suitable algorithm can take hours or even days. As they say, the best algorithm is the one that doesn't exist yet. There's a lot of big data in computer science and machine learning —we aren't just talking about your data. Programmers often feel overwhelmed by all the decisions to make when creating new algorithms. In this article, we'll show you some standard machine-learning algorithms you should know about to be an influential data scientist!
Support Vector Machines (SVM)
Support vector machines (SVM) are machine learning algorithm that maps arbitrary data to high-dimensional spaces, finding a hyperplane (a line separating two classes) that maximizes the margin between the hyperplane and the nearest data point. The SVM is an iterative method that can be trained by repeatedly approximating the optimal solution for small steps.
SVM is a non-linear classifier that takes advantage of the structure of high-dimensional spaces to find optimal discriminants between different classes. It is one of several non-linear kernel methods for multilabel classification.
Linear Regression
Linear regression is a technique used to predict continuous numerical outcomes based on independent variables. It is a supervised learning algorithm in which we want to make predictions on new data that we have not used to train the model. There are two types of linear regression, Simple Linear Regression, and Multiple Linear Regression.
In simple linear regression, we have one continuous independent variable and one continuous dependent variable.
In multiple regression, we have more than one continuous independent variable and one continuous dependent variable.
Logistic Regression
Logistic regression is a classification algorithm, which means that it will predict a discrete outcome. There are two types of logistic regression, binary logistic regression, and multinomial logistic regression.
Binary logistic regression is used when we have two discrete effects: pass or fail, fraud or not fraud, and so on.
Multinomial logistic regression is used when we have more than two discrete outcomes.
Decision Tree
The decision tree algorithm is a machine learning technique that makes predictions by analyzing the information in a set of observations.
The algorithm can predict the probability of an event occurring or the likelihood that a specific outcome will happen. It works by creating a tree structure based on the data and then using it to find general rules that can be applied to more complex situations.
In its simplest form, decision trees work by finding patterns in data. For example, suppose you have a database of customers who bought products from different stores and have demographic information about them. In that case, you could create a decision tree that predicts whether or not they would return for another purchase.
Naive Bayes
Naive Bayes machine learning algorithm is a supervised learning algorithm for classification. It can be used for prediction, estimation, and various continuous variables.
This algorithm uses the Bayes theorem to estimate the probability of an event given some evidence. The result of this estimation is called a posteriori probability (PP) or probability assigned to an event or label given a set of observations. Naive Bayes machine learning algorithm is one of the most popular machine learning algorithms used in many fields, including marketing, finance, text mining, etc.
KNN (K- Nearest Neighbors)
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbors) is an algorithm that learns a mapping from an input to a target. It is based on the concept of nearest neighbors, which means that if you know something about your closest neighbors, then you can use that information to predict what will happen next in the training data. This is called a "compound document" problem.
The KNN algorithm works by training a model to find the closest possible matches for a query document. Then, it uses the records most relative to the query as training examples and the rest as test data.
This is achieved using a metric called "distance" between two documents (or, more generally, between two instances). There are many different methods for calculating this distance: Euclidean distance, cosine similarity, etc., but they all have similar properties: they measure how far apart two objects are in terms of the number of links between them (or in terms of how many words they share). The larger this number gets compared to 1 (the ideal case), the better match we have found!
K-Means
K-means is an unsupervised learning algorithm that uses the principle of minimum distance to cluster data points into groups. It works by assigning each point in the data set to a group, or cluster, whose center is the point with the fewest total distances from each end. Then, the algorithm iteratively adjusts each point's location to maximize the within-cluster sum of squares (WCS) and minimize the between-clusters sum of squares (BSS).
K-means clustering involves calculating the centroid for each point by finding its distance to each other in its cluster and then adjusting that point's position to minimize its distance from all other issues in its collection. This can be done with a single weighted average or another function of all individual measures for each point.
K-means has been used extensively in many fields, including computer vision, machine learning, and pattern recognition. It's considered one of the simplest methods for clustering data due to its intuitive nature; however, it can be inefficient if implemented poorly due to overfitting problems that arise when using training data samples from only one class (such as all red dots).
Random Forest
The Random Forest Machine Learning Algorithms are a set of methods to predict future events' outcomes. The method is based on the idea that many decision trees are created using random subsets of training data. Then, these subsets are combined to produce new sets containing more information than any individual decision tree. This allows for better prediction because each tree has access to more information than previous ones, making finding patterns in the data more accessible.
Random Forest Algorithms can be used in numerous areas of business and technology, including marketing, finance, and e-commerce. They're particularly useful when applied to data sets that are difficult or expensive to analyze in other ways. For example, they could help companies understand consumer behavior by analyzing purchases made at different locations over time or across different demographics.
Dimensionality Reduction Algorithms
With all this data, we must be careful about how much of it we use. Using all of your information is called a full-data approach. Using too much data can slow down your algorithm or even cause it to crash, and that's not a good thing. You want to use as little data as possible to predict accurately. Dimensionality reduction algorithms are used when you want to reduce the amount of data used to train an algorithm. You can use these algorithms when you have a lot of data, but your algorithm might be too slow. There are many different dimensionality reduction algorithms, but three popular ones.
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
- Random Forest.
Gradient Boosting algorithms
Gradient boosting is an ensemble technique. The idea of an ensemble is to create a team of algorithms. Then each algorithm will specialize in predicting certain types of errors that the others aren't as good at predicting. When you combine them, you get a more accurate model. There are many different types of gradient-boosting algorithms that you can use in your models. Three of the most popular ones are
- Gradient boosting trees (GBTs)
- Adaptive gradient boosting trees (Ada Grad)
- Stochastic gradient boosting (SGDB)
Conclusion
Machine learning algorithms are a valuable tool to use when working with data. When choosing the correct machine learning algorithm, selecting an appropriate algorithm for your data and problem is essential. Many different types of machine learning algorithms are available for various tasks, such as regression, clustering, and classification. If you want to become a data scientist, you have to understand how machine learning algorithms work. In addition, different algorithms are best for other problems, so it is essential to have a broad knowledge of the different algorithms and when to use them.
Read More
Top Machine Learning Algorithms
Finding a suitable algorithm can take hours or even days. As they say, the best algorithm is the one that doesn't exist yet. There's a lot of big data in computer science and machine learning —we aren't just talking about your data. Programmers often feel overwhelmed by all the decisions to make when creating new algorithms. In this article, we'll show you some standard machine-learning algorithms you should know about to be an influential data scientist!
Support Vector Machines (SVM)
Support vector machines (SVM) are machine learning algorithm that maps arbitrary data to high-dimensional spaces, finding a hyperplane (a line separating two classes) that maximizes the margin between the hyperplane and the nearest data point. The SVM is an iterative method that can be trained by repeatedly approximating the optimal solution for small steps.
SVM is a non-linear classifier that takes advantage of the structure of high-dimensional spaces to find optimal discriminants between different classes. It is one of several non-linear kernel methods for multilabel classification.
Linear Regression
Linear regression is a technique used to predict continuous numerical outcomes based on independent variables. It is a supervised learning algorithm in which we want to make predictions on new data that we have not used to train the model. There are two types of linear regression, Simple Linear Regression, and Multiple Linear Regression.
In simple linear regression, we have one continuous independent variable and one continuous dependent variable.
In multiple regression, we have more than one continuous independent variable and one continuous dependent variable.
Logistic Regression
Logistic regression is a classification algorithm, which means that it will predict a discrete outcome. There are two types of logistic regression, binary logistic regression, and multinomial logistic regression.
Binary logistic regression is used when we have two discrete effects: pass or fail, fraud or not fraud, and so on.
Multinomial logistic regression is used when we have more than two discrete outcomes.
Decision Tree
The decision tree algorithm is a machine learning technique that makes predictions by analyzing the information in a set of observations.
The algorithm can predict the probability of an event occurring or the likelihood that a specific outcome will happen. It works by creating a tree structure based on the data and then using it to find general rules that can be applied to more complex situations.
In its simplest form, decision trees work by finding patterns in data. For example, suppose you have a database of customers who bought products from different stores and have demographic information about them. In that case, you could create a decision tree that predicts whether or not they would return for another purchase.
Naive Bayes
Naive Bayes machine learning algorithm is a supervised learning algorithm for classification. It can be used for prediction, estimation, and various continuous variables.
This algorithm uses the Bayes theorem to estimate the probability of an event given some evidence. The result of this estimation is called a posteriori probability (PP) or probability assigned to an event or label given a set of observations. Naive Bayes machine learning algorithm is one of the most popular machine learning algorithms used in many fields, including marketing, finance, text mining, etc.
KNN (K- Nearest Neighbors)
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbors) is an algorithm that learns a mapping from an input to a target. It is based on the concept of nearest neighbors, which means that if you know something about your closest neighbors, then you can use that information to predict what will happen next in the training data. This is called a "compound document" problem.
The KNN algorithm works by training a model to find the closest possible matches for a query document. Then, it uses the records most relative to the query as training examples and the rest as test data.
This is achieved using a metric called "distance" between two documents (or, more generally, between two instances). There are many different methods for calculating this distance: Euclidean distance, cosine similarity, etc., but they all have similar properties: they measure how far apart two objects are in terms of the number of links between them (or in terms of how many words they share). The larger this number gets compared to 1 (the ideal case), the better match we have found!
K-Means
K-means is an unsupervised learning algorithm that uses the principle of minimum distance to cluster data points into groups. It works by assigning each point in the data set to a group, or cluster, whose center is the point with the fewest total distances from each end. Then, the algorithm iteratively adjusts each point's location to maximize the within-cluster sum of squares (WCS) and minimize the between-clusters sum of squares (BSS).
K-means clustering involves calculating the centroid for each point by finding its distance to each other in its cluster and then adjusting that point's position to minimize its distance from all other issues in its collection. This can be done with a single weighted average or another function of all individual measures for each point.
K-means has been used extensively in many fields, including computer vision, machine learning, and pattern recognition. It's considered one of the simplest methods for clustering data due to its intuitive nature; however, it can be inefficient if implemented poorly due to overfitting problems that arise when using training data samples from only one class (such as all red dots).
Random Forest
The Random Forest Machine Learning Algorithms are a set of methods to predict future events' outcomes. The method is based on the idea that many decision trees are created using random subsets of training data. Then, these subsets are combined to produce new sets containing more information than any individual decision tree. This allows for better prediction because each tree has access to more information than previous ones, making finding patterns in the data more accessible.
Random Forest Algorithms can be used in numerous areas of business and technology, including marketing, finance, and e-commerce. They're particularly useful when applied to data sets that are difficult or expensive to analyze in other ways. For example, they could help companies understand consumer behavior by analyzing purchases made at different locations over time or across different demographics.
Dimensionality Reduction Algorithms
With all this data, we must be careful about how much of it we use. Using all of your information is called a full-data approach. Using too much data can slow down your algorithm or even cause it to crash, and that's not a good thing. You want to use as little data as possible to predict accurately. Dimensionality reduction algorithms are used when you want to reduce the amount of data used to train an algorithm. You can use these algorithms when you have a lot of data, but your algorithm might be too slow. There are many different dimensionality reduction algorithms, but three popular ones.
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
- Random Forest.
Gradient Boosting algorithms
Gradient boosting is an ensemble technique. The idea of an ensemble is to create a team of algorithms. Then each algorithm will specialize in predicting certain types of errors that the others aren't as good at predicting. When you combine them, you get a more accurate model. There are many different types of gradient-boosting algorithms that you can use in your models. Three of the most popular ones are
- Gradient boosting trees (GBTs)
- Adaptive gradient boosting trees (Ada Grad)
- Stochastic gradient boosting (SGDB)
Conclusion
Machine learning algorithms are a valuable tool to use when working with data. When choosing the correct machine learning algorithm, selecting an appropriate algorithm for your data and problem is essential. Many different types of machine learning algorithms are available for various tasks, such as regression, clustering, and classification. If you want to become a data scientist, you have to understand how machine learning algorithms work. In addition, different algorithms are best for other problems, so it is essential to have a broad knowledge of the different algorithms and when to use them.
Information Retrieval in Machine Learning
Information Retrieval in Machine Learning
Information retrieval is one of the many things that can be done in machine learning. Many must realize that such a simple yet powerful concept could be applied to many industries and business problems. In this article, we'll uncover why information retrieval makes perfect sense in an era of big data. It has been difficult for machine learning algorithms to find or retrieve relevant information about data. Information retrieval helps in locating related information from the given input. It can be used for any purpose where there are queries generated by humans, such as web crawling, question answering, and so on.
What is Information retrieval in machine learning?
Information retrieval is finding relevant documents, web pages, or other resources on the Web. This can be done by using a variety of search engines, including Google and Bing.
You often want to perform an information retrieval task on your data. For example, if you have a set of documents that you want to summarize, if you are interested in how people use your website, or if you want to understand how people interact with your company's products, then it makes sense to use information retrieval within machine learning.
The first step in performing an information retrieval task is gathering relevant data. Then we use this data to train our models to learn how to find relevant documents for us.
Why is Information retrieval important?
Information retrieval is an essential part of machine learning. It's the process of finding and retrieving information from a database. This can be done using algorithms that search through the database or user input.
Information retrieval is essential in machine learning because it allows for finding data patterns. Machine learning relies on discovering data patterns through supervised or unsupervised learning. There are many ways to do this, but one way is by using information retrieval methods to find relevant data.
In supervised learning problems, the algorithm uses keywords or other characteristics to find relevant data from the database.
Unsupervised learning problems are where there are no specific keywords or attributes for the algorithm; instead, it looks at patterns in various data sources to find relevant information.
How does Information retrieval work?
Information retrieval works in the following manner:
Input: The first step in information retrieval is to provide the system with a query. The query could be a few words or a particular sentence. The type of the input method depends on the query type. For example, if a user wants to find a picture of a cat, they would provide a picture of a cat as input. The input could be in the form of an image or other media.
Index: The next step would be indexing the query with all the related data. As the query is being indexed, the system would look for the terms in the query and then match them with related data.
Retrieve: Once the data has been matched, the system will retrieve all the data from the database.
Output: The system would then output the data with the query terms highlighted in bold.
Close: Once all the data has been retrieved and outputted, the information retrieval system will close.
Where is Information retrieval used?
Information retrieval is used in different forms of machine learning, such as question answering systems, web crawling systems, and many more. It can be used in almost any domain where humans generate queries. You can use it to find information from a database, books, or any other sources. Let us look at different types of systems where information retrieval could be used.
Question Answering Systems: Question Answering Systems are computer systems that can answer questions in natural language. The questions could be about a topic, past events, etc. The most common example of a question answering system is a virtual assistant.
Web Crawling Systems: Web Crawling Systems are computer programs that search the World Wide Web (WWW) to create a massive searchable database. They go through different web pages to find links to other pages, words and phrases that appear on those pages, and information about the authors of the pages.
Natural Language Processing: Natural Language Processing is the field of creating computer systems that can understand human languages. You can use information retrieval in natural language processing to find different meanings of a sentence or a word.
Semantics: Semantics is the study of the importance of words. You can use information retrieval for semantic analysis.
Types of Information Retrieval model
Information retrieval is a broad field that has many subfields. Each subfield studies a different aspect of information retrieval and brings new and creative ways to perform information retrieval. Let us look at three other information retrieval models that could be used in machine learning.
Classic IR Model
This model is used when there are no restrictions on the type of data or its format. It uses boolean operators such as AND, OR, and NOT to retrieve relevant results from large volumes of data. This model is based on indexing techniques that help to identify keywords contained in documents to direct users toward specific documents based on their relevance.
Non-Classic IR Model
This model has been developed to deal with large volumes of unstructured text such as e-mails, web pages, and other documents that cannot be indexed using CIRM techniques. The main features of this model include clustering techniques for identifying similar documents, extraction techniques for extracting relevant contents from clusters, and ranking techniques for ranking documents based on their relevancy score.
Alternative IR Model
The Alternative Information Retrieval Model (AIR) is a theoretical framework that has been used to account for the information retrieval behavior of users in a variety of different domains. The AIR model is based on two assumptions:
- Users will search for valuable and relevant information to their needs and wishes.
- Users will find the best match between their needs and the information they are searching for.
Difference between Information Retrieval and Data Retrieval
Information retrieval and data retrieval are two different concepts.
Data retrieval is finding and acquiring data from other sources such as web pages, images, documents, etc. Information retrieval is finding relevant information from a large set of data. It can be used for any purpose where there are queries generated by humans, such as web crawling, question answering, and so on.
Information retrieval uses various models to retrieve relevant results for a specific request. Data retrieval can be used for many purposes, such as finding information from a large data set. Data retrieval can be used to find information from extensive data collection.
Conclusion
Information retrieval is a broad field that applies to many subfields. It can be used in many forms of machine learning, such as natural language processing and question answering systems. It helps find data from large data sets with ease. It has helped to increase the performance of machines in many ways. We hope you now understand information retrieval and how it can be helpful in machine learning. Armed with this knowledge, you can be more aware of how it is used in various industries and how it can be applied more widely.
Read More
Information Retrieval in Machine Learning
Information retrieval is one of the many things that can be done in machine learning. Many must realize that such a simple yet powerful concept could be applied to many industries and business problems. In this article, we'll uncover why information retrieval makes perfect sense in an era of big data. It has been difficult for machine learning algorithms to find or retrieve relevant information about data. Information retrieval helps in locating related information from the given input. It can be used for any purpose where there are queries generated by humans, such as web crawling, question answering, and so on.
What is Information retrieval in machine learning?
Information retrieval is finding relevant documents, web pages, or other resources on the Web. This can be done by using a variety of search engines, including Google and Bing.
You often want to perform an information retrieval task on your data. For example, if you have a set of documents that you want to summarize, if you are interested in how people use your website, or if you want to understand how people interact with your company's products, then it makes sense to use information retrieval within machine learning.
The first step in performing an information retrieval task is gathering relevant data. Then we use this data to train our models to learn how to find relevant documents for us.
Why is Information retrieval important?
Information retrieval is an essential part of machine learning. It's the process of finding and retrieving information from a database. This can be done using algorithms that search through the database or user input.
Information retrieval is essential in machine learning because it allows for finding data patterns. Machine learning relies on discovering data patterns through supervised or unsupervised learning. There are many ways to do this, but one way is by using information retrieval methods to find relevant data.
In supervised learning problems, the algorithm uses keywords or other characteristics to find relevant data from the database.
Unsupervised learning problems are where there are no specific keywords or attributes for the algorithm; instead, it looks at patterns in various data sources to find relevant information.
How does Information retrieval work?
Information retrieval works in the following manner:
Input: The first step in information retrieval is to provide the system with a query. The query could be a few words or a particular sentence. The type of the input method depends on the query type. For example, if a user wants to find a picture of a cat, they would provide a picture of a cat as input. The input could be in the form of an image or other media.
Index: The next step would be indexing the query with all the related data. As the query is being indexed, the system would look for the terms in the query and then match them with related data.
Retrieve: Once the data has been matched, the system will retrieve all the data from the database.
Output: The system would then output the data with the query terms highlighted in bold.
Close: Once all the data has been retrieved and outputted, the information retrieval system will close.
Where is Information retrieval used?
Information retrieval is used in different forms of machine learning, such as question answering systems, web crawling systems, and many more. It can be used in almost any domain where humans generate queries. You can use it to find information from a database, books, or any other sources. Let us look at different types of systems where information retrieval could be used.
Question Answering Systems: Question Answering Systems are computer systems that can answer questions in natural language. The questions could be about a topic, past events, etc. The most common example of a question answering system is a virtual assistant.
Web Crawling Systems: Web Crawling Systems are computer programs that search the World Wide Web (WWW) to create a massive searchable database. They go through different web pages to find links to other pages, words and phrases that appear on those pages, and information about the authors of the pages.
Natural Language Processing: Natural Language Processing is the field of creating computer systems that can understand human languages. You can use information retrieval in natural language processing to find different meanings of a sentence or a word.
Semantics: Semantics is the study of the importance of words. You can use information retrieval for semantic analysis.
Types of Information Retrieval model
Information retrieval is a broad field that has many subfields. Each subfield studies a different aspect of information retrieval and brings new and creative ways to perform information retrieval. Let us look at three other information retrieval models that could be used in machine learning.
Classic IR Model
This model is used when there are no restrictions on the type of data or its format. It uses boolean operators such as AND, OR, and NOT to retrieve relevant results from large volumes of data. This model is based on indexing techniques that help to identify keywords contained in documents to direct users toward specific documents based on their relevance.
Non-Classic IR Model
This model has been developed to deal with large volumes of unstructured text such as e-mails, web pages, and other documents that cannot be indexed using CIRM techniques. The main features of this model include clustering techniques for identifying similar documents, extraction techniques for extracting relevant contents from clusters, and ranking techniques for ranking documents based on their relevancy score.
Alternative IR Model
The Alternative Information Retrieval Model (AIR) is a theoretical framework that has been used to account for the information retrieval behavior of users in a variety of different domains. The AIR model is based on two assumptions:
- Users will search for valuable and relevant information to their needs and wishes.
- Users will find the best match between their needs and the information they are searching for.
Difference between Information Retrieval and Data Retrieval
Information retrieval and data retrieval are two different concepts.
Data retrieval is finding and acquiring data from other sources such as web pages, images, documents, etc. Information retrieval is finding relevant information from a large set of data. It can be used for any purpose where there are queries generated by humans, such as web crawling, question answering, and so on.
Information retrieval uses various models to retrieve relevant results for a specific request. Data retrieval can be used for many purposes, such as finding information from a large data set. Data retrieval can be used to find information from extensive data collection.
Conclusion
Information retrieval is a broad field that applies to many subfields. It can be used in many forms of machine learning, such as natural language processing and question answering systems. It helps find data from large data sets with ease. It has helped to increase the performance of machines in many ways. We hope you now understand information retrieval and how it can be helpful in machine learning. Armed with this knowledge, you can be more aware of how it is used in various industries and how it can be applied more widely.
Software Quality Assurance:Ensuring Reliability &Performance
Software Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is one of the most important aspects of any software development project. But you might be skeptical about how important it is to have a QA team for your assignments because you think there are too many other things on your plate. Moreover, it would add more work to your team, which could cause you sleepless nights. Well, it's time to stop with all this thinking and start with proper planning for software testing to ensure that each of your projects will be delivered as expected by its customers/users.
Software QA professionals face a constantly changing landscape, making their job difficult because many products are never released. Still, QA professionals must remain persistent and take risks that can lead to failure. Still, they must never forget what matters: satisfying customers!
What is Software Quality Assurance?
Software quality assurance (SQA) is a process that helps to ensure the correctness, reliability, usability, and maintainability of software. If a program works correctly, the user will experience a satisfaction. If it does not work correctly, users will experience frustration. The process includes several activities: planning, analysis, design, testing, and documentation.
Software must be constructed so that it can be used by people who are not technical experts to operate it. This requires that the software be designed to be easy to use and understand. In addition, it must run on various platforms and systems. Finally, it must also be able to function as expected when all these factors are considered.
The goal of SQA is to make sure that your products meet their customers' expectations. This can be done in several ways:
- By ensuring that the requirements are understood and well-defined by all involved parties, including you and your stakeholders.
- By ensuring that there are no errors or omissions in the code.
- By performing regression testing to detect any new bugs that may have been introduced over time.
- Testing with real users and discovering if they have any concerns about your product.
Software Quality Assurance Importance
Quality assurance is an essential part of any software development process. In software development, quality assurance is the process of ensuring that a product meets its specified requirements. It involves many aspects, including testing, documentation and documentation review, regression testing, and others.
When developing a software product, it's not just about creating something that works - it's also about testing it to ensure it works properly. This requires you to test how well the software works, how well it performs under various conditions, and how robust it is against unexpected errors or bugs.
There are three main quality assurance tests: unit tests (end-to-end tests), integration tests, and system tests.
Unit tests check that each component works as expected.
Integration tests check whether multiple components work together correctly.
System tests check if all components work together as expected in a real-world scenario.
Software Quality Assurance Plan
A software quality assurance plan (SQAP) is a statement of how an organization ensures that its software product or system meets applicable standards. An SQAP should be developed for each product or system being developed, maintained, and operated.
The purpose of an SQAP is to provide clear direction on what needs to be done to ensure that the end product or system conforms to applicable standards. The plan documents and defines the roles and responsibilities of all parties involved in developing and implementing the program. The SQAP also describes the types of evidence required for meeting compliance requirements and maintenance activities necessary to maintain compliance.
The primary purpose of an SQAP is to provide direction on what needs to be done to ensure that products or systems meet applicable standards. An SQAP is a document that describes how an organization ensures that its products or systems meet applicable standards through testing processes, audits, reviews, and other means.
How Professionals Implement SAQ
Software quality assurance professionals implement software quality assurance processes to ensure the software quality produced by a software development organization. They evaluate, improve and extend the quality of software. They also help ensure that the requirements are met during the development process.
The role of a software quality assurance professional is to verify that a product meets its specifications and requirements before it is released to customers. This process includes reviewing documents such as test plans and cases to ensure they match the conditions. They may also check code for defects and fix them if necessary.
Software quality assurance professionals should know all phases of software development, including requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, and maintenance. This process is implemented through various methods, including testing, debugging, and documentation.
Software quality assurance involves the following steps:
First, identifying defects in software products using tests.
Analyzing data collected from tests to identify patterns that indicate the presence of defects.
Fixing defects identified by data analysis.
Documenting any changes made to the software during testing or after completion of testing.
Conclusion
Software quality assurance is, at its most basic level, a job that involves keeping an eye on the creation, modification, and usage of the software. There are many ways to accomplish this task from a structural standpoint. One way to ensure the quality of the software is by creating a software test plan. This is the first step in ensuring things work out for the best of your project. A comprehensive test plan can protect against pitfalls resulting from inferior code or poor development processes.
Without QA, the software risks not being fit for purpose and, therefore, not meeting the requirements. QA must test software and expose flaws so they can be corrected. The tests are created based on Test Requirements derived from the User Story or Feature Description. Tests must cover all of the specified features. Without comprehensive coverage, bugs will likely be missed resulting in poor-quality software. Setting up the environment for automated testing is a complex process. To support deployment, it requires a significant amount of stakeholder engagement to agree on the testing approach, test cases, and acceptance criteria.
Read More
Software Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is one of the most important aspects of any software development project. But you might be skeptical about how important it is to have a QA team for your assignments because you think there are too many other things on your plate. Moreover, it would add more work to your team, which could cause you sleepless nights. Well, it's time to stop with all this thinking and start with proper planning for software testing to ensure that each of your projects will be delivered as expected by its customers/users.
Software QA professionals face a constantly changing landscape, making their job difficult because many products are never released. Still, QA professionals must remain persistent and take risks that can lead to failure. Still, they must never forget what matters: satisfying customers!
What is Software Quality Assurance?
Software quality assurance (SQA) is a process that helps to ensure the correctness, reliability, usability, and maintainability of software. If a program works correctly, the user will experience a satisfaction. If it does not work correctly, users will experience frustration. The process includes several activities: planning, analysis, design, testing, and documentation.
Software must be constructed so that it can be used by people who are not technical experts to operate it. This requires that the software be designed to be easy to use and understand. In addition, it must run on various platforms and systems. Finally, it must also be able to function as expected when all these factors are considered.
The goal of SQA is to make sure that your products meet their customers' expectations. This can be done in several ways:
- By ensuring that the requirements are understood and well-defined by all involved parties, including you and your stakeholders.
- By ensuring that there are no errors or omissions in the code.
- By performing regression testing to detect any new bugs that may have been introduced over time.
- Testing with real users and discovering if they have any concerns about your product.
Software Quality Assurance Importance
Quality assurance is an essential part of any software development process. In software development, quality assurance is the process of ensuring that a product meets its specified requirements. It involves many aspects, including testing, documentation and documentation review, regression testing, and others.
When developing a software product, it's not just about creating something that works - it's also about testing it to ensure it works properly. This requires you to test how well the software works, how well it performs under various conditions, and how robust it is against unexpected errors or bugs.
There are three main quality assurance tests: unit tests (end-to-end tests), integration tests, and system tests.
Unit tests check that each component works as expected.
Integration tests check whether multiple components work together correctly.
System tests check if all components work together as expected in a real-world scenario.
Software Quality Assurance Plan
A software quality assurance plan (SQAP) is a statement of how an organization ensures that its software product or system meets applicable standards. An SQAP should be developed for each product or system being developed, maintained, and operated.
The purpose of an SQAP is to provide clear direction on what needs to be done to ensure that the end product or system conforms to applicable standards. The plan documents and defines the roles and responsibilities of all parties involved in developing and implementing the program. The SQAP also describes the types of evidence required for meeting compliance requirements and maintenance activities necessary to maintain compliance.
The primary purpose of an SQAP is to provide direction on what needs to be done to ensure that products or systems meet applicable standards. An SQAP is a document that describes how an organization ensures that its products or systems meet applicable standards through testing processes, audits, reviews, and other means.
How Professionals Implement SAQ
Software quality assurance professionals implement software quality assurance processes to ensure the software quality produced by a software development organization. They evaluate, improve and extend the quality of software. They also help ensure that the requirements are met during the development process.
The role of a software quality assurance professional is to verify that a product meets its specifications and requirements before it is released to customers. This process includes reviewing documents such as test plans and cases to ensure they match the conditions. They may also check code for defects and fix them if necessary.
Software quality assurance professionals should know all phases of software development, including requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, and maintenance. This process is implemented through various methods, including testing, debugging, and documentation.
Software quality assurance involves the following steps:
First, identifying defects in software products using tests.
Analyzing data collected from tests to identify patterns that indicate the presence of defects.
Fixing defects identified by data analysis.
Documenting any changes made to the software during testing or after completion of testing.
Conclusion
Software quality assurance is, at its most basic level, a job that involves keeping an eye on the creation, modification, and usage of the software. There are many ways to accomplish this task from a structural standpoint. One way to ensure the quality of the software is by creating a software test plan. This is the first step in ensuring things work out for the best of your project. A comprehensive test plan can protect against pitfalls resulting from inferior code or poor development processes.
Without QA, the software risks not being fit for purpose and, therefore, not meeting the requirements. QA must test software and expose flaws so they can be corrected. The tests are created based on Test Requirements derived from the User Story or Feature Description. Tests must cover all of the specified features. Without comprehensive coverage, bugs will likely be missed resulting in poor-quality software. Setting up the environment for automated testing is a complex process. To support deployment, it requires a significant amount of stakeholder engagement to agree on the testing approach, test cases, and acceptance criteria.
Data Encryption: Securing Information with Encryption Keys
Data Encryption
In the digital world, data encryption means encrypting sensitive data so that only authorized parties can access it. In the physical world, we're more familiar with personal security — like locking your bike or car. But what about our data? Data encryption involves transforming information into an unreadable form, thus protecting the information from being accessed by unauthorized individuals.
What is Data Encryption?
Data encryption is the process of encoding the contents of a file or message using an algorithm so that only authorized parties can access it. Data encryption uses a key to encrypt and decrypt the data. This key is generally stored on a separate piece of hardware known as a "cipher text," which is used for decryption. The key is then protected with an authentication code, which is used to verify that the key has not been tampered with since it was created.
Data encryption is used to secure sensitive information such as credit card numbers, medical records, and private bank account numbers from hackers who would otherwise be able to access them through unauthorized means.
Data encryption also prevents unauthorized people from reading your emails or texts on your phone. It's important to note that not all data encryption software is equal, so make sure you choose one that's compatible with your device before purchasing it!
How does Data Encryption Work?
Data Encryption, or Data Encryption Algorithm (DEA), is a method of encrypting data so that only authorized recipients can read it. The DEA is one of several encryption types used to secure data and protect confidentiality.
Data encryption works by scrambling the data into seemingly random sequences of numbers. Each time the data needs to be decrypted, it must be converted back into readable text. The purpose of this process is to make it difficult for anyone but the intended recipient to decipher the original message.
Data Encryption Algorithms are designed to be secure and efficient at protecting information from unauthorized parties such as hackers and governments. They do this by taking advantage of mathematical properties and vital public technologies that have been used for hundreds, if not thousands, of years.
What are the Benefits of Data Encryption?
Data Protection
Data encryption provides a high level of security for sensitive information. For example, data encryption prevents hackers from accessing personal information such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and bank account numbers by stripping them down to their binary form so that they cannot be read by software.
Authentication Protection
Encrypting files with a password prevents anyone from using the same password to access those files later. If you forget your password, no one will be able to get into your encrypted files without knowing your secret decryption key (not even you!). This means people cannot use stolen passwords to decrypt files without your permission!
Confidentiality Protection
Data encryption ensures that only authorized users can access specific files or information stored on a computer or storage device (such as USB sticks).
Data Integrity
Data that has been encrypted is entirely secure from being read, altered, or destroyed. Any third party cannot access it without the proper decryption keys.
Encryption Keys
The encryption key is a secret code that allows you to access your data. The encryption key can be generated by a user or automatically generated by the device. When you encrypt a file with an encryption key, the file becomes unreadable by anyone but you.
The encryption key is created in advance and stored on the device with which it will be used. The encryption key is usually held as part of the operating system's protected storage, so it cannot be accessed directly through any other application program.
There are two types of encryption keys: private and public. A private key only works with your computer or device and can only be used to decrypt files encrypted with that same private key. On the other hand, public keys can be used by anyone who has access to them and allows them to encrypt files using their public key instead of their private key.
When you use a public or private key to encrypt a file, nobody except those with access to those keys can open or read that file without knowing its password or passcode (unless they see another person's password).
Why is Data Encryption Necessary Today?
Data encryption is necessary today because the amount of data that needs to be stored is increasing at an alarming rate. The most common example of this is the growth in the number of devices in our lives that are connected to the internet. Therefore, one would expect their storage requirements to increase as these devices get more powerful. However, that's not necessarily true.
The fact is that there are now so many devices on the market that it's difficult for manufacturers to provide all of them with enough storage space to keep them running smoothly. That's why most modern smartphones and tablets come with internal memory capacities measured in gigabytes rather than terabytes — or even just gigabytes — despite having far more features than older models.
This trend will continue as more people adopt smartphones and tablets worldwide and create new web-connected devices such as home appliances and cars. The result will be an explosion in the storage capacity needed by those devices. And since there's no way to predict what size this capacity will be, data encryption is necessary today because we need a means of ensuring confidentiality while storing all those bits on our devices' hard drives.
Data encryption is essential and something that many of us take for granted. However, that might turn out to be a mistake. We think data encryption will become a more common and important topic as time goes on—and proper education will be vital to increasing security across the board.
Without a doubt, encryption is vital to the integrity of the business. It's an important aspect that can protect you from danger and help ensure your (and your customers') privacy. But it's not without its faults. Encryption methods are imperfect, and a determined hacker could still access sensitive data, even if encrypted. However, encryption is necessary for information management and will remain so for the foreseeable future.
Read More
Data Encryption
In the digital world, data encryption means encrypting sensitive data so that only authorized parties can access it. In the physical world, we're more familiar with personal security — like locking your bike or car. But what about our data? Data encryption involves transforming information into an unreadable form, thus protecting the information from being accessed by unauthorized individuals.
What is Data Encryption?
Data encryption is the process of encoding the contents of a file or message using an algorithm so that only authorized parties can access it. Data encryption uses a key to encrypt and decrypt the data. This key is generally stored on a separate piece of hardware known as a "cipher text," which is used for decryption. The key is then protected with an authentication code, which is used to verify that the key has not been tampered with since it was created.
Data encryption is used to secure sensitive information such as credit card numbers, medical records, and private bank account numbers from hackers who would otherwise be able to access them through unauthorized means.
Data encryption also prevents unauthorized people from reading your emails or texts on your phone. It's important to note that not all data encryption software is equal, so make sure you choose one that's compatible with your device before purchasing it!
How does Data Encryption Work?
Data Encryption, or Data Encryption Algorithm (DEA), is a method of encrypting data so that only authorized recipients can read it. The DEA is one of several encryption types used to secure data and protect confidentiality.
Data encryption works by scrambling the data into seemingly random sequences of numbers. Each time the data needs to be decrypted, it must be converted back into readable text. The purpose of this process is to make it difficult for anyone but the intended recipient to decipher the original message.
Data Encryption Algorithms are designed to be secure and efficient at protecting information from unauthorized parties such as hackers and governments. They do this by taking advantage of mathematical properties and vital public technologies that have been used for hundreds, if not thousands, of years.
What are the Benefits of Data Encryption?
Data Protection
Data encryption provides a high level of security for sensitive information. For example, data encryption prevents hackers from accessing personal information such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and bank account numbers by stripping them down to their binary form so that they cannot be read by software.
Authentication Protection
Encrypting files with a password prevents anyone from using the same password to access those files later. If you forget your password, no one will be able to get into your encrypted files without knowing your secret decryption key (not even you!). This means people cannot use stolen passwords to decrypt files without your permission!
Confidentiality Protection
Data encryption ensures that only authorized users can access specific files or information stored on a computer or storage device (such as USB sticks).
Data Integrity
Data that has been encrypted is entirely secure from being read, altered, or destroyed. Any third party cannot access it without the proper decryption keys.
Encryption Keys
The encryption key is a secret code that allows you to access your data. The encryption key can be generated by a user or automatically generated by the device. When you encrypt a file with an encryption key, the file becomes unreadable by anyone but you.
The encryption key is created in advance and stored on the device with which it will be used. The encryption key is usually held as part of the operating system's protected storage, so it cannot be accessed directly through any other application program.
There are two types of encryption keys: private and public. A private key only works with your computer or device and can only be used to decrypt files encrypted with that same private key. On the other hand, public keys can be used by anyone who has access to them and allows them to encrypt files using their public key instead of their private key.
When you use a public or private key to encrypt a file, nobody except those with access to those keys can open or read that file without knowing its password or passcode (unless they see another person's password).
Why is Data Encryption Necessary Today?
Data encryption is necessary today because the amount of data that needs to be stored is increasing at an alarming rate. The most common example of this is the growth in the number of devices in our lives that are connected to the internet. Therefore, one would expect their storage requirements to increase as these devices get more powerful. However, that's not necessarily true.
The fact is that there are now so many devices on the market that it's difficult for manufacturers to provide all of them with enough storage space to keep them running smoothly. That's why most modern smartphones and tablets come with internal memory capacities measured in gigabytes rather than terabytes — or even just gigabytes — despite having far more features than older models.
This trend will continue as more people adopt smartphones and tablets worldwide and create new web-connected devices such as home appliances and cars. The result will be an explosion in the storage capacity needed by those devices. And since there's no way to predict what size this capacity will be, data encryption is necessary today because we need a means of ensuring confidentiality while storing all those bits on our devices' hard drives.
Data encryption is essential and something that many of us take for granted. However, that might turn out to be a mistake. We think data encryption will become a more common and important topic as time goes on—and proper education will be vital to increasing security across the board.
Without a doubt, encryption is vital to the integrity of the business. It's an important aspect that can protect you from danger and help ensure your (and your customers') privacy. But it's not without its faults. Encryption methods are imperfect, and a determined hacker could still access sensitive data, even if encrypted. However, encryption is necessary for information management and will remain so for the foreseeable future.
Cloud storage enables secure, scalable, and remote access.
Cloud Storage and its Importance
Cloud storage plays a vital role in our day-to-day lives. This is evident from the rapid growth of cloud storage providers. Cloud-based storage providers have transformed how we save data, store private information, and transfer files to other locations. Cloud storage is the new hot sector, with all the companies jumping on the bandwagon. In this digital age, where everything is online, we want to save and keep all our data safe. Unfortunately, there are many instances in which we might lose all our files or data if we don't have a good backup in place! But what exactly is cloud storage? How does it work? Continue the blog to learn about these.
What is Cloud Storage?
Cloud storage is a type of computer storage that is accessible over the Internet. It is part of the cloud computing industry, including server hosting, network storage, and data management. Cloud storage differs from file servers and other types of centralized storage in that it is not owned by an organization or group but rather by a third-party provider who has access to your data as needed for their business purpose.
Cloud storage services typically allow users to store files in one place to access them anywhere on any device. They may also provide tools such as email, instant messaging, and calendars. Cloud storage can be accessed through web browsers or mobile apps on multiple computers and smartphones.
Cloud services are convenient because they allow you to store large amounts of data without worrying about maintaining physical space or spending money on hardware upgrades. Users can also pay only for what they use, unlike traditional methods where they purchase hard drives or other components upfront and pay for additional space yearly as their needs grow.
What is Cloud?
A cloud is a large data center that can be accessed remotely. It allows your application to run without the need for you to be physically present at a particular location.
For example, your software may only be used at home or work. You don't need to worry about transporting or storing data locally since it will all be stored in the cloud.
The benefit of using cloud computing is that you don't need to worry about storage space or maintenance costs since the company handling the storage and care will do it for you.
The Importance of Cloud Storage
Cloud data storage is generally less expensive than on-premises data storage. This is one of the most significant advantages of cloud data storage.
In addition, cloud data storage offers scalability for your business as your data storage needs increase. This also depends on which provider you choose to store your data. There are various storage options to choose from in cloud data storage. Cloud data storage can store and transfer multiple business data, including sensitive data.
In addition, cloud data storage offers data accessibility from any device connected to the internet. This can be particularly useful for businesses that want to give their employees the freedom to work remotely.
How does Cloud Storage work?
Cloud storage works on a different mechanism as compared to traditional data storage. Cloud-based storage works on a multi-tenant architecture, meaning they have multiple clients accessing their servers from a shared environment. This can be compared to a hotel where all the guests have access to the same kitchen and dining area.
Cloud storage uses a single system for storing, managing, and protecting data for multiple clients. The system is highly scalable and can quickly expand to accommodate increased customer demand.
There are different types of storage offered by cloud providers. While some offer only storage services, others also provide backup services.
The General Architecture of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage architecture comprises applications, networks, operating systems, hypervisors, and storage.
Applications consist of software used in storing and managing data.
The network is the interconnection between the client, application, and data center.
Operating systems are software that controls the hardware and software of the computer.
Hypervisors are software applications that manage virtual machines. Finally, storage is the place where data is stored.
Types of Cloud Service
There are many cloud storage services:
Software as a Service (SaaS): This service is used for business software. The software is hosted in the cloud and accessed over the internet by users. Software as a Service (SaaS) includes marketing and sales automation, human resource software, financial management software, etc.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS is a cloud service that gives all the tools one needs to build and run an application. This includes a programming language, a code editor, a runtime, a database, a file system, and an execution environment.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS is a cloud service that provides the infrastructure needed to run an application. This includes virtual machines, networks, storage, and load balancers.
Cloud Storage Providers
Google - The most popular cloud storage service is Google Drive. Google Drive comes with 15 GB of free cloud storage. Many users use Google Drive because of its simplicity and ease of use.
Amazon - Amazon comes with free cloud storage with 5 GB of free space for users. It also allows you to earn more free Amazon Drive space. You can earn up to 50 GB of free Amazon Drive space by participating in their referral program.
Microsoft - Microsoft OneDrive comes with 15 GB of free cloud storage space. You can refer your friends and earn an additional 5 GB of space.
Advantages of Cloud Storage
Cost Effective - Cloud storage can be much less expensive than traditional data storage.
Scalability - Cloud storage can scale as your needs change.
Convenience - Cloud storage can be accessed from any device.
Security - Cloud storage offers a high level of security and compliance with industry standards.
No upfront cost - You don't have to spend money to implement an effective backup.
Available as a service - Companies that provide cloud storage services make their product available, so you only pay for what you use.
Offsite backup - Cloud storage offers a convenient way to keep your essential files safe during a natural disaster.
No equipment - You don't have to purchase the hardware to store data onsite.
No technical knowledge - You don't have to have any special knowledge to use cloud storage.
Safety - Cloud storage services keep your data in a remote location. Hence, they're safe in case of a fire or other disaster at your business.
Variety of providers - A variety of providers offer cloud storage services, so you have many options when choosing a provider.
Conclusion
Cloud storage has become an essential part of business operations. It has proven a reliable and cost-effective way to store and share data. The wide range of providers and the growing demand for cloud storage are indicators of the growth of this sector.
Cloud storage offers an easy way to share data with partners and co-workers. It also makes it easier for remote employees to access files from home. Cloud storage is helpful for businesses that need extra storage space, but don-t have room for servers.
It's also beneficial for people who need to store sensitive information on an external server. Cloud storage is widely used for storing personal data like photos, videos, and emails. In addition, cloud storage lets you access your data from anywhere, on any device. These benefits make cloud storage an excellent choice for anyone who needs to store data online.
Read More
Cloud Storage and its Importance
Cloud storage plays a vital role in our day-to-day lives. This is evident from the rapid growth of cloud storage providers. Cloud-based storage providers have transformed how we save data, store private information, and transfer files to other locations. Cloud storage is the new hot sector, with all the companies jumping on the bandwagon. In this digital age, where everything is online, we want to save and keep all our data safe. Unfortunately, there are many instances in which we might lose all our files or data if we don't have a good backup in place! But what exactly is cloud storage? How does it work? Continue the blog to learn about these.
What is Cloud Storage?
Cloud storage is a type of computer storage that is accessible over the Internet. It is part of the cloud computing industry, including server hosting, network storage, and data management. Cloud storage differs from file servers and other types of centralized storage in that it is not owned by an organization or group but rather by a third-party provider who has access to your data as needed for their business purpose.
Cloud storage services typically allow users to store files in one place to access them anywhere on any device. They may also provide tools such as email, instant messaging, and calendars. Cloud storage can be accessed through web browsers or mobile apps on multiple computers and smartphones.
Cloud services are convenient because they allow you to store large amounts of data without worrying about maintaining physical space or spending money on hardware upgrades. Users can also pay only for what they use, unlike traditional methods where they purchase hard drives or other components upfront and pay for additional space yearly as their needs grow.
What is Cloud?
A cloud is a large data center that can be accessed remotely. It allows your application to run without the need for you to be physically present at a particular location.
For example, your software may only be used at home or work. You don't need to worry about transporting or storing data locally since it will all be stored in the cloud.
The benefit of using cloud computing is that you don't need to worry about storage space or maintenance costs since the company handling the storage and care will do it for you.
The Importance of Cloud Storage
Cloud data storage is generally less expensive than on-premises data storage. This is one of the most significant advantages of cloud data storage.
In addition, cloud data storage offers scalability for your business as your data storage needs increase. This also depends on which provider you choose to store your data. There are various storage options to choose from in cloud data storage. Cloud data storage can store and transfer multiple business data, including sensitive data.
In addition, cloud data storage offers data accessibility from any device connected to the internet. This can be particularly useful for businesses that want to give their employees the freedom to work remotely.
How does Cloud Storage work?
Cloud storage works on a different mechanism as compared to traditional data storage. Cloud-based storage works on a multi-tenant architecture, meaning they have multiple clients accessing their servers from a shared environment. This can be compared to a hotel where all the guests have access to the same kitchen and dining area.
Cloud storage uses a single system for storing, managing, and protecting data for multiple clients. The system is highly scalable and can quickly expand to accommodate increased customer demand.
There are different types of storage offered by cloud providers. While some offer only storage services, others also provide backup services.
The General Architecture of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage architecture comprises applications, networks, operating systems, hypervisors, and storage.
Applications consist of software used in storing and managing data.
The network is the interconnection between the client, application, and data center.
Operating systems are software that controls the hardware and software of the computer.
Hypervisors are software applications that manage virtual machines. Finally, storage is the place where data is stored.
Types of Cloud Service
There are many cloud storage services:
Software as a Service (SaaS): This service is used for business software. The software is hosted in the cloud and accessed over the internet by users. Software as a Service (SaaS) includes marketing and sales automation, human resource software, financial management software, etc.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS is a cloud service that gives all the tools one needs to build and run an application. This includes a programming language, a code editor, a runtime, a database, a file system, and an execution environment.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS is a cloud service that provides the infrastructure needed to run an application. This includes virtual machines, networks, storage, and load balancers.
Cloud Storage Providers
Google - The most popular cloud storage service is Google Drive. Google Drive comes with 15 GB of free cloud storage. Many users use Google Drive because of its simplicity and ease of use.
Amazon - Amazon comes with free cloud storage with 5 GB of free space for users. It also allows you to earn more free Amazon Drive space. You can earn up to 50 GB of free Amazon Drive space by participating in their referral program.
Microsoft - Microsoft OneDrive comes with 15 GB of free cloud storage space. You can refer your friends and earn an additional 5 GB of space.
Advantages of Cloud Storage
Cost Effective - Cloud storage can be much less expensive than traditional data storage.
Scalability - Cloud storage can scale as your needs change.
Convenience - Cloud storage can be accessed from any device.
Security - Cloud storage offers a high level of security and compliance with industry standards.
No upfront cost - You don't have to spend money to implement an effective backup.
Available as a service - Companies that provide cloud storage services make their product available, so you only pay for what you use.
Offsite backup - Cloud storage offers a convenient way to keep your essential files safe during a natural disaster.
No equipment - You don't have to purchase the hardware to store data onsite.
No technical knowledge - You don't have to have any special knowledge to use cloud storage.
Safety - Cloud storage services keep your data in a remote location. Hence, they're safe in case of a fire or other disaster at your business.
Variety of providers - A variety of providers offer cloud storage services, so you have many options when choosing a provider.
Conclusion
Cloud storage has become an essential part of business operations. It has proven a reliable and cost-effective way to store and share data. The wide range of providers and the growing demand for cloud storage are indicators of the growth of this sector.
Cloud storage offers an easy way to share data with partners and co-workers. It also makes it easier for remote employees to access files from home. Cloud storage is helpful for businesses that need extra storage space, but don-t have room for servers.
It's also beneficial for people who need to store sensitive information on an external server. Cloud storage is widely used for storing personal data like photos, videos, and emails. In addition, cloud storage lets you access your data from anywhere, on any device. These benefits make cloud storage an excellent choice for anyone who needs to store data online.
Everything You Need to Know About Kanban for Better Workflow
Everything You Need to Know About Kanban
Kanban is a lean management approach used in agile software development. Kanban originated as a project management tool and has been adapted to work with product development teams. It allows you to visualize the project's workflow and improve efficiency by visualizing what's next. So, is Kanban the proper optimization solution for your business? If the answer is yes, you'll love this article! In this article, we'll look at what Kanban is and why it's been so popular with different engineering teams. We'll also examine some of its advantages and disadvantages so that you can decide whether it's a good fit for your business.
What is Kanban?
Kanban is a visual management technique that helps teams focus on what they must do next to meet their goals. It's a popular way to help teams and individuals implement agile software development practices such as pair programming, test-driven development, continuous integration, and continuous deployment.
A Kanban board is a board that displays information in the form of cards or post-its, which represent work items (also called "tasks") that are ready for action or have just been completed. The cards can be arranged into columns, rows, and groups to show different levels of priority — or a project's velocity — and can be moved around when a card is completed or needs attention.
Kanban boards are typically used with agile software development tools like Scrum. Still, they can also be used in other environments where teams must keep track of project progress.
History of Kanban
Toyota first used the Kanban method in the car manufacturing industry in the 1940s. At that time, Kanban was used to visualize the workflow of the production line and identify the bottleneck.
The car industry was the first to adopt the Kanban method. It was initially used to visualize the workflow of the production line and place the backup in the system. This same method can be applied to any industry to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and create a more sustainable process.
How Does the Kanban Method Work?
The Kanban method uses visual signals and standardized work to create a smooth and predictable workflow. The Kanban method has three core elements: The product is visualized on a card placed on a Kanban board.
The Kanban board: This is a board that is displayed in the team's workspace. The Kanban board has columns that represent each stage of the workflow. –
A pull system: The product moves from one stage to another based on demand. When a team member has completed the previous task, they grab the next card from the top of the workflow. This ensures that the team is only working on the product when needed.
Visual signals: Visual signals that describe what's happening in the workflow can help to make the Kanban board interactive and engaging.
Why Kanban Method Is Popular?
The Kanban method improves workflow and efficiency by creating a visual system for tracking and prioritizing tasks. Kanban is interactive and engaging and provides a visual representation of what needs to be done. Kanban can be displayed in the team workspace or in a public space where team members, stakeholders, and other members of the organization can engage with the board.
Advantage of Kanban
Improved workflow: Kanban boards allow teams to visualize their workflow and identify bottlenecks and other factors that may slow them down. They also enable managers to see where their team members spend most of their time and identify areas that could use improvement.
Visibility: Kanban boards are visible to everyone on the team and anyone who engages with the board. This transparency creates a shared language around the project. In addition, it allows stakeholders and team members to understand where their work fits into the bigger picture.
Visualization: Kanban boards are tools that allow teams to create mental models of the project, visualize their workflow, and identify points of inefficiency.
Disadvantage of Kanban
Rigidity: Kanban boards are generally static and don't account for fluctuations in the amount of work being completed or the availability of team members. This can create rigidity in the workflow that can be difficult to adjust when the situation changes.
Limitations: Kanban boards are generally created and maintained by team members with specialized roles in the project. This can create an environment where other stakeholders feel left out of the process.
Standardization: Kanban is a standardized process that doesn't allow iteration and flexibility. This can make it difficult to adjust when a team member is out of commission, or there is a change in the project. It can also make it difficult for stakeholders to get involved in the process and contribute to the project.
Conclusion
Kanban can be a valuable tool in managing a design workflow. It's simple and easy to implement, and it should help you improve your organization's operation of projects from start to finish.
However, don't underestimate the power of Kanban. It's one of those pieces of software that can help you work faster and more effectively when used correctly in your workflow. So if you're looking to improve your productivity and streamline your workflow, consider giving Kanban a try. You might like it!
Read More
Everything You Need to Know About Kanban
Kanban is a lean management approach used in agile software development. Kanban originated as a project management tool and has been adapted to work with product development teams. It allows you to visualize the project's workflow and improve efficiency by visualizing what's next. So, is Kanban the proper optimization solution for your business? If the answer is yes, you'll love this article! In this article, we'll look at what Kanban is and why it's been so popular with different engineering teams. We'll also examine some of its advantages and disadvantages so that you can decide whether it's a good fit for your business.
What is Kanban?
Kanban is a visual management technique that helps teams focus on what they must do next to meet their goals. It's a popular way to help teams and individuals implement agile software development practices such as pair programming, test-driven development, continuous integration, and continuous deployment.
A Kanban board is a board that displays information in the form of cards or post-its, which represent work items (also called "tasks") that are ready for action or have just been completed. The cards can be arranged into columns, rows, and groups to show different levels of priority — or a project's velocity — and can be moved around when a card is completed or needs attention.
Kanban boards are typically used with agile software development tools like Scrum. Still, they can also be used in other environments where teams must keep track of project progress.
History of Kanban
Toyota first used the Kanban method in the car manufacturing industry in the 1940s. At that time, Kanban was used to visualize the workflow of the production line and identify the bottleneck.
The car industry was the first to adopt the Kanban method. It was initially used to visualize the workflow of the production line and place the backup in the system. This same method can be applied to any industry to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and create a more sustainable process.
How Does the Kanban Method Work?
The Kanban method uses visual signals and standardized work to create a smooth and predictable workflow. The Kanban method has three core elements: The product is visualized on a card placed on a Kanban board.
The Kanban board: This is a board that is displayed in the team's workspace. The Kanban board has columns that represent each stage of the workflow. –
A pull system: The product moves from one stage to another based on demand. When a team member has completed the previous task, they grab the next card from the top of the workflow. This ensures that the team is only working on the product when needed.
Visual signals: Visual signals that describe what's happening in the workflow can help to make the Kanban board interactive and engaging.
Why Kanban Method Is Popular?
The Kanban method improves workflow and efficiency by creating a visual system for tracking and prioritizing tasks. Kanban is interactive and engaging and provides a visual representation of what needs to be done. Kanban can be displayed in the team workspace or in a public space where team members, stakeholders, and other members of the organization can engage with the board.
Advantage of Kanban
Improved workflow: Kanban boards allow teams to visualize their workflow and identify bottlenecks and other factors that may slow them down. They also enable managers to see where their team members spend most of their time and identify areas that could use improvement.
Visibility: Kanban boards are visible to everyone on the team and anyone who engages with the board. This transparency creates a shared language around the project. In addition, it allows stakeholders and team members to understand where their work fits into the bigger picture.
Visualization: Kanban boards are tools that allow teams to create mental models of the project, visualize their workflow, and identify points of inefficiency.
Disadvantage of Kanban
Rigidity: Kanban boards are generally static and don't account for fluctuations in the amount of work being completed or the availability of team members. This can create rigidity in the workflow that can be difficult to adjust when the situation changes.
Limitations: Kanban boards are generally created and maintained by team members with specialized roles in the project. This can create an environment where other stakeholders feel left out of the process.
Standardization: Kanban is a standardized process that doesn't allow iteration and flexibility. This can make it difficult to adjust when a team member is out of commission, or there is a change in the project. It can also make it difficult for stakeholders to get involved in the process and contribute to the project.
Conclusion
Kanban can be a valuable tool in managing a design workflow. It's simple and easy to implement, and it should help you improve your organization's operation of projects from start to finish.
However, don't underestimate the power of Kanban. It's one of those pieces of software that can help you work faster and more effectively when used correctly in your workflow. So if you're looking to improve your productivity and streamline your workflow, consider giving Kanban a try. You might like it!


.webp)
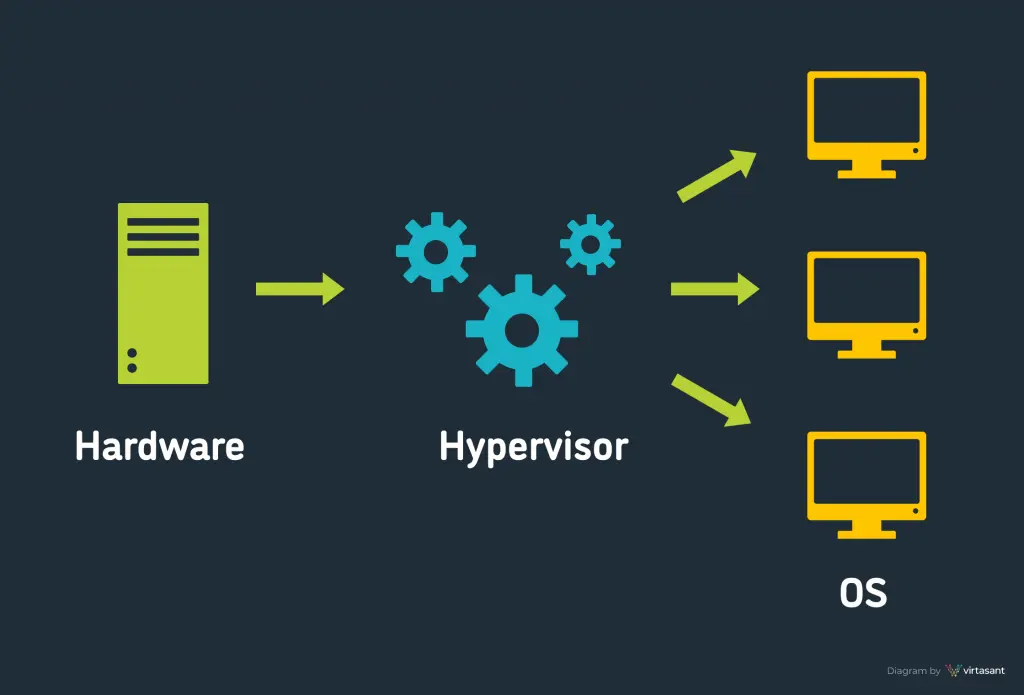

.jpg)



.png)










.png)





.png)
.png)











.png)




.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)




.png)
