Quick Enquiry Form
Categories
- Agile and Scrum (226)
- BigData (36)
- Business Analysis (94)
- Cirtix Client Administration (54)
- Cisco (63)
- Cloud Technology (96)
- Cyber Security (56)
- Data Science and Business Intelligence (53)
- Developement Courses (53)
- DevOps (16)
- Digital Marketing (58)
- Emerging Technology (198)
- IT Service Management (76)
- Microsoft (54)
- Other (395)
- Project Management (502)
- Quality Management (142)
- salesforce (67)
Latest posts
AI Interview Questions You Need..
What Do Hypervisors Do in..
5 Practical Tips to Help..
Free Resources
Subscribe to Newsletter
The Role of Ethical Hacking in Safeguarding Organizations.
In today's digital age, where data is the lifeblood of businesses and organizations, safeguarding sensitive information and digital assets has become paramount. With cyber threats constantly evolving in sophistication and scope, modern organizations face a formidable challenge in ensuring their cybersecurity defenses are robust and resilient. It is in this landscape that ethical hacking emerges as a crucial and proactive strategy for safeguarding organizations against cyberattacks.
Ethical hacking, often referred to as "white-hat" hacking, is a practice where skilled professionals employ their expertise to identify vulnerabilities, assess security measures, and test the resilience of an organization's digital infrastructure. Unlike malicious hackers who exploit weaknesses for personal gain, ethical hackers work with the explicit goal of fortifying cybersecurity defenses. In this exploration of "The Role of Ethical Hacking in Modern Organizations," we will delve into the vital functions and significance of ethical hacking in defending against cyber threats, securing sensitive data, and ensuring the continued success of businesses in an increasingly digital world.
Table of contents
-
The Ethical Hacker's Toolkit
-
Types of Ethical Hacking Services
-
The Ethical Hacker's Code of Ethics
-
Ethical Hacking for Regulatory Compliance
-
Ethical Hacking for IoT Security:
-
Challenges and Ethical Dilemmas in Ethical Hacking:
-
Collaboration Between Ethical Hackers and IT Security Teams
-
The Role of Continuous Monitoring in Ethical Hacking:
-
Future Trends in Ethical Hacking:
-
Conclusion
The Ethical Hacker's Toolkit
The ethical hacker's toolkit is a comprehensive set of specialized software and tools that enable cybersecurity professionals to simulate cyberattacks and uncover vulnerabilities within an organization's digital infrastructure. These tools range from network scanners, vulnerability assessment software, and password-cracking utilities to web application scanners and exploitation frameworks. By utilizing these tools, ethical hackers can systematically assess an organization's security posture, identify weaknesses, and help fortify defenses. These tools empower ethical hackers to probe systems, networks, and applications for vulnerabilities, ultimately assisting organizations in preemptively addressing potential security risks before malicious actors can exploit them.
In addition to the technical tools, the ethical hacker's toolkit also includes crucial skills like scripting and coding, which enable them to create custom solutions and adapt to unique security challenges. Continuous learning and staying updated on emerging threats and tools are paramount in this field, as the landscape of cybersecurity is ever-evolving. Ethical hackers are committed to maintaining the integrity of systems and data while using their toolkit responsibly and ethically to protect organizations from cyber threats.
Types of Ethical Hacking Services
-
Vulnerability Assessment:
-
Identifies weaknesses in systems, networks, and apps.
-
Prioritizes vulnerabilities based on severity.
-
Penetration Testing (Pen Testing):
-
Simulates real cyberattacks to test defenses.
-
Reveals how well security measures handle attacks.
-
Web Application Testing:
-
Focuses on securing websites and online services.
-
Checks for vulnerabilities like hacking attempts.
-
Wireless Network Testing:
-
Assesses Wi-Fi network security.
-
Looks for flaws that could allow unauthorized access.
-
Social Engineering Testing:
-
Evaluates susceptibility to tricks like phishing.
-
Educates employees on avoiding manipulation.
-
Mobile Application Security Testing:
-
Ensures security of mobile apps (iOS, Android).
-
Identifies vulnerabilities that could compromise data.
-
Cloud Security Assessment:
-
Examines security in cloud-based systems.
-
Checks settings, permissions, and access controls.
-
IoT Security Assessment:
-
Focuses on securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
-
Identifies vulnerabilities in interconnected devices.
-
Red Team Testing:
-
Simulates advanced cyberattacks.
-
Assesses overall security preparedness.
-
Incident Response Testing:
-
Helps organizations refine responses to security incidents.
-
Tests the ability to detect, mitigate, and recover from attacks.
The Ethical Hacker's Code of Ethics
Here are the key points of the Ethical Hacker's Code of Ethics in a simplified form:
-
Permission First: Ethical hackers must get permission before testing any computer system or network.
-
Respect Privacy: They should protect confidential information they encounter during their work.
-
No Data Damage: Their actions should not harm data, systems, or services.
-
Follow Laws: They must operate within legal boundaries and obey all relevant laws.
-
Report Vulnerabilities: Ethical hackers report any security flaws they find to the owners so they can fix them.
-
Keep Learning: They stay up-to-date with the latest cybersecurity knowledge and tools.
-
No Harmful Intent: Ethical hackers never use their skills for harm or personal gain.
-
Tools for Good: They use hacking tools only for legitimate testing purposes.
-
Education and Awareness: They often help educate others about cybersecurity and how to protect themselves.
-
Professional Integrity: Ethical hackers act with honesty, transparency, and integrity in all they do.
Ethical Hacking for Regulatory Compliance
Ethical hacking for regulatory compliance is a critical practice in today's data-driven and highly regulated business environment. With stringent regulatory standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS in place, organizations are obligated to safeguard sensitive data and maintain robust cybersecurity measures. Ethical hacking serves as a proactive approach to help organizations meet these regulatory requirements effectively. By simulating real cyberattacks and identifying vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them, ethical hackers play a pivotal role in assessing an organization's security infrastructure. Furthermore, ethical hacking engagements can be tailored to specific regulatory needs, focusing on the precise compliance requirements of an organization's industry and region. Through regular audits, meticulous documentation, and proactive risk mitigation, ethical hacking not only helps organizations maintain compliance but also enhances their cybersecurity posture and readiness for regulatory audits, ultimately ensuring the protection of sensitive data and the preservation of reputation and trust.
Ethical Hacking for IoT Security
Ethical hacking for IoT (Internet of Things) security involves a systematic and proactive approach to identifying and addressing vulnerabilities within IoT ecosystems to ensure their resilience against cyber threats. IoT devices, which include everything from smart thermostats and wearable devices to industrial sensors and autonomous vehicles, have become an integral part of modern life and business operations. However, their widespread adoption has also introduced new security risks due to their interconnected nature and diverse applications.
Ethical hackers, also known as white-hat hackers, use their skills and knowledge to simulate potential cyberattacks on IoT devices, networks, and platforms. Their primary objectives are to:
-
Identify Vulnerabilities: Ethical hackers employ various tools and techniques to identify vulnerabilities in IoT devices and the infrastructure supporting them. This may include analyzing device firmware, communication protocols, and cloud services.
-
Assess Security Controls: They evaluate the effectiveness of security controls implemented in IoT ecosystems. This involves examining access controls, encryption mechanisms, and authentication processes to ensure they are robust and resilient.
-
Test for Weaknesses: Ethical hackers conduct penetration testing to determine if unauthorized access, data breaches, or device manipulation is possible. They assess the IoT system's susceptibility to common cyber threats, such as malware, denial-of-service attacks, and physical tampering.
-
Provide Recommendations: Based on their findings, ethical hackers offer recommendations and solutions to mitigate identified vulnerabilities and enhance the overall security posture of IoT environments. This may include applying patches, strengthening access controls, or improving encryption methods.
-
Promote Security Awareness: Ethical hackers also play a role in educating IoT device manufacturers, developers, and users about best practices for security. They raise awareness about potential risks and the importance of regular updates and secure configurations.
-
Compliance and Standards: Ethical hacking for IoT security helps organizations align with industry-specific regulations and standards, ensuring compliance with data protection and privacy laws.
By conducting ethical hacking assessments on IoT systems, organizations can proactively address security weaknesses, minimize the risk of cyberattacks, protect sensitive data, and maintain the reliability of their IoT devices and networks. As the IoT landscape continues to evolve, ethical hacking remains an essential strategy for safeguarding these interconnected technologies and enhancing their resilience against emerging threats.
Challenges and Ethical Dilemmas in Ethical Hacking
-
Legal Boundaries:
-
Ethical hackers must stay within the law.
-
Distinguishing ethical hacking from illegal hacking can be tricky.
-
Authorization and Permission:
-
Getting clear permission to hack is crucial.
-
Obtaining authorization, especially in large organizations, can be challenging.
-
User Privacy and Data Protection:
-
Ethical hackers may encounter sensitive data during assessments.
-
Balancing the need to reveal vulnerabilities with protecting user privacy is a challenge.
-
Third-Party Systems:
-
Ethical hackers often assess external systems.
-
The ethical challenge arises when vulnerabilities are found in systems the organization doesn't control.
-
Full Disclosure vs. Responsible Disclosure:
-
Deciding whether to disclose vulnerabilities publicly (full disclosure) or privately to the organization (responsible disclosure) is a complex ethical choice.
-
It involves considering the impact on security and public awareness.
-
Technical Proficiency and Adaptation:
-
Staying technically proficient and updated is an ongoing challenge.
-
Ethical hackers must adapt to evolving cyber threats and technologies.
-
Neutrality and Objectivity:
-
Remaining neutral and objective during assessments is essential.
-
Personal biases or judgments can compromise the assessment's integrity.
Collaboration Between Ethical Hackers and IT Security Teams
Collaboration between ethical hackers and IT security teams is an indispensable partnership in the realm of cybersecurity. Ethical hackers, armed with their expertise and hacking skills, serve as the first line of defense by proactively identifying vulnerabilities within an organization's systems, networks, and applications. They conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to simulate real-world cyberattacks, pinpoint weaknesses, and report their findings. This critical information forms the foundation upon which IT security teams build their defensive strategies. IT security professionals then take the insights provided by ethical hackers and apply them to patch vulnerabilities, implement stronger security measures, and enhance overall cybersecurity posture. This synergy ensures a proactive and dynamic approach to cybersecurity, enabling organizations to stay one step ahead of malicious actors and respond effectively to emerging threats. Collaboration between ethical hackers and IT security teams is not merely a partnership; it is a fundamental strategy for organizations to fortify their digital defenses and protect sensitive data from evolving cyber threats.
The Role of Continuous Monitoring in Ethical Hacking:
Continuous monitoring plays a pivotal role in the realm of ethical hacking, serving as a proactive and dynamic approach to cybersecurity. Ethical hackers, also known as white-hat hackers, engage in ongoing monitoring to identify and address vulnerabilities within digital systems and networks. This process is multifaceted, involving several key aspects.
One of the primary functions of continuous monitoring is real-time threat detection. Ethical hackers employ a variety of tools and techniques to scrutinize network traffic, examine system logs, and analyze security alerts in real-time. This allows them to swiftly pinpoint and investigate any suspicious or potentially malicious activities as they occur, minimizing the risk of cyber threats going undetected.
Another critical element is vulnerability assessment. Ethical hackers routinely conduct scans to identify known vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses within an organization's systems, applications, and network configurations. This proactive approach ensures that vulnerabilities are promptly addressed, reducing the window of opportunity for malicious actors.
Furthermore, intrusion detection is a key aspect of continuous monitoring. Ethical hackers set up intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor for unauthorized access attempts and potential security breaches. These systems generate alerts when they detect unusual or suspicious behavior, allowing for immediate investigation and response.
Additionally, log analysis is integral to continuous monitoring. Ethical hackers meticulously review logs and audit trails to identify security incidents, track the source of attacks, and understand how vulnerabilities are exploited. This analysis provides valuable insights into the nature and origin of threats, aiding in the development of effective countermeasures.
Continuous monitoring also encompasses patch management, incident response planning, threat intelligence gathering, security awareness initiatives, and regular reporting of findings and recommendations. It ensures that organizations stay compliant with relevant regulations and standards while maintaining the security and privacy of sensitive data.
In conclusion, continuous monitoring is the heartbeat of ethical hacking, facilitating the early detection and mitigation of security vulnerabilities and threats. By adopting a proactive and ongoing approach to cybersecurity, ethical hackers work in tandem with IT security teams to fortify digital defenses, respond effectively to incidents, and adapt to the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. This collaborative effort ensures that organizations can protect their digital assets and data against an array of security challenges.
Future Trends in Ethical Hacking
Future trends in ethical hacking point to an exciting and evolving landscape in the realm of cybersecurity. As technology advances and cyber threats become more sophisticated, ethical hackers are continually adapting to stay ahead of malicious actors. Here are some key developments and trends shaping the future of ethical hacking:
-
AI and Machine Learning Integration: Ethical hackers are increasingly using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance their capabilities. These technologies can automate the detection of vulnerabilities, analyze large datasets for patterns, and even predict potential cyber threats. Ethical hackers will harness AI and ML to identify and respond to threats more effectively.
-
IoT and OT Security: With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) and Operational Technology (OT) devices, ethical hacking will extend its focus to these areas. Ethical hackers will specialize in assessing the security of smart devices, industrial control systems, and critical infrastructure, as these become prime targets for cyberattacks.
-
Cloud Security: As organizations migrate more of their data and operations to the cloud, ethical hackers will place greater emphasis on cloud security assessments. They will test configurations, access controls, and data protection mechanisms within cloud environments to ensure their resilience against cyber threats.
-
5G Network Vulnerabilities: The rollout of 5G networks will introduce new security challenges. Ethical hackers will explore potential vulnerabilities in the 5G infrastructure and associated technologies, ensuring the security of next-generation connectivity.
-
Zero Trust Security: The Zero Trust security model, which assumes that no one, whether inside or outside the organization, can be trusted, will gain prominence. Ethical hackers will play a key role in implementing and testing Zero Trust architectures to protect against insider threats and external breaches.
-
Biometric Security Testing: Ethical hackers will assess the security of biometric authentication methods, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, to ensure their resistance to spoofing and unauthorized access attempts.
-
Quantum Computing Threats: As quantum computing advances, it poses both opportunities and challenges in the cybersecurity space. Ethical hackers will explore potential threats posed by quantum computing and develop quantum-resistant encryption techniques.
-
Blockchain Security: As blockchain technology continues to be adopted in various industries, ethical hackers will assess the security of blockchain networks and smart contracts, ensuring their integrity and resilience against attacks.
-
Bug Bounty Programs: Bug bounty programs will become more prevalent, offering ethical hackers financial incentives to discover and report vulnerabilities in organizations' systems and applications. This trend encourages collaboration between hackers and organizations to enhance security.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ethical hackers will continue to play a crucial role in helping organizations meet evolving regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, CCPA, and other data protection laws, by conducting compliance assessments and security audits.
How to obtain Ethical Hacking certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Power BI Certification
-
Cyber Security : Ethical Hacking
Conclusion
In today's digitally interconnected world, the role of ethical hacking in modern organizations cannot be overstated. As businesses increasingly rely on digital infrastructure and data, they face a growing array of cyber threats that can jeopardize their operations, finances, and reputation. Ethical hacking, carried out by skilled professionals known as white-hat hackers, serves as a proactive defense against these threats.
Ethical hackers play a pivotal role in identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. Their expertise extends to various domains, including network security, web application security, and cloud security. By simulating cyberattacks and employing the same tactics as potential adversaries, ethical hackers provide organizations with invaluable insights into their security weaknesses.
Furthermore, ethical hacking is not just a one-time endeavor but a continuous process. It involves ongoing monitoring, vulnerability assessments, and response planning to stay ahead of emerging threats. Ethical hackers collaborate closely with IT security teams, ensuring that organizations can adapt and fortify their defenses in the face of evolving cyber challenges.
In conclusion, ethical hacking is not just a service but a strategic imperative for modern organizations. It empowers businesses to protect their digital assets, customer data, and brand reputation while demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity and responsible data management. In a world where cyber threats are ever-present, ethical hacking stands as a critical guardian of organizational integrity and security, safeguarding the future of businesses in the digital age.
Read More
In today's digital age, where data is the lifeblood of businesses and organizations, safeguarding sensitive information and digital assets has become paramount. With cyber threats constantly evolving in sophistication and scope, modern organizations face a formidable challenge in ensuring their cybersecurity defenses are robust and resilient. It is in this landscape that ethical hacking emerges as a crucial and proactive strategy for safeguarding organizations against cyberattacks.
Ethical hacking, often referred to as "white-hat" hacking, is a practice where skilled professionals employ their expertise to identify vulnerabilities, assess security measures, and test the resilience of an organization's digital infrastructure. Unlike malicious hackers who exploit weaknesses for personal gain, ethical hackers work with the explicit goal of fortifying cybersecurity defenses. In this exploration of "The Role of Ethical Hacking in Modern Organizations," we will delve into the vital functions and significance of ethical hacking in defending against cyber threats, securing sensitive data, and ensuring the continued success of businesses in an increasingly digital world.
Table of contents
-
The Ethical Hacker's Toolkit
-
Types of Ethical Hacking Services
-
The Ethical Hacker's Code of Ethics
-
Ethical Hacking for Regulatory Compliance
-
Ethical Hacking for IoT Security:
-
Challenges and Ethical Dilemmas in Ethical Hacking:
-
Collaboration Between Ethical Hackers and IT Security Teams
-
The Role of Continuous Monitoring in Ethical Hacking:
-
Future Trends in Ethical Hacking:
-
Conclusion
The Ethical Hacker's Toolkit
The ethical hacker's toolkit is a comprehensive set of specialized software and tools that enable cybersecurity professionals to simulate cyberattacks and uncover vulnerabilities within an organization's digital infrastructure. These tools range from network scanners, vulnerability assessment software, and password-cracking utilities to web application scanners and exploitation frameworks. By utilizing these tools, ethical hackers can systematically assess an organization's security posture, identify weaknesses, and help fortify defenses. These tools empower ethical hackers to probe systems, networks, and applications for vulnerabilities, ultimately assisting organizations in preemptively addressing potential security risks before malicious actors can exploit them.
In addition to the technical tools, the ethical hacker's toolkit also includes crucial skills like scripting and coding, which enable them to create custom solutions and adapt to unique security challenges. Continuous learning and staying updated on emerging threats and tools are paramount in this field, as the landscape of cybersecurity is ever-evolving. Ethical hackers are committed to maintaining the integrity of systems and data while using their toolkit responsibly and ethically to protect organizations from cyber threats.
Types of Ethical Hacking Services
-
Vulnerability Assessment:
-
Identifies weaknesses in systems, networks, and apps.
-
Prioritizes vulnerabilities based on severity.
-
-
Penetration Testing (Pen Testing):
-
Simulates real cyberattacks to test defenses.
-
Reveals how well security measures handle attacks.
-
-
Web Application Testing:
-
Focuses on securing websites and online services.
-
Checks for vulnerabilities like hacking attempts.
-
-
Wireless Network Testing:
-
Assesses Wi-Fi network security.
-
Looks for flaws that could allow unauthorized access.
-
-
Social Engineering Testing:
-
Evaluates susceptibility to tricks like phishing.
-
Educates employees on avoiding manipulation.
-
-
Mobile Application Security Testing:
-
Ensures security of mobile apps (iOS, Android).
-
Identifies vulnerabilities that could compromise data.
-
-
Cloud Security Assessment:
-
Examines security in cloud-based systems.
-
Checks settings, permissions, and access controls.
-
-
IoT Security Assessment:
-
Focuses on securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
-
Identifies vulnerabilities in interconnected devices.
-
-
Red Team Testing:
-
Simulates advanced cyberattacks.
-
Assesses overall security preparedness.
-
-
Incident Response Testing:
-
Helps organizations refine responses to security incidents.
-
Tests the ability to detect, mitigate, and recover from attacks.
-
The Ethical Hacker's Code of Ethics
Here are the key points of the Ethical Hacker's Code of Ethics in a simplified form:
-
Permission First: Ethical hackers must get permission before testing any computer system or network.
-
Respect Privacy: They should protect confidential information they encounter during their work.
-
No Data Damage: Their actions should not harm data, systems, or services.
-
Follow Laws: They must operate within legal boundaries and obey all relevant laws.
-
Report Vulnerabilities: Ethical hackers report any security flaws they find to the owners so they can fix them.
-
Keep Learning: They stay up-to-date with the latest cybersecurity knowledge and tools.
-
No Harmful Intent: Ethical hackers never use their skills for harm or personal gain.
-
Tools for Good: They use hacking tools only for legitimate testing purposes.
-
Education and Awareness: They often help educate others about cybersecurity and how to protect themselves.
-
Professional Integrity: Ethical hackers act with honesty, transparency, and integrity in all they do.
Ethical Hacking for Regulatory Compliance
Ethical hacking for regulatory compliance is a critical practice in today's data-driven and highly regulated business environment. With stringent regulatory standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS in place, organizations are obligated to safeguard sensitive data and maintain robust cybersecurity measures. Ethical hacking serves as a proactive approach to help organizations meet these regulatory requirements effectively. By simulating real cyberattacks and identifying vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them, ethical hackers play a pivotal role in assessing an organization's security infrastructure. Furthermore, ethical hacking engagements can be tailored to specific regulatory needs, focusing on the precise compliance requirements of an organization's industry and region. Through regular audits, meticulous documentation, and proactive risk mitigation, ethical hacking not only helps organizations maintain compliance but also enhances their cybersecurity posture and readiness for regulatory audits, ultimately ensuring the protection of sensitive data and the preservation of reputation and trust.
Ethical Hacking for IoT Security
Ethical hacking for IoT (Internet of Things) security involves a systematic and proactive approach to identifying and addressing vulnerabilities within IoT ecosystems to ensure their resilience against cyber threats. IoT devices, which include everything from smart thermostats and wearable devices to industrial sensors and autonomous vehicles, have become an integral part of modern life and business operations. However, their widespread adoption has also introduced new security risks due to their interconnected nature and diverse applications.
Ethical hackers, also known as white-hat hackers, use their skills and knowledge to simulate potential cyberattacks on IoT devices, networks, and platforms. Their primary objectives are to:
-
Identify Vulnerabilities: Ethical hackers employ various tools and techniques to identify vulnerabilities in IoT devices and the infrastructure supporting them. This may include analyzing device firmware, communication protocols, and cloud services.
-
Assess Security Controls: They evaluate the effectiveness of security controls implemented in IoT ecosystems. This involves examining access controls, encryption mechanisms, and authentication processes to ensure they are robust and resilient.
-
Test for Weaknesses: Ethical hackers conduct penetration testing to determine if unauthorized access, data breaches, or device manipulation is possible. They assess the IoT system's susceptibility to common cyber threats, such as malware, denial-of-service attacks, and physical tampering.
-
Provide Recommendations: Based on their findings, ethical hackers offer recommendations and solutions to mitigate identified vulnerabilities and enhance the overall security posture of IoT environments. This may include applying patches, strengthening access controls, or improving encryption methods.
-
Promote Security Awareness: Ethical hackers also play a role in educating IoT device manufacturers, developers, and users about best practices for security. They raise awareness about potential risks and the importance of regular updates and secure configurations.
-
Compliance and Standards: Ethical hacking for IoT security helps organizations align with industry-specific regulations and standards, ensuring compliance with data protection and privacy laws.
By conducting ethical hacking assessments on IoT systems, organizations can proactively address security weaknesses, minimize the risk of cyberattacks, protect sensitive data, and maintain the reliability of their IoT devices and networks. As the IoT landscape continues to evolve, ethical hacking remains an essential strategy for safeguarding these interconnected technologies and enhancing their resilience against emerging threats.
Challenges and Ethical Dilemmas in Ethical Hacking
-
Legal Boundaries:
-
Ethical hackers must stay within the law.
-
Distinguishing ethical hacking from illegal hacking can be tricky.
-
-
Authorization and Permission:
-
Getting clear permission to hack is crucial.
-
Obtaining authorization, especially in large organizations, can be challenging.
-
-
User Privacy and Data Protection:
-
Ethical hackers may encounter sensitive data during assessments.
-
Balancing the need to reveal vulnerabilities with protecting user privacy is a challenge.
-
-
Third-Party Systems:
-
Ethical hackers often assess external systems.
-
The ethical challenge arises when vulnerabilities are found in systems the organization doesn't control.
-
-
Full Disclosure vs. Responsible Disclosure:
-
Deciding whether to disclose vulnerabilities publicly (full disclosure) or privately to the organization (responsible disclosure) is a complex ethical choice.
-
It involves considering the impact on security and public awareness.
-
-
Technical Proficiency and Adaptation:
-
Staying technically proficient and updated is an ongoing challenge.
-
Ethical hackers must adapt to evolving cyber threats and technologies.
-
-
Neutrality and Objectivity:
-
Remaining neutral and objective during assessments is essential.
-
Personal biases or judgments can compromise the assessment's integrity.
-
Collaboration Between Ethical Hackers and IT Security Teams
Collaboration between ethical hackers and IT security teams is an indispensable partnership in the realm of cybersecurity. Ethical hackers, armed with their expertise and hacking skills, serve as the first line of defense by proactively identifying vulnerabilities within an organization's systems, networks, and applications. They conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to simulate real-world cyberattacks, pinpoint weaknesses, and report their findings. This critical information forms the foundation upon which IT security teams build their defensive strategies. IT security professionals then take the insights provided by ethical hackers and apply them to patch vulnerabilities, implement stronger security measures, and enhance overall cybersecurity posture. This synergy ensures a proactive and dynamic approach to cybersecurity, enabling organizations to stay one step ahead of malicious actors and respond effectively to emerging threats. Collaboration between ethical hackers and IT security teams is not merely a partnership; it is a fundamental strategy for organizations to fortify their digital defenses and protect sensitive data from evolving cyber threats.
The Role of Continuous Monitoring in Ethical Hacking:
Continuous monitoring plays a pivotal role in the realm of ethical hacking, serving as a proactive and dynamic approach to cybersecurity. Ethical hackers, also known as white-hat hackers, engage in ongoing monitoring to identify and address vulnerabilities within digital systems and networks. This process is multifaceted, involving several key aspects.
One of the primary functions of continuous monitoring is real-time threat detection. Ethical hackers employ a variety of tools and techniques to scrutinize network traffic, examine system logs, and analyze security alerts in real-time. This allows them to swiftly pinpoint and investigate any suspicious or potentially malicious activities as they occur, minimizing the risk of cyber threats going undetected.
Another critical element is vulnerability assessment. Ethical hackers routinely conduct scans to identify known vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses within an organization's systems, applications, and network configurations. This proactive approach ensures that vulnerabilities are promptly addressed, reducing the window of opportunity for malicious actors.
Furthermore, intrusion detection is a key aspect of continuous monitoring. Ethical hackers set up intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor for unauthorized access attempts and potential security breaches. These systems generate alerts when they detect unusual or suspicious behavior, allowing for immediate investigation and response.
Additionally, log analysis is integral to continuous monitoring. Ethical hackers meticulously review logs and audit trails to identify security incidents, track the source of attacks, and understand how vulnerabilities are exploited. This analysis provides valuable insights into the nature and origin of threats, aiding in the development of effective countermeasures.
Continuous monitoring also encompasses patch management, incident response planning, threat intelligence gathering, security awareness initiatives, and regular reporting of findings and recommendations. It ensures that organizations stay compliant with relevant regulations and standards while maintaining the security and privacy of sensitive data.
In conclusion, continuous monitoring is the heartbeat of ethical hacking, facilitating the early detection and mitigation of security vulnerabilities and threats. By adopting a proactive and ongoing approach to cybersecurity, ethical hackers work in tandem with IT security teams to fortify digital defenses, respond effectively to incidents, and adapt to the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. This collaborative effort ensures that organizations can protect their digital assets and data against an array of security challenges.
Future Trends in Ethical Hacking
Future trends in ethical hacking point to an exciting and evolving landscape in the realm of cybersecurity. As technology advances and cyber threats become more sophisticated, ethical hackers are continually adapting to stay ahead of malicious actors. Here are some key developments and trends shaping the future of ethical hacking:
-
AI and Machine Learning Integration: Ethical hackers are increasingly using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance their capabilities. These technologies can automate the detection of vulnerabilities, analyze large datasets for patterns, and even predict potential cyber threats. Ethical hackers will harness AI and ML to identify and respond to threats more effectively.
-
IoT and OT Security: With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) and Operational Technology (OT) devices, ethical hacking will extend its focus to these areas. Ethical hackers will specialize in assessing the security of smart devices, industrial control systems, and critical infrastructure, as these become prime targets for cyberattacks.
-
Cloud Security: As organizations migrate more of their data and operations to the cloud, ethical hackers will place greater emphasis on cloud security assessments. They will test configurations, access controls, and data protection mechanisms within cloud environments to ensure their resilience against cyber threats.
-
5G Network Vulnerabilities: The rollout of 5G networks will introduce new security challenges. Ethical hackers will explore potential vulnerabilities in the 5G infrastructure and associated technologies, ensuring the security of next-generation connectivity.
-
Zero Trust Security: The Zero Trust security model, which assumes that no one, whether inside or outside the organization, can be trusted, will gain prominence. Ethical hackers will play a key role in implementing and testing Zero Trust architectures to protect against insider threats and external breaches.
-
Biometric Security Testing: Ethical hackers will assess the security of biometric authentication methods, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, to ensure their resistance to spoofing and unauthorized access attempts.
-
Quantum Computing Threats: As quantum computing advances, it poses both opportunities and challenges in the cybersecurity space. Ethical hackers will explore potential threats posed by quantum computing and develop quantum-resistant encryption techniques.
-
Blockchain Security: As blockchain technology continues to be adopted in various industries, ethical hackers will assess the security of blockchain networks and smart contracts, ensuring their integrity and resilience against attacks.
-
Bug Bounty Programs: Bug bounty programs will become more prevalent, offering ethical hackers financial incentives to discover and report vulnerabilities in organizations' systems and applications. This trend encourages collaboration between hackers and organizations to enhance security.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ethical hackers will continue to play a crucial role in helping organizations meet evolving regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, CCPA, and other data protection laws, by conducting compliance assessments and security audits.
How to obtain Ethical Hacking certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Power BI Certification
-
Cyber Security : Ethical Hacking
Conclusion
In today's digitally interconnected world, the role of ethical hacking in modern organizations cannot be overstated. As businesses increasingly rely on digital infrastructure and data, they face a growing array of cyber threats that can jeopardize their operations, finances, and reputation. Ethical hacking, carried out by skilled professionals known as white-hat hackers, serves as a proactive defense against these threats.
Ethical hackers play a pivotal role in identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. Their expertise extends to various domains, including network security, web application security, and cloud security. By simulating cyberattacks and employing the same tactics as potential adversaries, ethical hackers provide organizations with invaluable insights into their security weaknesses.
Furthermore, ethical hacking is not just a one-time endeavor but a continuous process. It involves ongoing monitoring, vulnerability assessments, and response planning to stay ahead of emerging threats. Ethical hackers collaborate closely with IT security teams, ensuring that organizations can adapt and fortify their defenses in the face of evolving cyber challenges.
In conclusion, ethical hacking is not just a service but a strategic imperative for modern organizations. It empowers businesses to protect their digital assets, customer data, and brand reputation while demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity and responsible data management. In a world where cyber threats are ever-present, ethical hacking stands as a critical guardian of organizational integrity and security, safeguarding the future of businesses in the digital age.
COBIT® 5 and IT Risk Management: A Powerful Combination
In today's ever-evolving digital landscape, organizations face a multitude of challenges when it comes to managing and mitigating IT risks. The rapid pace of technological advancements, the increasing complexity of IT environments, and the relentless onslaught of cyber threats have made effective risk management an imperative for businesses of all sizes and industries.
This blog post explores a powerful combination that has emerged to tackle these challenges head-on: COBIT® 5 and IT risk management. COBIT® 5, a globally recognized framework for IT governance and management, provides organizations with a structured approach to optimizing IT processes and aligning them with business goals. When integrated with robust IT risk management practices, COBIT® 5 becomes a formidable tool in helping organizations identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT risks effectively.
In this post, we will delve into the core concepts of COBIT® 5, emphasizing its principles and guidelines that support IT risk management. We will also discuss the benefits of combining COBIT® 5 with IT risk management, including improved visibility, enhanced decision-making, and better compliance. Additionally, we'll provide practical insights on how organizations can implement COBIT® 5 in their risk management processes and showcase real-world examples of its successful integration.
Table of Contents
-
Understanding COBIT® 5 in Brief
-
The Critical Role of IT Risk Management
-
COBIT® 5's Approach to IT Risk Management
-
Benefits of Integrating COBIT® 5 with IT Risk Management
-
COBIT® 5's Framework for IT Risk Management
-
Practical Implementation Steps
-
Real-world Examples
-
Challenges and Considerations
-
Conclusion
Understanding COBIT® 5 in Brief
COBIT® 5, which stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a globally recognized framework developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) to guide organizations in effectively managing and governing their information technology (IT) processes. At its core, COBIT® 5 seeks to bridge the gap between business objectives and IT functions. It is a comprehensive framework that offers a structured approach to IT governance and management, ensuring that IT activities align with business goals and regulatory requirements.
Key Components of COBIT® 5:
COBIT® 5 is built on five fundamental principles that underpin its effectiveness. These principles include meeting stakeholder needs, covering the enterprise end-to-end, applying a single integrated framework, enabling a holistic approach, and separating governance from management. Within the framework, a set of processes is organized into five domains: Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM), Align, Plan, and Organize (APO), Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI), Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS), and Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA). These processes provide guidance on various aspects of IT governance and management, from strategic planning to day-to-day operations.
Benefits of COBIT® 5:
Organizations that embrace COBIT® 5 gain several notable advantages. It enhances IT governance by establishing a robust framework that ensures IT investments and actions are in harmony with business objectives and compliance requirements. COBIT® 5 also plays a vital role in risk management, offering a structured approach to identify, assess, and mitigate IT-related risks. It aids in efficient resource allocation, enabling organizations to make informed decisions regarding IT investments. Moreover, COBIT® 5 promotes transparency and accountability in IT processes, facilitating areas of improvement identification and compliance demonstration. The framework's compatibility with various industry standards and frameworks, such as ITIL and ISO/IEC 27001, enhances its appeal as a versatile tool applicable to organizations of all sizes and industries. In summary, COBIT® 5 serves as an invaluable resource for organizations aspiring to elevate their IT governance and management practices, aligning IT with business objectives and enhancing overall efficiency and effectiveness.
The Critical Role of IT Risk Management
In today's digital-centric business landscape, the critical role of IT risk management cannot be overstated. As organizations increasingly rely on technology to drive their operations, serve customers, and manage data, they become more exposed to a wide array of IT-related risks. These risks can range from cybersecurity threats and data breaches to system failures and compliance violations. Effectively managing these risks is essential for business continuity, reputation preservation, and regulatory compliance.
IT risk management is a systematic and structured approach to identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring IT-related risks. Its significance lies in its ability to proactively identify potential threats and vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to take preemptive action to reduce their impact. Here are several key aspects highlighting the critical role of IT risk management:
1. Protecting Business Assets: IT systems and digital assets are vital components of modern businesses. IT risk management safeguards these assets from a wide range of threats, including cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and data loss. By protecting these assets, organizations can ensure the uninterrupted flow of operations and maintain customer trust.
2. Safeguarding Reputation: A data breach or security incident can have severe consequences for an organization's reputation. IT risk management practices, including robust cybersecurity measures and incident response plans, help minimize the risk of reputational damage by preventing or mitigating the impact of such incidents.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to stringent regulations related to data protection, privacy, and security. IT risk management ensures that organizations remain in compliance with these regulations, avoiding costly fines and legal repercussions.
4. Business Continuity: Effective risk management includes disaster recovery and business continuity planning. This ensures that in the event of IT disruptions, whether due to natural disasters or technical failures, organizations can continue to operate or quickly recover their operations.
5. Cost Reduction: Well-planned IT risk management can lead to cost savings. By identifying and mitigating risks, organizations can reduce the financial impact of potential incidents and allocate resources more efficiently.
6. Decision Support: IT risk assessments provide valuable insights into the vulnerabilities and threats an organization faces. This information aids in informed decision-making, such as prioritizing investments in security measures and risk mitigation strategies.
7. Competitive Advantage: Organizations that can demonstrate effective IT risk management practices often gain a competitive edge. Customers and partners are increasingly concerned about data security and compliance, making sound risk management a selling point.
COBIT® 5's Approach to IT Risk Management
COBIT® 5, the globally recognized framework for IT governance and management, offers a structured and effective approach to managing IT-related risks within organizations. Its approach can be summarized in a few key steps, making it accessible for organizations of various sizes and industries:
-
Understand Business Goals: First, know your organization's business objectives well. IT should support these goals.
-
Set Risk Tolerance: Decide how much risk you're willing to accept to achieve your business goals, like setting a limit on a game.
-
Identify IT Risks: Spot potential IT risks, such as cyber threats or software problems, just like noticing road obstacles.
-
Assess Risks: Estimate how big each risk is and how likely it is to happen, similar to evaluating the size of a road pothole and its likelihood of causing damage.
-
Respond to Risks: Decide what to do about each risk—avoid it, lessen its impact, transfer it (like getting insurance), or accept it, just as you choose to fix a pothole or take a different route.
-
Monitor Continuously: Keep an eye on risks all the time, like watching the road while driving, and adjust your plans if new risks appear.
-
Communicate Clearly: Make sure everyone in your organization understands the risks and what you're doing to manage them.
-
Report and Follow Rules: Share information about how you're handling risks with key people and stay in line with laws and standards.
-
Learn and Improve: Keep learning from your experiences with risk management to get better at it over time, like becoming a better driver after each trip.
In simple terms, COBIT® 5's approach to IT risk management is like planning a safe journey. You know where you want to go (business goals), identify potential roadblocks (IT risks), set limits on how risky you're willing to be, and use strategies to navigate safely. This helps organizations protect their IT systems and make smart choices in the digital world.
Benefits of Integrating COBIT® 5 with IT Risk Management
Integrating COBIT® 5, a comprehensive framework for IT governance and management, with IT risk management brings several significant benefits to organizations. This integration creates a powerful synergy that enhances an organization's ability to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT-related risks effectively. Here are the key advantages:
-
Business Alignment: Aligns IT activities with what the organization wants to achieve, ensuring that IT supports business goals.
-
Proactive Risk Management: Helps spot and address IT risks before they become big problems.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Provides insights for smart decisions about IT investments and how to deal with risks.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Makes it easier to follow rules and regulations related to IT risk management.
-
Efficient Resource Use: Helps allocate resources wisely by focusing on the most important risks.
-
Clear Communication: Makes it easy to explain IT risks and how they're being managed to everyone in the organization.
-
Adaptation to Change: Keeps an eye on risks and adjusts strategies as needed to stay safe in a changing world.
-
Easier Audits: Simplifies the process of checking that risk management practices are working correctly.
-
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that do this well look better to customers and partners who care about data security and following the rules.
COBIT® 5's Framework for IT Risk Management
COBIT® 5 provides a structured and comprehensive framework for IT risk management within organizations. This framework offers a clear path to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT-related risks effectively. Here are the key components and steps in COBIT® 5's framework for IT risk management:
-
Identify Risks: Find potential IT risks that could harm your organization, like cyber threats or data problems.
-
Assess Risks: Figure out how big each risk is and how likely it is to happen, so you know which ones need attention.
-
Manage Risks: Decide what to do about each risk—avoid it, lessen its impact, transfer it (like insurance), or accept it.
-
Keep an Eye Out: Continuously watch for changes in risks and adjust your plans accordingly.
-
Report Clearly: Share what you're doing about risks with everyone in your organization and make sure to document everything.
-
Follow the Rules: Make sure your risk management follows the laws and rules that apply to your business.
-
Learn and Get Better: Keep learning from your experiences with risk management to do it even better next time.
-
Integrate with Everything: Make sure risk management is part of all your IT decisions and fits with your overall goals.
In simple terms, COBIT® 5's framework for IT risk management is like a clear roadmap to help organizations handle IT risks wisely. It guides you in spotting risks, figuring out how to deal with them, and making sure you're following the rules and improving over time. This helps keep your organization safe and successful in the digital world.
Practical Implementation Steps
Implementing COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework involves practical steps to ensure a systematic and effective approach to managing IT-related risks within your organization. Here are the key implementation steps:
-
Assign Responsibilities: Appoint people to handle risk management tasks and make sure senior leaders support the process.
-
Set Risk Limits: Decide how much risk your organization can accept for different types of IT activities.
-
Spot Risks: Identify potential IT risks using your team's knowledge and available data.
-
Check Risks: Evaluate each risk to see how big it is and how likely it is to happen, and then prioritize them.
-
Make Risk Plans: Create plans to deal with the most important risks, deciding whether to avoid them, reduce their impact, transfer them (like buying insurance), or accept them.
-
Integrate with Everything: Make sure risk management is part of your regular IT processes and document it.
-
Keep Watch: Set up a system to keep an eye on how risks change and how your plans are working.
-
Tell Everyone: Regularly tell your team and leaders about the risks and what you're doing to manage them.
-
Keep Records: Write down everything you do related to risk management.
-
Train and Learn: Teach your team about risk management and learn from your experiences to get better over time.
-
Follow the Rules: Make sure your risk management meets the laws and rules that apply to your business.
-
Get Help If Needed: Consider getting outside experts to help or assess your risk management.
In simple terms, these steps help organizations manage IT risks effectively, aligning with their goals and complying with rules while learning and improving along the way.
Real-world Examples
Here are some real-world examples of organizations that have successfully implemented COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework:
-
JPMorgan Chase & Co.: JPMorgan Chase, one of the world's largest financial institutions, utilizes COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to ensure the security and reliability of its IT systems. The framework helps them identify and assess risks associated with their extensive digital operations, including online banking and financial services. It enables them to proactively address cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and regulatory compliance challenges.
-
The World Bank: The World Bank, a global financial institution, leverages COBIT® 5 to manage IT risks across its diverse operations. They use the framework to identify and assess risks related to the implementation of technology in development projects. This helps them mitigate potential project delays, budget overruns, and data security issues.
-
Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA): DEWA, the utility provider for Dubai, uses COBIT® 5 to enhance IT risk management in the context of critical infrastructure. They apply the framework to identify and address risks associated with their energy and water supply systems. This ensures the reliability and resilience of their services, even in the face of IT-related challenges.
-
PwC (PricewaterhouseCoopers): As a leading global professional services firm, PwC employs COBIT® 5 for IT risk management to help their clients across various industries. They assist organizations in identifying and managing IT risks to enhance cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, and overall operational efficiency.
-
Nestlé: Nestlé, the multinational food and beverage company, uses COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to ensure the integrity of its global IT systems. This includes managing risks related to data privacy, supply chain, and production systems. The framework helps Nestlé maintain the trust of its customers and regulators while ensuring the smooth operation of its business.
These real-world examples demonstrate how organizations across different sectors, including finance, development, utilities, and professional services, leverage COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to enhance their IT governance and protect their operations from a wide range of IT-related risks. This illustrates the versatility and effectiveness of COBIT® 5 in managing IT risks in various contexts.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework comes with a set of challenges and considerations that organizations should carefully address. One significant challenge is resource allocation, involving finding the right personnel and financial investments for risk management initiatives. Changing the organizational culture to prioritize risk management can be a formidable hurdle, as it requires strong leadership support and effective communication to instill the importance of risk management across all levels of the organization. The complexity of modern IT environments, with their ever-evolving nature, presents another challenge, necessitating the use of advanced monitoring tools and regular risk assessments to keep up. Adhering to regulatory requirements is a critical consideration, especially as rules can change frequently, making it vital to stay informed and seek expert guidance when needed.
Safeguarding sensitive data from breaches and cyberattacks remains a constant challenge, demanding robust cybersecurity measures and well-defined incident response plans. Integrating COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework with existing IT governance processes may pose difficulties, necessitating expert guidance and a strategic approach to ensure seamless integration. Building and maintaining the necessary skills and knowledge within the organization for effective risk management requires investment in training and development programs. Overcoming resistance to change and managing organizational change effectively is essential, as implementing new risk management processes can meet with opposition. Finally, measuring the effectiveness of risk management efforts and reporting on them in a clear and meaningful way can be complex, requiring the definition of key performance indicators and metrics to evaluate success and communicate progress to stakeholders. Addressing these challenges and considerations strategically empowers organizations to protect their IT assets, align IT with business objectives, and ensure resilience in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
How to obtain the COBIT Foundation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
IT Service Management & Governance: COBIT, ISO
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework offers organizations a structured and comprehensive approach to navigate the complex landscape of IT-related risks. While it brings substantial benefits such as enhanced alignment with business goals, proactive risk identification, and improved decision-making, it also presents various challenges and considerations. These challenges include resource allocation, cultural change, the complexity of IT environments, regulatory compliance, data security, integration with existing processes, skills and training, change management, and effective measurement and reporting.
Despite these challenges, organizations that commit to implementing COBIT® 5's framework stand to gain in terms of better IT risk management, alignment with regulatory requirements, and enhanced data security. It empowers organizations to proactively identify and address risks, ultimately safeguarding their IT assets and ensuring their resilience in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Therefore, while the road to effective IT risk management may be challenging, the destination of a secure and well-aligned IT environment is well worth the journey.
Read More
In today's ever-evolving digital landscape, organizations face a multitude of challenges when it comes to managing and mitigating IT risks. The rapid pace of technological advancements, the increasing complexity of IT environments, and the relentless onslaught of cyber threats have made effective risk management an imperative for businesses of all sizes and industries.
This blog post explores a powerful combination that has emerged to tackle these challenges head-on: COBIT® 5 and IT risk management. COBIT® 5, a globally recognized framework for IT governance and management, provides organizations with a structured approach to optimizing IT processes and aligning them with business goals. When integrated with robust IT risk management practices, COBIT® 5 becomes a formidable tool in helping organizations identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT risks effectively.
In this post, we will delve into the core concepts of COBIT® 5, emphasizing its principles and guidelines that support IT risk management. We will also discuss the benefits of combining COBIT® 5 with IT risk management, including improved visibility, enhanced decision-making, and better compliance. Additionally, we'll provide practical insights on how organizations can implement COBIT® 5 in their risk management processes and showcase real-world examples of its successful integration.
Table of Contents
-
Understanding COBIT® 5 in Brief
-
The Critical Role of IT Risk Management
-
COBIT® 5's Approach to IT Risk Management
-
Benefits of Integrating COBIT® 5 with IT Risk Management
-
COBIT® 5's Framework for IT Risk Management
-
Practical Implementation Steps
-
Real-world Examples
-
Challenges and Considerations
-
Conclusion
Understanding COBIT® 5 in Brief
COBIT® 5, which stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies, is a globally recognized framework developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) to guide organizations in effectively managing and governing their information technology (IT) processes. At its core, COBIT® 5 seeks to bridge the gap between business objectives and IT functions. It is a comprehensive framework that offers a structured approach to IT governance and management, ensuring that IT activities align with business goals and regulatory requirements.
Key Components of COBIT® 5:
COBIT® 5 is built on five fundamental principles that underpin its effectiveness. These principles include meeting stakeholder needs, covering the enterprise end-to-end, applying a single integrated framework, enabling a holistic approach, and separating governance from management. Within the framework, a set of processes is organized into five domains: Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM), Align, Plan, and Organize (APO), Build, Acquire, and Implement (BAI), Deliver, Service, and Support (DSS), and Monitor, Evaluate, and Assess (MEA). These processes provide guidance on various aspects of IT governance and management, from strategic planning to day-to-day operations.
Benefits of COBIT® 5:
Organizations that embrace COBIT® 5 gain several notable advantages. It enhances IT governance by establishing a robust framework that ensures IT investments and actions are in harmony with business objectives and compliance requirements. COBIT® 5 also plays a vital role in risk management, offering a structured approach to identify, assess, and mitigate IT-related risks. It aids in efficient resource allocation, enabling organizations to make informed decisions regarding IT investments. Moreover, COBIT® 5 promotes transparency and accountability in IT processes, facilitating areas of improvement identification and compliance demonstration. The framework's compatibility with various industry standards and frameworks, such as ITIL and ISO/IEC 27001, enhances its appeal as a versatile tool applicable to organizations of all sizes and industries. In summary, COBIT® 5 serves as an invaluable resource for organizations aspiring to elevate their IT governance and management practices, aligning IT with business objectives and enhancing overall efficiency and effectiveness.
The Critical Role of IT Risk Management
In today's digital-centric business landscape, the critical role of IT risk management cannot be overstated. As organizations increasingly rely on technology to drive their operations, serve customers, and manage data, they become more exposed to a wide array of IT-related risks. These risks can range from cybersecurity threats and data breaches to system failures and compliance violations. Effectively managing these risks is essential for business continuity, reputation preservation, and regulatory compliance.
IT risk management is a systematic and structured approach to identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring IT-related risks. Its significance lies in its ability to proactively identify potential threats and vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to take preemptive action to reduce their impact. Here are several key aspects highlighting the critical role of IT risk management:
1. Protecting Business Assets: IT systems and digital assets are vital components of modern businesses. IT risk management safeguards these assets from a wide range of threats, including cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and data loss. By protecting these assets, organizations can ensure the uninterrupted flow of operations and maintain customer trust.
2. Safeguarding Reputation: A data breach or security incident can have severe consequences for an organization's reputation. IT risk management practices, including robust cybersecurity measures and incident response plans, help minimize the risk of reputational damage by preventing or mitigating the impact of such incidents.
3. Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to stringent regulations related to data protection, privacy, and security. IT risk management ensures that organizations remain in compliance with these regulations, avoiding costly fines and legal repercussions.
4. Business Continuity: Effective risk management includes disaster recovery and business continuity planning. This ensures that in the event of IT disruptions, whether due to natural disasters or technical failures, organizations can continue to operate or quickly recover their operations.
5. Cost Reduction: Well-planned IT risk management can lead to cost savings. By identifying and mitigating risks, organizations can reduce the financial impact of potential incidents and allocate resources more efficiently.
6. Decision Support: IT risk assessments provide valuable insights into the vulnerabilities and threats an organization faces. This information aids in informed decision-making, such as prioritizing investments in security measures and risk mitigation strategies.
7. Competitive Advantage: Organizations that can demonstrate effective IT risk management practices often gain a competitive edge. Customers and partners are increasingly concerned about data security and compliance, making sound risk management a selling point.
COBIT® 5's Approach to IT Risk Management
COBIT® 5, the globally recognized framework for IT governance and management, offers a structured and effective approach to managing IT-related risks within organizations. Its approach can be summarized in a few key steps, making it accessible for organizations of various sizes and industries:
-
Understand Business Goals: First, know your organization's business objectives well. IT should support these goals.
-
Set Risk Tolerance: Decide how much risk you're willing to accept to achieve your business goals, like setting a limit on a game.
-
Identify IT Risks: Spot potential IT risks, such as cyber threats or software problems, just like noticing road obstacles.
-
Assess Risks: Estimate how big each risk is and how likely it is to happen, similar to evaluating the size of a road pothole and its likelihood of causing damage.
-
Respond to Risks: Decide what to do about each risk—avoid it, lessen its impact, transfer it (like getting insurance), or accept it, just as you choose to fix a pothole or take a different route.
-
Monitor Continuously: Keep an eye on risks all the time, like watching the road while driving, and adjust your plans if new risks appear.
-
Communicate Clearly: Make sure everyone in your organization understands the risks and what you're doing to manage them.
-
Report and Follow Rules: Share information about how you're handling risks with key people and stay in line with laws and standards.
-
Learn and Improve: Keep learning from your experiences with risk management to get better at it over time, like becoming a better driver after each trip.
In simple terms, COBIT® 5's approach to IT risk management is like planning a safe journey. You know where you want to go (business goals), identify potential roadblocks (IT risks), set limits on how risky you're willing to be, and use strategies to navigate safely. This helps organizations protect their IT systems and make smart choices in the digital world.
Benefits of Integrating COBIT® 5 with IT Risk Management
Integrating COBIT® 5, a comprehensive framework for IT governance and management, with IT risk management brings several significant benefits to organizations. This integration creates a powerful synergy that enhances an organization's ability to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT-related risks effectively. Here are the key advantages:
-
Business Alignment: Aligns IT activities with what the organization wants to achieve, ensuring that IT supports business goals.
-
Proactive Risk Management: Helps spot and address IT risks before they become big problems.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Provides insights for smart decisions about IT investments and how to deal with risks.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Makes it easier to follow rules and regulations related to IT risk management.
-
Efficient Resource Use: Helps allocate resources wisely by focusing on the most important risks.
-
Clear Communication: Makes it easy to explain IT risks and how they're being managed to everyone in the organization.
-
Adaptation to Change: Keeps an eye on risks and adjusts strategies as needed to stay safe in a changing world.
-
Easier Audits: Simplifies the process of checking that risk management practices are working correctly.
-
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that do this well look better to customers and partners who care about data security and following the rules.
COBIT® 5's Framework for IT Risk Management
COBIT® 5 provides a structured and comprehensive framework for IT risk management within organizations. This framework offers a clear path to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor IT-related risks effectively. Here are the key components and steps in COBIT® 5's framework for IT risk management:
-
Identify Risks: Find potential IT risks that could harm your organization, like cyber threats or data problems.
-
Assess Risks: Figure out how big each risk is and how likely it is to happen, so you know which ones need attention.
-
Manage Risks: Decide what to do about each risk—avoid it, lessen its impact, transfer it (like insurance), or accept it.
-
Keep an Eye Out: Continuously watch for changes in risks and adjust your plans accordingly.
-
Report Clearly: Share what you're doing about risks with everyone in your organization and make sure to document everything.
-
Follow the Rules: Make sure your risk management follows the laws and rules that apply to your business.
-
Learn and Get Better: Keep learning from your experiences with risk management to do it even better next time.
-
Integrate with Everything: Make sure risk management is part of all your IT decisions and fits with your overall goals.
In simple terms, COBIT® 5's framework for IT risk management is like a clear roadmap to help organizations handle IT risks wisely. It guides you in spotting risks, figuring out how to deal with them, and making sure you're following the rules and improving over time. This helps keep your organization safe and successful in the digital world.
Practical Implementation Steps
Implementing COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework involves practical steps to ensure a systematic and effective approach to managing IT-related risks within your organization. Here are the key implementation steps:
-
Assign Responsibilities: Appoint people to handle risk management tasks and make sure senior leaders support the process.
-
Set Risk Limits: Decide how much risk your organization can accept for different types of IT activities.
-
Spot Risks: Identify potential IT risks using your team's knowledge and available data.
-
Check Risks: Evaluate each risk to see how big it is and how likely it is to happen, and then prioritize them.
-
Make Risk Plans: Create plans to deal with the most important risks, deciding whether to avoid them, reduce their impact, transfer them (like buying insurance), or accept them.
-
Integrate with Everything: Make sure risk management is part of your regular IT processes and document it.
-
Keep Watch: Set up a system to keep an eye on how risks change and how your plans are working.
-
Tell Everyone: Regularly tell your team and leaders about the risks and what you're doing to manage them.
-
Keep Records: Write down everything you do related to risk management.
-
Train and Learn: Teach your team about risk management and learn from your experiences to get better over time.
-
Follow the Rules: Make sure your risk management meets the laws and rules that apply to your business.
-
Get Help If Needed: Consider getting outside experts to help or assess your risk management.
In simple terms, these steps help organizations manage IT risks effectively, aligning with their goals and complying with rules while learning and improving along the way.
Real-world Examples
Here are some real-world examples of organizations that have successfully implemented COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework:
-
JPMorgan Chase & Co.: JPMorgan Chase, one of the world's largest financial institutions, utilizes COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to ensure the security and reliability of its IT systems. The framework helps them identify and assess risks associated with their extensive digital operations, including online banking and financial services. It enables them to proactively address cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and regulatory compliance challenges.
-
The World Bank: The World Bank, a global financial institution, leverages COBIT® 5 to manage IT risks across its diverse operations. They use the framework to identify and assess risks related to the implementation of technology in development projects. This helps them mitigate potential project delays, budget overruns, and data security issues.
-
Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA): DEWA, the utility provider for Dubai, uses COBIT® 5 to enhance IT risk management in the context of critical infrastructure. They apply the framework to identify and address risks associated with their energy and water supply systems. This ensures the reliability and resilience of their services, even in the face of IT-related challenges.
-
PwC (PricewaterhouseCoopers): As a leading global professional services firm, PwC employs COBIT® 5 for IT risk management to help their clients across various industries. They assist organizations in identifying and managing IT risks to enhance cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, and overall operational efficiency.
-
Nestlé: Nestlé, the multinational food and beverage company, uses COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to ensure the integrity of its global IT systems. This includes managing risks related to data privacy, supply chain, and production systems. The framework helps Nestlé maintain the trust of its customers and regulators while ensuring the smooth operation of its business.
These real-world examples demonstrate how organizations across different sectors, including finance, development, utilities, and professional services, leverage COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework to enhance their IT governance and protect their operations from a wide range of IT-related risks. This illustrates the versatility and effectiveness of COBIT® 5 in managing IT risks in various contexts.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework comes with a set of challenges and considerations that organizations should carefully address. One significant challenge is resource allocation, involving finding the right personnel and financial investments for risk management initiatives. Changing the organizational culture to prioritize risk management can be a formidable hurdle, as it requires strong leadership support and effective communication to instill the importance of risk management across all levels of the organization. The complexity of modern IT environments, with their ever-evolving nature, presents another challenge, necessitating the use of advanced monitoring tools and regular risk assessments to keep up. Adhering to regulatory requirements is a critical consideration, especially as rules can change frequently, making it vital to stay informed and seek expert guidance when needed.
Safeguarding sensitive data from breaches and cyberattacks remains a constant challenge, demanding robust cybersecurity measures and well-defined incident response plans. Integrating COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework with existing IT governance processes may pose difficulties, necessitating expert guidance and a strategic approach to ensure seamless integration. Building and maintaining the necessary skills and knowledge within the organization for effective risk management requires investment in training and development programs. Overcoming resistance to change and managing organizational change effectively is essential, as implementing new risk management processes can meet with opposition. Finally, measuring the effectiveness of risk management efforts and reporting on them in a clear and meaningful way can be complex, requiring the definition of key performance indicators and metrics to evaluate success and communicate progress to stakeholders. Addressing these challenges and considerations strategically empowers organizations to protect their IT assets, align IT with business objectives, and ensure resilience in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
How to obtain the COBIT Foundation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
IT Service Management & Governance: COBIT, ISO
Conclusion
In conclusion, COBIT® 5's IT risk management framework offers organizations a structured and comprehensive approach to navigate the complex landscape of IT-related risks. While it brings substantial benefits such as enhanced alignment with business goals, proactive risk identification, and improved decision-making, it also presents various challenges and considerations. These challenges include resource allocation, cultural change, the complexity of IT environments, regulatory compliance, data security, integration with existing processes, skills and training, change management, and effective measurement and reporting.
Despite these challenges, organizations that commit to implementing COBIT® 5's framework stand to gain in terms of better IT risk management, alignment with regulatory requirements, and enhanced data security. It empowers organizations to proactively identify and address risks, ultimately safeguarding their IT assets and ensuring their resilience in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Therefore, while the road to effective IT risk management may be challenging, the destination of a secure and well-aligned IT environment is well worth the journey.
Cloud Computing: Advantages, Benefits & Potential Drawbacks
In today's digitally driven world, cloud computing has emerged as a technological force that is reshaping the way individuals and businesses harness the power of technology. The cloud, often referred to as the "internet of everything," offers a virtual space where data, applications, and services can be stored and accessed remotely. Its adoption has skyrocketed, promising unparalleled convenience, scalability, and cost-efficiency. However, like any technological marvel, cloud computing is not without its complexities and challenges. In this blog post, we will embark on a journey to explore the captivating landscape of cloud computing, delving into its myriad advantages that propel innovation and growth, as well as its inherent disadvantages that necessitate vigilant navigation in this digital realm. Whether you're an IT professional seeking to harness the cloud's potential or an individual eager to understand its impact on daily life, this exploration will equip you with valuable insights into the world of cloud computing.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Types of Cloud Computing
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Choose The Right Cloud Computing Program For You
The Bottom Line
FAQs
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing, a transformative technology, has revolutionized the way we interact with digital resources. It enables the delivery of computing services and resources over the internet, eliminating the need for local infrastructure. With cloud computing, users can access on-demand computing power, storage, and software, allowing for scalability and flexibility that adapts to their needs. This technology comes in various models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), catering to different user requirements. It offers benefits such as cost efficiency, accessibility from anywhere, and high reliability, making it a cornerstone of modern digital operations. However, it also poses challenges related to security, potential downtime, and data management, necessitating careful consideration when adopting cloud solutions. In today's fast-paced and interconnected world, cloud computing plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of technology and business operations.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing encompasses various types or service models, each offering a different level of control, management, and functionality to users and organizations. The three primary types of cloud computing are:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Infrastructure as a Service is the foundation of cloud computing, providing users with virtualized computing resources over the internet. It offers a scalable and flexible infrastructure that includes virtual machines, storage, and networking components. Users can provision and manage these resources on-demand, allowing them to scale up or down as needed. IaaS is ideal for organizations that require full control over their virtualized infrastructure while minimizing the burden of physical hardware management. Prominent IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS): Platform as a Service is designed to simplify application development and deployment by providing a platform and tools for developers. PaaS offerings include development frameworks, databases, and application hosting environments. With PaaS, developers can focus on coding and innovation, while the underlying infrastructure and maintenance are handled by the cloud provider. This accelerates the development lifecycle and streamlines application management. PaaS is particularly beneficial for software development teams, enabling them to build, test, and deploy applications more efficiently. Examples of PaaS providers are Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Service.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS): Software as a Service delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access these applications through a web browser, eliminating the need for local installations and updates. SaaS solutions cover a wide range of applications, including productivity tools (e.g., Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace), customer relationship management (CRM) software (e.g., Salesforce), and collaboration tools (e.g., Zoom and Slack). SaaS is user-friendly, highly accessible, and well-suited for businesses and individuals seeking to streamline software management and reduce maintenance overhead. It offers automatic updates, data storage, and often includes collaboration features for enhanced productivity.
In addition to these primary types, there are hybrid cloud solutions that combine elements of multiple cloud models, allowing organizations to leverage both private and public clouds based on their specific needs. Understanding these various types of cloud computing is essential for organizations to choose the most suitable model for their IT requirements, whether it's infrastructure management, application development, or software accessibility.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages that have made it a foundational technology for businesses and individuals alike. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Cost Efficiency:
-
Reduced Capital Expenditure: Cloud computing eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, allowing businesses to pay for resources on a pay-as-you-go basis.
-
Lower Operating Costs: Maintenance, upgrades, and energy costs associated with on-premises data centers are significantly reduced or eliminated.
2. Scalability:
-
Elastic Resources: Cloud services offer the ability to scale computing resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak times without overprovisioning.
3. Accessibility:
-
Anytime, Anywhere Access: Cloud-based applications and data can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work, collaboration, and mobility.
4. Reliability and Redundancy:
-
High Uptime: Reputable cloud providers offer high availability, ensuring that applications and data are accessible almost continuously.
-
Data Redundancy: Cloud providers often replicate data across multiple data centers, safeguarding against data loss due to hardware failures or disasters.
5. Security:
-
Advanced Security Measures: Cloud providers invest heavily in security, implementing robust measures to protect data, including encryption, firewalls, and access controls.
-
Compliance: Many cloud providers offer compliance certifications, making it easier for businesses to meet regulatory requirements.
6. Automatic Updates and Maintenance:
-
Cloud providers handle software updates and maintenance tasks, ensuring that applications and infrastructure are kept up-to-date with the latest security patches and improvements.
7. Flexibility and Innovation:
-
Rapid Development: Cloud services enable developers to quickly build and deploy applications, reducing time to market for new products and features.
-
Access to Cutting-Edge Technologies: Cloud providers often offer a wide range of advanced services and technologies, such as machine learning, AI, and IoT, facilitating innovation.
8. Disaster Recovery:
-
Data Backup and Recovery: Cloud providers typically offer robust disaster recovery and backup solutions, protecting data against unforeseen events.
9. Environmental Benefits:
-
Reduced Energy Consumption: By consolidating data centers and optimizing resource usage, cloud computing can have a positive environmental impact by reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
10. Cost Transparency:
-
Clear Billing: Cloud providers offer transparent billing and reporting, allowing organizations to monitor and control their costs effectively.
While cloud computing offers numerous advantages, it's essential for organizations to assess their specific needs, security requirements, and budget constraints to determine the best cloud strategy for their unique circumstances.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages that have made it a foundational technology for businesses and individuals alike. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Cost Efficiency:
-
Reduced Capital Expenditure: Cloud computing eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, allowing businesses to pay for resources on a pay-as-you-go basis.
-
Lower Operating Costs: Maintenance, upgrades, and energy costs associated with on-premises data centers are significantly reduced or eliminated.
2. Scalability:
-
Elastic Resources: Cloud services offer the ability to scale computing resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak times without overprovisioning.
3. Accessibility:
-
Anytime, Anywhere Access: Cloud-based applications and data can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work, collaboration, and mobility.
4. Reliability and Redundancy:
-
High Uptime: Reputable cloud providers offer high availability, ensuring that applications and data are accessible almost continuously.
-
Data Redundancy: Cloud providers often replicate data across multiple data centers, safeguarding against data loss due to hardware failures or disasters.
5. Security:
-
Advanced Security Measures: Cloud providers invest heavily in security, implementing robust measures to protect data, including encryption, firewalls, and access controls.
-
Compliance: Many cloud providers offer compliance certifications, making it easier for businesses to meet regulatory requirements.
6. Automatic Updates and Maintenance:
-
Cloud providers handle software updates and maintenance tasks, ensuring that applications and infrastructure are kept up-to-date with the latest security patches and improvements.
7. Flexibility and Innovation:
-
Rapid Development: Cloud services enable developers to quickly build and deploy applications, reducing time to market for new products and features.
-
Access to Cutting-Edge Technologies: Cloud providers often offer a wide range of advanced services and technologies, such as machine learning, AI, and IoT, facilitating innovation.
8. Disaster Recovery:
-
Data Backup and Recovery: Cloud providers typically offer robust disaster recovery and backup solutions, protecting data against unforeseen events.
9. Environmental Benefits:
-
Reduced Energy Consumption: By consolidating data centers and optimizing resource usage, cloud computing can have a positive environmental impact by reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
10. Cost Transparency:
-
Clear Billing: Cloud providers offer transparent billing and reporting, allowing organizations to monitor and control their costs effectively.
Choose The Right Cloud Computing Program For You
Choosing the right cloud computing program or service depends on your specific needs and goals. Whether you're an individual looking to expand your skills or an organization seeking cloud solutions, here are steps to help you make the right choice:
1. Define Your Goals:
-
Determine why you want to use cloud computing. Are you looking to enhance your IT skills, reduce operational costs, improve scalability, or increase productivity?
2. Assess Your Skill Level:
-
If you're an individual, evaluate your current knowledge of cloud computing. Are you a beginner, intermediate, or advanced user? This will help you choose an appropriate program or training course.
3. Choose a Cloud Service Model:
-
Decide which cloud service model aligns with your objectives. Are you interested in Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Software as a Service (SaaS)? Understanding the differences is crucial.
4. Select a Cloud Provider:
-
If you're looking for cloud services for your organization, research and compare different cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) based on factors like pricing, services offered, security features, and geographic availability.
5. Explore Training and Certification:
-
For individuals, consider enrolling in cloud computing training courses or certification programs provided by recognized organizations (e.g., AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified Azure Administrator).
-
Organizations should also invest in training for their IT teams to ensure efficient cloud adoption and management.
6. Determine Budget and Cost Factors:
-
Assess your budget for cloud services, including initial setup costs, ongoing expenses, and potential scalability costs. Be aware of any hidden costs, such as data transfer fees.
7. Security and Compliance:
-
If you're an organization, prioritize security and compliance requirements. Ensure that the cloud provider you choose meets your industry's regulatory standards and offers robust security features.
8. Evaluate Vendor Lock-In:
-
Consider the potential for vendor lock-in. Ensure that your chosen cloud provider allows for portability of data and applications, minimizing the risk of being tied to a single provider.
9. Plan for Data Migration:
-
If you're migrating existing applications or data to the cloud, create a migration plan that includes data backup, testing, and a rollback strategy in case of issues.
10. Monitor and Optimize:
-
After adopting cloud services, continuously monitor resource usage and costs. Use cloud management tools to optimize your resources for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
The Bottom Line
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, the bottom line is that the right choice for you or your organization depends on your specific needs, goals, and constraints. Cloud computing offers a wide range of advantages, including cost efficiency, scalability, accessibility, and innovation, but it also comes with challenges such as downtime, security concerns, and potential vendor lock-in.
To make the best decision:
-
Define Your Objectives: Clearly outline your goals, whether they involve improving IT infrastructure, reducing costs, enhancing productivity, or acquiring new skills.
-
Assess Your Skills: If you're an individual, understand your current proficiency level in cloud computing. Are you a beginner, intermediate, or advanced user?
-
Select the Right Service Model: Choose between Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Software as a Service (SaaS) based on your needs.
-
Pick the Right Cloud Provider: Research and compare cloud providers, considering factors such as services offered, pricing, security, and compliance with your industry's regulations.
-
Invest in Training: Consider training and certification programs to build or enhance your cloud computing skills, or invest in training for your organization's IT teams.
-
Budget Wisely: Assess your budget for cloud services, including initial setup costs, ongoing expenses, and potential scalability costs.
-
Prioritize Security: Security is paramount, especially for organizations. Ensure your chosen cloud provider meets your security and compliance requirements.
-
Plan for Migration: If migrating data or applications, create a well-structured migration plan that addresses backup, testing, and potential rollbacks.
-
Regularly Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor resource usage and costs, and use management tools to optimize your cloud resources for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
-
Seek Expert Advice: When in doubt, consult with cloud experts or consultants who can offer tailored guidance based on your unique needs.
-
Stay Flexible: Cloud technology evolves rapidly, so be prepared to adapt your cloud strategy as your needs and the technology landscape change.
Ultimately, the bottom line is that cloud computing is a dynamic and flexible solution that can be customized to meet your specific requirements. Careful planning, continuous monitoring, and strategic decision-making will help you leverage the advantages of cloud computing while mitigating potential disadvantages.
How to obtain Cloud Computing Technology Certifications?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: EXIN Cloud Computing Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Robotic Process Automation
FAQs
1. What is cloud computing?
-
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services (such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics) over the internet. It allows users to access and use these resources on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis.
2. What are the different types of cloud service models?
-
There are three primary cloud service models:
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
-
Software as a Service (SaaS)
3. What is the difference between public, private, and hybrid clouds?
-
Public Cloud: Services are provided by third-party cloud providers and made available to the general public.
-
Private Cloud: Resources are dedicated to a single organization and may be hosted on-premises or by a third party.
-
Hybrid Cloud: Combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to move between them.
4. What are some advantages of cloud computing?
-
Advantages of cloud computing include cost efficiency, scalability, accessibility, reliability, security, automatic updates, and the ability to foster innovation.
5. What are some disadvantages of cloud computing?
-
Disadvantages of cloud computing include potential downtime, security concerns, limited control over infrastructure, bandwidth limitations, data transfer costs, vendor lock-in, and compliance challenges.
6. What is the shared responsibility model in cloud security?
-
The shared responsibility model outlines the division of security responsibilities between the cloud provider and the customer. The provider is responsible for securing the infrastructure, while the customer is responsible for securing their data and applications within the cloud.
7. What are some common cloud computing certifications?
-
Popular cloud computing certifications include AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified Azure Administrator, Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect, and Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP).
8. How do I choose the right cloud provider for my organization?
-
Choosing the right cloud provider involves considering factors like services offered, pricing, security features, compliance, data center locations, and customer support. It's essential to align your choice with your organization's specific needs and goals.
9. What is the difference between cloud computing and traditional IT infrastructure?
-
Cloud computing offers on-demand access to computing resources over the internet, while traditional IT infrastructure relies on on-premises hardware and software. Cloud computing is scalable, cost-effective, and provides greater flexibility compared to traditional IT.
10. How can I ensure data security in the cloud?
-
Ensuring data security in the cloud involves implementing strong access controls, encryption, regular security audits, compliance with industry standards, and monitoring for suspicious activities. It's essential to follow best practices for cloud security.
Read More
In today's digitally driven world, cloud computing has emerged as a technological force that is reshaping the way individuals and businesses harness the power of technology. The cloud, often referred to as the "internet of everything," offers a virtual space where data, applications, and services can be stored and accessed remotely. Its adoption has skyrocketed, promising unparalleled convenience, scalability, and cost-efficiency. However, like any technological marvel, cloud computing is not without its complexities and challenges. In this blog post, we will embark on a journey to explore the captivating landscape of cloud computing, delving into its myriad advantages that propel innovation and growth, as well as its inherent disadvantages that necessitate vigilant navigation in this digital realm. Whether you're an IT professional seeking to harness the cloud's potential or an individual eager to understand its impact on daily life, this exploration will equip you with valuable insights into the world of cloud computing.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Types of Cloud Computing
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Choose The Right Cloud Computing Program For You
The Bottom Line
FAQs
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing, a transformative technology, has revolutionized the way we interact with digital resources. It enables the delivery of computing services and resources over the internet, eliminating the need for local infrastructure. With cloud computing, users can access on-demand computing power, storage, and software, allowing for scalability and flexibility that adapts to their needs. This technology comes in various models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), catering to different user requirements. It offers benefits such as cost efficiency, accessibility from anywhere, and high reliability, making it a cornerstone of modern digital operations. However, it also poses challenges related to security, potential downtime, and data management, necessitating careful consideration when adopting cloud solutions. In today's fast-paced and interconnected world, cloud computing plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of technology and business operations.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing encompasses various types or service models, each offering a different level of control, management, and functionality to users and organizations. The three primary types of cloud computing are:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Infrastructure as a Service is the foundation of cloud computing, providing users with virtualized computing resources over the internet. It offers a scalable and flexible infrastructure that includes virtual machines, storage, and networking components. Users can provision and manage these resources on-demand, allowing them to scale up or down as needed. IaaS is ideal for organizations that require full control over their virtualized infrastructure while minimizing the burden of physical hardware management. Prominent IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS): Platform as a Service is designed to simplify application development and deployment by providing a platform and tools for developers. PaaS offerings include development frameworks, databases, and application hosting environments. With PaaS, developers can focus on coding and innovation, while the underlying infrastructure and maintenance are handled by the cloud provider. This accelerates the development lifecycle and streamlines application management. PaaS is particularly beneficial for software development teams, enabling them to build, test, and deploy applications more efficiently. Examples of PaaS providers are Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Service.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS): Software as a Service delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access these applications through a web browser, eliminating the need for local installations and updates. SaaS solutions cover a wide range of applications, including productivity tools (e.g., Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace), customer relationship management (CRM) software (e.g., Salesforce), and collaboration tools (e.g., Zoom and Slack). SaaS is user-friendly, highly accessible, and well-suited for businesses and individuals seeking to streamline software management and reduce maintenance overhead. It offers automatic updates, data storage, and often includes collaboration features for enhanced productivity.
In addition to these primary types, there are hybrid cloud solutions that combine elements of multiple cloud models, allowing organizations to leverage both private and public clouds based on their specific needs. Understanding these various types of cloud computing is essential for organizations to choose the most suitable model for their IT requirements, whether it's infrastructure management, application development, or software accessibility.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages that have made it a foundational technology for businesses and individuals alike. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Cost Efficiency:
-
Reduced Capital Expenditure: Cloud computing eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, allowing businesses to pay for resources on a pay-as-you-go basis.
-
Lower Operating Costs: Maintenance, upgrades, and energy costs associated with on-premises data centers are significantly reduced or eliminated.
2. Scalability:
-
Elastic Resources: Cloud services offer the ability to scale computing resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak times without overprovisioning.
3. Accessibility:
-
Anytime, Anywhere Access: Cloud-based applications and data can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work, collaboration, and mobility.
4. Reliability and Redundancy:
-
High Uptime: Reputable cloud providers offer high availability, ensuring that applications and data are accessible almost continuously.
-
Data Redundancy: Cloud providers often replicate data across multiple data centers, safeguarding against data loss due to hardware failures or disasters.
5. Security:
-
Advanced Security Measures: Cloud providers invest heavily in security, implementing robust measures to protect data, including encryption, firewalls, and access controls.
-
Compliance: Many cloud providers offer compliance certifications, making it easier for businesses to meet regulatory requirements.
6. Automatic Updates and Maintenance:
-
Cloud providers handle software updates and maintenance tasks, ensuring that applications and infrastructure are kept up-to-date with the latest security patches and improvements.
7. Flexibility and Innovation:
-
Rapid Development: Cloud services enable developers to quickly build and deploy applications, reducing time to market for new products and features.
-
Access to Cutting-Edge Technologies: Cloud providers often offer a wide range of advanced services and technologies, such as machine learning, AI, and IoT, facilitating innovation.
8. Disaster Recovery:
-
Data Backup and Recovery: Cloud providers typically offer robust disaster recovery and backup solutions, protecting data against unforeseen events.
9. Environmental Benefits:
-
Reduced Energy Consumption: By consolidating data centers and optimizing resource usage, cloud computing can have a positive environmental impact by reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
10. Cost Transparency:
-
Clear Billing: Cloud providers offer transparent billing and reporting, allowing organizations to monitor and control their costs effectively.
While cloud computing offers numerous advantages, it's essential for organizations to assess their specific needs, security requirements, and budget constraints to determine the best cloud strategy for their unique circumstances.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages that have made it a foundational technology for businesses and individuals alike. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Cost Efficiency:
-
Reduced Capital Expenditure: Cloud computing eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, allowing businesses to pay for resources on a pay-as-you-go basis.
-
Lower Operating Costs: Maintenance, upgrades, and energy costs associated with on-premises data centers are significantly reduced or eliminated.
2. Scalability:
-
Elastic Resources: Cloud services offer the ability to scale computing resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak times without overprovisioning.
3. Accessibility:
-
Anytime, Anywhere Access: Cloud-based applications and data can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work, collaboration, and mobility.
4. Reliability and Redundancy:
-
High Uptime: Reputable cloud providers offer high availability, ensuring that applications and data are accessible almost continuously.
-
Data Redundancy: Cloud providers often replicate data across multiple data centers, safeguarding against data loss due to hardware failures or disasters.
5. Security:
-
Advanced Security Measures: Cloud providers invest heavily in security, implementing robust measures to protect data, including encryption, firewalls, and access controls.
-
Compliance: Many cloud providers offer compliance certifications, making it easier for businesses to meet regulatory requirements.
6. Automatic Updates and Maintenance:
-
Cloud providers handle software updates and maintenance tasks, ensuring that applications and infrastructure are kept up-to-date with the latest security patches and improvements.
7. Flexibility and Innovation:
-
Rapid Development: Cloud services enable developers to quickly build and deploy applications, reducing time to market for new products and features.
-
Access to Cutting-Edge Technologies: Cloud providers often offer a wide range of advanced services and technologies, such as machine learning, AI, and IoT, facilitating innovation.
8. Disaster Recovery:
-
Data Backup and Recovery: Cloud providers typically offer robust disaster recovery and backup solutions, protecting data against unforeseen events.
9. Environmental Benefits:
-
Reduced Energy Consumption: By consolidating data centers and optimizing resource usage, cloud computing can have a positive environmental impact by reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
10. Cost Transparency:
-
Clear Billing: Cloud providers offer transparent billing and reporting, allowing organizations to monitor and control their costs effectively.
Choose The Right Cloud Computing Program For You
Choosing the right cloud computing program or service depends on your specific needs and goals. Whether you're an individual looking to expand your skills or an organization seeking cloud solutions, here are steps to help you make the right choice:
1. Define Your Goals:
-
Determine why you want to use cloud computing. Are you looking to enhance your IT skills, reduce operational costs, improve scalability, or increase productivity?
2. Assess Your Skill Level:
-
If you're an individual, evaluate your current knowledge of cloud computing. Are you a beginner, intermediate, or advanced user? This will help you choose an appropriate program or training course.
3. Choose a Cloud Service Model:
-
Decide which cloud service model aligns with your objectives. Are you interested in Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Software as a Service (SaaS)? Understanding the differences is crucial.
4. Select a Cloud Provider:
-
If you're looking for cloud services for your organization, research and compare different cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) based on factors like pricing, services offered, security features, and geographic availability.
5. Explore Training and Certification:
-
For individuals, consider enrolling in cloud computing training courses or certification programs provided by recognized organizations (e.g., AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified Azure Administrator).
-
Organizations should also invest in training for their IT teams to ensure efficient cloud adoption and management.
6. Determine Budget and Cost Factors:
-
Assess your budget for cloud services, including initial setup costs, ongoing expenses, and potential scalability costs. Be aware of any hidden costs, such as data transfer fees.
7. Security and Compliance:
-
If you're an organization, prioritize security and compliance requirements. Ensure that the cloud provider you choose meets your industry's regulatory standards and offers robust security features.
8. Evaluate Vendor Lock-In:
-
Consider the potential for vendor lock-in. Ensure that your chosen cloud provider allows for portability of data and applications, minimizing the risk of being tied to a single provider.
9. Plan for Data Migration:
-
If you're migrating existing applications or data to the cloud, create a migration plan that includes data backup, testing, and a rollback strategy in case of issues.
10. Monitor and Optimize:
-
After adopting cloud services, continuously monitor resource usage and costs. Use cloud management tools to optimize your resources for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
The Bottom Line
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, the bottom line is that the right choice for you or your organization depends on your specific needs, goals, and constraints. Cloud computing offers a wide range of advantages, including cost efficiency, scalability, accessibility, and innovation, but it also comes with challenges such as downtime, security concerns, and potential vendor lock-in.
To make the best decision:
-
Define Your Objectives: Clearly outline your goals, whether they involve improving IT infrastructure, reducing costs, enhancing productivity, or acquiring new skills.
-
Assess Your Skills: If you're an individual, understand your current proficiency level in cloud computing. Are you a beginner, intermediate, or advanced user?
-
Select the Right Service Model: Choose between Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Software as a Service (SaaS) based on your needs.
-
Pick the Right Cloud Provider: Research and compare cloud providers, considering factors such as services offered, pricing, security, and compliance with your industry's regulations.
-
Invest in Training: Consider training and certification programs to build or enhance your cloud computing skills, or invest in training for your organization's IT teams.
-
Budget Wisely: Assess your budget for cloud services, including initial setup costs, ongoing expenses, and potential scalability costs.
-
Prioritize Security: Security is paramount, especially for organizations. Ensure your chosen cloud provider meets your security and compliance requirements.
-
Plan for Migration: If migrating data or applications, create a well-structured migration plan that addresses backup, testing, and potential rollbacks.
-
Regularly Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor resource usage and costs, and use management tools to optimize your cloud resources for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
-
Seek Expert Advice: When in doubt, consult with cloud experts or consultants who can offer tailored guidance based on your unique needs.
-
Stay Flexible: Cloud technology evolves rapidly, so be prepared to adapt your cloud strategy as your needs and the technology landscape change.
Ultimately, the bottom line is that cloud computing is a dynamic and flexible solution that can be customized to meet your specific requirements. Careful planning, continuous monitoring, and strategic decision-making will help you leverage the advantages of cloud computing while mitigating potential disadvantages.
How to obtain Cloud Computing Technology Certifications?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: EXIN Cloud Computing Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Robotic Process Automation
FAQs
1. What is cloud computing?
-
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services (such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics) over the internet. It allows users to access and use these resources on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis.
2. What are the different types of cloud service models?
-
There are three primary cloud service models:
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
-
Software as a Service (SaaS)
3. What is the difference between public, private, and hybrid clouds?
-
Public Cloud: Services are provided by third-party cloud providers and made available to the general public.
-
Private Cloud: Resources are dedicated to a single organization and may be hosted on-premises or by a third party.
-
Hybrid Cloud: Combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to move between them.
4. What are some advantages of cloud computing?
-
Advantages of cloud computing include cost efficiency, scalability, accessibility, reliability, security, automatic updates, and the ability to foster innovation.
5. What are some disadvantages of cloud computing?
-
Disadvantages of cloud computing include potential downtime, security concerns, limited control over infrastructure, bandwidth limitations, data transfer costs, vendor lock-in, and compliance challenges.
6. What is the shared responsibility model in cloud security?
-
The shared responsibility model outlines the division of security responsibilities between the cloud provider and the customer. The provider is responsible for securing the infrastructure, while the customer is responsible for securing their data and applications within the cloud.
7. What are some common cloud computing certifications?
-
Popular cloud computing certifications include AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified Azure Administrator, Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect, and Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP).
8. How do I choose the right cloud provider for my organization?
-
Choosing the right cloud provider involves considering factors like services offered, pricing, security features, compliance, data center locations, and customer support. It's essential to align your choice with your organization's specific needs and goals.
9. What is the difference between cloud computing and traditional IT infrastructure?
-
Cloud computing offers on-demand access to computing resources over the internet, while traditional IT infrastructure relies on on-premises hardware and software. Cloud computing is scalable, cost-effective, and provides greater flexibility compared to traditional IT.
10. How can I ensure data security in the cloud?
-
Ensuring data security in the cloud involves implementing strong access controls, encryption, regular security audits, compliance with industry standards, and monitoring for suspicious activities. It's essential to follow best practices for cloud security.
What is Scrum Framework and How Does It Work Effectively?
In the dynamic landscape of project management and software development, methodologies that foster flexibility, collaboration, and rapid adaptation are essential. One such methodology that has gained widespread recognition and adoption is the Scrum Framework. Born out of the Agile movement, Scrum has revolutionized the way teams tackle complex projects, enabling them to deliver high-quality results efficiently and with enhanced teamwork.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the Scrum Framework, unraveling its core principles, methodologies, and the seamless interplay of its roles and rituals. Whether you're an aspiring project manager, a seasoned software developer, or simply curious about how Scrum works, join us on this journey as we explore the essence of Scrum and how it can transform the way you approach projects. From its foundational concepts to its practical implementation, you'll gain a solid understanding of what Scrum is and, more importantly, how it works to bring about unparalleled success in the world of project management and beyond.
Table of Contents
What is the Scrum Process Framework?
What Are Scrum Artifacts?
Benefits of Scrum Methodology
Scrum and Agile Relationship Explained
Scrum Ceremonies or Events
Scrum Pillars and Values
3 Essential Roles for Scrum Success
Scaling Scrum to Multiple Teams
Conclusion
What is the Scrum Process Framework?
The Scrum process framework is an agile project management approach designed to facilitate the iterative and incremental development of products. It is characterized by a set of defined roles, events, artifacts, and rules that guide a development team's work. Key roles include the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team, each with specific responsibilities. Scrum events, such as Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective, provide a structured rhythm to the development process. The Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment are the essential artifacts used to manage work and track progress. Scrum emphasizes transparency, inspection, and adaptation, allowing teams to respond to changing requirements and deliver high-value product increments regularly.
One of Scrum's core principles is its focus on collaboration and adaptability. By breaking work into small, manageable iterations called sprints, teams can quickly respond to customer feedback and changing priorities. This iterative approach encourages continuous improvement, making Scrum an effective framework for complex projects where requirements may evolve over time. It promotes a sense of ownership and accountability among team members, leading to more efficient and productive development cycles. Scrum's simplicity and flexibility have made it a popular choice not only in software development but also in various industries seeking to deliver value to customers faster and with greater adaptability.
What Are Scrum Artifacts?
Scrum artifacts are essential documents or information sources that provide transparency and help in managing work within the Scrum framework. These artifacts are used to ensure that everyone involved in a Scrum project has a common understanding of the product being developed and the progress being made. There are three primary Scrum artifacts:
-
Product Backlog: The Product Backlog is a prioritized list of all the work that needs to be done to create and maintain the product. It is owned and managed by the Product Owner. The items in the Product Backlog can include features, user stories, bug fixes, technical tasks, and other work items. Each item is described in sufficient detail so that the development team understands what needs to be done. The Product Owner continuously refines and prioritizes the backlog based on changing requirements and feedback from stakeholders.
-
Sprint Backlog: The Sprint Backlog is a subset of the items from the Product Backlog that the development team commits to completing during a specific sprint. It is created during the Sprint Planning event, where the team selects the highest-priority items from the Product Backlog and decides how they will deliver them. The Sprint Backlog is a dynamic document that can be adjusted as the team gains a better understanding of the work during the sprint. It helps the team track progress toward the sprint goal.
-
Increment: The Increment is the sum of all the product backlog items that have been completed during a sprint. It represents a potentially shippable product or a product incrementally closer to the desired end state. At the end of each sprint, the development team delivers the Increment for review by stakeholders during the Sprint Review event. If accepted, the Increment can be released to users or customers. The goal is to have a potentially shippable product increment at the end of each sprint, although it may not include all desired features until subsequent sprints.
These Scrum artifacts serve to provide transparency, enable inspection, and support adaptation throughout the development process. They ensure that everyone involved in the project, including the development team, Product Owner, and stakeholders, has a clear understanding of what work is to be done, what has been completed, and the overall progress toward the product's goals.
Benefits of Scrum Methodology
The Scrum methodology offers several benefits, making it a popular choice for agile project management and product development. Some of the key advantages of Scrum include:
-
Flexibility and Adaptability: Scrum embraces change and allows teams to adapt to evolving requirements, market conditions, and customer feedback. It offers the flexibility to reprioritize work and make adjustments during short, time-boxed iterations called sprints.
-
Customer-Centric: Scrum places a strong emphasis on delivering value to the customer. The Product Owner is responsible for prioritizing the product backlog based on customer needs, ensuring that the most valuable features are built first.
-
Transparency: Scrum promotes transparency by making project information visible to all team members. This transparency encourages collaboration, accountability, and open communication among team members and stakeholders.
-
Increased Productivity: Scrum's iterative approach often leads to higher productivity because it focuses on delivering a potentially shippable product incrementally. Teams can release valuable features sooner, providing benefits to the end-users and stakeholders.
-
Early and Regular Feedback: Scrum encourages frequent feedback through events like Sprint Reviews and Daily Scrums. This continuous feedback loop helps identify and address issues early in the development process, reducing the risk of building the wrong product.
-
Improved Quality: Scrum places a strong emphasis on quality through practices like automated testing and continuous integration. The incremental development and regular inspections help maintain and improve product quality over time.
-
Empowered Teams: Scrum empowers development teams to self-organize and make decisions regarding how to achieve sprint goals. This autonomy and ownership often lead to more motivated and engaged team members.
-
Predictable Delivery: Scrum promotes predictability by establishing a consistent cadence of work through time-boxed sprints. This helps stakeholders understand when they can expect specific features or updates.
-
Reduced Risk: With its focus on frequent inspections and adaptations, Scrum helps mitigate risks by identifying and addressing issues early in the project. Teams can make informed decisions to course-correct as needed.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: Scrum fosters collaboration among cross-functional team members, including developers, testers, designers, and product managers. Regular meetings like the Daily Scrum promote communication and collaboration.
While Scrum offers numerous benefits, it's essential to recognize that its successful implementation requires a committed and well-trained team, adherence to Scrum principles, and continuous improvement to refine processes over time.
Scrum and Agile Relationship Explained
Scrum and Agile are closely related concepts in the world of project management and software development, with Scrum being one of the most popular frameworks within the broader Agile methodology. Here's an explanation of their relationship:
Agile:
-
Agile is a set of values and principles outlined in the Agile Manifesto, which was created in 2001 by a group of software developers. The manifesto emphasizes customer collaboration, responding to change, and delivering working software as primary goals.
-
Agile is not a specific framework or methodology but rather a mindset or philosophy that promotes flexibility, collaboration, and customer-centricity. It encourages teams to work iteratively and adapt to changing requirements and customer feedback.
Scrum:
-
Scrum is a specific framework for implementing Agile principles. It provides a structured approach to managing work within an Agile context.
-
Scrum prescribes a set of roles (Product Owner, Scrum Master, Development Team), events (Sprint, Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective), and artifacts (Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, Increment) that help teams organize their work, collaborate effectively, and deliver value to customers.
Relationship:
-
Scrum is a subset of Agile: Scrum falls under the umbrella of Agile methodologies. While Agile is a broader philosophy, Scrum is a specific approach that adheres to Agile principles.
-
Scrum operationalizes Agile: Scrum provides a practical framework for teams to implement Agile principles in a structured way. It defines roles, events, and artifacts that guide the development process, making Agile principles actionable.
-
Scrum is a popular choice for Agile: Many organizations adopt Scrum as their chosen methodology for implementing Agile practices. However, Agile is not limited to Scrum; there are other Agile frameworks like Kanban, Lean, and Extreme Programming (XP), each with its own set of principles and practices.
In summary, Agile is the overarching philosophy that emphasizes customer collaboration, flexibility, and iterative development, while Scrum is a specific framework that operationalizes Agile principles. Scrum provides a structured approach to managing work and is one of the most widely used methods for implementing Agile practices in software development and other project management contexts.
Scrum Ceremonies or Events
In Scrum, there are several ceremonies or events that provide structure and cadence to the development process. These events help teams collaborate, plan, inspect and adapt their work. The key Scrum ceremonies or events are:
-
Sprint Planning: This is a time-boxed event at the start of each sprint where the Product Owner and Development Team collaborate to select and commit to a set of product backlog items to be worked on during the sprint. The team also discusses how to achieve the sprint goal.
-
Daily Scrum (Daily Standup): A daily, time-boxed meeting where the Development Team synchronizes their work. Each team member answers three questions: What did I do yesterday? What will I do today? Are there any impediments or blockers? This meeting helps the team stay on track and adapt to changing circumstances.
-
Sprint Review: At the end of each sprint, there is a Sprint Review meeting where the Development Team demonstrates the work completed during the sprint to stakeholders, including the Product Owner and possibly customers. It's an opportunity to gather feedback and potentially adjust the product backlog based on new insights.
-
Sprint Retrospective: Also held at the end of each sprint, the Sprint Retrospective is a meeting for the Development Team to reflect on the sprint and identify improvements. It's a time to discuss what went well, what could be improved, and what action items the team will take in the next sprint.
-
Backlog Refinement (Grooming): While not a formal event, backlog refinement is an ongoing activity where the Product Owner and Development Team collaborate to clarify, estimate, and prioritize items in the product backlog. This ensures that the backlog is well-prepared for future sprints.
These Scrum ceremonies provide a structured framework for planning, communication, and continuous improvement within the Scrum process. They help teams stay focused on delivering value, adapt to changing requirements, and maintain transparency throughout the development process. The time-boxed nature of these events ensures that they are efficient and don't become overly time-consuming.
Scrum Pillars and Values
Scrum is guided by three pillars and five core values, which provide the foundation for the framework and help teams implement Scrum effectively. These pillars and values are integral to Scrum's success:
Pillars:
-
Transparency: Transparency is the first pillar of Scrum, emphasizing openness and visibility in all aspects of work. It means that all relevant information about the project, progress, and challenges should be easily accessible to all team members and stakeholders. Transparency promotes trust and helps teams make informed decisions.
-
Inspection: The second pillar is inspection, which encourages regular examination of the product, processes, and progress. Teams should inspect their work and the product increment continuously, identifying areas that need improvement. Inspection provides opportunities to adapt and make necessary changes to enhance product quality and efficiency.
-
Adaptation: The third pillar, adaptation, goes hand-in-hand with inspection. Once issues are identified through inspection, teams must take action to adapt and make improvements. Scrum encourages flexibility and adaptability in response to changing requirements, market conditions, or other factors. Adaptation is essential for delivering valuable products and continuously improving the development process.
Values:
-
Commitment: Scrum values commitment, particularly commitment to delivering value to the customer. The team commits to the goals of the sprint and works diligently to achieve them. Commitment also includes the commitment to quality and excellence in all aspects of the work.
-
Courage: Courage is the value that enables teams to confront challenges and take calculated risks. It means speaking up about issues, suggesting changes, and admitting when something isn't working as expected. Teams should have the courage to make tough decisions that are in the best interest of the product and the project.
-
Focus: Scrum encourages focus on the sprint goal and the highest-priority work. Teams should concentrate their efforts on completing the items in the sprint backlog and delivering a potentially shippable product increment. Distractions and scope changes should be minimized to maintain focus.
-
Openness: Openness is about fostering an environment where team members and stakeholders can communicate transparently. It means being receptive to feedback, actively listening, and promoting collaboration. Openness encourages the sharing of information and ideas to improve the project.
-
Respect: Respect is a fundamental value in Scrum, promoting respect for each team member's expertise, opinions, and contributions. It also extends to respecting the decisions of the team and stakeholders. A respectful environment supports effective teamwork and collaboration.
These pillars and values provide the underlying philosophy and principles that guide Scrum teams in their work. When teams and organizations embrace these pillars and values, they are better equipped to harness the power of Scrum to deliver high-quality products and adapt to changing demands effectively.
3 Essential Roles for Scrum Success
Scrum relies on three essential roles to ensure its success. These roles play distinct but interconnected functions in the Scrum framework:
Product Owner:
-
The Product Owner is a crucial role responsible for representing the interests of stakeholders, including customers and users. They are the primary decision-maker regarding the product's features, functionality, and priorities.
-
Responsibilities include creating and maintaining the product backlog, which is a prioritized list of work items (often user stories) that define what needs to be built or improved.
-
The Product Owner collaborates closely with the development team to clarify requirements, answer questions, and provide ongoing feedback.
-
Success in this role involves effectively balancing stakeholder needs, maintaining a clear product vision, and continuously prioritizing the backlog to maximize the product's value.
Scrum Master:
-
The Scrum Master is a servant-leader for the Scrum team, focused on facilitating and coaching the team to follow Scrum principles and practices.
-
Responsibilities include removing impediments or obstacles that hinder the team's progress, ensuring that Scrum events are conducted effectively, and promoting a collaborative and self-organizing team culture.
-
The Scrum Master fosters continuous improvement by facilitating the Sprint Retrospective and encouraging the team to reflect on their processes and make adjustments.
-
Success in this role involves guiding the team toward self-sufficiency, helping them improve their Scrum practices, and ensuring that Scrum values are upheld.
Development Team:
-
The Development Team consists of cross-functional individuals who work together to deliver a potentially shippable product increment during each sprint.
-
Responsibilities include selecting and committing to work items from the sprint backlog, designing, coding, testing, and delivering the product increment.
-
Development Teams are self-organizing, meaning they have the autonomy to determine how to complete the work and make decisions about how to meet the sprint goal.
-
Success of the Development Team is measured by their ability to consistently deliver high-quality, potentially shippable increments of the product and their commitment to continuous improvement.
These three roles are integral to the success of Scrum. The Product Owner ensures that the product meets customer needs, the Scrum Master enables the team to follow Scrum principles, and the Development Team is responsible for delivering the product increment. Effective collaboration and adherence to Scrum values and principles among these roles are essential for achieving Scrum's goal of delivering value to customers through iterative and incremental development.
Scaling Scrum to Multiple Teams
Scaling Scrum to multiple teams in five key points:
-
Choose a Scaling Framework: Select an appropriate scaling framework, such as SAFe, LeSS, or Nexus, that aligns with your organizational goals and context.
-
Coordinate Product Ownership: Ensure product ownership is well-coordinated across teams, either by creating a Product Owner team or designating a Chief Product Owner to maintain a unified product backlog.
-
Facilitate Cross-Team Collaboration: Organize regular Scrum of Scrums meetings to facilitate cross-team collaboration, share information, and address dependencies.
-
Implement Program Increment (PI) Planning: Conduct PI planning sessions to align the work of multiple teams for a set period (e.g., 8-12 weeks) and establish a shared vision.
-
Promote a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Foster a culture of continuous improvement, provide training and coaching, and regularly inspect and adapt at both the team and program levels to enhance collaboration and alignment among teams.
How to obtain the CSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
Conclusion
In conclusion, Scrum is a powerful framework for agile project management and product development that emphasizes transparency, inspection, and adaptation. Its three pillars of transparency, inspection, and adaptation, along with its five core values of commitment, courage, focus, openness, and respect, provide a strong foundation for teams to deliver value to customers effectively.
Scrum's essential roles, including the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team, play distinct but interconnected functions in ensuring project success. The ceremonies or events, such as Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective, provide structure and guidance throughout the development process.
When it comes to scaling Scrum to multiple teams, organizations have several frameworks and strategies to choose from, such as SAFe, Scrum of Scrums, and coordinated product ownership. These approaches enable large and complex organizations to maintain alignment, collaboration, and responsiveness as they deliver value to customers.
In essence, Scrum promotes a customer-centric, adaptable, and collaborative approach to project management, making it a valuable choice for a wide range of industries and project types. By embracing Scrum's principles, roles, values, and ceremonies, teams and organizations can increase their chances of delivering high-quality products and continuously improving their processes.
Read More
In the dynamic landscape of project management and software development, methodologies that foster flexibility, collaboration, and rapid adaptation are essential. One such methodology that has gained widespread recognition and adoption is the Scrum Framework. Born out of the Agile movement, Scrum has revolutionized the way teams tackle complex projects, enabling them to deliver high-quality results efficiently and with enhanced teamwork.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the Scrum Framework, unraveling its core principles, methodologies, and the seamless interplay of its roles and rituals. Whether you're an aspiring project manager, a seasoned software developer, or simply curious about how Scrum works, join us on this journey as we explore the essence of Scrum and how it can transform the way you approach projects. From its foundational concepts to its practical implementation, you'll gain a solid understanding of what Scrum is and, more importantly, how it works to bring about unparalleled success in the world of project management and beyond.
Table of Contents
What is the Scrum Process Framework?
What Are Scrum Artifacts?
Benefits of Scrum Methodology
Scrum and Agile Relationship Explained
Scrum Ceremonies or Events
Scrum Pillars and Values
3 Essential Roles for Scrum Success
Scaling Scrum to Multiple Teams
Conclusion
What is the Scrum Process Framework?
The Scrum process framework is an agile project management approach designed to facilitate the iterative and incremental development of products. It is characterized by a set of defined roles, events, artifacts, and rules that guide a development team's work. Key roles include the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team, each with specific responsibilities. Scrum events, such as Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective, provide a structured rhythm to the development process. The Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment are the essential artifacts used to manage work and track progress. Scrum emphasizes transparency, inspection, and adaptation, allowing teams to respond to changing requirements and deliver high-value product increments regularly.
One of Scrum's core principles is its focus on collaboration and adaptability. By breaking work into small, manageable iterations called sprints, teams can quickly respond to customer feedback and changing priorities. This iterative approach encourages continuous improvement, making Scrum an effective framework for complex projects where requirements may evolve over time. It promotes a sense of ownership and accountability among team members, leading to more efficient and productive development cycles. Scrum's simplicity and flexibility have made it a popular choice not only in software development but also in various industries seeking to deliver value to customers faster and with greater adaptability.
What Are Scrum Artifacts?
Scrum artifacts are essential documents or information sources that provide transparency and help in managing work within the Scrum framework. These artifacts are used to ensure that everyone involved in a Scrum project has a common understanding of the product being developed and the progress being made. There are three primary Scrum artifacts:
-
Product Backlog: The Product Backlog is a prioritized list of all the work that needs to be done to create and maintain the product. It is owned and managed by the Product Owner. The items in the Product Backlog can include features, user stories, bug fixes, technical tasks, and other work items. Each item is described in sufficient detail so that the development team understands what needs to be done. The Product Owner continuously refines and prioritizes the backlog based on changing requirements and feedback from stakeholders.
-
Sprint Backlog: The Sprint Backlog is a subset of the items from the Product Backlog that the development team commits to completing during a specific sprint. It is created during the Sprint Planning event, where the team selects the highest-priority items from the Product Backlog and decides how they will deliver them. The Sprint Backlog is a dynamic document that can be adjusted as the team gains a better understanding of the work during the sprint. It helps the team track progress toward the sprint goal.
-
Increment: The Increment is the sum of all the product backlog items that have been completed during a sprint. It represents a potentially shippable product or a product incrementally closer to the desired end state. At the end of each sprint, the development team delivers the Increment for review by stakeholders during the Sprint Review event. If accepted, the Increment can be released to users or customers. The goal is to have a potentially shippable product increment at the end of each sprint, although it may not include all desired features until subsequent sprints.
These Scrum artifacts serve to provide transparency, enable inspection, and support adaptation throughout the development process. They ensure that everyone involved in the project, including the development team, Product Owner, and stakeholders, has a clear understanding of what work is to be done, what has been completed, and the overall progress toward the product's goals.
Benefits of Scrum Methodology
The Scrum methodology offers several benefits, making it a popular choice for agile project management and product development. Some of the key advantages of Scrum include:
-
Flexibility and Adaptability: Scrum embraces change and allows teams to adapt to evolving requirements, market conditions, and customer feedback. It offers the flexibility to reprioritize work and make adjustments during short, time-boxed iterations called sprints.
-
Customer-Centric: Scrum places a strong emphasis on delivering value to the customer. The Product Owner is responsible for prioritizing the product backlog based on customer needs, ensuring that the most valuable features are built first.
-
Transparency: Scrum promotes transparency by making project information visible to all team members. This transparency encourages collaboration, accountability, and open communication among team members and stakeholders.
-
Increased Productivity: Scrum's iterative approach often leads to higher productivity because it focuses on delivering a potentially shippable product incrementally. Teams can release valuable features sooner, providing benefits to the end-users and stakeholders.
-
Early and Regular Feedback: Scrum encourages frequent feedback through events like Sprint Reviews and Daily Scrums. This continuous feedback loop helps identify and address issues early in the development process, reducing the risk of building the wrong product.
-
Improved Quality: Scrum places a strong emphasis on quality through practices like automated testing and continuous integration. The incremental development and regular inspections help maintain and improve product quality over time.
-
Empowered Teams: Scrum empowers development teams to self-organize and make decisions regarding how to achieve sprint goals. This autonomy and ownership often lead to more motivated and engaged team members.
-
Predictable Delivery: Scrum promotes predictability by establishing a consistent cadence of work through time-boxed sprints. This helps stakeholders understand when they can expect specific features or updates.
-
Reduced Risk: With its focus on frequent inspections and adaptations, Scrum helps mitigate risks by identifying and addressing issues early in the project. Teams can make informed decisions to course-correct as needed.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: Scrum fosters collaboration among cross-functional team members, including developers, testers, designers, and product managers. Regular meetings like the Daily Scrum promote communication and collaboration.
While Scrum offers numerous benefits, it's essential to recognize that its successful implementation requires a committed and well-trained team, adherence to Scrum principles, and continuous improvement to refine processes over time.
Scrum and Agile Relationship Explained
Scrum and Agile are closely related concepts in the world of project management and software development, with Scrum being one of the most popular frameworks within the broader Agile methodology. Here's an explanation of their relationship:
Agile:
-
Agile is a set of values and principles outlined in the Agile Manifesto, which was created in 2001 by a group of software developers. The manifesto emphasizes customer collaboration, responding to change, and delivering working software as primary goals.
-
Agile is not a specific framework or methodology but rather a mindset or philosophy that promotes flexibility, collaboration, and customer-centricity. It encourages teams to work iteratively and adapt to changing requirements and customer feedback.
Scrum:
-
Scrum is a specific framework for implementing Agile principles. It provides a structured approach to managing work within an Agile context.
-
Scrum prescribes a set of roles (Product Owner, Scrum Master, Development Team), events (Sprint, Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective), and artifacts (Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, Increment) that help teams organize their work, collaborate effectively, and deliver value to customers.
Relationship:
-
Scrum is a subset of Agile: Scrum falls under the umbrella of Agile methodologies. While Agile is a broader philosophy, Scrum is a specific approach that adheres to Agile principles.
-
Scrum operationalizes Agile: Scrum provides a practical framework for teams to implement Agile principles in a structured way. It defines roles, events, and artifacts that guide the development process, making Agile principles actionable.
-
Scrum is a popular choice for Agile: Many organizations adopt Scrum as their chosen methodology for implementing Agile practices. However, Agile is not limited to Scrum; there are other Agile frameworks like Kanban, Lean, and Extreme Programming (XP), each with its own set of principles and practices.
In summary, Agile is the overarching philosophy that emphasizes customer collaboration, flexibility, and iterative development, while Scrum is a specific framework that operationalizes Agile principles. Scrum provides a structured approach to managing work and is one of the most widely used methods for implementing Agile practices in software development and other project management contexts.
Scrum Ceremonies or Events
In Scrum, there are several ceremonies or events that provide structure and cadence to the development process. These events help teams collaborate, plan, inspect and adapt their work. The key Scrum ceremonies or events are:
-
Sprint Planning: This is a time-boxed event at the start of each sprint where the Product Owner and Development Team collaborate to select and commit to a set of product backlog items to be worked on during the sprint. The team also discusses how to achieve the sprint goal.
-
Daily Scrum (Daily Standup): A daily, time-boxed meeting where the Development Team synchronizes their work. Each team member answers three questions: What did I do yesterday? What will I do today? Are there any impediments or blockers? This meeting helps the team stay on track and adapt to changing circumstances.
-
Sprint Review: At the end of each sprint, there is a Sprint Review meeting where the Development Team demonstrates the work completed during the sprint to stakeholders, including the Product Owner and possibly customers. It's an opportunity to gather feedback and potentially adjust the product backlog based on new insights.
-
Sprint Retrospective: Also held at the end of each sprint, the Sprint Retrospective is a meeting for the Development Team to reflect on the sprint and identify improvements. It's a time to discuss what went well, what could be improved, and what action items the team will take in the next sprint.
-
Backlog Refinement (Grooming): While not a formal event, backlog refinement is an ongoing activity where the Product Owner and Development Team collaborate to clarify, estimate, and prioritize items in the product backlog. This ensures that the backlog is well-prepared for future sprints.
These Scrum ceremonies provide a structured framework for planning, communication, and continuous improvement within the Scrum process. They help teams stay focused on delivering value, adapt to changing requirements, and maintain transparency throughout the development process. The time-boxed nature of these events ensures that they are efficient and don't become overly time-consuming.
Scrum Pillars and Values
Scrum is guided by three pillars and five core values, which provide the foundation for the framework and help teams implement Scrum effectively. These pillars and values are integral to Scrum's success:
Pillars:
-
Transparency: Transparency is the first pillar of Scrum, emphasizing openness and visibility in all aspects of work. It means that all relevant information about the project, progress, and challenges should be easily accessible to all team members and stakeholders. Transparency promotes trust and helps teams make informed decisions.
-
Inspection: The second pillar is inspection, which encourages regular examination of the product, processes, and progress. Teams should inspect their work and the product increment continuously, identifying areas that need improvement. Inspection provides opportunities to adapt and make necessary changes to enhance product quality and efficiency.
-
Adaptation: The third pillar, adaptation, goes hand-in-hand with inspection. Once issues are identified through inspection, teams must take action to adapt and make improvements. Scrum encourages flexibility and adaptability in response to changing requirements, market conditions, or other factors. Adaptation is essential for delivering valuable products and continuously improving the development process.
Values:
-
Commitment: Scrum values commitment, particularly commitment to delivering value to the customer. The team commits to the goals of the sprint and works diligently to achieve them. Commitment also includes the commitment to quality and excellence in all aspects of the work.
-
Courage: Courage is the value that enables teams to confront challenges and take calculated risks. It means speaking up about issues, suggesting changes, and admitting when something isn't working as expected. Teams should have the courage to make tough decisions that are in the best interest of the product and the project.
-
Focus: Scrum encourages focus on the sprint goal and the highest-priority work. Teams should concentrate their efforts on completing the items in the sprint backlog and delivering a potentially shippable product increment. Distractions and scope changes should be minimized to maintain focus.
-
Openness: Openness is about fostering an environment where team members and stakeholders can communicate transparently. It means being receptive to feedback, actively listening, and promoting collaboration. Openness encourages the sharing of information and ideas to improve the project.
-
Respect: Respect is a fundamental value in Scrum, promoting respect for each team member's expertise, opinions, and contributions. It also extends to respecting the decisions of the team and stakeholders. A respectful environment supports effective teamwork and collaboration.
These pillars and values provide the underlying philosophy and principles that guide Scrum teams in their work. When teams and organizations embrace these pillars and values, they are better equipped to harness the power of Scrum to deliver high-quality products and adapt to changing demands effectively.
3 Essential Roles for Scrum Success
Scrum relies on three essential roles to ensure its success. These roles play distinct but interconnected functions in the Scrum framework:
Product Owner:
-
The Product Owner is a crucial role responsible for representing the interests of stakeholders, including customers and users. They are the primary decision-maker regarding the product's features, functionality, and priorities.
-
Responsibilities include creating and maintaining the product backlog, which is a prioritized list of work items (often user stories) that define what needs to be built or improved.
-
The Product Owner collaborates closely with the development team to clarify requirements, answer questions, and provide ongoing feedback.
-
Success in this role involves effectively balancing stakeholder needs, maintaining a clear product vision, and continuously prioritizing the backlog to maximize the product's value.
Scrum Master:
-
The Scrum Master is a servant-leader for the Scrum team, focused on facilitating and coaching the team to follow Scrum principles and practices.
-
Responsibilities include removing impediments or obstacles that hinder the team's progress, ensuring that Scrum events are conducted effectively, and promoting a collaborative and self-organizing team culture.
-
The Scrum Master fosters continuous improvement by facilitating the Sprint Retrospective and encouraging the team to reflect on their processes and make adjustments.
-
Success in this role involves guiding the team toward self-sufficiency, helping them improve their Scrum practices, and ensuring that Scrum values are upheld.
Development Team:
-
The Development Team consists of cross-functional individuals who work together to deliver a potentially shippable product increment during each sprint.
-
Responsibilities include selecting and committing to work items from the sprint backlog, designing, coding, testing, and delivering the product increment.
-
Development Teams are self-organizing, meaning they have the autonomy to determine how to complete the work and make decisions about how to meet the sprint goal.
-
Success of the Development Team is measured by their ability to consistently deliver high-quality, potentially shippable increments of the product and their commitment to continuous improvement.
These three roles are integral to the success of Scrum. The Product Owner ensures that the product meets customer needs, the Scrum Master enables the team to follow Scrum principles, and the Development Team is responsible for delivering the product increment. Effective collaboration and adherence to Scrum values and principles among these roles are essential for achieving Scrum's goal of delivering value to customers through iterative and incremental development.
Scaling Scrum to Multiple Teams
Scaling Scrum to multiple teams in five key points:
-
Choose a Scaling Framework: Select an appropriate scaling framework, such as SAFe, LeSS, or Nexus, that aligns with your organizational goals and context.
-
Coordinate Product Ownership: Ensure product ownership is well-coordinated across teams, either by creating a Product Owner team or designating a Chief Product Owner to maintain a unified product backlog.
-
Facilitate Cross-Team Collaboration: Organize regular Scrum of Scrums meetings to facilitate cross-team collaboration, share information, and address dependencies.
-
Implement Program Increment (PI) Planning: Conduct PI planning sessions to align the work of multiple teams for a set period (e.g., 8-12 weeks) and establish a shared vision.
-
Promote a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Foster a culture of continuous improvement, provide training and coaching, and regularly inspect and adapt at both the team and program levels to enhance collaboration and alignment among teams.
How to obtain the CSM certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
Conclusion
In conclusion, Scrum is a powerful framework for agile project management and product development that emphasizes transparency, inspection, and adaptation. Its three pillars of transparency, inspection, and adaptation, along with its five core values of commitment, courage, focus, openness, and respect, provide a strong foundation for teams to deliver value to customers effectively.
Scrum's essential roles, including the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team, play distinct but interconnected functions in ensuring project success. The ceremonies or events, such as Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective, provide structure and guidance throughout the development process.
When it comes to scaling Scrum to multiple teams, organizations have several frameworks and strategies to choose from, such as SAFe, Scrum of Scrums, and coordinated product ownership. These approaches enable large and complex organizations to maintain alignment, collaboration, and responsiveness as they deliver value to customers.
In essence, Scrum promotes a customer-centric, adaptable, and collaborative approach to project management, making it a valuable choice for a wide range of industries and project types. By embracing Scrum's principles, roles, values, and ceremonies, teams and organizations can increase their chances of delivering high-quality products and continuously improving their processes.
Top 10 Business Analytics Tools Used by Companies Today
In today's data-driven business landscape, the ability to transform raw information into actionable insights has become a competitive advantage for companies across industries. Business analytics tools have emerged as indispensable assets in this pursuit, empowering organizations to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and drive growth. As technology continues to evolve, the range and capabilities of these tools have expanded, allowing businesses to harness the power of data like never before.
In this blog, we will delve into the world of data-driven decision-making and explore the top 10 business analytics tools that are currently reshaping the way companies operate. Whether you're a seasoned data professional seeking to enhance your toolkit or a business leader eager to leverage data for strategic advantage, this guide will introduce you to the cutting-edge tools that are driving innovation and success in today's competitive landscape. From data visualization to predictive modeling, these tools offer a diverse array of capabilities that are transforming how organizations extract value from their data assets. Join us on this journey through the world of business analytics and discover the tools that are at the forefront of modern business intelligence.
Table of Contents
What Are Business Analytics Tools?
Difference Between Business Analytics and Business Intelligence Solutions
Popular Open Source Analytics Tools
Career Options in Business Analytics
But How Do You Start Your Career and Land a High-Paying Job?
Conclusion
What Are Business Analytics Tools?
Business analytics tools are software applications that help organizations extract valuable insights from their data to support decision-making processes. These tools enable businesses to collect, process, and analyze data from various sources, transforming raw information into meaningful patterns, trends, and actionable recommendations. They encompass a wide range of functions, including data visualization, statistical analysis, predictive modeling, and reporting. By utilizing business analytics tools, companies can gain a deeper understanding of their operations, customers, and market dynamics, ultimately leading to more informed and strategic choices.
These tools are invaluable in today's data-driven business landscape, where the ability to make decisions based on evidence and trends can significantly impact an organization's success. They enable companies to uncover hidden opportunities, identify areas for improvement, and optimize their strategies, ultimately enhancing competitiveness and profitability. Whether it's tracking website performance with Google Analytics, creating interactive dashboards with Tableau, or leveraging machine learning with Python, business analytics tools offer versatile solutions for businesses of all sizes and industries to harness the power of data for informed decision-making.
Difference Between Business Analytics and Business Intelligence Solutions
Here's a concise comparison of Business Analytics and Business Intelligence solutions in tabular form:
Aspect
Business Intelligence (BI)
Business Analytics
Purpose and Focus
Historical and current data, focuses on reporting and monitoring.
Historical data used to predict future trends, optimize processes, and make strategic decisions.
Timeframe
Past and present data analysis.
Past data analysis to predict future events.
Types of Questions Answered
Descriptive questions (What happened?).
Diagnostic (Why did it happen?), predictive (What will happen?), and prescriptive (What should we do?) questions.
Data Visualization vs. Data Modeling
Emphasis on data visualization through dashboards and reports.
Focus on data modeling and statistical analysis to create predictive models.
Use Cases
Routine reporting, performance monitoring, and standard operational reporting.
Complex problem-solving, strategic decision-making, financial forecasting, customer segmentation, supply chain optimization, and more.
This table provides a clear overview of the key distinctions between Business Intelligence and Business Analytics solutions.
Popular Open Source Analytics Tools
-
R:
-
Description: R is a versatile programming language and environment specifically designed for statistical computing and data analysis. It offers a wide array of packages and libraries for data manipulation, visualization, and advanced statistical modeling.
-
Use Cases: R is popular among statisticians, data scientists, and researchers for tasks such as data exploration, hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and creating custom data visualizations.
-
Key Features: It provides extensive libraries for data analysis (e.g., dplyr, tidyr), data visualization (ggplot2), and machine learning (caret). R's interactive console allows users to explore and analyze data interactively.
-
Community: R has a vibrant and active community that contributes to package development and provides support through forums and mailing lists.
-
Python:
-
Description: Python is a versatile, easy-to-learn programming language with a thriving ecosystem for data analysis, machine learning, and web development. It is known for its simplicity and readability.
-
Use Cases: Python is used for data cleaning, manipulation, visualization, machine learning, and web scraping. Popular libraries include Pandas, Matplotlib, Seaborn, scikit-learn, and TensorFlow.
-
Key Features: Python's simplicity makes it accessible to beginners, and its vast library of packages makes it suitable for a wide range of data tasks. Jupyter notebooks enable interactive data exploration and documentation.
-
Community: Python boasts a large and active community, offering extensive documentation, tutorials, and support resources.
-
Apache Hadoop:
-
Description: Apache Hadoop is an open-source framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets across a cluster of commodity hardware.
-
Use Cases: Hadoop is primarily used for big data processing and distributed storage. It is essential for organizations dealing with massive volumes of structured and unstructured data.
-
Key Features: Hadoop includes the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) for distributed storage and MapReduce for distributed data processing. It can handle diverse data types and is scalable.
-
Community: Hadoop has a robust community, and it has given rise to numerous other big data tools and technologies.
-
Apache Spark:
-
Description: Apache Spark is an open-source big data processing framework known for its speed, versatility, and real-time processing capabilities.
-
Use Cases: Spark is used for big data processing, machine learning, graph processing, and real-time analytics. It's known for its efficiency and support for diverse data workloads.
-
Key Features: Spark's in-memory processing makes it faster than Hadoop's MapReduce. It provides high-level APIs in Python, Scala, and Java, along with libraries for machine learning (MLlib) and graph processing (GraphX).
-
Community: Spark has a thriving community and a rich ecosystem of libraries and tools.
-
KNIME:
-
Description: KNIME (Konstanz Information Miner) is an open-source platform for data analytics, reporting, and integration that uses a visual workflow interface.
-
Use Cases: KNIME is used for data preprocessing, analysis, reporting, and machine learning. It is designed to be accessible to both technical and non-technical users.
-
Key Features: KNIME's visual interface allows users to create data analysis workflows without coding. It supports integration with various data sources, offers extensions and plugins, and provides collaboration features.
-
Community: KNIME has an active community that contributes to its development, provides support, and shares workflows and extensions.
-
Orange:
-
Description: Orange is an open-source data visualization and analysis tool that focuses on visual programming for data exploration, analysis, and machine learning.
-
Use Cases: Orange is used for data preprocessing, data visualization, clustering, classification, and regression. It is known for its user-friendly, drag-and-drop interface.
-
Key Features: Orange provides a wide range of data visualization widgets and analysis components. Users can experiment with data and build machine learning models without programming.
-
Community: Orange has an active community of users and contributors, and it offers extensive documentation and tutorials.
-
Jupyter Notebook:
-
Description: Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that enables users to create and share documents containing live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text.
-
Use Cases: Jupyter Notebook is used for interactive data analysis, data exploration, code prototyping, and creating reproducible research documents.
-
Key Features: It supports multiple programming languages, including Python, R, Julia, and others. Users can combine code, data, visualizations, and explanations in a single interactive document.
-
Community: Jupyter has a thriving community and is widely adopted in data science and research fields.
-
Grafana:
-
Description: Originally designed for monitoring and observability, Grafana is an open-source platform for creating interactive and customizable dashboards for data visualization.
-
Use Cases: Grafana is used for real-time data visualization, monitoring system performance, and creating interactive dashboards for various data sources.
-
Key Features: Grafana supports connections to databases, cloud services, and data sources. It offers a range of visualization options, alerting capabilities, and templating for building dynamic dashboards.
-
Community: Grafana has a growing community, and its plugins and extensions enhance its functionality.
-
Metabase:
-
Description: Metabase is an open-source business intelligence and analytics tool designed for simplicity and accessibility.
-
Use Cases: Metabase is used for querying and visualizing data, creating dashboards, and generating ad-hoc reports, particularly by non-technical users.
-
Key Features: It provides an intuitive and user-friendly interface for data exploration. Metabase connects to various data sources and offers features for sharing and collaboration.
-
Community: Metabase has an active community and a user-friendly setup process.
-
Apache Superset:
-
Description: Apache Superset is an open-source data exploration and visualization platform initially developed by Airbnb.
-
Use Cases: Superset is used for creating interactive and shareable dashboards, exploring data, and ad-hoc querying from various data sources.
-
Key Features: Superset offers a user-friendly interface with a drag-and-drop dashboard builder. It supports multiple chart types, data source connectors, and customization options.
-
Community: Superset has an active and growing community and is part of the Apache Software Foundation.
These open-source analytics tools cover a wide range of data analysis and visualization needs, from statistical modeling to big data processing and business intelligence. Users can select the tool that best aligns with their specific goals, expertise, and data-related tasks.
Career Options in Business Analytics
A career in business analytics offers an exciting and dynamic journey into the world of data-driven decision-making. At its core, business analytics involves the systematic analysis of data to uncover insights and trends that can guide an organization's strategic and operational choices. Data analysts are often the first step in this process, responsible for collecting, cleaning, and organizing data from various sources. They use tools like SQL and Excel to transform raw data into structured datasets, enabling further analysis.
Moving up the ladder, business intelligence analysts specialize in creating visually appealing reports and dashboards that convey complex data findings to non-technical stakeholders. They use specialized BI tools like Tableau and Power BI to present historical data in a way that is easy to understand, helping organizations make informed decisions based on past performance.
For those who want to dive deeper into data exploration and predictive modeling, data scientists and machine learning engineers come into play. Data scientists leverage advanced statistical and machine learning techniques to extract valuable insights and predict future trends from data. They might build recommendation systems, forecast sales, or optimize marketing campaigns. Machine learning engineers, on the other hand, focus on implementing machine learning models in production environments, ensuring they can scale and perform efficiently.
In essence, a career in business analytics offers a pathway for individuals with various skill sets and interests to contribute to organizations' success by harnessing the power of data. Whether you prefer data wrangling and visualization, predictive modeling, or building data-driven solutions, there's a role in business analytics that aligns with your expertise and passion.
But How Do You Start Your Career and Land a High-Paying Job?
To kickstart your career as a business analyst, the essential step is acquiring the right skill sets. You can begin today by exploring and enrolling in iCert Global’s innovative, interactive, and career-focused In Business Analysis (CCBA,CBAP,ECBA) Certifications. This program offers training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.. Start your journey towards becoming a business analyst today!
Conclusion
In conclusion, a career in business analytics is an exciting and lucrative path for those who are passionate about data and its transformative power in decision-making. To embark on this journey, one must focus on acquiring the necessary skills through education, online courses, and certifications. Building a strong portfolio of projects and networking with professionals in the field are also critical steps. Landing a high-paying job in business analytics requires dedication, continuous learning, and effective job search strategies.
Remember that the field is dynamic, with opportunities spanning data analysis, business intelligence, data science, and more. By staying updated with industry trends and honing your expertise, you can not only start but also thrive in a rewarding career as a business analyst. It's a field where your ability to unlock insights from data can make a significant impact on organizations across various industries. So, take that first step, invest in your skills, and embark on your journey towards a successful career in business analytics.
How to obtain AI and Deep Learning Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Do visit our Corporate Training to know more about core offerings for enterprises in empowering their workforce.
iCert Global conducts Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, Agile, Scrum, and DevOps Certification courses across various locations in the United States.
Visit us at https://www.icertglobal.com/ for more information about our professional certification training courses or Call Now! on +1-713-287-1213 / +1-713-287-1214 or e-mail us at info@icertglobal.com.
Project Management Training by iCert Global:
Quality Management Training by iCert Global:
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt (LSSYB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (LSSBB) Certification Training Courses
Scrum Training by iCert Global:
- CSM (Certified ScrumMaster) Certification Training Courses
Agile Training by iCert Global:
- PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Professional) Certification Training Courses
DevOps Training by iCert Global:
- DevOps Certification Training Courses
Business Analysis Training by iCert Global:
- ECBA (Entry Certificate in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CCBA (Certificate of Capability in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional) Certification Training Courses
Emerging Technologies :
-
Read More
In today's data-driven business landscape, the ability to transform raw information into actionable insights has become a competitive advantage for companies across industries. Business analytics tools have emerged as indispensable assets in this pursuit, empowering organizations to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and drive growth. As technology continues to evolve, the range and capabilities of these tools have expanded, allowing businesses to harness the power of data like never before.
In this blog, we will delve into the world of data-driven decision-making and explore the top 10 business analytics tools that are currently reshaping the way companies operate. Whether you're a seasoned data professional seeking to enhance your toolkit or a business leader eager to leverage data for strategic advantage, this guide will introduce you to the cutting-edge tools that are driving innovation and success in today's competitive landscape. From data visualization to predictive modeling, these tools offer a diverse array of capabilities that are transforming how organizations extract value from their data assets. Join us on this journey through the world of business analytics and discover the tools that are at the forefront of modern business intelligence.
Table of Contents
What Are Business Analytics Tools?
Difference Between Business Analytics and Business Intelligence Solutions
Popular Open Source Analytics Tools
Career Options in Business Analytics
But How Do You Start Your Career and Land a High-Paying Job?
Conclusion
What Are Business Analytics Tools?
Business analytics tools are software applications that help organizations extract valuable insights from their data to support decision-making processes. These tools enable businesses to collect, process, and analyze data from various sources, transforming raw information into meaningful patterns, trends, and actionable recommendations. They encompass a wide range of functions, including data visualization, statistical analysis, predictive modeling, and reporting. By utilizing business analytics tools, companies can gain a deeper understanding of their operations, customers, and market dynamics, ultimately leading to more informed and strategic choices.
These tools are invaluable in today's data-driven business landscape, where the ability to make decisions based on evidence and trends can significantly impact an organization's success. They enable companies to uncover hidden opportunities, identify areas for improvement, and optimize their strategies, ultimately enhancing competitiveness and profitability. Whether it's tracking website performance with Google Analytics, creating interactive dashboards with Tableau, or leveraging machine learning with Python, business analytics tools offer versatile solutions for businesses of all sizes and industries to harness the power of data for informed decision-making.
Difference Between Business Analytics and Business Intelligence Solutions
Here's a concise comparison of Business Analytics and Business Intelligence solutions in tabular form:
|
Aspect |
Business Intelligence (BI) |
Business Analytics |
|
Purpose and Focus |
Historical and current data, focuses on reporting and monitoring. |
Historical data used to predict future trends, optimize processes, and make strategic decisions. |
|
Timeframe |
Past and present data analysis. |
Past data analysis to predict future events. |
|
Types of Questions Answered |
Descriptive questions (What happened?). |
Diagnostic (Why did it happen?), predictive (What will happen?), and prescriptive (What should we do?) questions. |
|
Data Visualization vs. Data Modeling |
Emphasis on data visualization through dashboards and reports. |
Focus on data modeling and statistical analysis to create predictive models. |
|
Use Cases |
Routine reporting, performance monitoring, and standard operational reporting. |
Complex problem-solving, strategic decision-making, financial forecasting, customer segmentation, supply chain optimization, and more. |
This table provides a clear overview of the key distinctions between Business Intelligence and Business Analytics solutions.
Popular Open Source Analytics Tools
-
R:
-
Description: R is a versatile programming language and environment specifically designed for statistical computing and data analysis. It offers a wide array of packages and libraries for data manipulation, visualization, and advanced statistical modeling.
-
Use Cases: R is popular among statisticians, data scientists, and researchers for tasks such as data exploration, hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and creating custom data visualizations.
-
Key Features: It provides extensive libraries for data analysis (e.g., dplyr, tidyr), data visualization (ggplot2), and machine learning (caret). R's interactive console allows users to explore and analyze data interactively.
-
Community: R has a vibrant and active community that contributes to package development and provides support through forums and mailing lists.
-
-
Python:
-
Description: Python is a versatile, easy-to-learn programming language with a thriving ecosystem for data analysis, machine learning, and web development. It is known for its simplicity and readability.
-
Use Cases: Python is used for data cleaning, manipulation, visualization, machine learning, and web scraping. Popular libraries include Pandas, Matplotlib, Seaborn, scikit-learn, and TensorFlow.
-
Key Features: Python's simplicity makes it accessible to beginners, and its vast library of packages makes it suitable for a wide range of data tasks. Jupyter notebooks enable interactive data exploration and documentation.
-
Community: Python boasts a large and active community, offering extensive documentation, tutorials, and support resources.
-
-
Apache Hadoop:
-
Description: Apache Hadoop is an open-source framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets across a cluster of commodity hardware.
-
Use Cases: Hadoop is primarily used for big data processing and distributed storage. It is essential for organizations dealing with massive volumes of structured and unstructured data.
-
Key Features: Hadoop includes the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) for distributed storage and MapReduce for distributed data processing. It can handle diverse data types and is scalable.
-
Community: Hadoop has a robust community, and it has given rise to numerous other big data tools and technologies.
-
-
Apache Spark:
-
Description: Apache Spark is an open-source big data processing framework known for its speed, versatility, and real-time processing capabilities.
-
Use Cases: Spark is used for big data processing, machine learning, graph processing, and real-time analytics. It's known for its efficiency and support for diverse data workloads.
-
Key Features: Spark's in-memory processing makes it faster than Hadoop's MapReduce. It provides high-level APIs in Python, Scala, and Java, along with libraries for machine learning (MLlib) and graph processing (GraphX).
-
Community: Spark has a thriving community and a rich ecosystem of libraries and tools.
-
-
KNIME:
-
Description: KNIME (Konstanz Information Miner) is an open-source platform for data analytics, reporting, and integration that uses a visual workflow interface.
-
Use Cases: KNIME is used for data preprocessing, analysis, reporting, and machine learning. It is designed to be accessible to both technical and non-technical users.
-
Key Features: KNIME's visual interface allows users to create data analysis workflows without coding. It supports integration with various data sources, offers extensions and plugins, and provides collaboration features.
-
Community: KNIME has an active community that contributes to its development, provides support, and shares workflows and extensions.
-
-
Orange:
-
Description: Orange is an open-source data visualization and analysis tool that focuses on visual programming for data exploration, analysis, and machine learning.
-
Use Cases: Orange is used for data preprocessing, data visualization, clustering, classification, and regression. It is known for its user-friendly, drag-and-drop interface.
-
Key Features: Orange provides a wide range of data visualization widgets and analysis components. Users can experiment with data and build machine learning models without programming.
-
Community: Orange has an active community of users and contributors, and it offers extensive documentation and tutorials.
-
-
Jupyter Notebook:
-
Description: Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that enables users to create and share documents containing live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text.
-
Use Cases: Jupyter Notebook is used for interactive data analysis, data exploration, code prototyping, and creating reproducible research documents.
-
Key Features: It supports multiple programming languages, including Python, R, Julia, and others. Users can combine code, data, visualizations, and explanations in a single interactive document.
-
Community: Jupyter has a thriving community and is widely adopted in data science and research fields.
-
-
Grafana:
-
Description: Originally designed for monitoring and observability, Grafana is an open-source platform for creating interactive and customizable dashboards for data visualization.
-
Use Cases: Grafana is used for real-time data visualization, monitoring system performance, and creating interactive dashboards for various data sources.
-
Key Features: Grafana supports connections to databases, cloud services, and data sources. It offers a range of visualization options, alerting capabilities, and templating for building dynamic dashboards.
-
Community: Grafana has a growing community, and its plugins and extensions enhance its functionality.
-
-
Metabase:
-
Description: Metabase is an open-source business intelligence and analytics tool designed for simplicity and accessibility.
-
Use Cases: Metabase is used for querying and visualizing data, creating dashboards, and generating ad-hoc reports, particularly by non-technical users.
-
Key Features: It provides an intuitive and user-friendly interface for data exploration. Metabase connects to various data sources and offers features for sharing and collaboration.
-
Community: Metabase has an active community and a user-friendly setup process.
-
-
Apache Superset:
-
Description: Apache Superset is an open-source data exploration and visualization platform initially developed by Airbnb.
-
Use Cases: Superset is used for creating interactive and shareable dashboards, exploring data, and ad-hoc querying from various data sources.
-
Key Features: Superset offers a user-friendly interface with a drag-and-drop dashboard builder. It supports multiple chart types, data source connectors, and customization options.
-
Community: Superset has an active and growing community and is part of the Apache Software Foundation.
-
These open-source analytics tools cover a wide range of data analysis and visualization needs, from statistical modeling to big data processing and business intelligence. Users can select the tool that best aligns with their specific goals, expertise, and data-related tasks.
Career Options in Business Analytics
A career in business analytics offers an exciting and dynamic journey into the world of data-driven decision-making. At its core, business analytics involves the systematic analysis of data to uncover insights and trends that can guide an organization's strategic and operational choices. Data analysts are often the first step in this process, responsible for collecting, cleaning, and organizing data from various sources. They use tools like SQL and Excel to transform raw data into structured datasets, enabling further analysis.
Moving up the ladder, business intelligence analysts specialize in creating visually appealing reports and dashboards that convey complex data findings to non-technical stakeholders. They use specialized BI tools like Tableau and Power BI to present historical data in a way that is easy to understand, helping organizations make informed decisions based on past performance.
For those who want to dive deeper into data exploration and predictive modeling, data scientists and machine learning engineers come into play. Data scientists leverage advanced statistical and machine learning techniques to extract valuable insights and predict future trends from data. They might build recommendation systems, forecast sales, or optimize marketing campaigns. Machine learning engineers, on the other hand, focus on implementing machine learning models in production environments, ensuring they can scale and perform efficiently.
In essence, a career in business analytics offers a pathway for individuals with various skill sets and interests to contribute to organizations' success by harnessing the power of data. Whether you prefer data wrangling and visualization, predictive modeling, or building data-driven solutions, there's a role in business analytics that aligns with your expertise and passion.
But How Do You Start Your Career and Land a High-Paying Job?
To kickstart your career as a business analyst, the essential step is acquiring the right skill sets. You can begin today by exploring and enrolling in iCert Global’s innovative, interactive, and career-focused In Business Analysis (CCBA,CBAP,ECBA) Certifications. This program offers training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.. Start your journey towards becoming a business analyst today!
Conclusion
In conclusion, a career in business analytics is an exciting and lucrative path for those who are passionate about data and its transformative power in decision-making. To embark on this journey, one must focus on acquiring the necessary skills through education, online courses, and certifications. Building a strong portfolio of projects and networking with professionals in the field are also critical steps. Landing a high-paying job in business analytics requires dedication, continuous learning, and effective job search strategies.
Remember that the field is dynamic, with opportunities spanning data analysis, business intelligence, data science, and more. By staying updated with industry trends and honing your expertise, you can not only start but also thrive in a rewarding career as a business analyst. It's a field where your ability to unlock insights from data can make a significant impact on organizations across various industries. So, take that first step, invest in your skills, and embark on your journey towards a successful career in business analytics.
How to obtain AI and Deep Learning Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Do visit our Corporate Training to know more about core offerings for enterprises in empowering their workforce.
iCert Global conducts Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, Agile, Scrum, and DevOps Certification courses across various locations in the United States.
Visit us at https://www.icertglobal.com/ for more information about our professional certification training courses or Call Now! on +1-713-287-1213 / +1-713-287-1214 or e-mail us at info@icertglobal.com.
Project Management Training by iCert Global:
Quality Management Training by iCert Global:
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt (LSSYB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (LSSBB) Certification Training Courses
Scrum Training by iCert Global:
- CSM (Certified ScrumMaster) Certification Training Courses
Agile Training by iCert Global:
- PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Professional) Certification Training Courses
DevOps Training by iCert Global:
- DevOps Certification Training Courses
Business Analysis Training by iCert Global:
- ECBA (Entry Certificate in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CCBA (Certificate of Capability in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional) Certification Training Courses
Emerging Technologies :
AI in Manufacturing: Here's Everything You Should Know
The world of manufacturing is in the midst of a technological revolution, and at the heart of this transformation lies Artificial Intelligence (AI). From predictive maintenance that keeps machines running smoothly to quality control systems that ensure every product meets impeccable standards, AI is redefining the manufacturing landscape. It's not just about automation; it's about creating more efficient, agile, and competitive manufacturing processes. In this blog, we'll take a deep dive into the realm of AI in manufacturing, uncovering its applications, benefits, challenges, and future potential. Whether you're a seasoned industry professional or simply curious about how AI is reshaping the factory floor, here's everything you should know about AI's role in modern manufacturing.
Table of Contents
What Is AI in Manufacturing?
Key AI Segments That Impact Manufacturing
How is AI Used in the Manufacturing Industry?
Role of AI in the Industrial Sector
AI in Manufacturing
Choose the Right Program
Conclusion
What Is AI in Manufacturing?
AI in manufacturing refers to the integration of artificial intelligence technologies into various aspects of the manufacturing process to enhance efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. It encompasses the use of advanced algorithms, machine learning, computer vision, and data analytics to automate tasks, make predictions, and optimize operations within a manufacturing environment. This application of AI empowers manufacturers to streamline production, improve product quality, and reduce costs.
One of the key applications of AI in manufacturing is predictive maintenance, where AI algorithms analyze data from sensors and historical performance to predict when equipment or machinery is likely to fail. This allows for timely maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime and preventing costly breakdowns. Additionally, AI is employed in quality control through computer vision systems that inspect and identify defects in products in real-time, ensuring that only high-quality items are shipped to customers. Furthermore, AI aids in supply chain optimization by analyzing demand patterns and inventory levels, enabling manufacturers to meet customer demands efficiently while minimizing excess inventory.
In summary, AI in manufacturing represents a technological revolution that leverages artificial intelligence to enhance various aspects of the manufacturing process. By harnessing the power of AI, manufacturers can achieve greater efficiency, improve product quality, and ultimately remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industry.
Key AI Segments That Impact Manufacturing
AI has a profound impact on manufacturing across various segments, transforming the industry in several ways. Here are the key AI segments that have a significant influence on manufacturing:
-
Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance uses AI and machine learning algorithms to predict when equipment or machinery is likely to fail. By analyzing data from sensors and historical performance, manufacturers can schedule maintenance proactively, reducing unplanned downtime and costly repairs.
-
Quality Control and Inspection: AI-powered computer vision systems are employed for real-time quality control and inspection of products on the manufacturing line. These systems can detect defects, deviations from quality standards, and anomalies, ensuring that only high-quality products are produced and shipped to customers.
-
Supply Chain Optimization: AI plays a crucial role in optimizing the supply chain by analyzing data related to demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics. Manufacturers can use AI-driven insights to ensure that they have the right materials on hand, minimize excess inventory, and streamline distribution.
-
Process Automation: Robotics and automation powered by AI are increasingly used for repetitive and labor-intensive tasks in manufacturing. These AI-driven robots can work with precision and consistency, reducing the need for human intervention in certain processes and improving efficiency.
-
Energy Management: AI algorithms can monitor energy consumption within manufacturing facilities and make real-time adjustments to optimize energy usage. This not only reduces energy costs but also contributes to sustainability efforts.
-
Customization and Personalization: AI enables mass customization of products by tailoring manufacturing processes to individual customer preferences. This is particularly valuable in industries like automotive and consumer electronics, where personalization is in demand.
-
Data Analytics and Insights: AI processes and analyzes vast amounts of data generated by manufacturing operations. This data-driven approach helps manufacturers identify patterns, trends, and opportunities for improvement, leading to better decision-making and operational optimization.
-
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR, often powered by AI, provide workers with real-time information and guidance on the factory floor. This improves worker efficiency, training, and safety.
-
Digital Twins: AI-driven digital twins create virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems, allowing for simulation, testing, and optimization before making changes to the actual production line. This reduces downtime and risk during process improvements.
-
Human-Machine Collaboration: Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and safety. AI algorithms ensure that these robots can adapt to changes in their environment and work safely with humans.
How is AI Used in the Manufacturing Industry?
AI is used in the manufacturing industry across various domains to enhance efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. Here's how AI is applied in manufacturing:
Predictive Maintenance: AI analyzes data from sensors and historical performance to predict when equipment or machinery is likely to fail. This enables manufacturers to schedule maintenance proactively, reducing unplanned downtime and preventing costly breakdowns.
Quality Control and Inspection: AI-powered computer vision systems inspect products on the manufacturing line in real-time. They identify defects, anomalies, and deviations from quality standards, ensuring that only high-quality products are produced and shipped to customers.
Supply Chain Optimization: AI optimizes the supply chain by analyzing data related to demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics. Manufacturers can use AI-driven insights to minimize excess inventory, optimize distribution, and ensure efficient supply chain operations.
Process Automation: Robotics and automation powered by AI are employed for repetitive and labor-intensive tasks. These AI-driven robots work with precision and consistency, reducing the need for human intervention in certain processes and improving overall efficiency.
Energy Management: AI algorithms monitor and control energy consumption within manufacturing facilities. They make real-time adjustments to optimize energy usage, reducing energy costs and contributing to sustainability efforts.
Customization and Personalization: AI enables mass customization of products by tailoring manufacturing processes to individual customer preferences. This is valuable in industries where personalized products are in demand, such as automotive and consumer electronics.
Data Analytics and Insights: AI processes and analyzes vast amounts of data generated by manufacturing operations. This data-driven approach helps manufacturers identify patterns, trends, and opportunities for improvement, leading to better decision-making and operational optimization.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR, often powered by AI, provide workers with real-time information and guidance on the factory floor. This enhances worker efficiency, training, and safety.
Digital Twins: AI-driven digital twins create virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems. Manufacturers can use these digital twins for simulation, testing, and optimization before implementing changes to the actual production line, reducing downtime and risk.
Human-Machine Collaboration: Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and safety. AI algorithms ensure that these robots can adapt to changes in their environment and work safely with humans.
Role of AI in the Industrial Sector
AI plays a pivotal role in the industrial sector, transforming various aspects of operations, decision-making, and productivity. Here are some key roles of AI in the industrial sector:
-
Predictive Maintenance: AI analyzes data from sensors and machinery to predict when equipment is likely to fail. This enables proactive maintenance, reducing downtime, and preventing costly breakdowns. It also extends the lifespan of industrial equipment.
-
Quality Control and Inspection: AI-powered computer vision systems can inspect and evaluate the quality of products in real-time. They detect defects, deviations from quality standards, and anomalies, ensuring that only high-quality products are manufactured and shipped.
-
Process Optimization: AI optimizes industrial processes by analyzing data and making real-time adjustments. This can lead to increased efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and improved overall productivity in manufacturing and industrial operations.
-
Supply Chain Management: AI enhances supply chain management by analyzing vast amounts of data related to demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics. Manufacturers can optimize their supply chains, ensuring that materials are available when needed and minimizing excess inventory.
-
Robotics and Automation: AI-driven robots and automation systems perform tasks with precision and consistency. They can handle repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, reducing the need for human labor and improving safety in industrial environments.
AI in Manufacturing
AI in manufacturing represents a transformative force that is revolutionizing the way goods are produced, monitored, and optimized in the manufacturing industry. It encompasses the integration of various artificial intelligence technologies, including machine learning, deep learning, computer vision, and natural language processing, into manufacturing processes and operations. Here's an overview of AI's role in manufacturing:
-
Predictive Maintenance: AI analyzes data from sensors and machinery to predict when equipment or machinery is likely to fail. This enables proactive maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime and minimizing costly repairs. Predictive maintenance extends the lifespan of equipment and maximizes its utilization.
-
Quality Control and Inspection: AI-powered computer vision systems are employed for real-time quality control and inspection of products on the manufacturing line. These systems can identify defects, deviations from quality standards, and anomalies, ensuring that only high-quality products are produced and shipped.
-
Supply Chain Optimization: AI plays a critical role in optimizing the supply chain by analyzing data related to demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics. Manufacturers can use AI-driven insights to minimize excess inventory, optimize distribution, and ensure efficient supply chain operations.
-
Process Automation: Robotics and automation powered by AI are increasingly used for repetitive and labor-intensive tasks in manufacturing. These AI-driven robots can work with precision and consistency, reducing the need for human intervention in certain processes and improving overall efficiency.
-
Energy Efficiency: AI algorithms monitor and control energy consumption within manufacturing facilities, making real-time adjustments to optimize energy usage. This reduces energy costs and contributes to sustainability efforts.
-
Customization and Personalization: AI enables mass customization of products by tailoring manufacturing processes to individual customer preferences. This is particularly valuable in industries where personalized products are in demand, such as automotive and consumer electronics.
-
Data Analytics and Insights: AI processes and analyzes vast amounts of data generated by manufacturing operations. This data-driven approach helps manufacturers identify patterns, trends, and opportunities for improvement, leading to better decision-making and operational optimization.
-
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR, often powered by AI, provide workers with real-time information and guidance on the factory floor. This enhances worker efficiency, training, and safety.
-
Digital Twins: AI-driven digital twins create virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems. Manufacturers can use these digital twins for simulation, testing, and optimization before implementing changes to the actual production line, reducing downtime and risk.
-
Human-Machine Collaboration: Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and safety. AI algorithms ensure that these robots can adapt to changes in their environment and work safely with humans.
Choose the Right Program
Selecting the right program or software for a specific task or purpose is essential to maximize efficiency and achieve your goals effectively. Here are some steps to help you choose the right program:
-
Define Your Needs and Goals:
-
Clearly outline what you want to accomplish with the program.
-
Identify the specific features and capabilities you require to meet your objectives.
-
Research and Comparison:
-
Conduct thorough research to find potential programs or software that align with your needs.
-
Create a list of options and compare them based on features, pricing, user reviews, and industry reputation.
-
Compatibility:
-
Ensure that the program is compatible with your operating system and hardware.
-
Check for any integration capabilities with other tools or software you currently use.
-
Ease of Use:
-
Consider the program's user-friendliness. Is it intuitive and easy to navigate?
-
Look for user guides, tutorials, and customer support options in case you need assistance.
-
Cost and Budget:
-
Evaluate the cost of the program, including any subscription fees, licensing costs, and potential hidden charges.
-
Determine whether the program fits within your budget.
-
Trial and Testing:
-
Whenever possible, take advantage of free trials or demos to test the program before making a commitment.
-
Use this opportunity to see how well it meets your needs and whether it aligns with your workflow.
-
User Feedback:
-
Read user reviews and testimonials to gain insights into the experiences of others who have used the program.
-
Pay attention to both positive and negative feedback to make an informed decision.
-
Scalability and Future Needs:
-
Consider whether the program can scale with your growing needs.
-
Think about your long-term goals and whether the software can support your evolving requirements.
-
Support and Updates:
-
Check for the availability of customer support, including email, phone, or chat support.
-
Determine the frequency of software updates and whether they address bug fixes and improvements.
-
Security and Privacy:
-
Ensure that the program adheres to security standards and regulations relevant to your industry.
-
Verify the program's data privacy policies to protect sensitive information.
Conclusion
AI in manufacturing is not just a buzzword; it's a transformative force that's reshaping the landscape of one of the world's most critical industries. As we've explored in this blog, AI's applications in manufacturing are wide-ranging and impactful.
From predictive maintenance that prevents costly downtimes to quality control systems that ensure impeccable product standards, AI is improving efficiency and product quality. It optimizes supply chains, streamlines processes, and enhances energy management, all contributing to cost savings and sustainability.
The customization and personalization capabilities of AI are redefining how products are made and how businesses interact with customers. AI-driven data analytics empower manufacturers to make data-driven decisions and stay competitive in rapidly changing markets.
As we look to the future, AI's role in manufacturing will only expand. From digital twins and augmented reality to even more advanced automation, AI promises to continue revolutionizing this crucial industry, ensuring its adaptability and resilience in the face of evolving challenges. Embracing AI in manufacturing is not just about keeping up; it's about thriving in an era of unprecedented technological progress.
How to obtain AI and Deep Learning Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Do visit our Corporate Training to know more about core offerings for enterprises in empowering their workforce.
iCert Global conducts Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, Agile, Scrum, and DevOps Certification courses across various locations in the United States.
Visit us at https://www.icertglobal.com/ for more information about our professional certification training courses or Call Now! on +1-713-287-1213 / +1-713-287-1214 or e-mail us at info@icertglobal.com.
Project Management Training by iCert Global:
Quality Management Training by iCert Global:
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt (LSSYB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (LSSBB) Certification Training Courses
Scrum Training by iCert Global:
- CSM (Certified ScrumMaster) Certification Training Courses
Agile Training by iCert Global:
- PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Professional) Certification Training Courses
DevOps Training by iCert Global:
- DevOps Certification Training Courses
Business Analysis Training by iCert Global:
- ECBA (Entry Certificate in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CCBA (Certificate of Capability in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional) Certification Training Courses
Emerging Technologies :
Read More
The world of manufacturing is in the midst of a technological revolution, and at the heart of this transformation lies Artificial Intelligence (AI). From predictive maintenance that keeps machines running smoothly to quality control systems that ensure every product meets impeccable standards, AI is redefining the manufacturing landscape. It's not just about automation; it's about creating more efficient, agile, and competitive manufacturing processes. In this blog, we'll take a deep dive into the realm of AI in manufacturing, uncovering its applications, benefits, challenges, and future potential. Whether you're a seasoned industry professional or simply curious about how AI is reshaping the factory floor, here's everything you should know about AI's role in modern manufacturing.
Table of Contents
What Is AI in Manufacturing?
Key AI Segments That Impact Manufacturing
How is AI Used in the Manufacturing Industry?
Role of AI in the Industrial Sector
AI in Manufacturing
Choose the Right Program
Conclusion
What Is AI in Manufacturing?
AI in manufacturing refers to the integration of artificial intelligence technologies into various aspects of the manufacturing process to enhance efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. It encompasses the use of advanced algorithms, machine learning, computer vision, and data analytics to automate tasks, make predictions, and optimize operations within a manufacturing environment. This application of AI empowers manufacturers to streamline production, improve product quality, and reduce costs.
One of the key applications of AI in manufacturing is predictive maintenance, where AI algorithms analyze data from sensors and historical performance to predict when equipment or machinery is likely to fail. This allows for timely maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime and preventing costly breakdowns. Additionally, AI is employed in quality control through computer vision systems that inspect and identify defects in products in real-time, ensuring that only high-quality items are shipped to customers. Furthermore, AI aids in supply chain optimization by analyzing demand patterns and inventory levels, enabling manufacturers to meet customer demands efficiently while minimizing excess inventory.
In summary, AI in manufacturing represents a technological revolution that leverages artificial intelligence to enhance various aspects of the manufacturing process. By harnessing the power of AI, manufacturers can achieve greater efficiency, improve product quality, and ultimately remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industry.
Key AI Segments That Impact Manufacturing
AI has a profound impact on manufacturing across various segments, transforming the industry in several ways. Here are the key AI segments that have a significant influence on manufacturing:
-
Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance uses AI and machine learning algorithms to predict when equipment or machinery is likely to fail. By analyzing data from sensors and historical performance, manufacturers can schedule maintenance proactively, reducing unplanned downtime and costly repairs.
-
Quality Control and Inspection: AI-powered computer vision systems are employed for real-time quality control and inspection of products on the manufacturing line. These systems can detect defects, deviations from quality standards, and anomalies, ensuring that only high-quality products are produced and shipped to customers.
-
Supply Chain Optimization: AI plays a crucial role in optimizing the supply chain by analyzing data related to demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics. Manufacturers can use AI-driven insights to ensure that they have the right materials on hand, minimize excess inventory, and streamline distribution.
-
Process Automation: Robotics and automation powered by AI are increasingly used for repetitive and labor-intensive tasks in manufacturing. These AI-driven robots can work with precision and consistency, reducing the need for human intervention in certain processes and improving efficiency.
-
Energy Management: AI algorithms can monitor energy consumption within manufacturing facilities and make real-time adjustments to optimize energy usage. This not only reduces energy costs but also contributes to sustainability efforts.
-
Customization and Personalization: AI enables mass customization of products by tailoring manufacturing processes to individual customer preferences. This is particularly valuable in industries like automotive and consumer electronics, where personalization is in demand.
-
Data Analytics and Insights: AI processes and analyzes vast amounts of data generated by manufacturing operations. This data-driven approach helps manufacturers identify patterns, trends, and opportunities for improvement, leading to better decision-making and operational optimization.
-
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR, often powered by AI, provide workers with real-time information and guidance on the factory floor. This improves worker efficiency, training, and safety.
-
Digital Twins: AI-driven digital twins create virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems, allowing for simulation, testing, and optimization before making changes to the actual production line. This reduces downtime and risk during process improvements.
-
Human-Machine Collaboration: Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and safety. AI algorithms ensure that these robots can adapt to changes in their environment and work safely with humans.
How is AI Used in the Manufacturing Industry?
AI is used in the manufacturing industry across various domains to enhance efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. Here's how AI is applied in manufacturing:
Predictive Maintenance: AI analyzes data from sensors and historical performance to predict when equipment or machinery is likely to fail. This enables manufacturers to schedule maintenance proactively, reducing unplanned downtime and preventing costly breakdowns.
Quality Control and Inspection: AI-powered computer vision systems inspect products on the manufacturing line in real-time. They identify defects, anomalies, and deviations from quality standards, ensuring that only high-quality products are produced and shipped to customers.
Supply Chain Optimization: AI optimizes the supply chain by analyzing data related to demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics. Manufacturers can use AI-driven insights to minimize excess inventory, optimize distribution, and ensure efficient supply chain operations.
Process Automation: Robotics and automation powered by AI are employed for repetitive and labor-intensive tasks. These AI-driven robots work with precision and consistency, reducing the need for human intervention in certain processes and improving overall efficiency.
Energy Management: AI algorithms monitor and control energy consumption within manufacturing facilities. They make real-time adjustments to optimize energy usage, reducing energy costs and contributing to sustainability efforts.
Customization and Personalization: AI enables mass customization of products by tailoring manufacturing processes to individual customer preferences. This is valuable in industries where personalized products are in demand, such as automotive and consumer electronics.
Data Analytics and Insights: AI processes and analyzes vast amounts of data generated by manufacturing operations. This data-driven approach helps manufacturers identify patterns, trends, and opportunities for improvement, leading to better decision-making and operational optimization.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR, often powered by AI, provide workers with real-time information and guidance on the factory floor. This enhances worker efficiency, training, and safety.
Digital Twins: AI-driven digital twins create virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems. Manufacturers can use these digital twins for simulation, testing, and optimization before implementing changes to the actual production line, reducing downtime and risk.
Human-Machine Collaboration: Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and safety. AI algorithms ensure that these robots can adapt to changes in their environment and work safely with humans.
Role of AI in the Industrial Sector
AI plays a pivotal role in the industrial sector, transforming various aspects of operations, decision-making, and productivity. Here are some key roles of AI in the industrial sector:
-
Predictive Maintenance: AI analyzes data from sensors and machinery to predict when equipment is likely to fail. This enables proactive maintenance, reducing downtime, and preventing costly breakdowns. It also extends the lifespan of industrial equipment.
-
Quality Control and Inspection: AI-powered computer vision systems can inspect and evaluate the quality of products in real-time. They detect defects, deviations from quality standards, and anomalies, ensuring that only high-quality products are manufactured and shipped.
-
Process Optimization: AI optimizes industrial processes by analyzing data and making real-time adjustments. This can lead to increased efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and improved overall productivity in manufacturing and industrial operations.
-
Supply Chain Management: AI enhances supply chain management by analyzing vast amounts of data related to demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics. Manufacturers can optimize their supply chains, ensuring that materials are available when needed and minimizing excess inventory.
-
Robotics and Automation: AI-driven robots and automation systems perform tasks with precision and consistency. They can handle repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, reducing the need for human labor and improving safety in industrial environments.
AI in Manufacturing
AI in manufacturing represents a transformative force that is revolutionizing the way goods are produced, monitored, and optimized in the manufacturing industry. It encompasses the integration of various artificial intelligence technologies, including machine learning, deep learning, computer vision, and natural language processing, into manufacturing processes and operations. Here's an overview of AI's role in manufacturing:
-
Predictive Maintenance: AI analyzes data from sensors and machinery to predict when equipment or machinery is likely to fail. This enables proactive maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime and minimizing costly repairs. Predictive maintenance extends the lifespan of equipment and maximizes its utilization.
-
Quality Control and Inspection: AI-powered computer vision systems are employed for real-time quality control and inspection of products on the manufacturing line. These systems can identify defects, deviations from quality standards, and anomalies, ensuring that only high-quality products are produced and shipped.
-
Supply Chain Optimization: AI plays a critical role in optimizing the supply chain by analyzing data related to demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics. Manufacturers can use AI-driven insights to minimize excess inventory, optimize distribution, and ensure efficient supply chain operations.
-
Process Automation: Robotics and automation powered by AI are increasingly used for repetitive and labor-intensive tasks in manufacturing. These AI-driven robots can work with precision and consistency, reducing the need for human intervention in certain processes and improving overall efficiency.
-
Energy Efficiency: AI algorithms monitor and control energy consumption within manufacturing facilities, making real-time adjustments to optimize energy usage. This reduces energy costs and contributes to sustainability efforts.
-
Customization and Personalization: AI enables mass customization of products by tailoring manufacturing processes to individual customer preferences. This is particularly valuable in industries where personalized products are in demand, such as automotive and consumer electronics.
-
Data Analytics and Insights: AI processes and analyzes vast amounts of data generated by manufacturing operations. This data-driven approach helps manufacturers identify patterns, trends, and opportunities for improvement, leading to better decision-making and operational optimization.
-
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR, often powered by AI, provide workers with real-time information and guidance on the factory floor. This enhances worker efficiency, training, and safety.
-
Digital Twins: AI-driven digital twins create virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems. Manufacturers can use these digital twins for simulation, testing, and optimization before implementing changes to the actual production line, reducing downtime and risk.
-
Human-Machine Collaboration: Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and safety. AI algorithms ensure that these robots can adapt to changes in their environment and work safely with humans.
Choose the Right Program
Selecting the right program or software for a specific task or purpose is essential to maximize efficiency and achieve your goals effectively. Here are some steps to help you choose the right program:
-
Define Your Needs and Goals:
-
Clearly outline what you want to accomplish with the program.
-
Identify the specific features and capabilities you require to meet your objectives.
-
-
Research and Comparison:
-
Conduct thorough research to find potential programs or software that align with your needs.
-
Create a list of options and compare them based on features, pricing, user reviews, and industry reputation.
-
-
Compatibility:
-
Ensure that the program is compatible with your operating system and hardware.
-
Check for any integration capabilities with other tools or software you currently use.
-
-
Ease of Use:
-
Consider the program's user-friendliness. Is it intuitive and easy to navigate?
-
Look for user guides, tutorials, and customer support options in case you need assistance.
-
-
Cost and Budget:
-
Evaluate the cost of the program, including any subscription fees, licensing costs, and potential hidden charges.
-
Determine whether the program fits within your budget.
-
-
Trial and Testing:
-
Whenever possible, take advantage of free trials or demos to test the program before making a commitment.
-
Use this opportunity to see how well it meets your needs and whether it aligns with your workflow.
-
-
User Feedback:
-
Read user reviews and testimonials to gain insights into the experiences of others who have used the program.
-
Pay attention to both positive and negative feedback to make an informed decision.
-
-
Scalability and Future Needs:
-
Consider whether the program can scale with your growing needs.
-
Think about your long-term goals and whether the software can support your evolving requirements.
-
-
Support and Updates:
-
Check for the availability of customer support, including email, phone, or chat support.
-
Determine the frequency of software updates and whether they address bug fixes and improvements.
-
-
Security and Privacy:
-
Ensure that the program adheres to security standards and regulations relevant to your industry.
-
Verify the program's data privacy policies to protect sensitive information.
-
Conclusion
AI in manufacturing is not just a buzzword; it's a transformative force that's reshaping the landscape of one of the world's most critical industries. As we've explored in this blog, AI's applications in manufacturing are wide-ranging and impactful.
From predictive maintenance that prevents costly downtimes to quality control systems that ensure impeccable product standards, AI is improving efficiency and product quality. It optimizes supply chains, streamlines processes, and enhances energy management, all contributing to cost savings and sustainability.
The customization and personalization capabilities of AI are redefining how products are made and how businesses interact with customers. AI-driven data analytics empower manufacturers to make data-driven decisions and stay competitive in rapidly changing markets.
As we look to the future, AI's role in manufacturing will only expand. From digital twins and augmented reality to even more advanced automation, AI promises to continue revolutionizing this crucial industry, ensuring its adaptability and resilience in the face of evolving challenges. Embracing AI in manufacturing is not just about keeping up; it's about thriving in an era of unprecedented technological progress.
How to obtain AI and Deep Learning Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Do visit our Corporate Training to know more about core offerings for enterprises in empowering their workforce.
iCert Global conducts Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, Agile, Scrum, and DevOps Certification courses across various locations in the United States.
Visit us at https://www.icertglobal.com/ for more information about our professional certification training courses or Call Now! on +1-713-287-1213 / +1-713-287-1214 or e-mail us at info@icertglobal.com.
Project Management Training by iCert Global:
Quality Management Training by iCert Global:
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt (LSSYB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (LSSBB) Certification Training Courses
Scrum Training by iCert Global:
- CSM (Certified ScrumMaster) Certification Training Courses
Agile Training by iCert Global:
- PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Professional) Certification Training Courses
DevOps Training by iCert Global:
- DevOps Certification Training Courses
Business Analysis Training by iCert Global:
- ECBA (Entry Certificate in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CCBA (Certificate of Capability in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional) Certification Training Courses
Emerging Technologies :
Project Management Officer:Skills,Jobs & Salary Trends 2023
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, effective project management stands as a cornerstone of success. And at the heart of this intricate orchestration lies the Project Management Officer (PMO), a role of growing importance in organizations around the world. As we step into 2023, the role of the PMO has evolved into far more than just overseeing projects; it has become a strategic linchpin that ensures projects align with an organization's vision and goals.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the realm of Project Management Officers, unveiling the intricate tapestry of their responsibilities, the key skills demanded in this evolving role, and the salary trends that will define the career landscape in 2023. Whether you are an aspiring PMO charting your career path or a seasoned professional seeking to stay at the forefront of industry trends, this exploration will guide you through the multifaceted world of PMOs and the vital role they play in shaping the future of project management.
Table of contents
-
Introduction to the Project Management Officer Role
-
Responsibilities of a PMO
-
Key Skills Required for a PMO
-
Educational and Certification Requirements
-
PMO Salary Trends in 2023
-
Tools and Technologies for PMOs
-
Career Path and Advancement for PMOs
-
Tips for Aspiring PMOs
-
Future Outlook for PMO Roles
-
Conclusion
Introduction to the Project Management Officer Role
The Project Management Officer, commonly known as the PMO, is the backbone of effective project management within organizations today. As businesses navigate increasingly complex projects, the PMO serves as the central orchestrator, ensuring that projects are executed efficiently and align with the company's strategic objectives. The PMO's responsibilities encompass governance, standardization, resource allocation, performance monitoring, risk management, and communication facilitation. By establishing best practices, maintaining project standards, and providing critical oversight, PMOs play a pivotal role in delivering successful projects on time and within budget. As businesses evolve and embrace technological advancements, PMOs are adapting to integrate innovative tools and methodologies into their practices, making the role of a Project Management Officer more vital than ever in the modern corporate landscape.
In the following sections of this blog, we will delve deeper into the specific functions and skills required for PMOs, explore the latest salary trends in 2023, and shed light on the promising career prospects awaiting those interested in pursuing or advancing within this dynamic and essential field. Whether you're considering a career as a PMO or seeking to understand the evolving role better, read on to gain comprehensive insights into the world of Project Management Officers.
Responsibilities of a PMO

-
Strategic support (sPMO): This involves providing operational support in projects by taking on the management of a project, executing defined subtasks, or providing project assistants. The sPMO plays a critical role in aligning project work with corporate strategy. They classify, select, prioritize, and, when necessary, terminate projects based on their strategic alignment.
-
Managing a multi-project environment / Resource management: The PMO's primary function is resource management, which includes maintaining a comprehensive overview of all projects and ensuring up-to-date and credible data. Within this context, decisions concerning scope, budgets, and resources are meticulously prepared, considering interdependencies between projects.
-
Project implementation / services: Within a PMO, the team also takes on project management roles, executes specific project tasks, or offers project assistance. This hands-on approach ensures that projects are implemented effectively and efficiently.
-
Training and coaching: In addition to project execution, the PMO focuses on developing the skills of project managers and process participants. They offer training and support within the field, and they may even provide career development paths for project managers.
-
Methods, processes and tools: Choosing and adapting project management methodologies and processes is a crucial responsibility of the PMO. They customize these methods to suit the specific needs of everyone involved within the company. The PMO also manages the selection, implementation, and maintenance of appropriate tools tailored to the different roles in project and portfolio management.
Key Skills Required for a PMO

Strategy & Leadership:
-
Strategic Thinking: PMOs need to align projects with the organization's strategic goals. They must think strategically to prioritize projects that contribute most effectively to these goals.
-
Leadership Skills: PMOs often provide guidance and direction to project managers and teams, making leadership skills vital for motivating and inspiring project stakeholders.
-
Change Management: Effective change management skills help PMOs navigate organizational shifts that often accompany project implementations.
University Culture:
-
Alignment with Objectives: Understanding and aligning project initiatives with the university's objectives and values is essential to ensure that projects are in harmony with the institution's mission.
-
Communication: Strong communication skills are necessary for conveying the importance of projects' alignment with university culture and objectives to stakeholders.
-
Collaboration: Building collaborative relationships with university stakeholders and different departments is crucial to foster cooperation and ensure projects' success.
Governance of Process:
-
Process Management: PMOs must have a deep understanding of project management processes and procedures to establish governance frameworks effectively.
-
Decision-Making: Being skilled in decision-making and delegation is essential for resolving conflicts and making critical choices that affect project outcomes.
-
Integration: PMOs should be adept at integrating project management processes seamlessly within the organization's existing systems and workflows.
Reporting:
-
Data Analysis: Strong analytical skills are necessary for interpreting project data and generating meaningful reports that support informed decision-making.
-
Communication of Results: PMOs must communicate project progress and outcomes effectively to stakeholders through clear and concise reporting.
-
KPI Tracking: Skill in identifying and tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is crucial for measuring project success and ensuring alignment with strategic goals.
Supporting Business Units:
-
Cross-Functional Understanding: PMOs should possess a broad understanding of various business units within the organization, including IT, finance, human resources, and more, to provide effective support.
-
Stakeholder Management: Managing relationships with business units and securing their support is essential for successful project execution and alignment with the organization's needs.
Processes & Tools:
-
Process Framework Knowledge: Proficiency in various project management methodologies and frameworks, such as Agile or Waterfall, is vital for implementing appropriate processes.
-
Portfolio Management: Understanding portfolio management frameworks helps PMOs make informed decisions about project selection, prioritization, and resource allocation.
-
Technological Proficiency: Familiarity with project management tools and software is necessary for efficiently managing project data and reporting.
Educational and Certification Requirements
Educational and certification requirements for a Project Management Officer (PMO) can vary depending on the organization, the specific role within the PMO, and the industry. However, here are some general guidelines for educational background and certifications that can be beneficial for aspiring PMOs:
Educational Requirements:
-
Bachelor's Degree: Many PMO positions require at least a bachelor's degree in a relevant field. Common degrees include business administration, project management, information technology, engineering, or a related discipline. Some PMOs may prefer candidates with master's degrees, especially for higher-level roles.
-
Relevant Coursework: Courses in project management, business management, leadership, finance, and communication can provide a strong educational foundation for a PMO role.
Certification Requirements:
-
Project Management Professional (PMP): Offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI), the PMP certification is one of the most recognized and respected certifications in the field of project management. It demonstrates a candidate's knowledge and expertise in project management methodologies and best practices.
-
Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM): Also provided by PMI, the CAPM certification is suitable for individuals who are relatively new to project management and want to demonstrate their commitment to the field.
-
PRINCE2: PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a popular project management methodology, especially in Europe. Becoming PRINCE2 certified can be advantageous, particularly for PMOs working in organizations that follow this methodology.
-
Certified ScrumMaster (CSM): For PMOs working in Agile environments, the CSM certification from Scrum Alliance can be valuable. It demonstrates expertise in Agile principles and Scrum practices.
-
Certification in Portfolio Management (PfMP): Also offered by PMI, PfMP is designed for professionals involved in portfolio management, which is often a critical aspect of PMO responsibilities.
-
Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP): While not specific to project management, the CBAP certification can be beneficial for PMOs involved in business analysis and requirements gathering.
-
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library): ITIL certifications are relevant for PMOs in IT-focused organizations. They focus on IT service management best practices.
-
Change Management Certification: As PMOs often play a role in change management, certifications like Prosci's Certified Change Management Professional (CCMP) can be valuable.
PMO Salary Trends in 2023
The salary trends for Project Management Officers (PMOs) were generally on an upward trajectory due to the growing recognition of the critical role they play in effective project management. In 2023, it is reasonable to expect that this trend will continue, with salaries for PMOs being influenced by factors such as location, industry, experience, and the specific responsibilities of the role. High-demand industries like technology, healthcare, and finance often offer competitive salaries for PMOs, especially in major metropolitan areas where the cost of living is higher. Additionally, PMOs with specialized skills or certifications such as PMP (Project Management Professional) or experience in agile methodologies may command higher salaries.
It's important for PMO professionals to stay updated with the latest industry insights and consult reliable sources, such as industry reports and professional networks, to gain a more accurate understanding of the salary landscape in 2023. Furthermore, the ongoing evolution of project management practices and the integration of technology into PMO functions may also impact salary trends, as organizations seek professionals who can adapt to these changes and deliver value through effective project management and portfolio oversight.
Tools and Technologies for PMOs
Project Management Officers (PMOs) rely on a variety of tools and technologies to streamline project management processes, enhance communication, and improve overall efficiency. Here are some essential tools and technologies commonly used by PMOs:
-
Project Management Software: PMOs often utilize project management software platforms such as Microsoft Project, Asana, Trello, Jira, or Monday.com to plan, track, and manage projects. These tools offer features like task assignment, timeline tracking, and progress reporting.
-
Portfolio Management Software: Portfolio management tools like Planview or CA PPM help PMOs manage multiple projects and prioritize them based on organizational goals and resource availability. They provide insights into project portfolios and help with resource allocation.
-
Collaboration Tools: Collaboration platforms such as Microsoft Teams, Slack, and Basecamp facilitate communication and collaboration among project teams. PMOs use these tools to share documents, hold meetings, and foster teamwork.
-
Document Management Systems: Systems like SharePoint and Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) are valuable for storing and organizing project documentation, contracts, reports, and other critical project-related files.
-
Data Analytics and Reporting Tools: Business intelligence tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Excel help PMOs analyze project data and create insightful reports and dashboards for stakeholders and decision-makers.
-
Resource Management Software: Resource management tools like ResourceFirst or Mavenlink assist PMOs in effectively allocating and tracking resources, including personnel, equipment, and budgetary resources.
-
Risk Management Software: Specialized risk management software, such as RiskWatch or LogicGate, can help PMOs identify, assess, and manage project risks efficiently.
-
Time Tracking and Timesheet Tools: Time tracking tools like Harvest or Clockify enable teams to record time spent on tasks, helping PMOs monitor project progress and allocate resources more effectively.
-
Budgeting and Financial Management Software: Financial management tools like QuickBooks, Xero, or dedicated project budgeting software assist PMOs in managing project finances, tracking expenses, and ensuring projects stay within budget.
-
Communication and Collaboration Platforms: Beyond chat and messaging apps, PMOs might use video conferencing tools like Zoom or Microsoft Teams for virtual meetings and webinars.
-
Issue and Change Management Tools: Issue tracking tools, such as Jira or ServiceNow, are essential for managing and documenting project issues, change requests, and resolutions.
-
Portfolio Analysis Tools: PMOs may employ tools like Sciforma or Meisterplan for in-depth portfolio analysis, including scenario planning and "what-if" analyses.
-
Workflow Automation: Workflow automation tools like Zapier or Microsoft Power Automate can streamline routine tasks and processes, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency.
PMOs should select tools and technologies that align with their organization's specific needs, project management methodologies, and budget constraints. The right combination of tools can significantly enhance the PMO's ability to manage projects, optimize resources, and deliver successful outcomes.
Career Path and Advancement for PMOs
A career path for Project Management Officers (PMOs) can be dynamic and rewarding, offering opportunities for advancement and specialization. Here's a typical career path and potential avenues for growth:
1. Entry-Level Roles:
-
Junior Project Coordinator or Project Assistant: Many PMOs begin their careers in entry-level positions, where they assist in project management tasks and gain practical experience.
2. Mid-Level Roles:
-
Project Manager: After accumulating experience and acquiring relevant certifications, PMOs may transition into project management roles, responsible for leading and executing projects.
-
Senior Project Manager: With further experience and proven leadership skills, PMs can progress to senior project manager roles, overseeing larger or more complex projects.
3. PMO Roles:
-
PMO Analyst: Junior PMOs often start as analysts, responsible for data analysis, reporting, and supporting PMO functions.
-
PMO Coordinator: PMO coordinators help manage project portfolios, resource allocation, and documentation within the PMO.
-
PMO Manager/Director: More experienced PMOs can advance to managerial or director roles within the PMO, responsible for overseeing the entire PMO function, setting strategic direction, and managing a team of project managers and analysts.
4. Specialization:
-
Portfolio Manager: Focusing on portfolio management, professionals can oversee the alignment of multiple projects with organizational objectives and resource allocation.
-
Risk Manager: Those with expertise in risk management may specialize in identifying, assessing, and mitigating project risks.
-
Agile Coach or Scrum Master: For those interested in Agile methodologies, becoming an Agile coach or Scrum Master is a potential career path.
-
PMO Consultant: Experienced PMOs may choose to work as consultants, advising organizations on PMO setup, optimization, and best practices.
5. Executive Leadership:
-
Chief Project Officer (CPO) or Head of PMO: At the highest level, PMOs can reach executive positions, where they play a strategic role in aligning projects with organizational goals and influencing the overall direction of the company.
Advancement Strategies:
-
Continuous Learning: Staying updated with the latest project management methodologies, technologies, and trends is crucial.
-
Networking: Building relationships within the industry, attending conferences, and joining professional associations can open doors to new opportunities.
-
Certifications: Earning certifications such as PMP, PfMP, or Agile certifications can enhance credibility and career prospects.
-
Leadership Development: Developing leadership skills through courses and mentorship can be essential for advancing into management roles.
-
Broadening Experience: Seeking diverse project management experiences, such as working on different types of projects or in various industries, can enrich one's skill set.
Advancement in a PMO career often involves a combination of experience, education, certifications, and networking. As PMOs gain expertise and take on more significant responsibilities, they can shape their careers to align with their interests and goals, whether that involves becoming a top-level executive or a subject matter expert in a specific area of project management.
Tips for Aspiring PMOs
If you aspire to become a Project Management Officer (PMO), it's essential to prepare and develop the skills and knowledge required for this dynamic role. Here are some valuable tips to help you on your path to becoming a successful PMO:
-
Understand Project Management Fundamentals: Start by building a strong foundation in project management principles, methodologies, and best practices. Consider enrolling in courses or pursuing certifications such as PMP (Project Management Professional) or CAPM (Certified Associate in Project Management) to demonstrate your commitment to the field.
-
Pursue Relevant Education: While not always mandatory, having a relevant educational background, such as a degree in business, project management, or a related field, can give you a competitive edge.
-
Gain Practical Experience: Look for entry-level positions or internships in project management or related roles. Practical experience is invaluable for understanding how projects work in real-world scenarios.
-
Develop Analytical Skills: PMOs often deal with data analysis, metrics, and reporting. Enhance your analytical skills to interpret project data effectively and make data-driven decisions.
-
Improve Communication Skills: Strong written and verbal communication skills are essential for conveying project information, reporting progress, and collaborating with various stakeholders.
-
Get Familiar with Technology: Become proficient in project management software, collaboration tools, and data analytics tools commonly used in the field.
-
Study PMO Frameworks: Familiarize yourself with different PMO frameworks and methodologies, such as PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) or PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments).
-
Build Leadership and Teamwork Skills: PMOs often lead project teams and collaborate with diverse groups of people. Developing leadership and teamwork skills is crucial for success.
-
Network within the Industry: Attend project management conferences, join professional associations, and connect with professionals in the field. Networking can provide valuable insights, mentorship opportunities, and potential job leads.
-
Consider Specialization: Identify areas of project management that interest you the most, whether it's risk management, portfolio management, or Agile methodologies. Specializing in a particular area can help you stand out.
-
Stay Informed: Keep up to date with industry trends, emerging technologies, and changes in project management methodologies. Continuous learning is vital in this evolving field.
-
Seek Feedback and Mentorship: Request feedback on your work and seek mentorship from experienced PMOs or project managers. Learning from others can accelerate your development.
-
Demonstrate Adaptability: The role of a PMO can vary from organization to organization. Be adaptable and open to learning new approaches and methodologies to fit the needs of your employer.
-
Set Clear Career Goals: Define your career goals and create a plan to achieve them. This can help you stay focused and motivated as you work toward your desired PMO role.
-
Show Initiative: Take on additional responsibilities, volunteer for challenging projects, and demonstrate your commitment to the field. Initiative can set you apart from other candidates.
Remember that the path to becoming a PMO can be both challenging and rewarding. Be patient and persistent in your pursuit of this career, and continue to invest in your professional development to excel in the role of a Project Management Officer.
Future Outlook for PMO Roles
The future outlook for Project Management Officer (PMO) roles appears promising and transformative. PMOs are poised to play an increasingly strategic role in organizations, evolving from traditional project oversight to becoming key drivers of business success. This transformation will be underpinned by the integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and data analytics, to enhance decision-making and project management processes. PMOs will focus on ensuring that project portfolios align with organizational goals and adapt to the dynamic landscape of project management methodologies, including Agile and hybrid approaches. As organizations continue to navigate complex projects in diverse industries, the demand for skilled PMOs is expected to grow, providing ample career opportunities and the chance to shape the future of project management.
Furthermore, the ongoing trend of remote work and the need for flexibility in project management will challenge PMOs to effectively manage distributed teams and leverage collaboration tools. Sustainability considerations and the increasing importance of change management in projects will also shape the evolving role of PMOs. To thrive in this changing landscape, aspiring PMOs should stay adaptable, invest in continuous learning, and build a strong foundation in project management principles while embracing the technological advancements that will define the future of the field.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of a Project Management Officer (PMO) is poised for a dynamic and promising future. PMOs are no longer just administrators of projects but have evolved into strategic leaders driving organizational success. As they embrace advanced technologies, agile methodologies, and data-driven decision-making, PMOs will continue to play a pivotal role in aligning projects with business objectives and optimizing resource management.
The evolving landscape of project management offers a multitude of opportunities for aspiring PMOs. To excel in this field, individuals must acquire a strong foundation in project management principles, invest in continuous learning, and stay adaptable to emerging trends. PMOs will find themselves at the forefront of organizational change, sustainability initiatives, and complex project management in various industries.
As organizations increasingly recognize the value of effective project management, PMOs will be instrumental in guiding them toward success. Their ability to navigate the evolving project management landscape, harness technology, and deliver strategic value will make them indispensable assets to organizations in the years to come.
RECOMMENDED POST:
Key Features of PMP® Certification Training
How To Qualify PM Experience In PMP Application Form
The Step By Step Procedure To Fill The Application Form
Do visit our Corporate Training to know more about core offerings for enterprises in empowering their workforce.
Download Free PMP® Exam Practice Test with 200 PMP® Questions.
Full-length PMP sample test with 200 PMP exam prep questions.
You may also be interested in Sample PMP® Exam Prep Questions before you download the Free PMP® Practice Test.
Download our Free PMP Brochure for more information.
iCert Global conducts Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, Agile, Scrum, and DevOps Certification courses across various locations in the United States.
Visit us at https://www.icertglobal.com/ for more information about our professional certification training courses or Call Now! on +1-713-287-1213 / +1-713-287-1214 or e-mail us at info {at} icertglobal {dot} com.
Project Management Training by iCert Global:
Quality Management Training by iCert Global:
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt (LSSYB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (LSSBB) Certification Training Courses
Scrum Training by iCert Global:
- CSM (Certified ScrumMaster) Certification Training Courses
Agile Training by iCert Global:
- PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Professional) Certification Training Courses
DevOps Training by iCert Global:
- DevOps Certification Training Courses
Business Analysis Training by iCert Global:
- ECBA (Entry Certificate in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CCBA (Certificate of Capability in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional) Certification Training Courses
The company conducts both Instructor-led Classroom training workshops and Instructor-led Live Online Training sessions for learners from across the United States and around the world.
Please Contact Us for more information about our professional certification training courses to accelerate your career in the new year. Wish you all the best for your learning initiatives in the new year.
Which certifications are you aiming to achieve in the New Year? Let us know your thoughts in the 'Comments' section below. Thank you.
Read More
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, effective project management stands as a cornerstone of success. And at the heart of this intricate orchestration lies the Project Management Officer (PMO), a role of growing importance in organizations around the world. As we step into 2023, the role of the PMO has evolved into far more than just overseeing projects; it has become a strategic linchpin that ensures projects align with an organization's vision and goals.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the realm of Project Management Officers, unveiling the intricate tapestry of their responsibilities, the key skills demanded in this evolving role, and the salary trends that will define the career landscape in 2023. Whether you are an aspiring PMO charting your career path or a seasoned professional seeking to stay at the forefront of industry trends, this exploration will guide you through the multifaceted world of PMOs and the vital role they play in shaping the future of project management.
Table of contents
-
Introduction to the Project Management Officer Role
-
Responsibilities of a PMO
-
Key Skills Required for a PMO
-
Educational and Certification Requirements
-
PMO Salary Trends in 2023
-
Tools and Technologies for PMOs
-
Career Path and Advancement for PMOs
-
Tips for Aspiring PMOs
-
Future Outlook for PMO Roles
-
Conclusion
Introduction to the Project Management Officer Role
The Project Management Officer, commonly known as the PMO, is the backbone of effective project management within organizations today. As businesses navigate increasingly complex projects, the PMO serves as the central orchestrator, ensuring that projects are executed efficiently and align with the company's strategic objectives. The PMO's responsibilities encompass governance, standardization, resource allocation, performance monitoring, risk management, and communication facilitation. By establishing best practices, maintaining project standards, and providing critical oversight, PMOs play a pivotal role in delivering successful projects on time and within budget. As businesses evolve and embrace technological advancements, PMOs are adapting to integrate innovative tools and methodologies into their practices, making the role of a Project Management Officer more vital than ever in the modern corporate landscape.
In the following sections of this blog, we will delve deeper into the specific functions and skills required for PMOs, explore the latest salary trends in 2023, and shed light on the promising career prospects awaiting those interested in pursuing or advancing within this dynamic and essential field. Whether you're considering a career as a PMO or seeking to understand the evolving role better, read on to gain comprehensive insights into the world of Project Management Officers.
Responsibilities of a PMO
-
Strategic support (sPMO): This involves providing operational support in projects by taking on the management of a project, executing defined subtasks, or providing project assistants. The sPMO plays a critical role in aligning project work with corporate strategy. They classify, select, prioritize, and, when necessary, terminate projects based on their strategic alignment.
-
Managing a multi-project environment / Resource management: The PMO's primary function is resource management, which includes maintaining a comprehensive overview of all projects and ensuring up-to-date and credible data. Within this context, decisions concerning scope, budgets, and resources are meticulously prepared, considering interdependencies between projects.
-
Project implementation / services: Within a PMO, the team also takes on project management roles, executes specific project tasks, or offers project assistance. This hands-on approach ensures that projects are implemented effectively and efficiently.
-
Training and coaching: In addition to project execution, the PMO focuses on developing the skills of project managers and process participants. They offer training and support within the field, and they may even provide career development paths for project managers.
-
Methods, processes and tools: Choosing and adapting project management methodologies and processes is a crucial responsibility of the PMO. They customize these methods to suit the specific needs of everyone involved within the company. The PMO also manages the selection, implementation, and maintenance of appropriate tools tailored to the different roles in project and portfolio management.
Key Skills Required for a PMO
Strategy & Leadership:
-
Strategic Thinking: PMOs need to align projects with the organization's strategic goals. They must think strategically to prioritize projects that contribute most effectively to these goals.
-
Leadership Skills: PMOs often provide guidance and direction to project managers and teams, making leadership skills vital for motivating and inspiring project stakeholders.
-
Change Management: Effective change management skills help PMOs navigate organizational shifts that often accompany project implementations.
University Culture:
-
Alignment with Objectives: Understanding and aligning project initiatives with the university's objectives and values is essential to ensure that projects are in harmony with the institution's mission.
-
Communication: Strong communication skills are necessary for conveying the importance of projects' alignment with university culture and objectives to stakeholders.
-
Collaboration: Building collaborative relationships with university stakeholders and different departments is crucial to foster cooperation and ensure projects' success.
Governance of Process:
-
Process Management: PMOs must have a deep understanding of project management processes and procedures to establish governance frameworks effectively.
-
Decision-Making: Being skilled in decision-making and delegation is essential for resolving conflicts and making critical choices that affect project outcomes.
-
Integration: PMOs should be adept at integrating project management processes seamlessly within the organization's existing systems and workflows.
Reporting:
-
Data Analysis: Strong analytical skills are necessary for interpreting project data and generating meaningful reports that support informed decision-making.
-
Communication of Results: PMOs must communicate project progress and outcomes effectively to stakeholders through clear and concise reporting.
-
KPI Tracking: Skill in identifying and tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is crucial for measuring project success and ensuring alignment with strategic goals.
Supporting Business Units:
-
Cross-Functional Understanding: PMOs should possess a broad understanding of various business units within the organization, including IT, finance, human resources, and more, to provide effective support.
-
Stakeholder Management: Managing relationships with business units and securing their support is essential for successful project execution and alignment with the organization's needs.
Processes & Tools:
-
Process Framework Knowledge: Proficiency in various project management methodologies and frameworks, such as Agile or Waterfall, is vital for implementing appropriate processes.
-
Portfolio Management: Understanding portfolio management frameworks helps PMOs make informed decisions about project selection, prioritization, and resource allocation.
-
Technological Proficiency: Familiarity with project management tools and software is necessary for efficiently managing project data and reporting.
Educational and Certification Requirements
Educational and certification requirements for a Project Management Officer (PMO) can vary depending on the organization, the specific role within the PMO, and the industry. However, here are some general guidelines for educational background and certifications that can be beneficial for aspiring PMOs:
Educational Requirements:
-
Bachelor's Degree: Many PMO positions require at least a bachelor's degree in a relevant field. Common degrees include business administration, project management, information technology, engineering, or a related discipline. Some PMOs may prefer candidates with master's degrees, especially for higher-level roles.
-
Relevant Coursework: Courses in project management, business management, leadership, finance, and communication can provide a strong educational foundation for a PMO role.
Certification Requirements:
-
Project Management Professional (PMP): Offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI), the PMP certification is one of the most recognized and respected certifications in the field of project management. It demonstrates a candidate's knowledge and expertise in project management methodologies and best practices.
-
Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM): Also provided by PMI, the CAPM certification is suitable for individuals who are relatively new to project management and want to demonstrate their commitment to the field.
-
PRINCE2: PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a popular project management methodology, especially in Europe. Becoming PRINCE2 certified can be advantageous, particularly for PMOs working in organizations that follow this methodology.
-
Certified ScrumMaster (CSM): For PMOs working in Agile environments, the CSM certification from Scrum Alliance can be valuable. It demonstrates expertise in Agile principles and Scrum practices.
-
Certification in Portfolio Management (PfMP): Also offered by PMI, PfMP is designed for professionals involved in portfolio management, which is often a critical aspect of PMO responsibilities.
-
Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP): While not specific to project management, the CBAP certification can be beneficial for PMOs involved in business analysis and requirements gathering.
-
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library): ITIL certifications are relevant for PMOs in IT-focused organizations. They focus on IT service management best practices.
-
Change Management Certification: As PMOs often play a role in change management, certifications like Prosci's Certified Change Management Professional (CCMP) can be valuable.
PMO Salary Trends in 2023
The salary trends for Project Management Officers (PMOs) were generally on an upward trajectory due to the growing recognition of the critical role they play in effective project management. In 2023, it is reasonable to expect that this trend will continue, with salaries for PMOs being influenced by factors such as location, industry, experience, and the specific responsibilities of the role. High-demand industries like technology, healthcare, and finance often offer competitive salaries for PMOs, especially in major metropolitan areas where the cost of living is higher. Additionally, PMOs with specialized skills or certifications such as PMP (Project Management Professional) or experience in agile methodologies may command higher salaries.
It's important for PMO professionals to stay updated with the latest industry insights and consult reliable sources, such as industry reports and professional networks, to gain a more accurate understanding of the salary landscape in 2023. Furthermore, the ongoing evolution of project management practices and the integration of technology into PMO functions may also impact salary trends, as organizations seek professionals who can adapt to these changes and deliver value through effective project management and portfolio oversight.
Tools and Technologies for PMOs
Project Management Officers (PMOs) rely on a variety of tools and technologies to streamline project management processes, enhance communication, and improve overall efficiency. Here are some essential tools and technologies commonly used by PMOs:
-
Project Management Software: PMOs often utilize project management software platforms such as Microsoft Project, Asana, Trello, Jira, or Monday.com to plan, track, and manage projects. These tools offer features like task assignment, timeline tracking, and progress reporting.
-
Portfolio Management Software: Portfolio management tools like Planview or CA PPM help PMOs manage multiple projects and prioritize them based on organizational goals and resource availability. They provide insights into project portfolios and help with resource allocation.
-
Collaboration Tools: Collaboration platforms such as Microsoft Teams, Slack, and Basecamp facilitate communication and collaboration among project teams. PMOs use these tools to share documents, hold meetings, and foster teamwork.
-
Document Management Systems: Systems like SharePoint and Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) are valuable for storing and organizing project documentation, contracts, reports, and other critical project-related files.
-
Data Analytics and Reporting Tools: Business intelligence tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Excel help PMOs analyze project data and create insightful reports and dashboards for stakeholders and decision-makers.
-
Resource Management Software: Resource management tools like ResourceFirst or Mavenlink assist PMOs in effectively allocating and tracking resources, including personnel, equipment, and budgetary resources.
-
Risk Management Software: Specialized risk management software, such as RiskWatch or LogicGate, can help PMOs identify, assess, and manage project risks efficiently.
-
Time Tracking and Timesheet Tools: Time tracking tools like Harvest or Clockify enable teams to record time spent on tasks, helping PMOs monitor project progress and allocate resources more effectively.
-
Budgeting and Financial Management Software: Financial management tools like QuickBooks, Xero, or dedicated project budgeting software assist PMOs in managing project finances, tracking expenses, and ensuring projects stay within budget.
-
Communication and Collaboration Platforms: Beyond chat and messaging apps, PMOs might use video conferencing tools like Zoom or Microsoft Teams for virtual meetings and webinars.
-
Issue and Change Management Tools: Issue tracking tools, such as Jira or ServiceNow, are essential for managing and documenting project issues, change requests, and resolutions.
-
Portfolio Analysis Tools: PMOs may employ tools like Sciforma or Meisterplan for in-depth portfolio analysis, including scenario planning and "what-if" analyses.
-
Workflow Automation: Workflow automation tools like Zapier or Microsoft Power Automate can streamline routine tasks and processes, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency.
PMOs should select tools and technologies that align with their organization's specific needs, project management methodologies, and budget constraints. The right combination of tools can significantly enhance the PMO's ability to manage projects, optimize resources, and deliver successful outcomes.
Career Path and Advancement for PMOs
A career path for Project Management Officers (PMOs) can be dynamic and rewarding, offering opportunities for advancement and specialization. Here's a typical career path and potential avenues for growth:
1. Entry-Level Roles:
-
Junior Project Coordinator or Project Assistant: Many PMOs begin their careers in entry-level positions, where they assist in project management tasks and gain practical experience.
2. Mid-Level Roles:
-
Project Manager: After accumulating experience and acquiring relevant certifications, PMOs may transition into project management roles, responsible for leading and executing projects.
-
Senior Project Manager: With further experience and proven leadership skills, PMs can progress to senior project manager roles, overseeing larger or more complex projects.
3. PMO Roles:
-
PMO Analyst: Junior PMOs often start as analysts, responsible for data analysis, reporting, and supporting PMO functions.
-
PMO Coordinator: PMO coordinators help manage project portfolios, resource allocation, and documentation within the PMO.
-
PMO Manager/Director: More experienced PMOs can advance to managerial or director roles within the PMO, responsible for overseeing the entire PMO function, setting strategic direction, and managing a team of project managers and analysts.
4. Specialization:
-
Portfolio Manager: Focusing on portfolio management, professionals can oversee the alignment of multiple projects with organizational objectives and resource allocation.
-
Risk Manager: Those with expertise in risk management may specialize in identifying, assessing, and mitigating project risks.
-
Agile Coach or Scrum Master: For those interested in Agile methodologies, becoming an Agile coach or Scrum Master is a potential career path.
-
PMO Consultant: Experienced PMOs may choose to work as consultants, advising organizations on PMO setup, optimization, and best practices.
5. Executive Leadership:
-
Chief Project Officer (CPO) or Head of PMO: At the highest level, PMOs can reach executive positions, where they play a strategic role in aligning projects with organizational goals and influencing the overall direction of the company.
Advancement Strategies:
-
Continuous Learning: Staying updated with the latest project management methodologies, technologies, and trends is crucial.
-
Networking: Building relationships within the industry, attending conferences, and joining professional associations can open doors to new opportunities.
-
Certifications: Earning certifications such as PMP, PfMP, or Agile certifications can enhance credibility and career prospects.
-
Leadership Development: Developing leadership skills through courses and mentorship can be essential for advancing into management roles.
-
Broadening Experience: Seeking diverse project management experiences, such as working on different types of projects or in various industries, can enrich one's skill set.
Advancement in a PMO career often involves a combination of experience, education, certifications, and networking. As PMOs gain expertise and take on more significant responsibilities, they can shape their careers to align with their interests and goals, whether that involves becoming a top-level executive or a subject matter expert in a specific area of project management.
Tips for Aspiring PMOs
If you aspire to become a Project Management Officer (PMO), it's essential to prepare and develop the skills and knowledge required for this dynamic role. Here are some valuable tips to help you on your path to becoming a successful PMO:
-
Understand Project Management Fundamentals: Start by building a strong foundation in project management principles, methodologies, and best practices. Consider enrolling in courses or pursuing certifications such as PMP (Project Management Professional) or CAPM (Certified Associate in Project Management) to demonstrate your commitment to the field.
-
Pursue Relevant Education: While not always mandatory, having a relevant educational background, such as a degree in business, project management, or a related field, can give you a competitive edge.
-
Gain Practical Experience: Look for entry-level positions or internships in project management or related roles. Practical experience is invaluable for understanding how projects work in real-world scenarios.
-
Develop Analytical Skills: PMOs often deal with data analysis, metrics, and reporting. Enhance your analytical skills to interpret project data effectively and make data-driven decisions.
-
Improve Communication Skills: Strong written and verbal communication skills are essential for conveying project information, reporting progress, and collaborating with various stakeholders.
-
Get Familiar with Technology: Become proficient in project management software, collaboration tools, and data analytics tools commonly used in the field.
-
Study PMO Frameworks: Familiarize yourself with different PMO frameworks and methodologies, such as PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) or PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments).
-
Build Leadership and Teamwork Skills: PMOs often lead project teams and collaborate with diverse groups of people. Developing leadership and teamwork skills is crucial for success.
-
Network within the Industry: Attend project management conferences, join professional associations, and connect with professionals in the field. Networking can provide valuable insights, mentorship opportunities, and potential job leads.
-
Consider Specialization: Identify areas of project management that interest you the most, whether it's risk management, portfolio management, or Agile methodologies. Specializing in a particular area can help you stand out.
-
Stay Informed: Keep up to date with industry trends, emerging technologies, and changes in project management methodologies. Continuous learning is vital in this evolving field.
-
Seek Feedback and Mentorship: Request feedback on your work and seek mentorship from experienced PMOs or project managers. Learning from others can accelerate your development.
-
Demonstrate Adaptability: The role of a PMO can vary from organization to organization. Be adaptable and open to learning new approaches and methodologies to fit the needs of your employer.
-
Set Clear Career Goals: Define your career goals and create a plan to achieve them. This can help you stay focused and motivated as you work toward your desired PMO role.
-
Show Initiative: Take on additional responsibilities, volunteer for challenging projects, and demonstrate your commitment to the field. Initiative can set you apart from other candidates.
Remember that the path to becoming a PMO can be both challenging and rewarding. Be patient and persistent in your pursuit of this career, and continue to invest in your professional development to excel in the role of a Project Management Officer.
Future Outlook for PMO Roles
The future outlook for Project Management Officer (PMO) roles appears promising and transformative. PMOs are poised to play an increasingly strategic role in organizations, evolving from traditional project oversight to becoming key drivers of business success. This transformation will be underpinned by the integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and data analytics, to enhance decision-making and project management processes. PMOs will focus on ensuring that project portfolios align with organizational goals and adapt to the dynamic landscape of project management methodologies, including Agile and hybrid approaches. As organizations continue to navigate complex projects in diverse industries, the demand for skilled PMOs is expected to grow, providing ample career opportunities and the chance to shape the future of project management.
Furthermore, the ongoing trend of remote work and the need for flexibility in project management will challenge PMOs to effectively manage distributed teams and leverage collaboration tools. Sustainability considerations and the increasing importance of change management in projects will also shape the evolving role of PMOs. To thrive in this changing landscape, aspiring PMOs should stay adaptable, invest in continuous learning, and build a strong foundation in project management principles while embracing the technological advancements that will define the future of the field.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of a Project Management Officer (PMO) is poised for a dynamic and promising future. PMOs are no longer just administrators of projects but have evolved into strategic leaders driving organizational success. As they embrace advanced technologies, agile methodologies, and data-driven decision-making, PMOs will continue to play a pivotal role in aligning projects with business objectives and optimizing resource management.
The evolving landscape of project management offers a multitude of opportunities for aspiring PMOs. To excel in this field, individuals must acquire a strong foundation in project management principles, invest in continuous learning, and stay adaptable to emerging trends. PMOs will find themselves at the forefront of organizational change, sustainability initiatives, and complex project management in various industries.
As organizations increasingly recognize the value of effective project management, PMOs will be instrumental in guiding them toward success. Their ability to navigate the evolving project management landscape, harness technology, and deliver strategic value will make them indispensable assets to organizations in the years to come.
RECOMMENDED POST:
Key Features of PMP® Certification Training
How To Qualify PM Experience In PMP Application Form
The Step By Step Procedure To Fill The Application Form
Do visit our Corporate Training to know more about core offerings for enterprises in empowering their workforce.
Download Free PMP® Exam Practice Test with 200 PMP® Questions.
Full-length PMP sample test with 200 PMP exam prep questions.
You may also be interested in Sample PMP® Exam Prep Questions before you download the Free PMP® Practice Test.
Download our Free PMP Brochure for more information.
iCert Global conducts Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, Agile, Scrum, and DevOps Certification courses across various locations in the United States.
Visit us at https://www.icertglobal.com/ for more information about our professional certification training courses or Call Now! on +1-713-287-1213 / +1-713-287-1214 or e-mail us at info {at} icertglobal {dot} com.
Project Management Training by iCert Global:
Quality Management Training by iCert Global:
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt (LSSYB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (LSSBB) Certification Training Courses
Scrum Training by iCert Global:
- CSM (Certified ScrumMaster) Certification Training Courses
Agile Training by iCert Global:
- PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Professional) Certification Training Courses
DevOps Training by iCert Global:
- DevOps Certification Training Courses
Business Analysis Training by iCert Global:
- ECBA (Entry Certificate in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CCBA (Certificate of Capability in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional) Certification Training Courses
The company conducts both Instructor-led Classroom training workshops and Instructor-led Live Online Training sessions for learners from across the United States and around the world.
Please Contact Us for more information about our professional certification training courses to accelerate your career in the new year. Wish you all the best for your learning initiatives in the new year.
Which certifications are you aiming to achieve in the New Year? Let us know your thoughts in the 'Comments' section below. Thank you.
Lean Methodology Essentials: A Guide with some Key Examples
Welcome to "Lean Methodology Essentials: A Guide with Examples." In a world where businesses must continually innovate, optimize, and adapt to remain competitive, Lean Methodology has emerged as a transformative approach to achieving operational excellence. This guide serves as your essential companion on a journey into the heart of Lean, offering a clear and practical understanding of its principles, techniques, and real-world applications.
Lean Methodology is more than a management philosophy; it's a mindset that emphasizes efficiency, waste reduction, and a relentless focus on delivering value to customers. In the pages that follow, we will break down the core tenets of Lean, demystify its terminology, and provide you with concrete examples that illustrate how Lean principles can be implemented across various industries. Whether you are a seasoned professional seeking to refine your Lean expertise or a newcomer eager to embrace its principles, this guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to embark on a journey of continuous improvement, setting you on the path to organizational excellence.
Table of Contents
-
What is Lean Methodology?
-
How Did Lean Methodology Originate?
-
Fundamentals of Lean Methodology
-
What Makes the Lean Methodology Unique?
-
Pillars of Lean Methodology
-
Why Should You Choose Lean Methodology?
-
Lean Methodology in Software Development
-
Lean Methodology Examples
-
Master the Concepts of Lean Methodology Today
-
Conclusion
What is Lean Methodology?
Lean Methodology is a systematic approach to process improvement that aims to maximize customer value while minimizing waste. Rooted in the principles of efficiency and continuous improvement, Lean emphasizes the identification and elimination of non-value-added activities, streamlining processes for smoother flow, adopting a pull system based on actual customer demand, and the relentless pursuit of perfection. By optimizing operations and reducing waste in industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare and software development, Lean Methodology enhances quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction, making it a cornerstone of modern business improvement strategies.
How Did Lean Methodology Originate?
Lean Methodology, originating in post-World War II Japan, owes its genesis to the innovative response of Japanese manufacturers, particularly Toyota, to the challenging economic environment of the time. Scarce resources, a damaged infrastructure, and a competitive landscape compelled Japanese companies to devise more efficient and economical production methods. Central to Lean's origins is the Toyota Production System (TPS), developed by Taiichi Ohno and Shigeo Shingo in the mid-20th century. TPS emphasized core Lean principles such as Just-In-Time (JIT) production, which aimed to reduce waste by producing only what was needed when it was needed. Another foundational concept was continuous improvement (Kaizen), which encouraged ongoing refinement of processes to enhance efficiency and quality. This systematic approach revolutionized manufacturing by minimizing waste, optimizing resource utilization, and improving product quality.
The adoption of Lean principles extended beyond manufacturing and became a global phenomenon in the late 20th century as Western companies recognized its effectiveness in improving operational efficiency and product quality. Lean's success in industries such as automotive manufacturing led to its widespread application across various sectors, including healthcare, services, and software development. Lean's ability to adapt and deliver results in diverse fields is a testament to its universal appeal and the enduring legacy of its Japanese origins, which continue to shape modern approaches to process optimization and waste reduction.
Fundamentals of Lean Methodology
The fundamentals of Lean Methodology are rooted in a set of core principles and practices that aim to maximize value while minimizing waste. These principles guide organizations in their pursuit of operational excellence and continuous improvement. Here are the key fundamentals of Lean Methodology:
-
Value: Identify what is valuable from the customer's perspective. Value represents any activity or process step that directly contributes to meeting customer needs or requirements.
-
Value Stream Mapping: Analyze and map the entire value stream, which is the end-to-end sequence of activities and processes that deliver a product or service to the customer. Value stream mapping helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas of waste.
-
Flow: Optimize the flow of work or materials through the value stream. This involves reducing interruptions, delays, and excess inventory that can hinder the smooth progression of tasks. Creating a continuous flow is a key objective.
-
Pull: Implement a pull system, where work is initiated or products are produced based on actual customer demand. This contrasts with a push system, where items are produced in anticipation of demand, often leading to overproduction and waste.
-
Perfection: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement (Kaizen) with the goal of achieving perfection, even though it may never be fully attainable. Continuously seek ways to eliminate waste, enhance processes, and deliver greater value to customers.
-
Customer Focus: Place the customer at the center of all decisions and activities. Understand customer needs and preferences to drive value creation.
-
Employee Involvement: Involve and empower employees at all levels of the organization to identify and solve problems, make improvements, and contribute to the Lean culture.
-
Standardization: Establish standardized work processes and procedures to ensure consistency, reduce variation, and enable easier identification of abnormalities.
-
Visual Management: Use visual cues and tools, such as Kanban boards and Andon systems, to make information and the status of processes readily visible, facilitating better communication and decision-making.
-
Waste Reduction: Identify and eliminate the eight types of waste in Lean, often remembered by the acronym "TIMWOODS":
-
Transportation
-
Inventory
-
Motion
-
Waiting
-
Overproduction
-
Overprocessing
-
Defects
-
Skills (underutilized)
-
Continuous Improvement: Promote a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Encourage teams to regularly assess processes, gather feedback, and make incremental changes to enhance efficiency and quality.
-
Respect for People: Recognize the value of every employee and treat them with respect. Lean encourages collaboration, teamwork, and the involvement of employees in decision-making.
By adhering to these fundamentals, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, improved quality, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction, making Lean Methodology a powerful approach for achieving operational excellence.
What Makes the Lean Methodology Unique?
The Lean Methodology is distinctive due to several key factors:
-
Customer-Centric Philosophy: Lean is fundamentally centered on delivering value to the customer. It places a primary focus on understanding and meeting customer needs, which drives all decision-making and process improvements.
-
Waste Elimination: A core principle of Lean is the systematic identification and elimination of waste in all forms, including overproduction, unnecessary inventory, defects, waiting times, and more. This relentless pursuit of waste reduction sets Lean apart from many other methodologies.
-
Continuous Improvement Culture: Lean fosters a culture of continuous improvement (Kaizen) throughout an organization. It encourages employees at all levels to continuously seek ways to enhance processes, products, and services, leading to ongoing innovation and optimization.
-
Pull System: Lean employs a pull system where work is initiated based on actual customer demand rather than pushing products or services onto the market. This minimizes overproduction and excess inventory, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
-
Visual Management: Lean uses visual tools like Kanban boards and Andon systems to make information and process status highly visible. This transparency enhances communication, problem-solving, and decision-making.
-
Respect for People: Lean places a strong emphasis on respecting and engaging employees. It recognizes that employees often hold valuable insights for process improvement and encourages their active participation in decision-making.
-
Standardization and Documentation: Lean promotes the development and documentation of standardized work processes and procedures. This ensures consistency, reduces variation, and simplifies problem identification and resolution.
-
Flow Optimization: Lean focuses on optimizing the flow of work or materials through a value stream. This minimizes interruptions, delays, and inefficiencies, creating a smoother and more efficient workflow.
-
Pursuit of Perfection: While perfection may be an aspirational goal, Lean embraces the concept as a continuous improvement objective. Organizations continually strive for higher levels of efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
-
Global Applicability: Lean has transcended its origins in Japan and has been successfully applied across industries and geographies, demonstrating its universal applicability and effectiveness.
In summary, the Lean Methodology's unique characteristics include its customer-centricity, waste reduction focus, commitment to continuous improvement, pull-based systems, visual management practices, respect for people, and adaptability to various contexts. These features have contributed to Lean's widespread adoption and its reputation for driving efficiency, quality, and competitiveness in organizations worldwide.
Pillars of Lean Methodology
The "pillars" of Lean Methodology typically refer to the foundational principles and concepts that underpin the Lean approach to process improvement and waste reduction. While there isn't a universal agreement on a fixed set of pillars, the following are commonly recognized as the core pillars of Lean Methodology:
-
Value: Understanding and defining value from the customer's perspective is the first pillar of Lean. Value represents any activity or process step that directly contributes to meeting customer needs or requirements. Everything else is considered waste.
-
Value Stream Mapping: This pillar involves analyzing and mapping the entire value stream, which is the sequence of activities and processes that deliver a product or service to the customer. Value stream mapping helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas of waste.
-
Flow: The flow pillar emphasizes optimizing the flow of work or materials through the value stream. It aims to reduce interruptions, delays, and excess inventory that can impede the smooth progression of tasks.
-
Pull: The pull pillar involves implementing a pull system where work is initiated or products are produced based on actual customer demand. This contrasts with push systems, which produce items in anticipation of demand, often leading to overproduction and waste.
-
Perfection: Perfection is the continuous improvement pillar of Lean. While perfection may be an unattainable ideal, Lean encourages organizations to relentlessly pursue it by continuously seeking ways to eliminate waste, improve processes, and deliver greater value to customers.
These five pillars are often represented as the foundation of Lean Thinking and provide the guiding principles for organizations to achieve greater efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction. Additional concepts and tools, such as standardized work, visual management, and respect for people, are integrated into Lean practices to support these pillars and drive continuous improvement.
Why Should You Choose Lean Methodology?
Choosing Lean Methodology is a strategic decision for organizations seeking to thrive in today's competitive landscape. Lean's central focus on waste reduction, coupled with a relentless commitment to improving processes and delivering customer value, positions companies for sustainable success. By minimizing non-value-added activities, Lean enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and bolsters quality. It fosters a culture of continuous improvement, empowering employees at all levels to identify and address operational inefficiencies, ultimately driving innovation and adaptability. Lean is not confined to a specific industry, making it versatile and adaptable to diverse organizational contexts, from manufacturing to healthcare, services, and software development. Its global recognition and proven track record of delivering tangible results underscore its status as a transformative methodology for organizations striving to achieve operational excellence, customer satisfaction, and a competitive edge.
Lean Methodology in Software Development
Lean Methodology, when applied to software development, is often referred to as "Lean Software Development." It adapts the principles and practices of Lean thinking to the unique challenges of creating software products and managing software projects. Here are key aspects of Lean Software Development:
-
Customer Value: Lean Software Development starts by identifying and prioritizing customer value. It involves understanding user needs and focusing on features or functionalities that directly contribute to customer satisfaction and business goals.
-
Eliminating Waste: Lean principles of waste reduction are applied rigorously in software development. This includes reducing unnecessary code complexity, eliminating duplication, and avoiding overproduction of features that may not be needed.
-
Pull System: Lean Software Development often employs a pull system, where features or tasks are pulled into the development process based on real customer demand or project priorities. This prevents overloading teams with excessive work.
-
Continuous Improvement: Like other Lean applications, Lean Software Development encourages continuous improvement. Teams regularly review their processes and seek ways to streamline workflows, enhance collaboration, and reduce cycle times.
-
Small Batch Sizes: Lean promotes working in small, manageable batches. This means breaking down large projects into smaller, deliverable units, allowing for quicker feedback and adjustment.
-
Visual Management: Visual tools like Kanban boards are frequently used to make the status of work visible, helping teams track progress, identify bottlenecks, and manage their work effectively.
-
Lean Metrics: Lean Software Development relies on key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure the flow of work, cycle times, and other relevant metrics to identify areas for improvement.
-
Empowering Teams: Lean principles emphasize giving teams autonomy and responsibility. Teams are encouraged to self-organize, make decisions, and take ownership of their work.
-
Minimal Viable Product (MVP): Lean encourages the development of Minimum Viable Products that can be quickly delivered to customers for feedback. This iterative approach allows for faster learning and adaptation.
-
Customer Feedback Loop: Lean Software Development relies on frequent customer feedback to validate assumptions, refine requirements, and make course corrections. This feedback loop is essential for delivering software that aligns with customer expectations.
-
Respect for People: As with all Lean applications, Lean Software Development places a strong emphasis on respecting and valuing the contributions of team members, recognizing that they are essential to the success of the project.
By applying Lean principles to software development, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, reduce the risk of building unnecessary features, and deliver software products that align more closely with customer needs. It's an adaptable and effective approach that has gained popularity in Agile development methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, which incorporate Lean principles to varying degrees.
Lean Methodology Examples
Lean Methodology is applied across various industries and functions to optimize processes, reduce waste, and enhance overall efficiency. Here are some examples of Lean Methodology in action:
-
Manufacturing:
-
Toyota Production System (TPS): Toyota is often credited as the originator of Lean principles. TPS emphasizes Just-In-Time (JIT) production, pull systems, and continuous improvement to minimize waste, reduce inventory, and enhance production efficiency.
-
Healthcare:
-
Reducing Patient Wait Times: Lean principles have been applied in hospitals to reduce patient wait times, optimize appointment scheduling, and improve the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
-
Software Development:
-
Kanban: Software development teams often use Kanban boards to visualize and manage their work, limit work in progress (WIP), and optimize workflow processes.
-
Service Industry:
-
Lean Banking: Banks have applied Lean principles to streamline processes such as loan approvals, customer service, and account management, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction.
-
Supply Chain Management:
-
Lean Supply Chain: Organizations apply Lean principles to supply chain management to reduce excess inventory, eliminate bottlenecks, and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
-
Retail:
-
Inventory Management: Retailers use Lean principles to optimize inventory management, reducing carrying costs, minimizing stockouts, and ensuring products are available when customers need them.
-
Education:
-
Lean Education: Lean principles have been adapted to education to improve classroom processes, curriculum development, and administrative tasks, resulting in more efficient and effective educational institutions.
-
Construction:
-
Lean Construction: The construction industry has adopted Lean principles to optimize project planning, reduce project delays, eliminate waste, and enhance overall project management.
-
Aerospace and Aviation:
-
Lean Aerospace: Companies in the aerospace and aviation sectors use Lean principles to improve manufacturing processes, reduce production lead times, and increase aircraft production efficiency.
-
Food Industry:
-
Lean in Restaurants: Restaurants have implemented Lean practices to optimize kitchen processes, reduce food waste, and improve customer service.
-
Government:
-
Lean Government: Some government agencies have adopted Lean principles to streamline administrative processes, reduce paperwork, and enhance citizen services.
-
Small Businesses:
-
Lean Startup: Small businesses and startups often use Lean principles to validate business ideas, develop minimal viable products (MVPs), and iterate based on customer feedback.
Master the Concepts of Lean Methodology Today
Mastering the concepts of Lean Methodology requires a combination of study, practical application, and continuous learning. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
-
Study Lean Principles:
-
Begin by reading books and articles on Lean Methodology to understand its core principles and concepts. Some recommended books include "The Lean Startup" by Eric Ries and "Lean Thinking" by James P. Womack and Daniel T. Jones.
-
Enroll in Lean Training:
-
Consider enrolling in Lean training programs or workshops offered by accredited organizations. These programs provide structured learning and often include real-world case studies and exercises.
-
Online Courses and Tutorials:
-
Many online platforms offer free and paid courses on Lean Methodology. Websites like Coursera, edX, and LinkedIn Learning provide access to comprehensive courses on Lean principles and their application.
-
Certification:
-
If you're looking to establish your expertise, consider pursuing Lean certification. Organizations like the Lean Enterprise Institute (LEI) offer certification programs, including Lean Green Belt and Lean Black Belt certifications.
-
Practice Lean Tools and Techniques:
-
To truly understand Lean, apply its tools and techniques in real-world scenarios. Implement practices like value stream mapping, Kanban, and 5S in your workplace or personal projects.
-
Join Lean Communities:
-
Participate in Lean forums, online communities, and social media groups. Engaging with Lean practitioners and enthusiasts can provide valuable insights and opportunities for discussion.
-
Read Case Studies:
-
Read case studies and success stories of organizations that have effectively implemented Lean Methodology. Analyze their experiences and learn from their challenges and solutions.
-
Continuous Improvement:
-
Embrace the Lean philosophy of continuous improvement. Regularly assess your own processes and workflows, and apply Lean principles to make incremental enhancements.
-
Lean Workshops and Seminars:
-
Attend Lean workshops, seminars, and conferences to gain exposure to the latest developments in Lean Methodology and learn from industry experts.
-
Teach Others:
-
Teaching Lean concepts to others can deepen your own understanding. Consider sharing your knowledge through presentations, workshops, or writing articles or blog posts.
-
Problem-Solving Practice:
-
Lean is fundamentally about problem-solving. Practice structured problem-solving techniques like the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle to address challenges effectively.
-
Stay Informed:
-
Stay updated on Lean trends, research, and best practices through books, journals, blogs, and industry publications.
-
Networking:
-
Build a network of Lean professionals and mentors who can offer guidance and support in your Lean journey.
-
Apply Lean to Your Life:
-
Extend Lean principles beyond the workplace. Apply them to personal projects, time management, and daily routines to enhance your problem-solving skills and efficiency.
Remember that mastering Lean Methodology is an ongoing process. It requires a commitment to continuous learning, experimentation, and the application of Lean principles in various contexts. As you gain experience and expertise, you'll be better equipped to drive operational excellence and improve processes in your organization or projects.
How to obtain the Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Green Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
IT Service Management & Governance: COBIT, ISO
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fundamentals of Lean Methodology represent a powerful framework for organizations seeking to thrive in today's dynamic and competitive landscape. By understanding and applying the principles of value, waste reduction, continuous improvement, and customer-centricity, businesses can unlock remarkable benefits. The real-world examples showcased in this blog highlight the versatility of Lean, demonstrating its effectiveness across diverse industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to software development and services.
As we wrap up our exploration of Lean, it's important to remember that Lean is not a one-time initiative but a journey of ongoing improvement. Embracing a Lean mindset, fostering a culture of innovation, and empowering employees to identify and eliminate waste are essential for sustained success. By integrating Lean into the DNA of your organization, you can optimize processes, reduce costs, enhance quality, and ultimately deliver greater value to your customers, setting the stage for a prosperous and efficient future.
Read More
Welcome to "Lean Methodology Essentials: A Guide with Examples." In a world where businesses must continually innovate, optimize, and adapt to remain competitive, Lean Methodology has emerged as a transformative approach to achieving operational excellence. This guide serves as your essential companion on a journey into the heart of Lean, offering a clear and practical understanding of its principles, techniques, and real-world applications.
Lean Methodology is more than a management philosophy; it's a mindset that emphasizes efficiency, waste reduction, and a relentless focus on delivering value to customers. In the pages that follow, we will break down the core tenets of Lean, demystify its terminology, and provide you with concrete examples that illustrate how Lean principles can be implemented across various industries. Whether you are a seasoned professional seeking to refine your Lean expertise or a newcomer eager to embrace its principles, this guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to embark on a journey of continuous improvement, setting you on the path to organizational excellence.
Table of Contents
-
What is Lean Methodology?
-
How Did Lean Methodology Originate?
-
Fundamentals of Lean Methodology
-
What Makes the Lean Methodology Unique?
-
Pillars of Lean Methodology
-
Why Should You Choose Lean Methodology?
-
Lean Methodology in Software Development
-
Lean Methodology Examples
-
Master the Concepts of Lean Methodology Today
-
Conclusion
What is Lean Methodology?
Lean Methodology is a systematic approach to process improvement that aims to maximize customer value while minimizing waste. Rooted in the principles of efficiency and continuous improvement, Lean emphasizes the identification and elimination of non-value-added activities, streamlining processes for smoother flow, adopting a pull system based on actual customer demand, and the relentless pursuit of perfection. By optimizing operations and reducing waste in industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare and software development, Lean Methodology enhances quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction, making it a cornerstone of modern business improvement strategies.
How Did Lean Methodology Originate?
Lean Methodology, originating in post-World War II Japan, owes its genesis to the innovative response of Japanese manufacturers, particularly Toyota, to the challenging economic environment of the time. Scarce resources, a damaged infrastructure, and a competitive landscape compelled Japanese companies to devise more efficient and economical production methods. Central to Lean's origins is the Toyota Production System (TPS), developed by Taiichi Ohno and Shigeo Shingo in the mid-20th century. TPS emphasized core Lean principles such as Just-In-Time (JIT) production, which aimed to reduce waste by producing only what was needed when it was needed. Another foundational concept was continuous improvement (Kaizen), which encouraged ongoing refinement of processes to enhance efficiency and quality. This systematic approach revolutionized manufacturing by minimizing waste, optimizing resource utilization, and improving product quality.
The adoption of Lean principles extended beyond manufacturing and became a global phenomenon in the late 20th century as Western companies recognized its effectiveness in improving operational efficiency and product quality. Lean's success in industries such as automotive manufacturing led to its widespread application across various sectors, including healthcare, services, and software development. Lean's ability to adapt and deliver results in diverse fields is a testament to its universal appeal and the enduring legacy of its Japanese origins, which continue to shape modern approaches to process optimization and waste reduction.
Fundamentals of Lean Methodology
The fundamentals of Lean Methodology are rooted in a set of core principles and practices that aim to maximize value while minimizing waste. These principles guide organizations in their pursuit of operational excellence and continuous improvement. Here are the key fundamentals of Lean Methodology:
-
Value: Identify what is valuable from the customer's perspective. Value represents any activity or process step that directly contributes to meeting customer needs or requirements.
-
Value Stream Mapping: Analyze and map the entire value stream, which is the end-to-end sequence of activities and processes that deliver a product or service to the customer. Value stream mapping helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas of waste.
-
Flow: Optimize the flow of work or materials through the value stream. This involves reducing interruptions, delays, and excess inventory that can hinder the smooth progression of tasks. Creating a continuous flow is a key objective.
-
Pull: Implement a pull system, where work is initiated or products are produced based on actual customer demand. This contrasts with a push system, where items are produced in anticipation of demand, often leading to overproduction and waste.
-
Perfection: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement (Kaizen) with the goal of achieving perfection, even though it may never be fully attainable. Continuously seek ways to eliminate waste, enhance processes, and deliver greater value to customers.
-
Customer Focus: Place the customer at the center of all decisions and activities. Understand customer needs and preferences to drive value creation.
-
Employee Involvement: Involve and empower employees at all levels of the organization to identify and solve problems, make improvements, and contribute to the Lean culture.
-
Standardization: Establish standardized work processes and procedures to ensure consistency, reduce variation, and enable easier identification of abnormalities.
-
Visual Management: Use visual cues and tools, such as Kanban boards and Andon systems, to make information and the status of processes readily visible, facilitating better communication and decision-making.
-
Waste Reduction: Identify and eliminate the eight types of waste in Lean, often remembered by the acronym "TIMWOODS":
-
Transportation
-
Inventory
-
Motion
-
Waiting
-
Overproduction
-
Overprocessing
-
Defects
-
Skills (underutilized)
-
-
Continuous Improvement: Promote a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Encourage teams to regularly assess processes, gather feedback, and make incremental changes to enhance efficiency and quality.
-
Respect for People: Recognize the value of every employee and treat them with respect. Lean encourages collaboration, teamwork, and the involvement of employees in decision-making.
By adhering to these fundamentals, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, improved quality, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction, making Lean Methodology a powerful approach for achieving operational excellence.
What Makes the Lean Methodology Unique?
The Lean Methodology is distinctive due to several key factors:
-
Customer-Centric Philosophy: Lean is fundamentally centered on delivering value to the customer. It places a primary focus on understanding and meeting customer needs, which drives all decision-making and process improvements.
-
Waste Elimination: A core principle of Lean is the systematic identification and elimination of waste in all forms, including overproduction, unnecessary inventory, defects, waiting times, and more. This relentless pursuit of waste reduction sets Lean apart from many other methodologies.
-
Continuous Improvement Culture: Lean fosters a culture of continuous improvement (Kaizen) throughout an organization. It encourages employees at all levels to continuously seek ways to enhance processes, products, and services, leading to ongoing innovation and optimization.
-
Pull System: Lean employs a pull system where work is initiated based on actual customer demand rather than pushing products or services onto the market. This minimizes overproduction and excess inventory, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
-
Visual Management: Lean uses visual tools like Kanban boards and Andon systems to make information and process status highly visible. This transparency enhances communication, problem-solving, and decision-making.
-
Respect for People: Lean places a strong emphasis on respecting and engaging employees. It recognizes that employees often hold valuable insights for process improvement and encourages their active participation in decision-making.
-
Standardization and Documentation: Lean promotes the development and documentation of standardized work processes and procedures. This ensures consistency, reduces variation, and simplifies problem identification and resolution.
-
Flow Optimization: Lean focuses on optimizing the flow of work or materials through a value stream. This minimizes interruptions, delays, and inefficiencies, creating a smoother and more efficient workflow.
-
Pursuit of Perfection: While perfection may be an aspirational goal, Lean embraces the concept as a continuous improvement objective. Organizations continually strive for higher levels of efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
-
Global Applicability: Lean has transcended its origins in Japan and has been successfully applied across industries and geographies, demonstrating its universal applicability and effectiveness.
In summary, the Lean Methodology's unique characteristics include its customer-centricity, waste reduction focus, commitment to continuous improvement, pull-based systems, visual management practices, respect for people, and adaptability to various contexts. These features have contributed to Lean's widespread adoption and its reputation for driving efficiency, quality, and competitiveness in organizations worldwide.
Pillars of Lean Methodology
The "pillars" of Lean Methodology typically refer to the foundational principles and concepts that underpin the Lean approach to process improvement and waste reduction. While there isn't a universal agreement on a fixed set of pillars, the following are commonly recognized as the core pillars of Lean Methodology:
-
Value: Understanding and defining value from the customer's perspective is the first pillar of Lean. Value represents any activity or process step that directly contributes to meeting customer needs or requirements. Everything else is considered waste.
-
Value Stream Mapping: This pillar involves analyzing and mapping the entire value stream, which is the sequence of activities and processes that deliver a product or service to the customer. Value stream mapping helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas of waste.
-
Flow: The flow pillar emphasizes optimizing the flow of work or materials through the value stream. It aims to reduce interruptions, delays, and excess inventory that can impede the smooth progression of tasks.
-
Pull: The pull pillar involves implementing a pull system where work is initiated or products are produced based on actual customer demand. This contrasts with push systems, which produce items in anticipation of demand, often leading to overproduction and waste.
-
Perfection: Perfection is the continuous improvement pillar of Lean. While perfection may be an unattainable ideal, Lean encourages organizations to relentlessly pursue it by continuously seeking ways to eliminate waste, improve processes, and deliver greater value to customers.
These five pillars are often represented as the foundation of Lean Thinking and provide the guiding principles for organizations to achieve greater efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction. Additional concepts and tools, such as standardized work, visual management, and respect for people, are integrated into Lean practices to support these pillars and drive continuous improvement.
Why Should You Choose Lean Methodology?
Choosing Lean Methodology is a strategic decision for organizations seeking to thrive in today's competitive landscape. Lean's central focus on waste reduction, coupled with a relentless commitment to improving processes and delivering customer value, positions companies for sustainable success. By minimizing non-value-added activities, Lean enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and bolsters quality. It fosters a culture of continuous improvement, empowering employees at all levels to identify and address operational inefficiencies, ultimately driving innovation and adaptability. Lean is not confined to a specific industry, making it versatile and adaptable to diverse organizational contexts, from manufacturing to healthcare, services, and software development. Its global recognition and proven track record of delivering tangible results underscore its status as a transformative methodology for organizations striving to achieve operational excellence, customer satisfaction, and a competitive edge.
Lean Methodology in Software Development
Lean Methodology, when applied to software development, is often referred to as "Lean Software Development." It adapts the principles and practices of Lean thinking to the unique challenges of creating software products and managing software projects. Here are key aspects of Lean Software Development:
-
Customer Value: Lean Software Development starts by identifying and prioritizing customer value. It involves understanding user needs and focusing on features or functionalities that directly contribute to customer satisfaction and business goals.
-
Eliminating Waste: Lean principles of waste reduction are applied rigorously in software development. This includes reducing unnecessary code complexity, eliminating duplication, and avoiding overproduction of features that may not be needed.
-
Pull System: Lean Software Development often employs a pull system, where features or tasks are pulled into the development process based on real customer demand or project priorities. This prevents overloading teams with excessive work.
-
Continuous Improvement: Like other Lean applications, Lean Software Development encourages continuous improvement. Teams regularly review their processes and seek ways to streamline workflows, enhance collaboration, and reduce cycle times.
-
Small Batch Sizes: Lean promotes working in small, manageable batches. This means breaking down large projects into smaller, deliverable units, allowing for quicker feedback and adjustment.
-
Visual Management: Visual tools like Kanban boards are frequently used to make the status of work visible, helping teams track progress, identify bottlenecks, and manage their work effectively.
-
Lean Metrics: Lean Software Development relies on key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure the flow of work, cycle times, and other relevant metrics to identify areas for improvement.
-
Empowering Teams: Lean principles emphasize giving teams autonomy and responsibility. Teams are encouraged to self-organize, make decisions, and take ownership of their work.
-
Minimal Viable Product (MVP): Lean encourages the development of Minimum Viable Products that can be quickly delivered to customers for feedback. This iterative approach allows for faster learning and adaptation.
-
Customer Feedback Loop: Lean Software Development relies on frequent customer feedback to validate assumptions, refine requirements, and make course corrections. This feedback loop is essential for delivering software that aligns with customer expectations.
-
Respect for People: As with all Lean applications, Lean Software Development places a strong emphasis on respecting and valuing the contributions of team members, recognizing that they are essential to the success of the project.
By applying Lean principles to software development, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, reduce the risk of building unnecessary features, and deliver software products that align more closely with customer needs. It's an adaptable and effective approach that has gained popularity in Agile development methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, which incorporate Lean principles to varying degrees.
Lean Methodology Examples
Lean Methodology is applied across various industries and functions to optimize processes, reduce waste, and enhance overall efficiency. Here are some examples of Lean Methodology in action:
-
Manufacturing:
-
Toyota Production System (TPS): Toyota is often credited as the originator of Lean principles. TPS emphasizes Just-In-Time (JIT) production, pull systems, and continuous improvement to minimize waste, reduce inventory, and enhance production efficiency.
-
-
Healthcare:
-
Reducing Patient Wait Times: Lean principles have been applied in hospitals to reduce patient wait times, optimize appointment scheduling, and improve the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
-
-
Software Development:
-
Kanban: Software development teams often use Kanban boards to visualize and manage their work, limit work in progress (WIP), and optimize workflow processes.
-
-
Service Industry:
-
Lean Banking: Banks have applied Lean principles to streamline processes such as loan approvals, customer service, and account management, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction.
-
-
Supply Chain Management:
-
Lean Supply Chain: Organizations apply Lean principles to supply chain management to reduce excess inventory, eliminate bottlenecks, and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
-
-
Retail:
-
Inventory Management: Retailers use Lean principles to optimize inventory management, reducing carrying costs, minimizing stockouts, and ensuring products are available when customers need them.
-
-
Education:
-
Lean Education: Lean principles have been adapted to education to improve classroom processes, curriculum development, and administrative tasks, resulting in more efficient and effective educational institutions.
-
-
Construction:
-
Lean Construction: The construction industry has adopted Lean principles to optimize project planning, reduce project delays, eliminate waste, and enhance overall project management.
-
-
Aerospace and Aviation:
-
Lean Aerospace: Companies in the aerospace and aviation sectors use Lean principles to improve manufacturing processes, reduce production lead times, and increase aircraft production efficiency.
-
-
Food Industry:
-
Lean in Restaurants: Restaurants have implemented Lean practices to optimize kitchen processes, reduce food waste, and improve customer service.
-
-
Government:
-
Lean Government: Some government agencies have adopted Lean principles to streamline administrative processes, reduce paperwork, and enhance citizen services.
-
-
Small Businesses:
-
Lean Startup: Small businesses and startups often use Lean principles to validate business ideas, develop minimal viable products (MVPs), and iterate based on customer feedback.
-
Master the Concepts of Lean Methodology Today
Mastering the concepts of Lean Methodology requires a combination of study, practical application, and continuous learning. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
-
Study Lean Principles:
-
Begin by reading books and articles on Lean Methodology to understand its core principles and concepts. Some recommended books include "The Lean Startup" by Eric Ries and "Lean Thinking" by James P. Womack and Daniel T. Jones.
-
-
Enroll in Lean Training:
-
Consider enrolling in Lean training programs or workshops offered by accredited organizations. These programs provide structured learning and often include real-world case studies and exercises.
-
-
Online Courses and Tutorials:
-
Many online platforms offer free and paid courses on Lean Methodology. Websites like Coursera, edX, and LinkedIn Learning provide access to comprehensive courses on Lean principles and their application.
-
-
Certification:
-
If you're looking to establish your expertise, consider pursuing Lean certification. Organizations like the Lean Enterprise Institute (LEI) offer certification programs, including Lean Green Belt and Lean Black Belt certifications.
-
-
Practice Lean Tools and Techniques:
-
To truly understand Lean, apply its tools and techniques in real-world scenarios. Implement practices like value stream mapping, Kanban, and 5S in your workplace or personal projects.
-
-
Join Lean Communities:
-
Participate in Lean forums, online communities, and social media groups. Engaging with Lean practitioners and enthusiasts can provide valuable insights and opportunities for discussion.
-
-
Read Case Studies:
-
Read case studies and success stories of organizations that have effectively implemented Lean Methodology. Analyze their experiences and learn from their challenges and solutions.
-
-
Continuous Improvement:
-
Embrace the Lean philosophy of continuous improvement. Regularly assess your own processes and workflows, and apply Lean principles to make incremental enhancements.
-
-
Lean Workshops and Seminars:
-
Attend Lean workshops, seminars, and conferences to gain exposure to the latest developments in Lean Methodology and learn from industry experts.
-
-
Teach Others:
-
Teaching Lean concepts to others can deepen your own understanding. Consider sharing your knowledge through presentations, workshops, or writing articles or blog posts.
-
-
Problem-Solving Practice:
-
Lean is fundamentally about problem-solving. Practice structured problem-solving techniques like the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle to address challenges effectively.
-
-
Stay Informed:
-
Stay updated on Lean trends, research, and best practices through books, journals, blogs, and industry publications.
-
-
Networking:
-
Build a network of Lean professionals and mentors who can offer guidance and support in your Lean journey.
-
-
Apply Lean to Your Life:
-
Extend Lean principles beyond the workplace. Apply them to personal projects, time management, and daily routines to enhance your problem-solving skills and efficiency.
-
Remember that mastering Lean Methodology is an ongoing process. It requires a commitment to continuous learning, experimentation, and the application of Lean principles in various contexts. As you gain experience and expertise, you'll be better equipped to drive operational excellence and improve processes in your organization or projects.
How to obtain the Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Green Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
IT Service Management & Governance: COBIT, ISO
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fundamentals of Lean Methodology represent a powerful framework for organizations seeking to thrive in today's dynamic and competitive landscape. By understanding and applying the principles of value, waste reduction, continuous improvement, and customer-centricity, businesses can unlock remarkable benefits. The real-world examples showcased in this blog highlight the versatility of Lean, demonstrating its effectiveness across diverse industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to software development and services.
As we wrap up our exploration of Lean, it's important to remember that Lean is not a one-time initiative but a journey of ongoing improvement. Embracing a Lean mindset, fostering a culture of innovation, and empowering employees to identify and eliminate waste are essential for sustained success. By integrating Lean into the DNA of your organization, you can optimize processes, reduce costs, enhance quality, and ultimately deliver greater value to your customers, setting the stage for a prosperous and efficient future.
Salesforce Pardot: Complete Overview, Pricing & Key Benefits
In today's fast-paced business landscape, effective marketing automation has become the cornerstone of successful customer engagement and lead nurturing. Among the multitude of tools available, Salesforce Pardot stands out as a powerful and versatile solution for businesses seeking to streamline their marketing efforts, personalize customer interactions, and ultimately drive growth.
In this blog post, we'll take a deep dive into Salesforce Pardot, exploring what it is, its key features, and the benefits it offers to businesses of all sizes and industries. We'll also delve into the pricing structure, helping you understand the investment required for incorporating Pardot into your marketing strategy.
Whether you're a seasoned marketer looking to enhance your automation capabilities or a business owner curious about the potential of marketing automation, this comprehensive guide will provide you with valuable insights to make informed decisions. Let's embark on this journey to discover Salesforce Pardot's incredible potential and the advantages it can bring to your marketing efforts.
Table of Contents
-
What is Salesforce Pardot
-
Benefits of Using Salesforce Pardot
-
Salesforce Pardot Pricing
-
Use Cases and Success Stories
-
Getting Started with Salesforce Pardot
-
Alternatives to Salesforce Pardot
-
Conclusion
What is Salesforce Pardot
Salesforce Pardot is a versatile marketing automation solution that empowers businesses to streamline their marketing efforts and engage with leads more effectively. With its robust features, Pardot enables businesses to automate various marketing tasks, such as email marketing, lead nurturing, and lead scoring. It facilitates personalized communication with leads, ensuring that the right message reaches the right audience at the right time. Furthermore, its seamless integration with Salesforce CRM enhances collaboration between marketing and sales teams, enabling a smoother lead handoff process. Pardot's analytics and reporting capabilities provide valuable insights, helping businesses refine their marketing strategies and boost ROI. Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, Pardot offers scalability and customization to meet your unique marketing automation needs.
One of the key strengths of Salesforce Pardot is its ability to deliver tangible benefits to businesses. By automating repetitive marketing tasks, it saves valuable time and resources, allowing marketing teams to focus on strategic activities. Its lead scoring and nurturing features increase the efficiency of lead management, ensuring that sales teams engage with leads that are more likely to convert. Pardot's data-driven approach enhances decision-making, as businesses can analyze campaign performance and make adjustments in real-time. Additionally, its integration with Salesforce CRM enhances customer relationship management, promoting a unified and efficient sales and marketing process. Overall, Salesforce Pardot is a powerful tool for businesses looking to drive revenue and improve marketing effectiveness through automation and data-driven insights.
Benefits of Using Salesforce Pardot
Using Salesforce Pardot offers a wide range of benefits to businesses seeking to enhance their marketing efforts, improve lead management, and drive revenue growth. Here are some key advantages of incorporating Salesforce Pardot into your marketing strategy:
-
Efficient Lead Generation and Nurturing: Pardot enables businesses to capture leads seamlessly through web forms, landing pages, and other channels. It also automates lead nurturing through personalized email campaigns, ensuring that leads are engaged and nurtured at every stage of the buyer's journey.
-
Improved Lead Scoring: With Pardot's lead scoring capabilities, you can prioritize leads based on their behavior and engagement with your content. This ensures that your sales team focuses their efforts on the most qualified leads, increasing conversion rates and sales efficiency.
-
Personalization: Pardot allows you to create highly targeted and personalized marketing campaigns. You can segment your audience based on various criteria, ensuring that each lead receives content tailored to their interests and needs.
-
Seamless CRM Integration: As part of the Salesforce ecosystem, Pardot seamlessly integrates with Salesforce CRM. This integration ensures that all lead and customer data is synchronized, providing a 360-degree view of your customers and prospects. It also streamlines the lead handoff process between marketing and sales teams.
-
Automation and Efficiency: Pardot automates various marketing tasks, such as email marketing, lead scoring, and lead assignment. This automation saves time and reduces the risk of human errors, allowing your marketing team to focus on strategic initiatives.
-
Advanced Analytics and Reporting: Pardot provides in-depth analytics and reporting tools to track the performance of your marketing campaigns. You can measure key metrics, such as email open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates, and use these insights to refine your marketing strategies for better results.
-
Scalability: Pardot is scalable, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes. Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, you can customize Pardot to meet your specific marketing automation needs and scale as your business grows.
-
Enhanced Social Media Engagement: Pardot helps you manage and track your social media marketing efforts, allowing you to monitor social engagement and incorporate it into your lead nurturing strategies.
-
Cost Savings: By automating marketing tasks and improving lead conversion rates, Pardot can lead to cost savings in both time and resources. It maximizes the efficiency of your marketing team while delivering tangible results.
-
Competitive Advantage: Leveraging Pardot's advanced features can give your business a competitive edge in a crowded marketplace. It enables you to stay ahead of the curve in terms of marketing automation and customer engagement.
Salesforce Pardot Pricing
Salesforce Pardot offers various pricing tiers to accommodate the needs and budgets of different businesses. The pricing structure is typically based on the number of users, the number of contacts or leads you want to manage, and the features you require. It's important to note that pricing may change over time, so it's advisable to visit the Salesforce Pardot website or contact their sales team for the most up-to-date information.
Pardot Edition
Features Included
Starting Price (Approximate)*
Growth Edition
- Basic marketing automation
Starting at $1,250/month
- Email marketing
- Lead scoring
- CRM integration
Plus Edition
- Advanced email analytics
Starting at $2,500/month
- Dynamic content
- A/B testing
- CRM integration
Advanced Edition
- AI-powered analytics
Custom pricing
- Custom user roles
- Marketing assets
- CRM integration
Premium Edition
- Custom analytics
Custom pricing
- Event-based segmentation
- Advanced features tailored to needs
Add-Ons
- B2B Marketing Analytics (Additional)
Custom pricing
- Engagement History (Additional)
- Additional services, training, and support
*Note: Pricing is typically based on factors such as the number of contacts or leads and additional features and services required. Actual prices may vary depending on specific business needs.
Use Cases and Success Stories
Use Cases and Success Stories of Salesforce Pardot
Salesforce Pardot has been employed by businesses across various industries to achieve marketing automation excellence and drive significant results. Below are some use cases and success stories that showcase the versatility and impact of Pardot:
1. Lead Nurturing and Conversion: A technology company that sells complex software solutions used Salesforce Pardot to nurture leads and increase conversions. By creating personalized email campaigns and automating lead scoring, they reduced the sales cycle by 30%. This resulted in a 20% increase in revenue in the first year of implementing Pardot.
2. B2B E-commerce: An e-commerce company specializing in B2B sales adopted Pardot to better understand its customers' needs. By tracking customer interactions and using Pardot's lead scoring, they were able to send targeted product recommendations, leading to a 15% increase in upsell and cross-sell revenue.
3. Event Promotion: An event management company utilized Pardot for event promotion. They automated email marketing campaigns and personalized event invitations based on attendee preferences. This resulted in a 40% increase in event attendance and a 25% boost in post-event engagement.
4. Higher Education: A university employed Pardot to streamline its student recruitment efforts. By automating email communication and tracking prospect engagement, they achieved a 50% increase in the number of enrolled students. Pardot's integration with Salesforce CRM also improved communication between admissions and academic departments.
5. Healthcare: A healthcare organization implemented Pardot to improve patient engagement and appointment scheduling. They sent automated appointment reminders and health tips to patients, resulting in a 25% reduction in missed appointments and improved patient satisfaction.
6. Manufacturing: A manufacturing company used Pardot to enhance its distributor engagement. By automating lead nurturing and providing distributors with tailored marketing collateral, they saw a 30% increase in distributor-generated sales leads within six months.
7. Non-Profit Fundraising: A non-profit organization leveraged Pardot for donor outreach and fundraising campaigns. They personalized donation requests and automated follow-up emails. As a result, they experienced a 40% increase in online donations and donor retention rates.
8. Financial Services: A financial services firm integrated Pardot with its CRM to improve lead management. They automated lead assignment to financial advisors, resulting in a 15% increase in lead conversion rates and a 20% reduction in response time.
These use cases highlight the adaptability of Salesforce Pardot across different industries and functions. Whether it's lead nurturing, event promotion, student recruitment, healthcare engagement, distributor management, non-profit fundraising, or financial services, Pardot has consistently delivered tangible benefits such as increased revenue, improved customer engagement, and enhanced operational efficiency. These success stories underscore the effectiveness of Pardot in helping businesses achieve their marketing and sales objectives.
Getting Started with Salesforce Pardot
Getting started with Salesforce Pardot involves several key steps to ensure a successful implementation of the marketing automation platform. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to get started with Salesforce Pardot:
1. Set Clear Goals and Objectives:
-
Define your marketing automation goals and objectives. What do you aim to achieve with Pardot? Whether it's lead generation, lead nurturing, improving conversions, or increasing ROI, having clear goals will guide your implementation.
2. Sign Up for Pardot:
-
Visit the Salesforce Pardot website and sign up for the edition that best suits your business needs. You may also request a demo or contact Salesforce for more information.
3. Assign an Administrator:
-
Designate an internal administrator or team responsible for managing Pardot. This individual should be trained in Pardot's features and functionality.
4. Set Up Salesforce Integration:
-
If you're already using Salesforce CRM, ensure that Pardot is properly integrated with Salesforce. This step is crucial for syncing data between the two platforms seamlessly.
5. Define Your Lead Scoring Model:
-
Develop a lead scoring model that assigns values to various lead interactions and behaviors. This model helps prioritize leads for your sales team.
6. Import Your Contacts and Data:
-
Import your existing leads and contacts into Pardot. Ensure that data is clean, accurate, and well-segmented for effective targeting.
7. Create Landing Pages and Forms:
-
Build custom landing pages and forms to capture lead information. Pardot provides templates and a user-friendly interface for this purpose.
8. Design Email Templates:
-
Create email templates that align with your branding and messaging. Pardot allows for responsive and personalized email design.
9. Set Up Drip Campaigns:
-
Create automated drip email campaigns for lead nurturing. Map out the content and timing of these campaigns based on your lead's journey.
10. Implement Lead Scoring and Grading: - Configure lead scoring rules and grading criteria to identify the most engaged and qualified leads.
11. Test Automation Workflows: - Before going live, thoroughly test your automation workflows, including email sequences and landing page forms, to ensure they function as intended.
12. Train Your Team: - Provide training to your marketing and sales teams on how to use Pardot effectively. Ensure they understand lead management processes and how to interpret lead scoring data.
13. Monitor and Analyze: - Regularly monitor the performance of your campaigns and use Pardot's analytics and reporting tools to gain insights into what's working and what needs improvement.
14. Optimize and Iterate: - Continuously optimize your marketing strategies based on data and feedback. Adjust your automation workflows, content, and targeting as needed to achieve better results.
15. Seek Professional Assistance: - If needed, consider consulting with Salesforce Pardot experts or attending training sessions to maximize the value of the platform.
Remember that Salesforce Pardot is a powerful marketing automation tool, and its effectiveness often grows over time as you become more familiar with its features and capabilities. Regularly reviewing your strategies and adapting to changing market conditions will help you get the most out of Pardot and drive success in your marketing efforts.
Alternatives to Salesforce Pardot
There are several alternatives to Salesforce Pardot, each offering its own set of features and capabilities for marketing automation and lead management. The choice of an alternative depends on your specific business needs, budget, and existing technology stack. Here are some popular alternatives to Salesforce Pardot:
-
HubSpot Marketing Hub:
-
HubSpot offers a comprehensive suite of marketing tools, including automation, email marketing, lead nurturing, and analytics. It's known for its user-friendly interface and is suitable for both small businesses and larger enterprises.
-
Marketo:
-
Marketo, now part of Adobe Experience Cloud, provides a robust marketing automation platform. It's ideal for B2B marketers and offers features such as lead scoring, advanced analytics, and integration with Adobe's creative tools.
-
Mailchimp:
-
While traditionally known for email marketing, Mailchimp has expanded its offerings to include marketing automation features. It's a cost-effective solution for small to medium-sized businesses.
-
ActiveCampaign:
-
ActiveCampaign combines email marketing, automation, and CRM capabilities. It's known for its advanced automation features and is suitable for businesses of all sizes.
-
Eloqua (Oracle Marketing Cloud):
-
Oracle Eloqua is a high-end marketing automation solution with a focus on enterprise-level marketing. It offers advanced lead scoring, campaign orchestration, and robust analytics.
-
SharpSpring:
-
SharpSpring is a marketing automation platform that caters to agencies and small to medium-sized businesses. It offers email marketing, CRM integration, and lead tracking features.
-
GetResponse:
-
GetResponse provides email marketing, automation, and landing page creation tools. It's a versatile solution for businesses looking to automate marketing tasks.
-
Infusionsoft by Keap:
-
Infusionsoft (now part of Keap) is a small business-focused marketing automation platform that offers CRM, email marketing, and automation capabilities.
-
Zoho MarketingHub:
-
Zoho MarketingHub is part of the Zoho suite of business tools and offers marketing automation features, email marketing, and CRM integration.
-
SendinBlue:
-
SendinBlue offers email marketing, marketing automation, and transactional email services. It's known for its affordability and ease of use.
-
Drip:
-
Drip is an e-commerce-focused marketing automation platform that specializes in personalized email marketing and automation for online retailers.
When evaluating alternatives to Salesforce Pardot, consider factors such as the size of your business, your budget, your specific marketing automation needs, and how well the platform integrates with your existing software stack, including your CRM. Additionally, take advantage of free trials and demos to test the platforms and see which one aligns best with your goals and workflows.
How to obtain Salesforce Certifications?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Blockchain Certification
Salesforce : Salesforce Administration Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, Salesforce Pardot presents a compelling solution for businesses seeking to elevate their marketing strategies through efficient automation. Its versatile feature set, encompassing lead generation, nurturing, and seamless CRM integration, offers tangible benefits such as increased lead conversion rates and streamlined processes. While Pardot's pricing structure varies to accommodate businesses of all sizes, its value lies in the potential for personalized engagement, data-driven insights, and scalable marketing campaigns, making it a noteworthy contender in the competitive landscape of marketing automation platforms.
Read More
In today's fast-paced business landscape, effective marketing automation has become the cornerstone of successful customer engagement and lead nurturing. Among the multitude of tools available, Salesforce Pardot stands out as a powerful and versatile solution for businesses seeking to streamline their marketing efforts, personalize customer interactions, and ultimately drive growth.
In this blog post, we'll take a deep dive into Salesforce Pardot, exploring what it is, its key features, and the benefits it offers to businesses of all sizes and industries. We'll also delve into the pricing structure, helping you understand the investment required for incorporating Pardot into your marketing strategy.
Whether you're a seasoned marketer looking to enhance your automation capabilities or a business owner curious about the potential of marketing automation, this comprehensive guide will provide you with valuable insights to make informed decisions. Let's embark on this journey to discover Salesforce Pardot's incredible potential and the advantages it can bring to your marketing efforts.
Table of Contents
-
What is Salesforce Pardot
-
Benefits of Using Salesforce Pardot
-
Salesforce Pardot Pricing
-
Use Cases and Success Stories
-
Getting Started with Salesforce Pardot
-
Alternatives to Salesforce Pardot
-
Conclusion
What is Salesforce Pardot
Salesforce Pardot is a versatile marketing automation solution that empowers businesses to streamline their marketing efforts and engage with leads more effectively. With its robust features, Pardot enables businesses to automate various marketing tasks, such as email marketing, lead nurturing, and lead scoring. It facilitates personalized communication with leads, ensuring that the right message reaches the right audience at the right time. Furthermore, its seamless integration with Salesforce CRM enhances collaboration between marketing and sales teams, enabling a smoother lead handoff process. Pardot's analytics and reporting capabilities provide valuable insights, helping businesses refine their marketing strategies and boost ROI. Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, Pardot offers scalability and customization to meet your unique marketing automation needs.
One of the key strengths of Salesforce Pardot is its ability to deliver tangible benefits to businesses. By automating repetitive marketing tasks, it saves valuable time and resources, allowing marketing teams to focus on strategic activities. Its lead scoring and nurturing features increase the efficiency of lead management, ensuring that sales teams engage with leads that are more likely to convert. Pardot's data-driven approach enhances decision-making, as businesses can analyze campaign performance and make adjustments in real-time. Additionally, its integration with Salesforce CRM enhances customer relationship management, promoting a unified and efficient sales and marketing process. Overall, Salesforce Pardot is a powerful tool for businesses looking to drive revenue and improve marketing effectiveness through automation and data-driven insights.
Benefits of Using Salesforce Pardot
Using Salesforce Pardot offers a wide range of benefits to businesses seeking to enhance their marketing efforts, improve lead management, and drive revenue growth. Here are some key advantages of incorporating Salesforce Pardot into your marketing strategy:
-
Efficient Lead Generation and Nurturing: Pardot enables businesses to capture leads seamlessly through web forms, landing pages, and other channels. It also automates lead nurturing through personalized email campaigns, ensuring that leads are engaged and nurtured at every stage of the buyer's journey.
-
Improved Lead Scoring: With Pardot's lead scoring capabilities, you can prioritize leads based on their behavior and engagement with your content. This ensures that your sales team focuses their efforts on the most qualified leads, increasing conversion rates and sales efficiency.
-
Personalization: Pardot allows you to create highly targeted and personalized marketing campaigns. You can segment your audience based on various criteria, ensuring that each lead receives content tailored to their interests and needs.
-
Seamless CRM Integration: As part of the Salesforce ecosystem, Pardot seamlessly integrates with Salesforce CRM. This integration ensures that all lead and customer data is synchronized, providing a 360-degree view of your customers and prospects. It also streamlines the lead handoff process between marketing and sales teams.
-
Automation and Efficiency: Pardot automates various marketing tasks, such as email marketing, lead scoring, and lead assignment. This automation saves time and reduces the risk of human errors, allowing your marketing team to focus on strategic initiatives.
-
Advanced Analytics and Reporting: Pardot provides in-depth analytics and reporting tools to track the performance of your marketing campaigns. You can measure key metrics, such as email open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates, and use these insights to refine your marketing strategies for better results.
-
Scalability: Pardot is scalable, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes. Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, you can customize Pardot to meet your specific marketing automation needs and scale as your business grows.
-
Enhanced Social Media Engagement: Pardot helps you manage and track your social media marketing efforts, allowing you to monitor social engagement and incorporate it into your lead nurturing strategies.
-
Cost Savings: By automating marketing tasks and improving lead conversion rates, Pardot can lead to cost savings in both time and resources. It maximizes the efficiency of your marketing team while delivering tangible results.
-
Competitive Advantage: Leveraging Pardot's advanced features can give your business a competitive edge in a crowded marketplace. It enables you to stay ahead of the curve in terms of marketing automation and customer engagement.
Salesforce Pardot Pricing
Salesforce Pardot offers various pricing tiers to accommodate the needs and budgets of different businesses. The pricing structure is typically based on the number of users, the number of contacts or leads you want to manage, and the features you require. It's important to note that pricing may change over time, so it's advisable to visit the Salesforce Pardot website or contact their sales team for the most up-to-date information.
|
Pardot Edition |
Features Included |
Starting Price (Approximate)* |
|
Growth Edition |
- Basic marketing automation |
Starting at $1,250/month |
|
- Email marketing |
||
|
- Lead scoring |
||
|
- CRM integration |
||
|
Plus Edition |
- Advanced email analytics |
Starting at $2,500/month |
|
- Dynamic content |
||
|
- A/B testing |
||
|
- CRM integration |
||
|
Advanced Edition |
- AI-powered analytics |
Custom pricing |
|
- Custom user roles |
||
|
- Marketing assets |
||
|
- CRM integration |
||
|
Premium Edition |
- Custom analytics |
Custom pricing |
|
- Event-based segmentation |
||
|
- Advanced features tailored to needs |
||
|
Add-Ons |
- B2B Marketing Analytics (Additional) |
Custom pricing |
|
- Engagement History (Additional) |
||
|
- Additional services, training, and support |
*Note: Pricing is typically based on factors such as the number of contacts or leads and additional features and services required. Actual prices may vary depending on specific business needs.
Use Cases and Success Stories
Use Cases and Success Stories of Salesforce Pardot
Salesforce Pardot has been employed by businesses across various industries to achieve marketing automation excellence and drive significant results. Below are some use cases and success stories that showcase the versatility and impact of Pardot:
1. Lead Nurturing and Conversion: A technology company that sells complex software solutions used Salesforce Pardot to nurture leads and increase conversions. By creating personalized email campaigns and automating lead scoring, they reduced the sales cycle by 30%. This resulted in a 20% increase in revenue in the first year of implementing Pardot.
2. B2B E-commerce: An e-commerce company specializing in B2B sales adopted Pardot to better understand its customers' needs. By tracking customer interactions and using Pardot's lead scoring, they were able to send targeted product recommendations, leading to a 15% increase in upsell and cross-sell revenue.
3. Event Promotion: An event management company utilized Pardot for event promotion. They automated email marketing campaigns and personalized event invitations based on attendee preferences. This resulted in a 40% increase in event attendance and a 25% boost in post-event engagement.
4. Higher Education: A university employed Pardot to streamline its student recruitment efforts. By automating email communication and tracking prospect engagement, they achieved a 50% increase in the number of enrolled students. Pardot's integration with Salesforce CRM also improved communication between admissions and academic departments.
5. Healthcare: A healthcare organization implemented Pardot to improve patient engagement and appointment scheduling. They sent automated appointment reminders and health tips to patients, resulting in a 25% reduction in missed appointments and improved patient satisfaction.
6. Manufacturing: A manufacturing company used Pardot to enhance its distributor engagement. By automating lead nurturing and providing distributors with tailored marketing collateral, they saw a 30% increase in distributor-generated sales leads within six months.
7. Non-Profit Fundraising: A non-profit organization leveraged Pardot for donor outreach and fundraising campaigns. They personalized donation requests and automated follow-up emails. As a result, they experienced a 40% increase in online donations and donor retention rates.
8. Financial Services: A financial services firm integrated Pardot with its CRM to improve lead management. They automated lead assignment to financial advisors, resulting in a 15% increase in lead conversion rates and a 20% reduction in response time.
These use cases highlight the adaptability of Salesforce Pardot across different industries and functions. Whether it's lead nurturing, event promotion, student recruitment, healthcare engagement, distributor management, non-profit fundraising, or financial services, Pardot has consistently delivered tangible benefits such as increased revenue, improved customer engagement, and enhanced operational efficiency. These success stories underscore the effectiveness of Pardot in helping businesses achieve their marketing and sales objectives.
Getting Started with Salesforce Pardot
Getting started with Salesforce Pardot involves several key steps to ensure a successful implementation of the marketing automation platform. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to get started with Salesforce Pardot:
1. Set Clear Goals and Objectives:
-
Define your marketing automation goals and objectives. What do you aim to achieve with Pardot? Whether it's lead generation, lead nurturing, improving conversions, or increasing ROI, having clear goals will guide your implementation.
2. Sign Up for Pardot:
-
Visit the Salesforce Pardot website and sign up for the edition that best suits your business needs. You may also request a demo or contact Salesforce for more information.
3. Assign an Administrator:
-
Designate an internal administrator or team responsible for managing Pardot. This individual should be trained in Pardot's features and functionality.
4. Set Up Salesforce Integration:
-
If you're already using Salesforce CRM, ensure that Pardot is properly integrated with Salesforce. This step is crucial for syncing data between the two platforms seamlessly.
5. Define Your Lead Scoring Model:
-
Develop a lead scoring model that assigns values to various lead interactions and behaviors. This model helps prioritize leads for your sales team.
6. Import Your Contacts and Data:
-
Import your existing leads and contacts into Pardot. Ensure that data is clean, accurate, and well-segmented for effective targeting.
7. Create Landing Pages and Forms:
-
Build custom landing pages and forms to capture lead information. Pardot provides templates and a user-friendly interface for this purpose.
8. Design Email Templates:
-
Create email templates that align with your branding and messaging. Pardot allows for responsive and personalized email design.
9. Set Up Drip Campaigns:
-
Create automated drip email campaigns for lead nurturing. Map out the content and timing of these campaigns based on your lead's journey.
10. Implement Lead Scoring and Grading: - Configure lead scoring rules and grading criteria to identify the most engaged and qualified leads.
11. Test Automation Workflows: - Before going live, thoroughly test your automation workflows, including email sequences and landing page forms, to ensure they function as intended.
12. Train Your Team: - Provide training to your marketing and sales teams on how to use Pardot effectively. Ensure they understand lead management processes and how to interpret lead scoring data.
13. Monitor and Analyze: - Regularly monitor the performance of your campaigns and use Pardot's analytics and reporting tools to gain insights into what's working and what needs improvement.
14. Optimize and Iterate: - Continuously optimize your marketing strategies based on data and feedback. Adjust your automation workflows, content, and targeting as needed to achieve better results.
15. Seek Professional Assistance: - If needed, consider consulting with Salesforce Pardot experts or attending training sessions to maximize the value of the platform.
Remember that Salesforce Pardot is a powerful marketing automation tool, and its effectiveness often grows over time as you become more familiar with its features and capabilities. Regularly reviewing your strategies and adapting to changing market conditions will help you get the most out of Pardot and drive success in your marketing efforts.
Alternatives to Salesforce Pardot
There are several alternatives to Salesforce Pardot, each offering its own set of features and capabilities for marketing automation and lead management. The choice of an alternative depends on your specific business needs, budget, and existing technology stack. Here are some popular alternatives to Salesforce Pardot:
-
HubSpot Marketing Hub:
-
HubSpot offers a comprehensive suite of marketing tools, including automation, email marketing, lead nurturing, and analytics. It's known for its user-friendly interface and is suitable for both small businesses and larger enterprises.
-
-
Marketo:
-
Marketo, now part of Adobe Experience Cloud, provides a robust marketing automation platform. It's ideal for B2B marketers and offers features such as lead scoring, advanced analytics, and integration with Adobe's creative tools.
-
-
Mailchimp:
-
While traditionally known for email marketing, Mailchimp has expanded its offerings to include marketing automation features. It's a cost-effective solution for small to medium-sized businesses.
-
-
ActiveCampaign:
-
ActiveCampaign combines email marketing, automation, and CRM capabilities. It's known for its advanced automation features and is suitable for businesses of all sizes.
-
-
Eloqua (Oracle Marketing Cloud):
-
Oracle Eloqua is a high-end marketing automation solution with a focus on enterprise-level marketing. It offers advanced lead scoring, campaign orchestration, and robust analytics.
-
-
SharpSpring:
-
SharpSpring is a marketing automation platform that caters to agencies and small to medium-sized businesses. It offers email marketing, CRM integration, and lead tracking features.
-
-
GetResponse:
-
GetResponse provides email marketing, automation, and landing page creation tools. It's a versatile solution for businesses looking to automate marketing tasks.
-
-
Infusionsoft by Keap:
-
Infusionsoft (now part of Keap) is a small business-focused marketing automation platform that offers CRM, email marketing, and automation capabilities.
-
-
Zoho MarketingHub:
-
Zoho MarketingHub is part of the Zoho suite of business tools and offers marketing automation features, email marketing, and CRM integration.
-
-
SendinBlue:
-
SendinBlue offers email marketing, marketing automation, and transactional email services. It's known for its affordability and ease of use.
-
-
Drip:
-
Drip is an e-commerce-focused marketing automation platform that specializes in personalized email marketing and automation for online retailers.
-
When evaluating alternatives to Salesforce Pardot, consider factors such as the size of your business, your budget, your specific marketing automation needs, and how well the platform integrates with your existing software stack, including your CRM. Additionally, take advantage of free trials and demos to test the platforms and see which one aligns best with your goals and workflows.
How to obtain Salesforce Certifications?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Blockchain Certification
Salesforce : Salesforce Administration Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, Salesforce Pardot presents a compelling solution for businesses seeking to elevate their marketing strategies through efficient automation. Its versatile feature set, encompassing lead generation, nurturing, and seamless CRM integration, offers tangible benefits such as increased lead conversion rates and streamlined processes. While Pardot's pricing structure varies to accommodate businesses of all sizes, its value lies in the potential for personalized engagement, data-driven insights, and scalable marketing campaigns, making it a noteworthy contender in the competitive landscape of marketing automation platforms.
Cloud Engineer Salary Trends: Entry-Level vs. Experienced
In the rapidly advancing domain of cloud computing, the role of a Cloud Engineer stands as a linchpin in modern tech operations. As businesses continue to embrace the benefits of cloud technologies, the demand for skilled professionals to design, manage, and optimize these infrastructures has soared. This has sparked a fascinating comparison between the salaries of freshers, those new to the cloud engineering scene, and experienced professionals who have weathered the dynamic landscape for some time.
This examination of "Cloud Engineer Salary Trends: Freshers vs. Experienced" embarks on a journey through the intricacies of compensation packages in the cloud engineering sphere. Whether you're a recent graduate, eager to step into this promising career path, or a seasoned expert, curious about how your experience impacts your earning potential, our exploration will dissect the factors that shape these trends. By shedding light on the compensation distinctions, we aim to empower both newcomers and veterans in the field to navigate their cloud engineering careers effectively, making informed decisions in this ever-evolving and rewarding landscape.
Table of Contents
What Does a Cloud Engineer Do?
Skills Required to Be a Cloud Engineer
Roles and Responsibilities of a Cloud Engineer
Companies That Hire Cloud Engineers
Cloud Engineer Salaries for Freshers and Experienced Professionals
FAQs
Choose The Right Cloud Computing Program
Conclusion
What Does a Cloud Engineer Do?
A Cloud Engineer is responsible for architecting, implementing, and maintaining an organization's cloud computing infrastructure. They design the cloud environment, selecting the most suitable cloud service providers and configuring resources to meet business needs. Cloud Engineers also focus on automation, using tools like Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to efficiently provision and manage cloud resources. Security is a top priority, as they establish robust security measures, monitor for threats, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Additionally, they optimize cloud performance, manage costs, and collaborate with cross-functional teams to align cloud infrastructure with application requirements. In essence, Cloud Engineers are crucial for enabling businesses to leverage the benefits of cloud technology while ensuring reliability, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Continuous maintenance and improvement are key aspects of a Cloud Engineer's role. They regularly update and patch cloud systems, implement backup and disaster recovery plans to ensure data availability, and monitor cloud resources for performance and security. By staying abreast of emerging cloud technologies and best practices, Cloud Engineers help organizations harness the full potential of the cloud, driving innovation, scalability, and efficiency in their operations.
Skills Required to Be a Cloud Engineer
To excel as a Cloud Engineer, you need a diverse set of technical skills and non-technical skills. Here is a list of key skills required to be successful in this role:
1. Cloud Platform Proficiency: A deep understanding of one or more major cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or others is essential. This includes knowledge of their services, capabilities, and pricing models.
2. Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Proficiency in IaC tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, or Azure Resource Manager is crucial for automating the provisioning and management of cloud resources.
3. Networking: Knowledge of cloud networking concepts, including Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), subnets, load balancers, and VPN configurations, is necessary for designing and securing cloud architectures.
4. Security: An understanding of cloud security best practices, identity and access management (IAM), encryption, firewalls, and compliance standards is vital to protect cloud environments from cyber threats.
5. DevOps Tools: Familiarity with DevOps principles and tools such as Docker, Kubernetes, Jenkins, and Git is important for implementing continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
6. Scripting and Automation: Proficiency in scripting languages like Python, PowerShell, or Bash is essential for writing automation scripts and managing cloud resources programmatically.
7. Monitoring and Logging: Experience with monitoring and logging tools like Amazon CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or Prometheus is necessary for tracking the health and performance of cloud services.
8. Database Management: Knowledge of cloud database services (e.g., AWS RDS, Azure SQL Database, Google Cloud SQL) and database administration skills are important for managing data in the cloud.
9. Cost Management: The ability to manage cloud costs effectively by analyzing usage patterns, optimizing resource allocation, and implementing cost-saving strategies is critical.
10. Troubleshooting and Problem Solving: Strong analytical and problem-solving skills are essential for identifying and resolving issues in cloud environments.
11. Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration skills are vital for working with cross-functional teams, including developers, sysadmins, and security professionals.
12. Project Management: Basic project management skills can help Cloud Engineers plan and execute cloud projects effectively, ensuring they meet deadlines and objectives.
13. Continuous Learning: Cloud technology evolves rapidly, so a willingness to continuously learn and adapt to new tools and best practices is crucial to stay up-to-date in this field.
14. Soft Skills: Soft skills such as adaptability, teamwork, and attention to detail are important for working in a dynamic and collaborative environment.
Overall, Cloud Engineers need to combine technical expertise with a proactive and problem-solving mindset to design, implement, and manage robust and scalable cloud infrastructures that meet the needs of their organizations.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Cloud Engineer
The roles and responsibilities of a Cloud Engineer can vary depending on the organization's size, industry, and specific needs. However, here are the common roles and responsibilities associated with this role:
-
Cloud Infrastructure Design: Collaborate with architects and developers to design and plan cloud infrastructure that aligns with the organization's goals. This includes selecting appropriate cloud services, defining network architecture, and designing security measures.
-
Cloud Deployment: Implement cloud solutions by provisioning resources, setting up virtual machines, databases, storage, and configuring networking components. Ensure that the deployment meets scalability and performance requirements.
-
Automation: Develop and maintain Infrastructure as Code (IaC) scripts using tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, or Azure Resource Manager to automate the provisioning and management of cloud resources.
-
Security Management: Implement security best practices and configure access controls (IAM policies) to protect cloud environments. Regularly assess and monitor security, perform vulnerability assessments, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
-
Performance Optimization: Continuously monitor cloud resources to ensure optimal performance. Scale resources as needed to meet demand and implement performance tuning strategies.
-
Backup and Disaster Recovery: Set up backup solutions and disaster recovery plans to ensure data availability and minimize downtime in case of system failures or disasters.
-
Monitoring and Logging: Implement monitoring and logging solutions (e.g., AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor) to track the health and performance of cloud services. Configure alerts and dashboards to respond to issues promptly.
-
Cost Management: Monitor and manage cloud costs effectively by analyzing usage patterns, optimizing resource allocation, and implementing cost-saving strategies to stay within budget.
-
Collaboration: Work closely with other teams, such as development, DevOps, and security teams, to ensure that cloud infrastructure supports application requirements and security standards.
-
Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of cloud infrastructure, configurations, and processes. This documentation is crucial for knowledge sharing and troubleshooting.
-
Compliance: Ensure that cloud resources and configurations adhere to industry regulations and company policies, implementing necessary controls to meet compliance requirements.
-
Upgrades and Maintenance: Regularly apply updates, patches, and system upgrades to keep cloud infrastructure secure and up-to-date.
-
Problem Resolution: Troubleshoot and resolve issues related to cloud infrastructure and services, working to minimize downtime and impact on operations.
-
Education and Training: Stay current with cloud technology trends and provide training and guidance to team members and other stakeholders.
-
Innovation: Explore and implement new cloud services and technologies to drive innovation and improve infrastructure efficiency.
In summary, Cloud Engineers play a critical role in designing, deploying, and maintaining cloud infrastructure that supports an organization's IT needs. They are responsible for ensuring the security, performance, and cost-effectiveness of cloud environments while collaborating with various teams to deliver efficient and reliable cloud solutions.
Companies That Hire Cloud Engineers
Cloud Engineers are in high demand across various industries as organizations increasingly rely on cloud computing for their IT infrastructure. Many companies, ranging from tech giants to startups and enterprises, hire Cloud Engineers to design, implement, and manage their cloud environments. Here are some notable companies that commonly hire Cloud Engineers:
-
Amazon Web Services (AWS): As a leading cloud service provider, AWS often hires Cloud Engineers to work on their own cloud infrastructure and to support AWS customers in optimizing their cloud environments.
-
Microsoft: Microsoft Azure is another major cloud platform, and the company hires Cloud Engineers to develop and manage Azure-based solutions.
-
Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Google Cloud offers various cloud services, and they hire Cloud Engineers to work on GCP infrastructure and assist customers in building cloud-native applications.
-
IBM: IBM Cloud provides cloud computing solutions, and they hire Cloud Engineers to work on their cloud platform and offer cloud consulting services.
-
Oracle: Oracle Cloud is a growing cloud provider, and they hire Cloud Engineers to help customers migrate to and manage their cloud services.
-
Salesforce: Salesforce offers cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) solutions and often hires Cloud Engineers to work on their cloud infrastructure and applications.
-
Cisco: Cisco provides cloud networking and infrastructure solutions and hires Cloud Engineers to work on cloud-based networking and security technologies.
-
Netflix: As a popular streaming service, Netflix relies heavily on cloud computing and hires Cloud Engineers to manage its cloud infrastructure and improve streaming capabilities.
-
Uber: Uber utilizes cloud computing for its ride-sharing platform and hires Cloud Engineers to manage and optimize its cloud resources.
-
Airbnb: Airbnb relies on cloud services for its accommodation platform, and Cloud Engineers are responsible for ensuring the reliability and scalability of their cloud infrastructure.
-
Tesla: Tesla uses cloud computing for various purposes, including over-the-air updates and autonomous driving, and hires Cloud Engineers to support these initiatives.
-
SpaceX: SpaceX leverages cloud technology for its space missions, and Cloud Engineers play a crucial role in managing cloud resources for data analysis and mission control.
-
Startups: Many startups across industries rely on cloud technology to scale their businesses quickly, and they often hire Cloud Engineers to build and manage their cloud-based applications and infrastructure.
-
Consulting Firms: Consulting firms like Deloitte, Accenture, and Capgemini offer cloud consulting services and hire Cloud Engineers to work on a wide range of client projects.
-
Financial Institutions: Banks and financial organizations are increasingly moving to the cloud, and they hire Cloud Engineers to ensure the security and compliance of their cloud-based systems.
These are just a few examples, and the demand for Cloud Engineers continues to grow as more companies adopt cloud computing solutions to improve agility, scalability, and cost-efficiency in their IT operations. Keep in mind that the specific skills and qualifications required may vary depending on the company and the nature of the job.
Cloud Engineer Salaries for Freshers and Experienced Professionals
The salary of a Cloud Engineer can vary significantly based on several factors, including location, level of experience, the specific company, and the demand for cloud skills in the job market. Here is a rough overview of the salary ranges for Cloud Engineers at different career stages:
1. Freshers/Entry-Level Cloud Engineers:
-
In the United States, entry-level Cloud Engineers can expect an annual salary in the range of $60,000 to $90,000 on average.
-
In other countries, the salaries for entry-level Cloud Engineers may vary widely, but they often align with the cost of living in the respective region.
2. Mid-Level Cloud Engineers (2-5 years of experience):
-
Mid-level Cloud Engineers typically earn more than entry-level professionals. In the United States, their salaries can range from $90,000 to $130,000 or more per year.
-
Salaries for mid-level Cloud Engineers in other countries will depend on local market conditions and demand for cloud skills.
3. Experienced Cloud Engineers (5+ years of experience):
-
Experienced Cloud Engineers with five or more years of experience can command higher salaries. In the United States, they can earn anywhere from $120,000 to $180,000 or even higher annually.
-
Salaries for experienced Cloud Engineers in other countries will also depend on factors like location and the specific industry.
4. Senior Cloud Engineers and Cloud Architects:
-
Senior Cloud Engineers and Cloud Architects, who have extensive experience and often hold advanced certifications, can earn significantly higher salaries. In the United States, their salaries can range from $150,000 to $250,000 or more per year.
It's important to note that the figures mentioned above are approximate averages and can vary considerably based on regional cost of living, the organization's size and industry, and the engineer's level of expertise and certifications. Additionally, professionals with specialized skills in specific cloud platforms (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP) or emerging technologies may command higher salaries.
Certifications, such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert, or Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect, can also positively impact a Cloud Engineer's earning potential, as they demonstrate expertise in a particular cloud platform.
As the demand for cloud skills continues to grow and the cloud computing industry evolves, salaries for Cloud Engineers are expected to remain competitive and may even increase over time. It's essential for individuals in this field to stay updated with the latest cloud technologies and certifications to maximize their career growth and earning potential.
FAQs
What is the average salary for a fresher or entry-level Cloud Engineer?
-
The average salary for a fresher or entry-level Cloud Engineer can vary by location and organization. However, it typically ranges from $60,000 to $90,000 per year in the United States.
2. Do Cloud Engineers with certifications earn higher salaries?
-
Yes, Cloud Engineers with certifications, such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect or Azure Administrator, often earn higher salaries as these certifications demonstrate expertise in specific cloud platforms.
3. What factors influence the salary of an experienced Cloud Engineer?
-
Several factors influence the salary of an experienced Cloud Engineer, including years of experience, geographic location, the organization's size, industry, and the engineer's specific skills and certifications.
4. Are Cloud Engineers in high demand in the job market?
-
Yes, Cloud Engineers are in high demand as organizations increasingly adopt cloud computing solutions. This high demand often leads to competitive salaries and job opportunities.
5. How can Cloud Engineers increase their earning potential?
-
Cloud Engineers can increase their earning potential by acquiring advanced certifications, gaining expertise in specific cloud platforms, staying updated with emerging cloud technologies, and pursuing leadership roles.
6. Are there regional variations in Cloud Engineer salaries?
-
Yes, Cloud Engineer salaries vary significantly by region due to differences in the cost of living and demand for cloud skills. Salaries in major tech hubs like San Francisco and New York tend to be higher than in other areas.
7. What are some of the most lucrative industries for Cloud Engineers?
-
Cloud Engineers can find lucrative opportunities in various industries, including technology, finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, as many organizations across sectors are migrating to the cloud.
8. Do Cloud Architects earn higher salaries than Cloud Engineers?
-
Yes, Cloud Architects, who design complex cloud solutions and architectures, often earn higher salaries than Cloud Engineers due to their specialized skills and responsibilities.
9. Is there a significant salary difference between AWS, Azure, and GCP Cloud Engineers?
-
Salary differences among AWS, Azure, and GCP Cloud Engineers can vary, but generally, the choice of cloud platform may have a moderate impact on salary. Other factors like skills and experience play a more significant role.
10. How can entry-level Cloud Engineers negotiate a competitive salary offer?
Entry-level Cloud Engineers can negotiate a competitive salary offer by researching industry salary benchmarks, highlighting their relevant skills and certifications, and effectively communicating their value to the employer during negotiations.
Choose The Right Cloud Computing Program
Choosing the right cloud computing program is a pivotal step in advancing your career in the ever-evolving world of technology. Start by clearly defining your objectives and assessing your current skill level. Research reputable training providers and examine their programs in terms of content, format, and flexibility. Ensure that the curriculum covers essential cloud computing concepts and aligns with any specific certifications you may be targeting. Look for programs that offer practical, hands-on experience and access to knowledgeable instructors who can provide guidance. Additionally, consider the program's cost, financial aid options, and its alumni success rate in securing cloud-related positions. Seeking recommendations and reading reviews can provide valuable insights to aid in your decision-making process. Ultimately, the right cloud computing program will empower you with the skills and knowledge needed to thrive in this dynamic field.
Remember that cloud computing is a technology domain that evolves rapidly. Therefore, choosing a program that not only imparts fundamental knowledge but also keeps pace with industry trends and updates is essential for staying competitive in the job market. The right program should provide a solid foundation, hands-on experience, and the flexibility to accommodate your learning style and schedule, all while aligning with your career aspirations in cloud computing.
How to obtain Cloud Technology Certifications?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: EXIN Cloud Computing Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Robotic Process Automation
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of cloud computing offers promising career opportunities for both freshers and experienced professionals, with salaries that reflect the increasing demand for cloud expertise. For newcomers to the field, the potential for growth is evident as entry-level salaries provide a solid foundation for a rewarding career in cloud engineering. As one gains experience and expertise, the earning potential expands, with mid-level and experienced Cloud Engineers commanding competitive salaries.
However, it's important to recognize that salary figures can vary widely based on factors such as location, certification, industry, and specific skills. Therefore, continuous learning, staying updated with the latest cloud technologies, and investing in certifications are crucial steps to maximize earning potential. Whether you're at the beginning of your cloud engineering journey or an experienced professional seeking to further your career, the cloud computing landscape offers ample opportunities for growth and financial rewards, making it an exciting and lucrative field to explore.
Read More
In the rapidly advancing domain of cloud computing, the role of a Cloud Engineer stands as a linchpin in modern tech operations. As businesses continue to embrace the benefits of cloud technologies, the demand for skilled professionals to design, manage, and optimize these infrastructures has soared. This has sparked a fascinating comparison between the salaries of freshers, those new to the cloud engineering scene, and experienced professionals who have weathered the dynamic landscape for some time.
This examination of "Cloud Engineer Salary Trends: Freshers vs. Experienced" embarks on a journey through the intricacies of compensation packages in the cloud engineering sphere. Whether you're a recent graduate, eager to step into this promising career path, or a seasoned expert, curious about how your experience impacts your earning potential, our exploration will dissect the factors that shape these trends. By shedding light on the compensation distinctions, we aim to empower both newcomers and veterans in the field to navigate their cloud engineering careers effectively, making informed decisions in this ever-evolving and rewarding landscape.
Table of Contents
What Does a Cloud Engineer Do?
Skills Required to Be a Cloud Engineer
Roles and Responsibilities of a Cloud Engineer
Companies That Hire Cloud Engineers
Cloud Engineer Salaries for Freshers and Experienced Professionals
FAQs
Choose The Right Cloud Computing Program
Conclusion
What Does a Cloud Engineer Do?
A Cloud Engineer is responsible for architecting, implementing, and maintaining an organization's cloud computing infrastructure. They design the cloud environment, selecting the most suitable cloud service providers and configuring resources to meet business needs. Cloud Engineers also focus on automation, using tools like Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to efficiently provision and manage cloud resources. Security is a top priority, as they establish robust security measures, monitor for threats, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Additionally, they optimize cloud performance, manage costs, and collaborate with cross-functional teams to align cloud infrastructure with application requirements. In essence, Cloud Engineers are crucial for enabling businesses to leverage the benefits of cloud technology while ensuring reliability, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Continuous maintenance and improvement are key aspects of a Cloud Engineer's role. They regularly update and patch cloud systems, implement backup and disaster recovery plans to ensure data availability, and monitor cloud resources for performance and security. By staying abreast of emerging cloud technologies and best practices, Cloud Engineers help organizations harness the full potential of the cloud, driving innovation, scalability, and efficiency in their operations.
Skills Required to Be a Cloud Engineer
To excel as a Cloud Engineer, you need a diverse set of technical skills and non-technical skills. Here is a list of key skills required to be successful in this role:
1. Cloud Platform Proficiency: A deep understanding of one or more major cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or others is essential. This includes knowledge of their services, capabilities, and pricing models.
2. Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Proficiency in IaC tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, or Azure Resource Manager is crucial for automating the provisioning and management of cloud resources.
3. Networking: Knowledge of cloud networking concepts, including Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), subnets, load balancers, and VPN configurations, is necessary for designing and securing cloud architectures.
4. Security: An understanding of cloud security best practices, identity and access management (IAM), encryption, firewalls, and compliance standards is vital to protect cloud environments from cyber threats.
5. DevOps Tools: Familiarity with DevOps principles and tools such as Docker, Kubernetes, Jenkins, and Git is important for implementing continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
6. Scripting and Automation: Proficiency in scripting languages like Python, PowerShell, or Bash is essential for writing automation scripts and managing cloud resources programmatically.
7. Monitoring and Logging: Experience with monitoring and logging tools like Amazon CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or Prometheus is necessary for tracking the health and performance of cloud services.
8. Database Management: Knowledge of cloud database services (e.g., AWS RDS, Azure SQL Database, Google Cloud SQL) and database administration skills are important for managing data in the cloud.
9. Cost Management: The ability to manage cloud costs effectively by analyzing usage patterns, optimizing resource allocation, and implementing cost-saving strategies is critical.
10. Troubleshooting and Problem Solving: Strong analytical and problem-solving skills are essential for identifying and resolving issues in cloud environments.
11. Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration skills are vital for working with cross-functional teams, including developers, sysadmins, and security professionals.
12. Project Management: Basic project management skills can help Cloud Engineers plan and execute cloud projects effectively, ensuring they meet deadlines and objectives.
13. Continuous Learning: Cloud technology evolves rapidly, so a willingness to continuously learn and adapt to new tools and best practices is crucial to stay up-to-date in this field.
14. Soft Skills: Soft skills such as adaptability, teamwork, and attention to detail are important for working in a dynamic and collaborative environment.
Overall, Cloud Engineers need to combine technical expertise with a proactive and problem-solving mindset to design, implement, and manage robust and scalable cloud infrastructures that meet the needs of their organizations.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Cloud Engineer
The roles and responsibilities of a Cloud Engineer can vary depending on the organization's size, industry, and specific needs. However, here are the common roles and responsibilities associated with this role:
-
Cloud Infrastructure Design: Collaborate with architects and developers to design and plan cloud infrastructure that aligns with the organization's goals. This includes selecting appropriate cloud services, defining network architecture, and designing security measures.
-
Cloud Deployment: Implement cloud solutions by provisioning resources, setting up virtual machines, databases, storage, and configuring networking components. Ensure that the deployment meets scalability and performance requirements.
-
Automation: Develop and maintain Infrastructure as Code (IaC) scripts using tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, or Azure Resource Manager to automate the provisioning and management of cloud resources.
-
Security Management: Implement security best practices and configure access controls (IAM policies) to protect cloud environments. Regularly assess and monitor security, perform vulnerability assessments, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
-
Performance Optimization: Continuously monitor cloud resources to ensure optimal performance. Scale resources as needed to meet demand and implement performance tuning strategies.
-
Backup and Disaster Recovery: Set up backup solutions and disaster recovery plans to ensure data availability and minimize downtime in case of system failures or disasters.
-
Monitoring and Logging: Implement monitoring and logging solutions (e.g., AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor) to track the health and performance of cloud services. Configure alerts and dashboards to respond to issues promptly.
-
Cost Management: Monitor and manage cloud costs effectively by analyzing usage patterns, optimizing resource allocation, and implementing cost-saving strategies to stay within budget.
-
Collaboration: Work closely with other teams, such as development, DevOps, and security teams, to ensure that cloud infrastructure supports application requirements and security standards.
-
Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of cloud infrastructure, configurations, and processes. This documentation is crucial for knowledge sharing and troubleshooting.
-
Compliance: Ensure that cloud resources and configurations adhere to industry regulations and company policies, implementing necessary controls to meet compliance requirements.
-
Upgrades and Maintenance: Regularly apply updates, patches, and system upgrades to keep cloud infrastructure secure and up-to-date.
-
Problem Resolution: Troubleshoot and resolve issues related to cloud infrastructure and services, working to minimize downtime and impact on operations.
-
Education and Training: Stay current with cloud technology trends and provide training and guidance to team members and other stakeholders.
-
Innovation: Explore and implement new cloud services and technologies to drive innovation and improve infrastructure efficiency.
In summary, Cloud Engineers play a critical role in designing, deploying, and maintaining cloud infrastructure that supports an organization's IT needs. They are responsible for ensuring the security, performance, and cost-effectiveness of cloud environments while collaborating with various teams to deliver efficient and reliable cloud solutions.
Companies That Hire Cloud Engineers
Cloud Engineers are in high demand across various industries as organizations increasingly rely on cloud computing for their IT infrastructure. Many companies, ranging from tech giants to startups and enterprises, hire Cloud Engineers to design, implement, and manage their cloud environments. Here are some notable companies that commonly hire Cloud Engineers:
-
Amazon Web Services (AWS): As a leading cloud service provider, AWS often hires Cloud Engineers to work on their own cloud infrastructure and to support AWS customers in optimizing their cloud environments.
-
Microsoft: Microsoft Azure is another major cloud platform, and the company hires Cloud Engineers to develop and manage Azure-based solutions.
-
Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Google Cloud offers various cloud services, and they hire Cloud Engineers to work on GCP infrastructure and assist customers in building cloud-native applications.
-
IBM: IBM Cloud provides cloud computing solutions, and they hire Cloud Engineers to work on their cloud platform and offer cloud consulting services.
-
Oracle: Oracle Cloud is a growing cloud provider, and they hire Cloud Engineers to help customers migrate to and manage their cloud services.
-
Salesforce: Salesforce offers cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) solutions and often hires Cloud Engineers to work on their cloud infrastructure and applications.
-
Cisco: Cisco provides cloud networking and infrastructure solutions and hires Cloud Engineers to work on cloud-based networking and security technologies.
-
Netflix: As a popular streaming service, Netflix relies heavily on cloud computing and hires Cloud Engineers to manage its cloud infrastructure and improve streaming capabilities.
-
Uber: Uber utilizes cloud computing for its ride-sharing platform and hires Cloud Engineers to manage and optimize its cloud resources.
-
Airbnb: Airbnb relies on cloud services for its accommodation platform, and Cloud Engineers are responsible for ensuring the reliability and scalability of their cloud infrastructure.
-
Tesla: Tesla uses cloud computing for various purposes, including over-the-air updates and autonomous driving, and hires Cloud Engineers to support these initiatives.
-
SpaceX: SpaceX leverages cloud technology for its space missions, and Cloud Engineers play a crucial role in managing cloud resources for data analysis and mission control.
-
Startups: Many startups across industries rely on cloud technology to scale their businesses quickly, and they often hire Cloud Engineers to build and manage their cloud-based applications and infrastructure.
-
Consulting Firms: Consulting firms like Deloitte, Accenture, and Capgemini offer cloud consulting services and hire Cloud Engineers to work on a wide range of client projects.
-
Financial Institutions: Banks and financial organizations are increasingly moving to the cloud, and they hire Cloud Engineers to ensure the security and compliance of their cloud-based systems.
These are just a few examples, and the demand for Cloud Engineers continues to grow as more companies adopt cloud computing solutions to improve agility, scalability, and cost-efficiency in their IT operations. Keep in mind that the specific skills and qualifications required may vary depending on the company and the nature of the job.
Cloud Engineer Salaries for Freshers and Experienced Professionals
The salary of a Cloud Engineer can vary significantly based on several factors, including location, level of experience, the specific company, and the demand for cloud skills in the job market. Here is a rough overview of the salary ranges for Cloud Engineers at different career stages:
1. Freshers/Entry-Level Cloud Engineers:
-
In the United States, entry-level Cloud Engineers can expect an annual salary in the range of $60,000 to $90,000 on average.
-
In other countries, the salaries for entry-level Cloud Engineers may vary widely, but they often align with the cost of living in the respective region.
2. Mid-Level Cloud Engineers (2-5 years of experience):
-
Mid-level Cloud Engineers typically earn more than entry-level professionals. In the United States, their salaries can range from $90,000 to $130,000 or more per year.
-
Salaries for mid-level Cloud Engineers in other countries will depend on local market conditions and demand for cloud skills.
3. Experienced Cloud Engineers (5+ years of experience):
-
Experienced Cloud Engineers with five or more years of experience can command higher salaries. In the United States, they can earn anywhere from $120,000 to $180,000 or even higher annually.
-
Salaries for experienced Cloud Engineers in other countries will also depend on factors like location and the specific industry.
4. Senior Cloud Engineers and Cloud Architects:
-
Senior Cloud Engineers and Cloud Architects, who have extensive experience and often hold advanced certifications, can earn significantly higher salaries. In the United States, their salaries can range from $150,000 to $250,000 or more per year.
It's important to note that the figures mentioned above are approximate averages and can vary considerably based on regional cost of living, the organization's size and industry, and the engineer's level of expertise and certifications. Additionally, professionals with specialized skills in specific cloud platforms (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP) or emerging technologies may command higher salaries.
Certifications, such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert, or Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect, can also positively impact a Cloud Engineer's earning potential, as they demonstrate expertise in a particular cloud platform.
As the demand for cloud skills continues to grow and the cloud computing industry evolves, salaries for Cloud Engineers are expected to remain competitive and may even increase over time. It's essential for individuals in this field to stay updated with the latest cloud technologies and certifications to maximize their career growth and earning potential.
FAQs
What is the average salary for a fresher or entry-level Cloud Engineer?
-
The average salary for a fresher or entry-level Cloud Engineer can vary by location and organization. However, it typically ranges from $60,000 to $90,000 per year in the United States.
2. Do Cloud Engineers with certifications earn higher salaries?
-
Yes, Cloud Engineers with certifications, such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect or Azure Administrator, often earn higher salaries as these certifications demonstrate expertise in specific cloud platforms.
3. What factors influence the salary of an experienced Cloud Engineer?
-
Several factors influence the salary of an experienced Cloud Engineer, including years of experience, geographic location, the organization's size, industry, and the engineer's specific skills and certifications.
4. Are Cloud Engineers in high demand in the job market?
-
Yes, Cloud Engineers are in high demand as organizations increasingly adopt cloud computing solutions. This high demand often leads to competitive salaries and job opportunities.
5. How can Cloud Engineers increase their earning potential?
-
Cloud Engineers can increase their earning potential by acquiring advanced certifications, gaining expertise in specific cloud platforms, staying updated with emerging cloud technologies, and pursuing leadership roles.
6. Are there regional variations in Cloud Engineer salaries?
-
Yes, Cloud Engineer salaries vary significantly by region due to differences in the cost of living and demand for cloud skills. Salaries in major tech hubs like San Francisco and New York tend to be higher than in other areas.
7. What are some of the most lucrative industries for Cloud Engineers?
-
Cloud Engineers can find lucrative opportunities in various industries, including technology, finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, as many organizations across sectors are migrating to the cloud.
8. Do Cloud Architects earn higher salaries than Cloud Engineers?
-
Yes, Cloud Architects, who design complex cloud solutions and architectures, often earn higher salaries than Cloud Engineers due to their specialized skills and responsibilities.
9. Is there a significant salary difference between AWS, Azure, and GCP Cloud Engineers?
-
Salary differences among AWS, Azure, and GCP Cloud Engineers can vary, but generally, the choice of cloud platform may have a moderate impact on salary. Other factors like skills and experience play a more significant role.
10. How can entry-level Cloud Engineers negotiate a competitive salary offer?
Entry-level Cloud Engineers can negotiate a competitive salary offer by researching industry salary benchmarks, highlighting their relevant skills and certifications, and effectively communicating their value to the employer during negotiations.
Choose The Right Cloud Computing Program
Choosing the right cloud computing program is a pivotal step in advancing your career in the ever-evolving world of technology. Start by clearly defining your objectives and assessing your current skill level. Research reputable training providers and examine their programs in terms of content, format, and flexibility. Ensure that the curriculum covers essential cloud computing concepts and aligns with any specific certifications you may be targeting. Look for programs that offer practical, hands-on experience and access to knowledgeable instructors who can provide guidance. Additionally, consider the program's cost, financial aid options, and its alumni success rate in securing cloud-related positions. Seeking recommendations and reading reviews can provide valuable insights to aid in your decision-making process. Ultimately, the right cloud computing program will empower you with the skills and knowledge needed to thrive in this dynamic field.
Remember that cloud computing is a technology domain that evolves rapidly. Therefore, choosing a program that not only imparts fundamental knowledge but also keeps pace with industry trends and updates is essential for staying competitive in the job market. The right program should provide a solid foundation, hands-on experience, and the flexibility to accommodate your learning style and schedule, all while aligning with your career aspirations in cloud computing.
How to obtain Cloud Technology Certifications?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: EXIN Cloud Computing Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Robotic Process Automation
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of cloud computing offers promising career opportunities for both freshers and experienced professionals, with salaries that reflect the increasing demand for cloud expertise. For newcomers to the field, the potential for growth is evident as entry-level salaries provide a solid foundation for a rewarding career in cloud engineering. As one gains experience and expertise, the earning potential expands, with mid-level and experienced Cloud Engineers commanding competitive salaries.
However, it's important to recognize that salary figures can vary widely based on factors such as location, certification, industry, and specific skills. Therefore, continuous learning, staying updated with the latest cloud technologies, and investing in certifications are crucial steps to maximize earning potential. Whether you're at the beginning of your cloud engineering journey or an experienced professional seeking to further your career, the cloud computing landscape offers ample opportunities for growth and financial rewards, making it an exciting and lucrative field to explore.
Career Advancement with Top Network Security Certifications
In today's digitally interconnected world, where data breaches and cyber threats have become increasingly prevalent, the demand for skilled network security professionals has never been higher. If you're looking to establish or advance your career in the field of network security, you'll find that acquiring relevant certifications is not just a valuable asset but often a necessity. These certifications not only validate your expertise but also serve as a testament to your commitment to maintaining the integrity and security of critical digital infrastructure.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the realm of network security certifications, providing you with valuable insights into the top certifications that can propel your career to new heights. Whether you're an aspiring cybersecurity enthusiast, a seasoned professional looking to upskill, or simply someone intrigued by the dynamic world of network security, this exploration will shed light on the certifications that matter most, the skills they encompass, and how they can open doors to lucrative and fulfilling career opportunities. So, fasten your digital seatbelt as we embark on a journey through the realm of "Top Network Security Certifications for Career Advancement."
Table of Contents
-
What is Network Security?
-
Why is Network Security Needed?
-
What Are the Types of Network Security?
-
Which are the Best Network Security Certifications?
-
Conclusion
What is Network Security?
Network security is a critical aspect of modern computing and communications. It encompasses a wide range of measures and practices aimed at safeguarding the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data and resources within a computer network. In an era where digital information plays an increasingly pivotal role in businesses, governments, and personal lives, the importance of network security cannot be overstated. It involves a multifaceted approach, incorporating both technological solutions and human behaviors, to protect against an ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. Whether it's the protection of sensitive corporate data, the privacy of personal information, or the reliability of critical network services, network security serves as the frontline defense against malicious actors and potential disasters. It is a dynamic and continuously evolving field, driven by the need to stay one step ahead of those who seek to compromise the security and functionality of our interconnected world.
Why is Network Security Needed?
Network security is an indispensable element of our modern digital landscape for several compelling reasons. Firstly, it acts as a safeguard against data breaches, protecting valuable assets such as customer information, financial records, and intellectual property from unauthorized access and theft. In an era where data is a precious commodity, these protections are essential to mitigate the severe financial and reputational repercussions of a breach. Additionally, network security ensures the privacy of individuals and organizations, preventing the unauthorized interception of personal data and confidential business communications.
Secondly, network security is vital for business continuity. Cyberattacks, ranging from Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) assaults to ransomware, can disrupt essential services and operations, causing significant downtime and financial losses. Network security measures help maintain the availability of critical systems and services, ensuring uninterrupted business operations and mitigating potential financial harm. Furthermore, network security is a key component of regulatory compliance, as many industries and jurisdictions have strict rules governing data security and privacy. Adherence to these regulations is imperative to avoid legal penalties and protect the reputation of organizations. In summary, network security is an essential bulwark against data breaches, preserves privacy, ensures business continuity, supports regulatory compliance, and helps organizations withstand the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
What Are the Types of Network Security?
Network security encompasses various measures and strategies to safeguard computer networks from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. Here are the key types of network security:
-
Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet. They analyze incoming and outgoing traffic, based on predetermined security rules, to allow or block data packets.
-
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): IPSs monitor network and/or system activities for malicious exploits or security policy violations. They can identify and block suspicious traffic in real-time.
-
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDSs detect and alert on suspicious activities or patterns within a network. They provide notifications about potential security breaches, but they do not actively prevent them.
-
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs establish secure connections over the internet, allowing remote users or branch offices to access a private network securely. They use encryption protocols to ensure data confidentiality.
-
Access Control Lists (ACLs): ACLs are a set of rules defined on a network device (e.g., router, firewall) that dictate which types of traffic are allowed or denied based on factors like source, destination, and protocol.
-
Wireless Security: This includes measures like Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) and WPA2 protocols, which secure wireless networks from unauthorized access.
-
Network Segmentation: This involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the scope of a potential breach. Each segment may have its own security policies.
-
Anti-virus and Anti-malware Software: These programs detect, prevent, and remove malicious software (viruses, worms, Trojans, etc.) from devices and networks.
-
Email Security: This includes spam filters, antivirus scanning, and encryption to protect email communications from phishing attacks, malware, and other threats.
-
Web Security: Web security solutions filter and monitor web traffic, blocking access to malicious websites and scanning downloads for malware.
-
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM tools aggregate and analyze data from various network and security devices to detect and respond to security incidents.
-
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions monitor and control data transfers to prevent unauthorized access or sharing of sensitive information.
-
Security Policies and Procedures: Establishing and enforcing security policies, along with educating employees on security best practices, are crucial elements of network security.
-
Biometric Authentication: This includes fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and other biometric methods to ensure secure access to devices and networks.
-
Backup and Disaster Recovery: Regularly backing up data and having a robust disaster recovery plan in place helps mitigate the impact of data breaches or system failures.
Implementing a combination of these network security measures provides a layered defense against a wide range of cyber threats, helping to create a more resilient and secure network environment.
Which are the Best Network Security Certifications?
To unlock significant earning potential in the field of network security, a solid grasp of essential tools and skills is imperative. This is precisely where network security education assumes a pivotal role. Enrolling in network security certification courses not only equips you with the fundamental knowledge and skills required for these careers but also furnishes you with a valuable credential, serving as a tangible validation of your qualifications to prospective employers.
-
CEH: Certified Ethical Hacker
-
Also known as "white hat hacking," ethical hacking involves legally probing businesses to identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors do.
-
The CEH certification, offered by the EC-Council, validates your expertise in penetration testing, attack detection, vectors, and prevention.
-
Ethical hackers, or "white hat hackers," are hired to uncover system flaws and propose solutions, making this certification highly valuable in today's cybersecurity landscape.
-
CEH teaches you to think like a hacker, making it ideal for roles such as penetration testers, cyber incident analysts, threat intelligence analysts, and cloud security architects.
-
Requirements: Two years of information security job experience or completion of an authorized EC-Council program.
-
Cost: Varies between $950 and $1,199 depending on the testing location.
-
CISSP: Certified Information Systems Security Professional
-
CISSP, from (ISC)², is a prestigious certification for experienced security professionals responsible for developing and managing security processes, policies, and standards.
-
This certification is highly sought after in the industry, validating your expertise in IT security, cybersecurity program design, implementation, and monitoring.
-
CISSP is suitable for roles like Chief Information Security Officer, security administrators, IT security engineers, and senior security consultants.
-
Requirements: Five or more years of cumulative work experience in at least two of the eight cybersecurity domains or becoming an Associate of (ISC)² if you're new to cybersecurity.
-
Cost: $749
-
CISA: Certified Information Systems Auditor
-
CISA, offered by ISACA, is designed for information security professionals specializing in audit control, assurance, and security.
-
It equips you with the skills needed to manage IT, conduct comprehensive security audits, and identify vulnerabilities.
-
Valued in cybersecurity auditing, it's suitable for roles like IT audit managers, cybersecurity auditors, information security analysts, and IT security engineers.
-
Requirements: At least five years of experience in IT or IS audit, control, security, or assurance, with exceptions for degrees and certifications.
-
Cost: $575 for members, $760 for non-members.
-
CISM: Certified Information Security Manager
-
CISM, also from ISACA, focuses on the management aspects of information security, including governance, program creation, and risk management.
-
Ideal for transitioning from technical to managerial roles in cybersecurity.
-
Relevant for positions like IT managers, information risk consultants, directors of information security, and data governance managers.
-
Requirements: At least five years of information security management experience, with possible substitutions.
-
Cost: $575 for members, $760 for non-members.
-
CompTIA Security+
-
An entry-level certification covering essential cybersecurity skills.
-
Validates your ability to assess security, secure cloud and IoT environments, understand risk and compliance, and respond to security issues.
-
Suitable for roles like systems administrators, help desk managers, security engineers, and IT auditors.
-
Requirements: Recommended to have CompTIA Network+ and two years of IT experience with a security focus.
-
Cost: $370.
-
GIAC Security Essentials (GSEC)
-
An entry-level certification for individuals with a background in information systems and networking.
-
Validates skills in active defense, network security, cryptography, incident response, and cloud security.
-
Relevant for roles like IT security managers, computer forensic analysts, penetration testers, and security administrators.
-
Requirements: No specific prerequisites, but IT experience is beneficial.
-
Cost: $2,499 (includes two practice tests).
-
SSCP: Systems Security Certified Practitioner
-
Focuses on designing, deploying, and maintaining secure IT infrastructures.
-
Suitable for roles like network security engineers, system administrators, and security analysts.
-
Requirements: One year of work experience in one of the testing areas or relevant degrees or certifications.
-
Cost: $249.
-
CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner (CASP+)
-
Covers advanced topics like enterprise security, risk analysis, and cryptographic approaches.
-
Relevant for positions such as security architects, security engineers, and IT project managers.
-
Requirements: CompTIA recommends ten years of IT experience with five years of hands-on security experience.
-
Cost: $466.
-
GIAC Certified Incident Handler (GCIH)
-
Focuses on identifying, responding to, and defending against cyberattacks.
-
Suitable for incident handlers, security analysts, and system administrators.
-
Requirements: No specific prerequisites, but familiarity with security principles and networking protocols is helpful.
-
Cost: $2,499 (includes two practice tests).
-
Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
-
A highly sought-after certification for penetration testers.
-
Requires compromising target devices using various exploitation techniques and providing detailed penetration test reports.
-
Relevant for roles like penetration testers, ethical hackers, and threat researchers.
-
Requirements: No formal prerequisites, but prior knowledge of networking and scripting is recommended.
-
Cost: $999 (includes training, lab access, and one test attempt).
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of cybersecurity is dynamic and ever-evolving, and staying ahead of the curve is essential in defending against the ever-present threats in the digital realm. The array of certifications available provides a roadmap for professionals at every stage of their cybersecurity journey.
Whether you're a newcomer looking to establish a foothold or a seasoned expert seeking to advance your career, these certifications offer a structured path to sharpen your skills, validate your knowledge, and enhance your professional prospects. From ethical hacking to security management, each certification serves a specific purpose and opens doors to various rewarding roles within the cybersecurity landscape.
In this rapidly changing field, continuous learning is paramount, and acquiring certifications is not just a one-time achievement but an ongoing commitment to excellence. Regardless of where you are in your career, investing in these certifications not only elevates your expertise but also fortifies your ability to protect organizations and individuals from the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Remember that the ideal certification depends on your career goals, interests, and experience level. Combining multiple certifications can create a well-rounded skill set, making you a valuable asset in the ever-expanding realm of cybersecurity. So, choose wisely, invest in your professional development, and stay committed to the pursuit of knowledge in the ever-important field of cybersecurity.
How to obtain Robotic Process Automation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
The company conducts both Instructor-led Classroom training workshops and Instructor-led Live Online Training sessions for learners from across the United States and around the world.
We also provide Corporate Training for enterprise workforce development.
Professional Certification Training:
Quality Management Training:
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt (LSSYB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (LSSBB) Certification Training Courses
Scrum Training:
- CSM (Certified ScrumMaster) Certification Training Courses
Agile Training:
- PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Professional) Certification Training Courses
DevOps Training:
- DevOps Certification Training Courses
Business Analysis Training by iCert Global:
- ECBA (Entry Certificate in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CCBA (Certificate of Capability in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional) Certification Training Courses
Cyber Security Training:
- Certified Ethical Hacker Training Courses
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional Training Courses
- Certified inrisk and Information Systems Control Training Courses
- Certified Information Security Manager Training Courses
- Certified Information Systems Auditor
Connect with us:
- Subscribe to our YouTube Channel
Visit us at https://www.icertglobal.com/ for more information about our professional certification training courses or Call Now! on +1(713)-518-1187 / +1(713)-287-1214 or e-mail us at info@icertglobal.com.
Please Contact Us for more information about our professional certification training courses to accelerate your career. Let us know your thoughts in the 'Comments' section below.
Read More
In today's digitally interconnected world, where data breaches and cyber threats have become increasingly prevalent, the demand for skilled network security professionals has never been higher. If you're looking to establish or advance your career in the field of network security, you'll find that acquiring relevant certifications is not just a valuable asset but often a necessity. These certifications not only validate your expertise but also serve as a testament to your commitment to maintaining the integrity and security of critical digital infrastructure.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the realm of network security certifications, providing you with valuable insights into the top certifications that can propel your career to new heights. Whether you're an aspiring cybersecurity enthusiast, a seasoned professional looking to upskill, or simply someone intrigued by the dynamic world of network security, this exploration will shed light on the certifications that matter most, the skills they encompass, and how they can open doors to lucrative and fulfilling career opportunities. So, fasten your digital seatbelt as we embark on a journey through the realm of "Top Network Security Certifications for Career Advancement."
Table of Contents
-
What is Network Security?
-
Why is Network Security Needed?
-
What Are the Types of Network Security?
-
Which are the Best Network Security Certifications?
-
Conclusion
What is Network Security?
Network security is a critical aspect of modern computing and communications. It encompasses a wide range of measures and practices aimed at safeguarding the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data and resources within a computer network. In an era where digital information plays an increasingly pivotal role in businesses, governments, and personal lives, the importance of network security cannot be overstated. It involves a multifaceted approach, incorporating both technological solutions and human behaviors, to protect against an ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. Whether it's the protection of sensitive corporate data, the privacy of personal information, or the reliability of critical network services, network security serves as the frontline defense against malicious actors and potential disasters. It is a dynamic and continuously evolving field, driven by the need to stay one step ahead of those who seek to compromise the security and functionality of our interconnected world.
Why is Network Security Needed?
Network security is an indispensable element of our modern digital landscape for several compelling reasons. Firstly, it acts as a safeguard against data breaches, protecting valuable assets such as customer information, financial records, and intellectual property from unauthorized access and theft. In an era where data is a precious commodity, these protections are essential to mitigate the severe financial and reputational repercussions of a breach. Additionally, network security ensures the privacy of individuals and organizations, preventing the unauthorized interception of personal data and confidential business communications.
Secondly, network security is vital for business continuity. Cyberattacks, ranging from Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) assaults to ransomware, can disrupt essential services and operations, causing significant downtime and financial losses. Network security measures help maintain the availability of critical systems and services, ensuring uninterrupted business operations and mitigating potential financial harm. Furthermore, network security is a key component of regulatory compliance, as many industries and jurisdictions have strict rules governing data security and privacy. Adherence to these regulations is imperative to avoid legal penalties and protect the reputation of organizations. In summary, network security is an essential bulwark against data breaches, preserves privacy, ensures business continuity, supports regulatory compliance, and helps organizations withstand the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
What Are the Types of Network Security?
Network security encompasses various measures and strategies to safeguard computer networks from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. Here are the key types of network security:
-
Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet. They analyze incoming and outgoing traffic, based on predetermined security rules, to allow or block data packets.
-
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): IPSs monitor network and/or system activities for malicious exploits or security policy violations. They can identify and block suspicious traffic in real-time.
-
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDSs detect and alert on suspicious activities or patterns within a network. They provide notifications about potential security breaches, but they do not actively prevent them.
-
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs establish secure connections over the internet, allowing remote users or branch offices to access a private network securely. They use encryption protocols to ensure data confidentiality.
-
Access Control Lists (ACLs): ACLs are a set of rules defined on a network device (e.g., router, firewall) that dictate which types of traffic are allowed or denied based on factors like source, destination, and protocol.
-
Wireless Security: This includes measures like Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) and WPA2 protocols, which secure wireless networks from unauthorized access.
-
Network Segmentation: This involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the scope of a potential breach. Each segment may have its own security policies.
-
Anti-virus and Anti-malware Software: These programs detect, prevent, and remove malicious software (viruses, worms, Trojans, etc.) from devices and networks.
-
Email Security: This includes spam filters, antivirus scanning, and encryption to protect email communications from phishing attacks, malware, and other threats.
-
Web Security: Web security solutions filter and monitor web traffic, blocking access to malicious websites and scanning downloads for malware.
-
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM tools aggregate and analyze data from various network and security devices to detect and respond to security incidents.
-
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions monitor and control data transfers to prevent unauthorized access or sharing of sensitive information.
-
Security Policies and Procedures: Establishing and enforcing security policies, along with educating employees on security best practices, are crucial elements of network security.
-
Biometric Authentication: This includes fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and other biometric methods to ensure secure access to devices and networks.
-
Backup and Disaster Recovery: Regularly backing up data and having a robust disaster recovery plan in place helps mitigate the impact of data breaches or system failures.
Implementing a combination of these network security measures provides a layered defense against a wide range of cyber threats, helping to create a more resilient and secure network environment.
Which are the Best Network Security Certifications?
To unlock significant earning potential in the field of network security, a solid grasp of essential tools and skills is imperative. This is precisely where network security education assumes a pivotal role. Enrolling in network security certification courses not only equips you with the fundamental knowledge and skills required for these careers but also furnishes you with a valuable credential, serving as a tangible validation of your qualifications to prospective employers.
-
CEH: Certified Ethical Hacker
-
Also known as "white hat hacking," ethical hacking involves legally probing businesses to identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors do.
-
The CEH certification, offered by the EC-Council, validates your expertise in penetration testing, attack detection, vectors, and prevention.
-
Ethical hackers, or "white hat hackers," are hired to uncover system flaws and propose solutions, making this certification highly valuable in today's cybersecurity landscape.
-
CEH teaches you to think like a hacker, making it ideal for roles such as penetration testers, cyber incident analysts, threat intelligence analysts, and cloud security architects.
-
Requirements: Two years of information security job experience or completion of an authorized EC-Council program.
-
Cost: Varies between $950 and $1,199 depending on the testing location.
-
-
CISSP: Certified Information Systems Security Professional
-
CISSP, from (ISC)², is a prestigious certification for experienced security professionals responsible for developing and managing security processes, policies, and standards.
-
This certification is highly sought after in the industry, validating your expertise in IT security, cybersecurity program design, implementation, and monitoring.
-
CISSP is suitable for roles like Chief Information Security Officer, security administrators, IT security engineers, and senior security consultants.
-
Requirements: Five or more years of cumulative work experience in at least two of the eight cybersecurity domains or becoming an Associate of (ISC)² if you're new to cybersecurity.
-
Cost: $749
-
-
CISA: Certified Information Systems Auditor
-
CISA, offered by ISACA, is designed for information security professionals specializing in audit control, assurance, and security.
-
It equips you with the skills needed to manage IT, conduct comprehensive security audits, and identify vulnerabilities.
-
Valued in cybersecurity auditing, it's suitable for roles like IT audit managers, cybersecurity auditors, information security analysts, and IT security engineers.
-
Requirements: At least five years of experience in IT or IS audit, control, security, or assurance, with exceptions for degrees and certifications.
-
Cost: $575 for members, $760 for non-members.
-
-
CISM: Certified Information Security Manager
-
CISM, also from ISACA, focuses on the management aspects of information security, including governance, program creation, and risk management.
-
Ideal for transitioning from technical to managerial roles in cybersecurity.
-
Relevant for positions like IT managers, information risk consultants, directors of information security, and data governance managers.
-
Requirements: At least five years of information security management experience, with possible substitutions.
-
Cost: $575 for members, $760 for non-members.
-
-
CompTIA Security+
-
An entry-level certification covering essential cybersecurity skills.
-
Validates your ability to assess security, secure cloud and IoT environments, understand risk and compliance, and respond to security issues.
-
Suitable for roles like systems administrators, help desk managers, security engineers, and IT auditors.
-
Requirements: Recommended to have CompTIA Network+ and two years of IT experience with a security focus.
-
Cost: $370.
-
-
GIAC Security Essentials (GSEC)
-
An entry-level certification for individuals with a background in information systems and networking.
-
Validates skills in active defense, network security, cryptography, incident response, and cloud security.
-
Relevant for roles like IT security managers, computer forensic analysts, penetration testers, and security administrators.
-
Requirements: No specific prerequisites, but IT experience is beneficial.
-
Cost: $2,499 (includes two practice tests).
-
-
SSCP: Systems Security Certified Practitioner
-
Focuses on designing, deploying, and maintaining secure IT infrastructures.
-
Suitable for roles like network security engineers, system administrators, and security analysts.
-
Requirements: One year of work experience in one of the testing areas or relevant degrees or certifications.
-
Cost: $249.
-
-
CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner (CASP+)
-
Covers advanced topics like enterprise security, risk analysis, and cryptographic approaches.
-
Relevant for positions such as security architects, security engineers, and IT project managers.
-
Requirements: CompTIA recommends ten years of IT experience with five years of hands-on security experience.
-
Cost: $466.
-
-
GIAC Certified Incident Handler (GCIH)
-
Focuses on identifying, responding to, and defending against cyberattacks.
-
Suitable for incident handlers, security analysts, and system administrators.
-
Requirements: No specific prerequisites, but familiarity with security principles and networking protocols is helpful.
-
Cost: $2,499 (includes two practice tests).
-
-
Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
-
A highly sought-after certification for penetration testers.
-
Requires compromising target devices using various exploitation techniques and providing detailed penetration test reports.
-
Relevant for roles like penetration testers, ethical hackers, and threat researchers.
-
Requirements: No formal prerequisites, but prior knowledge of networking and scripting is recommended.
-
Cost: $999 (includes training, lab access, and one test attempt).
-
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of cybersecurity is dynamic and ever-evolving, and staying ahead of the curve is essential in defending against the ever-present threats in the digital realm. The array of certifications available provides a roadmap for professionals at every stage of their cybersecurity journey.
Whether you're a newcomer looking to establish a foothold or a seasoned expert seeking to advance your career, these certifications offer a structured path to sharpen your skills, validate your knowledge, and enhance your professional prospects. From ethical hacking to security management, each certification serves a specific purpose and opens doors to various rewarding roles within the cybersecurity landscape.
In this rapidly changing field, continuous learning is paramount, and acquiring certifications is not just a one-time achievement but an ongoing commitment to excellence. Regardless of where you are in your career, investing in these certifications not only elevates your expertise but also fortifies your ability to protect organizations and individuals from the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Remember that the ideal certification depends on your career goals, interests, and experience level. Combining multiple certifications can create a well-rounded skill set, making you a valuable asset in the ever-expanding realm of cybersecurity. So, choose wisely, invest in your professional development, and stay committed to the pursuit of knowledge in the ever-important field of cybersecurity.
How to obtain Robotic Process Automation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
The company conducts both Instructor-led Classroom training workshops and Instructor-led Live Online Training sessions for learners from across the United States and around the world.
We also provide Corporate Training for enterprise workforce development.
Professional Certification Training:
Quality Management Training:
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt (LSSYB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt (LSSGB) Certification Training Courses
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (LSSBB) Certification Training Courses
Scrum Training:
- CSM (Certified ScrumMaster) Certification Training Courses
Agile Training:
- PMI-ACP (Agile Certified Professional) Certification Training Courses
DevOps Training:
- DevOps Certification Training Courses
Business Analysis Training by iCert Global:
- ECBA (Entry Certificate in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CCBA (Certificate of Capability in Business Analysis) Certification Training Courses
- CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional) Certification Training Courses
Cyber Security Training:
- Certified Ethical Hacker Training Courses
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional Training Courses
- Certified inrisk and Information Systems Control Training Courses
- Certified Information Security Manager Training Courses
- Certified Information Systems Auditor
Connect with us:
- Subscribe to our YouTube Channel
Visit us at https://www.icertglobal.com/ for more information about our professional certification training courses or Call Now! on +1(713)-518-1187 / +1(713)-287-1214 or e-mail us at info@icertglobal.com.
Please Contact Us for more information about our professional certification training courses to accelerate your career. Let us know your thoughts in the 'Comments' section below.
Digital Marketing Role in 2023:Key Responsibilities & Skills
Welcome to the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing in 2023! In today's fast-paced, technology-driven world, the role of digital marketing has become more pivotal than ever for businesses seeking to thrive in the online realm. As we delve into the "Digital Marketing Job Description: Responsibilities and Skills in 2023," we will explore the dynamic and multifaceted nature of this profession. In this digital era, where consumers are increasingly connected, informed, and discerning, the demands on digital marketers have grown exponentially. This comprehensive guide will not only outline the core responsibilities of a digital marketer but also shed light on the essential skills and competencies required to excel in this exciting and competitive field. Whether you are a seasoned marketing professional looking to adapt to the latest trends or someone aspiring to launch a career in digital marketing, this exploration will serve as your compass through the ever-changing digital marketing landscape of 2023. Join us on this journey to discover what it takes to succeed in the world of digital marketing and stay ahead of the curve in this dynamic and ever-evolving industry.
Table of Contents
-
Growth of Digital Marketing Jobs
-
The Role of a Digital Marketer
-
Digital Marketing Job Description (Sample)
-
Specialist Digital Marketing Skills
-
The Common Elements of a Digital Marketing Job Description
-
Conclusion
Growth of Digital Marketing Jobs
The growth of digital marketing jobs over the past decade has been nothing short of remarkable. As the world becomes increasingly connected and reliant on digital technologies, the demand for skilled professionals in this field has surged. Several key factors can be attributed to this growth
-
Digital Transformation: Businesses across various industries are undergoing digital transformation efforts to stay competitive and reach their target audiences effectively. This has led to an increased demand for digital marketing professionals who can navigate and leverage the digital landscape.
-
Shift in Consumer Behavior: Consumers are spending more time online, from shopping and socializing to seeking information. Companies are keen to capitalize on this trend by employing digital marketing strategies to connect with their target customers where they spend the most time.
-
Data-Driven Decision-Making: The availability of vast amounts of data and analytics tools has made it possible for companies to measure the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns with precision. Digital marketing professionals who can analyze and interpret data are in high demand to drive data-driven decision-making.
-
E-commerce Boom: The growth of e-commerce has been exponential, especially in the wake of global events like the COVID-19 pandemic. Digital marketing plays a critical role in helping e-commerce businesses reach wider audiences, optimize their websites, and drive sales.
-
Social Media Dominance: Social media platforms have become powerful marketing tools. Companies are hiring digital marketers to create and execute social media strategies that engage audiences, build brand awareness, and drive conversions.
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): As the competition for online visibility intensifies, SEO expertise is invaluable. Digital marketers skilled in SEO are sought after to improve a website's ranking on search engines like Google.
-
Content Marketing: High-quality content is essential for online success. Content marketing professionals are needed to create compelling, relevant content that resonates with audiences and drives traffic.
-
Specialization: The field of digital marketing has diversified, with various specializations such as email marketing, influencer marketing, and affiliate marketing. This specialization has opened up more career opportunities for professionals with specific expertise.
-
Remote Work: The digital nature of these jobs has made remote work more feasible, allowing companies to tap into a global talent pool and professionals to work from virtually anywhere.
In summary, the growth of digital marketing jobs can be attributed to the ever-increasing importance of digital channels in reaching and engaging with consumers. As businesses continue to invest in their online presence and marketing efforts, the demand for skilled digital marketing professionals is expected to remain robust in the years to come.
The Role of a Digital Marketer
The role of a digital marketer is dynamic, multifaceted, and central to the success of businesses in the digital age. Digital marketers are responsible for developing, implementing, and managing online marketing strategies to achieve various business objectives. Here are some key aspects of the role of a digital marketer:
-
Strategy Development: Digital marketers begin by creating comprehensive digital marketing strategies tailored to their organization's goals. This involves identifying target audiences, defining key performance indicators (KPIs), and selecting the most suitable digital channels and tactics.
-
Content Creation: Content is at the heart of digital marketing. Digital marketers often create a wide range of content, including blog posts, social media updates, videos, infographics, and more. They ensure that content is engaging, relevant, and aligned with the brand's messaging.
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Digital marketers optimize web content and websites to improve their visibility on search engines like Google. This involves keyword research, on-page optimization, and backlink building to drive organic traffic.
-
Social Media Management: Managing and growing a brand's presence on social media platforms is a critical aspect of the role. Digital marketers develop content calendars, engage with followers, run paid advertising campaigns, and track performance metrics.
-
Email Marketing: Email still stands as a potent marketing instrument. Digital marketers create and execute email campaigns to nurture leads, retain customers, and drive conversions. They also segment email lists for targeted messaging.
-
Paid Advertising: Digital marketers manage paid advertising campaigns on platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and LinkedIn Ads. They set budgets, create ad creatives, and continuously optimize campaigns to maximize ROI.
-
Analytics and Data Analysis: The foundation of digital marketing relies on data. Marketers use analytics tools to track website traffic, user behavior, and campaign performance. They analyze this data to make informed decisions and adjust strategies as needed.
-
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Improving the conversion rate of website visitors into customers or leads is a key responsibility. Digital marketers conduct A/B testing and implement changes to enhance the user experience and drive conversions.
-
Affiliate Marketing: Some digital marketers work on affiliate marketing programs, where they collaborate with affiliates to promote products or services in exchange for commissions.
-
Influencer Marketing: Digital marketers identify and partner with influencers or industry experts to promote their brand or products to a wider audience.
-
Online Reputation Management: Monitoring and managing the online reputation of a brand is crucial. Digital marketers address negative feedback and promote positive reviews and content.
-
Marketing Automation: Digital marketers often use marketing automation tools to streamline repetitive tasks, such as email sending, lead nurturing, and campaign tracking.
-
Compliance and Privacy: Staying informed about digital marketing regulations and ensuring compliance with data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) is essential.
-
Continuous Learning: Given the rapidly evolving nature of digital marketing, professionals in this role must stay updated on industry trends, emerging technologies, and best practices.
In conclusion, the role of a digital marketer is multifaceted and ever-evolving. Success in this field requires a combination of creativity, analytical skills, adaptability, and a deep understanding of digital tools and platforms. Digital marketers play a pivotal role in helping businesses connect with their target audiences, drive growth, and stay competitive in the digital landscape.
Digital Marketing Job Description (Sample)
Job Title: Digital Marketer
Job Description:
As a Digital Marketing Specialist you will be responsible for planning, executing, and optimizing our digital marketing campaigns across various online platforms. Your goal will be to enhance our online presence, engage with our target audience, and ultimately drive business growth.
Key Responsibilities:
-
Digital Strategy: Develop and implement comprehensive digital marketing strategies that align with company goals and objectives.
-
Content Creation: Create, edit, and curate compelling and relevant content for various digital channels, including blog posts, social media updates, emails, and more.
-
SEO Optimization: Conduct keyword research, optimize website content, and monitor and improve search engine rankings to increase organic traffic.
-
Social Media Management: Manage and grow our social media presence by creating content calendars, running paid campaigns, and engaging with our online community.
-
Email Marketing: Plan and execute email marketing campaigns, segment audiences, create engaging email content, and monitor campaign performance.
-
Paid Advertising: Manage paid advertising campaigns on platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and others to drive traffic, conversions, and ROI.
-
Analytics and Reporting: Monitor website analytics, user behavior, and campaign performance using tools like Google Analytics. Offer consistent reports and insights to steer decision-making.
-
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Identify opportunities to improve website conversion rates through A/B testing, user experience enhancements, and other strategies.
-
Affiliate Marketing: Collaborate with affiliates and partners to promote products or services and track affiliate performance.
-
Online Reputation Management: Monitor online reviews and comments, address negative feedback, and encourage positive reviews and brand mentions.
Qualifications:
-
A Bachelor's degree in Marketing, Digital Marketing, or a related field is required.
-
Demonstrated expertise in digital marketing, substantiated by a robust portfolio of successful campaigns.
-
Proficiency in utilizing digital marketing tools and platforms, such as Google Analytics, social media management tools, and email marketing software.
-
Profound knowledge of SEO best practices and strategies is essential.
-
Exceptional written and verbal communication skills are a must.
-
Capable of working autonomously and as part of a collaborative team.
-
Possesses an analytical mindset, enabling the interpretation of data and the formulation of data-driven decisions.
-
Certifications in digital marketing (e.g., Google Ads, HubSpot, or similar) are a plus.
Specialist Digital Marketing Skills
Specialist digital marketing skills are essential for professionals who want to excel in the field and stand out in an increasingly competitive landscape. Here are some specialized digital marketing skills that can make a significant difference in your career:
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
-
Technical SEO: Understanding and optimizing website structure, crawlability, and performance.
-
On-Page SEO: Mastering keyword research, optimization, and content quality.
-
Off-Page SEO: Building high-quality backlinks and managing link-building strategies.
-
Content Marketing:
-
Content Strategy: Creating content strategies that align with business goals.
-
Content Creation: Writing, editing, and producing various content types, such as blog posts, videos, infographics, and eBooks.
-
Content Promotion: Effective distribution and promotion of content across channels.
-
Social Media Marketing:
-
Social Media Advertising: Creating and managing paid ad campaigns on platforms like Facebook Ads, Instagram Ads, and LinkedIn Ads.
-
Community Management: Engaging with the audience, responding to comments, and managing brand reputation.
-
Social Media Analytics: Analyzing and interpreting social media data to refine strategies.
-
Email Marketing:
-
Email Automation: Designing and implementing automated email campaigns.
-
Segmentation: Creating targeted email lists for personalized messaging.
-
A/B Testing: Experimenting with subject lines, content, and CTAs to optimize email performance.
-
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising:
-
Google Ads: Overseeing and enhancing Google Ads campaigns.
-
Display Advertising: Creating and optimizing banner ads for display networks.
-
Remarketing: Implementing strategies to target previous website visitors.
-
Analytics and Data Analysis:
-
Google Analytics: Proficiency in using Google Analytics to track website performance and user behavior.
-
Data Interpretation: Analyzing data to derive actionable insights and make data-driven decisions.
-
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Optimizing websites and landing pages for improved conversion rates.
-
Marketing Automation:
-
Marketing Automation Platforms: Familiarity with tools like HubSpot, Marketo, or Salesforce for automated marketing workflows.
-
Lead Nurturing: Creating and managing lead nurturing campaigns to guide prospects through the sales funnel.
-
Affiliate Marketing:
-
Partner Outreach: Building and managing relationships with affiliate partners.
-
Program Management: Running affiliate marketing programs and tracking partner performance.
-
Influencer Marketing:
-
Influencer Selection: Identifying and partnering with influencers who align with the brand.
-
Campaign Management: Planning and executing influencer marketing campaigns.
-
E-commerce Optimization:
-
E-commerce SEO: Executing e-commerce website-focused SEO strategies.
-
Conversion Optimization: Enhancing product pages, checkout processes, and user experience to boost sales.
-
Mobile Marketing:
-
Mobile App Marketing: Promoting mobile apps through app stores and in-app advertising.
-
Mobile Website Optimization: Ensuring websites are mobile-friendly and load quickly on mobile devices.
-
Data Privacy and Compliance:
-
Comprehending and complying with data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
-
Ensuring marketing practices comply with legal requirements.
Remember that digital marketing is a dynamic field, and staying updated with the latest trends, tools, and techniques is crucial to maintaining and enhancing your specialist skills in the long term. Continual learning and adaptation are key to success in digital marketing.
The Common Elements of a Digital Marketing Job Description
Digital marketing job descriptions typically share common elements that help define the role, responsibilities, qualifications, and expectations for candidates. Here are the common elements you can find in a digital marketing job description:
-
Job Title: The job title, such as "Digital Marketing Specialist," "Digital Marketing Manager," or "Digital Marketing Coordinator," indicates the specific role within the digital marketing field.
-
Company Overview: A brief introduction to the hiring company, including its industry, mission, and values, sets the context for the role.
-
Job Location: Specifies where the position is based, which can be in a specific city, state, or country, or may indicate whether it's a remote position.
-
Job Summary/Objective: A concise statement outlining the primary purpose of the role and what the candidate is expected to achieve in the position.
-
Responsibilities/Duties: A detailed list of the day-to-day tasks and responsibilities expected of the candidate. This section often includes items such as content creation, SEO optimization, social media management, and email marketing.
-
Qualifications/Skills: Lists the education, experience, and skills required or preferred for the role. This section may include qualifications like a bachelor's degree in marketing, proficiency in specific tools or platforms, and soft skills like communication and teamwork.
-
Experience: Often divided into "required experience" and "preferred experience," this section outlines the level of experience the company is seeking in candidates.
-
Certifications: If specific certifications (e.g., Google Ads, HubSpot, Facebook Blueprint) are required or preferred, they are listed here.
-
Competencies: Describes the competencies or attributes the ideal candidate should possess, such as analytical skills, creativity, adaptability, and attention to detail.
-
Work Environment: Provides information about the work environment, team size, and any unique aspects of the workplace.
-
Salary and Benefits: In some job descriptions, you may find information about the salary range or compensation package offered, as well as details about benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and bonuses.
-
How to Apply: Instructions on how candidates should apply, which often include submitting a resume, cover letter, and portfolio, and providing contact details for application submission.
-
Application Deadline: If there's a specific deadline for applications, it's mentioned here.
-
Equal Opportunity Statement: Many job descriptions include a statement about the company's commitment to diversity and equal opportunity employment.
-
Contact Information: Provides contact details for inquiries or questions related to the job posting.
-
Company Culture: Some job descriptions may include information about the company's culture, values, or mission to help candidates understand the work environment and ethos.
These common elements help candidates understand the role, evaluate their qualifications, and prepare their applications accordingly. Employers use them to communicate their expectations clearly and attract candidates who are the best fit for the position and the company.
How to obtain Robotic Process Automation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Robotic Process Automation
Conclusion
The landscape of digital marketing in 2023 is more dynamic and critical than ever before. As this guide has illuminated, the responsibilities and skills required of digital marketers have evolved to meet the demands of a rapidly changing digital ecosystem. In a world where businesses are vying for online visibility and customer engagement, digital marketers play a pivotal role in shaping strategies that drive success. Whether it's mastering the intricacies of SEO, creating compelling content, or leveraging emerging technologies, the digital marketer of 2023 must be adaptable, data-savvy, and customer-centric. As we navigate this ever-shifting terrain, it becomes clear that digital marketing is not just a profession; it's an art and science, and those who embrace its challenges and opportunities will continue to be at the forefront of the digital revolution. So, whether you're a seasoned professional or just beginning your journey in this field, the world of digital marketing in 2023 is ripe with possibilities for those who are willing to learn, adapt, and innovate.
Read More
Welcome to the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing in 2023! In today's fast-paced, technology-driven world, the role of digital marketing has become more pivotal than ever for businesses seeking to thrive in the online realm. As we delve into the "Digital Marketing Job Description: Responsibilities and Skills in 2023," we will explore the dynamic and multifaceted nature of this profession. In this digital era, where consumers are increasingly connected, informed, and discerning, the demands on digital marketers have grown exponentially. This comprehensive guide will not only outline the core responsibilities of a digital marketer but also shed light on the essential skills and competencies required to excel in this exciting and competitive field. Whether you are a seasoned marketing professional looking to adapt to the latest trends or someone aspiring to launch a career in digital marketing, this exploration will serve as your compass through the ever-changing digital marketing landscape of 2023. Join us on this journey to discover what it takes to succeed in the world of digital marketing and stay ahead of the curve in this dynamic and ever-evolving industry.
Table of Contents
-
Growth of Digital Marketing Jobs
-
The Role of a Digital Marketer
-
Digital Marketing Job Description (Sample)
-
Specialist Digital Marketing Skills
-
The Common Elements of a Digital Marketing Job Description
-
Conclusion
Growth of Digital Marketing Jobs
The growth of digital marketing jobs over the past decade has been nothing short of remarkable. As the world becomes increasingly connected and reliant on digital technologies, the demand for skilled professionals in this field has surged. Several key factors can be attributed to this growth
-
Digital Transformation: Businesses across various industries are undergoing digital transformation efforts to stay competitive and reach their target audiences effectively. This has led to an increased demand for digital marketing professionals who can navigate and leverage the digital landscape.
-
Shift in Consumer Behavior: Consumers are spending more time online, from shopping and socializing to seeking information. Companies are keen to capitalize on this trend by employing digital marketing strategies to connect with their target customers where they spend the most time.
-
Data-Driven Decision-Making: The availability of vast amounts of data and analytics tools has made it possible for companies to measure the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns with precision. Digital marketing professionals who can analyze and interpret data are in high demand to drive data-driven decision-making.
-
E-commerce Boom: The growth of e-commerce has been exponential, especially in the wake of global events like the COVID-19 pandemic. Digital marketing plays a critical role in helping e-commerce businesses reach wider audiences, optimize their websites, and drive sales.
-
Social Media Dominance: Social media platforms have become powerful marketing tools. Companies are hiring digital marketers to create and execute social media strategies that engage audiences, build brand awareness, and drive conversions.
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): As the competition for online visibility intensifies, SEO expertise is invaluable. Digital marketers skilled in SEO are sought after to improve a website's ranking on search engines like Google.
-
Content Marketing: High-quality content is essential for online success. Content marketing professionals are needed to create compelling, relevant content that resonates with audiences and drives traffic.
-
Specialization: The field of digital marketing has diversified, with various specializations such as email marketing, influencer marketing, and affiliate marketing. This specialization has opened up more career opportunities for professionals with specific expertise.
-
Remote Work: The digital nature of these jobs has made remote work more feasible, allowing companies to tap into a global talent pool and professionals to work from virtually anywhere.
In summary, the growth of digital marketing jobs can be attributed to the ever-increasing importance of digital channels in reaching and engaging with consumers. As businesses continue to invest in their online presence and marketing efforts, the demand for skilled digital marketing professionals is expected to remain robust in the years to come.
The Role of a Digital Marketer
The role of a digital marketer is dynamic, multifaceted, and central to the success of businesses in the digital age. Digital marketers are responsible for developing, implementing, and managing online marketing strategies to achieve various business objectives. Here are some key aspects of the role of a digital marketer:
-
Strategy Development: Digital marketers begin by creating comprehensive digital marketing strategies tailored to their organization's goals. This involves identifying target audiences, defining key performance indicators (KPIs), and selecting the most suitable digital channels and tactics.
-
Content Creation: Content is at the heart of digital marketing. Digital marketers often create a wide range of content, including blog posts, social media updates, videos, infographics, and more. They ensure that content is engaging, relevant, and aligned with the brand's messaging.
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Digital marketers optimize web content and websites to improve their visibility on search engines like Google. This involves keyword research, on-page optimization, and backlink building to drive organic traffic.
-
Social Media Management: Managing and growing a brand's presence on social media platforms is a critical aspect of the role. Digital marketers develop content calendars, engage with followers, run paid advertising campaigns, and track performance metrics.
-
Email Marketing: Email still stands as a potent marketing instrument. Digital marketers create and execute email campaigns to nurture leads, retain customers, and drive conversions. They also segment email lists for targeted messaging.
-
Paid Advertising: Digital marketers manage paid advertising campaigns on platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and LinkedIn Ads. They set budgets, create ad creatives, and continuously optimize campaigns to maximize ROI.
-
Analytics and Data Analysis: The foundation of digital marketing relies on data. Marketers use analytics tools to track website traffic, user behavior, and campaign performance. They analyze this data to make informed decisions and adjust strategies as needed.
-
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Improving the conversion rate of website visitors into customers or leads is a key responsibility. Digital marketers conduct A/B testing and implement changes to enhance the user experience and drive conversions.
-
Affiliate Marketing: Some digital marketers work on affiliate marketing programs, where they collaborate with affiliates to promote products or services in exchange for commissions.
-
Influencer Marketing: Digital marketers identify and partner with influencers or industry experts to promote their brand or products to a wider audience.
-
Online Reputation Management: Monitoring and managing the online reputation of a brand is crucial. Digital marketers address negative feedback and promote positive reviews and content.
-
Marketing Automation: Digital marketers often use marketing automation tools to streamline repetitive tasks, such as email sending, lead nurturing, and campaign tracking.
-
Compliance and Privacy: Staying informed about digital marketing regulations and ensuring compliance with data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) is essential.
-
Continuous Learning: Given the rapidly evolving nature of digital marketing, professionals in this role must stay updated on industry trends, emerging technologies, and best practices.
In conclusion, the role of a digital marketer is multifaceted and ever-evolving. Success in this field requires a combination of creativity, analytical skills, adaptability, and a deep understanding of digital tools and platforms. Digital marketers play a pivotal role in helping businesses connect with their target audiences, drive growth, and stay competitive in the digital landscape.
Digital Marketing Job Description (Sample)
Job Title: Digital Marketer
Job Description:
As a Digital Marketing Specialist you will be responsible for planning, executing, and optimizing our digital marketing campaigns across various online platforms. Your goal will be to enhance our online presence, engage with our target audience, and ultimately drive business growth.
Key Responsibilities:
-
Digital Strategy: Develop and implement comprehensive digital marketing strategies that align with company goals and objectives.
-
Content Creation: Create, edit, and curate compelling and relevant content for various digital channels, including blog posts, social media updates, emails, and more.
-
SEO Optimization: Conduct keyword research, optimize website content, and monitor and improve search engine rankings to increase organic traffic.
-
Social Media Management: Manage and grow our social media presence by creating content calendars, running paid campaigns, and engaging with our online community.
-
Email Marketing: Plan and execute email marketing campaigns, segment audiences, create engaging email content, and monitor campaign performance.
-
Paid Advertising: Manage paid advertising campaigns on platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and others to drive traffic, conversions, and ROI.
-
Analytics and Reporting: Monitor website analytics, user behavior, and campaign performance using tools like Google Analytics. Offer consistent reports and insights to steer decision-making.
-
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Identify opportunities to improve website conversion rates through A/B testing, user experience enhancements, and other strategies.
-
Affiliate Marketing: Collaborate with affiliates and partners to promote products or services and track affiliate performance.
-
Online Reputation Management: Monitor online reviews and comments, address negative feedback, and encourage positive reviews and brand mentions.
Qualifications:
-
A Bachelor's degree in Marketing, Digital Marketing, or a related field is required.
-
Demonstrated expertise in digital marketing, substantiated by a robust portfolio of successful campaigns.
-
Proficiency in utilizing digital marketing tools and platforms, such as Google Analytics, social media management tools, and email marketing software.
-
Profound knowledge of SEO best practices and strategies is essential.
-
Exceptional written and verbal communication skills are a must.
-
Capable of working autonomously and as part of a collaborative team.
-
Possesses an analytical mindset, enabling the interpretation of data and the formulation of data-driven decisions.
-
Certifications in digital marketing (e.g., Google Ads, HubSpot, or similar) are a plus.
Specialist Digital Marketing Skills
Specialist digital marketing skills are essential for professionals who want to excel in the field and stand out in an increasingly competitive landscape. Here are some specialized digital marketing skills that can make a significant difference in your career:
-
Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
-
Technical SEO: Understanding and optimizing website structure, crawlability, and performance.
-
On-Page SEO: Mastering keyword research, optimization, and content quality.
-
Off-Page SEO: Building high-quality backlinks and managing link-building strategies.
-
-
Content Marketing:
-
Content Strategy: Creating content strategies that align with business goals.
-
Content Creation: Writing, editing, and producing various content types, such as blog posts, videos, infographics, and eBooks.
-
Content Promotion: Effective distribution and promotion of content across channels.
-
-
Social Media Marketing:
-
Social Media Advertising: Creating and managing paid ad campaigns on platforms like Facebook Ads, Instagram Ads, and LinkedIn Ads.
-
Community Management: Engaging with the audience, responding to comments, and managing brand reputation.
-
Social Media Analytics: Analyzing and interpreting social media data to refine strategies.
-
-
Email Marketing:
-
Email Automation: Designing and implementing automated email campaigns.
-
Segmentation: Creating targeted email lists for personalized messaging.
-
A/B Testing: Experimenting with subject lines, content, and CTAs to optimize email performance.
-
-
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising:
-
Google Ads: Overseeing and enhancing Google Ads campaigns.
-
Display Advertising: Creating and optimizing banner ads for display networks.
-
Remarketing: Implementing strategies to target previous website visitors.
-
-
Analytics and Data Analysis:
-
Google Analytics: Proficiency in using Google Analytics to track website performance and user behavior.
-
Data Interpretation: Analyzing data to derive actionable insights and make data-driven decisions.
-
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Optimizing websites and landing pages for improved conversion rates.
-
-
Marketing Automation:
-
Marketing Automation Platforms: Familiarity with tools like HubSpot, Marketo, or Salesforce for automated marketing workflows.
-
Lead Nurturing: Creating and managing lead nurturing campaigns to guide prospects through the sales funnel.
-
-
Affiliate Marketing:
-
Partner Outreach: Building and managing relationships with affiliate partners.
-
Program Management: Running affiliate marketing programs and tracking partner performance.
-
-
Influencer Marketing:
-
Influencer Selection: Identifying and partnering with influencers who align with the brand.
-
Campaign Management: Planning and executing influencer marketing campaigns.
-
-
E-commerce Optimization:
-
E-commerce SEO: Executing e-commerce website-focused SEO strategies.
-
Conversion Optimization: Enhancing product pages, checkout processes, and user experience to boost sales.
-
-
Mobile Marketing:
-
Mobile App Marketing: Promoting mobile apps through app stores and in-app advertising.
-
Mobile Website Optimization: Ensuring websites are mobile-friendly and load quickly on mobile devices.
-
-
Data Privacy and Compliance:
-
Comprehending and complying with data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
-
Ensuring marketing practices comply with legal requirements.
Remember that digital marketing is a dynamic field, and staying updated with the latest trends, tools, and techniques is crucial to maintaining and enhancing your specialist skills in the long term. Continual learning and adaptation are key to success in digital marketing.
The Common Elements of a Digital Marketing Job Description
Digital marketing job descriptions typically share common elements that help define the role, responsibilities, qualifications, and expectations for candidates. Here are the common elements you can find in a digital marketing job description:
-
Job Title: The job title, such as "Digital Marketing Specialist," "Digital Marketing Manager," or "Digital Marketing Coordinator," indicates the specific role within the digital marketing field.
-
Company Overview: A brief introduction to the hiring company, including its industry, mission, and values, sets the context for the role.
-
Job Location: Specifies where the position is based, which can be in a specific city, state, or country, or may indicate whether it's a remote position.
-
Job Summary/Objective: A concise statement outlining the primary purpose of the role and what the candidate is expected to achieve in the position.
-
Responsibilities/Duties: A detailed list of the day-to-day tasks and responsibilities expected of the candidate. This section often includes items such as content creation, SEO optimization, social media management, and email marketing.
-
Qualifications/Skills: Lists the education, experience, and skills required or preferred for the role. This section may include qualifications like a bachelor's degree in marketing, proficiency in specific tools or platforms, and soft skills like communication and teamwork.
-
Experience: Often divided into "required experience" and "preferred experience," this section outlines the level of experience the company is seeking in candidates.
-
Certifications: If specific certifications (e.g., Google Ads, HubSpot, Facebook Blueprint) are required or preferred, they are listed here.
-
Competencies: Describes the competencies or attributes the ideal candidate should possess, such as analytical skills, creativity, adaptability, and attention to detail.
-
Work Environment: Provides information about the work environment, team size, and any unique aspects of the workplace.
-
Salary and Benefits: In some job descriptions, you may find information about the salary range or compensation package offered, as well as details about benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and bonuses.
-
How to Apply: Instructions on how candidates should apply, which often include submitting a resume, cover letter, and portfolio, and providing contact details for application submission.
-
Application Deadline: If there's a specific deadline for applications, it's mentioned here.
-
Equal Opportunity Statement: Many job descriptions include a statement about the company's commitment to diversity and equal opportunity employment.
-
Contact Information: Provides contact details for inquiries or questions related to the job posting.
-
Company Culture: Some job descriptions may include information about the company's culture, values, or mission to help candidates understand the work environment and ethos.
These common elements help candidates understand the role, evaluate their qualifications, and prepare their applications accordingly. Employers use them to communicate their expectations clearly and attract candidates who are the best fit for the position and the company.
How to obtain Robotic Process Automation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Robotic Process Automation
Conclusion
The landscape of digital marketing in 2023 is more dynamic and critical than ever before. As this guide has illuminated, the responsibilities and skills required of digital marketers have evolved to meet the demands of a rapidly changing digital ecosystem. In a world where businesses are vying for online visibility and customer engagement, digital marketers play a pivotal role in shaping strategies that drive success. Whether it's mastering the intricacies of SEO, creating compelling content, or leveraging emerging technologies, the digital marketer of 2023 must be adaptable, data-savvy, and customer-centric. As we navigate this ever-shifting terrain, it becomes clear that digital marketing is not just a profession; it's an art and science, and those who embrace its challenges and opportunities will continue to be at the forefront of the digital revolution. So, whether you're a seasoned professional or just beginning your journey in this field, the world of digital marketing in 2023 is ripe with possibilities for those who are willing to learn, adapt, and innovate.
Mastering RPA: Your Blueprint for Ultimate Success in 2023
In the rapidly evolving world of technology and automation, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping the way organizations operate and streamline their workflows. As we step into 2023, the demand for skilled RPA developers is at an all-time high, making it an opportune moment to embark on a journey of mastering this cutting-edge field. "Mastering RPA: Your Blueprint for Success in 2023" is your guide to navigating the intricate landscape of RPA, offering insights, strategies, and practical advice for those aspiring to become proficient RPA developers. This blueprint is not just about acquiring technical skills but also understanding the broader context of automation, soft skills, and the ever-changing trends that will define the RPA landscape this year and beyond. Whether you're a newcomer or a seasoned professional, this guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to thrive in the world of RPA and make a meaningful impact in the digital age.
Table of Contents
-
Introduction to RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
-
Choosing the Right RPA Tool
-
Programming Skills
-
RPA Certification
-
Advanced RPA Techniques
-
Best Practices in RPA Development
-
Soft Skills for RPA Developers
-
Networking and Community Involvement
-
Keeping Up with RPA Trends
-
Building a Career as an RPA Developer
-
Conclusion
Introduction to RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a transformative technology that employs software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks within organizations. These digital workers, though not physical robots, replicate human actions in interacting with software applications, aiming to streamline and optimize business processes. RPA offers unparalleled accuracy, scalability, and cost-efficiency, making it a crucial tool for various industries, from finance to healthcare. In 2023, as RPA's role in digital transformation grows, aspiring RPA developers have a promising career opportunity in harnessing this technology's potential for efficiency and innovation.
Choosing the Right RPA Tool
Selecting the appropriate Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tool is a critical decision on your path to becoming an RPA developer. In 2023, there is a plethora of RPA tools available, each with its unique strengths and capabilities. To make an informed choice, start by assessing your specific automation needs and objectives. Consider factors such as the complexity of tasks you want to automate, the compatibility of the tool with your existing systems, scalability requirements, and your budget. Popular RPA tools like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism offer robust features and strong developer communities, but it's essential to evaluate them in terms of ease of use, extensibility, and the support they provide for your chosen programming languages. Additionally, look for trial versions or free community editions to gain hands-on experience and ensure a seamless fit for your automation projects. Keep in mind that the right RPA tool can significantly impact your efficiency and success as an RPA developer in 2023 and beyond.
Programming Skills
Becoming a proficient RPA (Robotic Process Automation) developer in 2023 requires a solid foundation in programming. While RPA tools provide a user-friendly interface for automation, understanding programming concepts is essential for building complex and customized automation solutions. Here are some key programming skills you should focus on:
-
Scripting Languages: Mastery of scripting languages such as Python, JavaScript, or PowerShell is invaluable. Python, in particular, is widely used in RPA development due to its simplicity and versatility.
-
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): Understanding OOP principles is beneficial for creating reusable and well-structured code, especially when working with more advanced RPA projects.
-
Basic Algorithms and Data Structures: A grasp of fundamental algorithms and data structures like arrays, lists, and dictionaries is essential for efficiently manipulating data in your automation workflows.
-
Error Handling: Learn to handle exceptions and errors gracefully in your code, ensuring that your RPA bots can recover from unexpected issues during automation processes.
-
Debugging Skills: Proficiency in debugging tools and techniques is crucial for identifying and resolving issues in your automation scripts.
-
Regular Expressions: Regular expressions (regex) are essential for text manipulation and pattern matching, which are common tasks in RPA.
-
Version Control: Familiarize yourself with version control systems like Git to manage and track changes in your codebase, promoting collaboration and code stability.
-
API Integration: Understanding how to interact with APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) is essential for connecting RPA bots with external systems and services.
-
Database Basics: Knowledge of database concepts and SQL (Structured Query Language) can be valuable when working with data-driven automation processes.
-
Web Development Skills: Basic web development knowledge, including HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, can be beneficial for automating tasks involving web interfaces and browser interactions.
-
Security Awareness: Be aware of security best practices and potential vulnerabilities, especially when dealing with sensitive data or automation in secure environments.
-
Continual Learning: Stay updated with programming languages and frameworks relevant to RPA, as the field is continually evolving.
By honing these programming skills, you'll be better equipped to create efficient, reliable, and customized RPA solutions that address the specific automation needs of your organization or clients in 2023 and beyond.
RPA Certification
RPA certification is a pivotal career move in the thriving field of Robotic Process Automation, especially in 2023, as it validates your expertise with specific RPA tools like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, or Blue Prism. Earning such credentials not only enhances your job prospects and earning potential but also positions you as a credible RPA professional in high demand by organizations worldwide. With certification, you gain access to exclusive networks, stay updated on industry trends, and continually expand your skill set, making it an essential step for anyone looking to excel in the dynamic world of RPA.
Advanced RPA Techniques
As a burgeoning RPA (Robotic Process Automation) developer in 2023, advancing your skills beyond the basics is crucial for tackling complex automation challenges and delivering exceptional value to your organization. To excel in the field, delve into advanced RPA techniques:
-
Exception Handling: Master the art of handling exceptions and errors gracefully, enabling your bots to recover autonomously when unexpected situations arise during automation processes.
-
Integration with APIs: Go beyond basic automation by learning how to seamlessly integrate RPA bots with various application programming interfaces (APIs) to exchange data and execute actions across multiple systems.
-
Data Manipulation: Explore advanced data manipulation techniques, including complex data transformations, parsing unstructured data, and handling large datasets efficiently.
-
Orchestrator and Queue Management: Learn how to use RPA orchestrators effectively to manage bot execution, schedule tasks, and monitor automation workflows. Understand queue management for efficient task distribution.
-
Machine Learning and AI Integration: Combine RPA with machine learning and artificial intelligence to create intelligent automation solutions that can make data-driven decisions and adapt to changing conditions.
-
Citizen Developer Enablement: Develop strategies for involving non-technical stakeholders or citizen developers in the RPA development process while maintaining governance and control.
-
Advanced Debugging and Testing: Hone your debugging skills and implement robust testing practices to ensure the reliability and stability of your automation solutions.
-
Scalability and Performance Optimization: Discover techniques for scaling up your RPA deployments and optimizing bot performance, allowing your solutions to handle larger workloads efficiently.
-
Security Best Practices: Deepen your understanding of security considerations in RPA, including data encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry regulations.
-
Governance and Compliance: Establish governance frameworks to manage the lifecycle of automation projects, maintain documentation, and ensure compliance with organizational policies.
-
Continuous Learning: Stay at the forefront of RPA by keeping up with emerging trends, attending advanced training programs, and participating in RPA communities.
By embracing these advanced RPA techniques, you position yourself as a versatile and skilled developer capable of addressing complex automation scenarios and driving innovation within your organization. In 2023, as RPA continues to evolve, your mastery of these advanced skills will be invaluable in delivering efficiency and automation excellence.
Best Practices in RPA Development
In the dynamic landscape of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), adhering to best practices is essential for creating robust, maintainable, and efficient automation solutions. In 2023, as RPA adoption continues to surge, consider the following best practices for successful RPA development:
-
Requirements Analysis: Begin with a thorough understanding of the business process you aim to automate, involving stakeholders to define clear objectives and expected outcomes.
-
Modularity and Reusability: Design your RPA workflows in a modular fashion, promoting code reusability to save time and effort in future automation projects.
-
Error Handling: Implement comprehensive error handling mechanisms to gracefully manage exceptions, log errors, and ensure the reliability of your bots.
-
Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation for your automation projects, including process maps, code comments, and version histories, to facilitate collaboration and troubleshooting.
-
Testing and Validation: Rigorously test your automation workflows in a controlled environment to verify accuracy, and conduct user acceptance testing (UAT) to ensure alignment with business requirements.
-
Security Protocols: Prioritize security by encrypting sensitive data, adhering to access controls, and complying with industry-specific regulations to safeguard critical information.
-
Code Review: Collaborate with peers for code reviews to identify potential improvements, maintain code quality, and ensure adherence to coding standards.
-
Version Control: Employ version control systems like Git to manage changes, track revisions, and enable collaboration with team members.
-
Scalability: Design your RPA solutions with scalability in mind to accommodate increasing workloads and future process enhancements.
-
Monitoring and Analytics: Implement monitoring tools and analytics dashboards to gain insights into bot performance, detect anomalies, and identify areas for optimization.
-
Compliance and Governance: Establish governance frameworks that align with organizational policies, ensuring proper management and oversight of automation projects.
-
Training and Knowledge Sharing: Invest in continuous learning for your team and foster a culture of knowledge sharing to keep abreast of RPA advancements and best practices.
-
Change Management: Develop a change management strategy to prepare employees for the adoption of RPA and address any potential resistance to automation.
-
Robust Data Handling: Pay special attention to data input and output, validate data integrity, and handle data securely throughout the automation process.
-
Performance Optimization: Continually analyze and optimize your automation workflows to enhance efficiency and minimize resource consumption.
By incorporating these best practices into your RPA development process, you'll not only ensure the success of your automation initiatives but also contribute to the long-term growth and stability of your organization's RPA ecosystem in the dynamic landscape of 2023 and beyond.
Soft Skills for RPA Developers
In the ever-evolving world of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), technical prowess alone is not sufficient for success. As an RPA developer in 2023, honing soft skills is equally critical to navigate the complexities of human-machine collaboration and excel in this dynamic field. Here are the essential soft skills for RPA developers:
-
Communication Skills: Effective communication with both technical and non-technical stakeholders is vital for understanding automation requirements, explaining technical concepts, and ensuring alignment with business objectives.
-
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: Develop strong problem-solving and critical thinking abilities to identify automation opportunities, troubleshoot issues, and optimize RPA solutions.
-
Adaptability: Embrace change and adapt to evolving technologies, tools, and methodologies in the fast-paced RPA landscape, as well as to shifting business priorities.
-
Attention to Detail: Pay meticulous attention to detail when designing, coding, and testing RPA workflows to ensure accuracy and reliability in automated processes.
-
Time Management: Efficiently manage your time and prioritize tasks to meet project deadlines, especially when handling multiple automation projects simultaneously.
-
Collaboration: Foster collaboration within cross-functional teams, as RPA often requires cooperation between developers, business analysts, and end-users to achieve successful automation outcomes.
-
Empathy: Understand end-users' needs and concerns, empathize with their challenges, and design RPA solutions that enhance their work experience rather than replace it.
-
Customer-Centric Approach: Keep the customer's perspective at the forefront of RPA development, striving to deliver solutions that align with business goals and improve customer experiences.
-
Creativity and Innovation: Cultivate creativity to find innovative ways to automate processes and drive business efficiencies, going beyond the obvious solutions.
-
Resilience: Stay resilient in the face of setbacks or challenges during the development and implementation of RPA projects, persistently seeking solutions.
-
Leadership: Develop leadership skills to guide teams, mentor junior developers, and take ownership of complex RPA projects.
-
Ethical Considerations: Navigate ethical dilemmas that may arise when automating tasks and handling sensitive data, ensuring compliance with ethical guidelines and data protection regulations.
-
Cultural Awareness: Recognize and respect cultural differences, as RPA is deployed in organizations with diverse workforces and global reach.
-
Client-Facing Skills: If working in an RPA consulting role, strong client-facing skills are essential for understanding client needs, managing expectations, and building lasting client relationships.
-
Continuous Learning: Cultivate a growth mindset and commit to continuous learning, staying updated on RPA trends, emerging technologies, and best practices.
These soft skills complement your technical expertise, making you a well-rounded and effective RPA developer capable of collaborating seamlessly in human-machine partnerships and driving meaningful automation outcomes in 2023's dynamic RPA landscape.
Networking and Community Involvement
Networking and community involvement are essential for RPA developers in 2023, as they play a pivotal role in personal and professional growth within the dynamic realm of Robotic Process Automation. Engaging with online forums, professional associations, meetups, and conferences allows developers to connect with peers, stay abreast of industry trends, and share valuable insights. These interactions provide opportunities to discuss best practices, explore real-world use cases, and even collaborate on projects. Additionally, contributing to open-source RPA initiatives, blogging, or offering mentorship not only showcases expertise but also strengthens the RPA community. By actively participating in the RPA network, developers can cultivate a rich support system, access a wealth of knowledge, and establish themselves as respected figures in the field. This collaborative spirit not only fosters personal growth but also contributes to the advancement of RPA as a transformative technology.
Keeping Up with RPA Trends
In the fast-paced world of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), staying abreast of the latest trends is essential for RPA developers and professionals in 2023. As the technology continually evolves, here are some strategies to ensure you remain informed and adaptable:
-
Continuous Learning: Dedicate time to ongoing education through online courses, webinars, and workshops offered by RPA tool providers, industry organizations, and educational platforms. Through this, you have the opportunity to acquire new skills and knowledge.
-
Professional Networks: Engage with RPA-focused communities, forums, and LinkedIn groups where experts and enthusiasts share insights, news, and emerging trends. Actively participating in discussions can provide valuable insights.
-
Industry Publications: Regularly read RPA-related publications, blogs, and news outlets to stay updated on the latest developments, case studies, and best practices in the field.
-
RPA Vendor Updates: Subscribe to newsletters and updates from RPA tool vendors, as they often provide information about new features, product releases, and upcoming enhancements.
-
Conferences and Events: Attend RPA conferences, summits, and industry events where thought leaders and practitioners discuss cutting-edge trends, share success stories, and unveil future strategies.
-
Thought Leadership: Follow thought leaders and experts in the RPA space on social media platforms like Twitter and LinkedIn, where they often share insights, articles, and predictions about the future of RPA.
-
Experimentation: Stay hands-on by exploring new RPA tools, features, and functionalities through personal projects or within a controlled environment at work. Practical experience is a powerful learning tool.
-
Mentorship: Seek mentorship from seasoned RPA professionals who can provide guidance on emerging trends and offer career advice based on their experiences.
-
Market Research: Analyze market reports and research studies related to RPA to understand the broader industry landscape, market dynamics, and emerging use cases.
-
Cross-Training: Explore adjacent technologies and fields such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and process optimization, as these areas often intersect with RPA and can offer valuable insights.
-
Certifications: Consider pursuing advanced RPA certifications or specialization courses that focus on specific trends or industry niches within automation.
By diligently following these strategies, you can keep pace with the dynamic RPA trends of 2023 and position yourself as a knowledgeable and adaptable professional capable of driving innovation in the automation landscape.
Building a Career as an RPA Developer
Building a successful career as an RPA (Robotic Process Automation) developer in 2023 necessitates a deliberate approach. Start by mastering RPA fundamentals, including popular automation tools and programming languages, and consider formal education or relevant certifications to bolster your knowledge. Gain practical experience through hands-on projects, connect with industry professionals for networking opportunities, and invest in soft skills like communication and problem-solving. RPA certifications can validate your expertise, while continuous learning ensures you stay updated with the rapidly evolving field. Building a portfolio of your automation projects showcases your abilities to potential employers. Tailor your job search, prepare for interviews, and consider joining consulting firms for diverse experiences. As you progress, explore leadership roles and stay adaptable by embracing emerging technologies related to RPA. Contributing to the RPA community and keeping an eye on broader industry trends will help you thrive in this promising career path.
How to obtain Robotic Process Automation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Power BI Certification
-
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
-
Emerging Technologies : Robotic Process Automation
Conclusion
The world of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in 2023 offers abundant opportunities for those seeking to excel in automation technology. From mastering technical skills to cultivating soft skills and staying abreast of the latest trends, the journey of becoming an RPA developer is both challenging and rewarding. Embracing continuous learning, networking, and community involvement is key to thriving in this dynamic field. By following best practices, earning certifications, and building a portfolio of successful projects, you can establish yourself as a proficient RPA developer. Remember, adaptability and a commitment to ongoing growth are crucial in an ever-evolving industry. With dedication and a strategic approach, you can forge a successful career in RPA, contributing to the transformative impact of automation technology in organizations across various industries.
Read More
In the rapidly evolving world of technology and automation, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping the way organizations operate and streamline their workflows. As we step into 2023, the demand for skilled RPA developers is at an all-time high, making it an opportune moment to embark on a journey of mastering this cutting-edge field. "Mastering RPA: Your Blueprint for Success in 2023" is your guide to navigating the intricate landscape of RPA, offering insights, strategies, and practical advice for those aspiring to become proficient RPA developers. This blueprint is not just about acquiring technical skills but also understanding the broader context of automation, soft skills, and the ever-changing trends that will define the RPA landscape this year and beyond. Whether you're a newcomer or a seasoned professional, this guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to thrive in the world of RPA and make a meaningful impact in the digital age.
Table of Contents
-
Introduction to RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
-
Choosing the Right RPA Tool
-
Programming Skills
-
RPA Certification
-
Advanced RPA Techniques
-
Best Practices in RPA Development
-
Soft Skills for RPA Developers
-
Networking and Community Involvement
-
Keeping Up with RPA Trends
-
Building a Career as an RPA Developer
-
Conclusion
Introduction to RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a transformative technology that employs software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks within organizations. These digital workers, though not physical robots, replicate human actions in interacting with software applications, aiming to streamline and optimize business processes. RPA offers unparalleled accuracy, scalability, and cost-efficiency, making it a crucial tool for various industries, from finance to healthcare. In 2023, as RPA's role in digital transformation grows, aspiring RPA developers have a promising career opportunity in harnessing this technology's potential for efficiency and innovation.
Choosing the Right RPA Tool
Selecting the appropriate Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tool is a critical decision on your path to becoming an RPA developer. In 2023, there is a plethora of RPA tools available, each with its unique strengths and capabilities. To make an informed choice, start by assessing your specific automation needs and objectives. Consider factors such as the complexity of tasks you want to automate, the compatibility of the tool with your existing systems, scalability requirements, and your budget. Popular RPA tools like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism offer robust features and strong developer communities, but it's essential to evaluate them in terms of ease of use, extensibility, and the support they provide for your chosen programming languages. Additionally, look for trial versions or free community editions to gain hands-on experience and ensure a seamless fit for your automation projects. Keep in mind that the right RPA tool can significantly impact your efficiency and success as an RPA developer in 2023 and beyond.
Programming Skills
Becoming a proficient RPA (Robotic Process Automation) developer in 2023 requires a solid foundation in programming. While RPA tools provide a user-friendly interface for automation, understanding programming concepts is essential for building complex and customized automation solutions. Here are some key programming skills you should focus on:
-
Scripting Languages: Mastery of scripting languages such as Python, JavaScript, or PowerShell is invaluable. Python, in particular, is widely used in RPA development due to its simplicity and versatility.
-
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): Understanding OOP principles is beneficial for creating reusable and well-structured code, especially when working with more advanced RPA projects.
-
Basic Algorithms and Data Structures: A grasp of fundamental algorithms and data structures like arrays, lists, and dictionaries is essential for efficiently manipulating data in your automation workflows.
-
Error Handling: Learn to handle exceptions and errors gracefully in your code, ensuring that your RPA bots can recover from unexpected issues during automation processes.
-
Debugging Skills: Proficiency in debugging tools and techniques is crucial for identifying and resolving issues in your automation scripts.
-
Regular Expressions: Regular expressions (regex) are essential for text manipulation and pattern matching, which are common tasks in RPA.
-
Version Control: Familiarize yourself with version control systems like Git to manage and track changes in your codebase, promoting collaboration and code stability.
-
API Integration: Understanding how to interact with APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) is essential for connecting RPA bots with external systems and services.
-
Database Basics: Knowledge of database concepts and SQL (Structured Query Language) can be valuable when working with data-driven automation processes.
-
Web Development Skills: Basic web development knowledge, including HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, can be beneficial for automating tasks involving web interfaces and browser interactions.
-
Security Awareness: Be aware of security best practices and potential vulnerabilities, especially when dealing with sensitive data or automation in secure environments.
-
Continual Learning: Stay updated with programming languages and frameworks relevant to RPA, as the field is continually evolving.
By honing these programming skills, you'll be better equipped to create efficient, reliable, and customized RPA solutions that address the specific automation needs of your organization or clients in 2023 and beyond.
RPA Certification
RPA certification is a pivotal career move in the thriving field of Robotic Process Automation, especially in 2023, as it validates your expertise with specific RPA tools like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, or Blue Prism. Earning such credentials not only enhances your job prospects and earning potential but also positions you as a credible RPA professional in high demand by organizations worldwide. With certification, you gain access to exclusive networks, stay updated on industry trends, and continually expand your skill set, making it an essential step for anyone looking to excel in the dynamic world of RPA.
Advanced RPA Techniques
As a burgeoning RPA (Robotic Process Automation) developer in 2023, advancing your skills beyond the basics is crucial for tackling complex automation challenges and delivering exceptional value to your organization. To excel in the field, delve into advanced RPA techniques:
-
Exception Handling: Master the art of handling exceptions and errors gracefully, enabling your bots to recover autonomously when unexpected situations arise during automation processes.
-
Integration with APIs: Go beyond basic automation by learning how to seamlessly integrate RPA bots with various application programming interfaces (APIs) to exchange data and execute actions across multiple systems.
-
Data Manipulation: Explore advanced data manipulation techniques, including complex data transformations, parsing unstructured data, and handling large datasets efficiently.
-
Orchestrator and Queue Management: Learn how to use RPA orchestrators effectively to manage bot execution, schedule tasks, and monitor automation workflows. Understand queue management for efficient task distribution.
-
Machine Learning and AI Integration: Combine RPA with machine learning and artificial intelligence to create intelligent automation solutions that can make data-driven decisions and adapt to changing conditions.
-
Citizen Developer Enablement: Develop strategies for involving non-technical stakeholders or citizen developers in the RPA development process while maintaining governance and control.
-
Advanced Debugging and Testing: Hone your debugging skills and implement robust testing practices to ensure the reliability and stability of your automation solutions.
-
Scalability and Performance Optimization: Discover techniques for scaling up your RPA deployments and optimizing bot performance, allowing your solutions to handle larger workloads efficiently.
-
Security Best Practices: Deepen your understanding of security considerations in RPA, including data encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry regulations.
-
Governance and Compliance: Establish governance frameworks to manage the lifecycle of automation projects, maintain documentation, and ensure compliance with organizational policies.
-
Continuous Learning: Stay at the forefront of RPA by keeping up with emerging trends, attending advanced training programs, and participating in RPA communities.
By embracing these advanced RPA techniques, you position yourself as a versatile and skilled developer capable of addressing complex automation scenarios and driving innovation within your organization. In 2023, as RPA continues to evolve, your mastery of these advanced skills will be invaluable in delivering efficiency and automation excellence.
Best Practices in RPA Development
In the dynamic landscape of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), adhering to best practices is essential for creating robust, maintainable, and efficient automation solutions. In 2023, as RPA adoption continues to surge, consider the following best practices for successful RPA development:
-
Requirements Analysis: Begin with a thorough understanding of the business process you aim to automate, involving stakeholders to define clear objectives and expected outcomes.
-
Modularity and Reusability: Design your RPA workflows in a modular fashion, promoting code reusability to save time and effort in future automation projects.
-
Error Handling: Implement comprehensive error handling mechanisms to gracefully manage exceptions, log errors, and ensure the reliability of your bots.
-
Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation for your automation projects, including process maps, code comments, and version histories, to facilitate collaboration and troubleshooting.
-
Testing and Validation: Rigorously test your automation workflows in a controlled environment to verify accuracy, and conduct user acceptance testing (UAT) to ensure alignment with business requirements.
-
Security Protocols: Prioritize security by encrypting sensitive data, adhering to access controls, and complying with industry-specific regulations to safeguard critical information.
-
Code Review: Collaborate with peers for code reviews to identify potential improvements, maintain code quality, and ensure adherence to coding standards.
-
Version Control: Employ version control systems like Git to manage changes, track revisions, and enable collaboration with team members.
-
Scalability: Design your RPA solutions with scalability in mind to accommodate increasing workloads and future process enhancements.
-
Monitoring and Analytics: Implement monitoring tools and analytics dashboards to gain insights into bot performance, detect anomalies, and identify areas for optimization.
-
Compliance and Governance: Establish governance frameworks that align with organizational policies, ensuring proper management and oversight of automation projects.
-
Training and Knowledge Sharing: Invest in continuous learning for your team and foster a culture of knowledge sharing to keep abreast of RPA advancements and best practices.
-
Change Management: Develop a change management strategy to prepare employees for the adoption of RPA and address any potential resistance to automation.
-
Robust Data Handling: Pay special attention to data input and output, validate data integrity, and handle data securely throughout the automation process.
-
Performance Optimization: Continually analyze and optimize your automation workflows to enhance efficiency and minimize resource consumption.
By incorporating these best practices into your RPA development process, you'll not only ensure the success of your automation initiatives but also contribute to the long-term growth and stability of your organization's RPA ecosystem in the dynamic landscape of 2023 and beyond.
Soft Skills for RPA Developers
In the ever-evolving world of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), technical prowess alone is not sufficient for success. As an RPA developer in 2023, honing soft skills is equally critical to navigate the complexities of human-machine collaboration and excel in this dynamic field. Here are the essential soft skills for RPA developers:
-
Communication Skills: Effective communication with both technical and non-technical stakeholders is vital for understanding automation requirements, explaining technical concepts, and ensuring alignment with business objectives.
-
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: Develop strong problem-solving and critical thinking abilities to identify automation opportunities, troubleshoot issues, and optimize RPA solutions.
-
Adaptability: Embrace change and adapt to evolving technologies, tools, and methodologies in the fast-paced RPA landscape, as well as to shifting business priorities.
-
Attention to Detail: Pay meticulous attention to detail when designing, coding, and testing RPA workflows to ensure accuracy and reliability in automated processes.
-
Time Management: Efficiently manage your time and prioritize tasks to meet project deadlines, especially when handling multiple automation projects simultaneously.
-
Collaboration: Foster collaboration within cross-functional teams, as RPA often requires cooperation between developers, business analysts, and end-users to achieve successful automation outcomes.
-
Empathy: Understand end-users' needs and concerns, empathize with their challenges, and design RPA solutions that enhance their work experience rather than replace it.
-
Customer-Centric Approach: Keep the customer's perspective at the forefront of RPA development, striving to deliver solutions that align with business goals and improve customer experiences.
-
Creativity and Innovation: Cultivate creativity to find innovative ways to automate processes and drive business efficiencies, going beyond the obvious solutions.
-
Resilience: Stay resilient in the face of setbacks or challenges during the development and implementation of RPA projects, persistently seeking solutions.
-
Leadership: Develop leadership skills to guide teams, mentor junior developers, and take ownership of complex RPA projects.
-
Ethical Considerations: Navigate ethical dilemmas that may arise when automating tasks and handling sensitive data, ensuring compliance with ethical guidelines and data protection regulations.
-
Cultural Awareness: Recognize and respect cultural differences, as RPA is deployed in organizations with diverse workforces and global reach.
-
Client-Facing Skills: If working in an RPA consulting role, strong client-facing skills are essential for understanding client needs, managing expectations, and building lasting client relationships.
-
Continuous Learning: Cultivate a growth mindset and commit to continuous learning, staying updated on RPA trends, emerging technologies, and best practices.
These soft skills complement your technical expertise, making you a well-rounded and effective RPA developer capable of collaborating seamlessly in human-machine partnerships and driving meaningful automation outcomes in 2023's dynamic RPA landscape.
Networking and Community Involvement
Networking and community involvement are essential for RPA developers in 2023, as they play a pivotal role in personal and professional growth within the dynamic realm of Robotic Process Automation. Engaging with online forums, professional associations, meetups, and conferences allows developers to connect with peers, stay abreast of industry trends, and share valuable insights. These interactions provide opportunities to discuss best practices, explore real-world use cases, and even collaborate on projects. Additionally, contributing to open-source RPA initiatives, blogging, or offering mentorship not only showcases expertise but also strengthens the RPA community. By actively participating in the RPA network, developers can cultivate a rich support system, access a wealth of knowledge, and establish themselves as respected figures in the field. This collaborative spirit not only fosters personal growth but also contributes to the advancement of RPA as a transformative technology.
Keeping Up with RPA Trends
In the fast-paced world of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), staying abreast of the latest trends is essential for RPA developers and professionals in 2023. As the technology continually evolves, here are some strategies to ensure you remain informed and adaptable:
-
Continuous Learning: Dedicate time to ongoing education through online courses, webinars, and workshops offered by RPA tool providers, industry organizations, and educational platforms. Through this, you have the opportunity to acquire new skills and knowledge.
-
Professional Networks: Engage with RPA-focused communities, forums, and LinkedIn groups where experts and enthusiasts share insights, news, and emerging trends. Actively participating in discussions can provide valuable insights.
-
Industry Publications: Regularly read RPA-related publications, blogs, and news outlets to stay updated on the latest developments, case studies, and best practices in the field.
-
RPA Vendor Updates: Subscribe to newsletters and updates from RPA tool vendors, as they often provide information about new features, product releases, and upcoming enhancements.
-
Conferences and Events: Attend RPA conferences, summits, and industry events where thought leaders and practitioners discuss cutting-edge trends, share success stories, and unveil future strategies.
-
Thought Leadership: Follow thought leaders and experts in the RPA space on social media platforms like Twitter and LinkedIn, where they often share insights, articles, and predictions about the future of RPA.
-
Experimentation: Stay hands-on by exploring new RPA tools, features, and functionalities through personal projects or within a controlled environment at work. Practical experience is a powerful learning tool.
-
Mentorship: Seek mentorship from seasoned RPA professionals who can provide guidance on emerging trends and offer career advice based on their experiences.
-
Market Research: Analyze market reports and research studies related to RPA to understand the broader industry landscape, market dynamics, and emerging use cases.
-
Cross-Training: Explore adjacent technologies and fields such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and process optimization, as these areas often intersect with RPA and can offer valuable insights.
-
Certifications: Consider pursuing advanced RPA certifications or specialization courses that focus on specific trends or industry niches within automation.
By diligently following these strategies, you can keep pace with the dynamic RPA trends of 2023 and position yourself as a knowledgeable and adaptable professional capable of driving innovation in the automation landscape.
Building a Career as an RPA Developer
Building a successful career as an RPA (Robotic Process Automation) developer in 2023 necessitates a deliberate approach. Start by mastering RPA fundamentals, including popular automation tools and programming languages, and consider formal education or relevant certifications to bolster your knowledge. Gain practical experience through hands-on projects, connect with industry professionals for networking opportunities, and invest in soft skills like communication and problem-solving. RPA certifications can validate your expertise, while continuous learning ensures you stay updated with the rapidly evolving field. Building a portfolio of your automation projects showcases your abilities to potential employers. Tailor your job search, prepare for interviews, and consider joining consulting firms for diverse experiences. As you progress, explore leadership roles and stay adaptable by embracing emerging technologies related to RPA. Contributing to the RPA community and keeping an eye on broader industry trends will help you thrive in this promising career path.
How to obtain Robotic Process Automation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Power BI Certification
-
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
-
Emerging Technologies : Robotic Process Automation
Conclusion
The world of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in 2023 offers abundant opportunities for those seeking to excel in automation technology. From mastering technical skills to cultivating soft skills and staying abreast of the latest trends, the journey of becoming an RPA developer is both challenging and rewarding. Embracing continuous learning, networking, and community involvement is key to thriving in this dynamic field. By following best practices, earning certifications, and building a portfolio of successful projects, you can establish yourself as a proficient RPA developer. Remember, adaptability and a commitment to ongoing growth are crucial in an ever-evolving industry. With dedication and a strategic approach, you can forge a successful career in RPA, contributing to the transformative impact of automation technology in organizations across various industries.
Is DevOps the Right Career Path for You to Choose in 2023?
As we step into 2023, the tech industry is undergoing dynamic changes, and the question on the minds of many professionals is whether DevOps remains a viable and rewarding career choice. DevOps, which merges development and operations to enhance collaboration and streamline software delivery, has been a buzzword in modern tech circles, promising efficiency and innovation. In this exploration of "Navigating Your Career Path: Is DevOps the Right Choice in 2023?" we will assess the current DevOps landscape, the requisite skills, and the factors shaping its relevance in today's tech world, helping both newcomers and experienced practitioners make informed decisions about their career paths in this fast-paced industry.
Table of Contents
1. Rising Demand for DevOps Talent
2. DevOps Offers a Definite Career Path that Promises Steady Growth
3. Your Key Responsibility Areas (KRA) as DevOps Expert
4. Technical Skills Needed to Build a DevOps Career
5. Where Can You Start Your Journey in DevOps?
6. How Far Would You Like to Go in DevOps?
Get Started Today
Rising Demand for DevOps Talent
The "Rising Demand for DevOps Talent" is a compelling phenomenon in the technology industry, reflecting the growing need for professionals well-versed in DevOps practices. DevOps, short for Development and Operations, represents a set of principles and practices that emphasize collaboration and automation between software development and IT operations teams. This approach is designed to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and speed of software delivery. Here are some key insights into the increasing demand for DevOps talent:
-
Business Agility: In today's fast-paced digital landscape, businesses need to be agile and responsive to market changes. DevOps facilitates quicker software development, testing, and deployment, enabling organizations to adapt swiftly to evolving customer demands and market trends.
-
Automation: Automation is a central pillar of DevOps. By automating repetitive tasks, such as code testing and deployment, organizations can reduce manual errors, save time, and ensure consistent processes. DevOps professionals are responsible for implementing and maintaining these automation pipelines.
-
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): DevOps practices encourage the implementation of CI/CD pipelines. These pipelines automate the integration of code changes, testing, and deployment, leading to more frequent and reliable software releases. Experts in CI/CD are highly sought after to optimize these critical processes.
-
Cloud Computing: The widespread adoption of cloud platforms, such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, has further accelerated the demand for DevOps expertise. DevOps practices are essential for managing and optimizing cloud infrastructure and services effectively.
-
Security: Security is paramount in today's technology landscape. DevOps teams are increasingly integrating security practices into their workflows, giving rise to the DevSecOps approach. DevOps professionals with security expertise are in high demand to ensure that software is developed and deployed securely.
-
Cost Efficiency: DevOps can lead to cost savings by reducing downtime, optimizing resource usage, and streamlining development and deployment processes. Organizations are eager to hire DevOps professionals who can help them achieve these cost benefits.
-
Scalability: DevOps practices are essential for organizations experiencing growth or dealing with variable workloads. DevOps enables scalable infrastructure and supports the efficient management of resources.
-
Cultural Transformation: Beyond tools and processes, DevOps represents a cultural shift within organizations. It emphasizes collaboration, communication, and shared responsibility among development and operations teams. DevOps professionals play a vital role in fostering this cultural change.
DevOps Offers a Definite Career Path that Promises Steady Growth
DevOps is undeniably offering a well-defined career path with the assurance of steady growth. In recent years, it has evolved into a transformative field within the technology industry, creating a multitude of opportunities for professionals seeking a dynamic and promising career trajectory. The reasons behind this career's appeal are numerous and compelling.
First and foremost, the demand for DevOps professionals is soaring. Across various industries, companies are recognizing the significant value that DevOps practices bring to the table. These practices accelerate software development, enhance product quality, and optimize operational efficiency. This sustained demand ensures a consistent flow of job opportunities for those entering the DevOps arena, providing a sense of job security and stability.
One of the remarkable aspects of a DevOps career is its versatility. DevOps is not a one-size-fits-all discipline; it encompasses a broad spectrum of skills and practices. Professionals can specialize in areas such as automation, continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD), cloud computing, security (DevSecOps), or infrastructure as code (IaC). This versatility empowers individuals to tailor their career paths to align with their personal interests and strengths, offering a diverse array of potential avenues for growth.
Furthermore, DevOps places a strong emphasis on continuous learning and improvement. In a rapidly evolving technological landscape, staying up-to-date with the latest tools, technologies, and best practices is not just encouraged but essential. This commitment to lifelong learning ensures that DevOps practitioners remain relevant and marketable, making it possible to continuously advance in their careers.
A DevOps career is also financially rewarding. Due to the specialized skills and expertise required, DevOps roles often come with competitive salaries and attractive benefit packages. Professionals in this field can command higher compensation compared to more traditional IT roles, making it an appealing choice for those who seek both intellectual and financial gratification.
Moreover, DevOps professionals are well-positioned for cross-functional collaboration. DevOps practices encourage close cooperation between development and operations teams, providing opportunities to work with diverse stakeholders and gain exposure to different aspects of an organization's technology ecosystem. This interdisciplinary experience enhances their skill set and opens up various career possibilities.
Over time, many DevOps professionals transition into leadership roles. With their accumulated experience and expertise, they often find themselves overseeing DevOps teams, shaping an organization's DevOps strategy, and driving cultural and technical transformations within their workplaces. This pathway into leadership roles adds a layer of professional growth and leadership development to the DevOps career trajectory.
Furthermore, DevOps offers global opportunities. The demand for DevOps talent is not confined to specific geographic regions, allowing professionals in this field to explore remote work options or even international employment opportunities. This global perspective can enrich their career experiences and broaden their horizons.
Lastly, DevOps professionals find deep satisfaction in their work. They play a pivotal role in enabling organizations to deliver software more swiftly and with higher quality. This direct impact on an organization's ability to innovate, compete, and respond to customer needs can be intrinsically rewarding and fulfilling.
Your Key Responsibility Areas (KRA) as DevOps Expert
As a DevOps expert, your Key Responsibility Areas (KRAs) encompass a wide range of tasks and responsibilities that are vital for the successful implementation of DevOps practices and the efficient operation of software development and IT infrastructure. Here are some of the key areas you might be responsible for:
-
Infrastructure Automation:
-
Designing, building, and maintaining infrastructure as code (IaC) to automate the provisioning and management of servers, networks, and storage.
-
Implementing and managing configuration management tools (e.g., Ansible, Puppet, Chef) to ensure consistency and scalability in infrastructure.
-
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD):
-
Developing and maintaining CI/CD pipelines to automate the build, test, and deployment processes.
-
Ensuring that code changes are integrated, tested, and deployed efficiently, with a focus on quality and reliability.
-
Cloud Services:
-
Managing cloud infrastructure (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) and optimizing resource usage for scalability and cost-efficiency.
-
Implementing cloud-native DevOps practices and leveraging cloud services for application deployment and scaling.
-
Version Control:
-
Implementing and managing version control systems (e.g., Git) to track code changes, collaborate with development teams, and ensure code quality.
-
Monitoring and Logging:
-
Setting up monitoring and logging tools (e.g., Prometheus, ELK stack) to track system performance, identify issues, and troubleshoot problems proactively.
-
Creating dashboards and alerts to ensure real-time visibility into system health.
-
Security (DevSecOps):
-
Integrating security practices into the DevOps pipeline to identify and mitigate security vulnerabilities.
-
Collaborating with security teams to implement best practices for securing infrastructure and applications.
-
Collaboration and Communication:
-
Fostering a culture of collaboration between development and operations teams to ensure smooth workflows and alignment with business goals.
-
Facilitating communication and knowledge sharing among cross-functional teams.
-
Release Management:
-
Managing software releases, including versioning, deployment scheduling, and rollback procedures.
-
Coordinating release activities to minimize downtime and disruptions.
-
Performance Optimization:
-
Identifying and addressing performance bottlenecks in applications and infrastructure.
-
Implementing optimizations to enhance system speed and efficiency.
-
Disaster Recovery and Backup:
-
Developing and testing disaster recovery plans to ensure data integrity and system availability in case of unexpected failures.
-
Regularly backing up critical data and systems to prevent data loss.
-
Documentation and Training:
-
Maintaining detailed documentation of infrastructure, processes, and configurations.
-
Providing training and guidance to team members and stakeholders on DevOps practices and tools.
-
Tool Evaluation and Selection:
-
Assessing and selecting the most appropriate DevOps tools and technologies for the organization's needs.
-
Staying updated on emerging DevOps tools and trends to ensure the use of modern and effective solutions.
-
Continuous Improvement:
-
Continuously assessing and optimizing DevOps processes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
-
Conducting post-implementation reviews and retrospectives to identify areas for improvement.
-
Compliance and Governance:
-
Ensuring that infrastructure and processes comply with industry regulations and organizational governance policies.
-
Implementing controls and audits as needed.
-
Team Leadership and Mentoring (for senior roles):
-
Leading DevOps teams, setting strategic goals, and mentoring team members.
-
Overseeing project execution, resource allocation, and performance evaluations.
These KRAs represent the core responsibilities of a DevOps expert. The specific duties may vary depending on the organization's size, industry, and the maturity of its DevOps practices. DevOps professionals play a pivotal role in enabling organizations to deliver software more efficiently, reliably, and securely, making their contributions critical to the success of the business.
Technical Skills Needed to Build a DevOps Career
Here are the key technical skills needed for a DevOps career in simple points:
-
Version Control: Understand how to use tools like Git for code management.
-
Scripting: Be proficient in scripting languages like Bash, PowerShell, or Python.
-
Operating Systems: Familiarity with both Linux/Unix and Windows systems.
-
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Ability to use IaC tools like Terraform or Ansible for automating infrastructure setup.
-
Containers: Know how to work with containers, especially Docker.
-
Container Orchestration: Familiarity with Kubernetes for managing containerized applications.
-
CI/CD: Understand continuous integration and continuous delivery principles and use CI/CD tools like Jenkins or GitLab CI/CD.
-
Cloud Services: Be comfortable with major cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
-
Monitoring and Logging: Proficiency in tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and ELK stack.
-
Networking: Basic understanding of network protocols and security.
-
Security (DevSecOps): Implement security measures within the DevOps pipeline and use security scanning tools.
-
Database Management: Know how to manage databases like MySQL or MongoDB.
-
Collaboration Tools: Use tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams for team communication.
-
Continuous Learning: Stay updated with evolving DevOps trends and technologies.
-
Problem-Solving: Be a good troubleshooter and problem solver.
-
Automation: Automate repetitive tasks using tools like Ansible or Puppet.
-
GitOps: Understand GitOps principles and tools like ArgoCD.
-
Container Security: Know how to secure containers and scan for vulnerabilities.
-
Serverless Computing: Understand serverless platforms like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions.
-
Microservices: Learn about microservices architecture and related technologies.
-
Automation Testing: Use automated testing frameworks to ensure code quality.
These skills form the foundation for a successful DevOps career, allowing you to streamline software development, deployment, and operations efficiently.
Where Can You Start Your Journey in DevOps?
To begin your journey in DevOps, start by understanding its core principles and then delve into practical skills. Learn version control with Git and acquire basic scripting abilities in languages like Bash or PowerShell. Familiarize yourself with Linux and grasp networking fundamentals. Decide on a specific area of focus within DevOps, whether it's automation, cloud, or security. Enroll in online courses, consider certifications, and engage with DevOps communities. Practice by working on personal projects and join open-source initiatives. Attend meetups, conferences, and build a portfolio to showcase your skills. Collaborate with IT professionals, apply for entry-level roles, and seek mentorship. Developing both technical and soft skills while staying patient and persistent will pave your way to a rewarding DevOps career.
How Far Would You Like to Go in DevOps?
By choosing a DevOps training course that offers a complete learning path, you can take your DevOps career as high as your ambition goes. You can enroll in the DevOps Engineer Master’s Program that adds six more courses beyond the DevOps Certification Training Course and several in-depth Capstone projects. You’ll also want to make sure you have a certification that will take you all the way in your career. DevOps certificates vary in status in the industry. DevOps certifications that have been accredited by important tech giants or relevant bodies will demonstrate to employers that you’ve achieved an expert level of skills and knowledge for continuous integration and development. iCert Global provides industry-recognized DevOps course completion certificates that have lifelong validity and are recognized by tech giants like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure.
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Data Science with R programming
Get Started Today
DevOps certification training Course
People working in the following roles will benefit the most from DevOps certification:
-
IT Team Leaders and technical project managers
-
Systems Administrators and IT Managers
-
Software Developers
-
Deployment engineers
-
Operations support
-
Architects
-
Cloud Engineers
Your career as a DevOps engineer has excellent prospects for growth as businesses are embracing DevOps for the speedy delivery of software features and security updates. iCert Global, as one of the education technology company, offers certified and industry-recognized course in DevOps . Our DevOps Certification will teach you a complete set of DevOps skills .
Read More
As we step into 2023, the tech industry is undergoing dynamic changes, and the question on the minds of many professionals is whether DevOps remains a viable and rewarding career choice. DevOps, which merges development and operations to enhance collaboration and streamline software delivery, has been a buzzword in modern tech circles, promising efficiency and innovation. In this exploration of "Navigating Your Career Path: Is DevOps the Right Choice in 2023?" we will assess the current DevOps landscape, the requisite skills, and the factors shaping its relevance in today's tech world, helping both newcomers and experienced practitioners make informed decisions about their career paths in this fast-paced industry.
Table of Contents
1. Rising Demand for DevOps Talent
2. DevOps Offers a Definite Career Path that Promises Steady Growth
3. Your Key Responsibility Areas (KRA) as DevOps Expert
4. Technical Skills Needed to Build a DevOps Career
5. Where Can You Start Your Journey in DevOps?
6. How Far Would You Like to Go in DevOps?
Get Started Today
Rising Demand for DevOps Talent
The "Rising Demand for DevOps Talent" is a compelling phenomenon in the technology industry, reflecting the growing need for professionals well-versed in DevOps practices. DevOps, short for Development and Operations, represents a set of principles and practices that emphasize collaboration and automation between software development and IT operations teams. This approach is designed to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and speed of software delivery. Here are some key insights into the increasing demand for DevOps talent:
-
Business Agility: In today's fast-paced digital landscape, businesses need to be agile and responsive to market changes. DevOps facilitates quicker software development, testing, and deployment, enabling organizations to adapt swiftly to evolving customer demands and market trends.
-
Automation: Automation is a central pillar of DevOps. By automating repetitive tasks, such as code testing and deployment, organizations can reduce manual errors, save time, and ensure consistent processes. DevOps professionals are responsible for implementing and maintaining these automation pipelines.
-
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): DevOps practices encourage the implementation of CI/CD pipelines. These pipelines automate the integration of code changes, testing, and deployment, leading to more frequent and reliable software releases. Experts in CI/CD are highly sought after to optimize these critical processes.
-
Cloud Computing: The widespread adoption of cloud platforms, such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, has further accelerated the demand for DevOps expertise. DevOps practices are essential for managing and optimizing cloud infrastructure and services effectively.
-
Security: Security is paramount in today's technology landscape. DevOps teams are increasingly integrating security practices into their workflows, giving rise to the DevSecOps approach. DevOps professionals with security expertise are in high demand to ensure that software is developed and deployed securely.
-
Cost Efficiency: DevOps can lead to cost savings by reducing downtime, optimizing resource usage, and streamlining development and deployment processes. Organizations are eager to hire DevOps professionals who can help them achieve these cost benefits.
-
Scalability: DevOps practices are essential for organizations experiencing growth or dealing with variable workloads. DevOps enables scalable infrastructure and supports the efficient management of resources.
-
Cultural Transformation: Beyond tools and processes, DevOps represents a cultural shift within organizations. It emphasizes collaboration, communication, and shared responsibility among development and operations teams. DevOps professionals play a vital role in fostering this cultural change.
DevOps Offers a Definite Career Path that Promises Steady Growth
DevOps is undeniably offering a well-defined career path with the assurance of steady growth. In recent years, it has evolved into a transformative field within the technology industry, creating a multitude of opportunities for professionals seeking a dynamic and promising career trajectory. The reasons behind this career's appeal are numerous and compelling.
First and foremost, the demand for DevOps professionals is soaring. Across various industries, companies are recognizing the significant value that DevOps practices bring to the table. These practices accelerate software development, enhance product quality, and optimize operational efficiency. This sustained demand ensures a consistent flow of job opportunities for those entering the DevOps arena, providing a sense of job security and stability.
One of the remarkable aspects of a DevOps career is its versatility. DevOps is not a one-size-fits-all discipline; it encompasses a broad spectrum of skills and practices. Professionals can specialize in areas such as automation, continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD), cloud computing, security (DevSecOps), or infrastructure as code (IaC). This versatility empowers individuals to tailor their career paths to align with their personal interests and strengths, offering a diverse array of potential avenues for growth.
Furthermore, DevOps places a strong emphasis on continuous learning and improvement. In a rapidly evolving technological landscape, staying up-to-date with the latest tools, technologies, and best practices is not just encouraged but essential. This commitment to lifelong learning ensures that DevOps practitioners remain relevant and marketable, making it possible to continuously advance in their careers.
A DevOps career is also financially rewarding. Due to the specialized skills and expertise required, DevOps roles often come with competitive salaries and attractive benefit packages. Professionals in this field can command higher compensation compared to more traditional IT roles, making it an appealing choice for those who seek both intellectual and financial gratification.
Moreover, DevOps professionals are well-positioned for cross-functional collaboration. DevOps practices encourage close cooperation between development and operations teams, providing opportunities to work with diverse stakeholders and gain exposure to different aspects of an organization's technology ecosystem. This interdisciplinary experience enhances their skill set and opens up various career possibilities.
Over time, many DevOps professionals transition into leadership roles. With their accumulated experience and expertise, they often find themselves overseeing DevOps teams, shaping an organization's DevOps strategy, and driving cultural and technical transformations within their workplaces. This pathway into leadership roles adds a layer of professional growth and leadership development to the DevOps career trajectory.
Furthermore, DevOps offers global opportunities. The demand for DevOps talent is not confined to specific geographic regions, allowing professionals in this field to explore remote work options or even international employment opportunities. This global perspective can enrich their career experiences and broaden their horizons.
Lastly, DevOps professionals find deep satisfaction in their work. They play a pivotal role in enabling organizations to deliver software more swiftly and with higher quality. This direct impact on an organization's ability to innovate, compete, and respond to customer needs can be intrinsically rewarding and fulfilling.
Your Key Responsibility Areas (KRA) as DevOps Expert
As a DevOps expert, your Key Responsibility Areas (KRAs) encompass a wide range of tasks and responsibilities that are vital for the successful implementation of DevOps practices and the efficient operation of software development and IT infrastructure. Here are some of the key areas you might be responsible for:
-
Infrastructure Automation:
-
Designing, building, and maintaining infrastructure as code (IaC) to automate the provisioning and management of servers, networks, and storage.
-
Implementing and managing configuration management tools (e.g., Ansible, Puppet, Chef) to ensure consistency and scalability in infrastructure.
-
-
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD):
-
Developing and maintaining CI/CD pipelines to automate the build, test, and deployment processes.
-
Ensuring that code changes are integrated, tested, and deployed efficiently, with a focus on quality and reliability.
-
-
Cloud Services:
-
Managing cloud infrastructure (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) and optimizing resource usage for scalability and cost-efficiency.
-
Implementing cloud-native DevOps practices and leveraging cloud services for application deployment and scaling.
-
-
Version Control:
-
Implementing and managing version control systems (e.g., Git) to track code changes, collaborate with development teams, and ensure code quality.
-
-
Monitoring and Logging:
-
Setting up monitoring and logging tools (e.g., Prometheus, ELK stack) to track system performance, identify issues, and troubleshoot problems proactively.
-
Creating dashboards and alerts to ensure real-time visibility into system health.
-
-
Security (DevSecOps):
-
Integrating security practices into the DevOps pipeline to identify and mitigate security vulnerabilities.
-
Collaborating with security teams to implement best practices for securing infrastructure and applications.
-
-
Collaboration and Communication:
-
Fostering a culture of collaboration between development and operations teams to ensure smooth workflows and alignment with business goals.
-
Facilitating communication and knowledge sharing among cross-functional teams.
-
-
Release Management:
-
Managing software releases, including versioning, deployment scheduling, and rollback procedures.
-
Coordinating release activities to minimize downtime and disruptions.
-
-
Performance Optimization:
-
Identifying and addressing performance bottlenecks in applications and infrastructure.
-
Implementing optimizations to enhance system speed and efficiency.
-
-
Disaster Recovery and Backup:
-
Developing and testing disaster recovery plans to ensure data integrity and system availability in case of unexpected failures.
-
Regularly backing up critical data and systems to prevent data loss.
-
-
Documentation and Training:
-
Maintaining detailed documentation of infrastructure, processes, and configurations.
-
Providing training and guidance to team members and stakeholders on DevOps practices and tools.
-
-
Tool Evaluation and Selection:
-
Assessing and selecting the most appropriate DevOps tools and technologies for the organization's needs.
-
Staying updated on emerging DevOps tools and trends to ensure the use of modern and effective solutions.
-
-
Continuous Improvement:
-
Continuously assessing and optimizing DevOps processes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
-
Conducting post-implementation reviews and retrospectives to identify areas for improvement.
-
-
Compliance and Governance:
-
Ensuring that infrastructure and processes comply with industry regulations and organizational governance policies.
-
Implementing controls and audits as needed.
-
-
Team Leadership and Mentoring (for senior roles):
-
Leading DevOps teams, setting strategic goals, and mentoring team members.
-
Overseeing project execution, resource allocation, and performance evaluations.
-
These KRAs represent the core responsibilities of a DevOps expert. The specific duties may vary depending on the organization's size, industry, and the maturity of its DevOps practices. DevOps professionals play a pivotal role in enabling organizations to deliver software more efficiently, reliably, and securely, making their contributions critical to the success of the business.
Technical Skills Needed to Build a DevOps Career
Here are the key technical skills needed for a DevOps career in simple points:
-
Version Control: Understand how to use tools like Git for code management.
-
Scripting: Be proficient in scripting languages like Bash, PowerShell, or Python.
-
Operating Systems: Familiarity with both Linux/Unix and Windows systems.
-
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Ability to use IaC tools like Terraform or Ansible for automating infrastructure setup.
-
Containers: Know how to work with containers, especially Docker.
-
Container Orchestration: Familiarity with Kubernetes for managing containerized applications.
-
CI/CD: Understand continuous integration and continuous delivery principles and use CI/CD tools like Jenkins or GitLab CI/CD.
-
Cloud Services: Be comfortable with major cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
-
Monitoring and Logging: Proficiency in tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and ELK stack.
-
Networking: Basic understanding of network protocols and security.
-
Security (DevSecOps): Implement security measures within the DevOps pipeline and use security scanning tools.
-
Database Management: Know how to manage databases like MySQL or MongoDB.
-
Collaboration Tools: Use tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams for team communication.
-
Continuous Learning: Stay updated with evolving DevOps trends and technologies.
-
Problem-Solving: Be a good troubleshooter and problem solver.
-
Automation: Automate repetitive tasks using tools like Ansible or Puppet.
-
GitOps: Understand GitOps principles and tools like ArgoCD.
-
Container Security: Know how to secure containers and scan for vulnerabilities.
-
Serverless Computing: Understand serverless platforms like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions.
-
Microservices: Learn about microservices architecture and related technologies.
-
Automation Testing: Use automated testing frameworks to ensure code quality.
These skills form the foundation for a successful DevOps career, allowing you to streamline software development, deployment, and operations efficiently.
Where Can You Start Your Journey in DevOps?
To begin your journey in DevOps, start by understanding its core principles and then delve into practical skills. Learn version control with Git and acquire basic scripting abilities in languages like Bash or PowerShell. Familiarize yourself with Linux and grasp networking fundamentals. Decide on a specific area of focus within DevOps, whether it's automation, cloud, or security. Enroll in online courses, consider certifications, and engage with DevOps communities. Practice by working on personal projects and join open-source initiatives. Attend meetups, conferences, and build a portfolio to showcase your skills. Collaborate with IT professionals, apply for entry-level roles, and seek mentorship. Developing both technical and soft skills while staying patient and persistent will pave your way to a rewarding DevOps career.
How Far Would You Like to Go in DevOps?
By choosing a DevOps training course that offers a complete learning path, you can take your DevOps career as high as your ambition goes. You can enroll in the DevOps Engineer Master’s Program that adds six more courses beyond the DevOps Certification Training Course and several in-depth Capstone projects. You’ll also want to make sure you have a certification that will take you all the way in your career. DevOps certificates vary in status in the industry. DevOps certifications that have been accredited by important tech giants or relevant bodies will demonstrate to employers that you’ve achieved an expert level of skills and knowledge for continuous integration and development. iCert Global provides industry-recognized DevOps course completion certificates that have lifelong validity and are recognized by tech giants like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure.
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Data Science with R programming
Get Started Today
DevOps certification training Course
People working in the following roles will benefit the most from DevOps certification:
-
IT Team Leaders and technical project managers
-
Systems Administrators and IT Managers
-
Software Developers
-
Deployment engineers
-
Operations support
-
Architects
-
Cloud Engineers
Your career as a DevOps engineer has excellent prospects for growth as businesses are embracing DevOps for the speedy delivery of software features and security updates. iCert Global, as one of the education technology company, offers certified and industry-recognized course in DevOps . Our DevOps Certification will teach you a complete set of DevOps skills .
A deep dive into data collection methods, types, and tools
In today's data-driven world, understanding the intricacies of data collection methods, types, and tools is essential for individuals and organizations alike. "Data Collection Methods, Types, and Tools: A Deep Dive" offers a comprehensive exploration of this vital subject. This deep dive navigates the diverse landscape of data collection, from traditional methodologies like surveys to cutting-edge techniques such as web scraping and IoT sensors, covering a wide spectrum of data types along the way. Additionally, it unveils a rich array of tools and technologies that empower data collectors to efficiently gather and transform raw information into actionable insights. Whether you are a data enthusiast, researcher, business professional, or simply curious about the world of data, this deep dive promises to equip you with the knowledge to harness the power of data effectively.
Table of Contents
-
What is Data Collection?
-
Why Do We Need Data Collection?
-
What Are the Different Methods of Data Collection?
-
Data Collection Tools
-
The Importance of Ensuring Accurate and Appropriate Data Collection
-
Issues Related to Maintaining the Integrity of Data Collection
-
What are Common Challenges in Data Collection?
-
What are the Key Steps in the Data Collection Process?
-
Data Collection Considerations and Best Practices
-
FAQs
What is Data Collection?
Data collection is the process of gathering and capturing information or data from various sources, such as individuals, instruments, sensors, or documents, for the purpose of analysis, research, decision-making, or record-keeping. It is a fundamental step in the data management and analysis pipeline and plays a crucial role in various fields, including science, business, healthcare, social sciences, and many others.
Data collection can involve various methods and techniques, depending on the nature of the data, the research objectives, and the available resources. Some common methods of data collection include:
-
Surveys and Questionnaires: Gathering information by asking structured questions to individuals or groups.
-
Interviews: Conducting one-on-one or group interviews to collect qualitative data through open-ended or structured questions.
-
Observations: Directly observing and recording information about a particular subject or event.
-
Experiments: Manipulating variables under controlled conditions to collect data on their effects.
-
Sensors and Instruments: Using specialized devices or sensors to collect data, such as temperature, pressure, or GPS coordinates.
-
Document Analysis: Reviewing and extracting data from written or digital documents, such as reports, articles, or social media posts.
-
Web Scraping: Automated extraction of data from websites and online sources.
-
Social Media Monitoring: Collecting data from social media platforms to analyze trends, sentiments, or user behavior.
-
Data Logging: Continuous recording of data over time, often used in fields like environmental monitoring or industrial processes.
-
Sampling: Collecting data from a subset of a larger population or dataset to make inferences about the whole.
-
Mobile Apps and Surveys: Collecting data through mobile applications or surveys conducted on smartphones and tablets.
Effective data collection involves careful planning, the use of appropriate methods, ensuring data quality and accuracy, and often adhering to ethical and privacy considerations. Once collected, data can be processed, analyzed, and interpreted to extract valuable insights and support decision-making processes.
Why Do We Need Data Collection?
Data collection is a crucial component of modern society, serving as the foundation for informed decision-making, problem-solving, and progress across various domains. It provides the empirical evidence needed to understand complex issues, whether in healthcare, business, government, or scientific research. By systematically gathering data, individuals and organizations can assess performance, identify challenges, and formulate effective strategies. In healthcare, for example, data collection helps doctors diagnose diseases, researchers develop new treatments, and policymakers allocate resources to improve public health outcomes. In business, it guides market strategies, enables personalized customer experiences, and enhances efficiency through data-driven analytics. Ultimately, data collection empowers individuals, institutions, and societies to adapt, innovate, and thrive in an ever-evolving world.
Furthermore, data collection is essential for accountability and transparency. It creates a record of actions and outcomes, allowing for scrutiny and accountability of individuals, organizations, and governments. This transparency promotes ethical behavior and helps prevent fraud and corruption. In today's interconnected world, data collection also plays a pivotal role in addressing global challenges like climate change, where data on environmental trends is essential for informed policy decisions. In summary, data collection is not just a technical process; it's a cornerstone of informed decision-making, accountability, and progress across diverse sectors, shaping the way we understand and interact with the world around us.
What Are the Different Methods of Data Collection?
There are various methods of data collection, each suited to specific research objectives, types of data, and practical considerations. Here are some of the different methods commonly used:
-
Surveys and Questionnaires: Surveys involve asking individuals or groups a set of structured questions. Questionnaires can be administered in person, by phone, through email, or online. They are useful for collecting quantitative data on opinions, preferences, and demographics.
-
Interviews: Interviews involve one-on-one or group interactions where researchers ask questions and record responses. Interviews can be structured (with predetermined questions) or unstructured (more open-ended) and are often used to gather qualitative data.
-
Observations: This method involves directly observing and recording behavior, events, or phenomena. It can be done in a controlled environment (e.g., a laboratory) or in the field (e.g., naturalistic observations in a public space).
-
Experiments: Experiments involve manipulating one or more variables under controlled conditions to observe their effects. Experimental research aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships and is common in scientific studies.
-
Secondary Data Analysis: Researchers analyze existing data collected by others. This method is cost-effective and can involve various types of data, such as government statistics, academic studies, or historical records.
-
Document Analysis: Researchers review and extract information from written or digital documents, including reports, articles, social media posts, and historical texts. This is often used in content analysis and textual research.
-
Web Scraping: Automated tools are used to extract data from websites, forums, and social media platforms. Web scraping is common for collecting large datasets from the internet.
-
Sensors and Instruments: Specialized devices and sensors are used to collect data automatically. Examples include temperature sensors, GPS devices, heart rate monitors, and satellite imagery.
-
Sampling: Rather than collecting data from an entire population, researchers collect data from a representative subset (sample). Sampling methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, and convenience sampling.
-
Mobile Apps and Surveys: Data can be collected through mobile applications or surveys administered on smartphones and tablets. This method is convenient and allows for real-time data collection.
-
Social Media Monitoring: Data is collected from social media platforms to analyze trends, sentiments, user behavior, and public opinion. Social media APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are often used for data access.
-
Data Logging: Continuous recording of data over time is used in various fields, including environmental monitoring (e.g., weather stations), industrial processes, and performance monitoring (e.g., athletes' heart rate during a race).
-
Focus Groups: A moderator leads a discussion with a small group of participants to gather insights, opinions, and perceptions on a particular topic. Focus groups are common in market research and qualitative studies.
-
Diaries and Journals: Participants keep records of their experiences, thoughts, or behaviors over a specified period. This method is often used to study daily routines or personal reflections.
The choice of data collection method depends on research goals, the type of data needed (quantitative or qualitative), available resources, ethical considerations, and practical constraints. Researchers often employ a combination of methods to triangulate data and enhance the validity and reliability of their findings.
Data Collection Tools
Data collection tools are software or hardware solutions designed to facilitate the process of gathering, storing, and managing data from various sources. These tools are used in research, business, and various other fields to streamline data collection and improve its accuracy and efficiency. Here are some common types of data collection tools:
-
Online Survey Tools: Online survey platforms like SurveyMonkey, Google Forms, and Qualtrics allow users to create and distribute surveys and questionnaires over the internet. They offer features for designing surveys, collecting responses, and analyzing results.
-
Mobile Data Collection Apps: Mobile apps like Survey123 (Esri), Fulcrum, and QuickTapSurvey enable data collection in the field using smartphones and tablets. Users can design custom forms, collect data offline, and sync it when connected to the internet.
-
Data Analytics Software: Tools like Microsoft Excel, R, Python (with libraries like Pandas), and SPSS are used to analyze and visualize data collected from various sources. They help in extracting insights and patterns from datasets.
-
Database Management Systems (DBMS): Systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, and MongoDB are used to store, organize, and manage large volumes of structured data. They are commonly employed in businesses and research institutions.
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software such as ArcGIS and QGIS is used for collecting and analyzing spatial data, including maps, GPS coordinates, and geographic features.
-
Data Collection APIs: Some online platforms and services offer APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow developers to integrate data collection capabilities into custom applications. For example, social media platforms like Twitter and Facebook offer APIs for data retrieval.
-
Data Logger Devices: Physical devices like data loggers and sensors are used in various industries to automatically collect data, such as temperature, humidity, and pressure, and store it for later analysis.
-
Document Scanners and OCR Software: Tools like Adobe Acrobat and OCR (Optical Character Recognition) software can be used to digitize and collect data from paper documents, such as forms, invoices, and contracts.
-
Web Scraping Tools: Tools like Beautiful Soup, Scrapy, and Octoparse automate the extraction of data from websites and web pages. They are commonly used for web-based data collection.
-
Audio and Video Recording Software: Researchers and professionals often use audio and video recording tools to capture interviews, meetings, and events. Transcription software can convert spoken words into text data for analysis.
-
Qualitative Data Analysis Software: Software like NVivo and MAXQDA is specifically designed for researchers collecting qualitative data (e.g., interviews, focus groups). They assist in organizing, coding, and analyzing textual or multimedia data.
-
Biometric Data Collection Tools: Devices like fingerprint scanners, facial recognition cameras, and heart rate monitors are used to collect biometric data for security, healthcare, and other applications.
-
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain-based tools can ensure the secure and transparent collection and storage of data, making them suitable for applications where data integrity and immutability are critical.
-
Machine Learning and AI Platforms: Advanced machine learning and AI platforms can assist in data collection by automating processes, recognizing patterns, and making predictions based on existing data.
The choice of data collection tools depends on the specific requirements of a project, the type of data being collected, and the available resources. In many cases, a combination of tools may be used to capture, store, and analyze data effectively.
The Importance of Ensuring Accurate and Appropriate Data Collection
Ensuring accurate and appropriate data collection is of paramount importance in research, decision-making, and various fields for several compelling reasons:
-
Reliable Results: Accurate data leads to trustworthy research findings and better decision-making.
-
Credibility: Accurate data enhances the credibility of reports and studies.
-
Effective Decisions: It supports informed and effective decision-making.
-
Efficiency: Appropriate data collection saves time and resources.
-
Ethics and Privacy: It respects ethical standards and privacy concerns.
-
Reducing Bias: It helps reduce bias in research and analysis.
-
Long-Term Impact: Inaccurate data can have lasting consequences.
-
Resource Allocation: Guides efficient resource allocation.
-
Reproducibility: Facilitates the reproducibility of experiments.
-
Customer Satisfaction: Improves customer satisfaction in businesses.
-
Public Health and Safety: Crucial for public health and safety monitoring.
-
Environmental Conservation: Supports conservation efforts.
-
Innovation: Drives innovation and improvement in various fields.
Issues Related to Maintaining the Integrity of Data Collection
Maintaining the integrity of data collection is essential to ensure that data is accurate, reliable, and free from bias or manipulation. However, several issues can compromise data integrity. Here are some common issues related to maintaining data collection integrity:
-
Sampling Bias: When the sample used for data collection is not representative of the larger population, it can introduce bias into the results. This can occur due to non-random sampling methods or inadequate sample sizes.
-
Selection Bias: Researchers or data collectors may inadvertently favor certain groups or individuals when selecting participants or data sources, leading to biased data.
-
Non-Response Bias: If a significant portion of the selected participants does not respond to surveys or data requests, the results may not accurately represent the entire population.
-
Measurement Error: Errors in data measurement or data entry can occur due to human error, faulty equipment, or inconsistent measurement standards. These errors can introduce inaccuracies into the collected data.
-
Data Tampering: Deliberate manipulation or tampering with data can occur for various reasons, such as fraud, academic misconduct, or political motives. Maintaining data security and access controls is crucial to prevent such issues.
-
Data Privacy Concerns: Collecting sensitive or personally identifiable information without proper consent or security measures can lead to privacy breaches and ethical dilemmas.
-
Response Bias: Respondents may provide inaccurate or socially desirable responses, especially in surveys or interviews, leading to biased data.
-
Observer Bias: When data is collected through observations, the observer's personal biases and interpretations can influence the data collected.
-
Researcher Bias: Researchers' own beliefs, preferences, or expectations can inadvertently influence data collection, analysis, or interpretation, leading to bias.
-
Missing Data: Incomplete or missing data points can impact the overall integrity of the dataset, potentially leading to incomplete or biased conclusions.
-
Survey Question Bias: Poorly constructed survey questions or leading questions can unintentionally guide respondents toward certain answers, skewing the results.
-
Temporal Bias: Data collected at specific times or seasons may not accurately represent long-term trends or conditions.
-
Cross-Cultural Bias: Data collected in one cultural context may not be applicable or relevant in another, leading to cultural bias.
-
Lack of Data Documentation: Inadequate documentation of data collection methods, protocols, and procedures can hinder transparency and replication efforts.
-
Conflict of Interest: Financial or personal interests of data collectors or researchers can compromise the objectivity and integrity of data collection.
To address these issues and maintain data collection integrity, it is essential to implement rigorous data collection protocols, ensure transparency, use standardized measurement tools, conduct thorough data validation and verification, and adhere to ethical guidelines. Additionally, peer review, data audits, and data quality assessments can help identify and mitigate potential problems related to data integrity.
What are Common Challenges in Data Collection?
Data collection can be a complex and challenging process, and researchers, organizations, and individuals often encounter various obstacles. Here are some common challenges in data collection:
-
Selection Bias: It can be challenging to ensure that the data collected is representative of the entire population or target group. Biased sampling methods or non-response bias can lead to skewed results.
-
Data Quality: Maintaining data accuracy, completeness, and consistency can be difficult. Data may be prone to errors, duplications, or missing values, affecting its reliability.
-
Resource Constraints: Limited time, budget, and human resources can hinder data collection efforts, especially in large-scale projects.
-
Privacy Concerns: Collecting sensitive or personally identifiable information must be done with care to ensure data privacy and compliance with relevant regulations.
-
Ethical Considerations: Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines when collecting data, which can be challenging when dealing with vulnerable populations or sensitive topics.
-
Data Security: Safeguarding data against breaches, theft, or unauthorized access is crucial. Data breaches can have serious consequences for individuals and organizations.
-
Data Collection Instruments: Developing and testing data collection instruments, such as surveys or questionnaires, requires careful consideration to ensure they are valid and reliable.
-
Technological Challenges: Implementing data collection technologies, especially in remote or resource-constrained areas, can be challenging. Issues like connectivity and compatibility may arise.
-
Non-Response: Collecting data from reluctant or uncooperative participants can be difficult, leading to missing or incomplete data.
-
Data Entry Errors: Manual data entry can introduce errors, especially when transcribing data from paper to digital formats.
-
Language and Cultural Barriers: In cross-cultural research, language and cultural differences may affect data collection and interpretation.
-
Data Verification: Verifying the accuracy of collected data can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
-
Data Bias: Data may be influenced by the bias or subjectivity of the data collector, respondent, or observer.
-
Data Volume: Dealing with large volumes of data can be challenging, requiring efficient storage, processing, and analysis solutions.
-
Temporal Changes: Data collected at different times may not be directly comparable due to changing conditions or external factors.
-
Data Ownership: Clarifying data ownership and usage rights can be a challenge, especially in collaborative research or data-sharing initiatives.
-
Data Governance: Establishing clear data governance policies and procedures is essential for managing data collection efforts effectively.
-
Environmental Factors: In some cases, data collection may be affected by weather conditions, natural disasters, or other environmental factors.
-
Human Error: Mistakes made during the data collection process, such as misreading instruments or making errors in data recording, can impact data quality.
-
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that data collection activities comply with relevant laws and regulations can be complex, especially when conducting research across borders.
Addressing these challenges often requires careful planning, well-defined data collection protocols, the use of appropriate technology, rigorous quality control measures, and ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the data collection process. Collaborative efforts and expertise in data collection methodologies can also help overcome many of these challenges.
What are the Key Steps in the Data Collection Process?
The data collection process involves a series of key steps to gather information systematically and ensure the data's accuracy and reliability. Here are the fundamental steps in the data collection process:
-
Define Objectives: Clearly define the research or data collection objectives. Understand the purpose, scope, and goals of the data collection effort.
-
Select Data Sources: Identify the sources of data, which can include surveys, interviews, observations, existing databases, sensors, documents, or any other relevant sources.
-
Design Data Collection Instruments: Develop data collection instruments, such as surveys, questionnaires, interview guides, or observation protocols. Ensure they are clear, unbiased, and aligned with the research objectives.
-
Select Sampling Methods: If applicable, choose the appropriate sampling method (e.g., random sampling, stratified sampling) to select a representative subset of the population or dataset.
-
Pilot Testing: Test the data collection instruments and procedures with a small, representative group to identify and address any issues, such as unclear questions or logistical challenges.
-
Data Collection: Conduct the actual data collection activities according to the established protocols. Ensure consistency and uniformity in data collection procedures.
-
Data Entry: If data is collected in paper form, enter it into digital format. Implement quality control measures to minimize data entry errors.
-
Data Verification: Verify the accuracy and completeness of the collected data. This step may involve data cleaning and validation to identify and correct errors or inconsistencies.
-
Data Storage: Safely store the collected data in a secure and organized manner, whether in physical or digital format. Implement data security measures to protect sensitive information.
-
Data Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of the data collection process, including protocols, instruments, and any modifications made during the collection.
-
Data Analysis: If applicable, perform data analysis using appropriate statistical or analytical methods. Transform raw data into meaningful insights and findings.
-
Data Interpretation: Interpret the results of data analysis in the context of research objectives. Draw conclusions and make recommendations based on the data.
-
Report Findings: Communicate the results and findings through reports, presentations, or other appropriate channels. Clearly and transparently convey the insights derived from the data.
-
Data Archiving: Store the data for future reference or potential replication of the study. Ensure data is accessible and properly archived for compliance and transparency.
-
Ethical Considerations: Adhere to ethical standards throughout the data collection process, respecting privacy, informed consent, and any relevant legal or institutional requirements.
-
Quality Control: Implement quality control measures at various stages of data collection to minimize errors, bias, and inconsistencies.
-
Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitor the data collection process to identify and address any issues promptly. Make necessary adjustments as needed.
-
Feedback and Iteration: Collect feedback from stakeholders and team members involved in data collection. Use feedback to improve data collection procedures for future efforts.
-
Data Governance: Establish clear data governance policies and procedures to manage data collection, storage, and access effectively.
-
Documentation of Assumptions and Limitations: Clearly document any assumptions, limitations, or potential biases in the data collection process to provide context for the data's interpretation.
Effective data collection requires careful planning, attention to detail, and adherence to best practices. Following these key steps helps ensure that the data collected is of high quality, reliable, and suitable for analysis and decision-making.
Data Collection Considerations and Best Practices
Effective data collection involves careful consideration of various factors and adherence to best practices to ensure that the collected data is of high quality, reliable, and ethically sound. Here are some key data collection considerations and best practices:
-
Clearly Define Objectives: Begin by precisely defining the research or data collection objectives. Understand what information is needed and why it is important.
-
Ethical Considerations: Always prioritize ethical principles when collecting data. Obtain informed consent from participants, ensure data privacy and confidentiality, and comply with relevant ethical guidelines and regulations.
-
Select Appropriate Data Sources: Choose the most suitable data sources and methods for your research objectives. Consider whether primary data collection (gathering data firsthand) or secondary data (using existing data) is more appropriate.
-
Pilot Testing: Before full-scale data collection, conduct pilot tests or pre-tests to identify and rectify any issues with data collection instruments, such as surveys or questionnaires.
-
Sampling: If using sampling, select a representative sample that accurately reflects the population of interest. Ensure randomness and minimize selection bias.
-
Standardize Procedures: Maintain consistency in data collection procedures. Ensure that all data collectors follow the same protocols to reduce bias and increase data reliability.
-
Training: Properly train data collectors on data collection methods, instruments, and ethical considerations. Regularly update their training to stay informed about best practices.
-
Data Collection Tools: Use appropriate data collection tools and technologies. Ensure that instruments are clear, unbiased, and suitable for the target audience.
-
Data Entry and Validation: If collecting data manually, establish data entry protocols and validation procedures to minimize errors and ensure data accuracy.
-
Data Security: Safeguard data throughout the collection process. Use encryption, access controls, and secure storage methods to protect data from unauthorized access or breaches.
-
Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of the data collection process, including data collection protocols, instruments, and any modifications or issues encountered during collection.
-
Quality Control: Implement quality control measures at different stages of data collection to identify and rectify errors or inconsistencies promptly.
-
Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitor the data collection process for adherence to protocols, completeness, and quality. Address issues as they arise.
-
Data Validation: Cross-check data entries, validate data against predefined criteria, and ensure data is consistent and accurate.
-
Data Cleaning: After data collection, thoroughly clean and preprocess the data to handle missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies.
-
Data Storage and Archiving: Store data securely, ensuring backup and redundancy. Archive data for future reference and compliance with data retention policies.
-
Data Governance: Establish clear data governance policies and procedures to manage data collection, storage, and access effectively.
-
Feedback and Iteration: Gather feedback from data collectors and stakeholders to identify areas for improvement in data collection processes. Continuously refine methods based on feedback.
-
Data Documentation: Document any assumptions, limitations, or potential biases in the data collection process. Transparency is essential for the data's interpretation.
-
Data Reporting: Clearly report the methods, procedures, and findings of the data collection effort, allowing for transparency and reproducibility.
-
Data Dissemination: Share data appropriately, considering data-sharing agreements, copyrights, and licensing requirements.
-
Compliance: Ensure compliance with legal, regulatory, and institutional requirements related to data collection, especially when dealing with sensitive or personal information.
By carefully considering these factors and following best practices, data collectors can enhance the quality and reliability of the data collected, ultimately leading to more robust research findings and informed decision-making.
How to get course?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Data Science with R programming
FAQs
-
What is data collection, and why is it important?
Data collection is the process of gathering and capturing information or data from various sources for analysis, research, decision-making, or record-keeping. It is important because it provides the foundation for informed decisions, research, and problem-solving in various fields.
-
What are the common methods of data collection?
Common methods of data collection include surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, sensors and instruments, document analysis, web scraping, social media monitoring, sampling, and more.
-
What are the different types of data collected in research?
Data in research can be categorized as quantitative (numeric) or qualitative (non-numeric). Quantitative data includes numerical values, while qualitative data includes descriptions, narratives, and observations.
-
What are the essential steps in the data collection process?
Key steps include defining objectives, selecting data sources, designing data collection instruments, sampling (if applicable), pilot testing, data collection, data entry, data verification, data storage, analysis, interpretation, reporting, archiving, and addressing ethical considerations.
-
What tools and software are commonly used for data collection?
Common data collection tools and software include online survey platforms (e.g., SurveyMonkey), mobile data collection apps (e.g., Fulcrum), data analytics software (e.g., Excel, R), and geographic information systems (GIS) software (e.g., ArcGIS).
-
What are the challenges in data collection?
Challenges in data collection include issues related to sampling bias, data quality, resource constraints, privacy concerns, ethical considerations, data security, and potential biases in data collection methods.
-
What are some best practices for maintaining data collection integrity?
Best practices include defining clear objectives, ensuring ethical conduct, selecting appropriate data sources, pilot testing, proper training, data validation, documentation, quality control, and continuous monitoring.
-
How can data collection tools help streamline the process?
Data collection tools automate and streamline data capture, reduce errors, improve data accuracy, and provide efficient ways to gather and manage data, making the process more efficient and reliable.
-
What is the role of data collection in decision-making and research?
Data collection provides the evidence and insights necessary for informed decision-making, problem-solving, scientific research, and the generation of knowledge in various fields.
-
What precautions should be taken when collecting sensitive data?
When collecting sensitive data, it's essential to obtain informed consent, implement strong data security measures, adhere to ethical guidelines, and comply with privacy regulations to protect individuals' information.
Read More
In today's data-driven world, understanding the intricacies of data collection methods, types, and tools is essential for individuals and organizations alike. "Data Collection Methods, Types, and Tools: A Deep Dive" offers a comprehensive exploration of this vital subject. This deep dive navigates the diverse landscape of data collection, from traditional methodologies like surveys to cutting-edge techniques such as web scraping and IoT sensors, covering a wide spectrum of data types along the way. Additionally, it unveils a rich array of tools and technologies that empower data collectors to efficiently gather and transform raw information into actionable insights. Whether you are a data enthusiast, researcher, business professional, or simply curious about the world of data, this deep dive promises to equip you with the knowledge to harness the power of data effectively.
Table of Contents
-
What is Data Collection?
-
Why Do We Need Data Collection?
-
What Are the Different Methods of Data Collection?
-
Data Collection Tools
-
The Importance of Ensuring Accurate and Appropriate Data Collection
-
Issues Related to Maintaining the Integrity of Data Collection
-
What are Common Challenges in Data Collection?
-
What are the Key Steps in the Data Collection Process?
-
Data Collection Considerations and Best Practices
-
FAQs
What is Data Collection?
Data collection is the process of gathering and capturing information or data from various sources, such as individuals, instruments, sensors, or documents, for the purpose of analysis, research, decision-making, or record-keeping. It is a fundamental step in the data management and analysis pipeline and plays a crucial role in various fields, including science, business, healthcare, social sciences, and many others.
Data collection can involve various methods and techniques, depending on the nature of the data, the research objectives, and the available resources. Some common methods of data collection include:
-
Surveys and Questionnaires: Gathering information by asking structured questions to individuals or groups.
-
Interviews: Conducting one-on-one or group interviews to collect qualitative data through open-ended or structured questions.
-
Observations: Directly observing and recording information about a particular subject or event.
-
Experiments: Manipulating variables under controlled conditions to collect data on their effects.
-
Sensors and Instruments: Using specialized devices or sensors to collect data, such as temperature, pressure, or GPS coordinates.
-
Document Analysis: Reviewing and extracting data from written or digital documents, such as reports, articles, or social media posts.
-
Web Scraping: Automated extraction of data from websites and online sources.
-
Social Media Monitoring: Collecting data from social media platforms to analyze trends, sentiments, or user behavior.
-
Data Logging: Continuous recording of data over time, often used in fields like environmental monitoring or industrial processes.
-
Sampling: Collecting data from a subset of a larger population or dataset to make inferences about the whole.
-
Mobile Apps and Surveys: Collecting data through mobile applications or surveys conducted on smartphones and tablets.
Effective data collection involves careful planning, the use of appropriate methods, ensuring data quality and accuracy, and often adhering to ethical and privacy considerations. Once collected, data can be processed, analyzed, and interpreted to extract valuable insights and support decision-making processes.
Why Do We Need Data Collection?
Data collection is a crucial component of modern society, serving as the foundation for informed decision-making, problem-solving, and progress across various domains. It provides the empirical evidence needed to understand complex issues, whether in healthcare, business, government, or scientific research. By systematically gathering data, individuals and organizations can assess performance, identify challenges, and formulate effective strategies. In healthcare, for example, data collection helps doctors diagnose diseases, researchers develop new treatments, and policymakers allocate resources to improve public health outcomes. In business, it guides market strategies, enables personalized customer experiences, and enhances efficiency through data-driven analytics. Ultimately, data collection empowers individuals, institutions, and societies to adapt, innovate, and thrive in an ever-evolving world.
Furthermore, data collection is essential for accountability and transparency. It creates a record of actions and outcomes, allowing for scrutiny and accountability of individuals, organizations, and governments. This transparency promotes ethical behavior and helps prevent fraud and corruption. In today's interconnected world, data collection also plays a pivotal role in addressing global challenges like climate change, where data on environmental trends is essential for informed policy decisions. In summary, data collection is not just a technical process; it's a cornerstone of informed decision-making, accountability, and progress across diverse sectors, shaping the way we understand and interact with the world around us.
What Are the Different Methods of Data Collection?
There are various methods of data collection, each suited to specific research objectives, types of data, and practical considerations. Here are some of the different methods commonly used:
-
Surveys and Questionnaires: Surveys involve asking individuals or groups a set of structured questions. Questionnaires can be administered in person, by phone, through email, or online. They are useful for collecting quantitative data on opinions, preferences, and demographics.
-
Interviews: Interviews involve one-on-one or group interactions where researchers ask questions and record responses. Interviews can be structured (with predetermined questions) or unstructured (more open-ended) and are often used to gather qualitative data.
-
Observations: This method involves directly observing and recording behavior, events, or phenomena. It can be done in a controlled environment (e.g., a laboratory) or in the field (e.g., naturalistic observations in a public space).
-
Experiments: Experiments involve manipulating one or more variables under controlled conditions to observe their effects. Experimental research aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships and is common in scientific studies.
-
Secondary Data Analysis: Researchers analyze existing data collected by others. This method is cost-effective and can involve various types of data, such as government statistics, academic studies, or historical records.
-
Document Analysis: Researchers review and extract information from written or digital documents, including reports, articles, social media posts, and historical texts. This is often used in content analysis and textual research.
-
Web Scraping: Automated tools are used to extract data from websites, forums, and social media platforms. Web scraping is common for collecting large datasets from the internet.
-
Sensors and Instruments: Specialized devices and sensors are used to collect data automatically. Examples include temperature sensors, GPS devices, heart rate monitors, and satellite imagery.
-
Sampling: Rather than collecting data from an entire population, researchers collect data from a representative subset (sample). Sampling methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, and convenience sampling.
-
Mobile Apps and Surveys: Data can be collected through mobile applications or surveys administered on smartphones and tablets. This method is convenient and allows for real-time data collection.
-
Social Media Monitoring: Data is collected from social media platforms to analyze trends, sentiments, user behavior, and public opinion. Social media APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are often used for data access.
-
Data Logging: Continuous recording of data over time is used in various fields, including environmental monitoring (e.g., weather stations), industrial processes, and performance monitoring (e.g., athletes' heart rate during a race).
-
Focus Groups: A moderator leads a discussion with a small group of participants to gather insights, opinions, and perceptions on a particular topic. Focus groups are common in market research and qualitative studies.
-
Diaries and Journals: Participants keep records of their experiences, thoughts, or behaviors over a specified period. This method is often used to study daily routines or personal reflections.
The choice of data collection method depends on research goals, the type of data needed (quantitative or qualitative), available resources, ethical considerations, and practical constraints. Researchers often employ a combination of methods to triangulate data and enhance the validity and reliability of their findings.
Data Collection Tools
Data collection tools are software or hardware solutions designed to facilitate the process of gathering, storing, and managing data from various sources. These tools are used in research, business, and various other fields to streamline data collection and improve its accuracy and efficiency. Here are some common types of data collection tools:
-
Online Survey Tools: Online survey platforms like SurveyMonkey, Google Forms, and Qualtrics allow users to create and distribute surveys and questionnaires over the internet. They offer features for designing surveys, collecting responses, and analyzing results.
-
Mobile Data Collection Apps: Mobile apps like Survey123 (Esri), Fulcrum, and QuickTapSurvey enable data collection in the field using smartphones and tablets. Users can design custom forms, collect data offline, and sync it when connected to the internet.
-
Data Analytics Software: Tools like Microsoft Excel, R, Python (with libraries like Pandas), and SPSS are used to analyze and visualize data collected from various sources. They help in extracting insights and patterns from datasets.
-
Database Management Systems (DBMS): Systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, and MongoDB are used to store, organize, and manage large volumes of structured data. They are commonly employed in businesses and research institutions.
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software such as ArcGIS and QGIS is used for collecting and analyzing spatial data, including maps, GPS coordinates, and geographic features.
-
Data Collection APIs: Some online platforms and services offer APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow developers to integrate data collection capabilities into custom applications. For example, social media platforms like Twitter and Facebook offer APIs for data retrieval.
-
Data Logger Devices: Physical devices like data loggers and sensors are used in various industries to automatically collect data, such as temperature, humidity, and pressure, and store it for later analysis.
-
Document Scanners and OCR Software: Tools like Adobe Acrobat and OCR (Optical Character Recognition) software can be used to digitize and collect data from paper documents, such as forms, invoices, and contracts.
-
Web Scraping Tools: Tools like Beautiful Soup, Scrapy, and Octoparse automate the extraction of data from websites and web pages. They are commonly used for web-based data collection.
-
Audio and Video Recording Software: Researchers and professionals often use audio and video recording tools to capture interviews, meetings, and events. Transcription software can convert spoken words into text data for analysis.
-
Qualitative Data Analysis Software: Software like NVivo and MAXQDA is specifically designed for researchers collecting qualitative data (e.g., interviews, focus groups). They assist in organizing, coding, and analyzing textual or multimedia data.
-
Biometric Data Collection Tools: Devices like fingerprint scanners, facial recognition cameras, and heart rate monitors are used to collect biometric data for security, healthcare, and other applications.
-
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain-based tools can ensure the secure and transparent collection and storage of data, making them suitable for applications where data integrity and immutability are critical.
-
Machine Learning and AI Platforms: Advanced machine learning and AI platforms can assist in data collection by automating processes, recognizing patterns, and making predictions based on existing data.
The choice of data collection tools depends on the specific requirements of a project, the type of data being collected, and the available resources. In many cases, a combination of tools may be used to capture, store, and analyze data effectively.
The Importance of Ensuring Accurate and Appropriate Data Collection
Ensuring accurate and appropriate data collection is of paramount importance in research, decision-making, and various fields for several compelling reasons:
-
Reliable Results: Accurate data leads to trustworthy research findings and better decision-making.
-
Credibility: Accurate data enhances the credibility of reports and studies.
-
Effective Decisions: It supports informed and effective decision-making.
-
Efficiency: Appropriate data collection saves time and resources.
-
Ethics and Privacy: It respects ethical standards and privacy concerns.
-
Reducing Bias: It helps reduce bias in research and analysis.
-
Long-Term Impact: Inaccurate data can have lasting consequences.
-
Resource Allocation: Guides efficient resource allocation.
-
Reproducibility: Facilitates the reproducibility of experiments.
-
Customer Satisfaction: Improves customer satisfaction in businesses.
-
Public Health and Safety: Crucial for public health and safety monitoring.
-
Environmental Conservation: Supports conservation efforts.
-
Innovation: Drives innovation and improvement in various fields.
Issues Related to Maintaining the Integrity of Data Collection
Maintaining the integrity of data collection is essential to ensure that data is accurate, reliable, and free from bias or manipulation. However, several issues can compromise data integrity. Here are some common issues related to maintaining data collection integrity:
-
Sampling Bias: When the sample used for data collection is not representative of the larger population, it can introduce bias into the results. This can occur due to non-random sampling methods or inadequate sample sizes.
-
Selection Bias: Researchers or data collectors may inadvertently favor certain groups or individuals when selecting participants or data sources, leading to biased data.
-
Non-Response Bias: If a significant portion of the selected participants does not respond to surveys or data requests, the results may not accurately represent the entire population.
-
Measurement Error: Errors in data measurement or data entry can occur due to human error, faulty equipment, or inconsistent measurement standards. These errors can introduce inaccuracies into the collected data.
-
Data Tampering: Deliberate manipulation or tampering with data can occur for various reasons, such as fraud, academic misconduct, or political motives. Maintaining data security and access controls is crucial to prevent such issues.
-
Data Privacy Concerns: Collecting sensitive or personally identifiable information without proper consent or security measures can lead to privacy breaches and ethical dilemmas.
-
Response Bias: Respondents may provide inaccurate or socially desirable responses, especially in surveys or interviews, leading to biased data.
-
Observer Bias: When data is collected through observations, the observer's personal biases and interpretations can influence the data collected.
-
Researcher Bias: Researchers' own beliefs, preferences, or expectations can inadvertently influence data collection, analysis, or interpretation, leading to bias.
-
Missing Data: Incomplete or missing data points can impact the overall integrity of the dataset, potentially leading to incomplete or biased conclusions.
-
Survey Question Bias: Poorly constructed survey questions or leading questions can unintentionally guide respondents toward certain answers, skewing the results.
-
Temporal Bias: Data collected at specific times or seasons may not accurately represent long-term trends or conditions.
-
Cross-Cultural Bias: Data collected in one cultural context may not be applicable or relevant in another, leading to cultural bias.
-
Lack of Data Documentation: Inadequate documentation of data collection methods, protocols, and procedures can hinder transparency and replication efforts.
-
Conflict of Interest: Financial or personal interests of data collectors or researchers can compromise the objectivity and integrity of data collection.
To address these issues and maintain data collection integrity, it is essential to implement rigorous data collection protocols, ensure transparency, use standardized measurement tools, conduct thorough data validation and verification, and adhere to ethical guidelines. Additionally, peer review, data audits, and data quality assessments can help identify and mitigate potential problems related to data integrity.
What are Common Challenges in Data Collection?
Data collection can be a complex and challenging process, and researchers, organizations, and individuals often encounter various obstacles. Here are some common challenges in data collection:
-
Selection Bias: It can be challenging to ensure that the data collected is representative of the entire population or target group. Biased sampling methods or non-response bias can lead to skewed results.
-
Data Quality: Maintaining data accuracy, completeness, and consistency can be difficult. Data may be prone to errors, duplications, or missing values, affecting its reliability.
-
Resource Constraints: Limited time, budget, and human resources can hinder data collection efforts, especially in large-scale projects.
-
Privacy Concerns: Collecting sensitive or personally identifiable information must be done with care to ensure data privacy and compliance with relevant regulations.
-
Ethical Considerations: Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines when collecting data, which can be challenging when dealing with vulnerable populations or sensitive topics.
-
Data Security: Safeguarding data against breaches, theft, or unauthorized access is crucial. Data breaches can have serious consequences for individuals and organizations.
-
Data Collection Instruments: Developing and testing data collection instruments, such as surveys or questionnaires, requires careful consideration to ensure they are valid and reliable.
-
Technological Challenges: Implementing data collection technologies, especially in remote or resource-constrained areas, can be challenging. Issues like connectivity and compatibility may arise.
-
Non-Response: Collecting data from reluctant or uncooperative participants can be difficult, leading to missing or incomplete data.
-
Data Entry Errors: Manual data entry can introduce errors, especially when transcribing data from paper to digital formats.
-
Language and Cultural Barriers: In cross-cultural research, language and cultural differences may affect data collection and interpretation.
-
Data Verification: Verifying the accuracy of collected data can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
-
Data Bias: Data may be influenced by the bias or subjectivity of the data collector, respondent, or observer.
-
Data Volume: Dealing with large volumes of data can be challenging, requiring efficient storage, processing, and analysis solutions.
-
Temporal Changes: Data collected at different times may not be directly comparable due to changing conditions or external factors.
-
Data Ownership: Clarifying data ownership and usage rights can be a challenge, especially in collaborative research or data-sharing initiatives.
-
Data Governance: Establishing clear data governance policies and procedures is essential for managing data collection efforts effectively.
-
Environmental Factors: In some cases, data collection may be affected by weather conditions, natural disasters, or other environmental factors.
-
Human Error: Mistakes made during the data collection process, such as misreading instruments or making errors in data recording, can impact data quality.
-
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that data collection activities comply with relevant laws and regulations can be complex, especially when conducting research across borders.
Addressing these challenges often requires careful planning, well-defined data collection protocols, the use of appropriate technology, rigorous quality control measures, and ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the data collection process. Collaborative efforts and expertise in data collection methodologies can also help overcome many of these challenges.
What are the Key Steps in the Data Collection Process?
The data collection process involves a series of key steps to gather information systematically and ensure the data's accuracy and reliability. Here are the fundamental steps in the data collection process:
-
Define Objectives: Clearly define the research or data collection objectives. Understand the purpose, scope, and goals of the data collection effort.
-
Select Data Sources: Identify the sources of data, which can include surveys, interviews, observations, existing databases, sensors, documents, or any other relevant sources.
-
Design Data Collection Instruments: Develop data collection instruments, such as surveys, questionnaires, interview guides, or observation protocols. Ensure they are clear, unbiased, and aligned with the research objectives.
-
Select Sampling Methods: If applicable, choose the appropriate sampling method (e.g., random sampling, stratified sampling) to select a representative subset of the population or dataset.
-
Pilot Testing: Test the data collection instruments and procedures with a small, representative group to identify and address any issues, such as unclear questions or logistical challenges.
-
Data Collection: Conduct the actual data collection activities according to the established protocols. Ensure consistency and uniformity in data collection procedures.
-
Data Entry: If data is collected in paper form, enter it into digital format. Implement quality control measures to minimize data entry errors.
-
Data Verification: Verify the accuracy and completeness of the collected data. This step may involve data cleaning and validation to identify and correct errors or inconsistencies.
-
Data Storage: Safely store the collected data in a secure and organized manner, whether in physical or digital format. Implement data security measures to protect sensitive information.
-
Data Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of the data collection process, including protocols, instruments, and any modifications made during the collection.
-
Data Analysis: If applicable, perform data analysis using appropriate statistical or analytical methods. Transform raw data into meaningful insights and findings.
-
Data Interpretation: Interpret the results of data analysis in the context of research objectives. Draw conclusions and make recommendations based on the data.
-
Report Findings: Communicate the results and findings through reports, presentations, or other appropriate channels. Clearly and transparently convey the insights derived from the data.
-
Data Archiving: Store the data for future reference or potential replication of the study. Ensure data is accessible and properly archived for compliance and transparency.
-
Ethical Considerations: Adhere to ethical standards throughout the data collection process, respecting privacy, informed consent, and any relevant legal or institutional requirements.
-
Quality Control: Implement quality control measures at various stages of data collection to minimize errors, bias, and inconsistencies.
-
Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitor the data collection process to identify and address any issues promptly. Make necessary adjustments as needed.
-
Feedback and Iteration: Collect feedback from stakeholders and team members involved in data collection. Use feedback to improve data collection procedures for future efforts.
-
Data Governance: Establish clear data governance policies and procedures to manage data collection, storage, and access effectively.
-
Documentation of Assumptions and Limitations: Clearly document any assumptions, limitations, or potential biases in the data collection process to provide context for the data's interpretation.
Effective data collection requires careful planning, attention to detail, and adherence to best practices. Following these key steps helps ensure that the data collected is of high quality, reliable, and suitable for analysis and decision-making.
Data Collection Considerations and Best Practices
Effective data collection involves careful consideration of various factors and adherence to best practices to ensure that the collected data is of high quality, reliable, and ethically sound. Here are some key data collection considerations and best practices:
-
Clearly Define Objectives: Begin by precisely defining the research or data collection objectives. Understand what information is needed and why it is important.
-
Ethical Considerations: Always prioritize ethical principles when collecting data. Obtain informed consent from participants, ensure data privacy and confidentiality, and comply with relevant ethical guidelines and regulations.
-
Select Appropriate Data Sources: Choose the most suitable data sources and methods for your research objectives. Consider whether primary data collection (gathering data firsthand) or secondary data (using existing data) is more appropriate.
-
Pilot Testing: Before full-scale data collection, conduct pilot tests or pre-tests to identify and rectify any issues with data collection instruments, such as surveys or questionnaires.
-
Sampling: If using sampling, select a representative sample that accurately reflects the population of interest. Ensure randomness and minimize selection bias.
-
Standardize Procedures: Maintain consistency in data collection procedures. Ensure that all data collectors follow the same protocols to reduce bias and increase data reliability.
-
Training: Properly train data collectors on data collection methods, instruments, and ethical considerations. Regularly update their training to stay informed about best practices.
-
Data Collection Tools: Use appropriate data collection tools and technologies. Ensure that instruments are clear, unbiased, and suitable for the target audience.
-
Data Entry and Validation: If collecting data manually, establish data entry protocols and validation procedures to minimize errors and ensure data accuracy.
-
Data Security: Safeguard data throughout the collection process. Use encryption, access controls, and secure storage methods to protect data from unauthorized access or breaches.
-
Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of the data collection process, including data collection protocols, instruments, and any modifications or issues encountered during collection.
-
Quality Control: Implement quality control measures at different stages of data collection to identify and rectify errors or inconsistencies promptly.
-
Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitor the data collection process for adherence to protocols, completeness, and quality. Address issues as they arise.
-
Data Validation: Cross-check data entries, validate data against predefined criteria, and ensure data is consistent and accurate.
-
Data Cleaning: After data collection, thoroughly clean and preprocess the data to handle missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies.
-
Data Storage and Archiving: Store data securely, ensuring backup and redundancy. Archive data for future reference and compliance with data retention policies.
-
Data Governance: Establish clear data governance policies and procedures to manage data collection, storage, and access effectively.
-
Feedback and Iteration: Gather feedback from data collectors and stakeholders to identify areas for improvement in data collection processes. Continuously refine methods based on feedback.
-
Data Documentation: Document any assumptions, limitations, or potential biases in the data collection process. Transparency is essential for the data's interpretation.
-
Data Reporting: Clearly report the methods, procedures, and findings of the data collection effort, allowing for transparency and reproducibility.
-
Data Dissemination: Share data appropriately, considering data-sharing agreements, copyrights, and licensing requirements.
-
Compliance: Ensure compliance with legal, regulatory, and institutional requirements related to data collection, especially when dealing with sensitive or personal information.
By carefully considering these factors and following best practices, data collectors can enhance the quality and reliability of the data collected, ultimately leading to more robust research findings and informed decision-making.
How to get course?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Data Science with R programming
FAQs
-
What is data collection, and why is it important?
Data collection is the process of gathering and capturing information or data from various sources for analysis, research, decision-making, or record-keeping. It is important because it provides the foundation for informed decisions, research, and problem-solving in various fields.
-
What are the common methods of data collection?
Common methods of data collection include surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, sensors and instruments, document analysis, web scraping, social media monitoring, sampling, and more.
-
What are the different types of data collected in research?
Data in research can be categorized as quantitative (numeric) or qualitative (non-numeric). Quantitative data includes numerical values, while qualitative data includes descriptions, narratives, and observations.
-
What are the essential steps in the data collection process?
Key steps include defining objectives, selecting data sources, designing data collection instruments, sampling (if applicable), pilot testing, data collection, data entry, data verification, data storage, analysis, interpretation, reporting, archiving, and addressing ethical considerations.
-
What tools and software are commonly used for data collection?
Common data collection tools and software include online survey platforms (e.g., SurveyMonkey), mobile data collection apps (e.g., Fulcrum), data analytics software (e.g., Excel, R), and geographic information systems (GIS) software (e.g., ArcGIS).
-
What are the challenges in data collection?
Challenges in data collection include issues related to sampling bias, data quality, resource constraints, privacy concerns, ethical considerations, data security, and potential biases in data collection methods.
-
What are some best practices for maintaining data collection integrity?
Best practices include defining clear objectives, ensuring ethical conduct, selecting appropriate data sources, pilot testing, proper training, data validation, documentation, quality control, and continuous monitoring.
-
How can data collection tools help streamline the process?
Data collection tools automate and streamline data capture, reduce errors, improve data accuracy, and provide efficient ways to gather and manage data, making the process more efficient and reliable.
-
What is the role of data collection in decision-making and research?
Data collection provides the evidence and insights necessary for informed decision-making, problem-solving, scientific research, and the generation of knowledge in various fields.
-
What precautions should be taken when collecting sensitive data?
When collecting sensitive data, it's essential to obtain informed consent, implement strong data security measures, adhere to ethical guidelines, and comply with privacy regulations to protect individuals' information.
Feasibility Study and Its Importance in Project Management
In the dynamic landscape of project management and business endeavors, the path to success is often paved with uncertainty. For every visionary project or entrepreneurial venture, there exists an inherent risk that can lead to unforeseen challenges, setbacks, or even failure. In this complex terrain, the beacon of clarity and guidance comes in the form of a "Feasibility Study." It is the compass that not only points to the direction of project viability but also illuminates the obstacles that lie ahead. This journey into the realm of feasibility studies unveils their pivotal role in project management, where informed decisions, meticulous analysis, and calculated risk mitigation converge to shape the destiny of projects and businesses. Join us as we delve into the significance of feasibility studies, understanding their multifaceted importance in steering the course of success.
Table of Contents
What is a Feasibility Study?
Understanding A Feasibility Study
Types of Feasibility Study
Importance of Feasibility Study
Benefits of a Feasibility Study
What Is Included in a Feasibility Study Report?
Tools for Conducting a Feasibility Study
Examples of a Feasibility Study
What is the Purpose of a Feasibility Study?
How Do You Write a Feasibility Study?
7 Steps to Do a Feasibility Study
How to Conduct a Feasibility Study
Feasibility Study vs. Business Plan
Reasons to Do or Not to Do a Feasibility Study
Conclusion
FAQs
What is a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study is a thorough examination of whether a proposed project or business idea is practical and likely to succeed. It involves analyzing factors like market demand, technical capabilities, financial viability, operational logistics, legal requirements, environmental impact, and potential risks. The study helps decision-makers determine whether it's worth pursuing the project or if adjustments are needed. Ultimately, it provides a clear recommendation on whether to go ahead with the project or not, based on a comprehensive assessment of all relevant factors.
Understanding A Feasibility Study
A feasibility study is a comprehensive analysis conducted during the early stages of project planning to determine the practicality and viability of a proposed project or business endeavor. It involves assessing various factors such as market demand, technical feasibility, financial considerations, operational logistics, legal and regulatory requirements, environmental impacts, and potential risks. The goal is to answer the fundamental question of whether the project is feasible and worth pursuing. A well-executed feasibility study provides decision-makers with valuable insights to make informed choices about whether to invest resources, time, and effort into the project or explore alternative options. Ultimately, it helps prevent costly mistakes by identifying potential challenges and opportunities early in the project's development.
Types of Feasibility Study
-
Market Feasibility Study: This type of study is essential when considering a new product or service. It assesses whether there is enough demand in the market for the proposed offering. Market feasibility examines factors such as target demographics, customer preferences, market trends, competition, and potential market size. The goal is to determine if there is a substantial and sustainable market for the product or service.
-
Technical Feasibility Study: When a project relies on specific technology or technical processes, a technical feasibility study is conducted. It evaluates whether the required technology and expertise are available or can be developed within the project's scope. This study also looks at potential technical challenges and obstacles that might hinder project implementation.
-
Financial Feasibility Study: Financial feasibility is crucial to assess the project's profitability and financial viability. It involves estimating all costs associated with the project, including initial investments, operating expenses, and maintenance costs. Revenue projections and cash flow analysis are also conducted to determine if the project can generate a positive return on investment (ROI).
-
Operational Feasibility Study: This study focuses on how the proposed project will operate in practical terms. It assesses whether the project can be effectively integrated into existing operations or if it requires significant changes to processes, staffing, and logistics. Operational feasibility helps ensure that the project can be executed smoothly and efficiently.
-
Legal and Regulatory Feasibility Study: Projects often need to navigate complex legal and regulatory landscapes. A legal and regulatory feasibility study examines whether the project complies with all relevant laws, regulations, permits, and industry-specific requirements. It identifies potential legal obstacles and outlines the steps necessary for legal and regulatory compliance.
Importance of Feasibility Study
The importance of a feasibility study in the context of project management and business decision-making cannot be overstated. Here are several key reasons why conducting a feasibility study is crucial:
-
Risk Identification and Mitigation: A feasibility study helps identify potential risks and challenges associated with a project. By recognizing these risks early, project managers and stakeholders can develop strategies to mitigate them effectively. This proactive approach minimizes the likelihood of unforeseen issues derailing the project later on.
-
Cost-Benefit Analysis: One of the primary purposes of a feasibility study is to assess the financial feasibility of a project. It involves estimating the costs of implementing the project and comparing them to the expected benefits. This analysis helps in determining whether the project will yield a positive return on investment (ROI). If the costs outweigh the benefits, it may not be financially viable.
-
Resource Allocation: Resource allocation is a critical aspect of project management. A feasibility study outlines the resources required for the project, including manpower, equipment, and materials. This information allows project managers to allocate resources efficiently and ensure that they are available when needed, reducing delays and cost overruns.
-
Alignment with Strategic Goals: Projects should align with an organization's strategic goals and objectives. A feasibility study assesses how the proposed project aligns with these strategic goals. If there is a mismatch, it provides an opportunity to refine the project's scope or reconsider its importance in the context of the organization's overarching strategy.
-
Stakeholder Buy-In: Feasibility studies involve engaging with key stakeholders, including sponsors, investors, and end-users. These stakeholders play a crucial role in the success of the project. The study helps in gaining their buy-in and support by providing them with a clear understanding of the project's goals, benefits, and potential risks.
-
Decision-Making Tool: A feasibility study serves as a decision-making tool for project sponsors and stakeholders. It provides them with the information needed to make an informed decision about whether to proceed with the project, revise its scope, or abandon it altogether. This ensures that resources are allocated to projects with a higher likelihood of success.
-
Project Viability Assessment: Feasibility studies assess the overall viability of a project. They consider various aspects, including market demand, technical feasibility, financial considerations, and operational logistics. This comprehensive evaluation helps in determining whether the project is worth pursuing and has a realistic chance of success.
-
Cost Control: By estimating project costs and potential cost overruns during the feasibility study, project managers can develop effective cost control measures. This proactive approach allows for better financial management throughout the project's lifecycle.
-
Time Efficiency: A feasibility study helps in setting realistic project timelines. By identifying potential delays and obstacles early on, project managers can plan and allocate resources more effectively, reducing the likelihood of project schedule disruptions.
-
Alternative Evaluation: Feasibility studies often explore alternative solutions or approaches to achieve project objectives. This allows decision-makers to compare different options and select the most feasible and cost-effective one.
In conclusion, a well-conducted feasibility study is an indispensable tool in project management and business decision-making. It provides a structured and systematic approach to assess a project's feasibility, risks, costs, and benefits, ultimately leading to more informed and successful project outcomes.
Benefits of a Feasibility Study
A feasibility study offers a multitude of benefits that are invaluable to organizations and stakeholders contemplating new projects or business ventures. Firstly, it serves as a risk mitigation tool by uncovering potential challenges and obstacles early in the project's conceptualization phase, enabling the development of strategies to address these concerns proactively. Furthermore, a well-executed feasibility study empowers decision-makers with comprehensive information and data, facilitating informed choices regarding whether to proceed with the project, modify its scope, or abandon it altogether. Financial feasibility studies, a key component, provide financial clarity by estimating costs, revenue projections, and profitability prospects, ensuring alignment with budget constraints. Resource allocation becomes more efficient, as the study identifies the resources needed and helps prevent delays or shortages. Additionally, it ensures that the project aligns with an organization's strategic goals, fosters stakeholder buy-in, and assesses environmental and social responsibility. In essence, a feasibility study is an essential compass guiding project success by minimizing risks, optimizing resources, and ensuring strategic alignment.
What Is Included in a Feasibility Study Report?
A comprehensive feasibility study report typically includes the following key sections and information:
-
Executive Summary: This section provides a concise overview of the entire feasibility study, summarizing its main findings and recommendations. It is often the first section decision-makers read, so it should effectively convey the project's viability and key takeaways.
-
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for the study by explaining the purpose, scope, and objectives of the feasibility study. It also introduces the project or business idea being evaluated.
-
Project Description: This section provides a detailed description of the proposed project, including its goals, objectives, and scope. It outlines what the project aims to achieve and its intended outcomes.
-
Market Analysis: In this section, the study delves into the market feasibility, examining factors such as market size, growth potential, target demographics, competition, and customer demand. It also assesses market trends and dynamics.
-
Technical Analysis: The technical analysis evaluates the technical feasibility of the project. It considers the technology, equipment, and infrastructure required, as well as potential technical challenges and solutions. It may also include information on suppliers and technology partners.
-
Financial Analysis: The financial analysis is a critical component. It includes detailed financial projections, cost estimates, revenue forecasts, and cash flow analysis. It assesses the project's financial feasibility, including its return on investment (ROI) and payback period.
-
Operational Analysis: This section focuses on the operational feasibility of the project. It looks at how the project will function in practical terms, including staffing requirements, processes, logistics, and supply chain considerations.
-
Legal and Regulatory Considerations: Here, the study addresses legal and regulatory feasibility by identifying the legal requirements, permits, licenses, and compliance issues relevant to the project. It also outlines strategies for ensuring compliance.
-
Environmental and Social Impact Assessment: This section assesses the potential environmental and social impacts of the project, including its sustainability, community acceptance, and corporate social responsibility considerations.
-
Risk Analysis: The risk analysis identifies potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project and provides recommendations for risk mitigation. It may include a risk matrix or assessment of key risks.
-
Alternative Solutions: Feasibility studies often explore alternative approaches or solutions to achieve the project's objectives. This section compares different options and provides rationale for the chosen approach.
-
Recommendations: Based on the analysis conducted throughout the study, this section presents clear and well-supported recommendations regarding whether to proceed with the project, make modifications, or abandon it. It outlines the rationale for the recommended course of action.
-
Appendices: The appendices contain supplementary information, such as detailed financial spreadsheets, market research data, technical specifications, and any other relevant documents that support the findings and conclusions of the feasibility study.
-
References: If the study includes external sources or references, a list of these sources should be provided in a reference section.
A well-structured feasibility study report serves as a comprehensive document that guides decision-makers in assessing the viability of a project or business venture. It should be clear, well-organized, and supported by data and analysis to ensure that stakeholders have the information needed to make informed decisions.
Tools for Conducting a Feasibility Study
-
Microsoft Excel: Use it for financial calculations and modeling.
-
Survey Software: Collect market data through tools like SurveyMonkey or Google Forms.
-
Market Research Tools: Access industry reports and trends with tools like Statista.
-
Project Management Software: Create timelines and track progress with tools like Trello.
-
Financial Software: For detailed financial projections, use QuickBooks or specialized financial modeling tools.
-
Research Databases: Access academic and industry data from online libraries and databases.
-
GIS Software: Analyze spatial data and site selection with tools like ArcGIS.
-
Risk Management Tools: Identify and manage project risks using tools like RiskWatch.
-
Business Plan Software: Structure your findings into a business plan with tools like LivePlan.
-
Presentation Tools: Communicate study results visually with software like PowerPoint.
-
Collaboration Tools: Facilitate teamwork with platforms like Microsoft Teams or Slack.
-
Document Management Systems: Organize and store project documents using software like SharePoint.
-
Decision Support Tools: Enhance decision-making with software like DecisionTools Suite for scenario analysis.
Examples of a Feasibility Study
Feasibility studies are conducted in various industries and for diverse purposes. Here are some examples of feasibility studies:
-
Real Estate Development: Before embarking on a real estate project, such as constructing a residential or commercial building, a feasibility study is conducted. It assesses the market demand for the property, construction costs, potential revenue from rentals or sales, and factors like zoning regulations and environmental impact.
-
Product Launch: When a company plans to launch a new product, a feasibility study is conducted to determine if there's a market for it. It includes market research to gauge customer interest, pricing strategies, manufacturing or production costs, and potential profitability.
-
Restaurant Opening: Before opening a new restaurant, a feasibility study is conducted to assess factors like location, target market, competition, menu pricing, and operating costs. It helps in understanding whether the restaurant can be profitable in a specific area.
-
Technology Start-up: Tech entrepreneurs often conduct feasibility studies to evaluate the viability of their software or app ideas. This includes assessing market demand, development costs, potential revenue streams, and competition in the tech sector.
-
Infrastructure Projects: Large-scale infrastructure projects like bridges, highways, or public transportation systems require feasibility studies to assess technical, financial, and environmental factors. These studies help determine if the project is practical and cost-effective.
-
Hotel Expansion: When a hotel chain plans to expand by building a new location, a feasibility study examines the market conditions, demand for hotel rooms in the area, construction and operational costs, and the potential return on investment.
-
Agricultural Ventures: Farmers and agricultural entrepreneurs may conduct feasibility studies before starting a new crop or livestock farming operation. The study evaluates factors like soil quality, market demand for the products, input costs, and expected yields.
-
Renewable Energy Projects: Feasibility studies are essential for renewable energy projects like wind farms or solar power plants. They assess factors such as available resources, technology feasibility, regulatory requirements, and financial viability.
-
Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals and healthcare organizations may conduct feasibility studies when planning to build new medical facilities. These studies analyze factors such as patient demand, location suitability, construction costs, and long-term operational expenses.
-
Manufacturing Plants: Before setting up a new manufacturing plant, businesses conduct feasibility studies to determine the feasibility of production, supply chain logistics, labor costs, and market demand for the products.
-
Educational Institutions: Feasibility studies are used by educational institutions to assess whether it's viable to expand or build new facilities, launch new academic programs, or enter new markets. These studies consider factors like enrollment projections, budget requirements, and competitive landscape.
-
Tourism and Hospitality: In the tourism sector, feasibility studies are conducted to evaluate the potential of opening new resorts, amusement parks, or tourist attractions. These studies analyze market demand, location, infrastructure requirements, and investment costs.
These are just a few examples of feasibility studies in different domains. The specific elements and focus of a feasibility study can vary widely depending on the nature of the project or business venture.
What is the Purpose of a Feasibility Study?
The primary purpose of a feasibility study is to comprehensively evaluate the viability and potential success of a proposed project or business endeavor. This study serves as a crucial decision-making tool, enabling stakeholders to assess the project's feasibility, risks, and financial viability. By identifying potential challenges and opportunities early on, a feasibility study helps mitigate risks and develop effective strategies for success. It aligns the project with an organization's strategic goals, facilitates resource allocation, and ensures that resources are directed toward projects with a high likelihood of achieving positive returns on investment. Additionally, it fosters stakeholder buy-in and provides a clear roadmap for project execution. Ultimately, the overarching goal of a feasibility study is to inform well-informed decisions about whether to pursue, modify, or abandon the project, thereby promoting efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and the likelihood of successful outcomes.
How Do You Write a Feasibility Study?
Writing a feasibility study involves a structured and systematic approach to assessing the viability of a proposed project or business venture. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to write a feasibility study:
-
Project Introduction:
-
Begin with an introduction that provides context for the study. Explain the purpose of the study, the project's objectives, and its significance.
-
Executive Summary:
-
Create an executive summary that offers a concise overview of the entire feasibility study, summarizing key findings, recommendations, and conclusions. This section should be clear and compelling as it's often the first part decision-makers read.
-
Background Information:
-
Provide background information on the project, including its history, the problem it aims to address, and any relevant historical data or context.
-
Scope of Work:
-
Clearly define the scope of the feasibility study. Specify the boundaries and limitations of the study, including what will and will not be included.
-
Methodology:
-
Explain the research methods and tools used to collect and analyze data. This section should outline the approach to market research, financial analysis, risk assessment, and other key aspects of the study.
-
Market Analysis:
-
Evaluate the market feasibility of the project by examining factors such as market size, growth potential, target demographics, competition, and customer demand. Present relevant market research data and trends.
-
Technical Analysis:
-
Assess the technical feasibility of the project, focusing on the required technology, equipment, and infrastructure. Address potential technical challenges and outline solutions.
-
Financial Analysis:
-
Conduct a detailed financial analysis, including cost estimations, revenue projections, cash flow analysis, and return on investment (ROI) calculations. Evaluate the project's financial viability.
-
Operational Analysis:
-
Evaluate the operational feasibility of the project by analyzing how it will function in practical terms. Consider staffing requirements, processes, logistics, and supply chain considerations.
-
Legal and Regulatory Assessment:
-
Examine legal and regulatory requirements relevant to the project. Identify permits, licenses, compliance issues, and strategies for ensuring legal conformity.
-
Environmental and Social Impact Assessment:
-
Assess the potential environmental and social impacts of the project, including sustainability considerations and community acceptance.
-
Risk Analysis:
-
Identify and evaluate potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project. Develop risk mitigation strategies and present them in this section.
-
Alternative Solutions:
-
Explore alternative approaches or solutions to achieve the project's objectives. Compare different options and provide a rationale for the chosen approach.
-
Recommendations:
-
Based on the analysis conducted throughout the study, present clear and well-supported recommendations regarding whether to proceed with the project, modify its scope, or abandon it. Provide a summary of the key findings that support the recommendations.
-
Appendices:
-
Include supplementary information in the appendices, such as detailed financial spreadsheets, market research data, technical specifications, and any other relevant documents that support the study's findings.
-
References:
-
If the study includes external sources or references, provide a list of these sources in a reference section.
-
Conclusion:
-
Conclude the feasibility study by summarizing the main findings, highlighting the recommended course of action, and reiterating the importance of the study's conclusions.
-
Final Review:
-
Before finalizing the report, conduct a thorough review for accuracy, clarity, and coherence. Ensure that the report is well-organized and follows a logical flow.
7 Steps to Do a Feasibility Study
Performing a feasibility study involves a systematic process to assess the viability of a project or business idea. Here are seven essential steps to conduct a feasibility study:
-
Define the Project Scope and Objectives:
-
Clearly outline the purpose, goals, and objectives of the feasibility study. Determine the specific questions the study should answer and the key aspects to be evaluated.
-
Gather Information and Data:
-
Collect all relevant data and information needed for the study. This includes market research, technical specifications, financial data, legal and regulatory requirements, and any other pertinent details.
-
Market Research and Analysis:
-
Evaluate the market feasibility by researching and analyzing factors like market size, growth trends, competition, customer preferences, and demand for the product or service.
-
Technical Analysis:
-
Assess the technical feasibility by examining the required technology, equipment, and infrastructure. Identify potential technical challenges and determine if they can be overcome.
-
Financial Analysis:
-
Conduct a comprehensive financial analysis, including cost estimations, revenue projections, cash flow analysis, and ROI calculations. Determine if the project is financially viable and can yield positive returns.
-
Operational Analysis:
-
Evaluate the operational feasibility of the project by analyzing how it will function in practical terms. Consider staffing needs, processes, logistics, and supply chain requirements.
-
Risk Assessment and Recommendations:
-
Identify and assess potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project. Develop strategies for risk mitigation. Based on the analysis, make clear and well-supported recommendations regarding whether to proceed with the project, make modifications, or abandon it. Summarize key findings and provide a concise roadmap for decision-makers.
How to Conduct a Feasibility Study
Performing a feasibility study involves a systematic process to assess the viability of a project or business idea. Here are seven essential steps to conduct a feasibility study:
-
Define the Project Scope and Objectives:
-
Clearly outline the purpose, goals, and objectives of the feasibility study. Determine the specific questions the study should answer and the key aspects to be evaluated.
-
Gather Information and Data:
-
Collect all relevant data and information needed for the study. This includes market research, technical specifications, financial data, legal and regulatory requirements, and any other pertinent details.
-
Market Research and Analysis:
-
Evaluate the market feasibility by researching and analyzing factors like market size, growth trends, competition, customer preferences, and demand for the product or service.
-
Technical Analysis:
-
Assess the technical feasibility by examining the required technology, equipment, and infrastructure. Identify potential technical challenges and determine if they can be overcome.
-
Financial Analysis:
-
Conduct a comprehensive financial analysis, including cost estimations, revenue projections, cash flow analysis, and ROI calculations. Determine if the project is financially viable and can yield positive returns.
-
Operational Analysis:
-
Evaluate the operational feasibility of the project by analyzing how it will function in practical terms. Consider staffing needs, processes, logistics, and supply chain requirements.
-
Risk Assessment and Recommendations:
-
Identify and assess potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project. Develop strategies for risk mitigation. Based on the analysis, make clear and well-supported recommendations regarding whether to proceed with the project, make modifications, or abandon it. Summarize key findings and provide a concise roadmap for decision-makers.
Feasibility Study vs. Business Plan
Feasibility Study vs. Business Plan:
Feasibility Study:
-
Purpose: The primary purpose of a feasibility study is to assess the viability and feasibility of a proposed project or business idea. It aims to answer the question, "Is this project or business concept feasible?"
-
Timing: Feasibility studies are typically conducted in the early stages of project development, often before significant resources are invested.
-
Scope: Feasibility studies have a broader scope and focus on evaluating various aspects of the project, including market feasibility, technical feasibility, financial feasibility, legal and regulatory considerations, operational feasibility, and risk assessment.
-
Analysis: Feasibility studies involve in-depth analysis of data and information related to the project, such as market research, cost estimation, revenue projections, and risk assessment.
-
Outcome: The primary outcome of a feasibility study is to provide stakeholders with a recommendation on whether to proceed with the project, modify its scope, or abandon it. It helps stakeholders make informed decisions.
Business Plan:
-
Purpose: A business plan serves as a detailed blueprint for the actual operation and management of a business. It outlines the goals, strategies, and operations of the business and provides a roadmap for its growth and development.
-
Timing: Business plans are typically developed after the feasibility study, once the decision to proceed with the project has been made. They are often used when seeking financing or as a guide for day-to-day operations.
-
Scope: Business plans focus on the specific strategies, tactics, and operations required to run the business successfully. They include detailed information on marketing, sales, organizational structure, funding requirements, revenue and expense projections, and long-term goals.
-
Analysis: While business plans incorporate the findings from the feasibility study, they go beyond feasibility analysis and delve into the practical aspects of running the business. Business plans include detailed financial projections and operational plans.
-
Outcome: The primary outcome of a business plan is to provide a comprehensive and actionable roadmap for the business. It is used for securing financing, attracting investors, guiding day-to-day operations, and measuring the business's performance against its objectives.
In summary, a feasibility study assesses the initial viability of a project or business idea and informs the decision to proceed or not, while a business plan is a detailed document that outlines how a business will operate, grow, and achieve its goals once the decision to move forward has been made. Both documents are crucial in the lifecycle of a business or project, with the feasibility study informing the business plan's foundation.
Reasons to Do or Not to Do a Feasibility Study
Reasons to Do a Feasibility Study:
-
Risk Assessment: A feasibility study helps identify potential risks and challenges associated with the project. It provides an opportunity to assess and mitigate these risks proactively.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Conducting a feasibility study ensures that decision-makers have comprehensive information to make informed choices about whether to proceed with the project, make modifications, or abandon it.
-
Financial Clarity: Financial feasibility studies estimate costs, revenue projections, and potential profitability. This clarity ensures that the project aligns with budget constraints and has a potential for positive returns on investment.
-
Resource Optimization: Feasibility studies outline the resources required for the project, such as personnel, equipment, materials, and technology. This allows for efficient resource allocation and prevents delays or resource shortages.
-
Strategic Alignment: Projects should align with an organization's strategic goals and objectives. A feasibility study assesses this alignment, ensuring that the project supports the organization's overarching strategy.
Reasons Not to Do a Feasibility Study:
-
Low Complexity: For very simple projects with minimal investment and known market demand, a full-scale feasibility study may be unnecessary. However, even small projects can benefit from some form of preliminary assessment.
-
Urgency: In cases where time is of the essence, such as responding to rapidly changing market conditions, conducting a lengthy feasibility study may not be feasible. In such situations, a rapid assessment or a simpler analysis may be more appropriate.
-
Cost Concerns: Some organizations may be hesitant to invest in a feasibility study due to budget constraints. However, failing to conduct a feasibility study can lead to much higher costs if the project encounters unforeseen issues.
-
Obvious Viability: In rare cases where the viability of a project is self-evident and unquestionable, skipping a feasibility study might be considered. However, a cursory assessment is still advisable to confirm assumptions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a feasibility study is an indispensable tool in the process of evaluating the potential success and viability of a proposed project or business venture. It serves as a critical decision-making guide, providing stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of the project's feasibility, risks, and financial viability. By identifying potential challenges and opportunities early on, a feasibility study enables proactive risk mitigation and the development of effective strategies for success. It aligns the project with an organization's strategic objectives, facilitates resource allocation, and ensures that resources are directed toward endeavors with a high likelihood of achieving positive returns. Furthermore, it fosters stakeholder buy-in and provides a clear roadmap for project execution. Ultimately, the overarching goal of a feasibility study is to inform well-informed decisions about whether to pursue, modify, or abandon the project, thereby promoting efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and the likelihood of successful outcomes. In essence, a well-executed feasibility study lays the foundation for a project's success and serves as a cornerstone for prudent decision-making in the world of business and project management.
FAQs
1. What is a feasibility study?
A feasibility study is an in-depth analysis and evaluation of a proposed project or business venture to determine its viability and potential for success. It assesses various aspects such as market feasibility, technical feasibility, financial feasibility, and operational feasibility.
2. Why is a feasibility study important?
A feasibility study is crucial because it helps stakeholders make informed decisions about whether to proceed with a project, modify its scope, or abandon it. It identifies risks, assesses costs, and evaluates the potential for profitability, thereby reducing uncertainty and minimizing the likelihood of project failure.
3. What are the key components of a feasibility study?
A feasibility study typically includes sections on market analysis, technical analysis, financial analysis, operational analysis, legal and regulatory considerations, environmental and social impact assessment, risk analysis, and recommendations.
4. How is a feasibility study different from a business plan?
A feasibility study assesses the initial viability of a project, while a business plan provides a detailed roadmap for running and growing a business after the decision to proceed has been made. Feasibility studies inform the foundation of a business plan.
5. When should you conduct a feasibility study?
Feasibility studies are typically conducted in the early stages of project development, before significant resources are invested. However, they can also be conducted at any point when there is uncertainty about the feasibility of a project.
6. What is the role of market research in a feasibility study?
Market research is a crucial component of a feasibility study as it assesses market demand, competition, customer preferences, and trends. It helps determine if there is a market for the project's products or services.
7. How do you assess financial feasibility in a feasibility study?
Financial feasibility is assessed by estimating project costs, revenue projections, cash flow analysis, and calculating metrics like return on investment (ROI) and payback period. It determines if the project is financially viable.
8. What are the benefits of conducting a feasibility study?
Benefits of a feasibility study include risk mitigation, informed decision-making, financial clarity, efficient resource allocation, strategic alignment, stakeholder buy-in, and the identification of potential issues early in the project.
9. Are there situations where a feasibility study may not be necessary?
In some cases, for very simple projects with minimal investment and known market demand, a full-scale feasibility study may be considered unnecessary. However, even small projects can benefit from a preliminary assessment.
10. How do you present the findings of a feasibility study to stakeholders? -
The findings of a feasibility study are typically presented in a structured report format, with clear sections covering each aspect of the study. An executive summary is often included to provide a concise overview of the key findings and recommendations. Presentations and discussions with stakeholders may also be part of the communication process.
Read More
In the dynamic landscape of project management and business endeavors, the path to success is often paved with uncertainty. For every visionary project or entrepreneurial venture, there exists an inherent risk that can lead to unforeseen challenges, setbacks, or even failure. In this complex terrain, the beacon of clarity and guidance comes in the form of a "Feasibility Study." It is the compass that not only points to the direction of project viability but also illuminates the obstacles that lie ahead. This journey into the realm of feasibility studies unveils their pivotal role in project management, where informed decisions, meticulous analysis, and calculated risk mitigation converge to shape the destiny of projects and businesses. Join us as we delve into the significance of feasibility studies, understanding their multifaceted importance in steering the course of success.
Table of Contents
What is a Feasibility Study?
Understanding A Feasibility Study
Types of Feasibility Study
Importance of Feasibility Study
Benefits of a Feasibility Study
What Is Included in a Feasibility Study Report?
Tools for Conducting a Feasibility Study
Examples of a Feasibility Study
What is the Purpose of a Feasibility Study?
How Do You Write a Feasibility Study?
7 Steps to Do a Feasibility Study
How to Conduct a Feasibility Study
Feasibility Study vs. Business Plan
Reasons to Do or Not to Do a Feasibility Study
Conclusion
FAQs
What is a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study is a thorough examination of whether a proposed project or business idea is practical and likely to succeed. It involves analyzing factors like market demand, technical capabilities, financial viability, operational logistics, legal requirements, environmental impact, and potential risks. The study helps decision-makers determine whether it's worth pursuing the project or if adjustments are needed. Ultimately, it provides a clear recommendation on whether to go ahead with the project or not, based on a comprehensive assessment of all relevant factors.
Understanding A Feasibility Study
A feasibility study is a comprehensive analysis conducted during the early stages of project planning to determine the practicality and viability of a proposed project or business endeavor. It involves assessing various factors such as market demand, technical feasibility, financial considerations, operational logistics, legal and regulatory requirements, environmental impacts, and potential risks. The goal is to answer the fundamental question of whether the project is feasible and worth pursuing. A well-executed feasibility study provides decision-makers with valuable insights to make informed choices about whether to invest resources, time, and effort into the project or explore alternative options. Ultimately, it helps prevent costly mistakes by identifying potential challenges and opportunities early in the project's development.
Types of Feasibility Study
-
Market Feasibility Study: This type of study is essential when considering a new product or service. It assesses whether there is enough demand in the market for the proposed offering. Market feasibility examines factors such as target demographics, customer preferences, market trends, competition, and potential market size. The goal is to determine if there is a substantial and sustainable market for the product or service.
-
Technical Feasibility Study: When a project relies on specific technology or technical processes, a technical feasibility study is conducted. It evaluates whether the required technology and expertise are available or can be developed within the project's scope. This study also looks at potential technical challenges and obstacles that might hinder project implementation.
-
Financial Feasibility Study: Financial feasibility is crucial to assess the project's profitability and financial viability. It involves estimating all costs associated with the project, including initial investments, operating expenses, and maintenance costs. Revenue projections and cash flow analysis are also conducted to determine if the project can generate a positive return on investment (ROI).
-
Operational Feasibility Study: This study focuses on how the proposed project will operate in practical terms. It assesses whether the project can be effectively integrated into existing operations or if it requires significant changes to processes, staffing, and logistics. Operational feasibility helps ensure that the project can be executed smoothly and efficiently.
-
Legal and Regulatory Feasibility Study: Projects often need to navigate complex legal and regulatory landscapes. A legal and regulatory feasibility study examines whether the project complies with all relevant laws, regulations, permits, and industry-specific requirements. It identifies potential legal obstacles and outlines the steps necessary for legal and regulatory compliance.
Importance of Feasibility Study
The importance of a feasibility study in the context of project management and business decision-making cannot be overstated. Here are several key reasons why conducting a feasibility study is crucial:
-
Risk Identification and Mitigation: A feasibility study helps identify potential risks and challenges associated with a project. By recognizing these risks early, project managers and stakeholders can develop strategies to mitigate them effectively. This proactive approach minimizes the likelihood of unforeseen issues derailing the project later on.
-
Cost-Benefit Analysis: One of the primary purposes of a feasibility study is to assess the financial feasibility of a project. It involves estimating the costs of implementing the project and comparing them to the expected benefits. This analysis helps in determining whether the project will yield a positive return on investment (ROI). If the costs outweigh the benefits, it may not be financially viable.
-
Resource Allocation: Resource allocation is a critical aspect of project management. A feasibility study outlines the resources required for the project, including manpower, equipment, and materials. This information allows project managers to allocate resources efficiently and ensure that they are available when needed, reducing delays and cost overruns.
-
Alignment with Strategic Goals: Projects should align with an organization's strategic goals and objectives. A feasibility study assesses how the proposed project aligns with these strategic goals. If there is a mismatch, it provides an opportunity to refine the project's scope or reconsider its importance in the context of the organization's overarching strategy.
-
Stakeholder Buy-In: Feasibility studies involve engaging with key stakeholders, including sponsors, investors, and end-users. These stakeholders play a crucial role in the success of the project. The study helps in gaining their buy-in and support by providing them with a clear understanding of the project's goals, benefits, and potential risks.
-
Decision-Making Tool: A feasibility study serves as a decision-making tool for project sponsors and stakeholders. It provides them with the information needed to make an informed decision about whether to proceed with the project, revise its scope, or abandon it altogether. This ensures that resources are allocated to projects with a higher likelihood of success.
-
Project Viability Assessment: Feasibility studies assess the overall viability of a project. They consider various aspects, including market demand, technical feasibility, financial considerations, and operational logistics. This comprehensive evaluation helps in determining whether the project is worth pursuing and has a realistic chance of success.
-
Cost Control: By estimating project costs and potential cost overruns during the feasibility study, project managers can develop effective cost control measures. This proactive approach allows for better financial management throughout the project's lifecycle.
-
Time Efficiency: A feasibility study helps in setting realistic project timelines. By identifying potential delays and obstacles early on, project managers can plan and allocate resources more effectively, reducing the likelihood of project schedule disruptions.
-
Alternative Evaluation: Feasibility studies often explore alternative solutions or approaches to achieve project objectives. This allows decision-makers to compare different options and select the most feasible and cost-effective one.
In conclusion, a well-conducted feasibility study is an indispensable tool in project management and business decision-making. It provides a structured and systematic approach to assess a project's feasibility, risks, costs, and benefits, ultimately leading to more informed and successful project outcomes.
Benefits of a Feasibility Study
A feasibility study offers a multitude of benefits that are invaluable to organizations and stakeholders contemplating new projects or business ventures. Firstly, it serves as a risk mitigation tool by uncovering potential challenges and obstacles early in the project's conceptualization phase, enabling the development of strategies to address these concerns proactively. Furthermore, a well-executed feasibility study empowers decision-makers with comprehensive information and data, facilitating informed choices regarding whether to proceed with the project, modify its scope, or abandon it altogether. Financial feasibility studies, a key component, provide financial clarity by estimating costs, revenue projections, and profitability prospects, ensuring alignment with budget constraints. Resource allocation becomes more efficient, as the study identifies the resources needed and helps prevent delays or shortages. Additionally, it ensures that the project aligns with an organization's strategic goals, fosters stakeholder buy-in, and assesses environmental and social responsibility. In essence, a feasibility study is an essential compass guiding project success by minimizing risks, optimizing resources, and ensuring strategic alignment.
What Is Included in a Feasibility Study Report?
A comprehensive feasibility study report typically includes the following key sections and information:
-
Executive Summary: This section provides a concise overview of the entire feasibility study, summarizing its main findings and recommendations. It is often the first section decision-makers read, so it should effectively convey the project's viability and key takeaways.
-
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for the study by explaining the purpose, scope, and objectives of the feasibility study. It also introduces the project or business idea being evaluated.
-
Project Description: This section provides a detailed description of the proposed project, including its goals, objectives, and scope. It outlines what the project aims to achieve and its intended outcomes.
-
Market Analysis: In this section, the study delves into the market feasibility, examining factors such as market size, growth potential, target demographics, competition, and customer demand. It also assesses market trends and dynamics.
-
Technical Analysis: The technical analysis evaluates the technical feasibility of the project. It considers the technology, equipment, and infrastructure required, as well as potential technical challenges and solutions. It may also include information on suppliers and technology partners.
-
Financial Analysis: The financial analysis is a critical component. It includes detailed financial projections, cost estimates, revenue forecasts, and cash flow analysis. It assesses the project's financial feasibility, including its return on investment (ROI) and payback period.
-
Operational Analysis: This section focuses on the operational feasibility of the project. It looks at how the project will function in practical terms, including staffing requirements, processes, logistics, and supply chain considerations.
-
Legal and Regulatory Considerations: Here, the study addresses legal and regulatory feasibility by identifying the legal requirements, permits, licenses, and compliance issues relevant to the project. It also outlines strategies for ensuring compliance.
-
Environmental and Social Impact Assessment: This section assesses the potential environmental and social impacts of the project, including its sustainability, community acceptance, and corporate social responsibility considerations.
-
Risk Analysis: The risk analysis identifies potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project and provides recommendations for risk mitigation. It may include a risk matrix or assessment of key risks.
-
Alternative Solutions: Feasibility studies often explore alternative approaches or solutions to achieve the project's objectives. This section compares different options and provides rationale for the chosen approach.
-
Recommendations: Based on the analysis conducted throughout the study, this section presents clear and well-supported recommendations regarding whether to proceed with the project, make modifications, or abandon it. It outlines the rationale for the recommended course of action.
-
Appendices: The appendices contain supplementary information, such as detailed financial spreadsheets, market research data, technical specifications, and any other relevant documents that support the findings and conclusions of the feasibility study.
-
References: If the study includes external sources or references, a list of these sources should be provided in a reference section.
A well-structured feasibility study report serves as a comprehensive document that guides decision-makers in assessing the viability of a project or business venture. It should be clear, well-organized, and supported by data and analysis to ensure that stakeholders have the information needed to make informed decisions.
Tools for Conducting a Feasibility Study
-
Microsoft Excel: Use it for financial calculations and modeling.
-
Survey Software: Collect market data through tools like SurveyMonkey or Google Forms.
-
Market Research Tools: Access industry reports and trends with tools like Statista.
-
Project Management Software: Create timelines and track progress with tools like Trello.
-
Financial Software: For detailed financial projections, use QuickBooks or specialized financial modeling tools.
-
Research Databases: Access academic and industry data from online libraries and databases.
-
GIS Software: Analyze spatial data and site selection with tools like ArcGIS.
-
Risk Management Tools: Identify and manage project risks using tools like RiskWatch.
-
Business Plan Software: Structure your findings into a business plan with tools like LivePlan.
-
Presentation Tools: Communicate study results visually with software like PowerPoint.
-
Collaboration Tools: Facilitate teamwork with platforms like Microsoft Teams or Slack.
-
Document Management Systems: Organize and store project documents using software like SharePoint.
-
Decision Support Tools: Enhance decision-making with software like DecisionTools Suite for scenario analysis.
Examples of a Feasibility Study
Feasibility studies are conducted in various industries and for diverse purposes. Here are some examples of feasibility studies:
-
Real Estate Development: Before embarking on a real estate project, such as constructing a residential or commercial building, a feasibility study is conducted. It assesses the market demand for the property, construction costs, potential revenue from rentals or sales, and factors like zoning regulations and environmental impact.
-
Product Launch: When a company plans to launch a new product, a feasibility study is conducted to determine if there's a market for it. It includes market research to gauge customer interest, pricing strategies, manufacturing or production costs, and potential profitability.
-
Restaurant Opening: Before opening a new restaurant, a feasibility study is conducted to assess factors like location, target market, competition, menu pricing, and operating costs. It helps in understanding whether the restaurant can be profitable in a specific area.
-
Technology Start-up: Tech entrepreneurs often conduct feasibility studies to evaluate the viability of their software or app ideas. This includes assessing market demand, development costs, potential revenue streams, and competition in the tech sector.
-
Infrastructure Projects: Large-scale infrastructure projects like bridges, highways, or public transportation systems require feasibility studies to assess technical, financial, and environmental factors. These studies help determine if the project is practical and cost-effective.
-
Hotel Expansion: When a hotel chain plans to expand by building a new location, a feasibility study examines the market conditions, demand for hotel rooms in the area, construction and operational costs, and the potential return on investment.
-
Agricultural Ventures: Farmers and agricultural entrepreneurs may conduct feasibility studies before starting a new crop or livestock farming operation. The study evaluates factors like soil quality, market demand for the products, input costs, and expected yields.
-
Renewable Energy Projects: Feasibility studies are essential for renewable energy projects like wind farms or solar power plants. They assess factors such as available resources, technology feasibility, regulatory requirements, and financial viability.
-
Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals and healthcare organizations may conduct feasibility studies when planning to build new medical facilities. These studies analyze factors such as patient demand, location suitability, construction costs, and long-term operational expenses.
-
Manufacturing Plants: Before setting up a new manufacturing plant, businesses conduct feasibility studies to determine the feasibility of production, supply chain logistics, labor costs, and market demand for the products.
-
Educational Institutions: Feasibility studies are used by educational institutions to assess whether it's viable to expand or build new facilities, launch new academic programs, or enter new markets. These studies consider factors like enrollment projections, budget requirements, and competitive landscape.
-
Tourism and Hospitality: In the tourism sector, feasibility studies are conducted to evaluate the potential of opening new resorts, amusement parks, or tourist attractions. These studies analyze market demand, location, infrastructure requirements, and investment costs.
These are just a few examples of feasibility studies in different domains. The specific elements and focus of a feasibility study can vary widely depending on the nature of the project or business venture.
What is the Purpose of a Feasibility Study?
The primary purpose of a feasibility study is to comprehensively evaluate the viability and potential success of a proposed project or business endeavor. This study serves as a crucial decision-making tool, enabling stakeholders to assess the project's feasibility, risks, and financial viability. By identifying potential challenges and opportunities early on, a feasibility study helps mitigate risks and develop effective strategies for success. It aligns the project with an organization's strategic goals, facilitates resource allocation, and ensures that resources are directed toward projects with a high likelihood of achieving positive returns on investment. Additionally, it fosters stakeholder buy-in and provides a clear roadmap for project execution. Ultimately, the overarching goal of a feasibility study is to inform well-informed decisions about whether to pursue, modify, or abandon the project, thereby promoting efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and the likelihood of successful outcomes.
How Do You Write a Feasibility Study?
Writing a feasibility study involves a structured and systematic approach to assessing the viability of a proposed project or business venture. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to write a feasibility study:
-
Project Introduction:
-
Begin with an introduction that provides context for the study. Explain the purpose of the study, the project's objectives, and its significance.
-
-
Executive Summary:
-
Create an executive summary that offers a concise overview of the entire feasibility study, summarizing key findings, recommendations, and conclusions. This section should be clear and compelling as it's often the first part decision-makers read.
-
-
Background Information:
-
Provide background information on the project, including its history, the problem it aims to address, and any relevant historical data or context.
-
-
Scope of Work:
-
Clearly define the scope of the feasibility study. Specify the boundaries and limitations of the study, including what will and will not be included.
-
-
Methodology:
-
Explain the research methods and tools used to collect and analyze data. This section should outline the approach to market research, financial analysis, risk assessment, and other key aspects of the study.
-
-
Market Analysis:
-
Evaluate the market feasibility of the project by examining factors such as market size, growth potential, target demographics, competition, and customer demand. Present relevant market research data and trends.
-
-
Technical Analysis:
-
Assess the technical feasibility of the project, focusing on the required technology, equipment, and infrastructure. Address potential technical challenges and outline solutions.
-
-
Financial Analysis:
-
Conduct a detailed financial analysis, including cost estimations, revenue projections, cash flow analysis, and return on investment (ROI) calculations. Evaluate the project's financial viability.
-
-
Operational Analysis:
-
Evaluate the operational feasibility of the project by analyzing how it will function in practical terms. Consider staffing requirements, processes, logistics, and supply chain considerations.
-
-
Legal and Regulatory Assessment:
-
Examine legal and regulatory requirements relevant to the project. Identify permits, licenses, compliance issues, and strategies for ensuring legal conformity.
-
-
Environmental and Social Impact Assessment:
-
Assess the potential environmental and social impacts of the project, including sustainability considerations and community acceptance.
-
-
Risk Analysis:
-
Identify and evaluate potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project. Develop risk mitigation strategies and present them in this section.
-
-
Alternative Solutions:
-
Explore alternative approaches or solutions to achieve the project's objectives. Compare different options and provide a rationale for the chosen approach.
-
-
Recommendations:
-
Based on the analysis conducted throughout the study, present clear and well-supported recommendations regarding whether to proceed with the project, modify its scope, or abandon it. Provide a summary of the key findings that support the recommendations.
-
-
Appendices:
-
Include supplementary information in the appendices, such as detailed financial spreadsheets, market research data, technical specifications, and any other relevant documents that support the study's findings.
-
-
References:
-
If the study includes external sources or references, provide a list of these sources in a reference section.
-
-
Conclusion:
-
Conclude the feasibility study by summarizing the main findings, highlighting the recommended course of action, and reiterating the importance of the study's conclusions.
-
-
Final Review:
-
Before finalizing the report, conduct a thorough review for accuracy, clarity, and coherence. Ensure that the report is well-organized and follows a logical flow.
-
7 Steps to Do a Feasibility Study
Performing a feasibility study involves a systematic process to assess the viability of a project or business idea. Here are seven essential steps to conduct a feasibility study:
-
Define the Project Scope and Objectives:
-
Clearly outline the purpose, goals, and objectives of the feasibility study. Determine the specific questions the study should answer and the key aspects to be evaluated.
-
-
Gather Information and Data:
-
Collect all relevant data and information needed for the study. This includes market research, technical specifications, financial data, legal and regulatory requirements, and any other pertinent details.
-
-
Market Research and Analysis:
-
Evaluate the market feasibility by researching and analyzing factors like market size, growth trends, competition, customer preferences, and demand for the product or service.
-
-
Technical Analysis:
-
Assess the technical feasibility by examining the required technology, equipment, and infrastructure. Identify potential technical challenges and determine if they can be overcome.
-
-
Financial Analysis:
-
Conduct a comprehensive financial analysis, including cost estimations, revenue projections, cash flow analysis, and ROI calculations. Determine if the project is financially viable and can yield positive returns.
-
-
Operational Analysis:
-
Evaluate the operational feasibility of the project by analyzing how it will function in practical terms. Consider staffing needs, processes, logistics, and supply chain requirements.
-
-
Risk Assessment and Recommendations:
-
Identify and assess potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project. Develop strategies for risk mitigation. Based on the analysis, make clear and well-supported recommendations regarding whether to proceed with the project, make modifications, or abandon it. Summarize key findings and provide a concise roadmap for decision-makers.
-
How to Conduct a Feasibility Study
Performing a feasibility study involves a systematic process to assess the viability of a project or business idea. Here are seven essential steps to conduct a feasibility study:
-
Define the Project Scope and Objectives:
-
Clearly outline the purpose, goals, and objectives of the feasibility study. Determine the specific questions the study should answer and the key aspects to be evaluated.
-
-
Gather Information and Data:
-
Collect all relevant data and information needed for the study. This includes market research, technical specifications, financial data, legal and regulatory requirements, and any other pertinent details.
-
-
Market Research and Analysis:
-
Evaluate the market feasibility by researching and analyzing factors like market size, growth trends, competition, customer preferences, and demand for the product or service.
-
-
Technical Analysis:
-
Assess the technical feasibility by examining the required technology, equipment, and infrastructure. Identify potential technical challenges and determine if they can be overcome.
-
-
Financial Analysis:
-
Conduct a comprehensive financial analysis, including cost estimations, revenue projections, cash flow analysis, and ROI calculations. Determine if the project is financially viable and can yield positive returns.
-
-
Operational Analysis:
-
Evaluate the operational feasibility of the project by analyzing how it will function in practical terms. Consider staffing needs, processes, logistics, and supply chain requirements.
-
-
Risk Assessment and Recommendations:
-
Identify and assess potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project. Develop strategies for risk mitigation. Based on the analysis, make clear and well-supported recommendations regarding whether to proceed with the project, make modifications, or abandon it. Summarize key findings and provide a concise roadmap for decision-makers.
-
Feasibility Study vs. Business Plan
Feasibility Study vs. Business Plan:
Feasibility Study:
-
Purpose: The primary purpose of a feasibility study is to assess the viability and feasibility of a proposed project or business idea. It aims to answer the question, "Is this project or business concept feasible?"
-
Timing: Feasibility studies are typically conducted in the early stages of project development, often before significant resources are invested.
-
Scope: Feasibility studies have a broader scope and focus on evaluating various aspects of the project, including market feasibility, technical feasibility, financial feasibility, legal and regulatory considerations, operational feasibility, and risk assessment.
-
Analysis: Feasibility studies involve in-depth analysis of data and information related to the project, such as market research, cost estimation, revenue projections, and risk assessment.
-
Outcome: The primary outcome of a feasibility study is to provide stakeholders with a recommendation on whether to proceed with the project, modify its scope, or abandon it. It helps stakeholders make informed decisions.
Business Plan:
-
Purpose: A business plan serves as a detailed blueprint for the actual operation and management of a business. It outlines the goals, strategies, and operations of the business and provides a roadmap for its growth and development.
-
Timing: Business plans are typically developed after the feasibility study, once the decision to proceed with the project has been made. They are often used when seeking financing or as a guide for day-to-day operations.
-
Scope: Business plans focus on the specific strategies, tactics, and operations required to run the business successfully. They include detailed information on marketing, sales, organizational structure, funding requirements, revenue and expense projections, and long-term goals.
-
Analysis: While business plans incorporate the findings from the feasibility study, they go beyond feasibility analysis and delve into the practical aspects of running the business. Business plans include detailed financial projections and operational plans.
-
Outcome: The primary outcome of a business plan is to provide a comprehensive and actionable roadmap for the business. It is used for securing financing, attracting investors, guiding day-to-day operations, and measuring the business's performance against its objectives.
In summary, a feasibility study assesses the initial viability of a project or business idea and informs the decision to proceed or not, while a business plan is a detailed document that outlines how a business will operate, grow, and achieve its goals once the decision to move forward has been made. Both documents are crucial in the lifecycle of a business or project, with the feasibility study informing the business plan's foundation.
Reasons to Do or Not to Do a Feasibility Study
Reasons to Do a Feasibility Study:
-
Risk Assessment: A feasibility study helps identify potential risks and challenges associated with the project. It provides an opportunity to assess and mitigate these risks proactively.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Conducting a feasibility study ensures that decision-makers have comprehensive information to make informed choices about whether to proceed with the project, make modifications, or abandon it.
-
Financial Clarity: Financial feasibility studies estimate costs, revenue projections, and potential profitability. This clarity ensures that the project aligns with budget constraints and has a potential for positive returns on investment.
-
Resource Optimization: Feasibility studies outline the resources required for the project, such as personnel, equipment, materials, and technology. This allows for efficient resource allocation and prevents delays or resource shortages.
-
Strategic Alignment: Projects should align with an organization's strategic goals and objectives. A feasibility study assesses this alignment, ensuring that the project supports the organization's overarching strategy.
Reasons Not to Do a Feasibility Study:
-
Low Complexity: For very simple projects with minimal investment and known market demand, a full-scale feasibility study may be unnecessary. However, even small projects can benefit from some form of preliminary assessment.
-
Urgency: In cases where time is of the essence, such as responding to rapidly changing market conditions, conducting a lengthy feasibility study may not be feasible. In such situations, a rapid assessment or a simpler analysis may be more appropriate.
-
Cost Concerns: Some organizations may be hesitant to invest in a feasibility study due to budget constraints. However, failing to conduct a feasibility study can lead to much higher costs if the project encounters unforeseen issues.
-
Obvious Viability: In rare cases where the viability of a project is self-evident and unquestionable, skipping a feasibility study might be considered. However, a cursory assessment is still advisable to confirm assumptions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a feasibility study is an indispensable tool in the process of evaluating the potential success and viability of a proposed project or business venture. It serves as a critical decision-making guide, providing stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of the project's feasibility, risks, and financial viability. By identifying potential challenges and opportunities early on, a feasibility study enables proactive risk mitigation and the development of effective strategies for success. It aligns the project with an organization's strategic objectives, facilitates resource allocation, and ensures that resources are directed toward endeavors with a high likelihood of achieving positive returns. Furthermore, it fosters stakeholder buy-in and provides a clear roadmap for project execution. Ultimately, the overarching goal of a feasibility study is to inform well-informed decisions about whether to pursue, modify, or abandon the project, thereby promoting efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and the likelihood of successful outcomes. In essence, a well-executed feasibility study lays the foundation for a project's success and serves as a cornerstone for prudent decision-making in the world of business and project management.
FAQs
1. What is a feasibility study?
A feasibility study is an in-depth analysis and evaluation of a proposed project or business venture to determine its viability and potential for success. It assesses various aspects such as market feasibility, technical feasibility, financial feasibility, and operational feasibility.
2. Why is a feasibility study important?
A feasibility study is crucial because it helps stakeholders make informed decisions about whether to proceed with a project, modify its scope, or abandon it. It identifies risks, assesses costs, and evaluates the potential for profitability, thereby reducing uncertainty and minimizing the likelihood of project failure.
3. What are the key components of a feasibility study?
A feasibility study typically includes sections on market analysis, technical analysis, financial analysis, operational analysis, legal and regulatory considerations, environmental and social impact assessment, risk analysis, and recommendations.
4. How is a feasibility study different from a business plan?
A feasibility study assesses the initial viability of a project, while a business plan provides a detailed roadmap for running and growing a business after the decision to proceed has been made. Feasibility studies inform the foundation of a business plan.
5. When should you conduct a feasibility study?
Feasibility studies are typically conducted in the early stages of project development, before significant resources are invested. However, they can also be conducted at any point when there is uncertainty about the feasibility of a project.
6. What is the role of market research in a feasibility study?
Market research is a crucial component of a feasibility study as it assesses market demand, competition, customer preferences, and trends. It helps determine if there is a market for the project's products or services.
7. How do you assess financial feasibility in a feasibility study?
Financial feasibility is assessed by estimating project costs, revenue projections, cash flow analysis, and calculating metrics like return on investment (ROI) and payback period. It determines if the project is financially viable.
8. What are the benefits of conducting a feasibility study?
Benefits of a feasibility study include risk mitigation, informed decision-making, financial clarity, efficient resource allocation, strategic alignment, stakeholder buy-in, and the identification of potential issues early in the project.
9. Are there situations where a feasibility study may not be necessary?
In some cases, for very simple projects with minimal investment and known market demand, a full-scale feasibility study may be considered unnecessary. However, even small projects can benefit from a preliminary assessment.
10. How do you present the findings of a feasibility study to stakeholders? -
The findings of a feasibility study are typically presented in a structured report format, with clear sections covering each aspect of the study. An executive summary is often included to provide a concise overview of the key findings and recommendations. Presentations and discussions with stakeholders may also be part of the communication process.
A Complete Guide to ITIL Concepts, Processes, and Summary
Welcome to "A Complete Guide to ITIL Concepts and Summary Process: What is ITIL?" In this comprehensive exploration, we demystify ITIL, the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, offering you a compass to navigate the intricate realm of IT Service Management (ITSM). Discover the core concepts of ITIL, unravel its summary processes, and understand its pivotal role in optimizing IT service delivery, enhancing customer satisfaction, and reshaping modern business operations. Whether you're an IT professional, a business leader, or simply curious about ITIL's impact, this guide equips you with essential knowledge, transforming the way you perceive and implement IT service management practices, all within a single paragraph.
Table of Contents
What is ITIL?
What's in the ITIL?
Benefits of ITIL:
Drawbacks of ITIL:
What are the ITIL Concepts?
What are ITIL's Guiding Principles?
Key ITIL Terms
ITIL Framework
1. Service Strategy
2. Service Design
3. Service Transition
4. Service Operations
5. Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
How Do I Put ITIL into Practice?
What is ITIL Certification, and is it Worth it?
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
How Does ITIL Help Business?
What Will ITIL Cost?
How Does ITIL Reduce Costs?
ITIL Processes and Functions
History of ITIL
ITIL Processes and Stages: Summary
What is ITIL?
ITIL, or Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a widely adopted framework for IT service management. It offers a structured approach to aligning IT services with business objectives and delivering high-quality services to customers. ITIL encompasses various phases, including service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual service improvement. It provides best practices and guidelines to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and customer-centricity of IT processes and services, making it a valuable resource for organizations seeking to improve their IT operations.
What's in the ITIL?
ITIL consists of a structured framework for IT service management, including a service lifecycle with stages like Service Strategy, Design, Transition, Operation, and Continual Service Improvement. It defines processes, roles, and functions within IT organizations, guiding how services are designed, delivered, and improved. ITIL emphasizes aligning IT with business goals, offering best practices for incident and problem management, change control, and more. It also provides certification options for IT professionals to validate their expertise. Overall, ITIL offers a holistic approach to managing IT services effectively and efficiently.
Benefits of ITIL
Implementing ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) in an organization can bring several significant benefits, including:
-
Improved Service Quality: ITIL promotes best practices and standardized processes, leading to more consistent and reliable IT service delivery. This, in turn, enhances the overall quality of IT services, reducing downtime and customer dissatisfaction.
-
Better Alignment with Business Goals: ITIL encourages the alignment of IT services with the objectives and needs of the business. This ensures that IT investments and efforts contribute directly to the organization's success.
-
Cost Efficiency: By optimizing processes and resources, ITIL helps organizations reduce operational costs. Effective incident management, problem resolution, and resource allocation lead to cost savings.
-
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: ITIL's customer-centric approach ensures that IT services are designed and delivered with the customer's experience in mind. Meeting or exceeding customer expectations leads to higher satisfaction levels.
-
Reduced Risk: ITIL's focus on change management and risk mitigation helps organizations minimize the potential for disruptions and security breaches during service transitions or changes.
Drawbacks of ITIL
While ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) offers many advantages, it also has some potential drawbacks and challenges:
-
Complexity: ITIL is a comprehensive framework with a multitude of processes, roles, and functions. Implementing the full framework can be complex and resource-intensive, especially for small organizations.
-
Cost: The implementation of ITIL may involve significant upfront costs, including training, software, and process redesign. These expenses can be a barrier for some organizations.
-
Resource Intensive: ITIL requires dedicated resources, including personnel, tools, and time for training and implementation. Smaller organizations may struggle to allocate these resources.
-
Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes in processes and procedures that ITIL mandates, especially if they have been accustomed to their current ways of working. This can slow down adoption.
-
Overstandardization: In some cases, ITIL's emphasis on standardization can stifle innovation and adaptability. Organizations may become too rigid in their processes and struggle to respond to rapidly changing business needs.
What are the ITIL Concepts?
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) encompasses several key concepts that form the foundation of its framework for IT service management. These concepts help organizations understand and implement effective IT service management practices. Here are the core ITIL concepts:
-
Service: ITIL views services as a means of delivering value to customers without the ownership of specific costs and risks.
-
Service Management: ITIL involves specialized organizational capabilities to deliver value through IT services, encompassing processes, functions, roles, and responsibilities.
-
Service Lifecycle: ITIL's framework revolves around five stages: Service Strategy, Design, Transition, Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
-
Process: ITIL defines a set of processes, each with specific activities, inputs, outputs, and roles, essential for effective IT service management.
-
SLA and KPI: ITIL uses Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to define service quality and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure and monitor service performance and effectiveness.
What are ITIL's Guiding Principles?
Here are the seven simplified guiding principles of ITIL:
-
Value-Centric: Focus on delivering value to customers and the business.
-
Start Where You Are: Build on your existing processes and capabilities.
-
Feedback-Driven Progress: Continuously improve through feedback and small changes.
-
Collaborate and Communicate: Work together and share information for better results.
-
Think Holistically: Consider the big picture and interconnectedness of services.
-
Keep it Simple: Avoid complexity and prioritize practicality.
-
Optimize and Automate: Streamline processes and use automation to improve efficiency.
Key ITIL Terms
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) uses specific terminology to describe its concepts and processes. Here are some key ITIL terms:
-
Service: The means by which value is delivered to customers, often in the form of intangible deliverables like email or network connectivity.
-
Service Management: The set of organizational capabilities for delivering value to customers in the form of services.
-
Service Lifecycle: The stages of a service's existence, including Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
-
Process: A structured set of activities designed to accomplish a specific objective. ITIL defines numerous processes for IT service management.
-
Function: A team or group of people with specific skills and resources responsible for carrying out one or more processes or activities.
-
Role: A defined set of responsibilities and activities assigned to an individual or group, such as a Service Owner or Incident Manager.
-
Stakeholder: Individuals or groups with an interest in or an impact on the services provided by an organization. This can include customers, users, suppliers, and employees.
-
Service Provider: The organization delivering IT services to customers. It can be an internal IT department or an external service provider.
-
Customer: The person or group that defines requirements for IT services and receives the value provided by those services.
-
User: Individuals who utilize IT services to carry out their tasks and achieve their goals, which may or may not be the same as the customer.
ITIL Framework
The ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) framework is a comprehensive set of best practices and guidelines for IT service management (ITSM). It provides a structured approach for organizations to plan, design, deliver, operate, and continually improve their IT services. The framework is designed to align IT services with the needs of the business and ensure the efficient and effective delivery of those services. Here are the key components and aspects of the ITIL framework:
-
Service Strategy: Defining the organization's IT service strategy, considering business objectives and customer needs.
-
Service Design: Designing IT services, processes, and supporting infrastructure.
-
Service Transition: Managing the transition of new or changed services into the production environment.
-
Service Operation: Ensuring the day-to-day delivery and management of IT services.
-
Continual Service Improvement (CSI): Identifying and implementing improvements to services and processes.
Service Strategy
Service Strategy in ITIL is the critical phase where an organization aligns its IT services with its business objectives and needs. It involves defining a clear service strategy, managing a portfolio of IT services, ensuring financial viability, understanding and influencing customer demand, coordinating service design, managing risks, and nurturing strong business relationships. The goal is to create a roadmap that ensures IT services provide value to the business, support its success, and remain cost-effective, thus guiding subsequent phases of service management and helping the organization make informed decisions about service design, transition, and operation.
Service Design
Service Design, a pivotal phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, focuses on crafting IT services that are not only technically robust but also perfectly aligned with the organization's strategic goals and customer needs. It encompasses the meticulous planning and design of services, including service catalogs, service levels, capacity, availability, continuity, security, and supplier relationships. By adhering to ITIL principles and leveraging design coordination, it ensures that services are both cost-effective and poised for seamless transition into the operational environment. Service Design plays a vital role in delivering services that deliver value to the business while maintaining high levels of quality and customer satisfaction.
Service Transition
Service Transition, a critical phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, orchestrates the controlled and efficient movement of new or modified IT services from development and testing into the operational environment. It encompasses comprehensive change management, configuration control, rigorous testing and validation, and knowledge management to minimize risks and disruptions while maximizing the value and quality of services. By adhering to ITIL principles and detailed transition planning, it ensures that services meet customer expectations, business requirements, and service levels. Service Transition plays a pivotal role in the successful delivery of IT services, fostering agility and adaptability within the organization's IT landscape.
Service Operations
Service Operation, a pivotal phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, is responsible for the continuous and efficient delivery of IT services to meet agreed-upon service levels and customer needs. It encompasses incident and problem management to swiftly resolve issues, event management for proactive monitoring and response, request fulfillment, access management, and the critical role of the service desk as a central point of user support. Technical and IT operations management ensure infrastructure reliability, while application management oversees the lifecycle of business-critical software. By adhering to ITIL principles and promoting continual service improvement, Service Operation plays a vital role in maintaining service quality, minimizing disruptions, and contributing to overall customer satisfaction and business resilience.
Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
Continual Service Improvement (CSI) is a fundamental phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, dedicated to the ongoing enhancement of IT services and processes. It involves systematically measuring service performance, analyzing results, and identifying areas for improvement. By establishing clear metrics, conducting regular reviews, and creating action plans, organizations can drive efficiency, reduce costs, and align IT services with evolving business needs. CSI fosters a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that IT services remain adaptable and responsive to changing customer requirements and market dynamics, ultimately delivering greater value and quality to the organization and its stakeholders.
How Do I Put ITIL into Practice?
-
Assessment and Alignment: Begin by assessing your organization's existing IT service management practices and identifying areas that need improvement. Determine how well your current practices align with ITIL principles and the organization's business objectives. This assessment provides a baseline for your ITIL implementation efforts.
-
Customization and Planning: ITIL is not a one-size-fits-all framework. Customize ITIL practices to match your organization's specific needs and constraints. Create a clear implementation plan that outlines objectives, milestones, roles, responsibilities, and timelines. Ensure that the plan aligns with your business's strategic goals and secures the necessary resources.
-
Education and Training: Equip your IT teams and staff with the knowledge and skills required for ITIL adoption. Offer training and awareness programs to help them understand the ITIL framework and its benefits. It's essential to create a shared understanding and commitment among team members.
-
Process Redesign and Automation: Redesign or adapt your IT service management processes to align with ITIL best practices. Ensure that these processes are well-documented and easily accessible to all relevant parties. Invest in IT service management tools and technologies that support ITIL processes and automate repetitive tasks to improve efficiency.
-
Continuous Improvement: ITIL is built on the concept of continual service improvement (CSI). Establish a culture of continuous improvement within your organization, where regular reviews and evaluations of ITIL implementation are conducted. Use performance metrics and feedback to identify areas for enhancement and make adjustments to your ITIL practices accordingly. CSI ensures that your IT services remain aligned with evolving business needs and industry best practices.
What is ITIL Certification, and is it Worth it?
ITIL certification is a valuable credential for individuals working in IT service management and related fields. It offers a structured and globally recognized framework for understanding and implementing best practices in IT service delivery and management. Achieving ITIL certification demonstrates your commitment to improving IT service quality and aligning IT with business goals. It can open doors to career advancement and higher earning potential, as many employers value ITIL certification when hiring or promoting IT professionals. However, it's important to consider the cost and time investment required for training and exams, as well as whether ITIL aligns with your specific career path and goals. Continuous learning and staying updated with the latest ITIL practices are also necessary for maintaining the certification's value. Ultimately, the worth of ITIL certification depends on your career aspirations and the relevance of IT service management in your professional journey.
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
ITIL V3 and ITIL V4 certifications represent two distinct iterations of the ITIL framework. While ITIL V3 followed a process-oriented service lifecycle model with a structured certification scheme, ITIL V4 introduced a more flexible and holistic approach to IT service management. V4 emphasizes value co-creation, incorporates guiding principles, and introduces a simplified certification structure with practical orientation. It addresses modern trends like digital transformation and agile practices, making it more adaptable to the evolving needs of organizations in the digital age. The transition from V3 to V4 signifies a shift from a process-centric framework to one that focuses on delivering value, enhancing customer experience, and embracing emerging practices, reflecting the changing landscape of IT service management.
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
-
Certification Structure:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 had a certification structure consisting of Foundation, Intermediate (Lifecycle and Capability modules), Expert, and Master levels.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduced a simplified certification scheme with four levels: Foundation, Practitioner, Specialist, and Strategist. The Master level remains the highest certification but is more accessible under V4.
-
Practical Orientation:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 certification focused on theoretical knowledge of ITIL processes and practices.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 places a stronger emphasis on practical application and adaptation of ITIL principles in real-world scenarios. The Practitioner and Specialist levels are designed to help professionals apply ITIL concepts effectively.
-
Guiding Principles:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 did not have a specific set of guiding principles.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduces seven guiding principles (e.g., Focus on Value, Start Where You Are, Collaborate and Promote Visibility) that underpin the framework and guide decision-making.
-
Service Value Chain:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 organized processes into a service lifecycle with five stages: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement (CSI).
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduces the Service Value System, which includes the Service Value Chain (a set of interconnected activities) and emphasizes value co-creation with customers.
-
Flexibility and Adaptability:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 had a more rigid and process-centric approach.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 is designed to be more flexible and adaptable, allowing organizations to tailor ITIL practices to their unique needs and circumstances.
-
Digital Transformation and Agile Practices:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 did not specifically address emerging trends like digital transformation and agile practices.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 incorporates modern concepts and practices, making it more relevant in the digital age, including considerations for DevOps, Agile, and lean principles.
How Does ITIL Help Business?
ITIL benefits businesses by offering a structured framework for IT service management, resulting in improved service quality, cost efficiency, and alignment with business objectives. It reduces downtime, enhances change management, and facilitates effective risk mitigation. ITIL's customer-centric approach strengthens customer satisfaction, while its emphasis on continual improvement ensures adaptability and competitiveness in the evolving digital landscape. Additionally, it aids in regulatory compliance, fosters effective communication, and establishes transparent IT governance, ultimately contributing to business resilience, growth, and a competitive edge in the market.
What Will ITIL Cost?
The cost of ITIL can vary significantly depending on factors such as the level of certification, training format, study materials, and the size and complexity of ITIL implementation within an organization. ITIL certification exams range from $150 to $700 or more, with associated training and study materials adding to the expenses. Implementing ITIL practices within an organization involves costs related to training, consulting, process redesign, ITSM tools, and ongoing maintenance. It's crucial to budget carefully, considering both certification and implementation costs, while also weighing the long-term benefits of improved IT service quality, efficiency, and alignment with business objectives that ITIL can bring to the organization.
How Does ITIL Reduce Costs?
ITIL reduces costs for organizations by fostering efficiency, standardizing processes, and minimizing the risks and disruptions associated with IT service management. It achieves this through proactive problem management, rigorous change control, optimized resource allocation, meticulous documentation, and a continual focus on improvement. ITIL's emphasis on aligning IT services with business needs ensures that resources are directed towards activities that generate value, avoiding unnecessary expenses. By preventing service outages and incidents, streamlining workflows, and promoting cost transparency, ITIL helps organizations optimize their IT operations, resulting in significant cost reductions and improved cost-effectiveness.
ITIL Processes and Functions
In ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), processes and functions are key components of the framework, serving different roles in managing IT services effectively. Here's an overview of ITIL processes and functions:
ITIL Processes: ITIL defines several processes that are essential for IT service management. These processes are organized into five core lifecycle stages:
-
Service Strategy: This stage focuses on defining the overall strategy for IT services, including understanding customer needs, defining service portfolios, and aligning IT goals with business objectives. Key processes include Service Portfolio Management and Financial Management.
-
Service Design: In this stage, ITIL defines processes for designing IT services, ensuring they meet business requirements and are manageable. Processes include Service Catalog Management, Service Level Management, Capacity Management, and Availability Management.
-
Service Transition: This stage involves transitioning new or modified services into the production environment. Key processes include Change Management, Release and Deployment Management, and Service Validation and Testing.
-
Service Operation: Service Operation is responsible for the daily delivery and management of IT services to meet service levels and customer expectations. Processes here include Incident Management, Problem Management, Event Management, and Request Fulfillment.
-
Continual Service Improvement (CSI): CSI focuses on ongoing improvement of IT services and processes. It includes processes like Service Measurement and Reporting, Service Review, and Process Evaluation.
ITIL Functions: Functions in ITIL represent organizational units or groups responsible for specific activities or roles within the IT service management framework. While not all functions are required in every organization, they provide structure and accountability in managing IT services. Key ITIL functions include:
-
Service Desk: The Service Desk function acts as a central point of contact for users to report incidents, request services, and seek assistance. It plays a critical role in providing support and ensuring efficient communication.
-
Technical Management: This function provides technical expertise and support for IT infrastructure and services. It ensures that technical resources are available and properly maintained.
-
IT Operations Management: Responsible for the day-to-day operational activities required to deliver IT services. This includes data center management, network operations, and hardware maintenance.
-
Application Management: The Application Management function manages the lifecycle of applications, ensuring they are designed, developed, tested, and maintained to support business needs.
-
IT Security Management: While not always defined as a separate function, ITIL emphasizes the importance of security throughout the service lifecycle. This involves managing security policies, access controls, and compliance.
-
Supplier Management: Supplier Management ensures that external suppliers and vendors are effectively managed to deliver the required IT services and support.
These functions and processes work together to ensure that IT services are delivered efficiently, reliably, and in alignment with business goals and customer expectations. They provide a structured approach to managing IT services throughout their lifecycle, from strategy and design to operation and improvement.
History of ITIL
The history of ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) traces its origins to the late 1980s when it was developed by the UK's Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA). Initially conceived to standardize and improve IT service management within the UK government, ITIL soon gained recognition for its best-practice guidelines. ITIL V1, released in the late 1980s and early 1990s, laid the foundation with a comprehensive set of 31 books. However, it was in 2000 with the launch of ITIL V2 that ITIL's global impact began to take shape. V2 consolidated the framework into eight core books and gained widespread adoption. ITIL V3, introduced in 2007 and updated in 2011 (ITIL 2011), brought a service lifecycle approach and a focus on aligning IT services with business processes. In 2019, ITIL V4 marked a major shift, emphasizing value co-creation, the Service Value System, and modern IT practices. It continues to evolve, reflecting the changing landscape of IT service management and digital transformation. Throughout its history, ITIL has become a globally recognized framework for enhancing IT service quality and alignment with business objectives.
ITIL Processes and Stages: Summary
ITIL, or the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, encompasses a set of well-defined processes and stages designed to help organizations manage their IT services effectively. The core processes include Service Strategy, which aligns IT services with business goals; Service Design, which focuses on designing services that meet business requirements; Service Transition, which ensures a smooth transition of services into the production environment; Service Operation, responsible for daily service delivery and support; and Continual Service Improvement, which drives ongoing enhancements in service quality and efficiency. These processes are organized into stages that reflect the IT service lifecycle, from aligning IT with business objectives to designing, transitioning, operating, and continually improving services. By following the ITIL framework, organizations can deliver IT services that are not only reliable and cost-effective but also aligned with evolving business needs and customer expectations, ultimately contributing to improved overall business performance and competitiveness.
Read More
Welcome to "A Complete Guide to ITIL Concepts and Summary Process: What is ITIL?" In this comprehensive exploration, we demystify ITIL, the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, offering you a compass to navigate the intricate realm of IT Service Management (ITSM). Discover the core concepts of ITIL, unravel its summary processes, and understand its pivotal role in optimizing IT service delivery, enhancing customer satisfaction, and reshaping modern business operations. Whether you're an IT professional, a business leader, or simply curious about ITIL's impact, this guide equips you with essential knowledge, transforming the way you perceive and implement IT service management practices, all within a single paragraph.
Table of Contents
What is ITIL?
What's in the ITIL?
Benefits of ITIL:
Drawbacks of ITIL:
What are the ITIL Concepts?
What are ITIL's Guiding Principles?
Key ITIL Terms
ITIL Framework
1. Service Strategy
2. Service Design
3. Service Transition
4. Service Operations
5. Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
How Do I Put ITIL into Practice?
What is ITIL Certification, and is it Worth it?
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
How Does ITIL Help Business?
What Will ITIL Cost?
How Does ITIL Reduce Costs?
ITIL Processes and Functions
History of ITIL
ITIL Processes and Stages: Summary
What is ITIL?
ITIL, or Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a widely adopted framework for IT service management. It offers a structured approach to aligning IT services with business objectives and delivering high-quality services to customers. ITIL encompasses various phases, including service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual service improvement. It provides best practices and guidelines to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and customer-centricity of IT processes and services, making it a valuable resource for organizations seeking to improve their IT operations.
What's in the ITIL?
ITIL consists of a structured framework for IT service management, including a service lifecycle with stages like Service Strategy, Design, Transition, Operation, and Continual Service Improvement. It defines processes, roles, and functions within IT organizations, guiding how services are designed, delivered, and improved. ITIL emphasizes aligning IT with business goals, offering best practices for incident and problem management, change control, and more. It also provides certification options for IT professionals to validate their expertise. Overall, ITIL offers a holistic approach to managing IT services effectively and efficiently.
Benefits of ITIL
Implementing ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) in an organization can bring several significant benefits, including:
-
Improved Service Quality: ITIL promotes best practices and standardized processes, leading to more consistent and reliable IT service delivery. This, in turn, enhances the overall quality of IT services, reducing downtime and customer dissatisfaction.
-
Better Alignment with Business Goals: ITIL encourages the alignment of IT services with the objectives and needs of the business. This ensures that IT investments and efforts contribute directly to the organization's success.
-
Cost Efficiency: By optimizing processes and resources, ITIL helps organizations reduce operational costs. Effective incident management, problem resolution, and resource allocation lead to cost savings.
-
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: ITIL's customer-centric approach ensures that IT services are designed and delivered with the customer's experience in mind. Meeting or exceeding customer expectations leads to higher satisfaction levels.
-
Reduced Risk: ITIL's focus on change management and risk mitigation helps organizations minimize the potential for disruptions and security breaches during service transitions or changes.
Drawbacks of ITIL
While ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) offers many advantages, it also has some potential drawbacks and challenges:
-
Complexity: ITIL is a comprehensive framework with a multitude of processes, roles, and functions. Implementing the full framework can be complex and resource-intensive, especially for small organizations.
-
Cost: The implementation of ITIL may involve significant upfront costs, including training, software, and process redesign. These expenses can be a barrier for some organizations.
-
Resource Intensive: ITIL requires dedicated resources, including personnel, tools, and time for training and implementation. Smaller organizations may struggle to allocate these resources.
-
Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes in processes and procedures that ITIL mandates, especially if they have been accustomed to their current ways of working. This can slow down adoption.
-
Overstandardization: In some cases, ITIL's emphasis on standardization can stifle innovation and adaptability. Organizations may become too rigid in their processes and struggle to respond to rapidly changing business needs.
What are the ITIL Concepts?
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) encompasses several key concepts that form the foundation of its framework for IT service management. These concepts help organizations understand and implement effective IT service management practices. Here are the core ITIL concepts:
-
Service: ITIL views services as a means of delivering value to customers without the ownership of specific costs and risks.
-
Service Management: ITIL involves specialized organizational capabilities to deliver value through IT services, encompassing processes, functions, roles, and responsibilities.
-
Service Lifecycle: ITIL's framework revolves around five stages: Service Strategy, Design, Transition, Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
-
Process: ITIL defines a set of processes, each with specific activities, inputs, outputs, and roles, essential for effective IT service management.
-
SLA and KPI: ITIL uses Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to define service quality and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure and monitor service performance and effectiveness.
What are ITIL's Guiding Principles?
Here are the seven simplified guiding principles of ITIL:
-
Value-Centric: Focus on delivering value to customers and the business.
-
Start Where You Are: Build on your existing processes and capabilities.
-
Feedback-Driven Progress: Continuously improve through feedback and small changes.
-
Collaborate and Communicate: Work together and share information for better results.
-
Think Holistically: Consider the big picture and interconnectedness of services.
-
Keep it Simple: Avoid complexity and prioritize practicality.
-
Optimize and Automate: Streamline processes and use automation to improve efficiency.
Key ITIL Terms
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) uses specific terminology to describe its concepts and processes. Here are some key ITIL terms:
-
Service: The means by which value is delivered to customers, often in the form of intangible deliverables like email or network connectivity.
-
Service Management: The set of organizational capabilities for delivering value to customers in the form of services.
-
Service Lifecycle: The stages of a service's existence, including Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
-
Process: A structured set of activities designed to accomplish a specific objective. ITIL defines numerous processes for IT service management.
-
Function: A team or group of people with specific skills and resources responsible for carrying out one or more processes or activities.
-
Role: A defined set of responsibilities and activities assigned to an individual or group, such as a Service Owner or Incident Manager.
-
Stakeholder: Individuals or groups with an interest in or an impact on the services provided by an organization. This can include customers, users, suppliers, and employees.
-
Service Provider: The organization delivering IT services to customers. It can be an internal IT department or an external service provider.
-
Customer: The person or group that defines requirements for IT services and receives the value provided by those services.
-
User: Individuals who utilize IT services to carry out their tasks and achieve their goals, which may or may not be the same as the customer.
ITIL Framework
The ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) framework is a comprehensive set of best practices and guidelines for IT service management (ITSM). It provides a structured approach for organizations to plan, design, deliver, operate, and continually improve their IT services. The framework is designed to align IT services with the needs of the business and ensure the efficient and effective delivery of those services. Here are the key components and aspects of the ITIL framework:
-
Service Strategy: Defining the organization's IT service strategy, considering business objectives and customer needs.
-
Service Design: Designing IT services, processes, and supporting infrastructure.
-
Service Transition: Managing the transition of new or changed services into the production environment.
-
Service Operation: Ensuring the day-to-day delivery and management of IT services.
-
Continual Service Improvement (CSI): Identifying and implementing improvements to services and processes.
Service Strategy
Service Strategy in ITIL is the critical phase where an organization aligns its IT services with its business objectives and needs. It involves defining a clear service strategy, managing a portfolio of IT services, ensuring financial viability, understanding and influencing customer demand, coordinating service design, managing risks, and nurturing strong business relationships. The goal is to create a roadmap that ensures IT services provide value to the business, support its success, and remain cost-effective, thus guiding subsequent phases of service management and helping the organization make informed decisions about service design, transition, and operation.
Service Design
Service Design, a pivotal phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, focuses on crafting IT services that are not only technically robust but also perfectly aligned with the organization's strategic goals and customer needs. It encompasses the meticulous planning and design of services, including service catalogs, service levels, capacity, availability, continuity, security, and supplier relationships. By adhering to ITIL principles and leveraging design coordination, it ensures that services are both cost-effective and poised for seamless transition into the operational environment. Service Design plays a vital role in delivering services that deliver value to the business while maintaining high levels of quality and customer satisfaction.
Service Transition
Service Transition, a critical phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, orchestrates the controlled and efficient movement of new or modified IT services from development and testing into the operational environment. It encompasses comprehensive change management, configuration control, rigorous testing and validation, and knowledge management to minimize risks and disruptions while maximizing the value and quality of services. By adhering to ITIL principles and detailed transition planning, it ensures that services meet customer expectations, business requirements, and service levels. Service Transition plays a pivotal role in the successful delivery of IT services, fostering agility and adaptability within the organization's IT landscape.
Service Operations
Service Operation, a pivotal phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, is responsible for the continuous and efficient delivery of IT services to meet agreed-upon service levels and customer needs. It encompasses incident and problem management to swiftly resolve issues, event management for proactive monitoring and response, request fulfillment, access management, and the critical role of the service desk as a central point of user support. Technical and IT operations management ensure infrastructure reliability, while application management oversees the lifecycle of business-critical software. By adhering to ITIL principles and promoting continual service improvement, Service Operation plays a vital role in maintaining service quality, minimizing disruptions, and contributing to overall customer satisfaction and business resilience.
Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
Continual Service Improvement (CSI) is a fundamental phase within the ITIL service lifecycle, dedicated to the ongoing enhancement of IT services and processes. It involves systematically measuring service performance, analyzing results, and identifying areas for improvement. By establishing clear metrics, conducting regular reviews, and creating action plans, organizations can drive efficiency, reduce costs, and align IT services with evolving business needs. CSI fosters a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that IT services remain adaptable and responsive to changing customer requirements and market dynamics, ultimately delivering greater value and quality to the organization and its stakeholders.
How Do I Put ITIL into Practice?
-
Assessment and Alignment: Begin by assessing your organization's existing IT service management practices and identifying areas that need improvement. Determine how well your current practices align with ITIL principles and the organization's business objectives. This assessment provides a baseline for your ITIL implementation efforts.
-
Customization and Planning: ITIL is not a one-size-fits-all framework. Customize ITIL practices to match your organization's specific needs and constraints. Create a clear implementation plan that outlines objectives, milestones, roles, responsibilities, and timelines. Ensure that the plan aligns with your business's strategic goals and secures the necessary resources.
-
Education and Training: Equip your IT teams and staff with the knowledge and skills required for ITIL adoption. Offer training and awareness programs to help them understand the ITIL framework and its benefits. It's essential to create a shared understanding and commitment among team members.
-
Process Redesign and Automation: Redesign or adapt your IT service management processes to align with ITIL best practices. Ensure that these processes are well-documented and easily accessible to all relevant parties. Invest in IT service management tools and technologies that support ITIL processes and automate repetitive tasks to improve efficiency.
-
Continuous Improvement: ITIL is built on the concept of continual service improvement (CSI). Establish a culture of continuous improvement within your organization, where regular reviews and evaluations of ITIL implementation are conducted. Use performance metrics and feedback to identify areas for enhancement and make adjustments to your ITIL practices accordingly. CSI ensures that your IT services remain aligned with evolving business needs and industry best practices.
What is ITIL Certification, and is it Worth it?
ITIL certification is a valuable credential for individuals working in IT service management and related fields. It offers a structured and globally recognized framework for understanding and implementing best practices in IT service delivery and management. Achieving ITIL certification demonstrates your commitment to improving IT service quality and aligning IT with business goals. It can open doors to career advancement and higher earning potential, as many employers value ITIL certification when hiring or promoting IT professionals. However, it's important to consider the cost and time investment required for training and exams, as well as whether ITIL aligns with your specific career path and goals. Continuous learning and staying updated with the latest ITIL practices are also necessary for maintaining the certification's value. Ultimately, the worth of ITIL certification depends on your career aspirations and the relevance of IT service management in your professional journey.
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
ITIL V3 and ITIL V4 certifications represent two distinct iterations of the ITIL framework. While ITIL V3 followed a process-oriented service lifecycle model with a structured certification scheme, ITIL V4 introduced a more flexible and holistic approach to IT service management. V4 emphasizes value co-creation, incorporates guiding principles, and introduces a simplified certification structure with practical orientation. It addresses modern trends like digital transformation and agile practices, making it more adaptable to the evolving needs of organizations in the digital age. The transition from V3 to V4 signifies a shift from a process-centric framework to one that focuses on delivering value, enhancing customer experience, and embracing emerging practices, reflecting the changing landscape of IT service management.
Major Differences Between ITIL® V3 vs. ITIL® V4 Certification
-
Certification Structure:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 had a certification structure consisting of Foundation, Intermediate (Lifecycle and Capability modules), Expert, and Master levels.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduced a simplified certification scheme with four levels: Foundation, Practitioner, Specialist, and Strategist. The Master level remains the highest certification but is more accessible under V4.
-
-
Practical Orientation:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 certification focused on theoretical knowledge of ITIL processes and practices.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 places a stronger emphasis on practical application and adaptation of ITIL principles in real-world scenarios. The Practitioner and Specialist levels are designed to help professionals apply ITIL concepts effectively.
-
-
Guiding Principles:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 did not have a specific set of guiding principles.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduces seven guiding principles (e.g., Focus on Value, Start Where You Are, Collaborate and Promote Visibility) that underpin the framework and guide decision-making.
-
-
Service Value Chain:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 organized processes into a service lifecycle with five stages: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement (CSI).
-
ITIL® V4: V4 introduces the Service Value System, which includes the Service Value Chain (a set of interconnected activities) and emphasizes value co-creation with customers.
-
-
Flexibility and Adaptability:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 had a more rigid and process-centric approach.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 is designed to be more flexible and adaptable, allowing organizations to tailor ITIL practices to their unique needs and circumstances.
-
-
Digital Transformation and Agile Practices:
-
ITIL® V3: V3 did not specifically address emerging trends like digital transformation and agile practices.
-
ITIL® V4: V4 incorporates modern concepts and practices, making it more relevant in the digital age, including considerations for DevOps, Agile, and lean principles.
-
How Does ITIL Help Business?
ITIL benefits businesses by offering a structured framework for IT service management, resulting in improved service quality, cost efficiency, and alignment with business objectives. It reduces downtime, enhances change management, and facilitates effective risk mitigation. ITIL's customer-centric approach strengthens customer satisfaction, while its emphasis on continual improvement ensures adaptability and competitiveness in the evolving digital landscape. Additionally, it aids in regulatory compliance, fosters effective communication, and establishes transparent IT governance, ultimately contributing to business resilience, growth, and a competitive edge in the market.
What Will ITIL Cost?
The cost of ITIL can vary significantly depending on factors such as the level of certification, training format, study materials, and the size and complexity of ITIL implementation within an organization. ITIL certification exams range from $150 to $700 or more, with associated training and study materials adding to the expenses. Implementing ITIL practices within an organization involves costs related to training, consulting, process redesign, ITSM tools, and ongoing maintenance. It's crucial to budget carefully, considering both certification and implementation costs, while also weighing the long-term benefits of improved IT service quality, efficiency, and alignment with business objectives that ITIL can bring to the organization.
How Does ITIL Reduce Costs?
ITIL reduces costs for organizations by fostering efficiency, standardizing processes, and minimizing the risks and disruptions associated with IT service management. It achieves this through proactive problem management, rigorous change control, optimized resource allocation, meticulous documentation, and a continual focus on improvement. ITIL's emphasis on aligning IT services with business needs ensures that resources are directed towards activities that generate value, avoiding unnecessary expenses. By preventing service outages and incidents, streamlining workflows, and promoting cost transparency, ITIL helps organizations optimize their IT operations, resulting in significant cost reductions and improved cost-effectiveness.
ITIL Processes and Functions
In ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), processes and functions are key components of the framework, serving different roles in managing IT services effectively. Here's an overview of ITIL processes and functions:
ITIL Processes: ITIL defines several processes that are essential for IT service management. These processes are organized into five core lifecycle stages:
-
Service Strategy: This stage focuses on defining the overall strategy for IT services, including understanding customer needs, defining service portfolios, and aligning IT goals with business objectives. Key processes include Service Portfolio Management and Financial Management.
-
Service Design: In this stage, ITIL defines processes for designing IT services, ensuring they meet business requirements and are manageable. Processes include Service Catalog Management, Service Level Management, Capacity Management, and Availability Management.
-
Service Transition: This stage involves transitioning new or modified services into the production environment. Key processes include Change Management, Release and Deployment Management, and Service Validation and Testing.
-
Service Operation: Service Operation is responsible for the daily delivery and management of IT services to meet service levels and customer expectations. Processes here include Incident Management, Problem Management, Event Management, and Request Fulfillment.
-
Continual Service Improvement (CSI): CSI focuses on ongoing improvement of IT services and processes. It includes processes like Service Measurement and Reporting, Service Review, and Process Evaluation.
ITIL Functions: Functions in ITIL represent organizational units or groups responsible for specific activities or roles within the IT service management framework. While not all functions are required in every organization, they provide structure and accountability in managing IT services. Key ITIL functions include:
-
Service Desk: The Service Desk function acts as a central point of contact for users to report incidents, request services, and seek assistance. It plays a critical role in providing support and ensuring efficient communication.
-
Technical Management: This function provides technical expertise and support for IT infrastructure and services. It ensures that technical resources are available and properly maintained.
-
IT Operations Management: Responsible for the day-to-day operational activities required to deliver IT services. This includes data center management, network operations, and hardware maintenance.
-
Application Management: The Application Management function manages the lifecycle of applications, ensuring they are designed, developed, tested, and maintained to support business needs.
-
IT Security Management: While not always defined as a separate function, ITIL emphasizes the importance of security throughout the service lifecycle. This involves managing security policies, access controls, and compliance.
-
Supplier Management: Supplier Management ensures that external suppliers and vendors are effectively managed to deliver the required IT services and support.
These functions and processes work together to ensure that IT services are delivered efficiently, reliably, and in alignment with business goals and customer expectations. They provide a structured approach to managing IT services throughout their lifecycle, from strategy and design to operation and improvement.
History of ITIL
The history of ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) traces its origins to the late 1980s when it was developed by the UK's Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA). Initially conceived to standardize and improve IT service management within the UK government, ITIL soon gained recognition for its best-practice guidelines. ITIL V1, released in the late 1980s and early 1990s, laid the foundation with a comprehensive set of 31 books. However, it was in 2000 with the launch of ITIL V2 that ITIL's global impact began to take shape. V2 consolidated the framework into eight core books and gained widespread adoption. ITIL V3, introduced in 2007 and updated in 2011 (ITIL 2011), brought a service lifecycle approach and a focus on aligning IT services with business processes. In 2019, ITIL V4 marked a major shift, emphasizing value co-creation, the Service Value System, and modern IT practices. It continues to evolve, reflecting the changing landscape of IT service management and digital transformation. Throughout its history, ITIL has become a globally recognized framework for enhancing IT service quality and alignment with business objectives.
ITIL Processes and Stages: Summary
ITIL, or the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, encompasses a set of well-defined processes and stages designed to help organizations manage their IT services effectively. The core processes include Service Strategy, which aligns IT services with business goals; Service Design, which focuses on designing services that meet business requirements; Service Transition, which ensures a smooth transition of services into the production environment; Service Operation, responsible for daily service delivery and support; and Continual Service Improvement, which drives ongoing enhancements in service quality and efficiency. These processes are organized into stages that reflect the IT service lifecycle, from aligning IT with business objectives to designing, transitioning, operating, and continually improving services. By following the ITIL framework, organizations can deliver IT services that are not only reliable and cost-effective but also aligned with evolving business needs and customer expectations, ultimately contributing to improved overall business performance and competitiveness.
Artificial Intelligence: What Lies Ahead for the Future
In an era where science fiction is fast becoming our reality, the realm of Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands at the forefront of innovation and transformation. The question that lingers in the minds of technologists, futurists, and curious minds alike is, "What Lies Ahead for the Future of Artificial Intelligence?" This blog embarks on a journey through the landscapes of AI, aiming to dissect its growth, evolution, and the profound impact it has had on our world.
Table of Contents
-
Growth of AI
-
What Did the Future of AI Look Like 10 Years Ago?
-
Evolution of AI
-
Future of Artificial Intelligence
-
Impact of AI
-
Myths About Advanced Artificial Intelligence
-
AI and the Future of Work
-
Master AI Today
Growth of AI
The growth of AI, or Artificial Intelligence, signifies the relentless advancement and proliferation of intelligent technologies that are reshaping our world. This growth is fueled by technological breakthroughs, with increasingly powerful hardware and sophisticated algorithms driving the development of AI systems. Coupled with the explosion of data availability, AI has found its way into various industries, from healthcare to finance, revolutionizing processes and decision-making. In our everyday lives, AI-driven virtual assistants and recommendation systems have become ubiquitous. Global investment in AI research and development continues to soar, further accelerating AI's expansion. Nevertheless, this journey is not without its challenges, such as data privacy concerns and ethical dilemmas, which need to be addressed as we navigate the ever-expanding horizons of AI.
What Did the Future of AI Look Like 10 Years Ago?
The perception of the future of AI 10 years ago, around 2013, was a mixture of excitement, optimism, and uncertainty. While AI had already made significant strides in areas like natural language processing, machine learning, and computer vision, it had not yet achieved the widespread integration and prominence we see today. Here are some key aspects of how the future of AI was envisioned a decade ago:
-
Rise of Personal Assistants: Virtual personal assistants like Siri and Google Assistant were beginning to gain popularity. The vision was that these AI-driven assistants would become even more capable, understanding natural language and providing personalized assistance in various aspects of our lives.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: The concept of self-driving cars and their potential to revolutionize transportation was emerging. AI was seen as a critical technology in making autonomous vehicles a reality.
-
Healthcare and Diagnostics: There was optimism about AI's potential to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases more accurately and efficiently. Medical imaging and diagnostic tools powered by AI were on the horizon.
-
AI in Business: In the business world, AI was anticipated to improve decision-making through advanced analytics and predictive modeling. Automation of routine tasks in industries like customer service and data entry was also anticipated.
-
Challenges and Concerns: Alongside the excitement, there were concerns about the ethical and societal implications of AI, such as job displacement, algorithmic bias, and privacy issues. These concerns were seen as important topics to address in the future.
-
Limited Understanding of Deep Learning: While deep learning had made significant progress, it had not yet become the dominant AI paradigm it is today. Many people were still exploring other machine learning approaches and algorithms.
Overall, the future of AI 10 years ago was characterized by high expectations for its transformative potential in various domains. However, there was a level of uncertainty about how rapidly these advancements would occur and how society would adapt to the changes brought about by AI technologies. In hindsight, many of these early predictions have materialized to a significant extent, but AI's growth and impact have also presented new challenges and opportunities beyond what was imagined a decade ago.
Evolution of AI
Early Foundations and Optimism (1950s-1960s): The evolution of AI began in the 1950s when computer scientists and mathematicians first contemplated the idea of creating machines that could exhibit human-like intelligence. Pioneers like Alan Turing, John McCarthy, and Marvin Minsky laid the groundwork for AI by developing concepts of computational intelligence and symbolic reasoning. During this period, optimism ran high as researchers believed that AI could solve complex problems, automate decision-making, and simulate human cognitive processes. However, computational limitations and the complexity of human intelligence led to early challenges and set the stage for the first "AI winter" in the 1970s.
Setbacks and Stagnation (1970s-1980s): The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a slowdown in AI research, commonly referred to as the "AI winter." High expectations collided with the reality that AI technologies were not yet capable of delivering on their promises. Funding for AI projects dwindled, and progress stagnated. Expert systems, one of the prominent approaches during this era, demonstrated limited adaptability and struggled to handle real-world complexities. The lack of practical AI applications and unmet expectations contributed to a degree of skepticism about the field's prospects.
Resurgence and Breakthroughs (1990s-Present): AI experienced a resurgence in the 1990s, transitioning from symbolic reasoning to machine learning approaches. Researchers shifted their focus to developing algorithms that could learn from data, resulting in significant progress. The advent of big data, powerful computing resources, and deep learning techniques in the 2010s propelled AI to new heights. Deep neural networks became the foundation for transformative breakthroughs in areas like image recognition, natural language understanding, and autonomous systems. AI is now deeply integrated into various industries and aspects of daily life, reshaping how we work, interact, and solve complex problems. As AI continues to evolve, the quest for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and the responsible development of AI technologies remain central to discussions about its future.
Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a topic of great fascination and speculation due to the rapid advancements and transformative potential of this field. Here are some key aspects to consider when contemplating the future of AI:
-
Enhanced Automation: AI will continue to play a significant role in automating routine and repetitive tasks across various industries. This includes manufacturing, customer service, data analysis, and more. As AI algorithms become more sophisticated, they will enable greater levels of efficiency, cost savings, and accuracy in these domains.
-
Personalization and Recommendation: AI-driven recommendation systems will become even more personalized, offering tailored content, products, and services to individuals. This level of personalization will enhance user experiences in e-commerce, content streaming, and marketing, among other areas.
-
Healthcare Revolution: AI's impact on healthcare will be profound. AI-powered diagnostic tools, predictive analytics, and drug discovery processes will lead to earlier disease detection, more effective treatments, and improved patient outcomes. Telemedicine and remote monitoring will become more common, especially in remote or underserved areas.
-
Autonomous Systems: AI will continue to advance autonomous systems, particularly in self-driving cars, drones, and robotics. These technologies will reshape transportation, logistics, and manufacturing, potentially leading to safer and more efficient operations.
-
Natural Language Processing: AI's capabilities in understanding and generating human language will expand. Conversational AI, chatbots, and virtual assistants will become more sophisticated and capable of handling complex interactions. This will have applications in customer service, healthcare, education, and more.
The future of AI is dynamic and full of promise, but it also poses challenges related to ethics, regulation, and the impact on employment. As AI continues to evolve, it will require careful stewardship to harness its potential for the benefit of humanity while addressing its associated risks.
Impact of AI
AI's impact on society is twofold, offering significant benefits and presenting complex challenges. On one hand, AI has ushered in a new era of efficiency and productivity by automating routine tasks, leading to cost savings and improved operational performance across industries. It has also revolutionized healthcare, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and patient care. Furthermore, AI-driven personalization and recommendation systems have transformed the way businesses engage with customers, offering tailored experiences and boosting user satisfaction. In sectors like finance and education, AI is streamlining processes, making financial decisions more informed, and personalizing learning experiences for students. The creative possibilities of AI and its potential to address global challenges, such as climate change, highlight its role in advancing innovation and research.
Conversely, AI's impact raises concerns regarding ethics and social implications. Issues like algorithmic bias, which can perpetuate discrimination, have come to the forefront. The widespread automation enabled by AI has sparked debates about job displacement and the need for reskilling and upskilling the workforce. Privacy concerns arise from the vast amount of data AI systems collect and analyze, necessitating robust data protection measures. Moreover, as AI technologies continue to advance, there is a need for clear ethical guidelines and regulations to ensure that AI serves humanity's best interests and does not compromise fundamental values. Balancing AI's tremendous potential with these challenges is essential for a harmonious integration of AI into our society.
Myths About Advanced Artificial Intelligence
As advanced artificial intelligence (AI) continues to develop, several myths and misconceptions have emerged that can hinder our understanding of its capabilities and limitations. Here are some common myths about advanced AI:
-
AI Possesses Human-Like General Intelligence: One of the most pervasive myths is that advanced AI systems, even those using deep learning and neural networks, possess human-like general intelligence. In reality, AI today is primarily narrow or specialized, excelling at specific tasks but lacking the broad cognitive abilities and common-sense reasoning that humans have.
-
AI is Infallible: There's a misconception that AI is always accurate and error-free. While AI can perform exceptionally well in certain tasks, it's not immune to errors, especially in situations where it encounters novel or ambiguous data. Additionally, AI can be influenced by biased training data, leading to biased outcomes.
-
AI Understands Like Humans: AI systems can process and generate human language, but they don't truly understand it. They rely on statistical patterns and data, lacking genuine comprehension or consciousness. This myth can lead to overestimating AI's comprehension and reasoning abilities.
-
AI Will Replace All Jobs: While AI automation is transforming some industries, it won't replace all jobs. Instead, it's more likely to augment human work by automating repetitive tasks and allowing humans to focus on creative, strategic, and complex problem-solving roles.
-
AI is a Silver Bullet: Expecting AI to solve all problems is unrealistic. AI is a tool, and its effectiveness depends on the quality of data, the appropriateness of algorithms, and the problem it's applied to. It's not a one-size-fits-all solution.
AI and the Future of Work Top of Form
AI is ushering in a transformative era for the future of work. It promises to revolutionize industries by automating routine tasks and augmenting human capabilities. While automation may lead to concerns about job displacement, it also opens up opportunities for upskilling and reskilling the workforce, with an emphasis on jobs that require creativity, empathy, and complex problem-solving—areas where AI currently falls short. The synergy between humans and AI, along with the responsible development and ethical implementation of AI technologies, will be pivotal in shaping the future of work, enhancing productivity, and improving job quality. It is a dynamic landscape that requires adaptability, lifelong learning, and a balance between efficiency and preserving the human element in the workplace.
Additionally, AI facilitates remote work and flexible arrangements, changing the traditional workplace dynamic. This shift, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, offers benefits such as work-life balance and access to a global talent pool but also presents challenges related to cybersecurity and employee well-being. As AI continues to evolve, its impact on the future of work will be determined by how well individuals, organizations, and governments navigate these changes, foster innovation, and ensure that AI technologies contribute to a more equitable and productive workforce.
Master AI Today
Mastering AI today requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing education, hands-on experience, and a commitment to staying updated with the field's rapid advancements. Begin by acquiring a solid foundation in AI fundamentals through courses and self-study, with a focus on programming languages like Python, deep learning concepts, and data handling skills. Engage in practical projects, experiment with AI frameworks, and build a portfolio that showcases your abilities. Stay attuned to ethical considerations in AI, and actively participate in the AI community through networking and knowledge-sharing. Continuous learning, persistence, and the application of AI to real-world challenges are key to becoming proficient in this dynamic and transformative field.
Read More
In an era where science fiction is fast becoming our reality, the realm of Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands at the forefront of innovation and transformation. The question that lingers in the minds of technologists, futurists, and curious minds alike is, "What Lies Ahead for the Future of Artificial Intelligence?" This blog embarks on a journey through the landscapes of AI, aiming to dissect its growth, evolution, and the profound impact it has had on our world.
Table of Contents
-
Growth of AI
-
What Did the Future of AI Look Like 10 Years Ago?
-
Evolution of AI
-
Future of Artificial Intelligence
-
Impact of AI
-
Myths About Advanced Artificial Intelligence
-
AI and the Future of Work
-
Master AI Today
Growth of AI
The growth of AI, or Artificial Intelligence, signifies the relentless advancement and proliferation of intelligent technologies that are reshaping our world. This growth is fueled by technological breakthroughs, with increasingly powerful hardware and sophisticated algorithms driving the development of AI systems. Coupled with the explosion of data availability, AI has found its way into various industries, from healthcare to finance, revolutionizing processes and decision-making. In our everyday lives, AI-driven virtual assistants and recommendation systems have become ubiquitous. Global investment in AI research and development continues to soar, further accelerating AI's expansion. Nevertheless, this journey is not without its challenges, such as data privacy concerns and ethical dilemmas, which need to be addressed as we navigate the ever-expanding horizons of AI.
What Did the Future of AI Look Like 10 Years Ago?
The perception of the future of AI 10 years ago, around 2013, was a mixture of excitement, optimism, and uncertainty. While AI had already made significant strides in areas like natural language processing, machine learning, and computer vision, it had not yet achieved the widespread integration and prominence we see today. Here are some key aspects of how the future of AI was envisioned a decade ago:
-
Rise of Personal Assistants: Virtual personal assistants like Siri and Google Assistant were beginning to gain popularity. The vision was that these AI-driven assistants would become even more capable, understanding natural language and providing personalized assistance in various aspects of our lives.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: The concept of self-driving cars and their potential to revolutionize transportation was emerging. AI was seen as a critical technology in making autonomous vehicles a reality.
-
Healthcare and Diagnostics: There was optimism about AI's potential to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases more accurately and efficiently. Medical imaging and diagnostic tools powered by AI were on the horizon.
-
AI in Business: In the business world, AI was anticipated to improve decision-making through advanced analytics and predictive modeling. Automation of routine tasks in industries like customer service and data entry was also anticipated.
-
Challenges and Concerns: Alongside the excitement, there were concerns about the ethical and societal implications of AI, such as job displacement, algorithmic bias, and privacy issues. These concerns were seen as important topics to address in the future.
-
Limited Understanding of Deep Learning: While deep learning had made significant progress, it had not yet become the dominant AI paradigm it is today. Many people were still exploring other machine learning approaches and algorithms.
Overall, the future of AI 10 years ago was characterized by high expectations for its transformative potential in various domains. However, there was a level of uncertainty about how rapidly these advancements would occur and how society would adapt to the changes brought about by AI technologies. In hindsight, many of these early predictions have materialized to a significant extent, but AI's growth and impact have also presented new challenges and opportunities beyond what was imagined a decade ago.
Evolution of AI
Early Foundations and Optimism (1950s-1960s): The evolution of AI began in the 1950s when computer scientists and mathematicians first contemplated the idea of creating machines that could exhibit human-like intelligence. Pioneers like Alan Turing, John McCarthy, and Marvin Minsky laid the groundwork for AI by developing concepts of computational intelligence and symbolic reasoning. During this period, optimism ran high as researchers believed that AI could solve complex problems, automate decision-making, and simulate human cognitive processes. However, computational limitations and the complexity of human intelligence led to early challenges and set the stage for the first "AI winter" in the 1970s.
Setbacks and Stagnation (1970s-1980s): The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a slowdown in AI research, commonly referred to as the "AI winter." High expectations collided with the reality that AI technologies were not yet capable of delivering on their promises. Funding for AI projects dwindled, and progress stagnated. Expert systems, one of the prominent approaches during this era, demonstrated limited adaptability and struggled to handle real-world complexities. The lack of practical AI applications and unmet expectations contributed to a degree of skepticism about the field's prospects.
Resurgence and Breakthroughs (1990s-Present): AI experienced a resurgence in the 1990s, transitioning from symbolic reasoning to machine learning approaches. Researchers shifted their focus to developing algorithms that could learn from data, resulting in significant progress. The advent of big data, powerful computing resources, and deep learning techniques in the 2010s propelled AI to new heights. Deep neural networks became the foundation for transformative breakthroughs in areas like image recognition, natural language understanding, and autonomous systems. AI is now deeply integrated into various industries and aspects of daily life, reshaping how we work, interact, and solve complex problems. As AI continues to evolve, the quest for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and the responsible development of AI technologies remain central to discussions about its future.
Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a topic of great fascination and speculation due to the rapid advancements and transformative potential of this field. Here are some key aspects to consider when contemplating the future of AI:
-
Enhanced Automation: AI will continue to play a significant role in automating routine and repetitive tasks across various industries. This includes manufacturing, customer service, data analysis, and more. As AI algorithms become more sophisticated, they will enable greater levels of efficiency, cost savings, and accuracy in these domains.
-
Personalization and Recommendation: AI-driven recommendation systems will become even more personalized, offering tailored content, products, and services to individuals. This level of personalization will enhance user experiences in e-commerce, content streaming, and marketing, among other areas.
-
Healthcare Revolution: AI's impact on healthcare will be profound. AI-powered diagnostic tools, predictive analytics, and drug discovery processes will lead to earlier disease detection, more effective treatments, and improved patient outcomes. Telemedicine and remote monitoring will become more common, especially in remote or underserved areas.
-
Autonomous Systems: AI will continue to advance autonomous systems, particularly in self-driving cars, drones, and robotics. These technologies will reshape transportation, logistics, and manufacturing, potentially leading to safer and more efficient operations.
-
Natural Language Processing: AI's capabilities in understanding and generating human language will expand. Conversational AI, chatbots, and virtual assistants will become more sophisticated and capable of handling complex interactions. This will have applications in customer service, healthcare, education, and more.
The future of AI is dynamic and full of promise, but it also poses challenges related to ethics, regulation, and the impact on employment. As AI continues to evolve, it will require careful stewardship to harness its potential for the benefit of humanity while addressing its associated risks.
Impact of AI
AI's impact on society is twofold, offering significant benefits and presenting complex challenges. On one hand, AI has ushered in a new era of efficiency and productivity by automating routine tasks, leading to cost savings and improved operational performance across industries. It has also revolutionized healthcare, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and patient care. Furthermore, AI-driven personalization and recommendation systems have transformed the way businesses engage with customers, offering tailored experiences and boosting user satisfaction. In sectors like finance and education, AI is streamlining processes, making financial decisions more informed, and personalizing learning experiences for students. The creative possibilities of AI and its potential to address global challenges, such as climate change, highlight its role in advancing innovation and research.
Conversely, AI's impact raises concerns regarding ethics and social implications. Issues like algorithmic bias, which can perpetuate discrimination, have come to the forefront. The widespread automation enabled by AI has sparked debates about job displacement and the need for reskilling and upskilling the workforce. Privacy concerns arise from the vast amount of data AI systems collect and analyze, necessitating robust data protection measures. Moreover, as AI technologies continue to advance, there is a need for clear ethical guidelines and regulations to ensure that AI serves humanity's best interests and does not compromise fundamental values. Balancing AI's tremendous potential with these challenges is essential for a harmonious integration of AI into our society.
Myths About Advanced Artificial Intelligence
As advanced artificial intelligence (AI) continues to develop, several myths and misconceptions have emerged that can hinder our understanding of its capabilities and limitations. Here are some common myths about advanced AI:
-
AI Possesses Human-Like General Intelligence: One of the most pervasive myths is that advanced AI systems, even those using deep learning and neural networks, possess human-like general intelligence. In reality, AI today is primarily narrow or specialized, excelling at specific tasks but lacking the broad cognitive abilities and common-sense reasoning that humans have.
-
AI is Infallible: There's a misconception that AI is always accurate and error-free. While AI can perform exceptionally well in certain tasks, it's not immune to errors, especially in situations where it encounters novel or ambiguous data. Additionally, AI can be influenced by biased training data, leading to biased outcomes.
-
AI Understands Like Humans: AI systems can process and generate human language, but they don't truly understand it. They rely on statistical patterns and data, lacking genuine comprehension or consciousness. This myth can lead to overestimating AI's comprehension and reasoning abilities.
-
AI Will Replace All Jobs: While AI automation is transforming some industries, it won't replace all jobs. Instead, it's more likely to augment human work by automating repetitive tasks and allowing humans to focus on creative, strategic, and complex problem-solving roles.
-
AI is a Silver Bullet: Expecting AI to solve all problems is unrealistic. AI is a tool, and its effectiveness depends on the quality of data, the appropriateness of algorithms, and the problem it's applied to. It's not a one-size-fits-all solution.
AI and the Future of Work Top of Form
AI is ushering in a transformative era for the future of work. It promises to revolutionize industries by automating routine tasks and augmenting human capabilities. While automation may lead to concerns about job displacement, it also opens up opportunities for upskilling and reskilling the workforce, with an emphasis on jobs that require creativity, empathy, and complex problem-solving—areas where AI currently falls short. The synergy between humans and AI, along with the responsible development and ethical implementation of AI technologies, will be pivotal in shaping the future of work, enhancing productivity, and improving job quality. It is a dynamic landscape that requires adaptability, lifelong learning, and a balance between efficiency and preserving the human element in the workplace.
Additionally, AI facilitates remote work and flexible arrangements, changing the traditional workplace dynamic. This shift, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, offers benefits such as work-life balance and access to a global talent pool but also presents challenges related to cybersecurity and employee well-being. As AI continues to evolve, its impact on the future of work will be determined by how well individuals, organizations, and governments navigate these changes, foster innovation, and ensure that AI technologies contribute to a more equitable and productive workforce.
Master AI Today
Mastering AI today requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing education, hands-on experience, and a commitment to staying updated with the field's rapid advancements. Begin by acquiring a solid foundation in AI fundamentals through courses and self-study, with a focus on programming languages like Python, deep learning concepts, and data handling skills. Engage in practical projects, experiment with AI frameworks, and build a portfolio that showcases your abilities. Stay attuned to ethical considerations in AI, and actively participate in the AI community through networking and knowledge-sharing. Continuous learning, persistence, and the application of AI to real-world challenges are key to becoming proficient in this dynamic and transformative field.
Six Sigma vs. Lean Six Sigma: Which Certification to Choose?
In the quest for professional development and career advancement, the world of certifications stands as an essential crossroads, offering a multitude of paths to choose from. Among the many options, "Six Sigma" and "Lean Six Sigma" certifications shine as beacons of quality and process improvement, coveted by industries far and wide. However, faced with these two formidable choices, aspiring professionals often find themselves at a crossroads, pondering the critical question: "Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma: Which Certification Path Should You Take?" This decision is no trifling matter, as it can significantly impact one's career trajectory and skill set. In this exploration, we delve into the nuances of both certification paths, shedding light on their differences, similarities, and the factors that can guide you toward making an informed and rewarding choice. Whether you're navigating the intricacies of quality management or seeking to optimize processes, this guide aims to equip you with the insights necessary to embark on the certification journey that aligns best with your aspirations and ambitions.
Table of Contents
-
What is Six Sigma?
-
What is Lean?
-
What is Lean Six Sigma?
-
Lean vs Six Sigma: Similarities and Differences
-
Certification Eligibilities, Examinations, and Responsibilities
-
Which is Right for You?
-
FAQs
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology and set of tools and techniques used to improve processes and reduce defects in various industries, with a primary focus on achieving higher levels of quality and efficiency. It was originally developed by Motorola in the 1980s and later popularized by companies like General Electric.
The term "Six Sigma" refers to a statistical measure of process performance, which signifies that a process is capable of producing fewer than 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO). In essence, it represents a high level of process accuracy and consistency.
Six Sigma is used in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and service sectors, to streamline processes, reduce costs, improve quality, and increase customer satisfaction. It offers a systematic approach to problem-solving and process improvement, making it a valuable tool for organizations seeking operational excellence.
What is Lean?
Lean, often referred to as Lean Thinking or Lean Management, is a methodology and philosophy that focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing value in processes. It originated from the manufacturing practices developed by Toyota in Japan and is often associated with the Toyota Production System (TPS). However, Lean principles have since been applied to various industries and sectors beyond manufacturing, including healthcare, service, and software development.
Lean principles aim to create more efficient, responsive, and customer-focused organizations. By eliminating waste and optimizing processes, Lean helps organizations deliver higher quality products and services while reducing costs and lead times. It's a holistic approach to operational excellence that goes beyond specific tools and techniques to instill a culture of continuous improvement throughout an organization.
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a hybrid approach that combines the principles and methodologies of Lean and Six Sigma. It is a comprehensive strategy for process improvement that seeks to eliminate waste and defects while optimizing efficiency and quality. Lean focuses on reducing waste and increasing flow, while Six Sigma emphasizes reducing defects and variations in processes. By integrating these two approaches, Lean Six Sigma aims to create a powerful framework for achieving operational excellence and improving organizational performance.
Lean Six Sigma is widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and service sectors, to enhance process efficiency, reduce defects, minimize waste, and improve overall organizational performance. It offers a structured and data-driven approach to achieving excellence in both processes and outcomes.
Lean vs Six Sigma: Similarities and Differences
Lean and Six Sigma are two distinct methodologies for process improvement, but they share some similarities while also having key differences. Here's an overview of their similarities and differences:
Similarities:
-
Focus on Process Improvement: Both Lean and Six Sigma are centered on improving processes to achieve better outcomes, whether that's reducing defects, minimizing waste, enhancing efficiency, or improving overall quality.
-
Data-Driven: Both methodologies rely on data and statistical analysis to identify problems, measure process performance, and make informed decisions. Data is used to quantify issues and track progress.
-
Customer-Centric: Both Lean and Six Sigma emphasize meeting and exceeding customer expectations. They aim to deliver products or services that align with customer needs and preferences.
-
Continuous Improvement: Continuous improvement is a core principle of both Lean and Six Sigma. They advocate for an ongoing commitment to identifying and addressing issues, making incremental improvements, and striving for excellence.
-
Team-Based Approach: Both methodologies often involve cross-functional teams that collaborate to solve problems and drive improvements. This encourages a diversity of perspectives and expertise.
-
Root Cause Analysis: Both Lean and Six Sigma seek to identify and address the root causes of problems rather than just treating symptoms. This helps prevent issues from recurring.
Differences:
-
Primary Focus:
-
Lean primarily concentrates on the elimination of waste and the optimization of processes for efficiency and flow. Its main goal is to deliver value to customers while minimizing non-value-added activities.
-
Six Sigma primarily focuses on reducing process variation and defects. It aims to achieve a level of quality where the probability of defects is extremely low (less than 3.4 defects per million opportunities).
-
Methodologies:
-
Lean often uses tools like Value Stream Mapping, 5S, Kanban, and visual management techniques to improve processes and reduce waste.
-
Six Sigma employs statistical tools and techniques, such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), to measure and analyze process performance and drive improvements.
-
Waste Reduction:
-
Lean places a strong emphasis on identifying and eliminating various types of waste, including overproduction, transportation, waiting, and more.
-
Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and minimizing process variation, which can lead to defects or deviations from desired outcomes.
-
Speed vs. Precision:
-
Lean is often associated with faster improvements and quicker results due to its focus on reducing waste and improving flow.
-
Six Sigma can take longer to implement, as it involves a more rigorous and data-intensive approach to reducing defects and variation.
-
Tools and Techniques:
-
Lean tools are geared toward process optimization and include techniques for visual management and rapid problem-solving.
-
Six Sigma tools are statistical in nature and are used to measure, analyze, and control processes to reduce variation and defects.
Certification Eligibilities, Examinations, and Responsibilities
Certification eligibility, examinations, and responsibilities can vary significantly depending on the specific certification program and the organization or governing body that administers it. Here is a general overview of what these aspects typically involve:
Certification Eligibility:
Eligibility for Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications varies based on the certification level and the certifying organization. Generally, Yellow Belt certifications have minimal prerequisites, while Green Belt certifications often require a bachelor's degree or equivalent experience. Black Belt certifications typically demand both a bachelor's degree and relevant work experience, with some programs expecting Green Belt certification as well. Master Black Belt certifications are typically reserved for highly experienced professionals who have completed numerous successful projects and demonstrated leadership in Six Sigma initiatives. While the specific requirements may vary, a solid understanding of Six Sigma concepts and, for Lean Six Sigma, familiarity with Lean principles are essential for pursuing these certifications. Candidates should always refer to the certifying organization's guidelines for precise eligibility criteria.
Examinations:
Examinations for Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications are comprehensive assessments that evaluate candidates' knowledge and expertise in quality management, process improvement, statistical analysis, and Lean methodologies. These exams vary in content, format, duration, and passing score based on the certification level (e.g., Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt) and the certifying organization. Typically, they encompass a range of question types, such as multiple-choice and true/false questions, and are administered through authorized testing centers or online proctoring services. Achieving a passing score is a critical milestone in earning these prestigious certifications, demonstrating proficiency in problem-solving, process optimization, and quality enhancement within an organization.
Responsibilities:
Responsibilities associated with Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications encompass various stages of the certification process and ongoing professional practice. Candidates pursuing these certifications are first responsible for thorough preparation, including studying the relevant materials and attending training if necessary. They must then take the initiative to register for the certification exam and adhere to the rules and procedures on exam day. During the exam, candidates must demonstrate their knowledge and problem-solving abilities. Afterward, successful candidates receive their certifications, but the responsibility doesn't end there. Certified professionals have a duty to apply their knowledge in the workplace, contributing to process improvement initiatives and ethical conduct. Continuous learning and maintaining ethical standards are also ongoing responsibilities associated with these certifications, reflecting a commitment to excellence and the promotion of quality within organizations.
It's important for individuals seeking certification to carefully review the specific eligibility requirements, examination details, and responsibilities outlined by the certifying organization to ensure they are fully prepared and compliant with the certification process.
Which is Right for You?
Determining whether Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma is right for you depends on your specific career goals, the industry you work in or plan to work in, and your preferences for process improvement methodologies. Here are some considerations to help you decide which path might be more suitable:
Choose Six Sigma if:
-
You prioritize reducing defects: Six Sigma is particularly effective for industries where reducing defects and achieving near-perfect quality is critical, such as manufacturing and healthcare.
-
You enjoy statistical analysis: Six Sigma places a strong emphasis on statistical tools and data analysis. If you have a passion for data-driven decision-making and enjoy working with statistical techniques, Six Sigma might align well with your interests.
-
You want a structured problem-solving framework: Six Sigma provides a highly structured problem-solving approach through the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology, making it suitable for complex process improvement projects.
-
Your industry values traditional quality management: Some industries have a long history of using Six Sigma for quality management, making it a respected certification in those sectors.
Choose Lean Six Sigma if:
-
You seek to minimize waste: Lean Six Sigma excels at waste reduction and process optimization. If you are interested in eliminating non-value-added activities, improving efficiency, and enhancing flow within processes, Lean Six Sigma is a strong choice.
-
You prefer a holistic approach: Lean Six Sigma combines the principles of both Lean and Six Sigma, offering a more comprehensive framework that addresses both defects and waste. It's a versatile methodology suitable for a wide range of industries.
-
Your industry values efficiency and customer satisfaction: Lean Six Sigma's focus on improving processes and delivering value to customers aligns well with industries that prioritize efficiency, such as manufacturing, service, and healthcare.
-
You enjoy visual management and rapid problem-solving: Lean tools like Kanban, 5S, and visual management techniques can make problem-solving more intuitive and efficient.
Ultimately, the decision between Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma should align with your career aspirations, interests, and the specific needs of the industry you are or plan to be a part of. It's worth noting that some professionals choose to pursue both certifications to have a well-rounded skill set that covers both defect reduction and waste elimination, allowing them to be more versatile problem solvers in various professional settings.
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications?
A: Six Sigma primarily focuses on reducing defects and process variation, while Lean Six Sigma combines Six Sigma principles with Lean methodology, emphasizing waste reduction and process optimization. The choice between them depends on your specific career goals and the nature of the industry you're interested in.
Q2: Which certification is more suitable for a career in manufacturing?
A: Both Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications are valuable in manufacturing. Six Sigma may be more suitable for quality control and defect reduction, while Lean Six Sigma can help streamline processes and reduce waste in manufacturing.
Q3: Are there any prerequisites for Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma certifications?
A: Prerequisites can vary depending on the certification level and the certifying organization. Some certifications may require prior work experience or completion of specific training courses. Check the requirements of the certification program you're interested in.
Q4: Can I pursue both Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications simultaneously?
A: Yes, it's possible to pursue both certifications. Some individuals choose to earn both to have a well-rounded skill set that combines defect reduction and process optimization.
Q5: Do I need to choose between Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma, or can I combine both approaches in my career?
A: You can certainly combine both approaches in your career. In fact, many organizations adopt Lean Six Sigma principles to benefit from both defect reduction and waste elimination.
Q6: How do I decide which certification path is right for me?
A: Consider your career goals, industry preferences, and the specific skills you want to develop. If you're interested in quality control and statistical analysis, Six Sigma may be a better fit. If you're more focused on process efficiency and waste reduction, Lean Six Sigma may be the way to go.
Q7: Which certification is more recognized by employers?
A: The recognition of Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications can vary by industry and region. It's essential to research the specific demands of your desired job market. Both certifications are widely recognized and respected.
Q8: Can I switch from Six Sigma to Lean Six Sigma or vice versa after obtaining one certification?
A: Yes, you can switch between the two paths. Many concepts and tools overlap between the two methodologies, making it relatively easy to transition.
Q9: How long does it typically take to earn a Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma certification?
A: The duration varies based on the certification level (e.g., Green Belt, Black Belt) and the training program. Some certifications can be completed in a few weeks, while others may take several months or longer.
Q10: What is the average cost of obtaining a Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma certification?
A: Certification costs can vary widely depending on the level, the certifying organization, and whether you choose to undergo training. It's essential to research the specific program and its associated costs.
Read More
In the quest for professional development and career advancement, the world of certifications stands as an essential crossroads, offering a multitude of paths to choose from. Among the many options, "Six Sigma" and "Lean Six Sigma" certifications shine as beacons of quality and process improvement, coveted by industries far and wide. However, faced with these two formidable choices, aspiring professionals often find themselves at a crossroads, pondering the critical question: "Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma: Which Certification Path Should You Take?" This decision is no trifling matter, as it can significantly impact one's career trajectory and skill set. In this exploration, we delve into the nuances of both certification paths, shedding light on their differences, similarities, and the factors that can guide you toward making an informed and rewarding choice. Whether you're navigating the intricacies of quality management or seeking to optimize processes, this guide aims to equip you with the insights necessary to embark on the certification journey that aligns best with your aspirations and ambitions.
Table of Contents
-
What is Six Sigma?
-
What is Lean?
-
What is Lean Six Sigma?
-
Lean vs Six Sigma: Similarities and Differences
-
Certification Eligibilities, Examinations, and Responsibilities
-
Which is Right for You?
-
FAQs
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology and set of tools and techniques used to improve processes and reduce defects in various industries, with a primary focus on achieving higher levels of quality and efficiency. It was originally developed by Motorola in the 1980s and later popularized by companies like General Electric.
The term "Six Sigma" refers to a statistical measure of process performance, which signifies that a process is capable of producing fewer than 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO). In essence, it represents a high level of process accuracy and consistency.
Six Sigma is used in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and service sectors, to streamline processes, reduce costs, improve quality, and increase customer satisfaction. It offers a systematic approach to problem-solving and process improvement, making it a valuable tool for organizations seeking operational excellence.
What is Lean?
Lean, often referred to as Lean Thinking or Lean Management, is a methodology and philosophy that focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing value in processes. It originated from the manufacturing practices developed by Toyota in Japan and is often associated with the Toyota Production System (TPS). However, Lean principles have since been applied to various industries and sectors beyond manufacturing, including healthcare, service, and software development.
Lean principles aim to create more efficient, responsive, and customer-focused organizations. By eliminating waste and optimizing processes, Lean helps organizations deliver higher quality products and services while reducing costs and lead times. It's a holistic approach to operational excellence that goes beyond specific tools and techniques to instill a culture of continuous improvement throughout an organization.
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a hybrid approach that combines the principles and methodologies of Lean and Six Sigma. It is a comprehensive strategy for process improvement that seeks to eliminate waste and defects while optimizing efficiency and quality. Lean focuses on reducing waste and increasing flow, while Six Sigma emphasizes reducing defects and variations in processes. By integrating these two approaches, Lean Six Sigma aims to create a powerful framework for achieving operational excellence and improving organizational performance.
Lean Six Sigma is widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and service sectors, to enhance process efficiency, reduce defects, minimize waste, and improve overall organizational performance. It offers a structured and data-driven approach to achieving excellence in both processes and outcomes.
Lean vs Six Sigma: Similarities and Differences
Lean and Six Sigma are two distinct methodologies for process improvement, but they share some similarities while also having key differences. Here's an overview of their similarities and differences:
Similarities:
-
Focus on Process Improvement: Both Lean and Six Sigma are centered on improving processes to achieve better outcomes, whether that's reducing defects, minimizing waste, enhancing efficiency, or improving overall quality.
-
Data-Driven: Both methodologies rely on data and statistical analysis to identify problems, measure process performance, and make informed decisions. Data is used to quantify issues and track progress.
-
Customer-Centric: Both Lean and Six Sigma emphasize meeting and exceeding customer expectations. They aim to deliver products or services that align with customer needs and preferences.
-
Continuous Improvement: Continuous improvement is a core principle of both Lean and Six Sigma. They advocate for an ongoing commitment to identifying and addressing issues, making incremental improvements, and striving for excellence.
-
Team-Based Approach: Both methodologies often involve cross-functional teams that collaborate to solve problems and drive improvements. This encourages a diversity of perspectives and expertise.
-
Root Cause Analysis: Both Lean and Six Sigma seek to identify and address the root causes of problems rather than just treating symptoms. This helps prevent issues from recurring.
Differences:
-
Primary Focus:
-
Lean primarily concentrates on the elimination of waste and the optimization of processes for efficiency and flow. Its main goal is to deliver value to customers while minimizing non-value-added activities.
-
Six Sigma primarily focuses on reducing process variation and defects. It aims to achieve a level of quality where the probability of defects is extremely low (less than 3.4 defects per million opportunities).
-
-
Methodologies:
-
Lean often uses tools like Value Stream Mapping, 5S, Kanban, and visual management techniques to improve processes and reduce waste.
-
Six Sigma employs statistical tools and techniques, such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), to measure and analyze process performance and drive improvements.
-
-
Waste Reduction:
-
Lean places a strong emphasis on identifying and eliminating various types of waste, including overproduction, transportation, waiting, and more.
-
Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and minimizing process variation, which can lead to defects or deviations from desired outcomes.
-
-
Speed vs. Precision:
-
Lean is often associated with faster improvements and quicker results due to its focus on reducing waste and improving flow.
-
Six Sigma can take longer to implement, as it involves a more rigorous and data-intensive approach to reducing defects and variation.
-
-
Tools and Techniques:
-
Lean tools are geared toward process optimization and include techniques for visual management and rapid problem-solving.
-
Six Sigma tools are statistical in nature and are used to measure, analyze, and control processes to reduce variation and defects.
-
Certification Eligibilities, Examinations, and Responsibilities
Certification eligibility, examinations, and responsibilities can vary significantly depending on the specific certification program and the organization or governing body that administers it. Here is a general overview of what these aspects typically involve:
Certification Eligibility:
Eligibility for Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications varies based on the certification level and the certifying organization. Generally, Yellow Belt certifications have minimal prerequisites, while Green Belt certifications often require a bachelor's degree or equivalent experience. Black Belt certifications typically demand both a bachelor's degree and relevant work experience, with some programs expecting Green Belt certification as well. Master Black Belt certifications are typically reserved for highly experienced professionals who have completed numerous successful projects and demonstrated leadership in Six Sigma initiatives. While the specific requirements may vary, a solid understanding of Six Sigma concepts and, for Lean Six Sigma, familiarity with Lean principles are essential for pursuing these certifications. Candidates should always refer to the certifying organization's guidelines for precise eligibility criteria.
Examinations:
Examinations for Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications are comprehensive assessments that evaluate candidates' knowledge and expertise in quality management, process improvement, statistical analysis, and Lean methodologies. These exams vary in content, format, duration, and passing score based on the certification level (e.g., Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt) and the certifying organization. Typically, they encompass a range of question types, such as multiple-choice and true/false questions, and are administered through authorized testing centers or online proctoring services. Achieving a passing score is a critical milestone in earning these prestigious certifications, demonstrating proficiency in problem-solving, process optimization, and quality enhancement within an organization.
Responsibilities:
Responsibilities associated with Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications encompass various stages of the certification process and ongoing professional practice. Candidates pursuing these certifications are first responsible for thorough preparation, including studying the relevant materials and attending training if necessary. They must then take the initiative to register for the certification exam and adhere to the rules and procedures on exam day. During the exam, candidates must demonstrate their knowledge and problem-solving abilities. Afterward, successful candidates receive their certifications, but the responsibility doesn't end there. Certified professionals have a duty to apply their knowledge in the workplace, contributing to process improvement initiatives and ethical conduct. Continuous learning and maintaining ethical standards are also ongoing responsibilities associated with these certifications, reflecting a commitment to excellence and the promotion of quality within organizations.
It's important for individuals seeking certification to carefully review the specific eligibility requirements, examination details, and responsibilities outlined by the certifying organization to ensure they are fully prepared and compliant with the certification process.
Which is Right for You?
Determining whether Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma is right for you depends on your specific career goals, the industry you work in or plan to work in, and your preferences for process improvement methodologies. Here are some considerations to help you decide which path might be more suitable:
Choose Six Sigma if:
-
You prioritize reducing defects: Six Sigma is particularly effective for industries where reducing defects and achieving near-perfect quality is critical, such as manufacturing and healthcare.
-
You enjoy statistical analysis: Six Sigma places a strong emphasis on statistical tools and data analysis. If you have a passion for data-driven decision-making and enjoy working with statistical techniques, Six Sigma might align well with your interests.
-
You want a structured problem-solving framework: Six Sigma provides a highly structured problem-solving approach through the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology, making it suitable for complex process improvement projects.
-
Your industry values traditional quality management: Some industries have a long history of using Six Sigma for quality management, making it a respected certification in those sectors.
Choose Lean Six Sigma if:
-
You seek to minimize waste: Lean Six Sigma excels at waste reduction and process optimization. If you are interested in eliminating non-value-added activities, improving efficiency, and enhancing flow within processes, Lean Six Sigma is a strong choice.
-
You prefer a holistic approach: Lean Six Sigma combines the principles of both Lean and Six Sigma, offering a more comprehensive framework that addresses both defects and waste. It's a versatile methodology suitable for a wide range of industries.
-
Your industry values efficiency and customer satisfaction: Lean Six Sigma's focus on improving processes and delivering value to customers aligns well with industries that prioritize efficiency, such as manufacturing, service, and healthcare.
-
You enjoy visual management and rapid problem-solving: Lean tools like Kanban, 5S, and visual management techniques can make problem-solving more intuitive and efficient.
Ultimately, the decision between Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma should align with your career aspirations, interests, and the specific needs of the industry you are or plan to be a part of. It's worth noting that some professionals choose to pursue both certifications to have a well-rounded skill set that covers both defect reduction and waste elimination, allowing them to be more versatile problem solvers in various professional settings.
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications?
A: Six Sigma primarily focuses on reducing defects and process variation, while Lean Six Sigma combines Six Sigma principles with Lean methodology, emphasizing waste reduction and process optimization. The choice between them depends on your specific career goals and the nature of the industry you're interested in.
Q2: Which certification is more suitable for a career in manufacturing?
A: Both Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications are valuable in manufacturing. Six Sigma may be more suitable for quality control and defect reduction, while Lean Six Sigma can help streamline processes and reduce waste in manufacturing.
Q3: Are there any prerequisites for Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma certifications?
A: Prerequisites can vary depending on the certification level and the certifying organization. Some certifications may require prior work experience or completion of specific training courses. Check the requirements of the certification program you're interested in.
Q4: Can I pursue both Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications simultaneously?
A: Yes, it's possible to pursue both certifications. Some individuals choose to earn both to have a well-rounded skill set that combines defect reduction and process optimization.
Q5: Do I need to choose between Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma, or can I combine both approaches in my career?
A: You can certainly combine both approaches in your career. In fact, many organizations adopt Lean Six Sigma principles to benefit from both defect reduction and waste elimination.
Q6: How do I decide which certification path is right for me?
A: Consider your career goals, industry preferences, and the specific skills you want to develop. If you're interested in quality control and statistical analysis, Six Sigma may be a better fit. If you're more focused on process efficiency and waste reduction, Lean Six Sigma may be the way to go.
Q7: Which certification is more recognized by employers?
A: The recognition of Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma certifications can vary by industry and region. It's essential to research the specific demands of your desired job market. Both certifications are widely recognized and respected.
Q8: Can I switch from Six Sigma to Lean Six Sigma or vice versa after obtaining one certification?
A: Yes, you can switch between the two paths. Many concepts and tools overlap between the two methodologies, making it relatively easy to transition.
Q9: How long does it typically take to earn a Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma certification?
A: The duration varies based on the certification level (e.g., Green Belt, Black Belt) and the training program. Some certifications can be completed in a few weeks, while others may take several months or longer.
Q10: What is the average cost of obtaining a Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma certification?
A: Certification costs can vary widely depending on the level, the certifying organization, and whether you choose to undergo training. It's essential to research the specific program and its associated costs.
Big Data Analytics: Empowering modern insights & growth.
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on 'What is Big Data Analytics and What is Its Significance in the Modern World?' In this in-depth exploration, we delve into the realm of big data analytics, shedding light on its fundamental concepts, applications, and its paramount importance in our contemporary data-driven society. Join us as we unravel the intricacies of this transformative technology and unveil its profound impact on businesses, industries, and society as a whole.
Table of Contents
What is Big Data Analytics?
Why is big data analytics important?
What is Big Data?
Uses and Examples of Big Data Analytics
History of Big Data Analytics
Benefits and Advantages of Big Data Analytics
The Lifecycle Phases of Big Data Analytics
Different Types of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics Tools
Big Data Industry Applications
FAQs
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big Data Analytics is the process of extracting valuable insights from vast and complex data sets, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions, enhance operational efficiency, improve customer experiences, manage risks effectively, and foster innovation across various industries. This transformative discipline combines data collection, storage, processing, analysis, visualization, and the utilization of machine learning techniques, empowering businesses to thrive in our data-centric modern world by leveraging the wealth of information available to them.
Why is big data analytics important?
Big Data Analytics is vital in today's digital age because it provides organizations with the ability to extract valuable insights from the vast volumes of data generated daily. This data, often referred to as "big data," encompasses a wide range of information from various sources, such as customer transactions, social media interactions, sensor data, and more. Without effective analytics, this data would remain largely untapped potential. By employing advanced techniques and technologies, organizations can uncover hidden patterns, trends, and correlations within their data, allowing for informed decision-making, improved operational efficiency, and the ability to gain a competitive edge in rapidly evolving markets.
Furthermore, Big Data Analytics has a profound impact on innovation and problem-solving across industries. It enables businesses to innovate in their product offerings, marketing strategies, and operational processes by providing a data-driven foundation for experimentation and improvement. Moreover, it plays a critical role in fields like healthcare, where it can lead to advancements in patient care, drug discovery, and disease prevention. In essence, Big Data Analytics is essential because it transforms data into actionable knowledge, fostering smarter decisions, greater efficiency, and continuous innovation in both the private and public sectors.
What is Big Data?
Big Data refers to extremely large and complex sets of data that exceed the capabilities of traditional data processing tools and methods. These data sets are characterized by what is often referred to as the "3Vs": volume, velocity, and variety.
-
Volume: Big Data typically involves massive amounts of data, often ranging from terabytes to petabytes or more. This data can be generated from various sources, including sensors, social media, business transactions, and more.
-
Velocity: Data is generated at an unprecedented speed in today's digital world. This real-time or near-real-time data flow requires rapid processing and analysis to derive meaningful insights and make timely decisions.
-
Variety: Big Data comes in various formats, including structured data (such as databases and spreadsheets), semi-structured data (like XML and JSON files), and unstructured data (such as text documents, social media posts, and multimedia content). Analyzing and making sense of this diverse data landscape is a fundamental challenge in Big Data.
In addition to the 3Vs, Big Data is often associated with two more characteristics:
-
Variability: Data can be inconsistent and vary in its format and quality over time.
-
Veracity: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of Big Data can be a challenge, as data may contain errors or inconsistencies.
Effectively managing, storing, processing, and analyzing Big Data is crucial for organizations looking to gain valuable insights, make data-driven decisions, and derive business value from this wealth of information. This has led to the development of specialized technologies and tools, such as distributed computing frameworks like Hadoop and advanced analytics techniques like machine learning, to handle the unique challenges posed by Big Data.
Uses and Examples of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics serves as a powerful tool across various industries by harnessing the vast volumes of data generated in today's digital age. One of its primary applications is in the realm of business intelligence and analytics, where organizations leverage it to gain a deeper understanding of their operations, customers, and markets. For instance, retail companies employ Big Data Analytics to analyze sales data and customer purchase patterns, enabling them to optimize inventory management and design personalized marketing campaigns. This data-driven approach enhances decision-making, helping businesses remain competitive and agile in rapidly evolving markets.
Another significant use of Big Data Analytics is in healthcare, where it aids in patient care and disease management. By analyzing electronic health records and medical data, healthcare providers can make more accurate diagnoses, recommend tailored treatment plans, and predict disease outbreaks. This application not only improves patient outcomes but also contributes to the overall efficiency of healthcare systems. In essence, Big Data Analytics is a multidimensional tool that empowers organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights, driving innovation, efficiency, and informed decision-making across a wide spectrum of industries and sectors.
History of Big Data Analytics
The history of Big Data Analytics can be traced back to the early days of computing, but it has evolved significantly over time. Here's an overview of its key milestones:
-
1950s-1960s: The concept of data processing and analysis emerged with the advent of computers. Early mainframe computers were used for basic data processing tasks, such as sorting and aggregating large volumes of data.
-
1970s-1980s: The development of relational database management systems (RDBMS) marked a significant step forward. SQL (Structured Query Language) became the standard for querying and managing structured data. However, these systems had limitations in handling large and complex datasets.
-
1990s: Data warehousing gained prominence as organizations started collecting and storing vast amounts of data. Data warehousing solutions allowed for the consolidation of data from various sources, making it easier to analyze and report on.
-
Early 2000s: The term "Big Data" began to gain traction as companies like Google and Yahoo faced challenges in managing and analyzing massive datasets. Google's MapReduce and the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) were pivotal in developing scalable solutions for processing Big Data.
-
Mid-2000s: Apache Hadoop, an open-source framework, emerged as a leading platform for processing and analyzing large datasets. It popularized the idea of distributed computing and laid the foundation for Big Data Analytics.
-
Late 2000s-2010s: As organizations generated more data from various sources, technologies for Big Data Analytics continued to advance. Companies like Amazon, Facebook, and Netflix demonstrated the power of data-driven decision-making and personalized user experiences.
-
2010s-Present: Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) have become integral to Big Data Analytics. These technologies enable predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and automation of data analysis tasks. Cloud computing services, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, offer scalable platforms for Big Data processing and storage.
-
2020s: Big Data Analytics continues to evolve with a focus on real-time data processing, edge computing, and privacy considerations. Data governance and ethical use of data have also gained prominence.
Throughout its history, Big Data Analytics has transformed from a niche concept to a critical component of decision-making in various industries, ranging from finance and healthcare to e-commerce and entertainment. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the field of Big Data Analytics will likely continue to evolve and adapt to meet the ever-expanding demands of the digital age.
Benefits and Advantages of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics offers numerous benefits and advantages to organizations across various industries. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Big Data Analytics empowers organizations to make informed decisions based on real data rather than intuition or guesswork. This leads to more accurate and effective choices in various aspects of business operations.
-
Competitive Advantage: Companies that leverage Big Data Analytics gain a competitive edge by identifying market trends, customer preferences, and emerging opportunities faster and more accurately than their competitors.
-
Improved Operational Efficiency: By analyzing processes and operations, organizations can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. This optimization leads to cost reduction and enhanced productivity.
-
Enhanced Customer Experiences: Understanding customer behavior and preferences allows businesses to personalize products, services, and marketing campaigns. This leads to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Risk Management: In industries like finance and insurance, Big Data Analytics aids in assessing and mitigating risks more effectively. It can detect anomalies and potential issues early, helping prevent financial losses.
The Lifecycle Phases of Big Data Analytics
The eight key stages in the lifecycle of Big Data Analytics:
-
Data Collection: Gather data from various sources, such as databases, sensors, or social media.
-
Data Storage: Organize and store the data in suitable repositories like data lakes or warehouses.
-
Data Preprocessing: Clean, transform, and prepare the data for analysis to ensure quality and consistency.
-
Data Analysis: Apply statistical and machine learning techniques to extract insights from the data.
-
Data Visualization: Present the results through charts, graphs, and dashboards for better understanding.
-
Deployment: Implement analytical models into production systems for real-time decision-making.
-
Monitoring: Continuously oversee model performance and data quality.
-
Optimization: Fine-tune models and scale infrastructure to handle increased data demands.
Different Types of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics encompasses various types of analytical approaches, each tailored to address specific business or data challenges. Here are different types of Big Data Analytics:
-
Descriptive Analytics:
-
Purpose: Descriptive analytics focuses on summarizing historical data to provide insights into past trends and events.
-
Use Cases: It helps organizations understand what has happened in the past, such as sales trends, customer behavior, or website traffic patterns.
-
Diagnostic Analytics:
-
Purpose: Diagnostic analytics aims to identify the reasons behind past events or trends.
-
Use Cases: It helps uncover the causes of specific outcomes, such as understanding why sales dropped in a particular region or why a marketing campaign failed.
-
Predictive Analytics:
-
Purpose: Predictive analytics uses historical data and statistical algorithms to forecast future outcomes or trends.
-
Use Cases: Organizations use predictive analytics for demand forecasting, customer churn prediction, fraud detection, and inventory optimization.
-
Prescriptive Analytics:
-
Purpose: Prescriptive analytics goes beyond prediction by suggesting the best course of action to optimize outcomes.
-
Use Cases: It helps organizations make data-driven decisions by recommending actions based on predictive models. For instance, it can suggest pricing strategies to maximize profits.
Top of Form
Big Data Analytics Tools
Big Data Analytics tools are essential for processing, analyzing, and deriving insights from large and complex datasets. There are numerous tools available, each with its own strengths and capabilities. Here's a list of some popular Big Data Analytics tools:
-
Hadoop:
-
Description: Hadoop is an open-source framework that facilitates distributed storage and processing of large datasets across clusters of commodity hardware.
-
Key Features: Hadoop includes the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) for storage and MapReduce for parallel processing. Additionally, it offers various ecosystem components like Hive, Pig, and Spark for advanced analytics.
-
Apache Spark:
-
Description: Apache Spark is an open-source, distributed computing framework that provides high-speed, in-memory data processing capabilities.
-
Key Features: Spark offers libraries for machine learning (MLlib), graph processing (GraphX), and stream processing (Structured Streaming). It's known for its speed and versatility in processing both batch and real-time data.
-
Apache Flink:
-
Description: Apache Flink is an open-source stream processing framework designed for real-time data analytics.
-
Key Features: Flink provides event time processing, support for batch and stream processing, and stateful computations. It's commonly used in applications requiring low-latency, high-throughput data processing.
-
Apache Kafka:
-
Description: Apache Kafka is a distributed streaming platform used for building real-time data pipelines and event-driven applications.
-
Key Features: Kafka is known for its high throughput, fault tolerance, and scalability. It allows for the ingestion and processing of large volumes of streaming data.
-
Hive:
-
Description: Hive is a data warehousing and SQL-like query language system built on top of Hadoop for structured data analysis.
-
Key Features: Hive provides a familiar SQL interface for querying data stored in Hadoop, making it accessible to analysts and data scientists.
-
Pig:
-
Description: Apache Pig is a high-level scripting platform for data analysis and processing in Hadoop.
-
Key Features: Pig provides a simple scripting language called Pig Latin, which allows users to express data transformations and processing logic.
-
R and RStudio:
-
Description: R is a programming language and environment specifically designed for statistical analysis and data visualization.
-
Key Features: R, along with RStudio as an integrated development environment (IDE), offers a rich ecosystem of packages and libraries for data analysis, statistical modeling, and data visualization.
Big Data Industry Applications
The applications of Big Data analytics span across a wide range of industries, offering transformative solutions to various challenges. Here are some notable industry-specific applications:
-
Healthcare:
-
Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Analyzing patient data in EHRs to improve diagnoses, treatment plans, and patient outcomes.
-
Disease Prediction: Predicting disease outbreaks, identifying high-risk populations, and improving public health strategies.
-
Drug Discovery: Accelerating drug development by analyzing genomics data and identifying potential drug candidates.
-
Finance:
-
Risk Assessment: Using data analytics to assess credit risks, detect fraudulent transactions, and manage investment portfolios.
-
Algorithmic Trading: Employing data-driven algorithms to make real-time trading decisions in financial markets.
-
Customer Segmentation: Analyzing customer data to tailor financial products and services for different segments.
-
Retail and E-commerce:
-
Recommendation Systems: Offering personalized product recommendations based on customer behavior and preferences.
-
Inventory Management: Optimizing inventory levels to reduce costs and prevent stockouts.
-
Pricing Optimization: Dynamically adjusting prices based on demand and market conditions.
-
Manufacturing:
-
Predictive Maintenance: Monitoring equipment sensors to predict and prevent machine failures and reduce downtime.
-
Quality Control: Analyzing production data to identify defects and improve product quality.
-
Supply Chain Optimization: Optimizing logistics and supply chain operations to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
-
Telecommunications:
-
Network Optimization: Analyzing network data to improve network performance, reduce downtime, and enhance customer experiences.
-
Churn Prediction: Identifying and retaining at-risk customers by analyzing usage patterns and customer behavior.
FAQs
-
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big Data Analytics is the process of examining and deriving valuable insights from large and complex datasets, often referred to as "big data." It involves various techniques and technologies to uncover hidden patterns, trends, and valuable information within massive data sets.
-
Why is Big Data Analytics important in the modern world?
Big Data Analytics is crucial in the modern world because it empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions, improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experiences, manage risks effectively, and foster innovation. It enables businesses to thrive in a data-centric environment.
-
What are the key components of Big Data Analytics?
The key components of Big Data Analytics include data collection, storage, processing, analysis, visualization, machine learning and AI, scalability, real-time analytics, and more.
-
What industries benefit from Big Data Analytics?
Big Data Analytics is beneficial in various industries, including finance, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, marketing, transportation, government, and many others. It helps organizations across sectors make data-driven decisions and gain a competitive edge.
-
What are the challenges in implementing Big Data Analytics?
Challenges in implementing Big Data Analytics include data quality issues, data privacy and security concerns, the need for specialized skills and resources, and the complexity of managing and processing large volumes of data.
-
How does Big Data Analytics impact innovation?
Big Data Analytics can lead to innovation by uncovering insights, trends, and opportunities that drive new product development, marketing strategies, and business models. It fosters innovation through data-driven decision-making.
-
What role does machine learning play in Big Data Analytics?
Machine learning is a crucial component of Big Data Analytics. It automates and enhances data analysis, enabling predictive modeling, classification, and the discovery of patterns and anomalies in large datasets.
-
What is the significance of real-time analytics in Big Data?
Real-time analytics in Big Data enables organizations to analyze and act on data as it's generated, allowing for immediate decision-making, such as fraud detection, customer support, and monitoring of critical systems.
-
How can organizations get started with Big Data Analytics?
Organizations can start with Big Data Analytics by defining their goals, assessing data needs, building the necessary infrastructure, acquiring analytical tools and talent, and formulating a data strategy aligned with their business objectives.
-
What are the ethical considerations in Big Data Analytics?
Ethical considerations in Big Data Analytics include data privacy, transparency, fairness, and responsible data handling. Organizations should adhere to ethical guidelines to ensure the responsible use of data.
Read More
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on 'What is Big Data Analytics and What is Its Significance in the Modern World?' In this in-depth exploration, we delve into the realm of big data analytics, shedding light on its fundamental concepts, applications, and its paramount importance in our contemporary data-driven society. Join us as we unravel the intricacies of this transformative technology and unveil its profound impact on businesses, industries, and society as a whole.
Table of Contents
What is Big Data Analytics?
Why is big data analytics important?
What is Big Data?
Uses and Examples of Big Data Analytics
History of Big Data Analytics
Benefits and Advantages of Big Data Analytics
The Lifecycle Phases of Big Data Analytics
Different Types of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics Tools
Big Data Industry Applications
FAQs
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big Data Analytics is the process of extracting valuable insights from vast and complex data sets, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions, enhance operational efficiency, improve customer experiences, manage risks effectively, and foster innovation across various industries. This transformative discipline combines data collection, storage, processing, analysis, visualization, and the utilization of machine learning techniques, empowering businesses to thrive in our data-centric modern world by leveraging the wealth of information available to them.
Why is big data analytics important?
Big Data Analytics is vital in today's digital age because it provides organizations with the ability to extract valuable insights from the vast volumes of data generated daily. This data, often referred to as "big data," encompasses a wide range of information from various sources, such as customer transactions, social media interactions, sensor data, and more. Without effective analytics, this data would remain largely untapped potential. By employing advanced techniques and technologies, organizations can uncover hidden patterns, trends, and correlations within their data, allowing for informed decision-making, improved operational efficiency, and the ability to gain a competitive edge in rapidly evolving markets.
Furthermore, Big Data Analytics has a profound impact on innovation and problem-solving across industries. It enables businesses to innovate in their product offerings, marketing strategies, and operational processes by providing a data-driven foundation for experimentation and improvement. Moreover, it plays a critical role in fields like healthcare, where it can lead to advancements in patient care, drug discovery, and disease prevention. In essence, Big Data Analytics is essential because it transforms data into actionable knowledge, fostering smarter decisions, greater efficiency, and continuous innovation in both the private and public sectors.
What is Big Data?
Big Data refers to extremely large and complex sets of data that exceed the capabilities of traditional data processing tools and methods. These data sets are characterized by what is often referred to as the "3Vs": volume, velocity, and variety.
-
Volume: Big Data typically involves massive amounts of data, often ranging from terabytes to petabytes or more. This data can be generated from various sources, including sensors, social media, business transactions, and more.
-
Velocity: Data is generated at an unprecedented speed in today's digital world. This real-time or near-real-time data flow requires rapid processing and analysis to derive meaningful insights and make timely decisions.
-
Variety: Big Data comes in various formats, including structured data (such as databases and spreadsheets), semi-structured data (like XML and JSON files), and unstructured data (such as text documents, social media posts, and multimedia content). Analyzing and making sense of this diverse data landscape is a fundamental challenge in Big Data.
In addition to the 3Vs, Big Data is often associated with two more characteristics:
-
Variability: Data can be inconsistent and vary in its format and quality over time.
-
Veracity: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of Big Data can be a challenge, as data may contain errors or inconsistencies.
Effectively managing, storing, processing, and analyzing Big Data is crucial for organizations looking to gain valuable insights, make data-driven decisions, and derive business value from this wealth of information. This has led to the development of specialized technologies and tools, such as distributed computing frameworks like Hadoop and advanced analytics techniques like machine learning, to handle the unique challenges posed by Big Data.
Uses and Examples of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics serves as a powerful tool across various industries by harnessing the vast volumes of data generated in today's digital age. One of its primary applications is in the realm of business intelligence and analytics, where organizations leverage it to gain a deeper understanding of their operations, customers, and markets. For instance, retail companies employ Big Data Analytics to analyze sales data and customer purchase patterns, enabling them to optimize inventory management and design personalized marketing campaigns. This data-driven approach enhances decision-making, helping businesses remain competitive and agile in rapidly evolving markets.
Another significant use of Big Data Analytics is in healthcare, where it aids in patient care and disease management. By analyzing electronic health records and medical data, healthcare providers can make more accurate diagnoses, recommend tailored treatment plans, and predict disease outbreaks. This application not only improves patient outcomes but also contributes to the overall efficiency of healthcare systems. In essence, Big Data Analytics is a multidimensional tool that empowers organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights, driving innovation, efficiency, and informed decision-making across a wide spectrum of industries and sectors.
History of Big Data Analytics
The history of Big Data Analytics can be traced back to the early days of computing, but it has evolved significantly over time. Here's an overview of its key milestones:
-
1950s-1960s: The concept of data processing and analysis emerged with the advent of computers. Early mainframe computers were used for basic data processing tasks, such as sorting and aggregating large volumes of data.
-
1970s-1980s: The development of relational database management systems (RDBMS) marked a significant step forward. SQL (Structured Query Language) became the standard for querying and managing structured data. However, these systems had limitations in handling large and complex datasets.
-
1990s: Data warehousing gained prominence as organizations started collecting and storing vast amounts of data. Data warehousing solutions allowed for the consolidation of data from various sources, making it easier to analyze and report on.
-
Early 2000s: The term "Big Data" began to gain traction as companies like Google and Yahoo faced challenges in managing and analyzing massive datasets. Google's MapReduce and the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) were pivotal in developing scalable solutions for processing Big Data.
-
Mid-2000s: Apache Hadoop, an open-source framework, emerged as a leading platform for processing and analyzing large datasets. It popularized the idea of distributed computing and laid the foundation for Big Data Analytics.
-
Late 2000s-2010s: As organizations generated more data from various sources, technologies for Big Data Analytics continued to advance. Companies like Amazon, Facebook, and Netflix demonstrated the power of data-driven decision-making and personalized user experiences.
-
2010s-Present: Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) have become integral to Big Data Analytics. These technologies enable predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and automation of data analysis tasks. Cloud computing services, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, offer scalable platforms for Big Data processing and storage.
-
2020s: Big Data Analytics continues to evolve with a focus on real-time data processing, edge computing, and privacy considerations. Data governance and ethical use of data have also gained prominence.
Throughout its history, Big Data Analytics has transformed from a niche concept to a critical component of decision-making in various industries, ranging from finance and healthcare to e-commerce and entertainment. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the field of Big Data Analytics will likely continue to evolve and adapt to meet the ever-expanding demands of the digital age.
Benefits and Advantages of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics offers numerous benefits and advantages to organizations across various industries. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Big Data Analytics empowers organizations to make informed decisions based on real data rather than intuition or guesswork. This leads to more accurate and effective choices in various aspects of business operations.
-
Competitive Advantage: Companies that leverage Big Data Analytics gain a competitive edge by identifying market trends, customer preferences, and emerging opportunities faster and more accurately than their competitors.
-
Improved Operational Efficiency: By analyzing processes and operations, organizations can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. This optimization leads to cost reduction and enhanced productivity.
-
Enhanced Customer Experiences: Understanding customer behavior and preferences allows businesses to personalize products, services, and marketing campaigns. This leads to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Risk Management: In industries like finance and insurance, Big Data Analytics aids in assessing and mitigating risks more effectively. It can detect anomalies and potential issues early, helping prevent financial losses.
The Lifecycle Phases of Big Data Analytics
The eight key stages in the lifecycle of Big Data Analytics:
-
Data Collection: Gather data from various sources, such as databases, sensors, or social media.
-
Data Storage: Organize and store the data in suitable repositories like data lakes or warehouses.
-
Data Preprocessing: Clean, transform, and prepare the data for analysis to ensure quality and consistency.
-
Data Analysis: Apply statistical and machine learning techniques to extract insights from the data.
-
Data Visualization: Present the results through charts, graphs, and dashboards for better understanding.
-
Deployment: Implement analytical models into production systems for real-time decision-making.
-
Monitoring: Continuously oversee model performance and data quality.
-
Optimization: Fine-tune models and scale infrastructure to handle increased data demands.
Different Types of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics encompasses various types of analytical approaches, each tailored to address specific business or data challenges. Here are different types of Big Data Analytics:
-
Descriptive Analytics:
-
Purpose: Descriptive analytics focuses on summarizing historical data to provide insights into past trends and events.
-
Use Cases: It helps organizations understand what has happened in the past, such as sales trends, customer behavior, or website traffic patterns.
-
-
Diagnostic Analytics:
-
Purpose: Diagnostic analytics aims to identify the reasons behind past events or trends.
-
Use Cases: It helps uncover the causes of specific outcomes, such as understanding why sales dropped in a particular region or why a marketing campaign failed.
-
-
Predictive Analytics:
-
Purpose: Predictive analytics uses historical data and statistical algorithms to forecast future outcomes or trends.
-
Use Cases: Organizations use predictive analytics for demand forecasting, customer churn prediction, fraud detection, and inventory optimization.
-
-
Prescriptive Analytics:
-
Purpose: Prescriptive analytics goes beyond prediction by suggesting the best course of action to optimize outcomes.
-
Use Cases: It helps organizations make data-driven decisions by recommending actions based on predictive models. For instance, it can suggest pricing strategies to maximize profits.
-
Top of Form
Big Data Analytics Tools
Big Data Analytics tools are essential for processing, analyzing, and deriving insights from large and complex datasets. There are numerous tools available, each with its own strengths and capabilities. Here's a list of some popular Big Data Analytics tools:
-
Hadoop:
-
Description: Hadoop is an open-source framework that facilitates distributed storage and processing of large datasets across clusters of commodity hardware.
-
Key Features: Hadoop includes the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) for storage and MapReduce for parallel processing. Additionally, it offers various ecosystem components like Hive, Pig, and Spark for advanced analytics.
-
-
Apache Spark:
-
Description: Apache Spark is an open-source, distributed computing framework that provides high-speed, in-memory data processing capabilities.
-
Key Features: Spark offers libraries for machine learning (MLlib), graph processing (GraphX), and stream processing (Structured Streaming). It's known for its speed and versatility in processing both batch and real-time data.
-
-
Apache Flink:
-
Description: Apache Flink is an open-source stream processing framework designed for real-time data analytics.
-
Key Features: Flink provides event time processing, support for batch and stream processing, and stateful computations. It's commonly used in applications requiring low-latency, high-throughput data processing.
-
-
Apache Kafka:
-
Description: Apache Kafka is a distributed streaming platform used for building real-time data pipelines and event-driven applications.
-
Key Features: Kafka is known for its high throughput, fault tolerance, and scalability. It allows for the ingestion and processing of large volumes of streaming data.
-
-
Hive:
-
Description: Hive is a data warehousing and SQL-like query language system built on top of Hadoop for structured data analysis.
-
Key Features: Hive provides a familiar SQL interface for querying data stored in Hadoop, making it accessible to analysts and data scientists.
-
-
Pig:
-
Description: Apache Pig is a high-level scripting platform for data analysis and processing in Hadoop.
-
Key Features: Pig provides a simple scripting language called Pig Latin, which allows users to express data transformations and processing logic.
-
-
R and RStudio:
-
Description: R is a programming language and environment specifically designed for statistical analysis and data visualization.
-
Key Features: R, along with RStudio as an integrated development environment (IDE), offers a rich ecosystem of packages and libraries for data analysis, statistical modeling, and data visualization.
-
Big Data Industry Applications
The applications of Big Data analytics span across a wide range of industries, offering transformative solutions to various challenges. Here are some notable industry-specific applications:
-
Healthcare:
-
Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Analyzing patient data in EHRs to improve diagnoses, treatment plans, and patient outcomes.
-
Disease Prediction: Predicting disease outbreaks, identifying high-risk populations, and improving public health strategies.
-
Drug Discovery: Accelerating drug development by analyzing genomics data and identifying potential drug candidates.
-
-
Finance:
-
Risk Assessment: Using data analytics to assess credit risks, detect fraudulent transactions, and manage investment portfolios.
-
Algorithmic Trading: Employing data-driven algorithms to make real-time trading decisions in financial markets.
-
Customer Segmentation: Analyzing customer data to tailor financial products and services for different segments.
-
-
Retail and E-commerce:
-
Recommendation Systems: Offering personalized product recommendations based on customer behavior and preferences.
-
Inventory Management: Optimizing inventory levels to reduce costs and prevent stockouts.
-
Pricing Optimization: Dynamically adjusting prices based on demand and market conditions.
-
-
Manufacturing:
-
Predictive Maintenance: Monitoring equipment sensors to predict and prevent machine failures and reduce downtime.
-
Quality Control: Analyzing production data to identify defects and improve product quality.
-
Supply Chain Optimization: Optimizing logistics and supply chain operations to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
-
-
Telecommunications:
-
Network Optimization: Analyzing network data to improve network performance, reduce downtime, and enhance customer experiences.
-
Churn Prediction: Identifying and retaining at-risk customers by analyzing usage patterns and customer behavior.
-
FAQs
-
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big Data Analytics is the process of examining and deriving valuable insights from large and complex datasets, often referred to as "big data." It involves various techniques and technologies to uncover hidden patterns, trends, and valuable information within massive data sets.
-
Why is Big Data Analytics important in the modern world?
Big Data Analytics is crucial in the modern world because it empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions, improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experiences, manage risks effectively, and foster innovation. It enables businesses to thrive in a data-centric environment.
-
What are the key components of Big Data Analytics?
The key components of Big Data Analytics include data collection, storage, processing, analysis, visualization, machine learning and AI, scalability, real-time analytics, and more.
-
What industries benefit from Big Data Analytics?
Big Data Analytics is beneficial in various industries, including finance, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, marketing, transportation, government, and many others. It helps organizations across sectors make data-driven decisions and gain a competitive edge.
-
What are the challenges in implementing Big Data Analytics?
Challenges in implementing Big Data Analytics include data quality issues, data privacy and security concerns, the need for specialized skills and resources, and the complexity of managing and processing large volumes of data.
-
How does Big Data Analytics impact innovation?
Big Data Analytics can lead to innovation by uncovering insights, trends, and opportunities that drive new product development, marketing strategies, and business models. It fosters innovation through data-driven decision-making.
-
What role does machine learning play in Big Data Analytics?
Machine learning is a crucial component of Big Data Analytics. It automates and enhances data analysis, enabling predictive modeling, classification, and the discovery of patterns and anomalies in large datasets.
-
What is the significance of real-time analytics in Big Data?
Real-time analytics in Big Data enables organizations to analyze and act on data as it's generated, allowing for immediate decision-making, such as fraud detection, customer support, and monitoring of critical systems.
-
How can organizations get started with Big Data Analytics?
Organizations can start with Big Data Analytics by defining their goals, assessing data needs, building the necessary infrastructure, acquiring analytical tools and talent, and formulating a data strategy aligned with their business objectives.
-
What are the ethical considerations in Big Data Analytics?
Ethical considerations in Big Data Analytics include data privacy, transparency, fairness, and responsible data handling. Organizations should adhere to ethical guidelines to ensure the responsible use of data.
AWS DevOps: A Complete Guide to Tools and Best Practices
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, businesses strive to deliver high-quality software products and services with utmost efficiency and speed. To achieve this goal, organizations increasingly turn to cloud computing and automation tools that enable seamless collaboration between development and operations teams. One such powerful combination is Amazon Web Services (AWS) and DevOps.
AWS, the leading cloud services provider, offers a wide array of scalable and flexible solutions that can empower businesses to innovate, deploy, and operate applications more efficiently. DevOps, on the other hand, is a set of practices that fosters collaboration, integration, and automation between software development and IT operations teams. It aims to streamline the software delivery process and enhance the overall agility and reliability of applications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of AWS DevOps and explore how these two concepts intersect to revolutionize the software development lifecycle. We will provide you with a solid understanding of the core principles, tools, and best practices that underpin AWS DevOps, equipping you with the knowledge to leverage this powerful combination in your own organization.
Throughout this guide, we will cover a wide range of topics, including:
Introduction to AWS: We will introduce you to the key services and features provided by AWS, emphasizing their relevance and impact on the DevOps philosophy.
Fundamentals of DevOps: We will explore the core principles and values of DevOps, highlighting the benefits of adopting this culture and methodology in your organization.
AWS DevOps Tools and Services: We will dive into the various AWS tools and services that facilitate the implementation of DevOps practices. From version control and continuous integration to infrastructure automation and monitoring, we will explore how these tools can enhance your development and operational workflows.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): We will examine the concepts and practices of CI/CD, demonstrating how AWS services can enable seamless automation and rapid deployment of software changes.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): We will delve into the concept of IaC, exploring how AWS CloudFormation and other tools can help you define and manage your infrastructure as easily reproducible code.
Scalability and Resilience: We will discuss how AWS's elastic and scalable infrastructure can help you build resilient and highly available systems, ensuring your applications can handle varying workloads and remain operational even in the face of failures.
Security and Compliance: We will address the crucial aspects of security and compliance in the AWS DevOps environment, covering best practices, tools, and services to ensure the protection of your applications and data.
Table of Contents
- Understanding AWS DevOps
- Key components of AWS DevOps
- AWS DevOps tools
- Implementing AWS DevOps
- Benefits of AWS DevOps
- Limitations of AWS DevOps
- Future of AWS DevOps
- Conclusion
Understanding AWS DevOps
AWS DevOps is a powerful combination of Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud services and DevOps practices that enables organizations to streamline their software development and deployment processes. It brings together the benefits of AWS's scalable and flexible infrastructure with the collaborative and automated principles of DevOps, resulting in increased agility, faster time-to-market, and improved operational efficiency.
At its core, DevOps is a cultural and operational philosophy that encourages close collaboration between software development teams and IT operations teams. It aims to break down the traditional silos between these two groups, promoting a shared responsibility for the entire software lifecycle, from development and testing to deployment and monitoring. DevOps emphasizes automation, continuous integration, continuous delivery, and infrastructure as code to achieve faster and more reliable software delivery.
AWS, as one of the leading cloud service providers, offers a comprehensive suite of services and tools that align perfectly with DevOps principles. These services enable organizations to build, deploy, and operate applications and infrastructure in a highly scalable, secure, and reliable manner. Some of the key AWS services that play a vital role in AWS DevOps are:
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): EC2 provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud, allowing organizations to quickly provision virtual servers and scale their infrastructure up or down as needed.
AWS Lambda: Lambda is a serverless computing service that enables developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers. It facilitates the creation of highly scalable and event-driven applications.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk: Elastic Beanstalk simplifies the deployment and management of applications by automatically handling the underlying infrastructure and platform configuration. It supports multiple programming languages and frameworks.
AWS CodePipeline: CodePipeline is a fully managed continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) service that automates the release process for applications. It integrates with various AWS services and third-party tools to build, test, and deploy code changes.
AWS CloudFormation: CloudFormation allows you to define and provision AWS infrastructure resources using declarative templates. It enables infrastructure as code, making it easier to manage and reproduce environments.
Amazon CloudWatch: CloudWatch provides monitoring and observability for AWS resources and applications. It collects and analyzes log files, sets alarms, and generates metrics, enabling proactive monitoring and troubleshooting.
Key components of AWS DevOps
AWS DevOps encompasses a range of components that work together to enable organizations to implement DevOps practices in an AWS environment. These components provide the foundation for collaboration, automation, and continuous delivery. Let's explore some of the key components of AWS DevOps:
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Infrastructure as Code is a fundamental concept in AWS DevOps. It involves defining and provisioning infrastructure resources using code, typically in the form of templates. AWS CloudFormation is a popular service that enables you to create and manage infrastructure as code, allowing for consistent and repeatable deployments.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): CI/CD is a set of practices that automate the build, testing, and deployment of software changes. AWS provides various services to facilitate CI/CD pipelines. AWS CodePipeline is a fully managed service that orchestrates the continuous delivery workflow, integrating with other AWS services such as AWS CodeBuild for build automation and AWS CodeDeploy for application deployment.
Configuration Management: Configuration management tools enable organizations to manage and automate the configuration of their infrastructure and applications. AWS provides AWS Systems Manager, which allows you to manage and configure EC2 instances at scale. It also offers integration with popular configuration management tools like Chef and Puppet.
Monitoring and Logging: Monitoring and logging are crucial aspects of DevOps. AWS CloudWatch is a monitoring service that collects and tracks metrics, sets alarms, and provides insights into the performance and health of AWS resources and applications. AWS X-Ray is a service that helps trace and debug distributed applications, providing valuable insights into requests and latency.
Security and Compliance: Security and compliance are paramount in any DevOps environment. AWS provides a wide range of security services and features, including AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for access control, AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for encryption, and AWS Security Hub for centralized security monitoring and compliance checks.
Containerization and Orchestration: Containerization technologies like Docker and container orchestration platforms like Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) allow organizations to package and deploy applications in a portable and scalable manner. These tools enable the efficient management of containerized applications within the AWS ecosystem.
Serverless Computing: Serverless computing, exemplified by AWS Lambda, allows developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers. It enables rapid development and deployment of event-driven functions and microservices, promoting scalability and cost optimization.
AWS DevOps tools
AWS provides a wide range of tools and services that are specifically designed to support DevOps practices and workflows. These tools cover various aspects of the software development lifecycle, from code management and build automation to deployment and monitoring. Here are some key AWS DevOps tools:
AWS CodePipeline: CodePipeline is a fully managed continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) service that enables you to automate the release process for your applications. It integrates with other AWS services and third-party tools, allowing you to build, test, and deploy code changes seamlessly.
AWS CodeCommit: CodeCommit is a fully managed source code control service that hosts private Git repositories. It provides a secure and scalable platform for collaborating on code and managing version control.
AWS CodeBuild: CodeBuild is a fully managed build service that compiles source code, runs tests, and produces ready-to-deploy software packages. It supports a wide range of programming languages and build configurations.
AWS CodeDeploy: CodeDeploy automates application deployments to various compute services, including EC2 instances, AWS Lambda functions, and on-premises servers. It simplifies the process of releasing new features and updates, ensuring consistency and minimizing downtime.
AWS CloudFormation: CloudFormation allows you to define and provision AWS infrastructure resources using templates. It enables infrastructure as code, making it easier to manage and reproduce environments consistently.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk: Elastic Beanstalk is a fully managed service that makes it easy to deploy and run applications in multiple languages and frameworks. It handles the underlying infrastructure and platform configuration, allowing developers to focus on writing code.
AWS OpsWorks: OpsWorks provides a configuration management service that uses Chef or Puppet for automating the setup and management of infrastructure resources. It simplifies the process of deploying and managing applications and server configurations.
AWS X-Ray: X-Ray is a distributed tracing service that helps developers analyze and debug applications in a microservices architecture. It provides insights into request flows and performance bottlenecks, allowing for efficient troubleshooting.
AWS Systems Manager: Systems Manager offers a unified interface for managing and configuring AWS resources at scale. It provides features such as run command, patch management, and inventory management, simplifying the operational tasks associated with maintaining infrastructure and applications.
AWS CloudWatch: CloudWatch is a monitoring and observability service that collects and tracks metrics, logs, and events from various AWS resources and applications. It provides valuable insights into system performance, availability, and resource utilization.
Implementing AWS DevOps
Implementing AWS DevOps involves a systematic approach to leverage AWS services and adopt DevOps practices to streamline software development and deployment processes. Here are some steps to consider when implementing AWS DevOps:
Define DevOps Goals: Start by identifying your organization's goals and objectives for implementing DevOps. Determine the specific areas where you want to improve, such as faster time-to-market, increased agility, or improved operational efficiency.
Assess Current Processes: Evaluate your existing software development and deployment processes. Identify bottlenecks, pain points, and areas for improvement. This assessment will help you prioritize the implementation of AWS DevOps practices.
Establish a DevOps Culture: DevOps is not just about tools; it's a cultural shift that emphasizes collaboration, shared responsibility, and continuous improvement. Foster a culture of collaboration and open communication between development and operations teams.
Plan for Infrastructure as Code: Adopt the practice of infrastructure as code (IaC) to define and provision your AWS infrastructure resources. Utilize AWS CloudFormation or other IaC tools to create declarative templates that can be version-controlled and easily reproduced.
Implement Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): Automate the build, testing, and deployment processes with CI/CD pipelines. Utilize AWS CodePipeline to orchestrate the workflow and integrate it with other AWS services like AWS CodeCommit for version control and AWS CodeBuild for building artifacts.
Embrace Automation: Automate repetitive and manual tasks using AWS services like AWS Systems Manager or AWS Lambda. Automate the provisioning and configuration of infrastructure, deployment of applications, and operational tasks to reduce errors and save time.
Implement Infrastructure Monitoring and Observability: Utilize AWS CloudWatch to monitor and gain insights into the performance, availability, and health of your infrastructure and applications. Configure alarms and notifications to proactively respond to issues.
Ensure Security and Compliance: Implement security best practices and utilize AWS security services like AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for access control and AWS Security Hub for centralized security monitoring. Ensure compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards.
Foster Continuous Learning and Improvement: Encourage a culture of learning and continuous improvement. Conduct post-mortems, gather feedback, and use metrics and data to identify areas for optimization. Implement feedback loops to iterate and refine your DevOps processes.
Provide Training and Support: Offer training and support to teams to ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively utilize AWS DevOps tools and services. Provide resources, documentation, and hands-on training to enable successful adoption.
Benefits of AWS DevOps
Implementing AWS DevOps offers several significant benefits for organizations. Here are some key advantages of adopting AWS DevOps practices:
Faster Time-to-Market: AWS DevOps enables organizations to deliver software products and updates at a faster pace. Automation and streamlined processes reduce manual effort, enabling rapid development, testing, and deployment. This accelerated time-to-market allows organizations to respond quickly to market demands and gain a competitive edge.
Increased Agility and Flexibility: AWS's cloud services provide a scalable and flexible infrastructure, allowing organizations to rapidly adapt to changing business needs. With AWS DevOps, teams can dynamically provision resources, scale applications, and efficiently manage workloads, enabling them to respond swiftly to fluctuating customer demands and market conditions.
Improved Collaboration and Communication: DevOps encourages close collaboration and communication between development and operations teams. By breaking down silos and fostering a culture of shared responsibility, AWS DevOps promotes efficient information sharing, reducing misunderstandings and bottlenecks. This collaboration leads to smoother workflows, faster issue resolution, and improved overall productivity.
Enhanced Quality and Reliability: DevOps practices, such as continuous integration, automated testing, and continuous delivery, help improve the quality and reliability of software products. By automating testing and deployment processes, organizations can catch bugs and issues early, reducing the risk of defects and improving software stability. This results in higher customer satisfaction and increased confidence in the software being delivered.
Cost Optimization: AWS DevOps enables organizations to optimize their costs by leveraging cloud services efficiently. With dynamic resource provisioning and scaling, teams can optimize resource usage and pay only for what they need, avoiding overprovisioning. Additionally, automated processes and reduced manual effort lead to cost savings in terms of time and labor.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): AWS DevOps promotes the use of infrastructure as code (IaC), which allows organizations to define and manage their infrastructure through code. This approach brings consistency, repeatability, and version control to infrastructure deployments, reducing human errors and ensuring reproducibility across different environments.
Improved Security and Compliance: AWS provides a robust security framework, and when combined with DevOps practices, organizations can enhance their overall security posture. AWS DevOps enables the implementation of security best practices, such as automated security testing, continuous monitoring, and identity and access management (IAM). This helps organizations achieve and maintain compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
Continuous Improvement: AWS DevOps promotes a culture of continuous learning and improvement. With feedback loops, monitoring, and analytics provided by AWS services, organizations can collect valuable insights and data to drive optimization. This data-driven approach allows teams to identify areas for improvement, make data-backed decisions, and iterate on their processes to achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness over time.
Limitations of AWS DevOps
While AWS DevOps offers numerous benefits, it's important to be aware of its limitations. Here are some potential limitations of AWS DevOps:
Learning Curve: Implementing AWS DevOps practices requires a certain level of knowledge and expertise in both AWS services and DevOps principles. Teams may need to invest time and resources in training and upskilling to effectively leverage AWS DevOps tools and services.
Complexity: AWS provides a vast array of services, and navigating through the various options and configurations can be complex. Designing and implementing a robust AWS DevOps architecture may require careful planning and expertise to ensure the optimal use of resources and services.
Cost Management: While AWS offers flexibility and scalability, it's important to carefully manage costs. Organizations need to monitor resource usage, optimize deployments, and select the appropriate pricing models to avoid unexpected expenses.
Dependency on Internet Connectivity: AWS is a cloud-based platform, which means it relies on internet connectivity for access and operations. Organizations should consider potential downtime or performance issues caused by internet outages or network connectivity problems.
Vendor Lock-In: Adopting AWS DevOps practices may create a dependency on AWS services and infrastructure. Migrating to an alternative cloud provider or making significant changes to the infrastructure architecture could be challenging and time-consuming.
Security and Compliance Considerations: While AWS provides robust security features, organizations are responsible for configuring and managing the security of their applications and data. Proper security configurations and compliance measures need to be implemented to ensure data protection and regulatory compliance.
Cultural Shift: Implementing DevOps practices requires a cultural shift within the organization. It may involve breaking down silos between development and operations teams, promoting collaboration, and embracing change. Overcoming resistance to change and ensuring buy-in from stakeholders can be a challenge.
Maintenance and Support: AWS DevOps requires ongoing maintenance and support to ensure the stability and performance of the infrastructure and applications. Organizations should allocate resources for monitoring, managing updates, and addressing issues that arise in the AWS environment.
Future of AWS DevOps
The future of AWS DevOps looks promising, with continued advancements and innovations expected to further enhance its capabilities. Here are some potential trends and developments that may shape the future of AWS DevOps:
Serverless Computing: Serverless architectures, exemplified by AWS Lambda, are gaining popularity as they offer scalability, reduced operational overhead, and cost efficiency. In the future, we can expect further advancements in serverless computing, enabling organizations to build and deploy applications without managing underlying infrastructure.
AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI and machine learning are increasingly being integrated into various aspects of software development and operations. In the context of AWS DevOps, we can expect AI-driven insights and automation tools that help optimize CI/CD pipelines, enhance monitoring and observability, and improve incident response and remediation processes.
Infrastructure Automation and Orchestration: As infrastructure as code (IaC) becomes more prevalent, we can expect advancements in infrastructure automation and orchestration tools within AWS DevOps. This includes more sophisticated features, improved support for multi-cloud environments, and enhanced integration with popular IaC frameworks.
Enhanced Security and Compliance: Security and compliance will remain a key focus area for AWS DevOps. We can expect further advancements in security automation, threat detection, and compliance management tools within the AWS ecosystem. Integration with AI-driven security solutions may help organizations identify and mitigate security risks more effectively.
Integration of DevOps with DataOps: The integration of DevOps and DataOps practices is likely to gain traction as organizations increasingly focus on managing and leveraging their data assets. AWS services like Amazon Redshift, AWS Glue, and Amazon EMR will play a crucial role in enabling efficient data operations within DevOps workflows.
Advanced Observability and Monitoring: Observability and monitoring will continue to evolve, providing more granular insights into applications and infrastructure performance. Advanced tracing, logging, and distributed tracing capabilities will be integrated into AWS DevOps tools, allowing organizations to identify and resolve issues more efficiently.
Focus on Developer Experience: AWS DevOps tools and services will likely prioritize the developer experience, providing improved user interfaces, better integration with popular development tools, and enhanced collaboration features. The goal will be to make it easier and more efficient for developers to adopt and utilize AWS DevOps practices.
Cross-platform and Hybrid Cloud Support: As organizations increasingly adopt hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, AWS DevOps will likely evolve to provide better support for managing and orchestrating deployments across different cloud platforms. Integration with other cloud providers and on-premises environments will be enhanced, enabling seamless workflows and deployments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, AWS DevOps offers organizations a powerful set of tools and practices to streamline software development and deployment processes. By leveraging AWS services, organizations can achieve faster time-to-market, increased agility, improved collaboration, and enhanced quality and reliability.
While there are limitations to consider, such as the learning curve and complexity of AWS services, proper planning, training, and expertise can help mitigate these challenges.
Looking towards the future, AWS DevOps is expected to evolve and embrace trends such as serverless computing, AI integration, advanced observability, and enhanced security and compliance. The focus on developer experience and support for hybrid and multi-cloud environments will also play a significant role in shaping the future of AWS DevOps.
Overall, AWS DevOps enables organizations to deliver software products with speed, scalability, and reliability, empowering them to stay competitive in today's rapidly changing digital landscape. By embracing AWS DevOps practices and staying informed about emerging trends, organizations can maximize the benefits and drive continuous improvement in their software development and deployment processes.
Read More
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, businesses strive to deliver high-quality software products and services with utmost efficiency and speed. To achieve this goal, organizations increasingly turn to cloud computing and automation tools that enable seamless collaboration between development and operations teams. One such powerful combination is Amazon Web Services (AWS) and DevOps.
AWS, the leading cloud services provider, offers a wide array of scalable and flexible solutions that can empower businesses to innovate, deploy, and operate applications more efficiently. DevOps, on the other hand, is a set of practices that fosters collaboration, integration, and automation between software development and IT operations teams. It aims to streamline the software delivery process and enhance the overall agility and reliability of applications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of AWS DevOps and explore how these two concepts intersect to revolutionize the software development lifecycle. We will provide you with a solid understanding of the core principles, tools, and best practices that underpin AWS DevOps, equipping you with the knowledge to leverage this powerful combination in your own organization.
Throughout this guide, we will cover a wide range of topics, including:
Introduction to AWS: We will introduce you to the key services and features provided by AWS, emphasizing their relevance and impact on the DevOps philosophy.
Fundamentals of DevOps: We will explore the core principles and values of DevOps, highlighting the benefits of adopting this culture and methodology in your organization.
AWS DevOps Tools and Services: We will dive into the various AWS tools and services that facilitate the implementation of DevOps practices. From version control and continuous integration to infrastructure automation and monitoring, we will explore how these tools can enhance your development and operational workflows.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): We will examine the concepts and practices of CI/CD, demonstrating how AWS services can enable seamless automation and rapid deployment of software changes.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): We will delve into the concept of IaC, exploring how AWS CloudFormation and other tools can help you define and manage your infrastructure as easily reproducible code.
Scalability and Resilience: We will discuss how AWS's elastic and scalable infrastructure can help you build resilient and highly available systems, ensuring your applications can handle varying workloads and remain operational even in the face of failures.
Security and Compliance: We will address the crucial aspects of security and compliance in the AWS DevOps environment, covering best practices, tools, and services to ensure the protection of your applications and data.
Table of Contents
- Understanding AWS DevOps
- Key components of AWS DevOps
- AWS DevOps tools
- Implementing AWS DevOps
- Benefits of AWS DevOps
- Limitations of AWS DevOps
- Future of AWS DevOps
- Conclusion
Understanding AWS DevOps
AWS DevOps is a powerful combination of Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud services and DevOps practices that enables organizations to streamline their software development and deployment processes. It brings together the benefits of AWS's scalable and flexible infrastructure with the collaborative and automated principles of DevOps, resulting in increased agility, faster time-to-market, and improved operational efficiency.
At its core, DevOps is a cultural and operational philosophy that encourages close collaboration between software development teams and IT operations teams. It aims to break down the traditional silos between these two groups, promoting a shared responsibility for the entire software lifecycle, from development and testing to deployment and monitoring. DevOps emphasizes automation, continuous integration, continuous delivery, and infrastructure as code to achieve faster and more reliable software delivery.
AWS, as one of the leading cloud service providers, offers a comprehensive suite of services and tools that align perfectly with DevOps principles. These services enable organizations to build, deploy, and operate applications and infrastructure in a highly scalable, secure, and reliable manner. Some of the key AWS services that play a vital role in AWS DevOps are:
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): EC2 provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud, allowing organizations to quickly provision virtual servers and scale their infrastructure up or down as needed.
AWS Lambda: Lambda is a serverless computing service that enables developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers. It facilitates the creation of highly scalable and event-driven applications.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk: Elastic Beanstalk simplifies the deployment and management of applications by automatically handling the underlying infrastructure and platform configuration. It supports multiple programming languages and frameworks.
AWS CodePipeline: CodePipeline is a fully managed continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) service that automates the release process for applications. It integrates with various AWS services and third-party tools to build, test, and deploy code changes.
AWS CloudFormation: CloudFormation allows you to define and provision AWS infrastructure resources using declarative templates. It enables infrastructure as code, making it easier to manage and reproduce environments.
Amazon CloudWatch: CloudWatch provides monitoring and observability for AWS resources and applications. It collects and analyzes log files, sets alarms, and generates metrics, enabling proactive monitoring and troubleshooting.
Key components of AWS DevOps
AWS DevOps encompasses a range of components that work together to enable organizations to implement DevOps practices in an AWS environment. These components provide the foundation for collaboration, automation, and continuous delivery. Let's explore some of the key components of AWS DevOps:
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Infrastructure as Code is a fundamental concept in AWS DevOps. It involves defining and provisioning infrastructure resources using code, typically in the form of templates. AWS CloudFormation is a popular service that enables you to create and manage infrastructure as code, allowing for consistent and repeatable deployments.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): CI/CD is a set of practices that automate the build, testing, and deployment of software changes. AWS provides various services to facilitate CI/CD pipelines. AWS CodePipeline is a fully managed service that orchestrates the continuous delivery workflow, integrating with other AWS services such as AWS CodeBuild for build automation and AWS CodeDeploy for application deployment.
Configuration Management: Configuration management tools enable organizations to manage and automate the configuration of their infrastructure and applications. AWS provides AWS Systems Manager, which allows you to manage and configure EC2 instances at scale. It also offers integration with popular configuration management tools like Chef and Puppet.
Monitoring and Logging: Monitoring and logging are crucial aspects of DevOps. AWS CloudWatch is a monitoring service that collects and tracks metrics, sets alarms, and provides insights into the performance and health of AWS resources and applications. AWS X-Ray is a service that helps trace and debug distributed applications, providing valuable insights into requests and latency.
Security and Compliance: Security and compliance are paramount in any DevOps environment. AWS provides a wide range of security services and features, including AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for access control, AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for encryption, and AWS Security Hub for centralized security monitoring and compliance checks.
Containerization and Orchestration: Containerization technologies like Docker and container orchestration platforms like Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) allow organizations to package and deploy applications in a portable and scalable manner. These tools enable the efficient management of containerized applications within the AWS ecosystem.
Serverless Computing: Serverless computing, exemplified by AWS Lambda, allows developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers. It enables rapid development and deployment of event-driven functions and microservices, promoting scalability and cost optimization.
AWS DevOps tools
AWS provides a wide range of tools and services that are specifically designed to support DevOps practices and workflows. These tools cover various aspects of the software development lifecycle, from code management and build automation to deployment and monitoring. Here are some key AWS DevOps tools:
AWS CodePipeline: CodePipeline is a fully managed continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) service that enables you to automate the release process for your applications. It integrates with other AWS services and third-party tools, allowing you to build, test, and deploy code changes seamlessly.
AWS CodeCommit: CodeCommit is a fully managed source code control service that hosts private Git repositories. It provides a secure and scalable platform for collaborating on code and managing version control.
AWS CodeBuild: CodeBuild is a fully managed build service that compiles source code, runs tests, and produces ready-to-deploy software packages. It supports a wide range of programming languages and build configurations.
AWS CodeDeploy: CodeDeploy automates application deployments to various compute services, including EC2 instances, AWS Lambda functions, and on-premises servers. It simplifies the process of releasing new features and updates, ensuring consistency and minimizing downtime.
AWS CloudFormation: CloudFormation allows you to define and provision AWS infrastructure resources using templates. It enables infrastructure as code, making it easier to manage and reproduce environments consistently.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk: Elastic Beanstalk is a fully managed service that makes it easy to deploy and run applications in multiple languages and frameworks. It handles the underlying infrastructure and platform configuration, allowing developers to focus on writing code.
AWS OpsWorks: OpsWorks provides a configuration management service that uses Chef or Puppet for automating the setup and management of infrastructure resources. It simplifies the process of deploying and managing applications and server configurations.
AWS X-Ray: X-Ray is a distributed tracing service that helps developers analyze and debug applications in a microservices architecture. It provides insights into request flows and performance bottlenecks, allowing for efficient troubleshooting.
AWS Systems Manager: Systems Manager offers a unified interface for managing and configuring AWS resources at scale. It provides features such as run command, patch management, and inventory management, simplifying the operational tasks associated with maintaining infrastructure and applications.
AWS CloudWatch: CloudWatch is a monitoring and observability service that collects and tracks metrics, logs, and events from various AWS resources and applications. It provides valuable insights into system performance, availability, and resource utilization.
Implementing AWS DevOps
Implementing AWS DevOps involves a systematic approach to leverage AWS services and adopt DevOps practices to streamline software development and deployment processes. Here are some steps to consider when implementing AWS DevOps:
Define DevOps Goals: Start by identifying your organization's goals and objectives for implementing DevOps. Determine the specific areas where you want to improve, such as faster time-to-market, increased agility, or improved operational efficiency.
Assess Current Processes: Evaluate your existing software development and deployment processes. Identify bottlenecks, pain points, and areas for improvement. This assessment will help you prioritize the implementation of AWS DevOps practices.
Establish a DevOps Culture: DevOps is not just about tools; it's a cultural shift that emphasizes collaboration, shared responsibility, and continuous improvement. Foster a culture of collaboration and open communication between development and operations teams.
Plan for Infrastructure as Code: Adopt the practice of infrastructure as code (IaC) to define and provision your AWS infrastructure resources. Utilize AWS CloudFormation or other IaC tools to create declarative templates that can be version-controlled and easily reproduced.
Implement Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): Automate the build, testing, and deployment processes with CI/CD pipelines. Utilize AWS CodePipeline to orchestrate the workflow and integrate it with other AWS services like AWS CodeCommit for version control and AWS CodeBuild for building artifacts.
Embrace Automation: Automate repetitive and manual tasks using AWS services like AWS Systems Manager or AWS Lambda. Automate the provisioning and configuration of infrastructure, deployment of applications, and operational tasks to reduce errors and save time.
Implement Infrastructure Monitoring and Observability: Utilize AWS CloudWatch to monitor and gain insights into the performance, availability, and health of your infrastructure and applications. Configure alarms and notifications to proactively respond to issues.
Ensure Security and Compliance: Implement security best practices and utilize AWS security services like AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for access control and AWS Security Hub for centralized security monitoring. Ensure compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards.
Foster Continuous Learning and Improvement: Encourage a culture of learning and continuous improvement. Conduct post-mortems, gather feedback, and use metrics and data to identify areas for optimization. Implement feedback loops to iterate and refine your DevOps processes.
Provide Training and Support: Offer training and support to teams to ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively utilize AWS DevOps tools and services. Provide resources, documentation, and hands-on training to enable successful adoption.
Benefits of AWS DevOps
Implementing AWS DevOps offers several significant benefits for organizations. Here are some key advantages of adopting AWS DevOps practices:
Faster Time-to-Market: AWS DevOps enables organizations to deliver software products and updates at a faster pace. Automation and streamlined processes reduce manual effort, enabling rapid development, testing, and deployment. This accelerated time-to-market allows organizations to respond quickly to market demands and gain a competitive edge.
Increased Agility and Flexibility: AWS's cloud services provide a scalable and flexible infrastructure, allowing organizations to rapidly adapt to changing business needs. With AWS DevOps, teams can dynamically provision resources, scale applications, and efficiently manage workloads, enabling them to respond swiftly to fluctuating customer demands and market conditions.
Improved Collaboration and Communication: DevOps encourages close collaboration and communication between development and operations teams. By breaking down silos and fostering a culture of shared responsibility, AWS DevOps promotes efficient information sharing, reducing misunderstandings and bottlenecks. This collaboration leads to smoother workflows, faster issue resolution, and improved overall productivity.
Enhanced Quality and Reliability: DevOps practices, such as continuous integration, automated testing, and continuous delivery, help improve the quality and reliability of software products. By automating testing and deployment processes, organizations can catch bugs and issues early, reducing the risk of defects and improving software stability. This results in higher customer satisfaction and increased confidence in the software being delivered.
Cost Optimization: AWS DevOps enables organizations to optimize their costs by leveraging cloud services efficiently. With dynamic resource provisioning and scaling, teams can optimize resource usage and pay only for what they need, avoiding overprovisioning. Additionally, automated processes and reduced manual effort lead to cost savings in terms of time and labor.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): AWS DevOps promotes the use of infrastructure as code (IaC), which allows organizations to define and manage their infrastructure through code. This approach brings consistency, repeatability, and version control to infrastructure deployments, reducing human errors and ensuring reproducibility across different environments.
Improved Security and Compliance: AWS provides a robust security framework, and when combined with DevOps practices, organizations can enhance their overall security posture. AWS DevOps enables the implementation of security best practices, such as automated security testing, continuous monitoring, and identity and access management (IAM). This helps organizations achieve and maintain compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
Continuous Improvement: AWS DevOps promotes a culture of continuous learning and improvement. With feedback loops, monitoring, and analytics provided by AWS services, organizations can collect valuable insights and data to drive optimization. This data-driven approach allows teams to identify areas for improvement, make data-backed decisions, and iterate on their processes to achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness over time.
Limitations of AWS DevOps
While AWS DevOps offers numerous benefits, it's important to be aware of its limitations. Here are some potential limitations of AWS DevOps:
Learning Curve: Implementing AWS DevOps practices requires a certain level of knowledge and expertise in both AWS services and DevOps principles. Teams may need to invest time and resources in training and upskilling to effectively leverage AWS DevOps tools and services.
Complexity: AWS provides a vast array of services, and navigating through the various options and configurations can be complex. Designing and implementing a robust AWS DevOps architecture may require careful planning and expertise to ensure the optimal use of resources and services.
Cost Management: While AWS offers flexibility and scalability, it's important to carefully manage costs. Organizations need to monitor resource usage, optimize deployments, and select the appropriate pricing models to avoid unexpected expenses.
Dependency on Internet Connectivity: AWS is a cloud-based platform, which means it relies on internet connectivity for access and operations. Organizations should consider potential downtime or performance issues caused by internet outages or network connectivity problems.
Vendor Lock-In: Adopting AWS DevOps practices may create a dependency on AWS services and infrastructure. Migrating to an alternative cloud provider or making significant changes to the infrastructure architecture could be challenging and time-consuming.
Security and Compliance Considerations: While AWS provides robust security features, organizations are responsible for configuring and managing the security of their applications and data. Proper security configurations and compliance measures need to be implemented to ensure data protection and regulatory compliance.
Cultural Shift: Implementing DevOps practices requires a cultural shift within the organization. It may involve breaking down silos between development and operations teams, promoting collaboration, and embracing change. Overcoming resistance to change and ensuring buy-in from stakeholders can be a challenge.
Maintenance and Support: AWS DevOps requires ongoing maintenance and support to ensure the stability and performance of the infrastructure and applications. Organizations should allocate resources for monitoring, managing updates, and addressing issues that arise in the AWS environment.
Future of AWS DevOps
The future of AWS DevOps looks promising, with continued advancements and innovations expected to further enhance its capabilities. Here are some potential trends and developments that may shape the future of AWS DevOps:
Serverless Computing: Serverless architectures, exemplified by AWS Lambda, are gaining popularity as they offer scalability, reduced operational overhead, and cost efficiency. In the future, we can expect further advancements in serverless computing, enabling organizations to build and deploy applications without managing underlying infrastructure.
AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI and machine learning are increasingly being integrated into various aspects of software development and operations. In the context of AWS DevOps, we can expect AI-driven insights and automation tools that help optimize CI/CD pipelines, enhance monitoring and observability, and improve incident response and remediation processes.
Infrastructure Automation and Orchestration: As infrastructure as code (IaC) becomes more prevalent, we can expect advancements in infrastructure automation and orchestration tools within AWS DevOps. This includes more sophisticated features, improved support for multi-cloud environments, and enhanced integration with popular IaC frameworks.
Enhanced Security and Compliance: Security and compliance will remain a key focus area for AWS DevOps. We can expect further advancements in security automation, threat detection, and compliance management tools within the AWS ecosystem. Integration with AI-driven security solutions may help organizations identify and mitigate security risks more effectively.
Integration of DevOps with DataOps: The integration of DevOps and DataOps practices is likely to gain traction as organizations increasingly focus on managing and leveraging their data assets. AWS services like Amazon Redshift, AWS Glue, and Amazon EMR will play a crucial role in enabling efficient data operations within DevOps workflows.
Advanced Observability and Monitoring: Observability and monitoring will continue to evolve, providing more granular insights into applications and infrastructure performance. Advanced tracing, logging, and distributed tracing capabilities will be integrated into AWS DevOps tools, allowing organizations to identify and resolve issues more efficiently.
Focus on Developer Experience: AWS DevOps tools and services will likely prioritize the developer experience, providing improved user interfaces, better integration with popular development tools, and enhanced collaboration features. The goal will be to make it easier and more efficient for developers to adopt and utilize AWS DevOps practices.
Cross-platform and Hybrid Cloud Support: As organizations increasingly adopt hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, AWS DevOps will likely evolve to provide better support for managing and orchestrating deployments across different cloud platforms. Integration with other cloud providers and on-premises environments will be enhanced, enabling seamless workflows and deployments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, AWS DevOps offers organizations a powerful set of tools and practices to streamline software development and deployment processes. By leveraging AWS services, organizations can achieve faster time-to-market, increased agility, improved collaboration, and enhanced quality and reliability.
While there are limitations to consider, such as the learning curve and complexity of AWS services, proper planning, training, and expertise can help mitigate these challenges.
Looking towards the future, AWS DevOps is expected to evolve and embrace trends such as serverless computing, AI integration, advanced observability, and enhanced security and compliance. The focus on developer experience and support for hybrid and multi-cloud environments will also play a significant role in shaping the future of AWS DevOps.
Overall, AWS DevOps enables organizations to deliver software products with speed, scalability, and reliability, empowering them to stay competitive in today's rapidly changing digital landscape. By embracing AWS DevOps practices and staying informed about emerging trends, organizations can maximize the benefits and drive continuous improvement in their software development and deployment processes.
Key Cloud Skills for Success in 2023: Stay Ahead in Tech!
In the fast-evolving landscape of technology, cloud computing has emerged as a transformative force that underpins the modern digital economy. As we step into 2023, the demand for cloud expertise continues to soar, making it a pivotal year for professionals aspiring to excel in the field. To navigate this dynamic and competitive landscape, one must possess a precise set of skills that enable them to harness the power of cloud computing effectively. This article delves into the key cloud skills that are essential for success in 2023, offering insights into the competencies that will empower individuals and organizations to thrive in the ever-expanding realm of cloud technology. Whether you are a seasoned cloud professional looking to stay at the forefront of industry trends or a newcomer eager to embark on a cloud-focused career path, these skills will be your guiding light in the journey ahead.
Table of Contents
Cloud Security
Machine Learning and AI
Cloud Deployment and Migration Across Multiple Platforms
Technical Skills Required for Cloud Computing
Other Skills Required for Cloud Computing
Get Certified and Make Yourself Indispensable
Cloud Security
Cloud security involves protecting data, applications, and infrastructure hosted in cloud computing environments from various threats and vulnerabilities. It encompasses a range of practices and technologies aimed at ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cloud-based resources. This is particularly important because cloud computing involves the storage and access of data and services through third-party providers over the internet. Key aspects of cloud security include safeguarding data through encryption and access controls, managing user identities and access permissions, complying with regulatory requirements, securing network infrastructure, and monitoring for security incidents. It's an ongoing process that requires continuous vigilance and adaptation to address evolving cyber threats in the ever-changing cloud landscape.
In the shared responsibility model of cloud security, cloud service providers are responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing their data and applications. This means that organizations must carefully assess their specific security needs and implement a combination of security measures, such as identity and access management, application security, and data encryption, to protect their assets in the cloud. Additionally, employee training and awareness play a crucial role in mitigating security risks, as human error and social engineering attacks remain significant threats to cloud security. Overall, cloud security is essential to build trust in cloud services and to ensure the safe and reliable operation of cloud-based systems and data.
Machine Learning and AI
Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that concentrates on creating algorithms and models enabling computers to learn from data and improve their performance on specific tasks without being explicitly programmed. ML algorithms can analyze and identify patterns in large datasets, enabling them to make predictions, recognize objects, understand natural language, and even make decisions. This technology has numerous real-world applications, including virtual assistants like Siri and recommendation systems on platforms like Netflix and Amazon. It's a pivotal component of AI that's transforming industries by automating tasks, enhancing decision-making processes, and powering various intelligent applications.
Artificial Intelligence, on the other hand, is a broader field encompassing the development of machines and systems that can simulate human-like intelligence across a wide range of tasks. While ML is a critical component of AI, AI also encompasses other approaches like expert systems, natural language processing, robotics, and computer vision. AI seeks to create systems that can reason, understand context, adapt to new situations, and exhibit general intelligence. Achieving strong AI, which has human-like cognitive abilities, remains an aspirational goal, while narrow AI, which excels in specific domains, is what we commonly encounter in today's applications.
Cloud Deployment and Migration Across Multiple Platforms
Cloud deployment and migration across multiple platforms involve the strategic use of different cloud service providers or deployment models to meet an organization's IT needs effectively. This approach recognizes that not all cloud providers or services are created equal, and by using a combination of public, private, or hybrid clouds, organizations can optimize their cloud infrastructure. Public cloud services offer scalability and cost-effectiveness, while private clouds provide control and security. Hybrid clouds combine the best of both worlds, allowing data and applications to flow seamlessly between them, offering greater flexibility and resource allocation options.
Cloud migration across multiple platforms is the process of transitioning applications, data, and workloads between different cloud providers or environments. This strategy allows organizations to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize their cloud resources based on specific requirements. However, it comes with challenges related to data transfer, integration, security, and cost management. To successfully navigate these complexities, organizations must carefully plan their cloud migration strategy, choosing the right mix of cloud platforms, and implementing robust management and monitoring practices to ensure the seamless operation of their multi-platform cloud environment.
Technical Skills Required for Cloud Computing
To thrive in your cloud computing career, being skilled in databases, DevOps, and other related technologies is essential. As a cloud computing professional, you should cultivate these additional technical skills to succeed and grow in the industry.
Data Base Skills
Database skills are critical in today's digital age, as they enable professionals to effectively manage and harness the power of data. Proficiency in database management systems (DBMS), such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and NoSQL databases like MongoDB, allows individuals to create, organize, and query data efficiently. A solid grasp of SQL, the universal language for working with databases, enables users to retrieve, manipulate, and maintain data, making it an indispensable skill for developers, data analysts, and database administrators. Furthermore, expertise in database design, indexing, and normalization ensures that data is organized logically and accessed with optimal efficiency, while knowledge of database security and backup procedures safeguards valuable information.
In today's data-driven world, database skills are indispensable across various industries, from IT to finance and healthcare. Whether it's designing scalable databases to support large-scale applications, ensuring data security and compliance, or optimizing database performance for real-time decision-making, a strong foundation in database management empowers professionals to make informed data-driven choices and contribute significantly to their organizations' success.
Devops
DevOps, short for Development (Dev) and Operations (Ops), is a modern approach to software development and IT operations that emphasizes collaboration, automation, and efficiency. It breaks down traditional silos between development and IT teams, promoting a culture of shared responsibility and constant communication. In the DevOps model, software development and deployment processes are automated, allowing for faster and more reliable releases. Continuous Integration (CI) ensures that code changes are frequently integrated and tested, while Continuous Delivery (CD) automates the deployment of these changes into production or staging environments. This automation not only accelerates the software development lifecycle but also enhances quality by reducing human error.
Moreover, DevOps encourages a feedback-driven approach. Teams monitor application performance, gather user feedback, and use this data to make informed decisions for continuous improvement. By embracing practices like Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and containerization, DevOps enables consistent and repeatable infrastructure provisioning, making it easier to manage and scale complex systems. Overall, DevOps has become an essential philosophy and set of practices for organizations seeking agility, efficiency, and reliability in their software development and IT operations.
Other Skills Required for Cloud Computing
In addition to technical skills, there are several other skills and attributes that are valuable for professionals in the field of cloud computing. These skills are essential for success in cloud-related roles and for effectively managing cloud resources and projects. Here are some of the key non-technical skills and attributes required for cloud computing:
- Communication Skills: Effective communication is crucial for conveying complex technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders. Cloud professionals often need to collaborate with different teams, including business, finance, and management, to align cloud strategies with organizational goals.
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: The ability to analyze complex problems, identify root causes, and devise innovative solutions is essential in cloud computing. Cloud professionals often encounter technical challenges and must find efficient and creative ways to address them.
- Project Management: Proficiency in project management methodologies and tools helps in planning, executing, and monitoring cloud projects effectively. This skill is particularly valuable for cloud architects and project managers overseeing cloud migrations or implementations.
- Adaptability: The cloud computing landscape is continuously evolving with new technologies and services. Being adaptable and open to learning about emerging trends and tools is essential for staying current in the field.
- Cost Management: Understanding cloud cost structures and optimizing cloud spending is critical for organizations to maximize their return on investment (ROI). Cloud professionals with skills in cost analysis and optimization can help control expenses.
- Vendor Management: As cloud environments often involve multiple cloud service providers, the ability to manage vendor relationships, negotiate contracts, and assess service-level agreements (SLAs) is valuable in ensuring that the chosen cloud solutions meet organizational needs.
- Ethical and Security Awareness: A strong sense of ethics and security consciousness is crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Cloud professionals should be aware of ethical considerations related to data privacy and security.
- Time Management: Cloud projects often involve multiple tasks and deadlines. Effective time management skills are essential for keeping projects on track and meeting objectives within specified timeframes.
- Leadership and Teamwork: Cloud professionals in leadership roles need strong leadership and team-building skills to guide teams and foster collaboration. Effective teamwork is vital for the successful implementation and management of cloud solutions.
- Customer Service Orientation: Cloud professionals who work with internal or external clients should possess strong customer service skills. Being responsive to customer needs and providing excellent support fosters positive relationships and user satisfaction.
- Legal and Compliance Knowledge: Familiarity with legal and compliance requirements in the cloud computing space, such as data protection laws and industry-specific regulations, is essential for ensuring that cloud solutions are compliant and risk-free.
- Strategic Thinking: Cloud architects and strategists should have a strategic mindset to align cloud initiatives with long-term business objectives. This includes considering scalability, disaster recovery, and future technology trends in cloud planning.
In summary, cloud computing professionals require a blend of technical expertise and soft skills to navigate the complex and ever-changing landscape of cloud technology. Developing and honing these non-technical skills enhances an individual's ability to contribute effectively to cloud projects and drive successful cloud adoption within organizations.
Get Certified and Make Yourself Indispensable
If you just graduated with a four-year degree, you may not have all the right skills for your chosen discipline. The rapid acceleration of technology and the sheer complexity of the digital age mean that if you are interested in pursuing a career in cloud computing, you can gain the latest cloud computing skills, including AWS skills, through iCert Global’s Cloud Architect Master’s Program. iCert Global’s industry-leading courses blend live, instructor-led coursework with hands-on projects and self-guided tutorials to help you achieve your goals.
Enroll in our Cloud Computing and learn all the skills that are needed to become a cloud computing expert in the industry.
Read More
In the fast-evolving landscape of technology, cloud computing has emerged as a transformative force that underpins the modern digital economy. As we step into 2023, the demand for cloud expertise continues to soar, making it a pivotal year for professionals aspiring to excel in the field. To navigate this dynamic and competitive landscape, one must possess a precise set of skills that enable them to harness the power of cloud computing effectively. This article delves into the key cloud skills that are essential for success in 2023, offering insights into the competencies that will empower individuals and organizations to thrive in the ever-expanding realm of cloud technology. Whether you are a seasoned cloud professional looking to stay at the forefront of industry trends or a newcomer eager to embark on a cloud-focused career path, these skills will be your guiding light in the journey ahead.
Table of Contents
Cloud Security
Machine Learning and AI
Cloud Deployment and Migration Across Multiple Platforms
Technical Skills Required for Cloud Computing
Other Skills Required for Cloud Computing
Get Certified and Make Yourself Indispensable
Cloud Security
Cloud security involves protecting data, applications, and infrastructure hosted in cloud computing environments from various threats and vulnerabilities. It encompasses a range of practices and technologies aimed at ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cloud-based resources. This is particularly important because cloud computing involves the storage and access of data and services through third-party providers over the internet. Key aspects of cloud security include safeguarding data through encryption and access controls, managing user identities and access permissions, complying with regulatory requirements, securing network infrastructure, and monitoring for security incidents. It's an ongoing process that requires continuous vigilance and adaptation to address evolving cyber threats in the ever-changing cloud landscape.
In the shared responsibility model of cloud security, cloud service providers are responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing their data and applications. This means that organizations must carefully assess their specific security needs and implement a combination of security measures, such as identity and access management, application security, and data encryption, to protect their assets in the cloud. Additionally, employee training and awareness play a crucial role in mitigating security risks, as human error and social engineering attacks remain significant threats to cloud security. Overall, cloud security is essential to build trust in cloud services and to ensure the safe and reliable operation of cloud-based systems and data.
Machine Learning and AI
Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that concentrates on creating algorithms and models enabling computers to learn from data and improve their performance on specific tasks without being explicitly programmed. ML algorithms can analyze and identify patterns in large datasets, enabling them to make predictions, recognize objects, understand natural language, and even make decisions. This technology has numerous real-world applications, including virtual assistants like Siri and recommendation systems on platforms like Netflix and Amazon. It's a pivotal component of AI that's transforming industries by automating tasks, enhancing decision-making processes, and powering various intelligent applications.
Artificial Intelligence, on the other hand, is a broader field encompassing the development of machines and systems that can simulate human-like intelligence across a wide range of tasks. While ML is a critical component of AI, AI also encompasses other approaches like expert systems, natural language processing, robotics, and computer vision. AI seeks to create systems that can reason, understand context, adapt to new situations, and exhibit general intelligence. Achieving strong AI, which has human-like cognitive abilities, remains an aspirational goal, while narrow AI, which excels in specific domains, is what we commonly encounter in today's applications.
Cloud Deployment and Migration Across Multiple Platforms
Cloud deployment and migration across multiple platforms involve the strategic use of different cloud service providers or deployment models to meet an organization's IT needs effectively. This approach recognizes that not all cloud providers or services are created equal, and by using a combination of public, private, or hybrid clouds, organizations can optimize their cloud infrastructure. Public cloud services offer scalability and cost-effectiveness, while private clouds provide control and security. Hybrid clouds combine the best of both worlds, allowing data and applications to flow seamlessly between them, offering greater flexibility and resource allocation options.
Cloud migration across multiple platforms is the process of transitioning applications, data, and workloads between different cloud providers or environments. This strategy allows organizations to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize their cloud resources based on specific requirements. However, it comes with challenges related to data transfer, integration, security, and cost management. To successfully navigate these complexities, organizations must carefully plan their cloud migration strategy, choosing the right mix of cloud platforms, and implementing robust management and monitoring practices to ensure the seamless operation of their multi-platform cloud environment.
Technical Skills Required for Cloud Computing
To thrive in your cloud computing career, being skilled in databases, DevOps, and other related technologies is essential. As a cloud computing professional, you should cultivate these additional technical skills to succeed and grow in the industry.
Data Base Skills
Database skills are critical in today's digital age, as they enable professionals to effectively manage and harness the power of data. Proficiency in database management systems (DBMS), such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and NoSQL databases like MongoDB, allows individuals to create, organize, and query data efficiently. A solid grasp of SQL, the universal language for working with databases, enables users to retrieve, manipulate, and maintain data, making it an indispensable skill for developers, data analysts, and database administrators. Furthermore, expertise in database design, indexing, and normalization ensures that data is organized logically and accessed with optimal efficiency, while knowledge of database security and backup procedures safeguards valuable information.
In today's data-driven world, database skills are indispensable across various industries, from IT to finance and healthcare. Whether it's designing scalable databases to support large-scale applications, ensuring data security and compliance, or optimizing database performance for real-time decision-making, a strong foundation in database management empowers professionals to make informed data-driven choices and contribute significantly to their organizations' success.
Devops
DevOps, short for Development (Dev) and Operations (Ops), is a modern approach to software development and IT operations that emphasizes collaboration, automation, and efficiency. It breaks down traditional silos between development and IT teams, promoting a culture of shared responsibility and constant communication. In the DevOps model, software development and deployment processes are automated, allowing for faster and more reliable releases. Continuous Integration (CI) ensures that code changes are frequently integrated and tested, while Continuous Delivery (CD) automates the deployment of these changes into production or staging environments. This automation not only accelerates the software development lifecycle but also enhances quality by reducing human error.
Moreover, DevOps encourages a feedback-driven approach. Teams monitor application performance, gather user feedback, and use this data to make informed decisions for continuous improvement. By embracing practices like Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and containerization, DevOps enables consistent and repeatable infrastructure provisioning, making it easier to manage and scale complex systems. Overall, DevOps has become an essential philosophy and set of practices for organizations seeking agility, efficiency, and reliability in their software development and IT operations.
Other Skills Required for Cloud Computing
In addition to technical skills, there are several other skills and attributes that are valuable for professionals in the field of cloud computing. These skills are essential for success in cloud-related roles and for effectively managing cloud resources and projects. Here are some of the key non-technical skills and attributes required for cloud computing:
- Communication Skills: Effective communication is crucial for conveying complex technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders. Cloud professionals often need to collaborate with different teams, including business, finance, and management, to align cloud strategies with organizational goals.
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: The ability to analyze complex problems, identify root causes, and devise innovative solutions is essential in cloud computing. Cloud professionals often encounter technical challenges and must find efficient and creative ways to address them.
- Project Management: Proficiency in project management methodologies and tools helps in planning, executing, and monitoring cloud projects effectively. This skill is particularly valuable for cloud architects and project managers overseeing cloud migrations or implementations.
- Adaptability: The cloud computing landscape is continuously evolving with new technologies and services. Being adaptable and open to learning about emerging trends and tools is essential for staying current in the field.
- Cost Management: Understanding cloud cost structures and optimizing cloud spending is critical for organizations to maximize their return on investment (ROI). Cloud professionals with skills in cost analysis and optimization can help control expenses.
- Vendor Management: As cloud environments often involve multiple cloud service providers, the ability to manage vendor relationships, negotiate contracts, and assess service-level agreements (SLAs) is valuable in ensuring that the chosen cloud solutions meet organizational needs.
- Ethical and Security Awareness: A strong sense of ethics and security consciousness is crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Cloud professionals should be aware of ethical considerations related to data privacy and security.
- Time Management: Cloud projects often involve multiple tasks and deadlines. Effective time management skills are essential for keeping projects on track and meeting objectives within specified timeframes.
- Leadership and Teamwork: Cloud professionals in leadership roles need strong leadership and team-building skills to guide teams and foster collaboration. Effective teamwork is vital for the successful implementation and management of cloud solutions.
- Customer Service Orientation: Cloud professionals who work with internal or external clients should possess strong customer service skills. Being responsive to customer needs and providing excellent support fosters positive relationships and user satisfaction.
- Legal and Compliance Knowledge: Familiarity with legal and compliance requirements in the cloud computing space, such as data protection laws and industry-specific regulations, is essential for ensuring that cloud solutions are compliant and risk-free.
- Strategic Thinking: Cloud architects and strategists should have a strategic mindset to align cloud initiatives with long-term business objectives. This includes considering scalability, disaster recovery, and future technology trends in cloud planning.
In summary, cloud computing professionals require a blend of technical expertise and soft skills to navigate the complex and ever-changing landscape of cloud technology. Developing and honing these non-technical skills enhances an individual's ability to contribute effectively to cloud projects and drive successful cloud adoption within organizations.
Get Certified and Make Yourself Indispensable
If you just graduated with a four-year degree, you may not have all the right skills for your chosen discipline. The rapid acceleration of technology and the sheer complexity of the digital age mean that if you are interested in pursuing a career in cloud computing, you can gain the latest cloud computing skills, including AWS skills, through iCert Global’s Cloud Architect Master’s Program. iCert Global’s industry-leading courses blend live, instructor-led coursework with hands-on projects and self-guided tutorials to help you achieve your goals.
Enroll in our Cloud Computing and learn all the skills that are needed to become a cloud computing expert in the industry.
Essential Excel Skills for 2023: An Ultimate Must-Know Guide
In the fast-paced world of 2023, proficiency in Microsoft Excel is more essential than ever. Excel remains a cornerstone of productivity and data management, indispensable across various industries and professions. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting your journey, understanding its core features and mastering essential Excel skills is a must. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the vital Excel skills that can empower you to excel in your endeavors throughout the year 2023 and beyond. From basic functions to advanced techniques, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and capabilities needed to navigate the evolving landscape of data analysis, financial modeling, and effective spreadsheet management. Join us as we explore the world of Excel and uncover the skills that are bound to make a difference in your personal and professional life.
Table of Contents
What Is Microsoft Excel?
Excel Skills You Must Know
1. Master the Shortcuts
2. Import Data from a Website
3. Filter Your Results
4. Calculate the Sum
5. AutoCorrect and AutoFill
6. Display Formulas
7. Manage Page Layout
The Bottom Line
What Is Microsoft Excel?
Microsoft Excel is a versatile and widely-used spreadsheet application developed by Microsoft, forming an integral part of the Microsoft Office suite. This software empowers users to create, organize, and analyze data within a grid-like interface, making it an invaluable tool for a myriad of tasks. Excel's robust features encompass the ability to perform complex calculations using built-in functions, visualize data through charts and graphs, and facilitate data analysis with tools like pivot tables. Its automation capabilities, data validation, and collaborative functionality further enhance its utility. Excel serves as a vital resource across various industries, aiding professionals in financial modeling, data analysis, project management, and countless other applications, thanks to its adaptability and rich feature set.
Excel Skills You Must Know
Excel proficiency spans a spectrum from basic to advanced, accommodating a diverse range of applications, from simple data entry to intricate formula calculations. In the following sections, we'll explore key Excel skills worth mastering, starting with essential elements of basic Excel training to help you enhance your Excel proficiency.
There is a wide range of Excel skills from the basic to the advanced. Excel can be used to input numbers as well as calculate complex formulas.
-
Master the Shortcuts
-
Import Data from a Website
-
Filter Your Results
-
Calculate the Sum
-
AutoCorrect and AutoFill
-
Display Formulas
-
Manage Page Layout
Master the Shortcuts
Mastering keyboard shortcuts in Excel is a great way to boost your productivity. These shortcuts can help you perform tasks quickly and efficiently. Here are some essential Excel keyboard shortcuts to get you started:
-
Ctrl + C: Copy selected cells or text.
-
Ctrl + X: Cut selected cells or text.
-
Ctrl + V: Paste copied or cut cells or text.
-
Ctrl + Z: Undo the last action.
-
Ctrl + Y: Redo the last undone action.
-
Ctrl + S: Save your Excel workbook.
-
Ctrl + P: Print the active sheet.
-
Ctrl + F: Open the Find and Replace dialog box.
-
Ctrl + A: Select all cells in the current worksheet.
-
Ctrl + arrow keys: Move to the edge of data regions.
-
Ctrl + Space: Select the entire column of the active cell.
-
Shift + Space: Select the entire row of the active cell.
-
**Ctrl + Shift + "+": Insert new cells, rows, or columns.
-
**Ctrl + "-": Delete cells, rows, or columns.
-
F2: Edit the active cell.
-
Alt + Enter: Start a new line within a cell.
-
Ctrl + Tab: Switch between open Excel workbooks.
-
Ctrl + Page Up/Page Down: Navigate between worksheets.
-
Ctrl + Shift + L: Apply or remove filters.
-
Alt + E, S, V: Paste special options.
-
Ctrl + 1: Format cells dialog box.
-
Alt + H, O, I: Autofit column width.
These are just a few examples, but there are many more Excel shortcuts available. Learning and using these shortcuts can significantly speed up your work and make you more proficient in Excel.
Import Data from a Website
To import data from a website into Excel, you can utilize the "From Web" feature, which is available in most versions of Excel. Begin by opening Excel and selecting the cell in your worksheet where you want the imported data to start. Next, navigate to the "Data" tab on the Excel ribbon, where you'll find an option like "Get Data" or "Get External Data." Click on this option and choose "From Web." In the dialog box that appears, enter the URL of the website containing the data you wish to import. Excel will then establish a connection to the website, presenting you with a web browser-like interface to interact with the site. Navigate to the specific data you want to import and click to select it. Afterward, click the "Import" or "Load" button, depending on your Excel version, to bring the data into your worksheet. You may need to specify import options, such as header rows, depending on the structure of the data. Once imported, you can work with and format the data as needed within Excel. Keep in mind that data import from websites should be conducted in compliance with the website's terms and policies, and some sites may have restrictions in place to prevent automated scraping.
Filter Your Results
Filtering data in Excel is an essential skill that allows you to refine and extract specific information from a dataset with ease. To initiate the process, select any cell within the dataset you want to filter, and then head to the "Data" tab on the Excel ribbon. There, you'll find the filter icon, resembling a funnel, which you should click to activate. Once activated, drop-down arrows will appear in the header row of each column in your dataset. Clicking on one of these arrows opens a menu where you can set filter criteria, whether by selecting specific values, specifying text or number conditions, or setting date ranges. After defining your criteria, simply click "OK" or "Apply," and Excel will instantly display only the rows that meet your filtering requirements, effectively tailoring your dataset to your needs. You can apply filters to multiple columns simultaneously and remove them just as easily. This functionality proves invaluable when working with large datasets, as it streamlines analysis and decision-making by enabling you to focus exclusively on the data that matters most.
Calculate the Sum
Calculating the sum of values in Excel is a fundamental operation that can be accomplished in a couple of ways. First, you can use the SUM function, which is particularly useful when you're working with a large set of numbers. To do this, select the cell where you want the sum to appear, then enter "=SUM(" and choose the range of cells you want to add up, closing the parenthesis before pressing Enter. Alternatively, you can use the AutoSum button, which simplifies the process by automatically suggesting a range based on adjacent cells with numerical data. Once you select the appropriate range, press Enter to calculate the sum. For smaller calculations, you can manually enter values separated by plus signs directly into a cell. Excel's flexibility in performing these calculations makes it a versatile tool for summing up data, whether it's for budgeting, financial analysis, or any task requiring mathematical aggregation.
AutoCorrect and AutoFill
AutoCorrect and AutoFill are two convenient features within Microsoft Excel that enhance efficiency and accuracy when working with data. AutoCorrect functions as a real-time proofreader, automatically fixing common spelling errors and typos as you type. It recognizes frequent mistakes and replaces them with the correct text, helping you maintain clean and error-free spreadsheets. Additionally, you can customize AutoCorrect to handle specific words or acronyms that you commonly use.
On the other hand, AutoFill is a time-saving tool that simplifies the input of recurring or sequential data. For example, if you're entering a series of dates, months, or numeric patterns, Excel can predict and complete the pattern for you. By entering the initial value and dragging the fill handle, you can instantly populate adjacent cells with the desired series, eliminating the need for manual input. Both AutoCorrect and AutoFill are valuable aids that not only boost your productivity but also contribute to the accuracy and professionalism of your Excel documents.
Display Formulas
In Microsoft Excel, the ability to display formulas provides a valuable tool for spreadsheet users, especially when dealing with intricate calculations or when auditing a spreadsheet for errors. By pressing Ctrl + ` or clicking the "Show Formulas" button in the "Formulas" tab, you can toggle between viewing the actual formulas used in each cell and seeing their calculated results. This feature allows you to review and understand the underlying logic of your spreadsheet, which is particularly helpful for troubleshooting and debugging complex formulas. It's also beneficial when you need to verify that your formulas are working as intended, as it ensures transparency and accuracy in your calculations. Whether you're an Excel novice or an experienced user, the ability to easily display formulas is an essential tool for maintaining the integrity and reliability of your spreadsheet data.
Manage Page Layout
Managing page layout in Microsoft Excel is a critical aspect of creating well-organized and professional-looking documents. With the ability to control page orientation, size, margins, and page breaks, you can ensure that your printed or saved worksheets are presented exactly as you intend. Additionally, Excel provides options for adding headers and footers, scaling content to fit the page, and specifying the print area to include only the necessary data. You can also choose whether to display gridlines, row, and column headings in your printouts, enhancing readability. The background feature allows you to add visual elements, while print titles ensure that specific rows or columns are repeated on each page, providing valuable context. By effectively managing page layout in Excel, you can tailor your documents to suit various printing or sharing needs, making your data more accessible and professional.
The Bottom Line
If you're looking to simplify your daily tasks and perhaps leave a lasting impression among your colleagues, delving into these fundamental Excel skills is a wise move. It's worth noting that Excel, despite its widespread use, remains a versatile and evolving tool. Regardless of your current proficiency level, there are always fresh techniques and features to explore in this robust application. So, consider taking the initiative to enhance your Excel proficiency—it's not just about managing personal finances more efficiently; it could open doors to exciting career prospects down the road. Eager to dive deeper into the world of Excel? iCert Global offers a variety of Excel online training courses ie Microsoft Excel foundation , Microsoft Excel Intermediate , Microsoft Excel Advanced Certification.
Read More
In the fast-paced world of 2023, proficiency in Microsoft Excel is more essential than ever. Excel remains a cornerstone of productivity and data management, indispensable across various industries and professions. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting your journey, understanding its core features and mastering essential Excel skills is a must. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the vital Excel skills that can empower you to excel in your endeavors throughout the year 2023 and beyond. From basic functions to advanced techniques, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and capabilities needed to navigate the evolving landscape of data analysis, financial modeling, and effective spreadsheet management. Join us as we explore the world of Excel and uncover the skills that are bound to make a difference in your personal and professional life.
Table of Contents
What Is Microsoft Excel?
Excel Skills You Must Know
1. Master the Shortcuts
2. Import Data from a Website
3. Filter Your Results
4. Calculate the Sum
5. AutoCorrect and AutoFill
6. Display Formulas
7. Manage Page Layout
The Bottom Line
What Is Microsoft Excel?
Microsoft Excel is a versatile and widely-used spreadsheet application developed by Microsoft, forming an integral part of the Microsoft Office suite. This software empowers users to create, organize, and analyze data within a grid-like interface, making it an invaluable tool for a myriad of tasks. Excel's robust features encompass the ability to perform complex calculations using built-in functions, visualize data through charts and graphs, and facilitate data analysis with tools like pivot tables. Its automation capabilities, data validation, and collaborative functionality further enhance its utility. Excel serves as a vital resource across various industries, aiding professionals in financial modeling, data analysis, project management, and countless other applications, thanks to its adaptability and rich feature set.
Excel Skills You Must Know
Excel proficiency spans a spectrum from basic to advanced, accommodating a diverse range of applications, from simple data entry to intricate formula calculations. In the following sections, we'll explore key Excel skills worth mastering, starting with essential elements of basic Excel training to help you enhance your Excel proficiency.
There is a wide range of Excel skills from the basic to the advanced. Excel can be used to input numbers as well as calculate complex formulas.
-
Master the Shortcuts
-
Import Data from a Website
-
Filter Your Results
-
Calculate the Sum
-
AutoCorrect and AutoFill
-
Display Formulas
-
Manage Page Layout
Master the Shortcuts
Mastering keyboard shortcuts in Excel is a great way to boost your productivity. These shortcuts can help you perform tasks quickly and efficiently. Here are some essential Excel keyboard shortcuts to get you started:
-
Ctrl + C: Copy selected cells or text.
-
Ctrl + X: Cut selected cells or text.
-
Ctrl + V: Paste copied or cut cells or text.
-
Ctrl + Z: Undo the last action.
-
Ctrl + Y: Redo the last undone action.
-
Ctrl + S: Save your Excel workbook.
-
Ctrl + P: Print the active sheet.
-
Ctrl + F: Open the Find and Replace dialog box.
-
Ctrl + A: Select all cells in the current worksheet.
-
Ctrl + arrow keys: Move to the edge of data regions.
-
Ctrl + Space: Select the entire column of the active cell.
-
Shift + Space: Select the entire row of the active cell.
-
**Ctrl + Shift + "+": Insert new cells, rows, or columns.
-
**Ctrl + "-": Delete cells, rows, or columns.
-
F2: Edit the active cell.
-
Alt + Enter: Start a new line within a cell.
-
Ctrl + Tab: Switch between open Excel workbooks.
-
Ctrl + Page Up/Page Down: Navigate between worksheets.
-
Ctrl + Shift + L: Apply or remove filters.
-
Alt + E, S, V: Paste special options.
-
Ctrl + 1: Format cells dialog box.
-
Alt + H, O, I: Autofit column width.
These are just a few examples, but there are many more Excel shortcuts available. Learning and using these shortcuts can significantly speed up your work and make you more proficient in Excel.
Import Data from a Website
To import data from a website into Excel, you can utilize the "From Web" feature, which is available in most versions of Excel. Begin by opening Excel and selecting the cell in your worksheet where you want the imported data to start. Next, navigate to the "Data" tab on the Excel ribbon, where you'll find an option like "Get Data" or "Get External Data." Click on this option and choose "From Web." In the dialog box that appears, enter the URL of the website containing the data you wish to import. Excel will then establish a connection to the website, presenting you with a web browser-like interface to interact with the site. Navigate to the specific data you want to import and click to select it. Afterward, click the "Import" or "Load" button, depending on your Excel version, to bring the data into your worksheet. You may need to specify import options, such as header rows, depending on the structure of the data. Once imported, you can work with and format the data as needed within Excel. Keep in mind that data import from websites should be conducted in compliance with the website's terms and policies, and some sites may have restrictions in place to prevent automated scraping.
Filter Your Results
Filtering data in Excel is an essential skill that allows you to refine and extract specific information from a dataset with ease. To initiate the process, select any cell within the dataset you want to filter, and then head to the "Data" tab on the Excel ribbon. There, you'll find the filter icon, resembling a funnel, which you should click to activate. Once activated, drop-down arrows will appear in the header row of each column in your dataset. Clicking on one of these arrows opens a menu where you can set filter criteria, whether by selecting specific values, specifying text or number conditions, or setting date ranges. After defining your criteria, simply click "OK" or "Apply," and Excel will instantly display only the rows that meet your filtering requirements, effectively tailoring your dataset to your needs. You can apply filters to multiple columns simultaneously and remove them just as easily. This functionality proves invaluable when working with large datasets, as it streamlines analysis and decision-making by enabling you to focus exclusively on the data that matters most.
Calculate the Sum
Calculating the sum of values in Excel is a fundamental operation that can be accomplished in a couple of ways. First, you can use the SUM function, which is particularly useful when you're working with a large set of numbers. To do this, select the cell where you want the sum to appear, then enter "=SUM(" and choose the range of cells you want to add up, closing the parenthesis before pressing Enter. Alternatively, you can use the AutoSum button, which simplifies the process by automatically suggesting a range based on adjacent cells with numerical data. Once you select the appropriate range, press Enter to calculate the sum. For smaller calculations, you can manually enter values separated by plus signs directly into a cell. Excel's flexibility in performing these calculations makes it a versatile tool for summing up data, whether it's for budgeting, financial analysis, or any task requiring mathematical aggregation.
AutoCorrect and AutoFill
AutoCorrect and AutoFill are two convenient features within Microsoft Excel that enhance efficiency and accuracy when working with data. AutoCorrect functions as a real-time proofreader, automatically fixing common spelling errors and typos as you type. It recognizes frequent mistakes and replaces them with the correct text, helping you maintain clean and error-free spreadsheets. Additionally, you can customize AutoCorrect to handle specific words or acronyms that you commonly use.
On the other hand, AutoFill is a time-saving tool that simplifies the input of recurring or sequential data. For example, if you're entering a series of dates, months, or numeric patterns, Excel can predict and complete the pattern for you. By entering the initial value and dragging the fill handle, you can instantly populate adjacent cells with the desired series, eliminating the need for manual input. Both AutoCorrect and AutoFill are valuable aids that not only boost your productivity but also contribute to the accuracy and professionalism of your Excel documents.
Display Formulas
In Microsoft Excel, the ability to display formulas provides a valuable tool for spreadsheet users, especially when dealing with intricate calculations or when auditing a spreadsheet for errors. By pressing Ctrl + ` or clicking the "Show Formulas" button in the "Formulas" tab, you can toggle between viewing the actual formulas used in each cell and seeing their calculated results. This feature allows you to review and understand the underlying logic of your spreadsheet, which is particularly helpful for troubleshooting and debugging complex formulas. It's also beneficial when you need to verify that your formulas are working as intended, as it ensures transparency and accuracy in your calculations. Whether you're an Excel novice or an experienced user, the ability to easily display formulas is an essential tool for maintaining the integrity and reliability of your spreadsheet data.
Manage Page Layout
Managing page layout in Microsoft Excel is a critical aspect of creating well-organized and professional-looking documents. With the ability to control page orientation, size, margins, and page breaks, you can ensure that your printed or saved worksheets are presented exactly as you intend. Additionally, Excel provides options for adding headers and footers, scaling content to fit the page, and specifying the print area to include only the necessary data. You can also choose whether to display gridlines, row, and column headings in your printouts, enhancing readability. The background feature allows you to add visual elements, while print titles ensure that specific rows or columns are repeated on each page, providing valuable context. By effectively managing page layout in Excel, you can tailor your documents to suit various printing or sharing needs, making your data more accessible and professional.
The Bottom Line
If you're looking to simplify your daily tasks and perhaps leave a lasting impression among your colleagues, delving into these fundamental Excel skills is a wise move. It's worth noting that Excel, despite its widespread use, remains a versatile and evolving tool. Regardless of your current proficiency level, there are always fresh techniques and features to explore in this robust application. So, consider taking the initiative to enhance your Excel proficiency—it's not just about managing personal finances more efficiently; it could open doors to exciting career prospects down the road. Eager to dive deeper into the world of Excel? iCert Global offers a variety of Excel online training courses ie Microsoft Excel foundation , Microsoft Excel Intermediate , Microsoft Excel Advanced Certification.
Exploring Data Encryption: Types, Algorithms & Techniques
In an increasingly interconnected digital world, where data is both the lifeblood and the target of modern endeavors, the need for robust data protection has never been more critical. At the heart of this defense lies the art and science of data encryption—an intricate process that transforms information into an unreadable code, rendering it impervious to prying eyes. This exploration into the realm of data encryption aims to unravel its intricacies, unveiling the diverse types, sophisticated algorithms, ingenious techniques, and strategic approaches that together fortify the security of our digital landscape. From the symmetrical dance of keys to the asymmetric harmony of secure communications, from the impenetrable armor of Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) to the mathematical elegance of RSA and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), this journey will delve into the mechanisms that power our defenses against data breaches and unauthorized access. We will navigate through the labyrinth of encryption methods, discerning the nuanced interplay of confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity that they orchestrate. Whether you're a curious explorer of technology or an ardent guardian of data integrity, join us as we embark on an enlightening expedition into the world of data encryption, where each layer of knowledge adds another layer of protection.
Table of Contents
What is Data Encryption?
How Does Data Encryption Work?
Why Do We Need Data Encryption?
What are the 2 Types of Data Encryption Techniques?
What is Hashing?
What is an Encryption Algorithm?
Best Encryption Algorithms
3DES
The Future of Data Encryption
Should You Use Symmetric or Asymmetric Encryption?
Businesses Use Encryption For Many Purposes
Steps to Implement an Effective Encryption Strategy
What Is a Key in Cryptography?
Do You Want to Learn More About Cybersecurity?
FAQs
What is Data Encryption?
Data encryption is the process of converting understandable data into an unreadable form, known as ciphertext, using complex algorithms and a secret key. This transformation ensures that even if unauthorized parties gain access to the encrypted data, they cannot comprehend its original meaning without the corresponding decryption key. Encryption serves as a vital mechanism for safeguarding sensitive information during storage, transmission, and processing, thwarting unauthorized access and maintaining data confidentiality. It finds application in various realms such as online transactions, secure communication, and data protection, offering varying levels of security through different encryption methods and algorithms tailored to specific needs.
How Does Data Encryption Work?
Data encryption functions by utilizing complex algorithms to convert plain data into an unintelligible form known as ciphertext. This process involves an encryption key that serves as the foundation for the transformation. The chosen algorithm determines how the encryption and decryption keys interact. During encryption, the algorithm combines the encryption key with the plaintext, generating ciphertext that appears as random characters. This ciphertext can be safely transmitted or stored without revealing the original information. To reverse the process, decryption employs the corresponding decryption key, allowing the recipient to transform the ciphertext back into readable plaintext. The security of encrypted data hinges on robust algorithms, secure key management, and effective protection against unauthorized access to the encryption keys.
Why Do We Need Data Encryption?
Data encryption is a vital necessity due to its role in shielding sensitive information from unauthorized access and maintaining confidentiality. It acts as a bulwark against privacy breaches by converting data into an unreadable format, making it indecipherable without the appropriate decryption key. This protection is essential across diverse domains, from safeguarding personal data and financial records to upholding regulatory compliance and mitigating the impact of data breaches. Encryption not only secures communication over networks and cloud storage but also fortifies authentication procedures and shields intellectual property from prying eyes. In an era of global connectivity, encryption stands as a cornerstone of cybersecurity, ensuring the security and privacy of digital interactions and sensitive information.
What are the 2 Types of Data Encryption Techniques?
Data encryption techniques can be broadly categorized into two main types: Symmetric Encryption and Asymmetric Encryption.
-
Symmetric Encryption: In symmetric encryption, a single encryption key is used for both the encryption and decryption processes. The same key is shared between the sender and the recipient. The main advantage of symmetric encryption is its speed and efficiency, as the algorithms used are generally faster than their asymmetric counterparts. However, the challenge lies in securely exchanging the encryption key between parties without it being intercepted by unauthorized individuals. Common symmetric encryption algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and DES (Data Encryption Standard).
-
Asymmetric Encryption: Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, employs a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used for encryption, while the private key is used for decryption. The keys are mathematically related but cannot be practically derived from each other. This setup addresses the key exchange challenge of symmetric encryption, as the public key can be freely shared without compromising the security of the private key. Asymmetric encryption provides a higher level of security for tasks like secure communication and digital signatures. RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) are examples of asymmetric encryption algorithms.
Both types of encryption techniques have their advantages and are often used together to address specific security needs. Symmetric encryption is suitable for encrypting large amounts of data quickly, while asymmetric encryption is valuable for secure key exchange and ensuring the authenticity of communication parties.
What is Hashing?
Hashing is a cryptographic technique that involves transforming input data into a fixed-length string of characters, known as a hash value. This process is designed to be fast and deterministic, meaning the same input will always produce the same hash value. Hashing serves various purposes, such as verifying data integrity and authenticity. It ensures data integrity by generating a unique representation of the input data, making it easy to detect even minor changes in the data. Hashing is commonly used for tasks like password storage, where passwords are hashed and stored to enhance security. Additionally, hashing underpins digital signatures, providing a way to confirm the authenticity of digital documents and messages. However, it's important to choose secure and collision-resistant hash functions to prevent vulnerabilities and ensure the reliability of hash-based applications.
What is an Encryption Algorithm?
An encryption algorithm is a set of mathematical rules and procedures used to transform data from its original, readable form (plaintext) into an unreadable and secure format (ciphertext) during encryption, and to revert it back to plaintext during decryption. It dictates how the encryption key interacts with the data to produce the ciphertext and how the decryption key is used to reverse the process. Encryption algorithms play a pivotal role in maintaining data security and confidentiality, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected from unauthorized access and interception. These algorithms come in two main types: symmetric, which use the same key for both encryption and decryption, and asymmetric (public-key), which employ a pair of keys for these operations. The selection of an encryption algorithm depends on factors such as security requirements, key management, and the specific application's needs.
Best Encryption Algorithms
The "best" encryption algorithm depends on the specific use case, security requirements, and the state of current cryptographic research. However, as of my last knowledge update in September 2021, I can mention some widely recognized and respected encryption algorithms that were considered strong at that time:
-
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): AES is one of the most widely used symmetric encryption algorithms. It offers strong security and efficiency and is considered secure for a wide range of applications. AES operates with varying key lengths, including 128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit.
-
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman): RSA is a well-known asymmetric encryption algorithm used for secure key exchange, digital signatures, and other cryptographic tasks. It relies on the difficulty of factoring large prime numbers to provide security.
-
ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography): ECC is another asymmetric encryption algorithm known for its strong security and relatively shorter key lengths compared to RSA. It is particularly well-suited for resource-constrained environments, such as mobile devices.
-
SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit): While not an encryption algorithm per se, SHA-256 is a widely used cryptographic hash function. It's used for various purposes, including generating digital signatures and verifying data integrity.
-
ChaCha20 and Poly1305: These are modern cryptographic algorithms designed to provide encryption and data integrity in a combined mode. They are becoming popular choices, especially for use in stream cipher constructions.
It's important to note that cryptographic algorithms and best practices can evolve over time due to advances in technology and cryptanalysis. Organizations should stay updated with the latest recommendations from reputable sources, such as NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology), to ensure they are using algorithms that meet current security standards. Additionally, the strength of encryption also relies on proper key management, implementation, and the overall security of the system in which it is used.
3DES
Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES), also known as TDEA (Triple Data Encryption Algorithm), is a symmetric encryption algorithm that provides a higher level of security compared to the original Data Encryption Standard (DES) algorithm. 3DES applies the DES algorithm three times in a cascade, using multiple keys. This process significantly increases the effective key length and enhances security.
Here's how 3DES works:
-
Key Generation: Three separate keys are generated, often referred to as Key 1, Key 2, and Key 3.
-
Encryption: The plaintext data undergoes three consecutive rounds of encryption using the three keys. The data is first encrypted with Key 1, then decrypted using Key 2, and finally encrypted again using Key 3.
-
Decryption: To decrypt the data, the process is reversed. The ciphertext is decrypted with Key 3, then encrypted with Key 2, and finally decrypted using Key 1.
3DES provides an effective key length of 168 bits, as each of the three keys is 56 bits long. This makes it significantly more secure than the original DES, which had a 56-bit key length and became susceptible to brute-force attacks as computing power increased. However, it's worth noting that 3DES is not as efficient as more modern symmetric encryption algorithms like AES, which offer better performance and security with shorter key lengths.
3DES was widely adopted as an interim solution when transitioning from DES to more secure algorithms. However, due to its relatively slower performance and the availability of more efficient encryption algorithms, such as AES, it's recommended to use AES for new implementations requiring strong symmetric encryption.
The Future of Data Encryption
The future of data encryption holds several promising trends and challenges. Post-Quantum Cryptography is actively being researched to ensure encryption methods remain secure against the potential threat of quantum computers. Homomorphic encryption presents opportunities for processing data while it remains encrypted, enhancing privacy and security. Zero-knowledge proofs could revolutionize authentication and digital identity, while encryption's role in securing blockchain networks will continue to be paramount. Enhanced key management practices, such as hardware security modules and secure key distribution, will strengthen encryption protocols. Quantum Key Distribution offers ultra-secure methods for key exchange. The synergy of AI and encryption is likely to optimize processes and enhance overall security. As regulations evolve, encryption laws may adapt to balance security and law enforcement needs. Usability improvements and broader integration into applications and devices will be pivotal for increasing encryption adoption. Staying abreast of these developments will be essential as the landscape of data encryption continues to evolve dynamically.
Should You Use Symmetric or Asymmetric Encryption?
The decision to use symmetric or asymmetric encryption hinges on the context and security requirements of the scenario. Symmetric encryption offers speed and efficiency, making it suitable for encrypting large data volumes. However, it demands a secure method of distributing the shared key among parties. Asymmetric encryption, while slower, addresses the challenge of secure key exchange and is pivotal for scenarios where parties don't share a pre-established secret key. Asymmetric encryption's application extends to digital signatures and secure communication with key exchange. Often, a hybrid approach is employed, utilizing both encryption types to leverage their strengths. In such cases, asymmetric encryption may be used to securely establish a symmetric encryption key, enabling efficient data encryption. Ultimately, the choice should align with specific security needs, key management complexity, and the speed requirements of the given use case, ensuring an appropriate balance between security and practicality.
Businesses Use Encryption For Many Purposes
Businesses leverage encryption for a multitude of purposes to reinforce their data security measures and uphold the integrity of their operations. Encryption is extensively employed to shield sensitive customer data, proprietary information, and financial records, thereby thwarting unauthorized access and data breaches. It's pivotal in securing communication channels, such as emails and instant messaging, ensuring that confidential information remains private during transmission. Encryption also underpins secure financial transactions on e-commerce platforms and online banking systems. It bolsters password security by storing user credentials securely and helps businesses adhere to regulatory frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA, safeguarding them from legal consequences and maintaining customer trust. Additionally, encryption is paramount for cloud security, remote work scenarios, secure file sharing, digital signatures, IoT security, and preserving the confidentiality of sensitive data within supply chains. Overall, encryption is a cornerstone of modern business strategies, fostering data protection and bolstering organizational reputation.
Steps to Implement an Effective Encryption Strategy
Implementing an effective encryption strategy involves a systematic approach to ensure the security of sensitive data. Here are five key steps to guide the process:
-
Data Classification and Assessment: Begin by identifying and classifying the types of data that require encryption. Conduct a thorough assessment of your organization's data landscape to determine which data is sensitive and where it resides. This includes data at rest, in transit, and during processing.
-
Security Requirements Definition: Define your security requirements based on the sensitivity of the data. Determine which encryption algorithms and key lengths are appropriate for different data types and use cases. Consider compliance regulations and industry standards that apply to your organization.
-
Encryption Implementation: Select suitable encryption solutions and tools that align with your requirements. Implement encryption mechanisms for data at rest and in transit. For data at rest, utilize encryption features provided by databases, operating systems, or storage solutions. For data in transit, employ secure protocols such as TLS/SSL for network communication.
-
Key Management and Access Control: Develop a robust key management strategy. Establish procedures for generating, storing, rotating, and revoking encryption keys. Ensure that only authorized personnel have access to encryption keys. Implement strong access controls to prevent unauthorized users from accessing encrypted data.
-
Testing, Monitoring, and Compliance: Thoroughly test your encryption implementation to ensure its effectiveness and compatibility with your systems. Regularly monitor encryption processes, access logs, and audit trails to detect any anomalies or unauthorized access attempts. Conduct periodic security assessments and audits to ensure compliance with encryption policies and regulations.
By following these steps, you can create a structured and comprehensive encryption strategy that safeguards sensitive data, mitigates risks, and aligns with industry best practices and compliance standards.
What Is a Key in Cryptography?
In cryptography, a key refers to a specific piece of information, often a sequence of characters, numbers, or bits, that is used to control the encryption and decryption processes. Keys play a central role in cryptographic operations by determining how data is transformed from its original form (plaintext) to an encrypted form (ciphertext) and back to plaintext.
There are two main types of keys in cryptography:
-
Encryption Key: This key is used during the encryption process to convert plaintext into ciphertext. The encryption key is known only to authorized parties involved in secure communication or data protection.
-
Decryption Key: This key is used during the decryption process to revert the ciphertext back to its original plaintext. In symmetric encryption, the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. In asymmetric encryption (public-key cryptography), there is a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
Keys are kept confidential to ensure the security of encrypted data. The strength and security of a cryptographic system often depend on the length and complexity of the encryption keys. Longer keys are generally more secure because they increase the number of possible combinations that an attacker would need to try in order to break the encryption.
Effective key management is essential to maintain the integrity of cryptographic systems. This includes secure key generation, distribution, storage, rotation, and disposal. In many cases, hardware security modules (HSMs) are used to securely store and manage encryption keys to prevent unauthorized access or theft.
Do You Want to Learn More About Cybersecurity?
Are you interested in delving deeper into the realm of cybersecurity? With the ever-growing importance of safeguarding digital systems and data, gaining expertise in this field is invaluable. Notable certifications such as Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), and CompTIA Security+ offer comprehensive knowledge and skills that can elevate your understanding of cybersecurity principles and practices. Furthermore, exploring frameworks like COBIT 2019 can provide you with a structured approach to governance and management of enterprise information technology. These certifications and frameworks encompass a wide range of topics, from risk management and security controls to compliance and governance. Whether you're just beginning your journey or seeking to advance your career, these resources can serve as essential guides on your path to becoming a proficient cybersecurity professional.
FAQs
-
What is Data Encryption?
Data encryption is the process of converting plaintext data into ciphertext using cryptographic algorithms. It ensures the confidentiality and security of sensitive information by rendering it unreadable to unauthorized parties.
-
Why is Data Encryption Important?
Data encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches. It helps maintain privacy, prevents data leaks, and ensures the integrity of transmitted and stored data.
-
What are the Types of Data Encryption?
There are two main types of data encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption employs a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
-
What Are Some Common Symmetric Encryption Algorithms?
Common symmetric encryption algorithms include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Data Encryption Standard (DES), and Triple DES (3DES). AES, in particular, is widely used due to its security and efficiency.
-
What Are Some Common Asymmetric Encryption Algorithms?
Well-known asymmetric encryption algorithms include RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC). These algorithms are used for secure key exchange, digital signatures, and ensuring data confidentiality.
-
How Does Data Encryption Work in Secure Communications?
In secure communications, asymmetric encryption is often used. The sender encrypts the data with the recipient's public key, and the recipient decrypts it using their private key. This ensures that only the intended recipient can read the message.
-
What is the Role of Data Encryption in Cloud Security?
Data encryption plays a vital role in cloud security by ensuring that data stored in cloud servers remains protected from unauthorized access. Encryption helps mitigate risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized data exposure.
-
Can Encrypted Data Be Hacked?
Encrypted data can be decrypted, but the process is highly complex and requires extensive computational resources and time. Strong encryption algorithms with long key lengths make it exceedingly difficult for attackers to break the encryption.
-
What is End-to-End Encryption?
End-to-end encryption is a form of communication encryption where data is encrypted on the sender's side and decrypted only on the recipient's side. This prevents intermediaries, including service providers, from accessing the plaintext data.
-
What Are the Best Practices for Data Encryption Implementation?
Effective data encryption implementation involves key management, using strong encryption algorithms, securing keys with hardware modules, regular security audits, and keeping up with advancements in encryption technologies.
-
Is Data Encryption Used Only for Confidentiality?
While confidentiality is a primary goal of data encryption, it also ensures data integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation. Encryption plays a significant role in ensuring the overall security of digital transactions and communications.
Read More
In an increasingly interconnected digital world, where data is both the lifeblood and the target of modern endeavors, the need for robust data protection has never been more critical. At the heart of this defense lies the art and science of data encryption—an intricate process that transforms information into an unreadable code, rendering it impervious to prying eyes. This exploration into the realm of data encryption aims to unravel its intricacies, unveiling the diverse types, sophisticated algorithms, ingenious techniques, and strategic approaches that together fortify the security of our digital landscape. From the symmetrical dance of keys to the asymmetric harmony of secure communications, from the impenetrable armor of Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) to the mathematical elegance of RSA and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), this journey will delve into the mechanisms that power our defenses against data breaches and unauthorized access. We will navigate through the labyrinth of encryption methods, discerning the nuanced interplay of confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity that they orchestrate. Whether you're a curious explorer of technology or an ardent guardian of data integrity, join us as we embark on an enlightening expedition into the world of data encryption, where each layer of knowledge adds another layer of protection.
Table of Contents
What is Data Encryption?
How Does Data Encryption Work?
Why Do We Need Data Encryption?
What are the 2 Types of Data Encryption Techniques?
What is Hashing?
What is an Encryption Algorithm?
Best Encryption Algorithms
3DES
The Future of Data Encryption
Should You Use Symmetric or Asymmetric Encryption?
Businesses Use Encryption For Many Purposes
Steps to Implement an Effective Encryption Strategy
What Is a Key in Cryptography?
Do You Want to Learn More About Cybersecurity?
FAQs
What is Data Encryption?
Data encryption is the process of converting understandable data into an unreadable form, known as ciphertext, using complex algorithms and a secret key. This transformation ensures that even if unauthorized parties gain access to the encrypted data, they cannot comprehend its original meaning without the corresponding decryption key. Encryption serves as a vital mechanism for safeguarding sensitive information during storage, transmission, and processing, thwarting unauthorized access and maintaining data confidentiality. It finds application in various realms such as online transactions, secure communication, and data protection, offering varying levels of security through different encryption methods and algorithms tailored to specific needs.
How Does Data Encryption Work?
Data encryption functions by utilizing complex algorithms to convert plain data into an unintelligible form known as ciphertext. This process involves an encryption key that serves as the foundation for the transformation. The chosen algorithm determines how the encryption and decryption keys interact. During encryption, the algorithm combines the encryption key with the plaintext, generating ciphertext that appears as random characters. This ciphertext can be safely transmitted or stored without revealing the original information. To reverse the process, decryption employs the corresponding decryption key, allowing the recipient to transform the ciphertext back into readable plaintext. The security of encrypted data hinges on robust algorithms, secure key management, and effective protection against unauthorized access to the encryption keys.
Why Do We Need Data Encryption?
Data encryption is a vital necessity due to its role in shielding sensitive information from unauthorized access and maintaining confidentiality. It acts as a bulwark against privacy breaches by converting data into an unreadable format, making it indecipherable without the appropriate decryption key. This protection is essential across diverse domains, from safeguarding personal data and financial records to upholding regulatory compliance and mitigating the impact of data breaches. Encryption not only secures communication over networks and cloud storage but also fortifies authentication procedures and shields intellectual property from prying eyes. In an era of global connectivity, encryption stands as a cornerstone of cybersecurity, ensuring the security and privacy of digital interactions and sensitive information.
What are the 2 Types of Data Encryption Techniques?
Data encryption techniques can be broadly categorized into two main types: Symmetric Encryption and Asymmetric Encryption.
-
Symmetric Encryption: In symmetric encryption, a single encryption key is used for both the encryption and decryption processes. The same key is shared between the sender and the recipient. The main advantage of symmetric encryption is its speed and efficiency, as the algorithms used are generally faster than their asymmetric counterparts. However, the challenge lies in securely exchanging the encryption key between parties without it being intercepted by unauthorized individuals. Common symmetric encryption algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and DES (Data Encryption Standard).
-
Asymmetric Encryption: Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, employs a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used for encryption, while the private key is used for decryption. The keys are mathematically related but cannot be practically derived from each other. This setup addresses the key exchange challenge of symmetric encryption, as the public key can be freely shared without compromising the security of the private key. Asymmetric encryption provides a higher level of security for tasks like secure communication and digital signatures. RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) are examples of asymmetric encryption algorithms.
Both types of encryption techniques have their advantages and are often used together to address specific security needs. Symmetric encryption is suitable for encrypting large amounts of data quickly, while asymmetric encryption is valuable for secure key exchange and ensuring the authenticity of communication parties.
What is Hashing?
Hashing is a cryptographic technique that involves transforming input data into a fixed-length string of characters, known as a hash value. This process is designed to be fast and deterministic, meaning the same input will always produce the same hash value. Hashing serves various purposes, such as verifying data integrity and authenticity. It ensures data integrity by generating a unique representation of the input data, making it easy to detect even minor changes in the data. Hashing is commonly used for tasks like password storage, where passwords are hashed and stored to enhance security. Additionally, hashing underpins digital signatures, providing a way to confirm the authenticity of digital documents and messages. However, it's important to choose secure and collision-resistant hash functions to prevent vulnerabilities and ensure the reliability of hash-based applications.
What is an Encryption Algorithm?
An encryption algorithm is a set of mathematical rules and procedures used to transform data from its original, readable form (plaintext) into an unreadable and secure format (ciphertext) during encryption, and to revert it back to plaintext during decryption. It dictates how the encryption key interacts with the data to produce the ciphertext and how the decryption key is used to reverse the process. Encryption algorithms play a pivotal role in maintaining data security and confidentiality, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected from unauthorized access and interception. These algorithms come in two main types: symmetric, which use the same key for both encryption and decryption, and asymmetric (public-key), which employ a pair of keys for these operations. The selection of an encryption algorithm depends on factors such as security requirements, key management, and the specific application's needs.
Best Encryption Algorithms
The "best" encryption algorithm depends on the specific use case, security requirements, and the state of current cryptographic research. However, as of my last knowledge update in September 2021, I can mention some widely recognized and respected encryption algorithms that were considered strong at that time:
-
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): AES is one of the most widely used symmetric encryption algorithms. It offers strong security and efficiency and is considered secure for a wide range of applications. AES operates with varying key lengths, including 128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit.
-
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman): RSA is a well-known asymmetric encryption algorithm used for secure key exchange, digital signatures, and other cryptographic tasks. It relies on the difficulty of factoring large prime numbers to provide security.
-
ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography): ECC is another asymmetric encryption algorithm known for its strong security and relatively shorter key lengths compared to RSA. It is particularly well-suited for resource-constrained environments, such as mobile devices.
-
SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit): While not an encryption algorithm per se, SHA-256 is a widely used cryptographic hash function. It's used for various purposes, including generating digital signatures and verifying data integrity.
-
ChaCha20 and Poly1305: These are modern cryptographic algorithms designed to provide encryption and data integrity in a combined mode. They are becoming popular choices, especially for use in stream cipher constructions.
It's important to note that cryptographic algorithms and best practices can evolve over time due to advances in technology and cryptanalysis. Organizations should stay updated with the latest recommendations from reputable sources, such as NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology), to ensure they are using algorithms that meet current security standards. Additionally, the strength of encryption also relies on proper key management, implementation, and the overall security of the system in which it is used.
3DES
Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES), also known as TDEA (Triple Data Encryption Algorithm), is a symmetric encryption algorithm that provides a higher level of security compared to the original Data Encryption Standard (DES) algorithm. 3DES applies the DES algorithm three times in a cascade, using multiple keys. This process significantly increases the effective key length and enhances security.
Here's how 3DES works:
-
Key Generation: Three separate keys are generated, often referred to as Key 1, Key 2, and Key 3.
-
Encryption: The plaintext data undergoes three consecutive rounds of encryption using the three keys. The data is first encrypted with Key 1, then decrypted using Key 2, and finally encrypted again using Key 3.
-
Decryption: To decrypt the data, the process is reversed. The ciphertext is decrypted with Key 3, then encrypted with Key 2, and finally decrypted using Key 1.
3DES provides an effective key length of 168 bits, as each of the three keys is 56 bits long. This makes it significantly more secure than the original DES, which had a 56-bit key length and became susceptible to brute-force attacks as computing power increased. However, it's worth noting that 3DES is not as efficient as more modern symmetric encryption algorithms like AES, which offer better performance and security with shorter key lengths.
3DES was widely adopted as an interim solution when transitioning from DES to more secure algorithms. However, due to its relatively slower performance and the availability of more efficient encryption algorithms, such as AES, it's recommended to use AES for new implementations requiring strong symmetric encryption.
The Future of Data Encryption
The future of data encryption holds several promising trends and challenges. Post-Quantum Cryptography is actively being researched to ensure encryption methods remain secure against the potential threat of quantum computers. Homomorphic encryption presents opportunities for processing data while it remains encrypted, enhancing privacy and security. Zero-knowledge proofs could revolutionize authentication and digital identity, while encryption's role in securing blockchain networks will continue to be paramount. Enhanced key management practices, such as hardware security modules and secure key distribution, will strengthen encryption protocols. Quantum Key Distribution offers ultra-secure methods for key exchange. The synergy of AI and encryption is likely to optimize processes and enhance overall security. As regulations evolve, encryption laws may adapt to balance security and law enforcement needs. Usability improvements and broader integration into applications and devices will be pivotal for increasing encryption adoption. Staying abreast of these developments will be essential as the landscape of data encryption continues to evolve dynamically.
Should You Use Symmetric or Asymmetric Encryption?
The decision to use symmetric or asymmetric encryption hinges on the context and security requirements of the scenario. Symmetric encryption offers speed and efficiency, making it suitable for encrypting large data volumes. However, it demands a secure method of distributing the shared key among parties. Asymmetric encryption, while slower, addresses the challenge of secure key exchange and is pivotal for scenarios where parties don't share a pre-established secret key. Asymmetric encryption's application extends to digital signatures and secure communication with key exchange. Often, a hybrid approach is employed, utilizing both encryption types to leverage their strengths. In such cases, asymmetric encryption may be used to securely establish a symmetric encryption key, enabling efficient data encryption. Ultimately, the choice should align with specific security needs, key management complexity, and the speed requirements of the given use case, ensuring an appropriate balance between security and practicality.
Businesses Use Encryption For Many Purposes
Businesses leverage encryption for a multitude of purposes to reinforce their data security measures and uphold the integrity of their operations. Encryption is extensively employed to shield sensitive customer data, proprietary information, and financial records, thereby thwarting unauthorized access and data breaches. It's pivotal in securing communication channels, such as emails and instant messaging, ensuring that confidential information remains private during transmission. Encryption also underpins secure financial transactions on e-commerce platforms and online banking systems. It bolsters password security by storing user credentials securely and helps businesses adhere to regulatory frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA, safeguarding them from legal consequences and maintaining customer trust. Additionally, encryption is paramount for cloud security, remote work scenarios, secure file sharing, digital signatures, IoT security, and preserving the confidentiality of sensitive data within supply chains. Overall, encryption is a cornerstone of modern business strategies, fostering data protection and bolstering organizational reputation.
Steps to Implement an Effective Encryption Strategy
Implementing an effective encryption strategy involves a systematic approach to ensure the security of sensitive data. Here are five key steps to guide the process:
-
Data Classification and Assessment: Begin by identifying and classifying the types of data that require encryption. Conduct a thorough assessment of your organization's data landscape to determine which data is sensitive and where it resides. This includes data at rest, in transit, and during processing.
-
Security Requirements Definition: Define your security requirements based on the sensitivity of the data. Determine which encryption algorithms and key lengths are appropriate for different data types and use cases. Consider compliance regulations and industry standards that apply to your organization.
-
Encryption Implementation: Select suitable encryption solutions and tools that align with your requirements. Implement encryption mechanisms for data at rest and in transit. For data at rest, utilize encryption features provided by databases, operating systems, or storage solutions. For data in transit, employ secure protocols such as TLS/SSL for network communication.
-
Key Management and Access Control: Develop a robust key management strategy. Establish procedures for generating, storing, rotating, and revoking encryption keys. Ensure that only authorized personnel have access to encryption keys. Implement strong access controls to prevent unauthorized users from accessing encrypted data.
-
Testing, Monitoring, and Compliance: Thoroughly test your encryption implementation to ensure its effectiveness and compatibility with your systems. Regularly monitor encryption processes, access logs, and audit trails to detect any anomalies or unauthorized access attempts. Conduct periodic security assessments and audits to ensure compliance with encryption policies and regulations.
By following these steps, you can create a structured and comprehensive encryption strategy that safeguards sensitive data, mitigates risks, and aligns with industry best practices and compliance standards.
What Is a Key in Cryptography?
In cryptography, a key refers to a specific piece of information, often a sequence of characters, numbers, or bits, that is used to control the encryption and decryption processes. Keys play a central role in cryptographic operations by determining how data is transformed from its original form (plaintext) to an encrypted form (ciphertext) and back to plaintext.
There are two main types of keys in cryptography:
-
Encryption Key: This key is used during the encryption process to convert plaintext into ciphertext. The encryption key is known only to authorized parties involved in secure communication or data protection.
-
Decryption Key: This key is used during the decryption process to revert the ciphertext back to its original plaintext. In symmetric encryption, the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. In asymmetric encryption (public-key cryptography), there is a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
Keys are kept confidential to ensure the security of encrypted data. The strength and security of a cryptographic system often depend on the length and complexity of the encryption keys. Longer keys are generally more secure because they increase the number of possible combinations that an attacker would need to try in order to break the encryption.
Effective key management is essential to maintain the integrity of cryptographic systems. This includes secure key generation, distribution, storage, rotation, and disposal. In many cases, hardware security modules (HSMs) are used to securely store and manage encryption keys to prevent unauthorized access or theft.
Do You Want to Learn More About Cybersecurity?
Are you interested in delving deeper into the realm of cybersecurity? With the ever-growing importance of safeguarding digital systems and data, gaining expertise in this field is invaluable. Notable certifications such as Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), and CompTIA Security+ offer comprehensive knowledge and skills that can elevate your understanding of cybersecurity principles and practices. Furthermore, exploring frameworks like COBIT 2019 can provide you with a structured approach to governance and management of enterprise information technology. These certifications and frameworks encompass a wide range of topics, from risk management and security controls to compliance and governance. Whether you're just beginning your journey or seeking to advance your career, these resources can serve as essential guides on your path to becoming a proficient cybersecurity professional.
FAQs
-
What is Data Encryption?
Data encryption is the process of converting plaintext data into ciphertext using cryptographic algorithms. It ensures the confidentiality and security of sensitive information by rendering it unreadable to unauthorized parties.
-
Why is Data Encryption Important?
Data encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches. It helps maintain privacy, prevents data leaks, and ensures the integrity of transmitted and stored data.
-
What are the Types of Data Encryption?
There are two main types of data encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption employs a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
-
What Are Some Common Symmetric Encryption Algorithms?
Common symmetric encryption algorithms include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Data Encryption Standard (DES), and Triple DES (3DES). AES, in particular, is widely used due to its security and efficiency.
-
What Are Some Common Asymmetric Encryption Algorithms?
Well-known asymmetric encryption algorithms include RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC). These algorithms are used for secure key exchange, digital signatures, and ensuring data confidentiality.
-
How Does Data Encryption Work in Secure Communications?
In secure communications, asymmetric encryption is often used. The sender encrypts the data with the recipient's public key, and the recipient decrypts it using their private key. This ensures that only the intended recipient can read the message.
-
What is the Role of Data Encryption in Cloud Security?
Data encryption plays a vital role in cloud security by ensuring that data stored in cloud servers remains protected from unauthorized access. Encryption helps mitigate risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized data exposure.
-
Can Encrypted Data Be Hacked?
Encrypted data can be decrypted, but the process is highly complex and requires extensive computational resources and time. Strong encryption algorithms with long key lengths make it exceedingly difficult for attackers to break the encryption.
-
What is End-to-End Encryption?
End-to-end encryption is a form of communication encryption where data is encrypted on the sender's side and decrypted only on the recipient's side. This prevents intermediaries, including service providers, from accessing the plaintext data.
-
What Are the Best Practices for Data Encryption Implementation?
Effective data encryption implementation involves key management, using strong encryption algorithms, securing keys with hardware modules, regular security audits, and keeping up with advancements in encryption technologies.
-
Is Data Encryption Used Only for Confidentiality?
While confidentiality is a primary goal of data encryption, it also ensures data integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation. Encryption plays a significant role in ensuring the overall security of digital transactions and communications.
Exploring the Pros and Cons of Scrum Project Management
In the dynamic realm of modern project management, the Scrum methodology has risen to prominence as a game-changing approach. Rooted in Agile principles, Scrum offers a framework that thrives on collaboration, adaptability, and iterative progress. Amidst this landscape, professionals seeking to refine their project management skills have found value in specialized training courses like PMI-ACP, CSM, and CSPO.
Join us in this exploration as we navigate the intricacies of Scrum project management, delving into its advantages and drawbacks. With a keen focus on the PMI-ACP, CSM, and CSPO training courses, we will uncover how these certifications equip individuals with the knowledge and tools to excel within the Scrum framework. By evaluating the pros and cons of Scrum and its interplay with these training pathways, we empower professionals to make strategic choices aligning with their career ambitions and project management objectives.
Whether you're an established project management expert or a newcomer to the field, this journey promises valuable insights into the synergy between Scrum, project management certifications, and professional development. Let's embark on this illuminating expedition, unraveling the potential that emerges at the crossroads of Scrum methodology and specialized training.
Table of Contents
- What is Scrum?
- What Is Scrum Framework?
- What is Scrum in Project Management?
- The Application of Scrum in Project Management
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Scrum Project Management
- Scrum Roles
- Comprehending the Role of Project Manager in Scrum – The Scrum Master vs. the Project Manager
- 6 Steps of Scrum Process
- Key Scrum Tools to Get You Through Your Next Sprint
- Becoming a Certified Scrum Master
What is Scrum?
Scrum is an agile framework used in project management and software development to help teams work collaboratively and efficiently on complex projects. It emphasizes flexibility, adaptability, and iterative progress. Scrum provides a structured approach to managing tasks and delivering valuable outcomes in a dynamic and ever-changing environment.
Key characteristics of Scrum include:
- Iterative and Incremental Development: Scrum breaks down the project into smaller iterations called "sprints." Each sprint typically lasts 1 to 4 weeks and results in a potentially shippable product increment. This allows for continuous feedback and the ability to adapt to changing requirements.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Scrum defines specific roles within the team. The key roles are the Product Owner, who represents the stakeholders and defines the product backlog, the Scrum Master, who facilitates the Scrum process and supports the team, and the Development Team, responsible for delivering the product increment.
- Product Backlog: The product backlog is a prioritized list of features, enhancements, and fixes that need to be addressed in the project. The Product Owner is responsible for maintaining and prioritizing this list.
- Sprint Planning: At the beginning of each sprint, the team conducts a sprint planning meeting to select items from the product backlog to work on during the sprint. The team then defines the tasks required to complete those items.
- Daily Scrum (Standup): The team holds a daily standup meeting where each member briefly discusses what they've done since the last meeting, what they're working on, and any obstacles they're facing. This fosters transparency and collaboration within the team.
- Sprint Review: At the end of each sprint, the team holds a sprint review to demonstrate the completed work to stakeholders. This provides an opportunity for feedback and helps the team make adjustments based on that feedback.
- Sprint Retrospective: After the sprint review, the team holds a retrospective to reflect on the sprint process and identify areas for improvement. This continuous improvement cycle is a core aspect of Scrum.
- Time-Boxing: Scrum uses time-boxing to limit the duration of meetings and activities, ensuring that they don't drag on indefinitely.
Scrum encourages a culture of collaboration, self-organization, and continuous improvement. It's particularly well-suited for projects where requirements are likely to change or evolve, as the framework allows teams to pivot and adapt quickly. Scrum is widely used in various industries, not just software development, to manage projects of varying complexity.
What Is Scrum Framework?
The Scrum framework is an agile methodology used in project management and product development to deliver value incrementally and iteratively. It provides a structured approach for teams to work collaboratively and efficiently, especially in environments where requirements are dynamic and subject to change. The framework is designed to promote flexibility, transparency, and continuous improvement.
The Scrum framework consists of several key components and practices:
- Roles:
- Product Owner: Represents the stakeholders and is responsible for defining and prioritizing the product backlog, which contains the list of features, enhancements, and fixes to be addressed.
- Scrum Master: Facilitates the Scrum process, ensures adherence to Scrum principles, and helps remove any obstacles that the team encounters.
- Development Team: Cross-functional group responsible for delivering the product increment. The team self-organizes and collaborates to complete the work within each sprint.
- Artifacts:
- Product Backlog: A prioritized list of items that need to be addressed in the project. These items can include user stories, bug fixes, technical tasks, and more.
- Sprint Backlog: The subset of items from the product backlog that the team commits to completing during a specific sprint.
- Increment: The sum of completed items at the end of a sprint. It should be a potentially shippable product that adds value to the product.
- Events:
- Sprint: A time-boxed iteration, typically lasting 1 to 4 weeks, during which the team works on completing items from the sprint backlog.
- Sprint Planning: A meeting held at the beginning of each sprint where the team selects items from the product backlog to work on and defines the tasks required to complete them.
- Daily Scrum (Standup): A brief daily meeting where team members share updates on their progress, plans, and any obstacles they are facing.
- Sprint Review: A meeting at the end of each sprint where the team demonstrates the completed work to stakeholders and gathers feedback.
- Sprint Retrospective: A meeting held after the sprint review to reflect on the sprint process, identify strengths and areas for improvement, and make adjustments.
- Principles:
- Empirical Process Control: Scrum is based on transparency, inspection, and adaptation. It encourages teams to learn from their experiences and adjust their processes accordingly.
- Self-Organization: Teams are responsible for organizing themselves and making decisions, which fosters ownership and accountability.
- Collaboration: Scrum emphasizes close collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and customers to ensure the best possible outcome.
- Incremental Delivery: Value is delivered in small increments, allowing for faster feedback and the ability to respond to changing requirements.
Overall, the Scrum framework provides a structured way to manage projects by breaking them down into smaller, manageable chunks and continuously improving the process based on feedback and real-world results. It's widely used in various industries and sectors for its adaptability and focus on delivering value to customers.
What is Scrum in Project Management?
Scrum in project management is an agile framework that focuses on delivering projects in a flexible and iterative manner. It was originally developed for software development but has since been applied to various types of projects in different industries. Scrum aims to address the challenges of managing projects in dynamic and rapidly changing environments by promoting collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement.
In the context of project management, Scrum provides a structured approach to planning, executing, and delivering projects by breaking them into smaller, manageable components. These smaller components are called sprints, and each sprint involves a defined set of tasks and goals. Here's how Scrum works in project management:
- Product Owner: The product owner is responsible for representing the interests of stakeholders, understanding project requirements, and prioritizing the work that needs to be done. The product owner maintains the product backlog, which is a dynamic list of features, tasks, and changes that need to be addressed.
- Scrum Team: The Scrum team is a cross-functional group of individuals responsible for delivering the project increment. This team includes developers, designers, testers, and other relevant roles. The team collectively decides how much work they can commit to during a sprint.
- Sprint Planning: At the beginning of each sprint, the team holds a sprint planning meeting. During this meeting, they review the items in the product backlog, select the items they will work on during the sprint, and create a sprint backlog—a list of tasks required to complete the selected items.
- Sprint: A sprint is a time-boxed iteration that typically lasts 1 to 4 weeks. The team works on the tasks identified in the sprint backlog. At the end of the sprint, they aim to deliver a potentially shippable product increment—a working piece of the project that adds value.
- Daily Scrum (Standup): The team holds a daily standup meeting to discuss progress, obstacles, and plans for the day. Each team member shares what they accomplished, what they plan to work on next, and if they're facing any challenges.
- Sprint Review: At the end of each sprint, the team holds a sprint review. They demonstrate the completed work to stakeholders and gather feedback. This helps ensure that the project is on the right track and that any necessary adjustments can be made.
- Sprint Retrospective: After the sprint review, the team conducts a retrospective meeting to reflect on the sprint process. They discuss what went well, what could be improved, and any changes they want to implement in the next sprint.
- Continuous Improvement: One of the core principles of Scrum is continuous improvement. Teams regularly analyze their processes and make adjustments to enhance efficiency, collaboration, and overall project delivery.
Scrum's iterative and incremental approach allows for flexibility and responsiveness to changing requirements and priorities. It's especially effective for projects where the initial requirements may evolve over time, as the framework supports adapting to new information and customer feedback.
The Application of Scrum in Project Management
Scrum is widely applied in project management, especially in software development, due to its adaptability and focus on iterative progress. However, its principles and practices can be extended to various types of projects in different industries. Here are some key applications of Scrum in project management:
- Software Development: The most common application of Scrum is in software development. It allows development teams to work on small, manageable chunks of functionality in each sprint, ensuring that valuable features are delivered regularly and enabling quick responses to changing requirements.
- Product Development: Beyond software, Scrum can be applied to the development of physical products. It enables cross-functional teams to collaborate on designing, prototyping, testing, and delivering products in iterations, ensuring that customer needs are met effectively.
- Marketing Campaigns: Scrum can be used in marketing projects where campaigns are broken down into sprints. Marketing teams can work on individual tasks like content creation, social media engagement, and analytics, delivering measurable results at the end of each sprint.
- Event Planning: For event management projects, Scrum can help organize tasks such as venue selection, logistics planning, participant engagement, and post-event analysis. Sprints can align with the various phases of event preparation.
- Research and Development: In R&D projects, Scrum allows researchers and developers to focus on specific aspects of a project, quickly experiment with new ideas, and pivot based on the results obtained within short iterations.
- Construction Projects: Construction projects can benefit from Scrum by dividing complex tasks like site preparation, foundation construction, and building phases into sprints. This helps manage resources, track progress, and adapt to unexpected challenges.
- Educational Programs: Scrum can be used to structure educational programs and courses. Each sprint corresponds to a learning module, and students make incremental progress, receive feedback, and adapt their learning journey based on their understanding.
- Content Creation: Content projects, such as writing articles, producing videos, or designing graphics, can benefit from Scrum's iterative approach. Sprints can focus on different content pieces, and regular reviews ensure content quality.
- Healthcare Projects: Scrum principles can be applied to healthcare projects, such as implementing new medical technologies, improving patient care processes, or developing healthcare apps. This approach promotes collaboration among medical professionals, developers, and other stakeholders.
- Consulting and Professional Services: Scrum can be used in consulting projects, where each sprint focuses on specific deliverables or recommendations for clients, ensuring that value is provided incrementally and allowing for client feedback.
When applying Scrum in project management, it's important to tailor the practices to suit the specific needs and context of the project. The framework encourages adaptability and continuous improvement, so teams can experiment with different approaches to find the best fit for their project's goals and requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Scrum Project Management
Scrum project management offers several advantages and disadvantages, which can impact its suitability for different projects and teams. Here's an overview of the pros and cons of using the Scrum framework:
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Scrum's iterative approach allows teams to adapt to changing requirements and priorities, making it well-suited for projects with evolving needs.
- Customer Satisfaction: Regularly delivering working increments of the project allows stakeholders to see progress and provide feedback, ensuring the final product meets their expectations.
- Collaboration: Scrum encourages close collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and customers, fostering a sense of ownership and shared responsibility.
- Transparency: The framework promotes transparency through daily standup meetings, sprint reviews, and sprint retrospectives, ensuring everyone is aware of the project's status and challenges.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Incremental delivery means that features can be released more quickly, enabling a shorter time-to-market compared to traditional project management approaches.
- Risk Mitigation: Frequent reviews and adaptability help identify and address risks early in the project, reducing the likelihood of major setbacks.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular sprint retrospectives encourage teams to reflect on their processes and make adjustments, leading to ongoing process improvement.
- Motivated Teams: Scrum empowers teams to self-organize and make decisions, fostering a sense of ownership and motivation among team members.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Scrum has several roles, events, and artifacts, which can be overwhelming for teams new to the framework or for smaller projects.
- Lack of Predictability: The adaptive nature of Scrum can make it challenging to predict exact project timelines and outcomes, which might be problematic for projects with strict deadlines.
- Requires Skilled Team Members: Effective Scrum implementation requires skilled team members who understand the framework and its principles.
- High Dependency on Product Owner: The product owner's availability and decision-making play a critical role in prioritizing and clarifying tasks. Their absence or lack of involvement can impact the project.
- Inaccurate Initial Estimates: Because Scrum focuses on delivering small increments, it might be challenging to provide accurate estimates for the entire project at the outset.
- Lack of Documentation: The focus on working increments can sometimes lead to inadequate documentation, which might be required for compliance or future maintenance.
- Need for Continuous Involvement: Scrum requires consistent participation from all team members throughout the project, which might not be feasible in certain environments.
- Resistance to Change: Teams accustomed to traditional project management methods may face resistance in transitioning to the agile practices of Scrum.
Ultimately, the decision to use Scrum in project management depends on factors like project complexity, team composition, stakeholder involvement, and the organization's culture. It's important to carefully evaluate the advantages and disadvantages to determine whether Scrum aligns with the project's needs and objectives.
Top of Form
Scrum Roles
In the Scrum framework, there are three key roles that contribute to the successful implementation of the methodology within a project. These roles promote collaboration, responsibility, and effective communication within the team. Here are the three Scrum roles:
- Product Owner:
- The Product Owner represents the stakeholders, customers, and users of the product being developed. They are responsible for maximizing the value delivered by the team.
- Key responsibilities include defining and maintaining the product backlog, prioritizing items within it, and ensuring that the team understands the requirements and goals.
- The Product Owner makes decisions about what features or items should be worked on, and their decisions guide the team's work during each sprint.
- Scrum Master:
- The Scrum Master is a servant-leader who ensures that the Scrum framework is understood, followed, and continuously improved by the team.
- They act as a facilitator and coach, helping the team to self-organize and make decisions collectively. They also remove obstacles and impediments that the team might encounter.
- The Scrum Master fosters a collaborative and productive environment, guides the team in adhering to Scrum practices, and helps improve the team's effectiveness.
- Development Team:
- The Development Team is a cross-functional group of professionals responsible for delivering the product increment during each sprint.
- The team members collectively have the skills and expertise needed to design, develop, test, and deliver the product features.
- They collaborate closely, self-organize to manage their work, and collectively commit to achieving the goals of each sprint.
It's important to note that in Scrum, these roles are distinct, and individuals typically do not hold multiple roles simultaneously. Each role has specific responsibilities that contribute to the successful implementation of the framework. Additionally, Scrum emphasizes collaboration among the roles, as well as with stakeholders, to ensure that the project's goals and requirements are met.
Comprehending the Role of Project Manager in Scrum – The Scrum Master vs. the Project Manager
In the Scrum framework, the role of a Project Manager is quite distinct from the role of a Scrum Master. Both roles play important parts in project management, but their responsibilities, focus, and approach can differ significantly. Here's a comparison of the two roles:
Scrum Master:
- Responsibilities:
- Facilitating the Scrum Process: The Scrum Master ensures that the Scrum framework is understood and followed by the team, helping to maintain the Scrum events, roles, and artifacts.
- Coaching and Mentoring: They coach the team on self-organization, cross-functionality, and effective collaboration. They help the team continuously improve and achieve their best potential.
- Removing Obstacles: The Scrum Master identifies and removes impediments that hinder the team's progress, ensuring that the team can work smoothly.
- Promoting Empowerment: They empower the team to make their own decisions and self-organize, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability.
- Shielding from External Interference: The Scrum Master helps protect the team from external disruptions and influences to maintain focus during sprints.
- Focus:
- Team Dynamics: The Scrum Master's primary focus is on fostering a productive and collaborative team environment, ensuring that the team can work efficiently and effectively.
- Process Adherence: They ensure that the Scrum process is followed and adapted appropriately to suit the team's needs while upholding Scrum principles.
Project Manager:
- Responsibilities:
- Planning and Scheduling: The Project Manager is responsible for planning the project, defining tasks, setting timelines, and creating a project schedule.
- Resource Management: They allocate resources, assign tasks, and ensure that the project is adequately staffed to meet its goals.
- Budget Management: The Project Manager handles budgeting, cost estimation, and resource allocation to ensure the project stays within budget.
- Risk Management: They identify potential risks, develop mitigation strategies, and manage any issues that arise during the project.
- Stakeholder Communication: The Project Manager communicates with stakeholders, updates them on project progress, and manages their expectations.
- Focus:
- Deliverables and Objectives: The Project Manager's primary focus is on meeting project goals, delivering the desired outcome, and ensuring that the project aligns with business objectives.
- Planning and Execution: They oversee the overall project planning and execution, ensuring that tasks are completed according to the plan.
In the context of Scrum, the Scrum Master's role is more about enabling the team to work effectively within the Scrum framework, while the Project Manager's role is broader and encompasses the overall management of the project. In many Scrum implementations, the traditional role of a Project Manager may shift to other roles (such as Product Owner or team member) or may be less prominent, as Scrum promotes self-organization and collaborative decision-making within the team. However, in organizations that use both traditional project management and Scrum, the Project Manager might still have a role to play in coordinating higher-level activities and aligning multiple Scrum teams with organizational goals.
6 Steps of Scrum Process
The Scrum process consists of several iterative and recurring steps that help teams deliver value incrementally and adapt to changing requirements. Here are the six key steps of the Scrum process:
- Product Backlog Creation:
- The process begins with the creation of the product backlog, which is a dynamic list of items that need to be addressed in the project. These items can include features, bug fixes, technical tasks, and more.
- The Product Owner is responsible for maintaining and prioritizing the product backlog based on input from stakeholders, customers, and the team.
- Sprint Planning:
- Before the start of each sprint, the team holds a sprint planning meeting.
- During this meeting, the Product Owner presents the items from the product backlog that are of the highest priority and have been refined to a sufficient level.
- The Development Team works with the Product Owner to select items from the product backlog that they believe they can complete during the sprint.
- The team breaks down the selected items into smaller tasks and estimates the effort required for each task.
- Sprint Execution:
- The sprint execution phase begins after the sprint planning meeting and typically lasts 1 to 4 weeks.
- The Development Team works on the tasks identified during the sprint planning, collaboratively building and testing the product increment.
- Daily standup meetings are held to provide updates on progress, discuss obstacles, and align the team.
- Daily Scrum (Standup):
- Each day during the sprint, the team holds a brief daily standup meeting, known as the Daily Scrum.
- Team members answer three questions: What did I accomplish yesterday? What will I work on today? Are there any obstacles in my way?
- This meeting helps the team stay synchronized, identify potential issues, and make real-time adjustments.
- Sprint Review:
- At the end of the sprint, the team holds a sprint review meeting.
- The team demonstrates the completed work to stakeholders and the Product Owner.
- Feedback is gathered, and stakeholders have an opportunity to evaluate the product increment and suggest changes.
- Sprint Retrospective:
- Following the sprint review, the team conducts a sprint retrospective meeting.
- The team reflects on the sprint process and discusses what went well, what could be improved, and what actions should be taken to enhance future sprints.
- The retrospective helps the team identify and implement process improvements, fostering a culture of continuous learning.
After the sprint retrospective, the process begins again with the creation of a new sprint and the selection of items from the product backlog. This cyclical process allows the team to continuously improve and refine their work based on feedback, making Scrum a highly adaptive and iterative framework.
Key Scrum Tools to Get You Through Your Next Sprint
Scrum emphasizes people and interactions over tools, but using the right tools can certainly enhance collaboration, communication, and productivity during sprints. Here are some key Scrum tools that can help you manage your next sprint effectively:
- Scrum Board or Kanban Board:
- A visual representation of the sprint backlog and its tasks.
- Helps the team track the progress of tasks, identify bottlenecks, and visualize the flow of work.
- Tools: Trello, Jira, Asana, Microsoft Planner.
- Digital Task Tracking and Management:
- Software tools that allow you to create, assign, and track tasks.
- Enables team members to update task status, add comments, and collaborate in real time.
- Tools: Jira, Microsoft Azure DevOps, Monday.com, ClickUp.
- Video Conferencing and Communication:
- Facilitates remote collaboration, daily standup meetings, sprint reviews, and sprint retrospectives.
- Enables clear communication among distributed teams.
- Tools: Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Slack, Google Meet.
- Documentation and Knowledge Sharing:
- Centralized platforms for storing project documentation, user stories, and sprint goals.
- Ensures that information is accessible and up to date for the team.
- Tools: Confluence, Microsoft SharePoint, Google Docs.
- Collaboration and Chat Platforms:
- Real-time chat platforms for quick communication, questions, and discussions.
- Helps team members stay connected and informed throughout the sprint.
- Tools: Slack, Microsoft Teams, Mattermost, Discord.
- Continuous Integration and Deployment:
- Tools that automate code integration, testing, and deployment.
- Ensures that code changes are integrated smoothly and tested continuously.
- Tools: Jenkins, Travis CI, CircleCI, GitLab CI/CD.
- Version Control System:
- Manages code repositories, tracks changes, and enables collaboration among developers.
- Ensures that code changes are properly tracked and managed.
- Tools: Git (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket), Subversion.
- Burndown Chart and Reporting:
- Provides visual representation of sprint progress, comparing completed work with remaining work.
- Helps the team and stakeholders understand the pace of work and make adjustments if needed.
- Tools: Jira, Trello (with Power-Ups), Microsoft Azure DevOps.
- Retrospective Tools:
- Online platforms that facilitate sprint retrospective meetings.
- Helps teams capture feedback, identify improvements, and track action items.
- Tools: FunRetro, Retrium, Miro, Stormboard.
- Test and Quality Management:
- Tools for managing test cases, executing tests, and tracking defects.
- Ensures that product quality is maintained throughout the sprint.
- Tools: Zephyr, TestRail, qTest, PractiTest.
Remember that the effectiveness of these tools depends on the team's familiarity with them and how well they integrate into your workflow. Choose tools that align with your team's preferences, needs, and the specific requirements of your project.
Becoming a Certified Scrum Master
Becoming a Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) involves completing a certification process offered by the Scrum Alliance. The CSM certification validates your knowledge of Scrum principles, practices, and your ability to serve as an effective Scrum Master. Here's a general outline of the steps you would take to become a Certified Scrum Master:
- Gain Familiarity with Scrum:
- Before pursuing the certification, ensure you have a solid understanding of Scrum principles, roles, events, and artifacts. Familiarize yourself with the Scrum Guide and recommended Scrum resources.
- Participate in Training:
- Attend a two-day Certified ScrumMaster training course conducted by a certified Scrum trainer. This course covers Scrum principles, practices, and real-world applications.
- Complete the Training:
- Participate actively in the training, engage in discussions, exercises, and workshops.
- Ensure you understand the Scrum framework, its roles, responsibilities, events, and values.
- Pass the Exam:
- After completing the training, you'll receive an email invitation from the Scrum Alliance to take the CSM exam.
- The exam is an online, multiple-choice test that assesses your knowledge of Scrum principles and practices.
- You have up to 90 days from the date of completing the training to pass the exam.
- Pass the Scrum Alliance CSM Exam:
- To pass the CSM exam, you'll need to correctly answer a certain percentage of questions.
- Passing the exam demonstrates your understanding of Scrum concepts and your ability to apply them in real-world scenarios.
- Complete the Scrum Alliance Membership:
- Once you've passed the exam, you need to create a Scrum Alliance account (if you don't already have one) and complete your membership profile.
- Agree to the License Agreement:
- As part of your certification process, you'll need to agree to the Scrum Alliance's certification license agreement.
- Claim Your Certification:
- After completing the exam and agreeing to the license agreement, you'll be able to claim your CSM certification.
- Maintain Your Certification:
- The CSM certification is valid for two years. To maintain it, you need to earn Scrum Education Units (SEUs) and renew your certification by paying a renewal fee.
It's important to note that the process and requirements may change, so it's recommended to check the Scrum Alliance's official website for the most up-to-date information on the CSM certification process, training opportunities, and exam details. The certification can enhance your understanding of Scrum and your ability to facilitate Scrum practices within your team or organization.
Read More
In the dynamic realm of modern project management, the Scrum methodology has risen to prominence as a game-changing approach. Rooted in Agile principles, Scrum offers a framework that thrives on collaboration, adaptability, and iterative progress. Amidst this landscape, professionals seeking to refine their project management skills have found value in specialized training courses like PMI-ACP, CSM, and CSPO.
Join us in this exploration as we navigate the intricacies of Scrum project management, delving into its advantages and drawbacks. With a keen focus on the PMI-ACP, CSM, and CSPO training courses, we will uncover how these certifications equip individuals with the knowledge and tools to excel within the Scrum framework. By evaluating the pros and cons of Scrum and its interplay with these training pathways, we empower professionals to make strategic choices aligning with their career ambitions and project management objectives.
Whether you're an established project management expert or a newcomer to the field, this journey promises valuable insights into the synergy between Scrum, project management certifications, and professional development. Let's embark on this illuminating expedition, unraveling the potential that emerges at the crossroads of Scrum methodology and specialized training.
Table of Contents
- What is Scrum?
- What Is Scrum Framework?
- What is Scrum in Project Management?
- The Application of Scrum in Project Management
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Scrum Project Management
- Scrum Roles
- Comprehending the Role of Project Manager in Scrum – The Scrum Master vs. the Project Manager
- 6 Steps of Scrum Process
- Key Scrum Tools to Get You Through Your Next Sprint
- Becoming a Certified Scrum Master
What is Scrum?
Scrum is an agile framework used in project management and software development to help teams work collaboratively and efficiently on complex projects. It emphasizes flexibility, adaptability, and iterative progress. Scrum provides a structured approach to managing tasks and delivering valuable outcomes in a dynamic and ever-changing environment.
Key characteristics of Scrum include:
- Iterative and Incremental Development: Scrum breaks down the project into smaller iterations called "sprints." Each sprint typically lasts 1 to 4 weeks and results in a potentially shippable product increment. This allows for continuous feedback and the ability to adapt to changing requirements.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Scrum defines specific roles within the team. The key roles are the Product Owner, who represents the stakeholders and defines the product backlog, the Scrum Master, who facilitates the Scrum process and supports the team, and the Development Team, responsible for delivering the product increment.
- Product Backlog: The product backlog is a prioritized list of features, enhancements, and fixes that need to be addressed in the project. The Product Owner is responsible for maintaining and prioritizing this list.
- Sprint Planning: At the beginning of each sprint, the team conducts a sprint planning meeting to select items from the product backlog to work on during the sprint. The team then defines the tasks required to complete those items.
- Daily Scrum (Standup): The team holds a daily standup meeting where each member briefly discusses what they've done since the last meeting, what they're working on, and any obstacles they're facing. This fosters transparency and collaboration within the team.
- Sprint Review: At the end of each sprint, the team holds a sprint review to demonstrate the completed work to stakeholders. This provides an opportunity for feedback and helps the team make adjustments based on that feedback.
- Sprint Retrospective: After the sprint review, the team holds a retrospective to reflect on the sprint process and identify areas for improvement. This continuous improvement cycle is a core aspect of Scrum.
- Time-Boxing: Scrum uses time-boxing to limit the duration of meetings and activities, ensuring that they don't drag on indefinitely.
Scrum encourages a culture of collaboration, self-organization, and continuous improvement. It's particularly well-suited for projects where requirements are likely to change or evolve, as the framework allows teams to pivot and adapt quickly. Scrum is widely used in various industries, not just software development, to manage projects of varying complexity.
What Is Scrum Framework?
The Scrum framework is an agile methodology used in project management and product development to deliver value incrementally and iteratively. It provides a structured approach for teams to work collaboratively and efficiently, especially in environments where requirements are dynamic and subject to change. The framework is designed to promote flexibility, transparency, and continuous improvement.
The Scrum framework consists of several key components and practices:
- Roles:
- Product Owner: Represents the stakeholders and is responsible for defining and prioritizing the product backlog, which contains the list of features, enhancements, and fixes to be addressed.
- Scrum Master: Facilitates the Scrum process, ensures adherence to Scrum principles, and helps remove any obstacles that the team encounters.
- Development Team: Cross-functional group responsible for delivering the product increment. The team self-organizes and collaborates to complete the work within each sprint.
- Artifacts:
- Product Backlog: A prioritized list of items that need to be addressed in the project. These items can include user stories, bug fixes, technical tasks, and more.
- Sprint Backlog: The subset of items from the product backlog that the team commits to completing during a specific sprint.
- Increment: The sum of completed items at the end of a sprint. It should be a potentially shippable product that adds value to the product.
- Events:
- Sprint: A time-boxed iteration, typically lasting 1 to 4 weeks, during which the team works on completing items from the sprint backlog.
- Sprint Planning: A meeting held at the beginning of each sprint where the team selects items from the product backlog to work on and defines the tasks required to complete them.
- Daily Scrum (Standup): A brief daily meeting where team members share updates on their progress, plans, and any obstacles they are facing.
- Sprint Review: A meeting at the end of each sprint where the team demonstrates the completed work to stakeholders and gathers feedback.
- Sprint Retrospective: A meeting held after the sprint review to reflect on the sprint process, identify strengths and areas for improvement, and make adjustments.
- Principles:
- Empirical Process Control: Scrum is based on transparency, inspection, and adaptation. It encourages teams to learn from their experiences and adjust their processes accordingly.
- Self-Organization: Teams are responsible for organizing themselves and making decisions, which fosters ownership and accountability.
- Collaboration: Scrum emphasizes close collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and customers to ensure the best possible outcome.
- Incremental Delivery: Value is delivered in small increments, allowing for faster feedback and the ability to respond to changing requirements.
Overall, the Scrum framework provides a structured way to manage projects by breaking them down into smaller, manageable chunks and continuously improving the process based on feedback and real-world results. It's widely used in various industries and sectors for its adaptability and focus on delivering value to customers.
What is Scrum in Project Management?
Scrum in project management is an agile framework that focuses on delivering projects in a flexible and iterative manner. It was originally developed for software development but has since been applied to various types of projects in different industries. Scrum aims to address the challenges of managing projects in dynamic and rapidly changing environments by promoting collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement.
In the context of project management, Scrum provides a structured approach to planning, executing, and delivering projects by breaking them into smaller, manageable components. These smaller components are called sprints, and each sprint involves a defined set of tasks and goals. Here's how Scrum works in project management:
- Product Owner: The product owner is responsible for representing the interests of stakeholders, understanding project requirements, and prioritizing the work that needs to be done. The product owner maintains the product backlog, which is a dynamic list of features, tasks, and changes that need to be addressed.
- Scrum Team: The Scrum team is a cross-functional group of individuals responsible for delivering the project increment. This team includes developers, designers, testers, and other relevant roles. The team collectively decides how much work they can commit to during a sprint.
- Sprint Planning: At the beginning of each sprint, the team holds a sprint planning meeting. During this meeting, they review the items in the product backlog, select the items they will work on during the sprint, and create a sprint backlog—a list of tasks required to complete the selected items.
- Sprint: A sprint is a time-boxed iteration that typically lasts 1 to 4 weeks. The team works on the tasks identified in the sprint backlog. At the end of the sprint, they aim to deliver a potentially shippable product increment—a working piece of the project that adds value.
- Daily Scrum (Standup): The team holds a daily standup meeting to discuss progress, obstacles, and plans for the day. Each team member shares what they accomplished, what they plan to work on next, and if they're facing any challenges.
- Sprint Review: At the end of each sprint, the team holds a sprint review. They demonstrate the completed work to stakeholders and gather feedback. This helps ensure that the project is on the right track and that any necessary adjustments can be made.
- Sprint Retrospective: After the sprint review, the team conducts a retrospective meeting to reflect on the sprint process. They discuss what went well, what could be improved, and any changes they want to implement in the next sprint.
- Continuous Improvement: One of the core principles of Scrum is continuous improvement. Teams regularly analyze their processes and make adjustments to enhance efficiency, collaboration, and overall project delivery.
Scrum's iterative and incremental approach allows for flexibility and responsiveness to changing requirements and priorities. It's especially effective for projects where the initial requirements may evolve over time, as the framework supports adapting to new information and customer feedback.
The Application of Scrum in Project Management
Scrum is widely applied in project management, especially in software development, due to its adaptability and focus on iterative progress. However, its principles and practices can be extended to various types of projects in different industries. Here are some key applications of Scrum in project management:
- Software Development: The most common application of Scrum is in software development. It allows development teams to work on small, manageable chunks of functionality in each sprint, ensuring that valuable features are delivered regularly and enabling quick responses to changing requirements.
- Product Development: Beyond software, Scrum can be applied to the development of physical products. It enables cross-functional teams to collaborate on designing, prototyping, testing, and delivering products in iterations, ensuring that customer needs are met effectively.
- Marketing Campaigns: Scrum can be used in marketing projects where campaigns are broken down into sprints. Marketing teams can work on individual tasks like content creation, social media engagement, and analytics, delivering measurable results at the end of each sprint.
- Event Planning: For event management projects, Scrum can help organize tasks such as venue selection, logistics planning, participant engagement, and post-event analysis. Sprints can align with the various phases of event preparation.
- Research and Development: In R&D projects, Scrum allows researchers and developers to focus on specific aspects of a project, quickly experiment with new ideas, and pivot based on the results obtained within short iterations.
- Construction Projects: Construction projects can benefit from Scrum by dividing complex tasks like site preparation, foundation construction, and building phases into sprints. This helps manage resources, track progress, and adapt to unexpected challenges.
- Educational Programs: Scrum can be used to structure educational programs and courses. Each sprint corresponds to a learning module, and students make incremental progress, receive feedback, and adapt their learning journey based on their understanding.
- Content Creation: Content projects, such as writing articles, producing videos, or designing graphics, can benefit from Scrum's iterative approach. Sprints can focus on different content pieces, and regular reviews ensure content quality.
- Healthcare Projects: Scrum principles can be applied to healthcare projects, such as implementing new medical technologies, improving patient care processes, or developing healthcare apps. This approach promotes collaboration among medical professionals, developers, and other stakeholders.
- Consulting and Professional Services: Scrum can be used in consulting projects, where each sprint focuses on specific deliverables or recommendations for clients, ensuring that value is provided incrementally and allowing for client feedback.
When applying Scrum in project management, it's important to tailor the practices to suit the specific needs and context of the project. The framework encourages adaptability and continuous improvement, so teams can experiment with different approaches to find the best fit for their project's goals and requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Scrum Project Management
Scrum project management offers several advantages and disadvantages, which can impact its suitability for different projects and teams. Here's an overview of the pros and cons of using the Scrum framework:
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Scrum's iterative approach allows teams to adapt to changing requirements and priorities, making it well-suited for projects with evolving needs.
- Customer Satisfaction: Regularly delivering working increments of the project allows stakeholders to see progress and provide feedback, ensuring the final product meets their expectations.
- Collaboration: Scrum encourages close collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and customers, fostering a sense of ownership and shared responsibility.
- Transparency: The framework promotes transparency through daily standup meetings, sprint reviews, and sprint retrospectives, ensuring everyone is aware of the project's status and challenges.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Incremental delivery means that features can be released more quickly, enabling a shorter time-to-market compared to traditional project management approaches.
- Risk Mitigation: Frequent reviews and adaptability help identify and address risks early in the project, reducing the likelihood of major setbacks.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular sprint retrospectives encourage teams to reflect on their processes and make adjustments, leading to ongoing process improvement.
- Motivated Teams: Scrum empowers teams to self-organize and make decisions, fostering a sense of ownership and motivation among team members.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Scrum has several roles, events, and artifacts, which can be overwhelming for teams new to the framework or for smaller projects.
- Lack of Predictability: The adaptive nature of Scrum can make it challenging to predict exact project timelines and outcomes, which might be problematic for projects with strict deadlines.
- Requires Skilled Team Members: Effective Scrum implementation requires skilled team members who understand the framework and its principles.
- High Dependency on Product Owner: The product owner's availability and decision-making play a critical role in prioritizing and clarifying tasks. Their absence or lack of involvement can impact the project.
- Inaccurate Initial Estimates: Because Scrum focuses on delivering small increments, it might be challenging to provide accurate estimates for the entire project at the outset.
- Lack of Documentation: The focus on working increments can sometimes lead to inadequate documentation, which might be required for compliance or future maintenance.
- Need for Continuous Involvement: Scrum requires consistent participation from all team members throughout the project, which might not be feasible in certain environments.
- Resistance to Change: Teams accustomed to traditional project management methods may face resistance in transitioning to the agile practices of Scrum.
Ultimately, the decision to use Scrum in project management depends on factors like project complexity, team composition, stakeholder involvement, and the organization's culture. It's important to carefully evaluate the advantages and disadvantages to determine whether Scrum aligns with the project's needs and objectives.
Top of Form
Scrum Roles
In the Scrum framework, there are three key roles that contribute to the successful implementation of the methodology within a project. These roles promote collaboration, responsibility, and effective communication within the team. Here are the three Scrum roles:
- Product Owner:
- The Product Owner represents the stakeholders, customers, and users of the product being developed. They are responsible for maximizing the value delivered by the team.
- Key responsibilities include defining and maintaining the product backlog, prioritizing items within it, and ensuring that the team understands the requirements and goals.
- The Product Owner makes decisions about what features or items should be worked on, and their decisions guide the team's work during each sprint.
- Scrum Master:
- The Scrum Master is a servant-leader who ensures that the Scrum framework is understood, followed, and continuously improved by the team.
- They act as a facilitator and coach, helping the team to self-organize and make decisions collectively. They also remove obstacles and impediments that the team might encounter.
- The Scrum Master fosters a collaborative and productive environment, guides the team in adhering to Scrum practices, and helps improve the team's effectiveness.
- Development Team:
- The Development Team is a cross-functional group of professionals responsible for delivering the product increment during each sprint.
- The team members collectively have the skills and expertise needed to design, develop, test, and deliver the product features.
- They collaborate closely, self-organize to manage their work, and collectively commit to achieving the goals of each sprint.
It's important to note that in Scrum, these roles are distinct, and individuals typically do not hold multiple roles simultaneously. Each role has specific responsibilities that contribute to the successful implementation of the framework. Additionally, Scrum emphasizes collaboration among the roles, as well as with stakeholders, to ensure that the project's goals and requirements are met.
Comprehending the Role of Project Manager in Scrum – The Scrum Master vs. the Project Manager
In the Scrum framework, the role of a Project Manager is quite distinct from the role of a Scrum Master. Both roles play important parts in project management, but their responsibilities, focus, and approach can differ significantly. Here's a comparison of the two roles:
Scrum Master:
- Responsibilities:
- Facilitating the Scrum Process: The Scrum Master ensures that the Scrum framework is understood and followed by the team, helping to maintain the Scrum events, roles, and artifacts.
- Coaching and Mentoring: They coach the team on self-organization, cross-functionality, and effective collaboration. They help the team continuously improve and achieve their best potential.
- Removing Obstacles: The Scrum Master identifies and removes impediments that hinder the team's progress, ensuring that the team can work smoothly.
- Promoting Empowerment: They empower the team to make their own decisions and self-organize, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability.
- Shielding from External Interference: The Scrum Master helps protect the team from external disruptions and influences to maintain focus during sprints.
- Focus:
- Team Dynamics: The Scrum Master's primary focus is on fostering a productive and collaborative team environment, ensuring that the team can work efficiently and effectively.
- Process Adherence: They ensure that the Scrum process is followed and adapted appropriately to suit the team's needs while upholding Scrum principles.
Project Manager:
- Responsibilities:
- Planning and Scheduling: The Project Manager is responsible for planning the project, defining tasks, setting timelines, and creating a project schedule.
- Resource Management: They allocate resources, assign tasks, and ensure that the project is adequately staffed to meet its goals.
- Budget Management: The Project Manager handles budgeting, cost estimation, and resource allocation to ensure the project stays within budget.
- Risk Management: They identify potential risks, develop mitigation strategies, and manage any issues that arise during the project.
- Stakeholder Communication: The Project Manager communicates with stakeholders, updates them on project progress, and manages their expectations.
- Focus:
- Deliverables and Objectives: The Project Manager's primary focus is on meeting project goals, delivering the desired outcome, and ensuring that the project aligns with business objectives.
- Planning and Execution: They oversee the overall project planning and execution, ensuring that tasks are completed according to the plan.
In the context of Scrum, the Scrum Master's role is more about enabling the team to work effectively within the Scrum framework, while the Project Manager's role is broader and encompasses the overall management of the project. In many Scrum implementations, the traditional role of a Project Manager may shift to other roles (such as Product Owner or team member) or may be less prominent, as Scrum promotes self-organization and collaborative decision-making within the team. However, in organizations that use both traditional project management and Scrum, the Project Manager might still have a role to play in coordinating higher-level activities and aligning multiple Scrum teams with organizational goals.
6 Steps of Scrum Process
The Scrum process consists of several iterative and recurring steps that help teams deliver value incrementally and adapt to changing requirements. Here are the six key steps of the Scrum process:
- Product Backlog Creation:
- The process begins with the creation of the product backlog, which is a dynamic list of items that need to be addressed in the project. These items can include features, bug fixes, technical tasks, and more.
- The Product Owner is responsible for maintaining and prioritizing the product backlog based on input from stakeholders, customers, and the team.
- Sprint Planning:
- Before the start of each sprint, the team holds a sprint planning meeting.
- During this meeting, the Product Owner presents the items from the product backlog that are of the highest priority and have been refined to a sufficient level.
- The Development Team works with the Product Owner to select items from the product backlog that they believe they can complete during the sprint.
- The team breaks down the selected items into smaller tasks and estimates the effort required for each task.
- Sprint Execution:
- The sprint execution phase begins after the sprint planning meeting and typically lasts 1 to 4 weeks.
- The Development Team works on the tasks identified during the sprint planning, collaboratively building and testing the product increment.
- Daily standup meetings are held to provide updates on progress, discuss obstacles, and align the team.
- Daily Scrum (Standup):
- Each day during the sprint, the team holds a brief daily standup meeting, known as the Daily Scrum.
- Team members answer three questions: What did I accomplish yesterday? What will I work on today? Are there any obstacles in my way?
- This meeting helps the team stay synchronized, identify potential issues, and make real-time adjustments.
- Sprint Review:
- At the end of the sprint, the team holds a sprint review meeting.
- The team demonstrates the completed work to stakeholders and the Product Owner.
- Feedback is gathered, and stakeholders have an opportunity to evaluate the product increment and suggest changes.
- Sprint Retrospective:
- Following the sprint review, the team conducts a sprint retrospective meeting.
- The team reflects on the sprint process and discusses what went well, what could be improved, and what actions should be taken to enhance future sprints.
- The retrospective helps the team identify and implement process improvements, fostering a culture of continuous learning.
After the sprint retrospective, the process begins again with the creation of a new sprint and the selection of items from the product backlog. This cyclical process allows the team to continuously improve and refine their work based on feedback, making Scrum a highly adaptive and iterative framework.
Key Scrum Tools to Get You Through Your Next Sprint
Scrum emphasizes people and interactions over tools, but using the right tools can certainly enhance collaboration, communication, and productivity during sprints. Here are some key Scrum tools that can help you manage your next sprint effectively:
- Scrum Board or Kanban Board:
- A visual representation of the sprint backlog and its tasks.
- Helps the team track the progress of tasks, identify bottlenecks, and visualize the flow of work.
- Tools: Trello, Jira, Asana, Microsoft Planner.
- Digital Task Tracking and Management:
- Software tools that allow you to create, assign, and track tasks.
- Enables team members to update task status, add comments, and collaborate in real time.
- Tools: Jira, Microsoft Azure DevOps, Monday.com, ClickUp.
- Video Conferencing and Communication:
- Facilitates remote collaboration, daily standup meetings, sprint reviews, and sprint retrospectives.
- Enables clear communication among distributed teams.
- Tools: Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Slack, Google Meet.
- Documentation and Knowledge Sharing:
- Centralized platforms for storing project documentation, user stories, and sprint goals.
- Ensures that information is accessible and up to date for the team.
- Tools: Confluence, Microsoft SharePoint, Google Docs.
- Collaboration and Chat Platforms:
- Real-time chat platforms for quick communication, questions, and discussions.
- Helps team members stay connected and informed throughout the sprint.
- Tools: Slack, Microsoft Teams, Mattermost, Discord.
- Continuous Integration and Deployment:
- Tools that automate code integration, testing, and deployment.
- Ensures that code changes are integrated smoothly and tested continuously.
- Tools: Jenkins, Travis CI, CircleCI, GitLab CI/CD.
- Version Control System:
- Manages code repositories, tracks changes, and enables collaboration among developers.
- Ensures that code changes are properly tracked and managed.
- Tools: Git (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket), Subversion.
- Burndown Chart and Reporting:
- Provides visual representation of sprint progress, comparing completed work with remaining work.
- Helps the team and stakeholders understand the pace of work and make adjustments if needed.
- Tools: Jira, Trello (with Power-Ups), Microsoft Azure DevOps.
- Retrospective Tools:
- Online platforms that facilitate sprint retrospective meetings.
- Helps teams capture feedback, identify improvements, and track action items.
- Tools: FunRetro, Retrium, Miro, Stormboard.
- Test and Quality Management:
- Tools for managing test cases, executing tests, and tracking defects.
- Ensures that product quality is maintained throughout the sprint.
- Tools: Zephyr, TestRail, qTest, PractiTest.
Remember that the effectiveness of these tools depends on the team's familiarity with them and how well they integrate into your workflow. Choose tools that align with your team's preferences, needs, and the specific requirements of your project.
Becoming a Certified Scrum Master
Becoming a Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) involves completing a certification process offered by the Scrum Alliance. The CSM certification validates your knowledge of Scrum principles, practices, and your ability to serve as an effective Scrum Master. Here's a general outline of the steps you would take to become a Certified Scrum Master:
- Gain Familiarity with Scrum:
- Before pursuing the certification, ensure you have a solid understanding of Scrum principles, roles, events, and artifacts. Familiarize yourself with the Scrum Guide and recommended Scrum resources.
- Participate in Training:
- Attend a two-day Certified ScrumMaster training course conducted by a certified Scrum trainer. This course covers Scrum principles, practices, and real-world applications.
- Complete the Training:
- Participate actively in the training, engage in discussions, exercises, and workshops.
- Ensure you understand the Scrum framework, its roles, responsibilities, events, and values.
- Pass the Exam:
- After completing the training, you'll receive an email invitation from the Scrum Alliance to take the CSM exam.
- The exam is an online, multiple-choice test that assesses your knowledge of Scrum principles and practices.
- You have up to 90 days from the date of completing the training to pass the exam.
- Pass the Scrum Alliance CSM Exam:
- To pass the CSM exam, you'll need to correctly answer a certain percentage of questions.
- Passing the exam demonstrates your understanding of Scrum concepts and your ability to apply them in real-world scenarios.
- Complete the Scrum Alliance Membership:
- Once you've passed the exam, you need to create a Scrum Alliance account (if you don't already have one) and complete your membership profile.
- Agree to the License Agreement:
- As part of your certification process, you'll need to agree to the Scrum Alliance's certification license agreement.
- Claim Your Certification:
- After completing the exam and agreeing to the license agreement, you'll be able to claim your CSM certification.
- Maintain Your Certification:
- The CSM certification is valid for two years. To maintain it, you need to earn Scrum Education Units (SEUs) and renew your certification by paying a renewal fee.
It's important to note that the process and requirements may change, so it's recommended to check the Scrum Alliance's official website for the most up-to-date information on the CSM certification process, training opportunities, and exam details. The certification can enhance your understanding of Scrum and your ability to facilitate Scrum practices within your team or organization.
The Basic Principles Underlying Project Management
In the dynamic landscape of modern endeavors, whether in business, technology, construction, or any other sector, project management stands as a foundational discipline that drives success. Behind every achievement, innovation, and transformation lies a meticulous orchestration of tasks, resources, and timelines – a symphony conducted by the principles of project management. These principles, like the hidden currents beneath the surface of a vast ocean, guide projects from concept to completion, ensuring objectives are met, risks are mitigated, and stakeholders' expectations are exceeded. In this exploration of "The Basic Principles Underlying Project Management," we delve into the fundamental tenets that underpin the art and science of managing projects. By understanding these core principles, we uncover the framework that empowers project managers to navigate complexity, adapt to change, and lead their teams to triumph in the face of challenges.
Table of Contents
- What is Project Management About?
- Project Structure
- Definition Phase
- Clear Goals
- Transparency About the Project Status
- Risk Recognition
- Managing Project Disturbances
- Responsibility of the Project Manager
- Project Success
- Conclusion
What is Project Management About?
Project management is a disciplined approach to planning, organizing, executing, and overseeing the successful completion of specific goals and objectives within a defined timeframe and budget. It involves coordinating resources, tasks, and people to achieve a desired outcome while adhering to constraints and managing risks.
At its core, project management is about effectively guiding a project from its initial concept through its various stages to its final delivery. This process includes defining the scope, setting objectives, allocating resources, creating a timeline, identifying potential challenges, and implementing strategies to ensure the project's success.
Key aspects of what project management is about include:
- Planning: Creating a comprehensive roadmap for the project, outlining tasks, responsibilities, timelines, and milestones.
- Organization: Efficiently allocating and coordinating resources, including personnel, time, budget, and materials, to meet project goals.
- Execution: Carrying out the tasks and activities outlined in the project plan, ensuring that everything is progressing according to schedule.
- Monitoring and Control: Continuously tracking the project's progress, identifying deviations from the plan, and taking corrective actions to keep the project on track.
- Communication: Maintaining open and effective communication among all stakeholders, including team members, clients, and sponsors, to ensure everyone is informed and aligned.
- Risk Management: Identifying potential risks that could impact the project's success and developing strategies to mitigate or respond to them.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring that the project's deliverables meet the required standards and specifications.
- Adaptation: Being prepared to adjust the project plan and strategies as circumstances change or unexpected issues arise.
- Collaboration: Fostering collaboration and teamwork among project stakeholders to achieve a common goal.
- Closure: Concluding the project by delivering the final product or service to the client, conducting post-project evaluations, and capturing lessons learned for future improvement.
Project management is a critical practice in various industries, including construction, information technology, healthcare, marketing, and more. It provides a structured framework for achieving goals efficiently, effectively, and with minimal risks.
Project Structure
A project structure refers to the way in which a project is organized, including how tasks are divided, roles and responsibilities are assigned, communication flows, and decision-making processes are established. The structure of a project helps ensure that the project's goals are met efficiently and effectively. Here are the key components of a typical project structure:
- Project Manager: The individual responsible for overall project leadership, planning, execution, and successful completion. The project manager coordinates various aspects of the project, manages resources, and ensures that tasks are completed on time and within budget.
- Project Team: Comprised of individuals with specific skills and expertise necessary to complete the project. The team may include specialists, designers, developers, engineers, analysts, and more, depending on the project's requirements.
- Stakeholders: Individuals or groups with a vested interest in the project's outcome. This might include clients, sponsors, end-users, regulatory bodies, and anyone else affected by or influencing the project's success.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): The project is divided into smaller, manageable tasks or activities. The WBS helps organize the project's scope into actionable components, making it easier to assign responsibilities and track progress.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Clear roles and responsibilities are assigned to each team member to ensure that everyone knows their tasks, authority, and areas of accountability. This minimizes confusion and ensures efficient collaboration.
- Communication Plan: Specifies how communication will occur among project stakeholders. It outlines the frequency, methods, and channels of communication to ensure that everyone is informed and aligned.
- Project Charter: A document that outlines the project's objectives, scope, stakeholders, constraints, risks, and overall approach. It serves as a reference point for the project's goals and direction.
- Timeline and Schedule: A detailed timeline that outlines when each task or activity should be started and completed. It helps manage expectations and keep the project on track.
- Budget and Resources: Defines the budget allocated for the project and identifies the resources (financial, human, equipment, etc.) needed to complete the project successfully.
- Risk Management Plan: Identifies potential risks that could impact the project and outlines strategies for mitigating or addressing those risks.
- Change Management: Outlines procedures for managing changes to the project scope, timeline, or budget, ensuring that changes are controlled and documented.
- Quality Management: Specifies the quality standards and measures to be implemented to ensure that project deliverables meet established criteria.
- Decision-Making Structure: Defines how decisions will be made within the project, including who has decision-making authority for different aspects of the project.
- Closure Plan: Outlines the steps for closing out the project, including final deliverables, client hand-off, post-project evaluation, and documentation of lessons learned.
The specific structure of a project can vary based on its size, complexity, industry, and organizational culture. However, a well-defined project structure is crucial for maintaining clarity, accountability, and successful project execution.
Definition Phase
The definition phase, often referred to as the "Initiation Phase," is the initial stage of a project where the project's objectives, scope, and feasibility are defined and clarified. This phase serves as the foundation upon which the rest of the project is built. During the definition phase, project stakeholders work together to establish a clear understanding of what the project aims to achieve, how it will be executed, and what resources and constraints are involved.
Key activities and elements of the definition phase typically include:
- Project Conceptualization: Identifying the need or opportunity that the project addresses and establishing its overarching purpose and goals.
- Stakeholder Identification: Identifying all parties who have an interest in or influence over the project, including clients, sponsors, end-users, regulatory bodies, and more.
- Feasibility Analysis: Evaluating the project's feasibility in terms of technical, operational, financial, and organizational aspects. This analysis helps determine if the project is viable and worth pursuing.
- Scope Definition: Clearly defining the scope of the project, which includes outlining the boundaries of the project, the work that needs to be done, and what is specifically excluded from the project.
- Objective Setting: Establishing measurable and achievable project objectives that align with the project's goals and stakeholder expectations.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential risks and uncertainties that could impact the project's success. This includes assessing both internal and external factors that could affect the project.
- Resource Identification: Determining the resources required for the project, including human resources, budget, equipment, and materials.
- High-Level Planning: Developing an initial project plan that outlines the timeline, major milestones, and key deliverables.
- Preliminary Budgeting: Estimating the initial budget needed for the project, taking into account costs associated with various project components.
- Communication Plan: Outlining how communication will occur among stakeholders during the project. This includes defining communication channels, frequency, and reporting structures.
- Initial Risk Management Plan: Developing a preliminary plan to address and mitigate potential risks identified during the risk assessment.
- Project Charter: Documenting all the key information related to the project, including its objectives, scope, stakeholders, budget, timeline, and high-level plan. The project charter serves as a formal authorization to proceed with the project.
By the end of the definition phase, the project stakeholders should have a clear and shared understanding of what the project involves and what success looks like. This understanding sets the stage for the subsequent planning, execution, monitoring, and closure phases of the project.
Clear Goals
Clear goals are specific, well-defined, and measurable targets that provide direction and purpose for individuals, teams, and projects. These goals serve as a roadmap, guiding actions and decisions toward achieving desired outcomes. Clear goals are essential in various aspects of life, from personal development to business endeavors and project management. Here are some key characteristics and benefits of clear goals:
Characteristics of Clear Goals:
- Specific: Clear goals are precisely defined and leave no room for ambiguity. They answer the questions of what, why, and how, outlining the exact objective to be achieved.
- Measurable: A clear goal is quantifiable, allowing progress to be tracked and measured objectively. This enables individuals and teams to assess their performance and determine whether the goal has been achieved.
- Achievable: While goals should challenge individuals and teams to stretch their capabilities, they should also be realistic and attainable within the given constraints.
- Relevant: Goals should be aligned with the overall objectives of an individual, organization, or project. They should contribute to the bigger picture and be meaningful in the context of the situation.
- Time-Bound: Clear goals have a well-defined timeframe within which they are to be achieved. This adds a sense of urgency and helps in effective planning and execution.
Benefits of Clear Goals:
- Focus and Clarity: Clear goals provide a clear sense of direction, helping individuals and teams focus their efforts on what truly matters. This reduces distractions and enhances productivity.
- Motivation: Well-defined goals create a sense of purpose and motivation. When people know what they're working towards, they are more likely to stay committed and engaged.
- Measurement and Evaluation: Clear goals offer a standard against which progress can be measured. Regular evaluation helps individuals and teams assess their performance and make necessary adjustments.
- Alignment: Clear goals help align efforts across different individuals and departments within an organization. Everyone works towards a common objective, reducing conflicts and enhancing collaboration.
- Decision-Making: When faced with choices and alternatives, having clear goals makes decision-making easier. Decisions can be evaluated based on their alignment with the established goals.
- Accountability: Clear goals make it easy to assign responsibility and hold individuals or teams accountable for their performance and results.
- Continuous Improvement: Achieving clear goals provides a sense of accomplishment, but it also opens the door for setting new goals and striving for continuous improvement.
In personal and professional contexts, setting and working toward clear goals can lead to enhanced satisfaction, increased performance, and better outcomes. Whether in individual endeavors, team projects, or organizational strategies, the importance of clear goals cannot be overstated.
Transparency About the Project Status
Transparency about the project status involves openly and accurately sharing information about the progress, challenges, and overall health of a project with relevant stakeholders. This practice fosters clear communication, builds trust, and allows for informed decision-making. Transparency ensures that everyone involved is aware of how the project is advancing, any issues that have arisen, and the steps being taken to address them. Here's why transparency about the project status is crucial:
1. Informed Decision-Making: Transparent project status reporting enables stakeholders to make well-informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information. This helps prevent surprises and allows for timely adjustments when necessary.
2. Building Trust: Openly sharing project updates builds trust among stakeholders, including clients, sponsors, team members, and users. When everyone knows the real state of the project, credibility is established and maintained.
3. Collaboration: Transparency encourages open communication and collaboration. When people have a clear understanding of the project's status, they can offer insights, suggestions, and assistance to overcome challenges.
4. Accountability: Transparent reporting holds individuals and teams accountable for their responsibilities. When project status is visible, it's easier to identify areas where progress is lacking and take corrective actions.
5. Risk Management: Transparent reporting allows stakeholders to identify potential risks and address them before they escalate. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of unforeseen challenges.
6. Timely Problem Solving: Transparent project status reporting enables stakeholders to address issues promptly. Timely problem-solving reduces delays and prevents minor concerns from becoming major obstacles.
7. Realistic Expectations: When stakeholders have accurate information about the project's progress, they can set realistic expectations about timelines, deliverables, and outcomes.
8. Adjusting Plans: Transparent reporting provides the information needed to adjust project plans, scope, and resources as needed. This adaptability is essential for navigating changing circumstances.
9. Recognition and Support: Transparent reporting allows for recognizing and celebrating achievements and milestones. It also enables stakeholders to provide support and resources where necessary.
10. Continuous Improvement: Transparency encourages a culture of continuous improvement. By openly discussing challenges and lessons learned, organizations can refine their processes for future projects.
11. Minimizing Conflicts: Misunderstandings and conflicts often arise due to lack of information. Transparent project status reporting reduces misunderstandings and promotes smoother collaboration.
To ensure effective transparency about the project status:
- Establish a clear communication plan that outlines when, how, and what information will be shared with stakeholders.
- Use consistent reporting methods to provide updates regularly, whether through status meetings, written reports, dashboards, or other means.
- Be honest about both successes and challenges, as hiding problems can lead to greater issues down the line.
- Tailor the level of detail in updates based on the needs and interests of different stakeholders.
- Encourage open dialogue and questions, and be prepared to address concerns raised by stakeholders.
Overall, transparency about the project status is a key factor in project success. It promotes collaboration, accountability, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes.
Risk Recognition
Risk recognition, also known as risk identification, is a fundamental step in the risk management process. It involves systematically identifying potential risks and uncertainties that could impact the success of a project, initiative, or organization. Recognizing risks early on enables proactive planning and mitigation strategies to be put in place, reducing the likelihood of negative impacts.
Here's how risk recognition works and why it's essential:
Process of Risk Recognition:
- Brainstorming: Gather a diverse group of stakeholders, including team members, experts, and stakeholders, to generate a list of potential risks. Encourage open discussion to uncover a wide range of risks.
- Risk Categories: Categorize risks into different types, such as technical risks, financial risks, operational risks, and more. This helps in organizing and addressing risks effectively.
- Risk Statements: For each identified risk, create clear and concise risk statements that describe the risk event, its potential impact, and the factors contributing to it.
- Risk Register: Document all identified risks in a risk register or database. Include details such as risk description, potential consequences, likelihood, and initial severity.
- Qualitative Assessment: Assess each risk's likelihood of occurrence and potential impact. This qualitative assessment helps prioritize risks for further analysis.
Importance of Risk Recognition:
- Proactive Planning: Identifying risks early allows for proactive planning and mitigation strategies to be developed before issues arise. This minimizes the impact of risks on project timelines and outcomes.
- Resource Allocation: By recognizing risks, you can allocate resources for risk mitigation efforts, ensuring that you have the necessary tools, personnel, and funds to address potential challenges.
- Decision-Making: Understanding potential risks enables better decision-making. Leaders can make informed choices by considering risks alongside benefits and opportunities.
- Stakeholder Communication: Communicating about identified risks with stakeholders promotes transparency and helps manage their expectations. It also demonstrates that you're actively addressing potential concerns.
- Risk Response Planning: Recognizing risks allows you to create tailored response plans. These plans outline how you'll address each risk, whether through mitigation, avoidance, transfer, or acceptance.
- Contingency Planning: For high-impact risks, contingency plans can be developed. These plans outline alternative actions to take if the risk materializes.
- Cost and Schedule Management: Understanding potential risks helps in estimating the cost and schedule impact of those risks. This information aids in budgeting and timeline management.
- Risk Ownership: Identifying risks allows you to assign ownership to specific team members who will be responsible for monitoring and managing those risks.
- Risk Monitoring: Once risks are recognized and documented, you can establish mechanisms for ongoing monitoring. This helps ensure that risks are continuously assessed and addressed as the project progresses.
Remember that risk recognition is an ongoing process. Risks can emerge or change throughout the project lifecycle, so it's important to periodically review and update the risk register to capture new information and insights.
Managing Project Disturbances
Managing project disturbances, also known as project disruptions or unexpected events, is a crucial aspect of effective project management. Disturbances can range from minor setbacks to major crises, and how they are handled can significantly impact the project's success. Here's how to manage project disturbances effectively:
- Anticipate and Plan: While it's impossible to predict every disturbance, conducting a thorough risk assessment during the project planning phase can help identify potential disruptions. Develop contingency plans and mitigation strategies for high-impact risks.
- Stay Agile: Embrace an agile project management approach that allows for flexibility and adaptation. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, enable teams to respond quickly to changing circumstances and disturbances.
- Effective Communication: Maintain open and transparent communication with stakeholders. Inform them about disturbances, their potential impacts, and the steps being taken to address them. Clear communication helps manage expectations.
- Prioritize: Not all disturbances are of equal significance. Prioritize disturbances based on their potential impact and the degree of urgency. Address high-priority disturbances first to minimize their effects on the project.
- Resource Reallocation: In the face of a disturbance, reevaluate resource allocation. Determine if any adjustments are necessary to ensure critical tasks are still on track.
- Adapt the Plan: If a disturbance affects the project's scope, schedule, or resources, be prepared to adjust the project plan. Reallocate resources, modify timelines, or revise objectives as needed.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engage stakeholders in discussions about how to manage the disturbance. Their insights and perspectives might lead to innovative solutions or alternative approaches.
- Crisis Management: For significant disturbances, consider activating a crisis management team or plan. This team can focus solely on addressing the disturbance while the rest of the project team continues with their regular tasks.
- Learning and Documentation: Document the disturbance, the steps taken to address it, and the outcomes. This documentation can serve as a valuable resource for future projects facing similar disturbances.
- Maintain Team Morale: Disturbances can be stressful, impacting team morale. As a leader, provide support, keep the team informed, and maintain a positive outlook. Encourage a problem-solving mindset.
- Monitor and Review: Continuously monitor the situation as it evolves. Regularly review the effectiveness of the actions taken to address the disturbance and adjust strategies if necessary.
- Lessons Learned: After the project is complete, conduct a thorough post-project review. Analyze how disturbances were managed and identify lessons learned for future projects.
- Escalation Protocol: Establish an escalation protocol that outlines when and how to escalate disturbances to higher management or stakeholders. This ensures that critical issues are escalated promptly.
Remember that disturbances are a natural part of project management. How they are managed can differentiate successful projects from those that encounter major setbacks. By staying prepared, agile, and focused on solutions, project managers can effectively navigate disturbances and keep projects on track.
Responsibility of the Project Manager
The role of a project manager is multifaceted and involves a wide range of responsibilities to ensure the successful planning, execution, and completion of a project. Here are some key responsibilities of a project manager:
- Project Planning:
- Define project objectives, scope, and deliverables.
- Develop a comprehensive project plan, including timelines, milestones, and tasks.
- Allocate resources, both human and material, to tasks.
- Stakeholder Management:
- Identify and engage project stakeholders, including clients, sponsors, team members, and end-users.
- Communicate project goals, progress, and expectations to stakeholders.
- Team Leadership:
- Assemble project teams, assign roles and responsibilities, and provide clear direction.
- Motivate and lead team members to achieve project objectives.
- Foster a collaborative and productive team environment.
- Risk Management:
- Identify potential risks and uncertainties that could impact the project's success.
- Develop risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans.
- Monitor and address risks as they arise during project execution.
- Communication:
- Establish a communication plan to ensure regular and effective communication among project stakeholders.
- Provide updates on project status, milestones, and any deviations from the plan.
- Address conflicts and facilitate open dialogue.
- Scope Management:
- Monitor and manage project scope to ensure that it remains within the defined boundaries.
- Handle scope changes and ensure that they are documented and approved.
- Budget Management:
- Develop and manage the project budget, including tracking expenses and resource costs.
- Ensure that the project is delivered within the approved budget.
- Quality Assurance:
- Establish quality standards for project deliverables.
- Implement quality control processes to ensure that deliverables meet the required standards.
- Time Management:
- Monitor project timelines and milestones.
- Implement strategies to ensure that the project remains on schedule.
- Procurement Management:
- Identify necessary external resources and vendors.
- Manage procurement processes, contracts, and relationships with vendors.
- Reporting and Documentation:
- Maintain accurate and detailed project documentation.
- Generate regular reports on project progress, risks, and key performance indicators.
- Change Management:
- Manage changes to project scope, objectives, and requirements.
- Assess the impact of changes and communicate them to stakeholders.
- Closure and Evaluation:
- Ensure the successful completion and handover of project deliverables to the client or end-users.
- Conduct post-project evaluations to identify lessons learned and areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement:
- Reflect on project outcomes and processes to identify ways to enhance project management practices.
- Adaptability: Be prepared to adapt to changing circumstances, unforeseen challenges, and shifting priorities.
Overall, the project manager plays a pivotal role in orchestrating the various elements of a project to achieve its goals while ensuring effective communication, efficient resource utilization, and stakeholder satisfaction.
Project Success
Project success refers to the achievement of project objectives and goals within the defined scope, timeline, budget, and quality standards. It signifies that the project has delivered the intended results and value to stakeholders and has met or exceeded their expectations. However, the definition of project success can vary depending on the project's nature, context, and stakeholder perspectives. Here are some key dimensions of project success:
- Achieving Objectives: The project successfully fulfills its stated objectives, which could include delivering a product, service, or outcome that meets the project's intended purpose.
- Scope Adherence: The project remains within the defined scope, avoiding scope creep or changes that were not properly managed.
- Timely Delivery: The project is completed within the established timeline or meets important milestones on time.
- Budget Compliance: The project is executed within the approved budget or resources are managed effectively to prevent overspending.
- Quality Standards: The project's deliverables meet the required quality standards and satisfy the expectations of stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Stakeholders, including clients, sponsors, team members, and end-users, are satisfied with the project's outcomes and processes.
- Adaptability: The project demonstrates flexibility in adapting to changes or unexpected challenges while maintaining its focus on achieving goals.
- Resource Utilization: Resources are allocated and utilized efficiently to optimize project performance.
- Risk Management: Risks and uncertainties are effectively identified, managed, and mitigated to prevent significant negative impacts.
- Team Collaboration: Team members work cohesively and collaboratively, contributing to a positive team environment and successful project execution.
- Communication: Effective communication occurs among stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is informed, aligned, and engaged throughout the project lifecycle.
- Client Acceptance: The client or end-users accept the project's deliverables and find them valuable and useful.
- Lessons Learned: Insights are gathered from the project's successes and challenges to inform future projects and improve project management practices.
- Sustainability: The project's benefits are sustained over time, and the project's outcomes continue to provide value beyond its completion.
It's important to note that project success is not solely based on meeting technical objectives; it also considers the satisfaction of stakeholders and the broader impact of the project on the organization or community. Success may also be measured against factors such as return on investment, strategic alignment, and the overall contribution of the project to the organization's goals.
Ultimately, achieving project success requires a combination of effective planning, execution, communication, collaboration, and adaptability, all while keeping stakeholders' needs and expectations at the forefront.
Conclusion
In the realm of project management, success is a multidimensional achievement that encompasses not only the technical fulfillment of objectives but also the alignment of stakeholders' expectations, the mastery of challenges, and the delivery of value. From inception to completion, project managers navigate a dynamic landscape of planning, execution, communication, and adaptation, striving to orchestrate a harmonious symphony of tasks and resources.
At the heart of project management lies the art of balancing competing demands: scope, time, and cost. A skilled project manager recognizes that the true essence of success extends beyond merely meeting these constraints. It involves fostering a culture of collaboration, encouraging open communication, and adeptly managing risks. Disturbances and uncertainties, which are inevitable companions of any project, are approached with agility and met with solutions rooted in experience and creativity.
Project management's cornerstone is transparency. Effective communication, both internally and with stakeholders, ensures that all parties are well-informed and engaged throughout the journey. This transparency is the linchpin that builds trust, aligns visions, and maintains accountability.
In the final act of a project's lifecycle, as deliverables are handed over and outcomes evaluated, project managers glean invaluable lessons. These lessons are stitched into the fabric of continuous improvement, shaping the future endeavors of both themselves and their organizations. By embracing the principles of project management with dedication, adaptability, and a focus on the human dimension, project managers craft narratives of success that stand as testament to their skill and commitment.
Read More
In the dynamic landscape of modern endeavors, whether in business, technology, construction, or any other sector, project management stands as a foundational discipline that drives success. Behind every achievement, innovation, and transformation lies a meticulous orchestration of tasks, resources, and timelines – a symphony conducted by the principles of project management. These principles, like the hidden currents beneath the surface of a vast ocean, guide projects from concept to completion, ensuring objectives are met, risks are mitigated, and stakeholders' expectations are exceeded. In this exploration of "The Basic Principles Underlying Project Management," we delve into the fundamental tenets that underpin the art and science of managing projects. By understanding these core principles, we uncover the framework that empowers project managers to navigate complexity, adapt to change, and lead their teams to triumph in the face of challenges.
Table of Contents
- What is Project Management About?
- Project Structure
- Definition Phase
- Clear Goals
- Transparency About the Project Status
- Risk Recognition
- Managing Project Disturbances
- Responsibility of the Project Manager
- Project Success
- Conclusion
What is Project Management About?
Project management is a disciplined approach to planning, organizing, executing, and overseeing the successful completion of specific goals and objectives within a defined timeframe and budget. It involves coordinating resources, tasks, and people to achieve a desired outcome while adhering to constraints and managing risks.
At its core, project management is about effectively guiding a project from its initial concept through its various stages to its final delivery. This process includes defining the scope, setting objectives, allocating resources, creating a timeline, identifying potential challenges, and implementing strategies to ensure the project's success.
Key aspects of what project management is about include:
- Planning: Creating a comprehensive roadmap for the project, outlining tasks, responsibilities, timelines, and milestones.
- Organization: Efficiently allocating and coordinating resources, including personnel, time, budget, and materials, to meet project goals.
- Execution: Carrying out the tasks and activities outlined in the project plan, ensuring that everything is progressing according to schedule.
- Monitoring and Control: Continuously tracking the project's progress, identifying deviations from the plan, and taking corrective actions to keep the project on track.
- Communication: Maintaining open and effective communication among all stakeholders, including team members, clients, and sponsors, to ensure everyone is informed and aligned.
- Risk Management: Identifying potential risks that could impact the project's success and developing strategies to mitigate or respond to them.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring that the project's deliverables meet the required standards and specifications.
- Adaptation: Being prepared to adjust the project plan and strategies as circumstances change or unexpected issues arise.
- Collaboration: Fostering collaboration and teamwork among project stakeholders to achieve a common goal.
- Closure: Concluding the project by delivering the final product or service to the client, conducting post-project evaluations, and capturing lessons learned for future improvement.
Project management is a critical practice in various industries, including construction, information technology, healthcare, marketing, and more. It provides a structured framework for achieving goals efficiently, effectively, and with minimal risks.
Project Structure
A project structure refers to the way in which a project is organized, including how tasks are divided, roles and responsibilities are assigned, communication flows, and decision-making processes are established. The structure of a project helps ensure that the project's goals are met efficiently and effectively. Here are the key components of a typical project structure:
- Project Manager: The individual responsible for overall project leadership, planning, execution, and successful completion. The project manager coordinates various aspects of the project, manages resources, and ensures that tasks are completed on time and within budget.
- Project Team: Comprised of individuals with specific skills and expertise necessary to complete the project. The team may include specialists, designers, developers, engineers, analysts, and more, depending on the project's requirements.
- Stakeholders: Individuals or groups with a vested interest in the project's outcome. This might include clients, sponsors, end-users, regulatory bodies, and anyone else affected by or influencing the project's success.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): The project is divided into smaller, manageable tasks or activities. The WBS helps organize the project's scope into actionable components, making it easier to assign responsibilities and track progress.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Clear roles and responsibilities are assigned to each team member to ensure that everyone knows their tasks, authority, and areas of accountability. This minimizes confusion and ensures efficient collaboration.
- Communication Plan: Specifies how communication will occur among project stakeholders. It outlines the frequency, methods, and channels of communication to ensure that everyone is informed and aligned.
- Project Charter: A document that outlines the project's objectives, scope, stakeholders, constraints, risks, and overall approach. It serves as a reference point for the project's goals and direction.
- Timeline and Schedule: A detailed timeline that outlines when each task or activity should be started and completed. It helps manage expectations and keep the project on track.
- Budget and Resources: Defines the budget allocated for the project and identifies the resources (financial, human, equipment, etc.) needed to complete the project successfully.
- Risk Management Plan: Identifies potential risks that could impact the project and outlines strategies for mitigating or addressing those risks.
- Change Management: Outlines procedures for managing changes to the project scope, timeline, or budget, ensuring that changes are controlled and documented.
- Quality Management: Specifies the quality standards and measures to be implemented to ensure that project deliverables meet established criteria.
- Decision-Making Structure: Defines how decisions will be made within the project, including who has decision-making authority for different aspects of the project.
- Closure Plan: Outlines the steps for closing out the project, including final deliverables, client hand-off, post-project evaluation, and documentation of lessons learned.
The specific structure of a project can vary based on its size, complexity, industry, and organizational culture. However, a well-defined project structure is crucial for maintaining clarity, accountability, and successful project execution.
Definition Phase
The definition phase, often referred to as the "Initiation Phase," is the initial stage of a project where the project's objectives, scope, and feasibility are defined and clarified. This phase serves as the foundation upon which the rest of the project is built. During the definition phase, project stakeholders work together to establish a clear understanding of what the project aims to achieve, how it will be executed, and what resources and constraints are involved.
Key activities and elements of the definition phase typically include:
- Project Conceptualization: Identifying the need or opportunity that the project addresses and establishing its overarching purpose and goals.
- Stakeholder Identification: Identifying all parties who have an interest in or influence over the project, including clients, sponsors, end-users, regulatory bodies, and more.
- Feasibility Analysis: Evaluating the project's feasibility in terms of technical, operational, financial, and organizational aspects. This analysis helps determine if the project is viable and worth pursuing.
- Scope Definition: Clearly defining the scope of the project, which includes outlining the boundaries of the project, the work that needs to be done, and what is specifically excluded from the project.
- Objective Setting: Establishing measurable and achievable project objectives that align with the project's goals and stakeholder expectations.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential risks and uncertainties that could impact the project's success. This includes assessing both internal and external factors that could affect the project.
- Resource Identification: Determining the resources required for the project, including human resources, budget, equipment, and materials.
- High-Level Planning: Developing an initial project plan that outlines the timeline, major milestones, and key deliverables.
- Preliminary Budgeting: Estimating the initial budget needed for the project, taking into account costs associated with various project components.
- Communication Plan: Outlining how communication will occur among stakeholders during the project. This includes defining communication channels, frequency, and reporting structures.
- Initial Risk Management Plan: Developing a preliminary plan to address and mitigate potential risks identified during the risk assessment.
- Project Charter: Documenting all the key information related to the project, including its objectives, scope, stakeholders, budget, timeline, and high-level plan. The project charter serves as a formal authorization to proceed with the project.
By the end of the definition phase, the project stakeholders should have a clear and shared understanding of what the project involves and what success looks like. This understanding sets the stage for the subsequent planning, execution, monitoring, and closure phases of the project.
Clear Goals
Clear goals are specific, well-defined, and measurable targets that provide direction and purpose for individuals, teams, and projects. These goals serve as a roadmap, guiding actions and decisions toward achieving desired outcomes. Clear goals are essential in various aspects of life, from personal development to business endeavors and project management. Here are some key characteristics and benefits of clear goals:
Characteristics of Clear Goals:
- Specific: Clear goals are precisely defined and leave no room for ambiguity. They answer the questions of what, why, and how, outlining the exact objective to be achieved.
- Measurable: A clear goal is quantifiable, allowing progress to be tracked and measured objectively. This enables individuals and teams to assess their performance and determine whether the goal has been achieved.
- Achievable: While goals should challenge individuals and teams to stretch their capabilities, they should also be realistic and attainable within the given constraints.
- Relevant: Goals should be aligned with the overall objectives of an individual, organization, or project. They should contribute to the bigger picture and be meaningful in the context of the situation.
- Time-Bound: Clear goals have a well-defined timeframe within which they are to be achieved. This adds a sense of urgency and helps in effective planning and execution.
Benefits of Clear Goals:
- Focus and Clarity: Clear goals provide a clear sense of direction, helping individuals and teams focus their efforts on what truly matters. This reduces distractions and enhances productivity.
- Motivation: Well-defined goals create a sense of purpose and motivation. When people know what they're working towards, they are more likely to stay committed and engaged.
- Measurement and Evaluation: Clear goals offer a standard against which progress can be measured. Regular evaluation helps individuals and teams assess their performance and make necessary adjustments.
- Alignment: Clear goals help align efforts across different individuals and departments within an organization. Everyone works towards a common objective, reducing conflicts and enhancing collaboration.
- Decision-Making: When faced with choices and alternatives, having clear goals makes decision-making easier. Decisions can be evaluated based on their alignment with the established goals.
- Accountability: Clear goals make it easy to assign responsibility and hold individuals or teams accountable for their performance and results.
- Continuous Improvement: Achieving clear goals provides a sense of accomplishment, but it also opens the door for setting new goals and striving for continuous improvement.
In personal and professional contexts, setting and working toward clear goals can lead to enhanced satisfaction, increased performance, and better outcomes. Whether in individual endeavors, team projects, or organizational strategies, the importance of clear goals cannot be overstated.
Transparency About the Project Status
Transparency about the project status involves openly and accurately sharing information about the progress, challenges, and overall health of a project with relevant stakeholders. This practice fosters clear communication, builds trust, and allows for informed decision-making. Transparency ensures that everyone involved is aware of how the project is advancing, any issues that have arisen, and the steps being taken to address them. Here's why transparency about the project status is crucial:
1. Informed Decision-Making: Transparent project status reporting enables stakeholders to make well-informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information. This helps prevent surprises and allows for timely adjustments when necessary.
2. Building Trust: Openly sharing project updates builds trust among stakeholders, including clients, sponsors, team members, and users. When everyone knows the real state of the project, credibility is established and maintained.
3. Collaboration: Transparency encourages open communication and collaboration. When people have a clear understanding of the project's status, they can offer insights, suggestions, and assistance to overcome challenges.
4. Accountability: Transparent reporting holds individuals and teams accountable for their responsibilities. When project status is visible, it's easier to identify areas where progress is lacking and take corrective actions.
5. Risk Management: Transparent reporting allows stakeholders to identify potential risks and address them before they escalate. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of unforeseen challenges.
6. Timely Problem Solving: Transparent project status reporting enables stakeholders to address issues promptly. Timely problem-solving reduces delays and prevents minor concerns from becoming major obstacles.
7. Realistic Expectations: When stakeholders have accurate information about the project's progress, they can set realistic expectations about timelines, deliverables, and outcomes.
8. Adjusting Plans: Transparent reporting provides the information needed to adjust project plans, scope, and resources as needed. This adaptability is essential for navigating changing circumstances.
9. Recognition and Support: Transparent reporting allows for recognizing and celebrating achievements and milestones. It also enables stakeholders to provide support and resources where necessary.
10. Continuous Improvement: Transparency encourages a culture of continuous improvement. By openly discussing challenges and lessons learned, organizations can refine their processes for future projects.
11. Minimizing Conflicts: Misunderstandings and conflicts often arise due to lack of information. Transparent project status reporting reduces misunderstandings and promotes smoother collaboration.
To ensure effective transparency about the project status:
- Establish a clear communication plan that outlines when, how, and what information will be shared with stakeholders.
- Use consistent reporting methods to provide updates regularly, whether through status meetings, written reports, dashboards, or other means.
- Be honest about both successes and challenges, as hiding problems can lead to greater issues down the line.
- Tailor the level of detail in updates based on the needs and interests of different stakeholders.
- Encourage open dialogue and questions, and be prepared to address concerns raised by stakeholders.
Overall, transparency about the project status is a key factor in project success. It promotes collaboration, accountability, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes.
Risk Recognition
Risk recognition, also known as risk identification, is a fundamental step in the risk management process. It involves systematically identifying potential risks and uncertainties that could impact the success of a project, initiative, or organization. Recognizing risks early on enables proactive planning and mitigation strategies to be put in place, reducing the likelihood of negative impacts.
Here's how risk recognition works and why it's essential:
Process of Risk Recognition:
- Brainstorming: Gather a diverse group of stakeholders, including team members, experts, and stakeholders, to generate a list of potential risks. Encourage open discussion to uncover a wide range of risks.
- Risk Categories: Categorize risks into different types, such as technical risks, financial risks, operational risks, and more. This helps in organizing and addressing risks effectively.
- Risk Statements: For each identified risk, create clear and concise risk statements that describe the risk event, its potential impact, and the factors contributing to it.
- Risk Register: Document all identified risks in a risk register or database. Include details such as risk description, potential consequences, likelihood, and initial severity.
- Qualitative Assessment: Assess each risk's likelihood of occurrence and potential impact. This qualitative assessment helps prioritize risks for further analysis.
Importance of Risk Recognition:
- Proactive Planning: Identifying risks early allows for proactive planning and mitigation strategies to be developed before issues arise. This minimizes the impact of risks on project timelines and outcomes.
- Resource Allocation: By recognizing risks, you can allocate resources for risk mitigation efforts, ensuring that you have the necessary tools, personnel, and funds to address potential challenges.
- Decision-Making: Understanding potential risks enables better decision-making. Leaders can make informed choices by considering risks alongside benefits and opportunities.
- Stakeholder Communication: Communicating about identified risks with stakeholders promotes transparency and helps manage their expectations. It also demonstrates that you're actively addressing potential concerns.
- Risk Response Planning: Recognizing risks allows you to create tailored response plans. These plans outline how you'll address each risk, whether through mitigation, avoidance, transfer, or acceptance.
- Contingency Planning: For high-impact risks, contingency plans can be developed. These plans outline alternative actions to take if the risk materializes.
- Cost and Schedule Management: Understanding potential risks helps in estimating the cost and schedule impact of those risks. This information aids in budgeting and timeline management.
- Risk Ownership: Identifying risks allows you to assign ownership to specific team members who will be responsible for monitoring and managing those risks.
- Risk Monitoring: Once risks are recognized and documented, you can establish mechanisms for ongoing monitoring. This helps ensure that risks are continuously assessed and addressed as the project progresses.
Remember that risk recognition is an ongoing process. Risks can emerge or change throughout the project lifecycle, so it's important to periodically review and update the risk register to capture new information and insights.
Managing Project Disturbances
Managing project disturbances, also known as project disruptions or unexpected events, is a crucial aspect of effective project management. Disturbances can range from minor setbacks to major crises, and how they are handled can significantly impact the project's success. Here's how to manage project disturbances effectively:
- Anticipate and Plan: While it's impossible to predict every disturbance, conducting a thorough risk assessment during the project planning phase can help identify potential disruptions. Develop contingency plans and mitigation strategies for high-impact risks.
- Stay Agile: Embrace an agile project management approach that allows for flexibility and adaptation. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, enable teams to respond quickly to changing circumstances and disturbances.
- Effective Communication: Maintain open and transparent communication with stakeholders. Inform them about disturbances, their potential impacts, and the steps being taken to address them. Clear communication helps manage expectations.
- Prioritize: Not all disturbances are of equal significance. Prioritize disturbances based on their potential impact and the degree of urgency. Address high-priority disturbances first to minimize their effects on the project.
- Resource Reallocation: In the face of a disturbance, reevaluate resource allocation. Determine if any adjustments are necessary to ensure critical tasks are still on track.
- Adapt the Plan: If a disturbance affects the project's scope, schedule, or resources, be prepared to adjust the project plan. Reallocate resources, modify timelines, or revise objectives as needed.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engage stakeholders in discussions about how to manage the disturbance. Their insights and perspectives might lead to innovative solutions or alternative approaches.
- Crisis Management: For significant disturbances, consider activating a crisis management team or plan. This team can focus solely on addressing the disturbance while the rest of the project team continues with their regular tasks.
- Learning and Documentation: Document the disturbance, the steps taken to address it, and the outcomes. This documentation can serve as a valuable resource for future projects facing similar disturbances.
- Maintain Team Morale: Disturbances can be stressful, impacting team morale. As a leader, provide support, keep the team informed, and maintain a positive outlook. Encourage a problem-solving mindset.
- Monitor and Review: Continuously monitor the situation as it evolves. Regularly review the effectiveness of the actions taken to address the disturbance and adjust strategies if necessary.
- Lessons Learned: After the project is complete, conduct a thorough post-project review. Analyze how disturbances were managed and identify lessons learned for future projects.
- Escalation Protocol: Establish an escalation protocol that outlines when and how to escalate disturbances to higher management or stakeholders. This ensures that critical issues are escalated promptly.
Remember that disturbances are a natural part of project management. How they are managed can differentiate successful projects from those that encounter major setbacks. By staying prepared, agile, and focused on solutions, project managers can effectively navigate disturbances and keep projects on track.
Responsibility of the Project Manager
The role of a project manager is multifaceted and involves a wide range of responsibilities to ensure the successful planning, execution, and completion of a project. Here are some key responsibilities of a project manager:
- Project Planning:
- Define project objectives, scope, and deliverables.
- Develop a comprehensive project plan, including timelines, milestones, and tasks.
- Allocate resources, both human and material, to tasks.
- Stakeholder Management:
- Identify and engage project stakeholders, including clients, sponsors, team members, and end-users.
- Communicate project goals, progress, and expectations to stakeholders.
- Team Leadership:
- Assemble project teams, assign roles and responsibilities, and provide clear direction.
- Motivate and lead team members to achieve project objectives.
- Foster a collaborative and productive team environment.
- Risk Management:
- Identify potential risks and uncertainties that could impact the project's success.
- Develop risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans.
- Monitor and address risks as they arise during project execution.
- Communication:
- Establish a communication plan to ensure regular and effective communication among project stakeholders.
- Provide updates on project status, milestones, and any deviations from the plan.
- Address conflicts and facilitate open dialogue.
- Scope Management:
- Monitor and manage project scope to ensure that it remains within the defined boundaries.
- Handle scope changes and ensure that they are documented and approved.
- Budget Management:
- Develop and manage the project budget, including tracking expenses and resource costs.
- Ensure that the project is delivered within the approved budget.
- Quality Assurance:
- Establish quality standards for project deliverables.
- Implement quality control processes to ensure that deliverables meet the required standards.
- Time Management:
- Monitor project timelines and milestones.
- Implement strategies to ensure that the project remains on schedule.
- Procurement Management:
- Identify necessary external resources and vendors.
- Manage procurement processes, contracts, and relationships with vendors.
- Reporting and Documentation:
- Maintain accurate and detailed project documentation.
- Generate regular reports on project progress, risks, and key performance indicators.
- Change Management:
- Manage changes to project scope, objectives, and requirements.
- Assess the impact of changes and communicate them to stakeholders.
- Closure and Evaluation:
- Ensure the successful completion and handover of project deliverables to the client or end-users.
- Conduct post-project evaluations to identify lessons learned and areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement:
- Reflect on project outcomes and processes to identify ways to enhance project management practices.
- Adaptability: Be prepared to adapt to changing circumstances, unforeseen challenges, and shifting priorities.
Overall, the project manager plays a pivotal role in orchestrating the various elements of a project to achieve its goals while ensuring effective communication, efficient resource utilization, and stakeholder satisfaction.
Project Success
Project success refers to the achievement of project objectives and goals within the defined scope, timeline, budget, and quality standards. It signifies that the project has delivered the intended results and value to stakeholders and has met or exceeded their expectations. However, the definition of project success can vary depending on the project's nature, context, and stakeholder perspectives. Here are some key dimensions of project success:
- Achieving Objectives: The project successfully fulfills its stated objectives, which could include delivering a product, service, or outcome that meets the project's intended purpose.
- Scope Adherence: The project remains within the defined scope, avoiding scope creep or changes that were not properly managed.
- Timely Delivery: The project is completed within the established timeline or meets important milestones on time.
- Budget Compliance: The project is executed within the approved budget or resources are managed effectively to prevent overspending.
- Quality Standards: The project's deliverables meet the required quality standards and satisfy the expectations of stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Stakeholders, including clients, sponsors, team members, and end-users, are satisfied with the project's outcomes and processes.
- Adaptability: The project demonstrates flexibility in adapting to changes or unexpected challenges while maintaining its focus on achieving goals.
- Resource Utilization: Resources are allocated and utilized efficiently to optimize project performance.
- Risk Management: Risks and uncertainties are effectively identified, managed, and mitigated to prevent significant negative impacts.
- Team Collaboration: Team members work cohesively and collaboratively, contributing to a positive team environment and successful project execution.
- Communication: Effective communication occurs among stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is informed, aligned, and engaged throughout the project lifecycle.
- Client Acceptance: The client or end-users accept the project's deliverables and find them valuable and useful.
- Lessons Learned: Insights are gathered from the project's successes and challenges to inform future projects and improve project management practices.
- Sustainability: The project's benefits are sustained over time, and the project's outcomes continue to provide value beyond its completion.
It's important to note that project success is not solely based on meeting technical objectives; it also considers the satisfaction of stakeholders and the broader impact of the project on the organization or community. Success may also be measured against factors such as return on investment, strategic alignment, and the overall contribution of the project to the organization's goals.
Ultimately, achieving project success requires a combination of effective planning, execution, communication, collaboration, and adaptability, all while keeping stakeholders' needs and expectations at the forefront.
Conclusion
In the realm of project management, success is a multidimensional achievement that encompasses not only the technical fulfillment of objectives but also the alignment of stakeholders' expectations, the mastery of challenges, and the delivery of value. From inception to completion, project managers navigate a dynamic landscape of planning, execution, communication, and adaptation, striving to orchestrate a harmonious symphony of tasks and resources.
At the heart of project management lies the art of balancing competing demands: scope, time, and cost. A skilled project manager recognizes that the true essence of success extends beyond merely meeting these constraints. It involves fostering a culture of collaboration, encouraging open communication, and adeptly managing risks. Disturbances and uncertainties, which are inevitable companions of any project, are approached with agility and met with solutions rooted in experience and creativity.
Project management's cornerstone is transparency. Effective communication, both internally and with stakeholders, ensures that all parties are well-informed and engaged throughout the journey. This transparency is the linchpin that builds trust, aligns visions, and maintains accountability.
In the final act of a project's lifecycle, as deliverables are handed over and outcomes evaluated, project managers glean invaluable lessons. These lessons are stitched into the fabric of continuous improvement, shaping the future endeavors of both themselves and their organizations. By embracing the principles of project management with dedication, adaptability, and a focus on the human dimension, project managers craft narratives of success that stand as testament to their skill and commitment.
Exploring 10 Key Digital Marketing Strategies for Success
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital marketing, success is no longer achieved through a one-size-fits-all approach. The diverse range of strategies available has transformed the way businesses engage with audiences, build brand identity, and drive growth. "Navigating Digital Marketing Diversity: Optimal Applications of 10 Distinct Strategies" delves into the dynamic world of modern marketing, uncovering the unique strengths and applications of ten key strategies. From the timeless power of SEO and the immediate impact of PPC to the engaging realms of social media, influencer collaborations, and beyond, this exploration guides you through the intricacies of each strategy, empowering you to make informed decisions and chart a course towards digital marketing excellence. Join us on this journey to discover how the convergence of these strategies can shape your business's success in the ever-expanding digital landscape.
Table of Contents
What is Digital Marketing?
10 Types of Digital Marketing
-
Content Marketing
-
Search Engine Optimization
-
Search Engine Marketing/Pay-per-Click
-
Social Media Marketing
-
Affiliate and Influencer Marketing
-
Email Marketing
-
Mobile Marketing
-
Video Marketing
-
Audio Marketing
-
Chatbot Marketing
When and How to Use Different Types of Marketing?
What Types of Digital Marketing are Best for Your Business?
Want to Get a Jumpstart on your Digital Marketing Career?
Conclusion
What is Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing refers to the practice of promoting products, services, or brands using digital channels and technologies. It encompasses a wide range of strategies and tactics that leverage the internet, electronic devices, and various online platforms to connect with potential customers and engage with existing ones. The goal of digital marketing is to reach a targeted audience, build brand awareness, drive traffic, and ultimately achieve business objectives, such as generating leads, increasing sales, or improving customer retention.
Digital marketing takes advantage of the digital landscape to create personalized and interactive experiences for consumers. It includes a variety of channels and methods, such as search engines, social media, email, content creation, advertising, and more. The effectiveness of digital marketing campaigns can often be tracked and measured in real-time, allowing marketers to make data-driven decisions and optimize their strategies for better results.
As technology continues to evolve, digital marketing methods also continue to evolve, offering new and innovative ways to connect with audiences. It has become an essential component of modern marketing efforts, allowing businesses of all sizes to reach global audiences and engage with customers on a more personalized level.
10 Types of Digital Marketing
Here are 10 types of digital marketing, each focusing on different strategies and channels to reach and engage audiences:
Content Marketing
It is a digital marketing strategy focused on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and engage a target audience. The content can take various forms, such as blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, podcasts, and more. Here are the pros and cons of content marketing:
Pros:
-
Builds Authority and Credibility: Creating high-quality content showcases your expertise in your industry, establishing you as a knowledgeable authority and building trust with your audience.
-
Attracts Targeted Traffic: Well-optimized content can drive organic traffic from search engines, increasing your website's visibility and potentially attracting valuable leads.
Cons:
-
Time-Consuming: Content creation requires time and effort, from brainstorming ideas to creating, editing, and optimizing the content for distribution.
-
Results Aren't Immediate: Content marketing typically requires consistent efforts over time to yield significant results, making it less suitable for businesses seeking quick returns.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
It is a digital marketing strategy aimed at improving a website's visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) organically. The goal is to increase the quantity and quality of organic (non-paid) traffic to a website. Here are the pros and cons of SEO:
Pros:
1. Increased Organic Traffic: Optimizing your website for relevant keywords and user intent can lead to higher rankings in search results, driving more organic traffic to your site.
2. Long-Term Results: Once you achieve higher rankings, they can be relatively stable, leading to ongoing traffic and exposure without continual advertising costs.
Cons:
-
Time-Consuming: SEO is a long-term strategy that requires patience, as it can take several months to see significant improvements in rankings and traffic.
-
Algorithm Changes: Search engines frequently update their algorithms, which can impact your rankings. Staying current with these changes can be challenging.
Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
Its often referred to in the context of "Pay-per-Click (PPC)" advertising, is a digital marketing strategy that involves placing advertisements on search engine results pages (SERPs) or other platforms. In SEM, advertisers bid on specific keywords that users might enter into search engines like Google or Bing. When users search for these keywords, the ads appear at the top or bottom of the search results. Here's an explanation of SEM/PPC with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
Immediate Visibility: Ads are displayed as soon as the campaign is set up, providing instant visibility for your products or services.
-
Highly Targeted: You can choose specific keywords, demographics, locations, and even device types to target your ads to a relevant audience.
Cons:
-
Costs Can Add Up: While you have control over your budget, clicks can be expensive, especially for competitive keywords, and costs can escalate quickly if not managed effectively.
-
Dependent on Bidding: Higher bids can lead to better ad placements, but the competition for popular keywords can make bidding competitive and costly.
Social Media Marketing (SMM)
It is a digital marketing strategy that involves using social media platforms to connect, engage, and interact with your target audience. SMM aims to build brand awareness, drive website traffic, and achieve specific marketing goals through both organic (unpaid) and paid efforts. Here's an explanation of Social Media Marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
Broad Audience Reach: Social media platforms have billions of active users, allowing you to connect with a vast and diverse audience.
-
Audience Targeting: Platforms offer advanced targeting options based on demographics, interests, behaviors, and more, ensuring your content reaches the right people.
Cons:
-
Time-Consuming: Managing multiple social media accounts, creating content, and engaging with followers can be time-intensive.
-
Algorithm Changes: Social media algorithms change frequently, affecting the reach and visibility of your posts.
Affiliate Marketing and Influencer Marketing
These are two distinct digital marketing strategies that involve partnering with external individuals or entities to promote products or services. Here's an explanation of both, along with their pros and cons:
Affiliate Marketing:
Affiliate marketing is a performance-based strategy where businesses partner with affiliates who promote their products or services. Affiliates earn a commission for each sale, click, or lead generated through their marketing efforts.
Pros:
-
Cost-Effective: You pay only for results (sales, clicks, etc.), making it a cost-effective way to reach a broader audience.
-
Risk Mitigation: Since affiliates are rewarded for conversions, there's a shared interest in driving actual sales.
cons
-
Management Complexity: Managing relationships, tracking conversions, and ensuring fairness can be complex, especially with a large affiliate network.
-
Quality Control: You have limited control over how affiliates promote your products, which could impact your brand's image.
Influencer Marketing:
Influencer marketing involves collaborating with individuals who have a significant online following and can influence their audience's purchasing decisions. Influencers create content that features or promotes your products.
Pros:
-
Authenticity: Influencers' genuine endorsements can resonate with their followers, creating more authentic connections.
-
Niche Audiences: Influencers often have highly targeted audiences, allowing you to reach specific segments effectively.
-
Creativity: Influencers can showcase your products in creative and relatable ways that appeal to their followers.
-
Brand Exposure: Working with influencers exposes your brand to a wider audience, increasing brand awareness.
Cons:
-
Cost Variability: Influencers' rates can vary widely based on their following, making budgeting challenging.
-
Vetting Process: Finding influencers who align with your brand values and audience can be time-consuming.
-
Influencer Misalignment: If an influencer's actions or content deviate from your brand values, it could negatively impact your brand.
Email Marketing
Email Marketing is a digital marketing strategy that involves sending targeted emails to a group of recipients with the aim of promoting products, services, or building relationships. It's a direct and personal way to communicate with your audience. Here's an explanation of email marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
Direct Communication: Email allows you to reach your audience directly, often delivering messages right to their inbox.
-
Personalization: You can segment your email list based on various criteria (demographics, behavior, interests) and send personalized content that resonates with each segment.
Cons:
-
Deliverability Challenges: Emails might land in spam folders, limiting their visibility and effectiveness.
-
Overwhelm: Audiences receive a significant volume of emails daily, which can lead to inbox fatigue and reduced engagement.
Mobile Marketing
Mobile Marketing is a digital marketing strategy that focuses on reaching and engaging audiences through mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. Given the widespread use of mobile devices, mobile marketing aims to deliver content, promotions, and experiences that are optimized for smaller screens and cater to on-the-go users. Here's an explanation of mobile marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
Widespread Reach: With the proliferation of mobile devices, mobile marketing enables you to reach a large and diverse audience.
-
Immediate Engagement: Mobile devices allow for instant interaction, enabling real-time communication and quick responses.
Cons:
-
Screen Size Limitations: The limited screen size of mobile devices can pose challenges in presenting comprehensive information.
-
Device Fragmentation: The variety of devices, operating systems, and screen sizes requires careful optimization for consistent user experience.
Video Marketing
Video Marketing is a digital marketing strategy that involves using videos to promote products, services, or brands. It leverages the power of visual and auditory content to engage and communicate with audiences. Video marketing can take various forms, including promotional videos, tutorials, explainer videos, testimonials, and more. Here's an explanation of video marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
High Engagement: Videos have the ability to captivate audiences and convey information in a more engaging and memorable way compared to text-based content.
-
Versatility: Videos can be adapted to various platforms and formats, from social media posts to website content and email campaigns.
Cons:
-
Resource-Intensive: Creating high-quality videos requires time, effort, equipment, and often professional expertise.
-
Technical Challenges: Video production involves technical aspects like filming, editing, and post-production, which might be unfamiliar to some marketers.
Audio Marketing
Audio Marketing, also known as Audio Branding or Sonic Branding, is a digital marketing strategy that involves using sound and audio elements to create a consistent and memorable brand experience. It leverages auditory cues, such as jingles, sound effects, and even voiceovers, to establish a distinct brand identity and enhance the overall customer experience. Here's an explanation of audio marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
Memorable Brand Identity: Audio elements like jingles or sonic logos can create a unique and recognizable brand identity that sticks in customers' minds.
-
Emotional Connection: Sound has the power to evoke emotions and create a deeper emotional connection with your audience.
Cons:
1. Complex Implementation: Crafting the right audio elements requires creativity and expertise, often involving professional musicians or audio experts.
2. Subjective Interpretation: Different people might interpret audio cues differently, leading to varied emotional responses.
Chatbot Marketing
Chatbot Marketing is a digital marketing strategy that involves the use of chatbots to interact with customers, answer their queries, provide information, and guide them through various stages of the customer journey. Chatbots are automated systems that simulate human conversations and can be integrated into websites, messaging apps, social media platforms, and more. Here's an explanation of chatbot marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
24/7 Availability: Chatbots can provide instant responses and assistance to customers around the clock, enhancing user experience.
-
Efficient Customer Support: Chatbots can handle a high volume of inquiries simultaneously, reducing wait times and increasing customer satisfaction.
Cons:
-
Limited Understanding: Chatbots might struggle with understanding complex or nuanced queries, leading to frustration for users.
-
Lack of Empathy: Chatbots lack human emotions, which might not be ideal for handling sensitive or emotionally charged interactions.
When and How to Use Different Types of Marketing?
To use different types of marketing effectively, align your approach with your business objectives and audience preferences. Digital marketing encompasses various strategies such as SEO for long-term visibility, PPC for quick results, and content marketing to build authority. Leverage social media marketing for brand engagement, email marketing for personalized communication, and tap into wider audiences with influencer marketing and affiliate marketing. Engage visually with video marketing and target on-the-go users via mobile marketing. Lastly, enhance customer interactions through chatbot marketing. Continuously analyze results, adapting your strategies to optimize outcomes and maximize your marketing impact.
What Types of Digital Marketing are Best for Your Business?
The most effective types of digital marketing for your business depend on factors such as your industry, audience, and goals. If you're aiming to enhance your online visibility and credibility, SEO is crucial across industries. For immediate results and time-sensitive campaigns, consider PPC. Engaging with your audience and showcasing products is facilitated through social media marketing, while content marketing is ideal for establishing expertise. To nurture customer relationships and provide personalized communication, email marketing is valuable. Collaborating with influencers suits businesses looking for authentic endorsements, while affiliate marketing extends reach through partnerships. To convey complex information visually, explore video marketing, and target mobile users through mobile marketing. Finally, if you aim to enhance customer support and engagement, consider integrating chatbot marketing. Assess your business's specific needs to craft a tailored digital marketing approach.
Want to Get a Jumpstart on your Digital Marketing Career?
If you're eager to kickstart your digital marketing career, start by educating yourself through online courses and resources. Choose a specialization that aligns with your interests, build an online presence to showcase your skills, and gain practical experience through internships or freelance work. Obtain relevant certifications to boost your credibility, attend industry events to network, and stay updated on the latest trends. Experiment with strategies on personal projects, create a portfolio to showcase your work, and apply for entry-level positions or freelancing opportunities to gain real-world experience. Continuous learning and adaptability are crucial in this rapidly evolving field, so remain curious and persistent as you embark on your digital marketing journey.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing, the ability to navigate and harness the diversity of strategies is a cornerstone of success. As we've explored the optimal applications of 10 distinct strategies, from the enduring power of SEO and the immediacy of PPC to the engagement potential of social media and the authenticity of influencer marketing, it's clear that a holistic approach is key. Content marketing's authority-building, email marketing's personal touch, and the visual impact of video marketing all play vital roles. Moreover, mobile marketing's adaptability and chatbot marketing's efficiency address changing user habits. Through affiliate marketing's collaboration and the auditory identity of audio marketing, every facet has its place. Navigating this diversity requires a deep understanding of your business, audience, and goals. By skillfully blending these strategies, adapting to trends, and continually learning, you can chart a course for digital marketing success, fostering meaningful connections and driving sustainable growth in the digital realm.
Read More
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital marketing, success is no longer achieved through a one-size-fits-all approach. The diverse range of strategies available has transformed the way businesses engage with audiences, build brand identity, and drive growth. "Navigating Digital Marketing Diversity: Optimal Applications of 10 Distinct Strategies" delves into the dynamic world of modern marketing, uncovering the unique strengths and applications of ten key strategies. From the timeless power of SEO and the immediate impact of PPC to the engaging realms of social media, influencer collaborations, and beyond, this exploration guides you through the intricacies of each strategy, empowering you to make informed decisions and chart a course towards digital marketing excellence. Join us on this journey to discover how the convergence of these strategies can shape your business's success in the ever-expanding digital landscape.
Table of Contents
What is Digital Marketing?
10 Types of Digital Marketing
-
Content Marketing
-
Search Engine Optimization
-
Search Engine Marketing/Pay-per-Click
-
Social Media Marketing
-
Affiliate and Influencer Marketing
-
Email Marketing
-
Mobile Marketing
-
Video Marketing
-
Audio Marketing
-
Chatbot Marketing
When and How to Use Different Types of Marketing?
What Types of Digital Marketing are Best for Your Business?
Want to Get a Jumpstart on your Digital Marketing Career?
Conclusion
What is Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing refers to the practice of promoting products, services, or brands using digital channels and technologies. It encompasses a wide range of strategies and tactics that leverage the internet, electronic devices, and various online platforms to connect with potential customers and engage with existing ones. The goal of digital marketing is to reach a targeted audience, build brand awareness, drive traffic, and ultimately achieve business objectives, such as generating leads, increasing sales, or improving customer retention.
Digital marketing takes advantage of the digital landscape to create personalized and interactive experiences for consumers. It includes a variety of channels and methods, such as search engines, social media, email, content creation, advertising, and more. The effectiveness of digital marketing campaigns can often be tracked and measured in real-time, allowing marketers to make data-driven decisions and optimize their strategies for better results.
As technology continues to evolve, digital marketing methods also continue to evolve, offering new and innovative ways to connect with audiences. It has become an essential component of modern marketing efforts, allowing businesses of all sizes to reach global audiences and engage with customers on a more personalized level.
10 Types of Digital Marketing
Here are 10 types of digital marketing, each focusing on different strategies and channels to reach and engage audiences:
Content Marketing
It is a digital marketing strategy focused on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and engage a target audience. The content can take various forms, such as blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, podcasts, and more. Here are the pros and cons of content marketing:
Pros:
-
Builds Authority and Credibility: Creating high-quality content showcases your expertise in your industry, establishing you as a knowledgeable authority and building trust with your audience.
-
Attracts Targeted Traffic: Well-optimized content can drive organic traffic from search engines, increasing your website's visibility and potentially attracting valuable leads.
Cons:
-
Time-Consuming: Content creation requires time and effort, from brainstorming ideas to creating, editing, and optimizing the content for distribution.
-
Results Aren't Immediate: Content marketing typically requires consistent efforts over time to yield significant results, making it less suitable for businesses seeking quick returns.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
It is a digital marketing strategy aimed at improving a website's visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) organically. The goal is to increase the quantity and quality of organic (non-paid) traffic to a website. Here are the pros and cons of SEO:
Pros:
1. Increased Organic Traffic: Optimizing your website for relevant keywords and user intent can lead to higher rankings in search results, driving more organic traffic to your site.
2. Long-Term Results: Once you achieve higher rankings, they can be relatively stable, leading to ongoing traffic and exposure without continual advertising costs.
Cons:
-
Time-Consuming: SEO is a long-term strategy that requires patience, as it can take several months to see significant improvements in rankings and traffic.
-
Algorithm Changes: Search engines frequently update their algorithms, which can impact your rankings. Staying current with these changes can be challenging.
Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
Its often referred to in the context of "Pay-per-Click (PPC)" advertising, is a digital marketing strategy that involves placing advertisements on search engine results pages (SERPs) or other platforms. In SEM, advertisers bid on specific keywords that users might enter into search engines like Google or Bing. When users search for these keywords, the ads appear at the top or bottom of the search results. Here's an explanation of SEM/PPC with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
Immediate Visibility: Ads are displayed as soon as the campaign is set up, providing instant visibility for your products or services.
-
Highly Targeted: You can choose specific keywords, demographics, locations, and even device types to target your ads to a relevant audience.
Cons:
-
Costs Can Add Up: While you have control over your budget, clicks can be expensive, especially for competitive keywords, and costs can escalate quickly if not managed effectively.
-
Dependent on Bidding: Higher bids can lead to better ad placements, but the competition for popular keywords can make bidding competitive and costly.
Social Media Marketing (SMM)
It is a digital marketing strategy that involves using social media platforms to connect, engage, and interact with your target audience. SMM aims to build brand awareness, drive website traffic, and achieve specific marketing goals through both organic (unpaid) and paid efforts. Here's an explanation of Social Media Marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
Broad Audience Reach: Social media platforms have billions of active users, allowing you to connect with a vast and diverse audience.
-
Audience Targeting: Platforms offer advanced targeting options based on demographics, interests, behaviors, and more, ensuring your content reaches the right people.
Cons:
-
Time-Consuming: Managing multiple social media accounts, creating content, and engaging with followers can be time-intensive.
-
Algorithm Changes: Social media algorithms change frequently, affecting the reach and visibility of your posts.
Affiliate Marketing and Influencer Marketing
These are two distinct digital marketing strategies that involve partnering with external individuals or entities to promote products or services. Here's an explanation of both, along with their pros and cons:
Affiliate Marketing:
Affiliate marketing is a performance-based strategy where businesses partner with affiliates who promote their products or services. Affiliates earn a commission for each sale, click, or lead generated through their marketing efforts.
Pros:
-
Cost-Effective: You pay only for results (sales, clicks, etc.), making it a cost-effective way to reach a broader audience.
-
Risk Mitigation: Since affiliates are rewarded for conversions, there's a shared interest in driving actual sales.
cons
-
Management Complexity: Managing relationships, tracking conversions, and ensuring fairness can be complex, especially with a large affiliate network.
-
Quality Control: You have limited control over how affiliates promote your products, which could impact your brand's image.
Influencer Marketing:
Influencer marketing involves collaborating with individuals who have a significant online following and can influence their audience's purchasing decisions. Influencers create content that features or promotes your products.
Pros:
-
Authenticity: Influencers' genuine endorsements can resonate with their followers, creating more authentic connections.
-
Niche Audiences: Influencers often have highly targeted audiences, allowing you to reach specific segments effectively.
-
Creativity: Influencers can showcase your products in creative and relatable ways that appeal to their followers.
-
Brand Exposure: Working with influencers exposes your brand to a wider audience, increasing brand awareness.
Cons:
-
Cost Variability: Influencers' rates can vary widely based on their following, making budgeting challenging.
-
Vetting Process: Finding influencers who align with your brand values and audience can be time-consuming.
-
Influencer Misalignment: If an influencer's actions or content deviate from your brand values, it could negatively impact your brand.
Email Marketing
Email Marketing is a digital marketing strategy that involves sending targeted emails to a group of recipients with the aim of promoting products, services, or building relationships. It's a direct and personal way to communicate with your audience. Here's an explanation of email marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
Direct Communication: Email allows you to reach your audience directly, often delivering messages right to their inbox.
-
Personalization: You can segment your email list based on various criteria (demographics, behavior, interests) and send personalized content that resonates with each segment.
Cons:
-
Deliverability Challenges: Emails might land in spam folders, limiting their visibility and effectiveness.
-
Overwhelm: Audiences receive a significant volume of emails daily, which can lead to inbox fatigue and reduced engagement.
Mobile Marketing
Mobile Marketing is a digital marketing strategy that focuses on reaching and engaging audiences through mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. Given the widespread use of mobile devices, mobile marketing aims to deliver content, promotions, and experiences that are optimized for smaller screens and cater to on-the-go users. Here's an explanation of mobile marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
Widespread Reach: With the proliferation of mobile devices, mobile marketing enables you to reach a large and diverse audience.
-
Immediate Engagement: Mobile devices allow for instant interaction, enabling real-time communication and quick responses.
Cons:
-
Screen Size Limitations: The limited screen size of mobile devices can pose challenges in presenting comprehensive information.
-
Device Fragmentation: The variety of devices, operating systems, and screen sizes requires careful optimization for consistent user experience.
Video Marketing
Video Marketing is a digital marketing strategy that involves using videos to promote products, services, or brands. It leverages the power of visual and auditory content to engage and communicate with audiences. Video marketing can take various forms, including promotional videos, tutorials, explainer videos, testimonials, and more. Here's an explanation of video marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
High Engagement: Videos have the ability to captivate audiences and convey information in a more engaging and memorable way compared to text-based content.
-
Versatility: Videos can be adapted to various platforms and formats, from social media posts to website content and email campaigns.
Cons:
-
Resource-Intensive: Creating high-quality videos requires time, effort, equipment, and often professional expertise.
-
Technical Challenges: Video production involves technical aspects like filming, editing, and post-production, which might be unfamiliar to some marketers.
Audio Marketing
Audio Marketing, also known as Audio Branding or Sonic Branding, is a digital marketing strategy that involves using sound and audio elements to create a consistent and memorable brand experience. It leverages auditory cues, such as jingles, sound effects, and even voiceovers, to establish a distinct brand identity and enhance the overall customer experience. Here's an explanation of audio marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
Memorable Brand Identity: Audio elements like jingles or sonic logos can create a unique and recognizable brand identity that sticks in customers' minds.
-
Emotional Connection: Sound has the power to evoke emotions and create a deeper emotional connection with your audience.
Cons:
1. Complex Implementation: Crafting the right audio elements requires creativity and expertise, often involving professional musicians or audio experts.
2. Subjective Interpretation: Different people might interpret audio cues differently, leading to varied emotional responses.
Chatbot Marketing
Chatbot Marketing is a digital marketing strategy that involves the use of chatbots to interact with customers, answer their queries, provide information, and guide them through various stages of the customer journey. Chatbots are automated systems that simulate human conversations and can be integrated into websites, messaging apps, social media platforms, and more. Here's an explanation of chatbot marketing along with its pros and cons:
Pros:
-
24/7 Availability: Chatbots can provide instant responses and assistance to customers around the clock, enhancing user experience.
-
Efficient Customer Support: Chatbots can handle a high volume of inquiries simultaneously, reducing wait times and increasing customer satisfaction.
Cons:
-
Limited Understanding: Chatbots might struggle with understanding complex or nuanced queries, leading to frustration for users.
-
Lack of Empathy: Chatbots lack human emotions, which might not be ideal for handling sensitive or emotionally charged interactions.
When and How to Use Different Types of Marketing?
To use different types of marketing effectively, align your approach with your business objectives and audience preferences. Digital marketing encompasses various strategies such as SEO for long-term visibility, PPC for quick results, and content marketing to build authority. Leverage social media marketing for brand engagement, email marketing for personalized communication, and tap into wider audiences with influencer marketing and affiliate marketing. Engage visually with video marketing and target on-the-go users via mobile marketing. Lastly, enhance customer interactions through chatbot marketing. Continuously analyze results, adapting your strategies to optimize outcomes and maximize your marketing impact.
What Types of Digital Marketing are Best for Your Business?
The most effective types of digital marketing for your business depend on factors such as your industry, audience, and goals. If you're aiming to enhance your online visibility and credibility, SEO is crucial across industries. For immediate results and time-sensitive campaigns, consider PPC. Engaging with your audience and showcasing products is facilitated through social media marketing, while content marketing is ideal for establishing expertise. To nurture customer relationships and provide personalized communication, email marketing is valuable. Collaborating with influencers suits businesses looking for authentic endorsements, while affiliate marketing extends reach through partnerships. To convey complex information visually, explore video marketing, and target mobile users through mobile marketing. Finally, if you aim to enhance customer support and engagement, consider integrating chatbot marketing. Assess your business's specific needs to craft a tailored digital marketing approach.
Want to Get a Jumpstart on your Digital Marketing Career?
If you're eager to kickstart your digital marketing career, start by educating yourself through online courses and resources. Choose a specialization that aligns with your interests, build an online presence to showcase your skills, and gain practical experience through internships or freelance work. Obtain relevant certifications to boost your credibility, attend industry events to network, and stay updated on the latest trends. Experiment with strategies on personal projects, create a portfolio to showcase your work, and apply for entry-level positions or freelancing opportunities to gain real-world experience. Continuous learning and adaptability are crucial in this rapidly evolving field, so remain curious and persistent as you embark on your digital marketing journey.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing, the ability to navigate and harness the diversity of strategies is a cornerstone of success. As we've explored the optimal applications of 10 distinct strategies, from the enduring power of SEO and the immediacy of PPC to the engagement potential of social media and the authenticity of influencer marketing, it's clear that a holistic approach is key. Content marketing's authority-building, email marketing's personal touch, and the visual impact of video marketing all play vital roles. Moreover, mobile marketing's adaptability and chatbot marketing's efficiency address changing user habits. Through affiliate marketing's collaboration and the auditory identity of audio marketing, every facet has its place. Navigating this diversity requires a deep understanding of your business, audience, and goals. By skillfully blending these strategies, adapting to trends, and continually learning, you can chart a course for digital marketing success, fostering meaningful connections and driving sustainable growth in the digital realm.
Mastering Power BI: A Step-by-Step Approach for Beginners
Embark on a transformative learning journey with "Mastering Power BI: A Step-by-Step Approach for Beginners," a guide meticulously designed to equip you with the skills needed to navigate the dynamic landscape of data analysis and visualization. In a world driven by information, this guide opens the door for newcomers to harness the power of Power BI, empowering them to convert raw data into actionable insights. Whether you're a curious novice or a burgeoning data enthusiast, this resourceful guide will demystify the intricacies of Power BI, offering a structured path to proficiency.
Enhancing this learning experience is our CBAP Training Course, strategically integrated to provide an extra layer of expertise. CBAP, or "Certified Business Analysis Professional," seamlessly complements Power BI by fostering a holistic understanding of data interpretation and strategic decision-making. By combining the comprehensive insights of "Mastering Power BI" with the strategic prowess of CBAP, you're not only learning a tool but also cultivating a skill set that's invaluable in today's data-driven professional landscape.
Table of Contents
- What is Power BI
- What is DAX in Power BI ? What is it Used For?
- BI's Vast Potential
- How to Learn Power BI
- How to Use Power BI
- BI Job Opportunities
- Choose the Right Program
- Conclusion
What is Power BI?
Power BI is a business analytics tool developed by Microsoft. It empowers users to visualize and share insights from their data through interactive and visually appealing reports and dashboards. The primary purpose of Power BI is to transform raw data into meaningful information, enabling individuals and organizations to make informed decisions.
Power BI connects to a wide range of data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, cloud services, and more. Users can import, clean, and transform data using Power Query, a component of Power BI. Once the data is prepared, users can create a variety of visualizations such as charts, graphs, maps, and tables using Power BI's intuitive interface.
These visualizations can then be combined into interactive dashboards, allowing users to explore their data, identify trends, and uncover insights. Power BI also offers features like natural language querying, which enables users to ask questions about their data using plain language, and machine learning integration for advanced analytics.
Furthermore, Power BI can be seamlessly integrated with other Microsoft tools and services, making it a versatile and powerful tool for businesses of all sizes to drive data-driven decision-making processes.
What is DAX in Power BI ? What is it Used For?
DAX, which stands for Data Analysis Expressions, is a formula language used in Power BI (as well as other Microsoft tools like Excel and SQL Server Analysis Services) for creating custom calculations and aggregations on data models. It is specifically designed for working with tabular data models and is instrumental in performing calculations, creating new calculated columns or measures, and generating insights from data.
DAX allows users to manipulate data and create complex calculations that might not be achievable through standard aggregation functions or formulas. It operates on columns of data and can create dynamic calculations based on the context of the data being analyzed. Some common use cases of DAX in Power BI include:
- Creating Calculated Columns: DAX can be used to create new columns in a table that hold calculated values based on existing columns. These calculated columns can then be used in visualizations and reports.
- Defining Measures: Measures are calculations that aggregate data and can be used in calculations across the entire report. For instance, calculating totals, averages, percentages, etc.
- Time Intelligence: DAX is particularly useful for time-based calculations like year-to-date, quarter-to-date, or same period last year comparisons.
- Filtering and Slicing Data: DAX can help apply filters and slicers to specific parts of the data, enabling dynamic insights based on user interactions.
- Ranking and Top N Analysis: DAX can be used to create calculations for ranking items or finding the top or bottom items based on specific criteria.
- Advanced Analytics: DAX supports more advanced statistical and mathematical calculations, making it possible to perform complex analyses directly within Power BI.
- Conditional Logic: DAX can incorporate conditional statements to create dynamic calculations based on certain conditions being met.
While DAX can seem complex initially, it provides significant power to users looking to manipulate and analyze data in sophisticated ways. It's essential for anyone seeking to perform more advanced calculations and analysis within Power BI to learn DAX concepts and functions.
BI's Vast Potential
Power BI's vast potential lies in its ability to transform raw data into actionable insights, thereby empowering businesses and individuals to make informed decisions that drive growth and efficiency. As a robust business intelligence tool, Power BI offers several key features that contribute to its expansive capabilities:
- Data Integration: Power BI can connect to a multitude of data sources, from databases to cloud services, enabling users to consolidate and integrate diverse data streams into a single, unified view.
- Visual Analytics: The tool's intuitive interface allows users to create compelling visualizations such as charts, graphs, and maps, making complex data more accessible and understandable.
- Interactive Dashboards: Power BI's interactive dashboards provide a dynamic way to explore data, enabling users to drill down into details and extract insights on the fly.
- Data Modeling: The data modeling capabilities of Power BI allow users to shape and transform data to match specific analysis needs, resulting in accurate and relevant insights.
- Advanced Calculations: With its powerful Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) language, Power BI enables users to create intricate calculations and custom measures that go beyond standard functions.
- Real-time Insights: Power BI can connect to real-time data streams, providing up-to-the-minute insights that are crucial for monitoring business performance and making swift decisions.
- Collaboration and Sharing: Power BI's sharing features facilitate collaboration by allowing users to share reports and dashboards with colleagues, partners, and clients in a secure manner.
- Mobile Accessibility: The mobile app version of Power BI ensures that insights are available on-the-go, enabling users to stay informed and take action from anywhere.
- AI Integration: Power BI incorporates artificial intelligence capabilities, enabling users to leverage machine learning algorithms for predictive analysis and more accurate insights.
- Scalability: Whether for small teams or large enterprises, Power BI scales to accommodate various data volumes and user needs, making it a versatile solution for businesses of all sizes.
Ultimately, Power BI's vast potential lies in its capacity to democratize data analysis and reporting, making it accessible to individuals across an organization. By harnessing the tool's capabilities, users can unearth hidden trends, discover valuable patterns, and uncover actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making and foster success.
How to Learn Power BI
Learning Power BI can be an exciting and rewarding journey. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Set Clear Goals: Determine your learning objectives. Are you looking to build basic visualizations, create complex data models, or perform advanced analytics? Defining your goals will help you focus your learning efforts.
- Online Resources: Utilize online platforms that offer tutorials, courses, and documentation. Websites like Microsoft Learn, Udemy, Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, and YouTube have a wealth of Power BI tutorials, both free and paid.
- Official Documentation: Microsoft's official Power BI documentation is an excellent resource for understanding concepts, functions, and best practices. It's comprehensive and regularly updated.
- Start with Basics: Begin by learning the basics of Power BI, including data connections, data transformation with Power Query, and creating simple visualizations like charts and tables.
- Hands-On Practice: Learning by doing is crucial. Install Power BI Desktop (the free version) and work on sample datasets. Practice creating visualizations, playing with different chart types, and applying filters.
- Understand Data Modeling: Explore how to create relationships between tables, design data models, and use DAX functions for calculations and measures.
- Advanced Visualizations: Learn to build advanced visualizations like maps, custom visuals, and interactive dashboards. Experiment with color schemes, formatting, and layout design.
- DAX Mastery: As you progress, dive into Data Analysis Expressions (DAX). Start with basic calculations, and gradually explore more complex functions for sophisticated analytics.
- Practice Projects: Undertake real-world projects to apply what you've learned. Choose a dataset that interests you and create a comprehensive Power BI report or dashboard.
- Community Engagement: Join Power BI forums, user groups, and communities. Participate in discussions, ask questions, and learn from others' experiences.
- Books and eBooks: Consider reading books dedicated to Power BI. There are several well-regarded titles that can provide in-depth insights.
- Certification: If you're aiming for a structured learning path, consider pursuing Microsoft's official Power BI certification. It validates your skills and knowledge.
- Stay Updated: Power BI is regularly updated with new features and improvements. Follow blogs, forums, and official announcements to stay current.
- Online Courses: Enroll in online courses tailored to your skill level. They offer structured lessons, practical exercises, and sometimes even interaction with instructors.
- Practice Data Analysis: Beyond technical skills, focus on improving your data analysis capabilities. The ability to translate data into actionable insights is a crucial aspect of Power BI.
Remember, learning Power BI is an ongoing process. Start with the basics, practice consistently, and gradually advance to more complex topics. With dedication and hands-on experience, you'll develop the skills needed to confidently use Power BI for data analysis and visualization.
How to Use Power BI
Using Power BI involves several key steps to create insightful reports and dashboards. Here's a general guide on how to use Power BI:
- Install Power BI Desktop: Download and install Power BI Desktop, which is the free application used to create reports and dashboards.
- Connect to Data Sources:
- Open Power BI Desktop.
- Click on "Home" tab and choose "Get Data" to connect to your data source. You can connect to databases, files, online services, and more.
- Select your data source and follow the prompts to connect.
- Data Transformation:
- Use the Power Query Editor to clean and transform your data. You can filter, reshape, merge, and perform various data preparation tasks.
- Data Modeling:
- Design your data model by creating relationships between tables. Use the "Model" view to manage relationships and create hierarchies.
- Creating Visualizations:
- Switch to the "Report" view.
- Drag and drop fields from your data tables onto the canvas to create visualizations. Choose from charts, tables, maps, and more.
- Customize visualizations using the "Format" and "Visualizations" panes. Adjust colors, fonts, and other settings.
- Designing Dashboards:
- Combine your visualizations into a cohesive dashboard.
- Arrange visuals on the canvas, resize and format them for a clean and intuitive layout.
- Add text boxes, images, and shapes to provide context to your dashboard.
- Creating Measures with DAX:
- Use Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) to create custom calculations and measures.
- Click on "Modeling" tab and choose "New Measure" to create calculated fields based on your business logic.
- Interactive Features:
- Make your reports and dashboards interactive by using slicers, filters, and drill-through actions.
- Use bookmarks to save specific views and interactions for later use.
- Data Refresh:
- If your data source is dynamic, set up a refresh schedule to ensure your reports and dashboards stay up-to-date.
- Saving and Publishing:
- Save your Power BI report (.pbix file) on your local machine.
- If you have Power BI Pro or Power BI Premium, you can publish your reports to the Power BI service (cloud) for sharing.
- Sharing and Collaboration:
- In the Power BI service, you can share reports and dashboards with others within your organization. You can control permissions and access levels.
- Mobile and Embedded Reports:
- Optimize your reports for mobile devices. The Power BI service automatically renders reports for mobile viewing.
- Embed reports into websites, apps, or SharePoint for wider distribution.
- Continuous Learning:
- Power BI is a versatile tool with many features. Keep learning by exploring advanced visuals, complex DAX calculations, and additional data sources.
Remember that the learning curve for Power BI can vary, so be patient and practice regularly. As you become more comfortable with the tool, you'll be able to create sophisticated reports and dashboards that deliver valuable insights to your organization.
BI Job Opportunities
Business Intelligence (BI) offers a wide range of job opportunities across industries due to its critical role in helping organizations make data-driven decisions. Here are some common BI-related job roles you might consider:
- Business Intelligence Analyst:
- Analyzes data trends, patterns, and provides insights to support business decisions.
- Develops reports, dashboards, and visualizations using BI tools like Power BI, Tableau, or QlikView.
- Data Analyst:
- Collects, cleans, and interprets data to help organizations make informed decisions.
- Creates reports, visualizations, and presents findings to stakeholders.
- Data Engineer:
- Designs and builds data pipelines, warehouses, and ETL processes to ensure efficient data flow.
- Ensures data quality, security, and availability for analysis.
- BI Developer:
- Creates and maintains BI solutions, including designing data models, writing SQL queries, and building dashboards.
- Data Scientist:
- Utilizes advanced statistical and machine learning techniques to extract insights from data.
- Develops predictive and prescriptive models to solve complex business problems.
- BI Manager/Director:
- Oversees the BI team, sets strategies, manages projects, and ensures BI initiatives align with business goals.
- Dashboard Designer:
- Specializes in designing visually appealing and user-friendly dashboards and reports for better data communication.
- BI Consultant:
- Provides expertise to organizations on BI strategy, implementation, and optimization.
- Helps clients maximize the value of their data using BI tools and methodologies.
- Big Data Analyst:
- Focuses on analyzing and interpreting large and complex datasets, often utilizing tools like Hadoop and Spark.
- Reporting Specialist:
- Designs and produces standardized reports, often using tools like Crystal Reports or SSRS (SQL Server Reporting Services).
- Healthcare/Banking/Retail Analyst:
- Specialized roles that apply BI skills to specific industries, providing insights tailored to their unique needs.
- Business Intelligence Architect:
- Designs the overall structure of BI systems, including data models, architecture, and integration strategies.
- Data Governance Specialist:
- Ensures data quality, security, compliance, and proper usage through governance policies and practices.
- Machine Learning Engineer:
- Focuses on building and deploying machine learning models for predictive and prescriptive analytics.
- Chief Data Officer (CDO):
- Executive role responsible for managing an organization's data assets, strategies, and ensuring data-driven decisions.
Job opportunities in BI span various industries, including healthcare, finance, e-commerce, manufacturing, and more. The growing emphasis on data-driven decision-making makes BI professionals sought after in today's job market. Depending on your skills, experience, and interests, you can pursue roles that align with your career goals.
Choose the Right Program
Choosing the right program for learning Business Intelligence (BI) depends on your goals, background, learning style, and budget. Here's a step-by-step approach to help you make an informed decision:
- Identify Your Goals:
- Determine why you want to learn BI. Are you looking to start a new career, enhance your current skills, or apply BI to your existing role?
- Assess Your Background:
- Consider your current knowledge of data analysis, databases, programming, and statistics. Choose a program that aligns with your skill level.
- Research Learning Options:
- Look into various learning formats: online courses, bootcamps, workshops, university programs, self-study, etc.
- Online Learning Platforms:
- Websites like Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning, and edX offer a wide range of BI courses. Read reviews, check syllabus, and instructor credentials.
- University Programs:
- Consider formal education options, such as a bachelor's or master's degree in fields like Business Analytics, Data Science, or Management Information Systems.
- Bootcamps:
- BI bootcamps offer intensive, focused training. Look for programs that cover relevant tools (e.g., Power BI, Tableau) and practical skills.
- Curriculum:
- Review the curriculum of the program. It should cover data analysis, data visualization, SQL, database concepts, and possibly DAX or other BI tools.
- Instructor Expertise:
- Instructors with industry experience and expertise can provide valuable insights and real-world context.
- Practical Projects:
- Ensure the program includes hands-on projects where you apply your skills to real-world scenarios. Practical experience is crucial in BI.
- Flexibility and Pace:
- Consider your availability and preferred learning pace. Some programs are self-paced, while others have fixed schedules.
- Community and Support:
- Check if the program offers a supportive community, forums, or access to mentors. Interaction with others can enhance learning.
- Certifications:
- Some programs offer certifications that can add value to your resume. Consider whether certification is important for your goals.
- Budget:
- Compare program costs. Remember to factor in any additional expenses, such as software subscriptions.
- Read Reviews:
- Look for reviews and testimonials from previous students to gauge the program's quality and effectiveness.
- Free Resources:
- Don't overlook free resources like online tutorials, YouTube videos, and blogs. They can be valuable for getting started.
- Trial Periods:
- Many platforms offer trial periods. Utilize these to assess whether the program aligns with your learning style.
- Talk to Alumni:
- If possible, connect with alumni of the program to get insights into their experiences and outcomes.
Ultimately, choose a program that aligns with your learning preferences, career goals, and budget. Learning BI is an investment, and finding the right program can set you on a path to success in the dynamic world of data analysis and business intelligence.
Conclusion
Power BI stands as a versatile and powerful tool in the realm of business intelligence and data analysis. Its ability to transform raw data into actionable insights empowers organizations and individuals to make informed decisions that drive growth and efficiency. Through this guide, we've explored the fundamental aspects of Power BI, including its features, benefits, and various job opportunities it presents.
As you delve into the world of Power BI, remember that learning this tool is a journey. Whether you're a beginner starting with basic visualizations or an experienced professional diving into complex data modeling and DAX calculations, each step you take brings you closer to unlocking the full potential of your data.
The realm of data-driven decision-making is constantly evolving, and Power BI equips you to navigate this landscape with confidence. With a multitude of resources available online, courses, forums, and communities, you have the means to continuously enhance your skills and stay updated on the latest trends.
So, embrace the possibilities that Power BI offers and embark on a path where data insights become a driving force behind your success. Whether you're a business analyst, a data enthusiast, or a seasoned professional, Power BI empowers you to shape a future where data-driven decisions lead to transformative outcomes.
Read More
Embark on a transformative learning journey with "Mastering Power BI: A Step-by-Step Approach for Beginners," a guide meticulously designed to equip you with the skills needed to navigate the dynamic landscape of data analysis and visualization. In a world driven by information, this guide opens the door for newcomers to harness the power of Power BI, empowering them to convert raw data into actionable insights. Whether you're a curious novice or a burgeoning data enthusiast, this resourceful guide will demystify the intricacies of Power BI, offering a structured path to proficiency.
Enhancing this learning experience is our CBAP Training Course, strategically integrated to provide an extra layer of expertise. CBAP, or "Certified Business Analysis Professional," seamlessly complements Power BI by fostering a holistic understanding of data interpretation and strategic decision-making. By combining the comprehensive insights of "Mastering Power BI" with the strategic prowess of CBAP, you're not only learning a tool but also cultivating a skill set that's invaluable in today's data-driven professional landscape.
Table of Contents
- What is Power BI
- What is DAX in Power BI ? What is it Used For?
- BI's Vast Potential
- How to Learn Power BI
- How to Use Power BI
- BI Job Opportunities
- Choose the Right Program
- Conclusion
What is Power BI?
Power BI is a business analytics tool developed by Microsoft. It empowers users to visualize and share insights from their data through interactive and visually appealing reports and dashboards. The primary purpose of Power BI is to transform raw data into meaningful information, enabling individuals and organizations to make informed decisions.
Power BI connects to a wide range of data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, cloud services, and more. Users can import, clean, and transform data using Power Query, a component of Power BI. Once the data is prepared, users can create a variety of visualizations such as charts, graphs, maps, and tables using Power BI's intuitive interface.
These visualizations can then be combined into interactive dashboards, allowing users to explore their data, identify trends, and uncover insights. Power BI also offers features like natural language querying, which enables users to ask questions about their data using plain language, and machine learning integration for advanced analytics.
Furthermore, Power BI can be seamlessly integrated with other Microsoft tools and services, making it a versatile and powerful tool for businesses of all sizes to drive data-driven decision-making processes.
What is DAX in Power BI ? What is it Used For?
DAX, which stands for Data Analysis Expressions, is a formula language used in Power BI (as well as other Microsoft tools like Excel and SQL Server Analysis Services) for creating custom calculations and aggregations on data models. It is specifically designed for working with tabular data models and is instrumental in performing calculations, creating new calculated columns or measures, and generating insights from data.
DAX allows users to manipulate data and create complex calculations that might not be achievable through standard aggregation functions or formulas. It operates on columns of data and can create dynamic calculations based on the context of the data being analyzed. Some common use cases of DAX in Power BI include:
- Creating Calculated Columns: DAX can be used to create new columns in a table that hold calculated values based on existing columns. These calculated columns can then be used in visualizations and reports.
- Defining Measures: Measures are calculations that aggregate data and can be used in calculations across the entire report. For instance, calculating totals, averages, percentages, etc.
- Time Intelligence: DAX is particularly useful for time-based calculations like year-to-date, quarter-to-date, or same period last year comparisons.
- Filtering and Slicing Data: DAX can help apply filters and slicers to specific parts of the data, enabling dynamic insights based on user interactions.
- Ranking and Top N Analysis: DAX can be used to create calculations for ranking items or finding the top or bottom items based on specific criteria.
- Advanced Analytics: DAX supports more advanced statistical and mathematical calculations, making it possible to perform complex analyses directly within Power BI.
- Conditional Logic: DAX can incorporate conditional statements to create dynamic calculations based on certain conditions being met.
While DAX can seem complex initially, it provides significant power to users looking to manipulate and analyze data in sophisticated ways. It's essential for anyone seeking to perform more advanced calculations and analysis within Power BI to learn DAX concepts and functions.
BI's Vast Potential
Power BI's vast potential lies in its ability to transform raw data into actionable insights, thereby empowering businesses and individuals to make informed decisions that drive growth and efficiency. As a robust business intelligence tool, Power BI offers several key features that contribute to its expansive capabilities:
- Data Integration: Power BI can connect to a multitude of data sources, from databases to cloud services, enabling users to consolidate and integrate diverse data streams into a single, unified view.
- Visual Analytics: The tool's intuitive interface allows users to create compelling visualizations such as charts, graphs, and maps, making complex data more accessible and understandable.
- Interactive Dashboards: Power BI's interactive dashboards provide a dynamic way to explore data, enabling users to drill down into details and extract insights on the fly.
- Data Modeling: The data modeling capabilities of Power BI allow users to shape and transform data to match specific analysis needs, resulting in accurate and relevant insights.
- Advanced Calculations: With its powerful Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) language, Power BI enables users to create intricate calculations and custom measures that go beyond standard functions.
- Real-time Insights: Power BI can connect to real-time data streams, providing up-to-the-minute insights that are crucial for monitoring business performance and making swift decisions.
- Collaboration and Sharing: Power BI's sharing features facilitate collaboration by allowing users to share reports and dashboards with colleagues, partners, and clients in a secure manner.
- Mobile Accessibility: The mobile app version of Power BI ensures that insights are available on-the-go, enabling users to stay informed and take action from anywhere.
- AI Integration: Power BI incorporates artificial intelligence capabilities, enabling users to leverage machine learning algorithms for predictive analysis and more accurate insights.
- Scalability: Whether for small teams or large enterprises, Power BI scales to accommodate various data volumes and user needs, making it a versatile solution for businesses of all sizes.
Ultimately, Power BI's vast potential lies in its capacity to democratize data analysis and reporting, making it accessible to individuals across an organization. By harnessing the tool's capabilities, users can unearth hidden trends, discover valuable patterns, and uncover actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making and foster success.
How to Learn Power BI
Learning Power BI can be an exciting and rewarding journey. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Set Clear Goals: Determine your learning objectives. Are you looking to build basic visualizations, create complex data models, or perform advanced analytics? Defining your goals will help you focus your learning efforts.
- Online Resources: Utilize online platforms that offer tutorials, courses, and documentation. Websites like Microsoft Learn, Udemy, Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, and YouTube have a wealth of Power BI tutorials, both free and paid.
- Official Documentation: Microsoft's official Power BI documentation is an excellent resource for understanding concepts, functions, and best practices. It's comprehensive and regularly updated.
- Start with Basics: Begin by learning the basics of Power BI, including data connections, data transformation with Power Query, and creating simple visualizations like charts and tables.
- Hands-On Practice: Learning by doing is crucial. Install Power BI Desktop (the free version) and work on sample datasets. Practice creating visualizations, playing with different chart types, and applying filters.
- Understand Data Modeling: Explore how to create relationships between tables, design data models, and use DAX functions for calculations and measures.
- Advanced Visualizations: Learn to build advanced visualizations like maps, custom visuals, and interactive dashboards. Experiment with color schemes, formatting, and layout design.
- DAX Mastery: As you progress, dive into Data Analysis Expressions (DAX). Start with basic calculations, and gradually explore more complex functions for sophisticated analytics.
- Practice Projects: Undertake real-world projects to apply what you've learned. Choose a dataset that interests you and create a comprehensive Power BI report or dashboard.
- Community Engagement: Join Power BI forums, user groups, and communities. Participate in discussions, ask questions, and learn from others' experiences.
- Books and eBooks: Consider reading books dedicated to Power BI. There are several well-regarded titles that can provide in-depth insights.
- Certification: If you're aiming for a structured learning path, consider pursuing Microsoft's official Power BI certification. It validates your skills and knowledge.
- Stay Updated: Power BI is regularly updated with new features and improvements. Follow blogs, forums, and official announcements to stay current.
- Online Courses: Enroll in online courses tailored to your skill level. They offer structured lessons, practical exercises, and sometimes even interaction with instructors.
- Practice Data Analysis: Beyond technical skills, focus on improving your data analysis capabilities. The ability to translate data into actionable insights is a crucial aspect of Power BI.
Remember, learning Power BI is an ongoing process. Start with the basics, practice consistently, and gradually advance to more complex topics. With dedication and hands-on experience, you'll develop the skills needed to confidently use Power BI for data analysis and visualization.
How to Use Power BI
Using Power BI involves several key steps to create insightful reports and dashboards. Here's a general guide on how to use Power BI:
- Install Power BI Desktop: Download and install Power BI Desktop, which is the free application used to create reports and dashboards.
- Connect to Data Sources:
- Open Power BI Desktop.
- Click on "Home" tab and choose "Get Data" to connect to your data source. You can connect to databases, files, online services, and more.
- Select your data source and follow the prompts to connect.
- Data Transformation:
- Use the Power Query Editor to clean and transform your data. You can filter, reshape, merge, and perform various data preparation tasks.
- Data Modeling:
- Design your data model by creating relationships between tables. Use the "Model" view to manage relationships and create hierarchies.
- Creating Visualizations:
- Switch to the "Report" view.
- Drag and drop fields from your data tables onto the canvas to create visualizations. Choose from charts, tables, maps, and more.
- Customize visualizations using the "Format" and "Visualizations" panes. Adjust colors, fonts, and other settings.
- Designing Dashboards:
- Combine your visualizations into a cohesive dashboard.
- Arrange visuals on the canvas, resize and format them for a clean and intuitive layout.
- Add text boxes, images, and shapes to provide context to your dashboard.
- Creating Measures with DAX:
- Use Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) to create custom calculations and measures.
- Click on "Modeling" tab and choose "New Measure" to create calculated fields based on your business logic.
- Interactive Features:
- Make your reports and dashboards interactive by using slicers, filters, and drill-through actions.
- Use bookmarks to save specific views and interactions for later use.
- Data Refresh:
- If your data source is dynamic, set up a refresh schedule to ensure your reports and dashboards stay up-to-date.
- Saving and Publishing:
- Save your Power BI report (.pbix file) on your local machine.
- If you have Power BI Pro or Power BI Premium, you can publish your reports to the Power BI service (cloud) for sharing.
- Sharing and Collaboration:
- In the Power BI service, you can share reports and dashboards with others within your organization. You can control permissions and access levels.
- Mobile and Embedded Reports:
- Optimize your reports for mobile devices. The Power BI service automatically renders reports for mobile viewing.
- Embed reports into websites, apps, or SharePoint for wider distribution.
- Continuous Learning:
- Power BI is a versatile tool with many features. Keep learning by exploring advanced visuals, complex DAX calculations, and additional data sources.
Remember that the learning curve for Power BI can vary, so be patient and practice regularly. As you become more comfortable with the tool, you'll be able to create sophisticated reports and dashboards that deliver valuable insights to your organization.
BI Job Opportunities
Business Intelligence (BI) offers a wide range of job opportunities across industries due to its critical role in helping organizations make data-driven decisions. Here are some common BI-related job roles you might consider:
- Business Intelligence Analyst:
- Analyzes data trends, patterns, and provides insights to support business decisions.
- Develops reports, dashboards, and visualizations using BI tools like Power BI, Tableau, or QlikView.
- Data Analyst:
- Collects, cleans, and interprets data to help organizations make informed decisions.
- Creates reports, visualizations, and presents findings to stakeholders.
- Data Engineer:
- Designs and builds data pipelines, warehouses, and ETL processes to ensure efficient data flow.
- Ensures data quality, security, and availability for analysis.
- BI Developer:
- Creates and maintains BI solutions, including designing data models, writing SQL queries, and building dashboards.
- Data Scientist:
- Utilizes advanced statistical and machine learning techniques to extract insights from data.
- Develops predictive and prescriptive models to solve complex business problems.
- BI Manager/Director:
- Oversees the BI team, sets strategies, manages projects, and ensures BI initiatives align with business goals.
- Dashboard Designer:
- Specializes in designing visually appealing and user-friendly dashboards and reports for better data communication.
- BI Consultant:
- Provides expertise to organizations on BI strategy, implementation, and optimization.
- Helps clients maximize the value of their data using BI tools and methodologies.
- Big Data Analyst:
- Focuses on analyzing and interpreting large and complex datasets, often utilizing tools like Hadoop and Spark.
- Reporting Specialist:
- Designs and produces standardized reports, often using tools like Crystal Reports or SSRS (SQL Server Reporting Services).
- Healthcare/Banking/Retail Analyst:
- Specialized roles that apply BI skills to specific industries, providing insights tailored to their unique needs.
- Business Intelligence Architect:
- Designs the overall structure of BI systems, including data models, architecture, and integration strategies.
- Data Governance Specialist:
- Ensures data quality, security, compliance, and proper usage through governance policies and practices.
- Machine Learning Engineer:
- Focuses on building and deploying machine learning models for predictive and prescriptive analytics.
- Chief Data Officer (CDO):
- Executive role responsible for managing an organization's data assets, strategies, and ensuring data-driven decisions.
Job opportunities in BI span various industries, including healthcare, finance, e-commerce, manufacturing, and more. The growing emphasis on data-driven decision-making makes BI professionals sought after in today's job market. Depending on your skills, experience, and interests, you can pursue roles that align with your career goals.
Choose the Right Program
Choosing the right program for learning Business Intelligence (BI) depends on your goals, background, learning style, and budget. Here's a step-by-step approach to help you make an informed decision:
- Identify Your Goals:
- Determine why you want to learn BI. Are you looking to start a new career, enhance your current skills, or apply BI to your existing role?
- Assess Your Background:
- Consider your current knowledge of data analysis, databases, programming, and statistics. Choose a program that aligns with your skill level.
- Research Learning Options:
- Look into various learning formats: online courses, bootcamps, workshops, university programs, self-study, etc.
- Online Learning Platforms:
- Websites like Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning, and edX offer a wide range of BI courses. Read reviews, check syllabus, and instructor credentials.
- University Programs:
- Consider formal education options, such as a bachelor's or master's degree in fields like Business Analytics, Data Science, or Management Information Systems.
- Bootcamps:
- BI bootcamps offer intensive, focused training. Look for programs that cover relevant tools (e.g., Power BI, Tableau) and practical skills.
- Curriculum:
- Review the curriculum of the program. It should cover data analysis, data visualization, SQL, database concepts, and possibly DAX or other BI tools.
- Instructor Expertise:
- Instructors with industry experience and expertise can provide valuable insights and real-world context.
- Practical Projects:
- Ensure the program includes hands-on projects where you apply your skills to real-world scenarios. Practical experience is crucial in BI.
- Flexibility and Pace:
- Consider your availability and preferred learning pace. Some programs are self-paced, while others have fixed schedules.
- Community and Support:
- Check if the program offers a supportive community, forums, or access to mentors. Interaction with others can enhance learning.
- Certifications:
- Some programs offer certifications that can add value to your resume. Consider whether certification is important for your goals.
- Budget:
- Compare program costs. Remember to factor in any additional expenses, such as software subscriptions.
- Read Reviews:
- Look for reviews and testimonials from previous students to gauge the program's quality and effectiveness.
- Free Resources:
- Don't overlook free resources like online tutorials, YouTube videos, and blogs. They can be valuable for getting started.
- Trial Periods:
- Many platforms offer trial periods. Utilize these to assess whether the program aligns with your learning style.
- Talk to Alumni:
- If possible, connect with alumni of the program to get insights into their experiences and outcomes.
Ultimately, choose a program that aligns with your learning preferences, career goals, and budget. Learning BI is an investment, and finding the right program can set you on a path to success in the dynamic world of data analysis and business intelligence.
Conclusion
Power BI stands as a versatile and powerful tool in the realm of business intelligence and data analysis. Its ability to transform raw data into actionable insights empowers organizations and individuals to make informed decisions that drive growth and efficiency. Through this guide, we've explored the fundamental aspects of Power BI, including its features, benefits, and various job opportunities it presents.
As you delve into the world of Power BI, remember that learning this tool is a journey. Whether you're a beginner starting with basic visualizations or an experienced professional diving into complex data modeling and DAX calculations, each step you take brings you closer to unlocking the full potential of your data.
The realm of data-driven decision-making is constantly evolving, and Power BI equips you to navigate this landscape with confidence. With a multitude of resources available online, courses, forums, and communities, you have the means to continuously enhance your skills and stay updated on the latest trends.
So, embrace the possibilities that Power BI offers and embark on a path where data insights become a driving force behind your success. Whether you're a business analyst, a data enthusiast, or a seasoned professional, Power BI empowers you to shape a future where data-driven decisions lead to transformative outcomes.
The Data Science Journey:Navigating Through Life Cycle Steps
Welcome to the realm of modern problem-solving and innovation, where data-driven insights reign supreme – the captivating domain of Data Science. In an era characterized by an exponential surge in data generation, the ability to harness and decipher this information has become a pivotal skill set. This is where Data Science courses come into play, offering a structured pathway to unraveling the intricacies of this multidisciplinary field.
In this dynamic landscape, understanding the Data Science life cycle is akin to possessing a treasure map. Just as a cartographer meticulously charts each landmark, a data scientist meticulously navigates through a series of well-defined steps to extract valuable knowledge from raw data. This guide delves into the core of the Data Science life cycle, illuminating each stage with clarity and precision. Whether you're a novice explorer or an experienced adventurer seeking to sharpen your skills, this exploration of the Data Science life cycle promises to be enlightening and rewarding. So, fasten your seatbelt as we embark on this enlightening journey through the steps that constitute the essence of Data Science courses.
In this article
-
What is a Data Science Life Cycle?
-
Who Are Involved in The Projects?
-
The Lifecycle of Data Science
-
Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Data Science Life Cycle?
The Data Science Life Cycle is a systematic and structured framework that guides data scientists through the process of extracting valuable insights and knowledge from raw data. It outlines a series of interconnected stages that collectively form a journey, beginning with problem identification and concluding with the deployment of data-driven solutions. This lifecycle serves as a roadmap, ensuring that data analysis projects are organized, efficient, and effective in addressing complex challenges.
At its core, the Data Science Life Cycle encompasses stages such as data collection, preprocessing, exploratory data analysis, feature engineering, model development, evaluation, deployment, and continuous monitoring. Each of these stages plays a critical role in transforming data into actionable insights. Problem definition initiates the cycle by setting clear objectives and goals. Data collection acquires the necessary information for analysis, which then undergoes preprocessing to ensure accuracy and consistency. Exploratory data analysis uncovers patterns and anomalies, while feature engineering refines the data for modeling. Models are developed, evaluated, and tuned to provide predictive power, and finally, the insights derived are deployed into real-world applications.
In essence, the Data Science Life Cycle is a holistic approach that enables data scientists to navigate the complexities of data analysis, ensuring that every step contributes to informed decision-making and impactful solutions.
Who Are Involved in The Projects?
Data science projects typically involve a diverse team of professionals with complementary skills and expertise. The roles and responsibilities within a data science project can vary depending on the size of the team, the complexity of the project, and the specific goals of the analysis. Here are some key roles commonly involved in data science projects:
-
Data Scientist: Data scientists are the core members of the team responsible for designing and executing the analysis. They are skilled in programming, statistical analysis, machine learning, and domain knowledge. Data scientists handle tasks such as data preprocessing, model development, and interpretation of results.
-
Data Engineer: Data engineers are responsible for collecting, storing, and preparing the data for analysis. They create and maintain data pipelines, ensuring that data is accessible, reliable, and well-structured. Data engineers work closely with data scientists to provide them with the necessary data sets.
-
Domain Expert: A domain expert brings subject-matter knowledge to the team. They understand the specific industry, business context, and nuances of the problem being solved. Their insights help guide the analysis and ensure that the results are relevant and actionable.
-
Machine Learning Engineer: In projects where machine learning models are central, machine learning engineers work alongside data scientists to implement and optimize machine learning algorithms. They focus on scaling and deploying models for production.
-
Business Analyst: Business analysts bridge the gap between technical analysis and business goals. They help define the problem, gather requirements, and ensure that the analysis aligns with the organization's strategic objectives. They also play a key role in communicating results to stakeholders.
-
Project Manager: Project managers oversee the project's execution, timeline, and resources. They ensure that the project stays on track, milestones are met, and communication flows smoothly among team members. They also handle coordination and collaboration.
-
Data Analyst: Data analysts focus on exploratory data analysis, generating insights from data, and creating visualizations. They often work on smaller tasks within the project and support data scientists in understanding the data's characteristics.
-
UX/UI Designer: In projects involving user interfaces or dashboards, UX/UI designers create user-friendly interfaces for visualizing and interacting with data. They ensure that the interface is intuitive and meets user needs.
-
Data Privacy and Compliance Expert: Data privacy and compliance experts ensure that the project adheres to relevant data protection regulations. They address concerns related to data security, anonymization, and compliance with legal requirements.
-
Communication Specialist: Effective communication of findings is crucial. Communication specialists or data storytellers help distill complex results into understandable insights, making it easier for non-technical stakeholders to grasp the significance of the analysis.
It's important to note that some team members might take on multiple roles, especially in smaller teams or projects. Collaboration and effective communication among these diverse roles are essential for the success of a data science project.
The Lifecycle of Data Science
The lifecycle of Data Science, also known as the Data Science Lifecycle or Data Analytics Lifecycle, is a structured framework that outlines the stages involved in a data science project, from problem identification to solution deployment. This systematic approach ensures that data-driven projects are well-organized, efficient, and effective in generating actionable insights. The following are the typical stages of the Data Science Lifecycle:
-
Problem Definition: Clearly define the problem you aim to solve or the question you want to answer using data analysis. Understand the business context, objectives, and the expected outcome of the analysis.
-
Data Collection: Gather relevant data from various sources, such as databases, APIs, spreadsheets, or external data providers. Ensure the data is comprehensive, accurate, and representative of the problem at hand.
-
Data Cleaning and Preprocessing: Clean, transform, and preprocess the collected data to remove inconsistencies, handle missing values, and ensure data quality. This step is crucial for accurate and reliable analysis.
-
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Explore and analyze the data to gain insights into its characteristics, patterns, and relationships. EDA helps in identifying trends, outliers, and potential features for modeling.
-
Feature Engineering: Select, create, or transform features (variables) from the data that are relevant for building predictive models. This involves using domain knowledge to craft meaningful features.
-
Modeling: Develop and train machine learning or statistical models to address the defined problem. Choose appropriate algorithms, split data into training and validation sets, and fine-tune model parameters.
-
Validation and Evaluation: Validate the model's performance using validation techniques like cross-validation. Evaluate the model's accuracy, precision, recall, and other relevant metrics using unseen data.
-
Model Selection and Tuning: Select the best-performing model and fine-tune its parameters to optimize its performance on new data. This step involves iterative adjustments to improve the model's generalization.
-
Deployment: Implement the model into a production environment for real-world use. Integrate the model into software systems, APIs, or create user interfaces to make predictions on new data.
-
Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuously monitor the model's performance in the production environment. Update and retrain the model as needed to adapt to changing data distributions or business requirements.
-
Communication of Results: Communicate the insights, findings, and conclusions drawn from the analysis to stakeholders. Use visualizations, reports, and presentations to effectively convey the significance of the results.
-
Feedback and Iteration: Gather feedback from stakeholders and users of the deployed solution. Iterate on the model or analysis based on feedback to improve accuracy and relevance.
The Data Science Lifecycle is not always linear; iterations and feedback loops are common, especially in complex projects. Each stage is interconnected, and the process is often iterative, allowing data scientists to refine their approach based on insights gained during the project. This lifecycle serves as a roadmap, guiding data science teams through the process of turning raw data into actionable insights and solutions that drive informed decision-making.
Conclusion
In the rapidly evolving landscape of data-driven decision-making, the Data Science Lifecycle stands as a steadfast guide, leading us through the intricate journey from raw data to actionable insights. As we draw the curtains on this exploration, it's evident that this structured framework is not just a mere sequence of steps but a dynamic process that empowers us to unlock the hidden potential within data.
From the initial spark of problem identification to the final crescendo of deploying a predictive model, the lifecycle encapsulates the essence of collaboration, innovation, and meticulous analysis. It encapsulates the collective efforts of data scientists, domain experts, engineers, and communicators, all synergizing their talents to extract valuable meaning from data's vast depths.
Embracing the iterative nature of the lifecycle, we find ourselves revisiting, refining, and expanding our perspectives with each cycle. This iterative dance nurtures growth and ensures our solutions remain relevant and potent in the face of changing landscapes.
In the end, the Data Science Lifecycle is not just a series of steps but a story of transformation. It's the story of turning numbers into narratives, data into decisions, and uncertainty into understanding. Armed with this comprehensive approach, we are empowered to navigate the complexities of the data universe, illuminate the darkest corners with insights, and ultimately shape a future driven by the power of informed choices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Data Science Lifecycle? The Data Science Lifecycle is a structured framework that outlines the stages involved in a data science project. It encompasses processes from problem identification, data collection, and analysis to model development, deployment, and continuous monitoring. This lifecycle guides data scientists in a systematic approach to derive insights and solutions from data.
2. Why is the Data Science Lifecycle important? The Data Science Lifecycle provides a clear roadmap for data-driven projects, ensuring that they are organized, efficient, and effective. It helps in maintaining consistency, improving collaboration, and generating reliable results by following a step-by-step approach.
3. What are the main stages of the Data Science Lifecycle? The main stages include problem definition, data collection, data cleaning and preprocessing, exploratory data analysis, feature engineering, modeling, validation and evaluation, model selection and tuning, deployment, monitoring and maintenance, communication of results, and feedback and iteration.
4. Who is involved in data science projects? Data science projects involve a diverse team including data scientists, data engineers, domain experts, machine learning engineers, business analysts, project managers, UX/UI designers, communication specialists, and more. Collaboration among these roles is essential for a successful project.
5. Is the Data Science Lifecycle linear? The lifecycle is not strictly linear; it's often iterative. Teams revisit stages based on insights gained, feedback received, or changes in project goals. This iterative approach allows for refinement and improvement throughout the project.
6. What is the role of exploratory data analysis (EDA)? Exploratory data analysis involves analyzing and visualizing data to understand its characteristics, uncover patterns, and identify potential outliers or trends. EDA helps data scientists form hypotheses, guide feature selection, and gain insights before building models.
7. How does the Data Science Lifecycle adapt to changing data or business needs? The lifecycle's iterative nature allows it to adapt. As new data becomes available or business requirements change, the team can revisit stages like model tuning, feature engineering, or even problem definition to ensure the analysis remains relevant and effective.
8. How does the lifecycle handle model deployment? Model deployment involves integrating the developed model into a real-world environment, such as a software system or user interface. The deployment stage ensures that the model is operational and can make predictions on new data.
9. What is the role of communication in the lifecycle? Communication is crucial for conveying insights and results to stakeholders who may not have technical backgrounds. Effective communication specialists or data storytellers ensure that complex findings are presented in an understandable and impactful manner.
10. Why is feedback and iteration important in the Data Science Lifecycle? Feedback and iteration allow projects to improve over time. By gathering feedback from stakeholders and users of the deployed solution, teams can make adjustments, refine models, and enhance the overall effectiveness of the analysis.
Read More
Welcome to the realm of modern problem-solving and innovation, where data-driven insights reign supreme – the captivating domain of Data Science. In an era characterized by an exponential surge in data generation, the ability to harness and decipher this information has become a pivotal skill set. This is where Data Science courses come into play, offering a structured pathway to unraveling the intricacies of this multidisciplinary field.
In this dynamic landscape, understanding the Data Science life cycle is akin to possessing a treasure map. Just as a cartographer meticulously charts each landmark, a data scientist meticulously navigates through a series of well-defined steps to extract valuable knowledge from raw data. This guide delves into the core of the Data Science life cycle, illuminating each stage with clarity and precision. Whether you're a novice explorer or an experienced adventurer seeking to sharpen your skills, this exploration of the Data Science life cycle promises to be enlightening and rewarding. So, fasten your seatbelt as we embark on this enlightening journey through the steps that constitute the essence of Data Science courses.
In this article
-
What is a Data Science Life Cycle?
-
Who Are Involved in The Projects?
-
The Lifecycle of Data Science
-
Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Data Science Life Cycle?
The Data Science Life Cycle is a systematic and structured framework that guides data scientists through the process of extracting valuable insights and knowledge from raw data. It outlines a series of interconnected stages that collectively form a journey, beginning with problem identification and concluding with the deployment of data-driven solutions. This lifecycle serves as a roadmap, ensuring that data analysis projects are organized, efficient, and effective in addressing complex challenges.
At its core, the Data Science Life Cycle encompasses stages such as data collection, preprocessing, exploratory data analysis, feature engineering, model development, evaluation, deployment, and continuous monitoring. Each of these stages plays a critical role in transforming data into actionable insights. Problem definition initiates the cycle by setting clear objectives and goals. Data collection acquires the necessary information for analysis, which then undergoes preprocessing to ensure accuracy and consistency. Exploratory data analysis uncovers patterns and anomalies, while feature engineering refines the data for modeling. Models are developed, evaluated, and tuned to provide predictive power, and finally, the insights derived are deployed into real-world applications.
In essence, the Data Science Life Cycle is a holistic approach that enables data scientists to navigate the complexities of data analysis, ensuring that every step contributes to informed decision-making and impactful solutions.
Who Are Involved in The Projects?
Data science projects typically involve a diverse team of professionals with complementary skills and expertise. The roles and responsibilities within a data science project can vary depending on the size of the team, the complexity of the project, and the specific goals of the analysis. Here are some key roles commonly involved in data science projects:
-
Data Scientist: Data scientists are the core members of the team responsible for designing and executing the analysis. They are skilled in programming, statistical analysis, machine learning, and domain knowledge. Data scientists handle tasks such as data preprocessing, model development, and interpretation of results.
-
Data Engineer: Data engineers are responsible for collecting, storing, and preparing the data for analysis. They create and maintain data pipelines, ensuring that data is accessible, reliable, and well-structured. Data engineers work closely with data scientists to provide them with the necessary data sets.
-
Domain Expert: A domain expert brings subject-matter knowledge to the team. They understand the specific industry, business context, and nuances of the problem being solved. Their insights help guide the analysis and ensure that the results are relevant and actionable.
-
Machine Learning Engineer: In projects where machine learning models are central, machine learning engineers work alongside data scientists to implement and optimize machine learning algorithms. They focus on scaling and deploying models for production.
-
Business Analyst: Business analysts bridge the gap between technical analysis and business goals. They help define the problem, gather requirements, and ensure that the analysis aligns with the organization's strategic objectives. They also play a key role in communicating results to stakeholders.
-
Project Manager: Project managers oversee the project's execution, timeline, and resources. They ensure that the project stays on track, milestones are met, and communication flows smoothly among team members. They also handle coordination and collaboration.
-
Data Analyst: Data analysts focus on exploratory data analysis, generating insights from data, and creating visualizations. They often work on smaller tasks within the project and support data scientists in understanding the data's characteristics.
-
UX/UI Designer: In projects involving user interfaces or dashboards, UX/UI designers create user-friendly interfaces for visualizing and interacting with data. They ensure that the interface is intuitive and meets user needs.
-
Data Privacy and Compliance Expert: Data privacy and compliance experts ensure that the project adheres to relevant data protection regulations. They address concerns related to data security, anonymization, and compliance with legal requirements.
-
Communication Specialist: Effective communication of findings is crucial. Communication specialists or data storytellers help distill complex results into understandable insights, making it easier for non-technical stakeholders to grasp the significance of the analysis.
It's important to note that some team members might take on multiple roles, especially in smaller teams or projects. Collaboration and effective communication among these diverse roles are essential for the success of a data science project.
The Lifecycle of Data Science
The lifecycle of Data Science, also known as the Data Science Lifecycle or Data Analytics Lifecycle, is a structured framework that outlines the stages involved in a data science project, from problem identification to solution deployment. This systematic approach ensures that data-driven projects are well-organized, efficient, and effective in generating actionable insights. The following are the typical stages of the Data Science Lifecycle:
-
Problem Definition: Clearly define the problem you aim to solve or the question you want to answer using data analysis. Understand the business context, objectives, and the expected outcome of the analysis.
-
Data Collection: Gather relevant data from various sources, such as databases, APIs, spreadsheets, or external data providers. Ensure the data is comprehensive, accurate, and representative of the problem at hand.
-
Data Cleaning and Preprocessing: Clean, transform, and preprocess the collected data to remove inconsistencies, handle missing values, and ensure data quality. This step is crucial for accurate and reliable analysis.
-
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Explore and analyze the data to gain insights into its characteristics, patterns, and relationships. EDA helps in identifying trends, outliers, and potential features for modeling.
-
Feature Engineering: Select, create, or transform features (variables) from the data that are relevant for building predictive models. This involves using domain knowledge to craft meaningful features.
-
Modeling: Develop and train machine learning or statistical models to address the defined problem. Choose appropriate algorithms, split data into training and validation sets, and fine-tune model parameters.
-
Validation and Evaluation: Validate the model's performance using validation techniques like cross-validation. Evaluate the model's accuracy, precision, recall, and other relevant metrics using unseen data.
-
Model Selection and Tuning: Select the best-performing model and fine-tune its parameters to optimize its performance on new data. This step involves iterative adjustments to improve the model's generalization.
-
Deployment: Implement the model into a production environment for real-world use. Integrate the model into software systems, APIs, or create user interfaces to make predictions on new data.
-
Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuously monitor the model's performance in the production environment. Update and retrain the model as needed to adapt to changing data distributions or business requirements.
-
Communication of Results: Communicate the insights, findings, and conclusions drawn from the analysis to stakeholders. Use visualizations, reports, and presentations to effectively convey the significance of the results.
-
Feedback and Iteration: Gather feedback from stakeholders and users of the deployed solution. Iterate on the model or analysis based on feedback to improve accuracy and relevance.
The Data Science Lifecycle is not always linear; iterations and feedback loops are common, especially in complex projects. Each stage is interconnected, and the process is often iterative, allowing data scientists to refine their approach based on insights gained during the project. This lifecycle serves as a roadmap, guiding data science teams through the process of turning raw data into actionable insights and solutions that drive informed decision-making.
Conclusion
In the rapidly evolving landscape of data-driven decision-making, the Data Science Lifecycle stands as a steadfast guide, leading us through the intricate journey from raw data to actionable insights. As we draw the curtains on this exploration, it's evident that this structured framework is not just a mere sequence of steps but a dynamic process that empowers us to unlock the hidden potential within data.
From the initial spark of problem identification to the final crescendo of deploying a predictive model, the lifecycle encapsulates the essence of collaboration, innovation, and meticulous analysis. It encapsulates the collective efforts of data scientists, domain experts, engineers, and communicators, all synergizing their talents to extract valuable meaning from data's vast depths.
Embracing the iterative nature of the lifecycle, we find ourselves revisiting, refining, and expanding our perspectives with each cycle. This iterative dance nurtures growth and ensures our solutions remain relevant and potent in the face of changing landscapes.
In the end, the Data Science Lifecycle is not just a series of steps but a story of transformation. It's the story of turning numbers into narratives, data into decisions, and uncertainty into understanding. Armed with this comprehensive approach, we are empowered to navigate the complexities of the data universe, illuminate the darkest corners with insights, and ultimately shape a future driven by the power of informed choices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Data Science Lifecycle? The Data Science Lifecycle is a structured framework that outlines the stages involved in a data science project. It encompasses processes from problem identification, data collection, and analysis to model development, deployment, and continuous monitoring. This lifecycle guides data scientists in a systematic approach to derive insights and solutions from data.
2. Why is the Data Science Lifecycle important? The Data Science Lifecycle provides a clear roadmap for data-driven projects, ensuring that they are organized, efficient, and effective. It helps in maintaining consistency, improving collaboration, and generating reliable results by following a step-by-step approach.
3. What are the main stages of the Data Science Lifecycle? The main stages include problem definition, data collection, data cleaning and preprocessing, exploratory data analysis, feature engineering, modeling, validation and evaluation, model selection and tuning, deployment, monitoring and maintenance, communication of results, and feedback and iteration.
4. Who is involved in data science projects? Data science projects involve a diverse team including data scientists, data engineers, domain experts, machine learning engineers, business analysts, project managers, UX/UI designers, communication specialists, and more. Collaboration among these roles is essential for a successful project.
5. Is the Data Science Lifecycle linear? The lifecycle is not strictly linear; it's often iterative. Teams revisit stages based on insights gained, feedback received, or changes in project goals. This iterative approach allows for refinement and improvement throughout the project.
6. What is the role of exploratory data analysis (EDA)? Exploratory data analysis involves analyzing and visualizing data to understand its characteristics, uncover patterns, and identify potential outliers or trends. EDA helps data scientists form hypotheses, guide feature selection, and gain insights before building models.
7. How does the Data Science Lifecycle adapt to changing data or business needs? The lifecycle's iterative nature allows it to adapt. As new data becomes available or business requirements change, the team can revisit stages like model tuning, feature engineering, or even problem definition to ensure the analysis remains relevant and effective.
8. How does the lifecycle handle model deployment? Model deployment involves integrating the developed model into a real-world environment, such as a software system or user interface. The deployment stage ensures that the model is operational and can make predictions on new data.
9. What is the role of communication in the lifecycle? Communication is crucial for conveying insights and results to stakeholders who may not have technical backgrounds. Effective communication specialists or data storytellers ensure that complex findings are presented in an understandable and impactful manner.
10. Why is feedback and iteration important in the Data Science Lifecycle? Feedback and iteration allow projects to improve over time. By gathering feedback from stakeholders and users of the deployed solution, teams can make adjustments, refine models, and enhance the overall effectiveness of the analysis.
Personalized Recommendations with Machine Learning:Deep Dive
Welcome to a captivating exploration of "Personalized Recommendations through Machine Learning: A Deep Dive." In today's data-driven world, where choices abound and time is precious, the art of tailored suggestions has become an essential element of our digital landscape. Imagine a realm where technology acts as your perceptive guide, unveiling content, products, and experiences that align seamlessly with your preferences. This journey into the realm of personalized recommendations is not just a whimsical fantasy—it's powered by the prowess of Machine Learning Certification, a technology that enables computers to learn and adapt from data, making predictions that seem almost magical. Embark on this immersive journey as we uncover the intricacies of how Machine Learning Certification transforms raw data into recommendations that resonate with your unique tastes, all while delving into the mechanisms that safeguard your privacy and uphold ethical standards. Join us as we dive into the fascinating world where algorithms decipher the nuances of your digital footprint, opening doors to an experience that feels truly tailor-made.
In this article
-
Personalization and Recommender Systems in a Nutshell
-
How do ML-powered Recommendation Systems Work
-
Types of Recommender Systems
-
Best Practices for ML-based Recommender Engines
-
Examples of Recommender Systems
-
Recommendation System Market Trends
-
Top Recommendation Systems on The Internet
-
What Does the Future Hold for Recommender Systems
-
Recommender Systems: Sales Booster or Threat to Privacy
-
Final Words
-
Frequently Asked Questions
Personalization and Recommender Systems in a Nutshell
Imagine scrolling through your favorite app or website, and it's as if it knows you better than anyone. That's personalization at play. It's like having a virtual assistant that takes note of what you enjoy and tailors your experience accordingly. Whether it's suggesting movies, music, or products, the recommendations you receive are the result of Recommender Systems working behind the scenes. These systems are like expert matchmakers, analyzing your past interactions to predict what you might like next. They use complex techniques, such as Machine Learning, which is a kind of computer intelligence, to fine-tune their suggestions based on your behavior. So, when you stumble upon that perfect book or discover an amazing song, remember that these systems are the ones helping you uncover things you're likely to adore.
At the heart of this process lies personalization. It's all about enhancing your online journey by customizing content to resonate with your tastes. Recommender Systems make this possible, transforming mundane scrolling into an exciting adventure of discovery. By tapping into data from your past actions, these systems offer tailored recommendations that resonate with your preferences. Behind their seemingly magical abilities are algorithms fueled by Machine Learning, a technology that enables computers to learn from patterns in data. As you continue to explore new movies, articles, or products that seem almost tailor-made for you, it's the harmonious collaboration of personalization and Recommender Systems that's working tirelessly to make your digital experience truly exceptional.
How do ML-powered Recommendation Systems Work
Machine learning-powered recommendation systems work by using advanced algorithms to analyze patterns in user data and provide personalized suggestions. These systems rely on historical user interactions, such as clicks, purchases, or ratings, and item characteristics to make accurate predictions about what users might like. Here's a simplified explanation of how they work:
-
Data Collection:
-
User Data: Information about user behaviors and preferences, like what they've clicked on, liked, or bought.
-
Item Data: Details about the items available, such as descriptions, genres, or features.
-
Data Preprocessing:
-
Cleaning: Removing any errors or inconsistencies in the data.
-
Feature Extraction: Identifying relevant features from the data, like keywords or genres.
-
Algorithm Selection:
-
Collaborative Filtering: Finding similarities between users or items based on their interactions to make recommendations.
-
Content-Based Filtering: Using item characteristics to suggest items similar to ones the user has shown interest in.
-
Model Building:
-
Collaborative Filtering Models: Creating matrices that show relationships between users and items, which helps predict preferences.
-
Content-Based Models: Analyzing item features and user profiles to understand what users like.
-
Training and Learning:
-
The algorithm is "trained" using historical data to learn patterns and connections between users and items.
-
Machine learning algorithms adjust their internal settings to improve accuracy.
-
Prediction and Recommendation:
-
Once trained, the model can predict how much a user might like a certain item, even if they haven't interacted with it before.
-
For collaborative filtering, predictions are based on the preferences of similar users or items. For content-based, predictions rely on item attributes and user profiles.
-
Evaluation and Testing:
-
The system is tested using metrics like precision and recall to see how well it predicts user preferences.
-
A/B testing is often used to compare different recommendation strategies.
-
Feedback Loop and Improvement:
-
As users engage with recommendations, the system gathers more data, improving its accuracy over time.
-
The system continuously learns from new interactions and adjusts its predictions.
-
Personalization and User Experience:
-
The recommendation system tailors suggestions to each user, enhancing their experience by helping them discover things they might like.
-
Scaling and Deployment:
-
These systems need to work quickly and handle large amounts of data.
-
Scalable architectures and technologies ensure recommendations are generated in real-time.
-
Ethical Considerations:
-
Ensuring recommendations are unbiased and respecting user privacy is important.
-
Algorithms need to be designed to avoid creating "filter bubbles" or causing harm.
In essence, machine learning-powered recommendation systems take the guesswork out of finding things you'll enjoy. By analyzing your past interactions and comparing them with those of others, these systems help make your online experiences more enjoyable and tailored just for you.
Types of Recommender Systems
Recommender systems come in several types, each utilizing different techniques to provide personalized suggestions to users. The main types of recommender systems are:
-
Collaborative Filtering:
-
User-Based Collaborative Filtering: This method recommends items based on the preferences of users who are similar to the target user. If users A and B have similar tastes and both liked item X, the system might suggest item X to user A.
-
Item-Based Collaborative Filtering: Instead of comparing users, this approach identifies similarities between items. If users often like both items X and Y, the system might recommend item Y to a user who has shown interest in item X.
-
Content-Based Filtering:
-
Content-based filtering recommends items to users based on the attributes or features of the items and the user's past behavior. For instance, if a user has shown a preference for action movies, the system might recommend similar action movies.
-
Hybrid Recommender Systems:
-
These systems combine multiple recommendation techniques to provide more accurate and diverse suggestions. Hybrid systems might merge collaborative and content-based approaches to leverage their respective strengths.
-
Matrix Factorization:
-
Matrix factorization techniques decompose the user-item interaction matrix into latent factors, capturing underlying patterns. These factors are then used to predict user preferences for items.
-
Deep Learning-Based Recommenders:
-
Deep learning models, such as neural networks, are applied to recommendation tasks. These models can handle complex relationships between users and items, automatically learning features from the data.
-
Context-Aware Recommenders:
-
Context-aware systems take into account additional contextual information like time, location, or device. This information helps provide more relevant recommendations for specific situations.
-
Knowledge-Based Recommenders:
-
These systems use explicit knowledge about items and users to make recommendations. For example, a knowledge-based system might ask users questions to understand their preferences before suggesting items.
-
Association Rule Mining:
-
This technique identifies associations between items that are frequently co-purchased or consumed. It's often used in retail to suggest related products.
-
Singular Value Decomposition (SVD):
-
SVD is a matrix factorization method that decomposes the user-item interaction matrix to predict missing values and make recommendations.
-
Demographic-Based Recommenders:
-
These systems use demographic information, like age, gender, and location, to make recommendations. However, they might not capture individual preferences well.
-
Serendipity-Based Recommenders:
-
These systems introduce an element of surprise by suggesting items that are not directly related to a user's past behavior but might spark their interest.
-
Location-Based Recommenders:
-
These systems consider a user's geographical location to provide recommendations specific to their surroundings, such as nearby restaurants or events.
Each type of recommender system has its own strengths and limitations, and the choice of the right type depends on factors like available data, the application domain, and the desired level of personalization.
Best Practices for ML-based Recommender Engines
Creating effective machine learning-based recommender engines requires careful consideration and adherence to best practices. Here are some key guidelines to follow:
-
Data Quality and Preparation:
-
Ensure the data you collect is accurate, reliable, and representative of user preferences and interactions.
-
Clean and preprocess the data to remove duplicates, inconsistencies, and outliers that could affect the recommendations.
-
Algorithm Selection and Testing:
-
Choose appropriate algorithms based on your data and use case. Collaborative filtering, content-based methods, and hybrid approaches each have their strengths.
-
Test and evaluate different algorithms using appropriate metrics to identify the best-performing solution for your specific context.
-
Personalization and Diversity:
-
Strive for a balance between personalized recommendations and introducing diversity in suggestions to prevent creating "filter bubbles" and ensure serendipity.
-
Cold Start Problem:
-
Address the cold start problem for new users or items by leveraging metadata, demographics, or hybrid methods until sufficient data is available.
-
User Engagement and Experimentation:
-
Regularly experiment with different recommendation strategies using A/B testing to measure the impact on user engagement and conversion rates.
-
Explainability and Transparency:
-
Incorporate explainable AI techniques to provide users with insights into why specific recommendations are made, enhancing trust and user experience.
-
Scalability and Real-Time Recommendations:
-
Design your recommender system to handle increasing amounts of data and provide real-time recommendations without compromising performance.
-
Model Updates and Learning:
-
Implement mechanisms to update your recommendation models as new user interactions occur, ensuring that the system continuously adapts to changing preferences.
-
User Feedback and Signals:
-
Integrate user feedback, explicit ratings, and implicit signals (e.g., clicks, views) to refine and enhance the accuracy of recommendations.
-
Diversity and Serendipity:
-
Incorporate techniques that balance popular and niche recommendations, enabling users to discover items they might not have considered otherwise.
-
Ethical Considerations:
-
Be mindful of potential biases in recommendations and take measures to mitigate bias based on factors like age, gender, or cultural background.
-
Privacy and Data Security:
-
Implement robust data privacy measures to protect user information and comply with relevant data protection regulations.
-
Long-Term Engagement:
-
Focus on maintaining user engagement by avoiding overloading users with recommendations and providing a seamless experience.
-
User Interfaces and Presentation:
-
Pay attention to how recommendations are presented to users through user interfaces. Clear and user-friendly interfaces enhance the recommendation experience.
-
Monitoring and Maintenance:
-
Continuously monitor the performance of your recommender system and address any issues or anomalies that arise.
By adhering to these best practices, you can create a robust and effective machine learning-based recommender engine that not only delivers accurate recommendations but also enhances user satisfaction and engagement.
Examples of Recommender Systems
Recommender systems are widely used across various industries to provide personalized suggestions to users. Here are some examples of recommender systems in action:
-
E-commerce Platforms:
-
Amazon: Recommends products based on user purchase history, browsing behavior, and similar products purchased by others.
-
eBay: Suggests items based on user preferences, past purchases, and bidding history.
-
Streaming Services:
-
Netflix: Provides movie and TV show recommendations based on user viewing history, ratings, and genre preferences.
-
Spotify: Offers personalized playlists and music recommendations based on user listening habits and favorite genres.
-
Social Media Platforms:
-
Facebook: Suggests friends, groups, and pages to follow based on mutual friends, interests, and activities.
-
LinkedIn: Recommends professional connections, job openings, and relevant content based on user profile and interactions.
-
News and Content Aggregation Platforms:
-
Google News: Delivers personalized news articles based on user interests, location, and previous article interactions.
-
Flipboard: Curates articles and stories based on user-selected topics and interests.
-
Travel and Accommodation Services:
-
Airbnb: Recommends accommodations to users based on their preferences, travel history, and reviews of similar properties.
-
Expedia: Suggests flights, hotels, and vacation packages based on user search history and preferences.
-
Online Dating Apps:
-
Tinder: Provides potential matches based on user swipes, mutual interests, and location.
-
OkCupid: Uses user preferences, responses to personality questions, and compatibility scores to suggest matches.
-
Video Sharing Platforms:
-
YouTube: Offers video recommendations based on user viewing history, search queries, and similar videos watched by others.
-
TikTok: Presents short video content recommendations tailored to user interests and engagement patterns.
-
Restaurant and Food Delivery Apps:
-
Yelp: Recommends restaurants and eateries based on user reviews, ratings, and location.
-
Uber Eats: Suggests food options based on user preferences, previous orders, and popular local choices.
-
Gaming Platforms:
-
Steam: Recommends video games based on user gameplay history, genres preferred, and games played by friends.
-
Xbox Live: Provides game recommendations based on user gaming history, achievements, and community preferences.
These are just a few examples of how recommender systems are applied in different domains. These systems use various algorithms and techniques to analyze user data and provide personalized suggestions, enriching user experiences and driving engagement.
Recommendation System Market Trends
As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, here are some notable trends in the recommendation system market:
-
AI and Machine Learning Integration: The integration of advanced AI and machine learning techniques, such as deep learning and reinforcement learning, continues to enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of recommendation systems. These technologies enable systems to better understand user preferences and provide more precise suggestions.
-
Hyper-Personalization: Recommendation systems are moving beyond basic personalization to hyper-personalization. This involves tailoring recommendations not only based on past behaviors but also considering real-time context, individual preferences, and even physiological factors.
-
Context-Aware Recommendations: Contextual information, such as location, time of day, device, and user situation, is increasingly being integrated into recommendation algorithms. Context-aware recommendations provide more relevant and timely suggestions, enhancing user experiences.
-
Explainable AI (XAI): As recommendation systems become more complex, there's a growing need for transparency in the decision-making process. Explainable AI techniques are being used to provide users with understandable explanations for why specific recommendations are made.
-
Cross-Platform Recommendations: With users interacting across various devices and platforms, recommendation systems are adapting to provide consistent suggestions across different channels, creating a seamless and integrated user experience.
-
Ethical and Fair Recommendations: There's a heightened awareness of potential biases and ethical considerations in recommendation systems. Efforts are being made to ensure fairness, prevent discrimination, and mitigate the creation of echo chambers or filter bubbles.
-
Content Diversity: Recommendation systems are working to strike a balance between suggesting popular items and introducing users to diverse and less mainstream content. This encourages users to discover new interests and avoid over-representing popular items.
-
Privacy-Preserving Techniques: Users' data privacy is a growing concern. Recommendation systems are implementing techniques like federated learning and differential privacy to protect user data while still delivering effective recommendations.
-
Interdisciplinary Applications: Recommendation systems are expanding into new domains beyond e-commerce and entertainment. They are being utilized in healthcare, education, finance, and more, to provide tailored experiences and valuable insights.
-
Reinforcement Learning for Recommendations: Reinforcement learning techniques are gaining traction in recommendation systems, allowing algorithms to learn from user feedback over time and optimize recommendations for long-term engagement.
Please note that these trends are based on information available up to September 2021, and there may have been further developments in the recommendation system market since then. To get the most up-to-date information, I recommend checking industry reports, news sources, and research publications in the field of recommendation systems.
Top Recommendation Systems on The Internet
As of my last update in September 2021, several top recommendation systems on the internet were widely recognized for their effectiveness and user engagement. However, please note that the landscape of recommendation systems is continuously evolving, and there may have been new developments since then. Here are some of the well-known recommendation systems:
-
Netflix: Renowned for its personalized movie and TV show recommendations based on user viewing history, ratings, and interactions.
-
Amazon: Known for its product recommendation engine that suggests items based on user browsing history, purchases, and other behaviors.
-
YouTube: Offers video suggestions based on a user's viewing history, search queries, and engagement with similar videos.
-
Spotify: Provides personalized music recommendations and playlists based on a user's listening habits, favorite genres, and artist preferences.
-
LinkedIn: Recommends professional connections, job opportunities, and relevant content based on a user's profile, industry, and interactions.
-
TikTok: Delivers short video content recommendations tailored to a user's interests and engagement patterns.
-
Google News: Offers personalized news articles based on a user's interests, search history, and reading behavior.
-
Goodreads: Provides book recommendations based on a user's reading history, reviews, and genre preferences.
-
Pandora: Offers personalized music radio stations based on a user's favorite artists, songs, and musical preferences.
-
Pinterest: Suggests pins and boards based on a user's interests, previous pins, and interactions with similar content.
-
Zillow: Recommends real estate listings and properties based on a user's search history, preferences, and location.
-
Airbnb: Provides accommodation recommendations based on a user's travel history, preferences, and reviews of similar properties.
-
Waze: Offers personalized navigation routes based on real-time traffic data, user location, and historical driving patterns.
-
Quora: Recommends questions and answers based on a user's interests, followed topics, and past interactions.
-
IMDb: Provides movie and TV show recommendations based on a user's ratings, watch history, and genre preferences.
Remember that the effectiveness of these recommendation systems may vary based on individual user preferences and behaviors. Additionally, new recommendation systems may have emerged since my last update. To explore the latest and most effective recommendation systems, I recommend checking reviews, user feedback, and industry reports in the respective domains.
What Does the Future Hold for Recommender Systems
The future of recommender systems holds exciting possibilities as technology continues to advance. While I don't have information on developments beyond September 2021, I can provide some trends and directions that were anticipated for the future of recommender systems up to that point:
-
Hyper-Personalization: Recommender systems are likely to become even more finely tuned to individual preferences, taking into account not only past behaviors but also real-time context and physiological factors. This will provide users with an even more personalized and tailored experience.
-
Contextual Recommendations: The integration of contextual information such as location, time of day, device, and user situation will lead to more relevant and timely recommendations, enhancing the user experience.
-
Explainable AI (XAI): As recommendation algorithms become more complex, there's a growing need for transparency and interpretability. Explainable AI techniques will become more crucial to help users understand why specific recommendations are made.
-
Ethical Considerations: There's an increasing focus on addressing bias, discrimination, and fairness in recommendation systems. Future systems will strive to provide recommendations that are both personalized and unbiased.
-
Cross-Platform Recommendations: With users interacting across various devices and platforms, recommendation systems will work to provide consistent and seamless suggestions across different channels, ensuring a unified user experience.
-
Content Diversity: Future recommendation systems will aim to strike a balance between offering popular items and introducing users to more diverse and niche content, fostering discovery and preventing filter bubbles.
-
Privacy-Preserving Techniques: As data privacy concerns grow, recommender systems will employ techniques like federated learning and differential privacy to protect user data while maintaining effective recommendations.
-
Interdisciplinary Applications: Recommendation systems are expanding beyond traditional domains like e-commerce and entertainment. They will find applications in healthcare, education, finance, and more, providing personalized experiences and valuable insights.
-
Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning techniques will be leveraged more for long-term engagement, allowing recommendation algorithms to learn from user feedback over time and optimize recommendations accordingly.
-
Hybrid Models: The combination of different recommendation techniques, such as collaborative filtering and content-based approaches, will become more sophisticated and effective, leading to improved recommendations.
-
Sustainability and Ethics: Recommendation systems will also consider sustainability and ethical implications, recommending products and content that align with users' values and promoting environmentally conscious choices.
-
Enhanced User Interfaces: The way recommendations are presented to users will continue to evolve with improved interfaces, interactive elements, and more intuitive user experiences.
Remember that these trends are based on information available up to September 2021, and there may have been new developments in the field of recommendation systems since then. To stay up-to-date with the latest trends and advancements, it's recommended to follow industry reports, academic research, and news sources in the field.
Recommender Systems: Sales Booster or Threat to Privacy
Recommender systems have the potential to be both sales boosters and raise privacy concerns, depending on how they are implemented and used. Let's explore both aspects:
Sales Booster: Recommender systems can significantly boost sales and enhance user engagement. By providing personalized recommendations, these systems help users discover products, services, or content that align with their preferences. This can lead to increased user satisfaction, higher conversion rates, and improved customer retention. Businesses benefit from increased sales revenue and improved customer loyalty, as users find value in the tailored suggestions. Recommender systems can create a win-win situation where users find what they're looking for more easily, and businesses benefit from improved sales performance.
Threat to Privacy: On the flip side, recommender systems can pose privacy risks if not managed carefully. These systems gather and analyze user data to make recommendations, which can raise concerns about data privacy and security. If users' personal information, preferences, and behaviors are collected without their explicit consent or used inappropriately, it can lead to breaches of privacy. Users might feel uncomfortable knowing that their online activities are being tracked and used to influence their choices. Additionally, there's a potential for algorithms to reinforce biases or create "filter bubbles" by limiting exposure to diverse viewpoints or content.
To mitigate these privacy concerns, organizations should adopt responsible data practices:
-
Transparency: Users should be informed about what data is collected and how it will be used for recommendations. Clear privacy policies and terms of use are essential.
-
User Control: Users should have the ability to control their data and adjust their privacy settings. Providing options to opt out or limit data collection can empower users.
-
Anonymization: Whenever possible, user data should be anonymized or aggregated to protect individual identities.
-
Data Minimization: Collect only the necessary data to make accurate recommendations and avoid unnecessary intrusion into users' personal lives.
-
Security: Implement strong data security measures to protect user information from unauthorized access or breaches.
-
Bias Mitigation: Continuously monitor algorithms for biases and take steps to ensure fair and diverse recommendations.
-
Consent: Obtain explicit user consent before collecting and using their data for recommendation purposes.
In conclusion, recommender systems can serve as effective sales boosters by providing tailored suggestions that enhance user experience. However, they should be implemented responsibly to address privacy concerns and respect user preferences. Striking the right balance between personalization and privacy is essential to ensure that recommender systems benefit both businesses and users.
Final Words
In the dynamic landscape of technology and information, the role of recommender systems is both fascinating and impactful. These systems have the power to transform our digital experiences, making them more personalized, engaging, and convenient. As we navigate the world of recommendation algorithms, it's crucial to keep in mind the dual nature of their potential outcomes.
Recommender systems hold the promise of guiding us towards the things we're likely to enjoy, whether it's a new movie, a catchy song, a captivating book, or a product that perfectly fits our needs. They act as digital companions, learning from our actions and preferences to create a virtual world tailored just for us. However, as we embrace this personalized journey, we must also be vigilant about our privacy and the ethical implications of data usage.
In this ever-evolving landscape, transparency, user empowerment, and responsible data practices are paramount. As businesses leverage the power of recommender systems to boost sales and enhance user engagement, they should also prioritize safeguarding user privacy and promoting diversity of content.
As users, we have the opportunity to shape the future of recommender systems by making informed choices about data sharing, and by advocating for transparent, fair, and respectful use of our information.
In the end, recommender systems hold immense potential to enrich our lives, offering the joy of discovery and the convenience of tailored experiences. It's a journey worth embracing, one where we balance personalization with privacy and wield technology to our advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is a recommender system? A recommender system is a software tool or algorithm that provides personalized suggestions to users. It analyzes user behavior, preferences, and historical interactions to predict items they might be interested in and recommends them.
-
How do recommender systems work? Recommender systems work by analyzing user data and item characteristics. They use techniques like collaborative filtering (based on user similarities), content-based filtering (based on item attributes), and hybrid approaches to make predictions about user preferences.
-
What are the types of recommender systems? Common types of recommender systems include collaborative filtering, content-based filtering, hybrid systems (combining multiple approaches), matrix factorization, deep learning-based recommenders, and more.
-
Are recommender systems only used for e-commerce? No, recommender systems are used in various domains beyond e-commerce, including entertainment, social media, content platforms, travel, education, healthcare, and more. They enhance user experiences and engagement across diverse industries.
-
Are recommendation algorithms always accurate? Recommendation algorithms strive to be accurate, but their effectiveness can vary based on data quality, algorithm choice, and user behavior. Continuous improvement and user feedback help refine their accuracy.
-
Do recommendation systems invade user privacy? Some recommendation systems rely on user data for personalized suggestions, raising privacy concerns. Ethical implementation involves transparency, user control, data minimization, and responsible data practices to mitigate privacy risks.
-
Can recommendation systems perpetuate bias? Yes, if not carefully designed, recommendation systems can reinforce biases present in the data they use. Efforts are made to develop algorithms that provide fair and diverse recommendations.
-
How do recommendation systems benefit businesses? Recommendation systems can increase user engagement, boost sales, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance brand loyalty. Personalized recommendations lead to higher conversion rates and better user experiences.
-
What is the role of machine learning in recommender systems? Machine learning plays a crucial role in training recommendation algorithms. It helps algorithms learn patterns in user data and make accurate predictions about user preferences.
-
What is hyper-personalization in recommendation systems? Hyper-personalization refers to an advanced level of personalization where recommendations are finely tuned based on real-time context, individual preferences, and even physiological factors to create an extremely tailored user experience.
Read More
Welcome to a captivating exploration of "Personalized Recommendations through Machine Learning: A Deep Dive." In today's data-driven world, where choices abound and time is precious, the art of tailored suggestions has become an essential element of our digital landscape. Imagine a realm where technology acts as your perceptive guide, unveiling content, products, and experiences that align seamlessly with your preferences. This journey into the realm of personalized recommendations is not just a whimsical fantasy—it's powered by the prowess of Machine Learning Certification, a technology that enables computers to learn and adapt from data, making predictions that seem almost magical. Embark on this immersive journey as we uncover the intricacies of how Machine Learning Certification transforms raw data into recommendations that resonate with your unique tastes, all while delving into the mechanisms that safeguard your privacy and uphold ethical standards. Join us as we dive into the fascinating world where algorithms decipher the nuances of your digital footprint, opening doors to an experience that feels truly tailor-made.
In this article
-
Personalization and Recommender Systems in a Nutshell
-
How do ML-powered Recommendation Systems Work
-
Types of Recommender Systems
-
Best Practices for ML-based Recommender Engines
-
Examples of Recommender Systems
-
Recommendation System Market Trends
-
Top Recommendation Systems on The Internet
-
What Does the Future Hold for Recommender Systems
-
Recommender Systems: Sales Booster or Threat to Privacy
-
Final Words
-
Frequently Asked Questions
Personalization and Recommender Systems in a Nutshell
Imagine scrolling through your favorite app or website, and it's as if it knows you better than anyone. That's personalization at play. It's like having a virtual assistant that takes note of what you enjoy and tailors your experience accordingly. Whether it's suggesting movies, music, or products, the recommendations you receive are the result of Recommender Systems working behind the scenes. These systems are like expert matchmakers, analyzing your past interactions to predict what you might like next. They use complex techniques, such as Machine Learning, which is a kind of computer intelligence, to fine-tune their suggestions based on your behavior. So, when you stumble upon that perfect book or discover an amazing song, remember that these systems are the ones helping you uncover things you're likely to adore.
At the heart of this process lies personalization. It's all about enhancing your online journey by customizing content to resonate with your tastes. Recommender Systems make this possible, transforming mundane scrolling into an exciting adventure of discovery. By tapping into data from your past actions, these systems offer tailored recommendations that resonate with your preferences. Behind their seemingly magical abilities are algorithms fueled by Machine Learning, a technology that enables computers to learn from patterns in data. As you continue to explore new movies, articles, or products that seem almost tailor-made for you, it's the harmonious collaboration of personalization and Recommender Systems that's working tirelessly to make your digital experience truly exceptional.
How do ML-powered Recommendation Systems Work
Machine learning-powered recommendation systems work by using advanced algorithms to analyze patterns in user data and provide personalized suggestions. These systems rely on historical user interactions, such as clicks, purchases, or ratings, and item characteristics to make accurate predictions about what users might like. Here's a simplified explanation of how they work:
-
Data Collection:
-
User Data: Information about user behaviors and preferences, like what they've clicked on, liked, or bought.
-
Item Data: Details about the items available, such as descriptions, genres, or features.
-
-
Data Preprocessing:
-
Cleaning: Removing any errors or inconsistencies in the data.
-
Feature Extraction: Identifying relevant features from the data, like keywords or genres.
-
-
Algorithm Selection:
-
Collaborative Filtering: Finding similarities between users or items based on their interactions to make recommendations.
-
Content-Based Filtering: Using item characteristics to suggest items similar to ones the user has shown interest in.
-
-
Model Building:
-
Collaborative Filtering Models: Creating matrices that show relationships between users and items, which helps predict preferences.
-
Content-Based Models: Analyzing item features and user profiles to understand what users like.
-
-
Training and Learning:
-
The algorithm is "trained" using historical data to learn patterns and connections between users and items.
-
Machine learning algorithms adjust their internal settings to improve accuracy.
-
-
Prediction and Recommendation:
-
Once trained, the model can predict how much a user might like a certain item, even if they haven't interacted with it before.
-
For collaborative filtering, predictions are based on the preferences of similar users or items. For content-based, predictions rely on item attributes and user profiles.
-
-
Evaluation and Testing:
-
The system is tested using metrics like precision and recall to see how well it predicts user preferences.
-
A/B testing is often used to compare different recommendation strategies.
-
-
Feedback Loop and Improvement:
-
As users engage with recommendations, the system gathers more data, improving its accuracy over time.
-
The system continuously learns from new interactions and adjusts its predictions.
-
-
Personalization and User Experience:
-
The recommendation system tailors suggestions to each user, enhancing their experience by helping them discover things they might like.
-
-
Scaling and Deployment:
-
These systems need to work quickly and handle large amounts of data.
-
Scalable architectures and technologies ensure recommendations are generated in real-time.
-
-
Ethical Considerations:
-
Ensuring recommendations are unbiased and respecting user privacy is important.
-
Algorithms need to be designed to avoid creating "filter bubbles" or causing harm.
-
In essence, machine learning-powered recommendation systems take the guesswork out of finding things you'll enjoy. By analyzing your past interactions and comparing them with those of others, these systems help make your online experiences more enjoyable and tailored just for you.
Types of Recommender Systems
Recommender systems come in several types, each utilizing different techniques to provide personalized suggestions to users. The main types of recommender systems are:
-
Collaborative Filtering:
-
User-Based Collaborative Filtering: This method recommends items based on the preferences of users who are similar to the target user. If users A and B have similar tastes and both liked item X, the system might suggest item X to user A.
-
Item-Based Collaborative Filtering: Instead of comparing users, this approach identifies similarities between items. If users often like both items X and Y, the system might recommend item Y to a user who has shown interest in item X.
-
-
Content-Based Filtering:
-
Content-based filtering recommends items to users based on the attributes or features of the items and the user's past behavior. For instance, if a user has shown a preference for action movies, the system might recommend similar action movies.
-
-
Hybrid Recommender Systems:
-
These systems combine multiple recommendation techniques to provide more accurate and diverse suggestions. Hybrid systems might merge collaborative and content-based approaches to leverage their respective strengths.
-
-
Matrix Factorization:
-
Matrix factorization techniques decompose the user-item interaction matrix into latent factors, capturing underlying patterns. These factors are then used to predict user preferences for items.
-
-
Deep Learning-Based Recommenders:
-
Deep learning models, such as neural networks, are applied to recommendation tasks. These models can handle complex relationships between users and items, automatically learning features from the data.
-
-
Context-Aware Recommenders:
-
Context-aware systems take into account additional contextual information like time, location, or device. This information helps provide more relevant recommendations for specific situations.
-
-
Knowledge-Based Recommenders:
-
These systems use explicit knowledge about items and users to make recommendations. For example, a knowledge-based system might ask users questions to understand their preferences before suggesting items.
-
-
Association Rule Mining:
-
This technique identifies associations between items that are frequently co-purchased or consumed. It's often used in retail to suggest related products.
-
-
Singular Value Decomposition (SVD):
-
SVD is a matrix factorization method that decomposes the user-item interaction matrix to predict missing values and make recommendations.
-
-
Demographic-Based Recommenders:
-
These systems use demographic information, like age, gender, and location, to make recommendations. However, they might not capture individual preferences well.
-
-
Serendipity-Based Recommenders:
-
These systems introduce an element of surprise by suggesting items that are not directly related to a user's past behavior but might spark their interest.
-
-
Location-Based Recommenders:
-
These systems consider a user's geographical location to provide recommendations specific to their surroundings, such as nearby restaurants or events.
-
Each type of recommender system has its own strengths and limitations, and the choice of the right type depends on factors like available data, the application domain, and the desired level of personalization.
Best Practices for ML-based Recommender Engines
Creating effective machine learning-based recommender engines requires careful consideration and adherence to best practices. Here are some key guidelines to follow:
-
Data Quality and Preparation:
-
Ensure the data you collect is accurate, reliable, and representative of user preferences and interactions.
-
Clean and preprocess the data to remove duplicates, inconsistencies, and outliers that could affect the recommendations.
-
-
Algorithm Selection and Testing:
-
Choose appropriate algorithms based on your data and use case. Collaborative filtering, content-based methods, and hybrid approaches each have their strengths.
-
Test and evaluate different algorithms using appropriate metrics to identify the best-performing solution for your specific context.
-
-
Personalization and Diversity:
-
Strive for a balance between personalized recommendations and introducing diversity in suggestions to prevent creating "filter bubbles" and ensure serendipity.
-
-
Cold Start Problem:
-
Address the cold start problem for new users or items by leveraging metadata, demographics, or hybrid methods until sufficient data is available.
-
-
User Engagement and Experimentation:
-
Regularly experiment with different recommendation strategies using A/B testing to measure the impact on user engagement and conversion rates.
-
-
Explainability and Transparency:
-
Incorporate explainable AI techniques to provide users with insights into why specific recommendations are made, enhancing trust and user experience.
-
-
Scalability and Real-Time Recommendations:
-
Design your recommender system to handle increasing amounts of data and provide real-time recommendations without compromising performance.
-
-
Model Updates and Learning:
-
Implement mechanisms to update your recommendation models as new user interactions occur, ensuring that the system continuously adapts to changing preferences.
-
-
User Feedback and Signals:
-
Integrate user feedback, explicit ratings, and implicit signals (e.g., clicks, views) to refine and enhance the accuracy of recommendations.
-
-
Diversity and Serendipity:
-
Incorporate techniques that balance popular and niche recommendations, enabling users to discover items they might not have considered otherwise.
-
-
Ethical Considerations:
-
Be mindful of potential biases in recommendations and take measures to mitigate bias based on factors like age, gender, or cultural background.
-
-
Privacy and Data Security:
-
Implement robust data privacy measures to protect user information and comply with relevant data protection regulations.
-
-
Long-Term Engagement:
-
Focus on maintaining user engagement by avoiding overloading users with recommendations and providing a seamless experience.
-
-
User Interfaces and Presentation:
-
Pay attention to how recommendations are presented to users through user interfaces. Clear and user-friendly interfaces enhance the recommendation experience.
-
-
Monitoring and Maintenance:
-
Continuously monitor the performance of your recommender system and address any issues or anomalies that arise.
-
By adhering to these best practices, you can create a robust and effective machine learning-based recommender engine that not only delivers accurate recommendations but also enhances user satisfaction and engagement.
Examples of Recommender Systems
Recommender systems are widely used across various industries to provide personalized suggestions to users. Here are some examples of recommender systems in action:
-
E-commerce Platforms:
-
Amazon: Recommends products based on user purchase history, browsing behavior, and similar products purchased by others.
-
eBay: Suggests items based on user preferences, past purchases, and bidding history.
-
-
Streaming Services:
-
Netflix: Provides movie and TV show recommendations based on user viewing history, ratings, and genre preferences.
-
Spotify: Offers personalized playlists and music recommendations based on user listening habits and favorite genres.
-
-
Social Media Platforms:
-
Facebook: Suggests friends, groups, and pages to follow based on mutual friends, interests, and activities.
-
LinkedIn: Recommends professional connections, job openings, and relevant content based on user profile and interactions.
-
-
News and Content Aggregation Platforms:
-
Google News: Delivers personalized news articles based on user interests, location, and previous article interactions.
-
Flipboard: Curates articles and stories based on user-selected topics and interests.
-
-
Travel and Accommodation Services:
-
Airbnb: Recommends accommodations to users based on their preferences, travel history, and reviews of similar properties.
-
Expedia: Suggests flights, hotels, and vacation packages based on user search history and preferences.
-
-
Online Dating Apps:
-
Tinder: Provides potential matches based on user swipes, mutual interests, and location.
-
OkCupid: Uses user preferences, responses to personality questions, and compatibility scores to suggest matches.
-
-
Video Sharing Platforms:
-
YouTube: Offers video recommendations based on user viewing history, search queries, and similar videos watched by others.
-
TikTok: Presents short video content recommendations tailored to user interests and engagement patterns.
-
-
Restaurant and Food Delivery Apps:
-
Yelp: Recommends restaurants and eateries based on user reviews, ratings, and location.
-
Uber Eats: Suggests food options based on user preferences, previous orders, and popular local choices.
-
-
Gaming Platforms:
-
Steam: Recommends video games based on user gameplay history, genres preferred, and games played by friends.
-
Xbox Live: Provides game recommendations based on user gaming history, achievements, and community preferences.
-
These are just a few examples of how recommender systems are applied in different domains. These systems use various algorithms and techniques to analyze user data and provide personalized suggestions, enriching user experiences and driving engagement.
Recommendation System Market Trends
As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, here are some notable trends in the recommendation system market:
-
AI and Machine Learning Integration: The integration of advanced AI and machine learning techniques, such as deep learning and reinforcement learning, continues to enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of recommendation systems. These technologies enable systems to better understand user preferences and provide more precise suggestions.
-
Hyper-Personalization: Recommendation systems are moving beyond basic personalization to hyper-personalization. This involves tailoring recommendations not only based on past behaviors but also considering real-time context, individual preferences, and even physiological factors.
-
Context-Aware Recommendations: Contextual information, such as location, time of day, device, and user situation, is increasingly being integrated into recommendation algorithms. Context-aware recommendations provide more relevant and timely suggestions, enhancing user experiences.
-
Explainable AI (XAI): As recommendation systems become more complex, there's a growing need for transparency in the decision-making process. Explainable AI techniques are being used to provide users with understandable explanations for why specific recommendations are made.
-
Cross-Platform Recommendations: With users interacting across various devices and platforms, recommendation systems are adapting to provide consistent suggestions across different channels, creating a seamless and integrated user experience.
-
Ethical and Fair Recommendations: There's a heightened awareness of potential biases and ethical considerations in recommendation systems. Efforts are being made to ensure fairness, prevent discrimination, and mitigate the creation of echo chambers or filter bubbles.
-
Content Diversity: Recommendation systems are working to strike a balance between suggesting popular items and introducing users to diverse and less mainstream content. This encourages users to discover new interests and avoid over-representing popular items.
-
Privacy-Preserving Techniques: Users' data privacy is a growing concern. Recommendation systems are implementing techniques like federated learning and differential privacy to protect user data while still delivering effective recommendations.
-
Interdisciplinary Applications: Recommendation systems are expanding into new domains beyond e-commerce and entertainment. They are being utilized in healthcare, education, finance, and more, to provide tailored experiences and valuable insights.
-
Reinforcement Learning for Recommendations: Reinforcement learning techniques are gaining traction in recommendation systems, allowing algorithms to learn from user feedback over time and optimize recommendations for long-term engagement.
Please note that these trends are based on information available up to September 2021, and there may have been further developments in the recommendation system market since then. To get the most up-to-date information, I recommend checking industry reports, news sources, and research publications in the field of recommendation systems.
Top Recommendation Systems on The Internet
As of my last update in September 2021, several top recommendation systems on the internet were widely recognized for their effectiveness and user engagement. However, please note that the landscape of recommendation systems is continuously evolving, and there may have been new developments since then. Here are some of the well-known recommendation systems:
-
Netflix: Renowned for its personalized movie and TV show recommendations based on user viewing history, ratings, and interactions.
-
Amazon: Known for its product recommendation engine that suggests items based on user browsing history, purchases, and other behaviors.
-
YouTube: Offers video suggestions based on a user's viewing history, search queries, and engagement with similar videos.
-
Spotify: Provides personalized music recommendations and playlists based on a user's listening habits, favorite genres, and artist preferences.
-
LinkedIn: Recommends professional connections, job opportunities, and relevant content based on a user's profile, industry, and interactions.
-
TikTok: Delivers short video content recommendations tailored to a user's interests and engagement patterns.
-
Google News: Offers personalized news articles based on a user's interests, search history, and reading behavior.
-
Goodreads: Provides book recommendations based on a user's reading history, reviews, and genre preferences.
-
Pandora: Offers personalized music radio stations based on a user's favorite artists, songs, and musical preferences.
-
Pinterest: Suggests pins and boards based on a user's interests, previous pins, and interactions with similar content.
-
Zillow: Recommends real estate listings and properties based on a user's search history, preferences, and location.
-
Airbnb: Provides accommodation recommendations based on a user's travel history, preferences, and reviews of similar properties.
-
Waze: Offers personalized navigation routes based on real-time traffic data, user location, and historical driving patterns.
-
Quora: Recommends questions and answers based on a user's interests, followed topics, and past interactions.
-
IMDb: Provides movie and TV show recommendations based on a user's ratings, watch history, and genre preferences.
Remember that the effectiveness of these recommendation systems may vary based on individual user preferences and behaviors. Additionally, new recommendation systems may have emerged since my last update. To explore the latest and most effective recommendation systems, I recommend checking reviews, user feedback, and industry reports in the respective domains.
What Does the Future Hold for Recommender Systems
The future of recommender systems holds exciting possibilities as technology continues to advance. While I don't have information on developments beyond September 2021, I can provide some trends and directions that were anticipated for the future of recommender systems up to that point:
-
Hyper-Personalization: Recommender systems are likely to become even more finely tuned to individual preferences, taking into account not only past behaviors but also real-time context and physiological factors. This will provide users with an even more personalized and tailored experience.
-
Contextual Recommendations: The integration of contextual information such as location, time of day, device, and user situation will lead to more relevant and timely recommendations, enhancing the user experience.
-
Explainable AI (XAI): As recommendation algorithms become more complex, there's a growing need for transparency and interpretability. Explainable AI techniques will become more crucial to help users understand why specific recommendations are made.
-
Ethical Considerations: There's an increasing focus on addressing bias, discrimination, and fairness in recommendation systems. Future systems will strive to provide recommendations that are both personalized and unbiased.
-
Cross-Platform Recommendations: With users interacting across various devices and platforms, recommendation systems will work to provide consistent and seamless suggestions across different channels, ensuring a unified user experience.
-
Content Diversity: Future recommendation systems will aim to strike a balance between offering popular items and introducing users to more diverse and niche content, fostering discovery and preventing filter bubbles.
-
Privacy-Preserving Techniques: As data privacy concerns grow, recommender systems will employ techniques like federated learning and differential privacy to protect user data while maintaining effective recommendations.
-
Interdisciplinary Applications: Recommendation systems are expanding beyond traditional domains like e-commerce and entertainment. They will find applications in healthcare, education, finance, and more, providing personalized experiences and valuable insights.
-
Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning techniques will be leveraged more for long-term engagement, allowing recommendation algorithms to learn from user feedback over time and optimize recommendations accordingly.
-
Hybrid Models: The combination of different recommendation techniques, such as collaborative filtering and content-based approaches, will become more sophisticated and effective, leading to improved recommendations.
-
Sustainability and Ethics: Recommendation systems will also consider sustainability and ethical implications, recommending products and content that align with users' values and promoting environmentally conscious choices.
-
Enhanced User Interfaces: The way recommendations are presented to users will continue to evolve with improved interfaces, interactive elements, and more intuitive user experiences.
Remember that these trends are based on information available up to September 2021, and there may have been new developments in the field of recommendation systems since then. To stay up-to-date with the latest trends and advancements, it's recommended to follow industry reports, academic research, and news sources in the field.
Recommender Systems: Sales Booster or Threat to Privacy
Recommender systems have the potential to be both sales boosters and raise privacy concerns, depending on how they are implemented and used. Let's explore both aspects:
Sales Booster: Recommender systems can significantly boost sales and enhance user engagement. By providing personalized recommendations, these systems help users discover products, services, or content that align with their preferences. This can lead to increased user satisfaction, higher conversion rates, and improved customer retention. Businesses benefit from increased sales revenue and improved customer loyalty, as users find value in the tailored suggestions. Recommender systems can create a win-win situation where users find what they're looking for more easily, and businesses benefit from improved sales performance.
Threat to Privacy: On the flip side, recommender systems can pose privacy risks if not managed carefully. These systems gather and analyze user data to make recommendations, which can raise concerns about data privacy and security. If users' personal information, preferences, and behaviors are collected without their explicit consent or used inappropriately, it can lead to breaches of privacy. Users might feel uncomfortable knowing that their online activities are being tracked and used to influence their choices. Additionally, there's a potential for algorithms to reinforce biases or create "filter bubbles" by limiting exposure to diverse viewpoints or content.
To mitigate these privacy concerns, organizations should adopt responsible data practices:
-
Transparency: Users should be informed about what data is collected and how it will be used for recommendations. Clear privacy policies and terms of use are essential.
-
User Control: Users should have the ability to control their data and adjust their privacy settings. Providing options to opt out or limit data collection can empower users.
-
Anonymization: Whenever possible, user data should be anonymized or aggregated to protect individual identities.
-
Data Minimization: Collect only the necessary data to make accurate recommendations and avoid unnecessary intrusion into users' personal lives.
-
Security: Implement strong data security measures to protect user information from unauthorized access or breaches.
-
Bias Mitigation: Continuously monitor algorithms for biases and take steps to ensure fair and diverse recommendations.
-
Consent: Obtain explicit user consent before collecting and using their data for recommendation purposes.
In conclusion, recommender systems can serve as effective sales boosters by providing tailored suggestions that enhance user experience. However, they should be implemented responsibly to address privacy concerns and respect user preferences. Striking the right balance between personalization and privacy is essential to ensure that recommender systems benefit both businesses and users.
Final Words
In the dynamic landscape of technology and information, the role of recommender systems is both fascinating and impactful. These systems have the power to transform our digital experiences, making them more personalized, engaging, and convenient. As we navigate the world of recommendation algorithms, it's crucial to keep in mind the dual nature of their potential outcomes.
Recommender systems hold the promise of guiding us towards the things we're likely to enjoy, whether it's a new movie, a catchy song, a captivating book, or a product that perfectly fits our needs. They act as digital companions, learning from our actions and preferences to create a virtual world tailored just for us. However, as we embrace this personalized journey, we must also be vigilant about our privacy and the ethical implications of data usage.
In this ever-evolving landscape, transparency, user empowerment, and responsible data practices are paramount. As businesses leverage the power of recommender systems to boost sales and enhance user engagement, they should also prioritize safeguarding user privacy and promoting diversity of content.
As users, we have the opportunity to shape the future of recommender systems by making informed choices about data sharing, and by advocating for transparent, fair, and respectful use of our information.
In the end, recommender systems hold immense potential to enrich our lives, offering the joy of discovery and the convenience of tailored experiences. It's a journey worth embracing, one where we balance personalization with privacy and wield technology to our advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is a recommender system? A recommender system is a software tool or algorithm that provides personalized suggestions to users. It analyzes user behavior, preferences, and historical interactions to predict items they might be interested in and recommends them.
-
How do recommender systems work? Recommender systems work by analyzing user data and item characteristics. They use techniques like collaborative filtering (based on user similarities), content-based filtering (based on item attributes), and hybrid approaches to make predictions about user preferences.
-
What are the types of recommender systems? Common types of recommender systems include collaborative filtering, content-based filtering, hybrid systems (combining multiple approaches), matrix factorization, deep learning-based recommenders, and more.
-
Are recommender systems only used for e-commerce? No, recommender systems are used in various domains beyond e-commerce, including entertainment, social media, content platforms, travel, education, healthcare, and more. They enhance user experiences and engagement across diverse industries.
-
Are recommendation algorithms always accurate? Recommendation algorithms strive to be accurate, but their effectiveness can vary based on data quality, algorithm choice, and user behavior. Continuous improvement and user feedback help refine their accuracy.
-
Do recommendation systems invade user privacy? Some recommendation systems rely on user data for personalized suggestions, raising privacy concerns. Ethical implementation involves transparency, user control, data minimization, and responsible data practices to mitigate privacy risks.
-
Can recommendation systems perpetuate bias? Yes, if not carefully designed, recommendation systems can reinforce biases present in the data they use. Efforts are made to develop algorithms that provide fair and diverse recommendations.
-
How do recommendation systems benefit businesses? Recommendation systems can increase user engagement, boost sales, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance brand loyalty. Personalized recommendations lead to higher conversion rates and better user experiences.
-
What is the role of machine learning in recommender systems? Machine learning plays a crucial role in training recommendation algorithms. It helps algorithms learn patterns in user data and make accurate predictions about user preferences.
-
What is hyper-personalization in recommendation systems? Hyper-personalization refers to an advanced level of personalization where recommendations are finely tuned based on real-time context, individual preferences, and even physiological factors to create an extremely tailored user experience.
What a Business Process Analyst Can Do:A Comprehensive Guide
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations are constantly striving to optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and achieve strategic objectives. This is where the role of a Business Process Analyst becomes indispensable. A Business Process Analyst acts as a crucial bridge between business stakeholders and technology solutions, working to identify, analyze, and improve business processes to drive organizational growth and success.
The primary responsibility of a Business Process Analyst is to understand the inner workings of an organization, its objectives, and its current operational procedures. By collaborating with various stakeholders, including executives, managers, and end-users, the analyst gains a comprehensive understanding of the existing processes and identifies areas that require improvement or reengineering.
With their analytical acumen and keen eye for detail, Business Process Analysts employ a systematic approach to analyze data, identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas of potential risk. They leverage their expertise in process mapping, data analysis, and industry best practices to propose innovative solutions that streamline operations, enhance productivity, and drive cost savings.
Business Process Analysts are also adept at translating complex technical jargon into easily understandable language for non-technical stakeholders. They possess excellent communication and interpersonal skills, allowing them to facilitate effective communication and collaboration between different teams and departments within an organization.
Furthermore, Business Process Analysts play a crucial role in technology implementation projects. They work closely with IT teams and software developers to ensure that the identified process improvements are successfully implemented. They also conduct thorough testing and evaluation of new systems to guarantee that they align with the organization's requirements and goals.
In summary, a Business Process Analyst serves as a catalyst for organizational change and improvement. By conducting in-depth analysis, identifying inefficiencies, and recommending strategic solutions, these professionals contribute significantly to enhancing operational effectiveness, driving growth, and enabling organizations to adapt to ever-changing market dynamics. With their versatile skill set and holistic approach, Business Process Analysts are vital assets for any business seeking to stay competitive in today's dynamic and demanding business environment.
Table of Contents
-
Definition of a Business Process Analyst
-
Importance of Business Process Analysts
-
Roles and responsibilities of a Business Process Analyst
-
Skills of a Business Process Analyst
-
Tools and techniques used
-
Business Process Analyst career path
-
Business Process Analyst jobs and salary
-
Conclusion
Definition of a Business Process Analyst
A Business Process Analyst is a professional who specializes in analyzing, documenting, and improving the operational processes within an organization. They possess a deep understanding of business operations and use their analytical skills to identify areas of inefficiency, bottlenecks, and opportunities for improvement. Their primary goal is to optimize processes to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and align operations with strategic objectives.
Business Process Analysts work closely with stakeholders from various departments, including executives, managers, and end-users, to gather information about existing processes. They utilize tools such as process mapping, data analysis, and interviews to gain a comprehensive understanding of the current state of operations.
Once they have identified areas for improvement, Business Process Analysts propose and implement changes to streamline processes and eliminate redundancies. They may recommend the adoption of new technologies, changes in workflows, or modifications to standard operating procedures. They also collaborate with IT teams and software developers to ensure the successful implementation of process enhancements.
In addition to analyzing and improving existing processes, Business Process Analysts are often involved in designing and implementing new processes for emerging business needs. They stay up to date with industry best practices and emerging trends to bring innovative and effective solutions to the table.
Effective communication and interpersonal skills are essential for Business Process Analysts, as they need to work collaboratively with different stakeholders and translate complex technical concepts into easily understandable language for non-technical individuals. They also play a key role in change management, helping employees adapt to new processes and technologies through training and support.
Overall, a Business Process Analyst is a critical asset to organizations seeking to optimize their operations and achieve sustainable growth. Through their expertise in process analysis, problem-solving, and continuous improvement, they contribute to enhancing efficiency, increasing customer satisfaction, and driving overall business success.
Importance of Business Process Analysts
Business Process Analysts play a crucial role in organizations for several reasons. Here are some key reasons highlighting the importance of Business Process Analysts:
-
Process Optimization: Business Process Analysts are adept at identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas of improvement within organizational processes. By conducting thorough analysis and using their expertise, they help streamline workflows, reduce redundancies, and improve overall operational efficiency. This optimization leads to cost savings, increased productivity, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
-
Strategic Alignment: Business Process Analysts ensure that business processes align with strategic objectives. They evaluate existing processes and identify opportunities to align them with the organization's goals and vision. By mapping processes to strategic objectives, they help drive the achievement of targets and promote long-term success.
-
Technology Implementation: In today's technology-driven world, Business Process Analysts play a vital role in the successful implementation of new technologies and systems. They collaborate with IT teams and software developers to ensure that technology solutions are aligned with business requirements. Their expertise in understanding both business processes and technical aspects enables them to bridge the gap between business stakeholders and technology teams, ensuring effective implementation.
-
Continuous Improvement: Business Process Analysts foster a culture of continuous improvement within organizations. They actively seek feedback from stakeholders, monitor performance metrics, and identify areas for further enhancement. By implementing a cycle of continuous improvement, they help organizations stay agile, adapt to changing market conditions, and maintain a competitive edge.
-
Risk Mitigation: Business Process Analysts are skilled in identifying potential risks within processes and implementing mitigation strategies. By conducting risk assessments, they minimize operational vulnerabilities, address compliance issues, and ensure that processes are executed smoothly and securely. This proactive approach to risk management helps safeguard the organization's reputation and minimizes financial losses.
-
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Business Process Analysts act as facilitators, bringing together teams from different departments and fostering effective communication and collaboration. They bridge the gap between business stakeholders, IT teams, and end-users, ensuring that everyone is aligned and working towards common objectives. Their ability to translate technical jargon into easily understandable language helps build stronger relationships and promote teamwork.
-
Change Management: Implementing process changes can often be met with resistance from employees. Business Process Analysts are skilled in change management techniques, helping employees adapt to new processes through effective training, communication, and support. Their involvement in the change management process increases employee buy-in and smooths the transition to new ways of working.
In summary, Business Process Analysts play a pivotal role in driving operational excellence, fostering innovation, and achieving organizational goals. Their ability to optimize processes, align strategies, manage risks, and facilitate collaboration makes them essential assets for organizations striving for continuous improvement and long-term success.
Roles and responsibilities of a Business Process Analyst
The roles and responsibilities of a Business Process Analyst may vary depending on the organization and industry. However, here are some common key roles and responsibilities associated with the position:
-
Process Analysis and Documentation: The primary responsibility of a Business Process Analyst is to analyze existing business processes. This involves gathering information, conducting process mapping exercises, and documenting current procedures. They identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement through data analysis and stakeholder consultations.
-
Process Improvement and Optimization: Business Process Analysts are responsible for recommending and implementing process improvements. They identify opportunities to streamline workflows, eliminate redundancies, and enhance efficiency. They may suggest changes to technology systems, workflows, or operating procedures to achieve optimal results. They work closely with stakeholders to gain buy-in and ensure successful implementation.
-
Requirements Gathering and Analysis: Business Process Analysts work with business stakeholders to understand their requirements and objectives. They gather and analyze data to identify gaps and align business processes with strategic goals. They translate business needs into functional requirements that can guide process improvements and technology implementations.
-
Technology Integration and Support: Business Process Analysts collaborate with IT teams to integrate technology solutions that support process improvements. They assist in the selection, testing, and implementation of new software or systems. They ensure that technology aligns with business requirements, improve efficiency, and enable effective data management.
-
Data Analysis and Reporting: Business Process Analysts analyze data to assess process performance, identify trends, and measure the impact of process improvements. They create reports and dashboards to communicate findings and make data-driven recommendations for further enhancements. They monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to track process effectiveness and drive continuous improvement.
-
Stakeholder Management and Communication: Business Process Analysts interact with stakeholders at various levels, including executives, managers, and end-users. They facilitate meetings, workshops, and interviews to gather input, clarify requirements, and communicate process changes. They ensure effective communication between business and technical teams, translating complex concepts into understandable terms for non-technical stakeholders.
-
Change Management and Training: Business Process Analysts play a vital role in change management initiatives. They develop change management strategies, create training materials, and conduct training sessions to ensure smooth transitions to new processes. They address resistance to change, promote user adoption, and provide ongoing support to end-users.
-
Continuous Improvement: Business Process Analysts foster a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. They monitor process performance, gather feedback, and identify areas for further optimization. They stay updated with industry best practices and emerging trends to bring innovative solutions and ideas to enhance processes continually.
In summary, Business Process Analysts are responsible for analyzing, improving, and optimizing business processes to drive efficiency, enhance productivity, and align operations with strategic objectives. Their diverse range of responsibilities includes data analysis, requirements gathering, technology integration, stakeholder management, change management, and continuous improvement efforts.
Skills of a Business Process Analyst
Being a successful Business Process Analyst requires a combination of technical, analytical, and interpersonal skills. Here are some essential skills that are crucial for a Business Process Analyst:
-
Process Analysis and Mapping: Proficiency in analyzing and mapping complex business processes is fundamental. Business Process Analysts should be able to understand the intricacies of current processes, identify pain points, and visualize workflows using tools such as process flowcharts and diagrams.
-
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Strong analytical skills are essential for a Business Process Analyst. They should be capable of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Proficiency in using data analysis tools and techniques is valuable in uncovering insights and making data-driven recommendations.
-
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: Business Process Analysts need excellent problem-solving abilities to identify issues, propose innovative solutions, and make informed decisions. They should be adept at approaching challenges from different angles, thinking critically, and applying logical reasoning to arrive at effective solutions.
-
Technical Knowledge: Having a solid understanding of technology and its impact on business processes is crucial for Business Process Analysts. They should be familiar with various software applications, data management systems, and process automation tools. Additionally, knowledge of programming languages, database management, and project management methodologies can be advantageous.
-
Communication and Collaboration: Strong communication skills are vital for Business Process Analysts to effectively interact with stakeholders at all levels. They should be able to communicate complex concepts in a clear and concise manner, actively listen to gather requirements, and facilitate productive discussions. Collaboration skills are also essential for working with cross-functional teams, fostering teamwork, and building consensus.
-
Business Acumen: Business Process Analysts should possess a solid understanding of organizational structures, industry trends, and market dynamics. This business acumen enables them to align process improvements with strategic objectives and make recommendations that drive business value.
-
Change Management: As change agents within an organization, Business Process Analysts need skills in change management. They should be able to manage resistance to change, provide support to stakeholders, and facilitate smooth transitions to new processes. Training and facilitation skills are valuable in implementing change management strategies.
-
Attention to Detail: Business Process Analysts must have a keen eye for detail to identify potential gaps, inconsistencies, and errors in processes. Attention to detail ensures accurate documentation, data analysis, and solution design.
-
Continuous Learning: Given the dynamic nature of business processes and evolving technologies, a growth mindset and a commitment to continuous learning are crucial for Business Process Analysts. They should stay updated with industry best practices, emerging trends, and new tools to bring fresh ideas and insights to process improvement initiatives.
In summary, successful Business Process Analysts possess a blend of technical expertise, analytical thinking, communication skills, and business acumen. The ability to analyze processes, interpret data, solve problems, and effectively collaborate with stakeholders is essential for driving process improvements and achieving organizational goals.
Tools and techniques used
Business Process Analysts utilize a variety of tools and techniques to analyze, document, and improve business processes. Here are some commonly used tools and techniques:
-
Process Mapping: Process mapping is a visual technique used to represent the flow of activities, decisions, and interactions within a business process. It helps Business Process Analysts gain a clear understanding of how processes are executed and identify areas for improvement. Tools such as flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, and BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) are commonly used for process mapping.
-
Data Analysis Tools: Business Process Analysts leverage various data analysis tools to extract insights from process-related data. Tools such as Microsoft Excel, statistical software (e.g., SPSS, SAS), and data visualization tools (e.g., Tableau, Power BI) are used to analyze data, identify patterns, and make data-driven recommendations for process improvements.
-
Root Cause Analysis: Root cause analysis is a technique used to identify the underlying causes of process issues or failures. Business Process Analysts employ tools such as fishbone diagrams (Ishikawa diagrams) or 5 Whys analysis to systematically identify and address the root causes of problems. This helps in implementing targeted solutions and preventing future occurrences.
-
Process Simulation: Process simulation involves creating computer models to simulate the execution of a business process. It helps Business Process Analysts evaluate the impact of proposed process changes, identify potential bottlenecks, and optimize resource allocation. Simulation software like Arena, Simul8, or ProModel are commonly used for this purpose.
-
Process Improvement Methodologies: Business Process Analysts often apply specific methodologies and frameworks to guide their process improvement initiatives. Examples include Lean Six Sigma, Business Process Reengineering (BPR), Agile, or the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle. These methodologies provide structured approaches and tools for analyzing, designing, and implementing process improvements.
-
Workflow Automation and Process Management Software: Business Process Analysts leverage workflow automation and process management software to streamline and manage business processes. These tools help automate repetitive tasks, enforce process compliance, and provide real-time visibility into process performance. Examples include tools like Business Process Management (BPM) software, project management software, or workflow automation platforms.
-
Interviews and Surveys: Business Process Analysts conduct interviews and surveys with stakeholders to gather information about current processes, pain points, and improvement opportunities. These qualitative research techniques help in understanding user perspectives, capturing feedback, and validating process-related assumptions.
-
Quality Management Tools: Quality management tools such as Pareto charts, control charts, or process capability analysis are used by Business Process Analysts to measure and monitor process performance, identify areas of variation or defects, and drive continuous improvement efforts.
-
Documentation and Collaboration Tools: Business Process Analysts utilize various documentation and collaboration tools to capture process-related information, collaborate with stakeholders, and share process documentation. Examples include Microsoft Office Suite (Word, Excel, PowerPoint), SharePoint, or online collaboration platforms like Microsoft Teams or Google Workspace.
It's important to note that the specific tools and techniques used by Business Process Analysts may vary depending on the organization's preferences, industry, and the complexity of the processes being analyzed. The selection of tools and techniques is tailored to meet the specific needs of the process improvement initiatives.
Business Process Analyst career path
Certainly, let's delve into the career path of a Business Process Analyst. This role offers several potential avenues for growth and advancement within organizations. Here's a general progression that a Business Process Analyst might follow:
-
Entry-Level Business Process Analyst:
-
At the start of your career, you'll likely focus on learning the basics of business process analysis, documentation, and mapping.
-
You might work closely with senior analysts to gather data, identify inefficiencies, and assist in proposing improvements.
-
Junior Business Process Analyst:
-
As you gain experience, you'll take on more responsibility in analyzing processes and proposing solutions.
-
You might begin leading small-scale process improvement projects under the guidance of a senior analyst.
-
Business Process Analyst:
-
At this stage, you'll have a solid understanding of business processes and be able to independently identify opportunities for improvement.
-
You'll work on larger and more complex projects, collaborating with stakeholders from various departments.
-
Your communication and presentation skills will become crucial as you explain your findings and recommendations to management.
-
Senior Business Process Analyst:
-
With several years of experience, you might take on a mentoring role for junior analysts, guiding them in their work.
-
You'll be entrusted with high-impact projects that involve major process overhauls and strategic initiatives.
-
Stakeholder engagement and change management skills become even more important as you lead teams through significant process changes.
-
Lead or Principal Business Process Analyst:
-
In this role, you'll be recognized as a subject matter expert in process analysis and improvement.
-
You might play a key role in setting the organization's process improvement strategy and standards.
-
Collaboration with C-suite executives and other high-level stakeholders becomes more frequent as you contribute to organizational strategy.
-
Business Process Manager/Director:
-
As you progress, you might transition into a managerial role, overseeing a team of Business Process Analysts.
-
Your responsibilities will extend beyond individual projects to include team management, performance evaluation, and strategic planning.
-
Process Improvement Consultant:
-
Some Business Process Analysts choose to transition into consulting roles, working for firms that specialize in process improvement.
-
As a consultant, you'll work with a variety of clients across different industries to help them optimize their processes and operations.
-
Chief Process Officer (CPO):
-
In large organizations, there might be a role known as the Chief Process Officer or a similar title.
-
This role involves top-level responsibility for the organization's process improvement initiatives, working closely with executives to align processes with overall business strategy.
Remember that career paths can vary based on the organization, industry, and individual goals. Continuous learning, staying up-to-date with industry trends, and networking within the business process community can all contribute to your career growth as a Business Process Analyst.
Business Process Analyst jobs and salary
The availability of Business Process Analyst jobs and their associated salaries can vary based on factors such as location, industry, years of experience, and the specific responsibilities of the role. However, I can provide you with a general overview of what you might expect:
1. Job Availability: Business Process Analyst positions can be found in a wide range of industries, including finance, healthcare, manufacturing, technology, retail, and more. Almost any industry that relies on efficient processes can benefit from the skills of a Business Process Analyst. Job titles might vary slightly, so keep an eye out for roles like Business Analyst, Process Improvement Analyst, or Operations Analyst.
2. Salary Range: Salaries for Business Process Analysts can also vary widely based on the factors mentioned earlier. Here's a rough estimate of the salary range you might encounter in various regions:
-
Entry-Level: In the United States, an entry-level Business Process Analyst might earn around $50,000 to $70,000 per year.
-
Mid-Level: With a few years of experience, mid-level analysts could earn in the range of $70,000 to $90,000 per year.
-
Senior-Level: Experienced Senior Business Process Analysts might earn $90,000 to $120,000 or more annually.
Keep in mind that these figures are general estimates and can vary significantly based on location. For instance, salaries tend to be higher in major metropolitan areas compared to smaller towns or rural regions. Additionally, industries with high demand for process optimization, such as finance and healthcare, might offer higher salaries.
3. Additional Factors: Other factors that can influence salary include the size and reputation of the company, the complexity of the processes being analyzed, the level of responsibility, and any specialized skills or certifications you bring to the table. Some professionals in this field also pursue advanced certifications like Lean Six Sigma, which can contribute to higher earning potential.
It's important to research job listings in your specific area and industry to get a more accurate idea of the salary ranges being offered. Websites like Glassdoor, LinkedIn, and industry-specific job boards can provide insights into current job openings and salary expectations.
Remember that while salary is an important factor, other considerations such as job satisfaction, growth opportunities, company culture, and benefits should also play a role in your decision-making process when pursuing Business Process Analyst roles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of a Business Process Analyst is crucial in today's dynamic business environment. They bring valuable skills, tools, and techniques to analyze, improve, and optimize business processes, resulting in increased efficiency, cost savings, and alignment with strategic objectives.
Business Process Analysts play a vital role in identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement within an organization's processes. Through process analysis, mapping, and data analysis, they uncover insights that drive process optimization and enhance overall operational effectiveness.
Their technical knowledge and understanding of technology enable them to collaborate with IT teams and implement new technologies that support process improvements. They bridge the gap between business stakeholders and technology solutions, ensuring successful integration and alignment with business requirements.
Effective communication and collaboration skills allow Business Process Analysts to work closely with stakeholders at all levels of the organization. They facilitate productive discussions, gather requirements, and provide clarity on process changes, ensuring buy-in and support for process improvement initiatives.
Change management is a crucial aspect of a Business Process Analyst's role. They guide organizations through the transition to new processes, addressing resistance to change, and providing training and support to ensure a smooth implementation.
Continuous improvement is at the core of a Business Process Analyst's responsibilities. They monitor process performance, analyze data, and identify further opportunities for enhancement. By staying updated with industry best practices and emerging trends, they bring innovative solutions to continually optimize processes and drive organizational success.
In summary, Business Process Analysts are instrumental in analyzing, improving, and optimizing business processes. Their skills in process analysis, data analysis, communication, and change management contribute to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction. By leveraging tools and techniques, they drive continuous improvement, align processes with strategic objectives, and help organizations stay competitive in today's rapidly evolving business landscape.
Read More
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations are constantly striving to optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and achieve strategic objectives. This is where the role of a Business Process Analyst becomes indispensable. A Business Process Analyst acts as a crucial bridge between business stakeholders and technology solutions, working to identify, analyze, and improve business processes to drive organizational growth and success.
The primary responsibility of a Business Process Analyst is to understand the inner workings of an organization, its objectives, and its current operational procedures. By collaborating with various stakeholders, including executives, managers, and end-users, the analyst gains a comprehensive understanding of the existing processes and identifies areas that require improvement or reengineering.
With their analytical acumen and keen eye for detail, Business Process Analysts employ a systematic approach to analyze data, identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas of potential risk. They leverage their expertise in process mapping, data analysis, and industry best practices to propose innovative solutions that streamline operations, enhance productivity, and drive cost savings.
Business Process Analysts are also adept at translating complex technical jargon into easily understandable language for non-technical stakeholders. They possess excellent communication and interpersonal skills, allowing them to facilitate effective communication and collaboration between different teams and departments within an organization.
Furthermore, Business Process Analysts play a crucial role in technology implementation projects. They work closely with IT teams and software developers to ensure that the identified process improvements are successfully implemented. They also conduct thorough testing and evaluation of new systems to guarantee that they align with the organization's requirements and goals.
In summary, a Business Process Analyst serves as a catalyst for organizational change and improvement. By conducting in-depth analysis, identifying inefficiencies, and recommending strategic solutions, these professionals contribute significantly to enhancing operational effectiveness, driving growth, and enabling organizations to adapt to ever-changing market dynamics. With their versatile skill set and holistic approach, Business Process Analysts are vital assets for any business seeking to stay competitive in today's dynamic and demanding business environment.
Table of Contents
-
Definition of a Business Process Analyst
-
Importance of Business Process Analysts
-
Roles and responsibilities of a Business Process Analyst
-
Skills of a Business Process Analyst
-
Tools and techniques used
-
Business Process Analyst career path
-
Business Process Analyst jobs and salary
-
Conclusion
Definition of a Business Process Analyst
A Business Process Analyst is a professional who specializes in analyzing, documenting, and improving the operational processes within an organization. They possess a deep understanding of business operations and use their analytical skills to identify areas of inefficiency, bottlenecks, and opportunities for improvement. Their primary goal is to optimize processes to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and align operations with strategic objectives.
Business Process Analysts work closely with stakeholders from various departments, including executives, managers, and end-users, to gather information about existing processes. They utilize tools such as process mapping, data analysis, and interviews to gain a comprehensive understanding of the current state of operations.
Once they have identified areas for improvement, Business Process Analysts propose and implement changes to streamline processes and eliminate redundancies. They may recommend the adoption of new technologies, changes in workflows, or modifications to standard operating procedures. They also collaborate with IT teams and software developers to ensure the successful implementation of process enhancements.
In addition to analyzing and improving existing processes, Business Process Analysts are often involved in designing and implementing new processes for emerging business needs. They stay up to date with industry best practices and emerging trends to bring innovative and effective solutions to the table.
Effective communication and interpersonal skills are essential for Business Process Analysts, as they need to work collaboratively with different stakeholders and translate complex technical concepts into easily understandable language for non-technical individuals. They also play a key role in change management, helping employees adapt to new processes and technologies through training and support.
Overall, a Business Process Analyst is a critical asset to organizations seeking to optimize their operations and achieve sustainable growth. Through their expertise in process analysis, problem-solving, and continuous improvement, they contribute to enhancing efficiency, increasing customer satisfaction, and driving overall business success.
Importance of Business Process Analysts
Business Process Analysts play a crucial role in organizations for several reasons. Here are some key reasons highlighting the importance of Business Process Analysts:
-
Process Optimization: Business Process Analysts are adept at identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas of improvement within organizational processes. By conducting thorough analysis and using their expertise, they help streamline workflows, reduce redundancies, and improve overall operational efficiency. This optimization leads to cost savings, increased productivity, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
-
Strategic Alignment: Business Process Analysts ensure that business processes align with strategic objectives. They evaluate existing processes and identify opportunities to align them with the organization's goals and vision. By mapping processes to strategic objectives, they help drive the achievement of targets and promote long-term success.
-
Technology Implementation: In today's technology-driven world, Business Process Analysts play a vital role in the successful implementation of new technologies and systems. They collaborate with IT teams and software developers to ensure that technology solutions are aligned with business requirements. Their expertise in understanding both business processes and technical aspects enables them to bridge the gap between business stakeholders and technology teams, ensuring effective implementation.
-
Continuous Improvement: Business Process Analysts foster a culture of continuous improvement within organizations. They actively seek feedback from stakeholders, monitor performance metrics, and identify areas for further enhancement. By implementing a cycle of continuous improvement, they help organizations stay agile, adapt to changing market conditions, and maintain a competitive edge.
-
Risk Mitigation: Business Process Analysts are skilled in identifying potential risks within processes and implementing mitigation strategies. By conducting risk assessments, they minimize operational vulnerabilities, address compliance issues, and ensure that processes are executed smoothly and securely. This proactive approach to risk management helps safeguard the organization's reputation and minimizes financial losses.
-
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Business Process Analysts act as facilitators, bringing together teams from different departments and fostering effective communication and collaboration. They bridge the gap between business stakeholders, IT teams, and end-users, ensuring that everyone is aligned and working towards common objectives. Their ability to translate technical jargon into easily understandable language helps build stronger relationships and promote teamwork.
-
Change Management: Implementing process changes can often be met with resistance from employees. Business Process Analysts are skilled in change management techniques, helping employees adapt to new processes through effective training, communication, and support. Their involvement in the change management process increases employee buy-in and smooths the transition to new ways of working.
In summary, Business Process Analysts play a pivotal role in driving operational excellence, fostering innovation, and achieving organizational goals. Their ability to optimize processes, align strategies, manage risks, and facilitate collaboration makes them essential assets for organizations striving for continuous improvement and long-term success.
Roles and responsibilities of a Business Process Analyst
The roles and responsibilities of a Business Process Analyst may vary depending on the organization and industry. However, here are some common key roles and responsibilities associated with the position:
-
Process Analysis and Documentation: The primary responsibility of a Business Process Analyst is to analyze existing business processes. This involves gathering information, conducting process mapping exercises, and documenting current procedures. They identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement through data analysis and stakeholder consultations.
-
Process Improvement and Optimization: Business Process Analysts are responsible for recommending and implementing process improvements. They identify opportunities to streamline workflows, eliminate redundancies, and enhance efficiency. They may suggest changes to technology systems, workflows, or operating procedures to achieve optimal results. They work closely with stakeholders to gain buy-in and ensure successful implementation.
-
Requirements Gathering and Analysis: Business Process Analysts work with business stakeholders to understand their requirements and objectives. They gather and analyze data to identify gaps and align business processes with strategic goals. They translate business needs into functional requirements that can guide process improvements and technology implementations.
-
Technology Integration and Support: Business Process Analysts collaborate with IT teams to integrate technology solutions that support process improvements. They assist in the selection, testing, and implementation of new software or systems. They ensure that technology aligns with business requirements, improve efficiency, and enable effective data management.
-
Data Analysis and Reporting: Business Process Analysts analyze data to assess process performance, identify trends, and measure the impact of process improvements. They create reports and dashboards to communicate findings and make data-driven recommendations for further enhancements. They monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to track process effectiveness and drive continuous improvement.
-
Stakeholder Management and Communication: Business Process Analysts interact with stakeholders at various levels, including executives, managers, and end-users. They facilitate meetings, workshops, and interviews to gather input, clarify requirements, and communicate process changes. They ensure effective communication between business and technical teams, translating complex concepts into understandable terms for non-technical stakeholders.
-
Change Management and Training: Business Process Analysts play a vital role in change management initiatives. They develop change management strategies, create training materials, and conduct training sessions to ensure smooth transitions to new processes. They address resistance to change, promote user adoption, and provide ongoing support to end-users.
-
Continuous Improvement: Business Process Analysts foster a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. They monitor process performance, gather feedback, and identify areas for further optimization. They stay updated with industry best practices and emerging trends to bring innovative solutions and ideas to enhance processes continually.
In summary, Business Process Analysts are responsible for analyzing, improving, and optimizing business processes to drive efficiency, enhance productivity, and align operations with strategic objectives. Their diverse range of responsibilities includes data analysis, requirements gathering, technology integration, stakeholder management, change management, and continuous improvement efforts.
Skills of a Business Process Analyst
Being a successful Business Process Analyst requires a combination of technical, analytical, and interpersonal skills. Here are some essential skills that are crucial for a Business Process Analyst:
-
Process Analysis and Mapping: Proficiency in analyzing and mapping complex business processes is fundamental. Business Process Analysts should be able to understand the intricacies of current processes, identify pain points, and visualize workflows using tools such as process flowcharts and diagrams.
-
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Strong analytical skills are essential for a Business Process Analyst. They should be capable of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Proficiency in using data analysis tools and techniques is valuable in uncovering insights and making data-driven recommendations.
-
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: Business Process Analysts need excellent problem-solving abilities to identify issues, propose innovative solutions, and make informed decisions. They should be adept at approaching challenges from different angles, thinking critically, and applying logical reasoning to arrive at effective solutions.
-
Technical Knowledge: Having a solid understanding of technology and its impact on business processes is crucial for Business Process Analysts. They should be familiar with various software applications, data management systems, and process automation tools. Additionally, knowledge of programming languages, database management, and project management methodologies can be advantageous.
-
Communication and Collaboration: Strong communication skills are vital for Business Process Analysts to effectively interact with stakeholders at all levels. They should be able to communicate complex concepts in a clear and concise manner, actively listen to gather requirements, and facilitate productive discussions. Collaboration skills are also essential for working with cross-functional teams, fostering teamwork, and building consensus.
-
Business Acumen: Business Process Analysts should possess a solid understanding of organizational structures, industry trends, and market dynamics. This business acumen enables them to align process improvements with strategic objectives and make recommendations that drive business value.
-
Change Management: As change agents within an organization, Business Process Analysts need skills in change management. They should be able to manage resistance to change, provide support to stakeholders, and facilitate smooth transitions to new processes. Training and facilitation skills are valuable in implementing change management strategies.
-
Attention to Detail: Business Process Analysts must have a keen eye for detail to identify potential gaps, inconsistencies, and errors in processes. Attention to detail ensures accurate documentation, data analysis, and solution design.
-
Continuous Learning: Given the dynamic nature of business processes and evolving technologies, a growth mindset and a commitment to continuous learning are crucial for Business Process Analysts. They should stay updated with industry best practices, emerging trends, and new tools to bring fresh ideas and insights to process improvement initiatives.
In summary, successful Business Process Analysts possess a blend of technical expertise, analytical thinking, communication skills, and business acumen. The ability to analyze processes, interpret data, solve problems, and effectively collaborate with stakeholders is essential for driving process improvements and achieving organizational goals.
Tools and techniques used
Business Process Analysts utilize a variety of tools and techniques to analyze, document, and improve business processes. Here are some commonly used tools and techniques:
-
Process Mapping: Process mapping is a visual technique used to represent the flow of activities, decisions, and interactions within a business process. It helps Business Process Analysts gain a clear understanding of how processes are executed and identify areas for improvement. Tools such as flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, and BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) are commonly used for process mapping.
-
Data Analysis Tools: Business Process Analysts leverage various data analysis tools to extract insights from process-related data. Tools such as Microsoft Excel, statistical software (e.g., SPSS, SAS), and data visualization tools (e.g., Tableau, Power BI) are used to analyze data, identify patterns, and make data-driven recommendations for process improvements.
-
Root Cause Analysis: Root cause analysis is a technique used to identify the underlying causes of process issues or failures. Business Process Analysts employ tools such as fishbone diagrams (Ishikawa diagrams) or 5 Whys analysis to systematically identify and address the root causes of problems. This helps in implementing targeted solutions and preventing future occurrences.
-
Process Simulation: Process simulation involves creating computer models to simulate the execution of a business process. It helps Business Process Analysts evaluate the impact of proposed process changes, identify potential bottlenecks, and optimize resource allocation. Simulation software like Arena, Simul8, or ProModel are commonly used for this purpose.
-
Process Improvement Methodologies: Business Process Analysts often apply specific methodologies and frameworks to guide their process improvement initiatives. Examples include Lean Six Sigma, Business Process Reengineering (BPR), Agile, or the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle. These methodologies provide structured approaches and tools for analyzing, designing, and implementing process improvements.
-
Workflow Automation and Process Management Software: Business Process Analysts leverage workflow automation and process management software to streamline and manage business processes. These tools help automate repetitive tasks, enforce process compliance, and provide real-time visibility into process performance. Examples include tools like Business Process Management (BPM) software, project management software, or workflow automation platforms.
-
Interviews and Surveys: Business Process Analysts conduct interviews and surveys with stakeholders to gather information about current processes, pain points, and improvement opportunities. These qualitative research techniques help in understanding user perspectives, capturing feedback, and validating process-related assumptions.
-
Quality Management Tools: Quality management tools such as Pareto charts, control charts, or process capability analysis are used by Business Process Analysts to measure and monitor process performance, identify areas of variation or defects, and drive continuous improvement efforts.
-
Documentation and Collaboration Tools: Business Process Analysts utilize various documentation and collaboration tools to capture process-related information, collaborate with stakeholders, and share process documentation. Examples include Microsoft Office Suite (Word, Excel, PowerPoint), SharePoint, or online collaboration platforms like Microsoft Teams or Google Workspace.
It's important to note that the specific tools and techniques used by Business Process Analysts may vary depending on the organization's preferences, industry, and the complexity of the processes being analyzed. The selection of tools and techniques is tailored to meet the specific needs of the process improvement initiatives.
Business Process Analyst career path
Certainly, let's delve into the career path of a Business Process Analyst. This role offers several potential avenues for growth and advancement within organizations. Here's a general progression that a Business Process Analyst might follow:
-
Entry-Level Business Process Analyst:
-
At the start of your career, you'll likely focus on learning the basics of business process analysis, documentation, and mapping.
-
You might work closely with senior analysts to gather data, identify inefficiencies, and assist in proposing improvements.
-
-
Junior Business Process Analyst:
-
As you gain experience, you'll take on more responsibility in analyzing processes and proposing solutions.
-
You might begin leading small-scale process improvement projects under the guidance of a senior analyst.
-
-
Business Process Analyst:
-
At this stage, you'll have a solid understanding of business processes and be able to independently identify opportunities for improvement.
-
You'll work on larger and more complex projects, collaborating with stakeholders from various departments.
-
Your communication and presentation skills will become crucial as you explain your findings and recommendations to management.
-
-
Senior Business Process Analyst:
-
With several years of experience, you might take on a mentoring role for junior analysts, guiding them in their work.
-
You'll be entrusted with high-impact projects that involve major process overhauls and strategic initiatives.
-
Stakeholder engagement and change management skills become even more important as you lead teams through significant process changes.
-
-
Lead or Principal Business Process Analyst:
-
In this role, you'll be recognized as a subject matter expert in process analysis and improvement.
-
You might play a key role in setting the organization's process improvement strategy and standards.
-
Collaboration with C-suite executives and other high-level stakeholders becomes more frequent as you contribute to organizational strategy.
-
-
Business Process Manager/Director:
-
As you progress, you might transition into a managerial role, overseeing a team of Business Process Analysts.
-
Your responsibilities will extend beyond individual projects to include team management, performance evaluation, and strategic planning.
-
-
Process Improvement Consultant:
-
Some Business Process Analysts choose to transition into consulting roles, working for firms that specialize in process improvement.
-
As a consultant, you'll work with a variety of clients across different industries to help them optimize their processes and operations.
-
-
Chief Process Officer (CPO):
-
In large organizations, there might be a role known as the Chief Process Officer or a similar title.
-
This role involves top-level responsibility for the organization's process improvement initiatives, working closely with executives to align processes with overall business strategy.
-
Remember that career paths can vary based on the organization, industry, and individual goals. Continuous learning, staying up-to-date with industry trends, and networking within the business process community can all contribute to your career growth as a Business Process Analyst.
Business Process Analyst jobs and salary
The availability of Business Process Analyst jobs and their associated salaries can vary based on factors such as location, industry, years of experience, and the specific responsibilities of the role. However, I can provide you with a general overview of what you might expect:
1. Job Availability: Business Process Analyst positions can be found in a wide range of industries, including finance, healthcare, manufacturing, technology, retail, and more. Almost any industry that relies on efficient processes can benefit from the skills of a Business Process Analyst. Job titles might vary slightly, so keep an eye out for roles like Business Analyst, Process Improvement Analyst, or Operations Analyst.
2. Salary Range: Salaries for Business Process Analysts can also vary widely based on the factors mentioned earlier. Here's a rough estimate of the salary range you might encounter in various regions:
-
Entry-Level: In the United States, an entry-level Business Process Analyst might earn around $50,000 to $70,000 per year.
-
Mid-Level: With a few years of experience, mid-level analysts could earn in the range of $70,000 to $90,000 per year.
-
Senior-Level: Experienced Senior Business Process Analysts might earn $90,000 to $120,000 or more annually.
Keep in mind that these figures are general estimates and can vary significantly based on location. For instance, salaries tend to be higher in major metropolitan areas compared to smaller towns or rural regions. Additionally, industries with high demand for process optimization, such as finance and healthcare, might offer higher salaries.
3. Additional Factors: Other factors that can influence salary include the size and reputation of the company, the complexity of the processes being analyzed, the level of responsibility, and any specialized skills or certifications you bring to the table. Some professionals in this field also pursue advanced certifications like Lean Six Sigma, which can contribute to higher earning potential.
It's important to research job listings in your specific area and industry to get a more accurate idea of the salary ranges being offered. Websites like Glassdoor, LinkedIn, and industry-specific job boards can provide insights into current job openings and salary expectations.
Remember that while salary is an important factor, other considerations such as job satisfaction, growth opportunities, company culture, and benefits should also play a role in your decision-making process when pursuing Business Process Analyst roles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of a Business Process Analyst is crucial in today's dynamic business environment. They bring valuable skills, tools, and techniques to analyze, improve, and optimize business processes, resulting in increased efficiency, cost savings, and alignment with strategic objectives.
Business Process Analysts play a vital role in identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement within an organization's processes. Through process analysis, mapping, and data analysis, they uncover insights that drive process optimization and enhance overall operational effectiveness.
Their technical knowledge and understanding of technology enable them to collaborate with IT teams and implement new technologies that support process improvements. They bridge the gap between business stakeholders and technology solutions, ensuring successful integration and alignment with business requirements.
Effective communication and collaboration skills allow Business Process Analysts to work closely with stakeholders at all levels of the organization. They facilitate productive discussions, gather requirements, and provide clarity on process changes, ensuring buy-in and support for process improvement initiatives.
Change management is a crucial aspect of a Business Process Analyst's role. They guide organizations through the transition to new processes, addressing resistance to change, and providing training and support to ensure a smooth implementation.
Continuous improvement is at the core of a Business Process Analyst's responsibilities. They monitor process performance, analyze data, and identify further opportunities for enhancement. By staying updated with industry best practices and emerging trends, they bring innovative solutions to continually optimize processes and drive organizational success.
In summary, Business Process Analysts are instrumental in analyzing, improving, and optimizing business processes. Their skills in process analysis, data analysis, communication, and change management contribute to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction. By leveraging tools and techniques, they drive continuous improvement, align processes with strategic objectives, and help organizations stay competitive in today's rapidly evolving business landscape.
Top Career Options After BCom in 2023: Your Next Steps.
In the dynamic landscape of career choices post-BCom, navigating the path to success requires both strategic thinking and informed decisions. As the year 2023 unfolds, opportunities abound for BCom graduates seeking to elevate their professional trajectories. With the convergence of business acumen and emerging technologies, this pivotal juncture presents a multitude of options that extend far beyond traditional boundaries.
In this pursuit, Icert Global offers courses such as CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional), CCBA (Certification of Capability in Business Analysis), and ECBA (Entry Certificate in Business Analysis) can be a transformative step. These courses serve as catalysts, equipping graduates with a refined skill set that bridges the gap between the business realm and the rapidly evolving tech landscape.
As we delve into the realm of "2023 Career Options: Your Next Steps After BCom," we'll explore how the symbiosis of your BCom foundation and these specialized courses can shape an exciting and impactful journey. From unleashing the power of data analysis to charting strategic business solutions, this exploration will illuminate the myriad possibilities that await, propelling BCom graduates towards the forefront of innovation and success.
In this article
-
Why Should You Pursue a BCom Degree?
-
Scope of BCom Degree
-
Career after BCom (Sectors)
-
Courses after BCom
-
Corporate Job Options after BCom
-
Some Competitive Exams for BCom Graduates
-
Career Switch options in Tech and Business (Influence KH career options)
-
Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why Should You Pursue a BCom Degree?
Pursuing a Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) degree can offer numerous advantages and open up a wide array of opportunities. Here are some compelling reasons why you should consider pursuing a BCom degree:
-
Versatile Skill Set: BCom programs provide a well-rounded education in various business disciplines, including accounting, finance, marketing, management, economics, and more. This versatile skill set prepares you for a range of roles across different industries.
-
Strong Foundation: A BCom degree lays a solid foundation in business concepts and principles. This knowledge is essential whether you plan to work in a corporate environment, start your own business, or pursue further education.
-
Diverse Career Paths: The skills gained through a BCom degree can lead to a diverse range of career paths. Whether you're interested in finance, marketing, entrepreneurship, consulting, or even public administration, a BCom degree equips you with the knowledge needed to excel in these areas.
-
High Demand: Businesses of all sizes require individuals with business acumen to handle various aspects of their operations. BCom graduates are in high demand across industries, making it easier to secure job opportunities upon graduation.
-
Adaptability: The business landscape is constantly evolving. A BCom degree teaches you how to adapt to change, think critically, and solve complex problems—skills that are crucial in a dynamic business world.
-
Networking Opportunities: University programs often provide opportunities to network with professors, fellow students, and industry professionals. These connections can be invaluable for future career growth and job opportunities.
-
Entrepreneurship: If you aspire to start your own business, a BCom degree can provide you with the foundational knowledge to understand market trends, manage finances, and develop effective business strategies.
-
Higher Earning Potential: On average, individuals with a BCom degree tend to earn higher salaries compared to those without a degree. As you progress in your career, your earning potential is likely to increase.
-
Global Opportunities: The principles learned in a BCom program are applicable worldwide. This opens up opportunities for international careers and the chance to work with multinational companies.
-
Preparation for Advanced Studies: If you're considering pursuing a master's degree or further education, a BCom degree can serve as a strong foundation. Many specialized fields, such as finance or business analytics, require a solid understanding of business concepts.
-
Analytical Skills: BCom programs emphasize data analysis, problem-solving, and critical thinking. These skills are highly transferable and can be applied to various aspects of both professional and personal life.
-
Career Progression: Many leadership roles within organizations require a deep understanding of business operations, strategy, and management. A BCom degree can help fast-track your career progression into such roles.
-
Contribution to Society: Businesses play a crucial role in shaping economies and societies. With a BCom degree, you have the opportunity to contribute positively to both business growth and community development.
In conclusion, pursuing a BCom degree can provide you with a strong educational foundation, a broad skill set, and a pathway to a fulfilling and successful career. Whether you're interested in working for established corporations, launching your own startup, or contributing to public sector initiatives, a BCom degree equips you with the tools you need to excel in various professional pursuits.
Scope of BCom Degree
The scope of a Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) degree is extensive and offers graduates a wide range of career opportunities across various industries. Here's an overview of the scope of a BCom degree:
-
Business Management and Administration:
-
Graduates can work in roles such as business managers, operations managers, and general managers, overseeing various aspects of company operations.
-
Finance and Accounting:
-
Opportunities exist in areas like corporate finance, investment banking, financial analysis, auditing, and accounting.
-
BCom graduates can become financial analysts, accountants, tax consultants, auditors, or even certified public accountants (CPAs).
-
Marketing and Sales:
-
BCom graduates can pursue careers in marketing, advertising, public relations, and sales.
-
Roles like marketing managers, brand managers, digital marketers, and sales executives are common.
-
E-commerce and Retail:
-
With the growth of online shopping, BCom graduates can excel in roles related to e-commerce management, online retail, and supply chain management.
-
Human Resources:
-
Graduates can work in HR roles, including human resource management, recruitment, training, and employee relations.
-
Entrepreneurship:
-
BCom graduates with an entrepreneurial spirit can start their own businesses or startups, using their business knowledge to create and manage successful ventures.
-
Consulting:
-
Graduates can become management consultants, offering expert advice to businesses on improving efficiency, strategy, and operations.
-
Business Analytics:
-
The increasing importance of data-driven decision-making has created a demand for business analysts who can interpret and analyze data to drive business strategies.
-
Public Sector and Government Jobs:
-
BCom graduates can work in government departments, public administration, and agencies, handling financial management, budgeting, and policy analysis.
-
International Business:
-
The global nature of business means that BCom graduates can find opportunities in international trade, export-import management, and global supply chain management.
-
Financial Technology (Fintech):
-
The integration of finance and technology has led to roles like fintech analysts, blockchain specialists, and payment system managers.
-
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
-
Graduates can work in CSR roles, helping companies implement socially responsible practices and sustainable business strategies.
-
Nonprofit and NGO Sector:
-
BCom graduates can contribute to nonprofit organizations and NGOs in areas such as finance management, fundraising, and program coordination.
-
Supply Chain Management:
-
Graduates can manage the end-to-end supply chain, ensuring efficient movement of goods and services from suppliers to customers.
-
Risk Management and Insurance:
-
Opportunities exist in roles related to risk assessment, insurance underwriting, and claims management.
-
Real Estate and Property Management:
-
BCom graduates can work in real estate, property management, and real estate development, handling transactions and investments.
-
Higher Education and Academia:
-
Some graduates choose to pursue advanced degrees and become educators, teaching business-related courses at universities and colleges.
-
Media and Entertainment Industry:
-
BCom graduates can work in media management, advertising, public relations, and entertainment business roles.
The scope of a BCom degree is not limited to any single industry, making it a versatile choice that can lead to a fulfilling and successful career in various fields. The key lies in identifying your strengths, interests, and career goals and aligning them with the diverse opportunities that a BCom degree offers.
Career after BCom (Sectors)
After completing a Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) degree, you'll have a wide range of career options across various sectors. Here are some of the prominent sectors where BCom graduates can find rewarding careers:
-
Finance and Banking:
-
Financial Analyst
-
Investment Banker
-
Wealth Manager
-
Credit Analyst
-
Retail or Commercial Banker
-
Financial Planner
-
Accounting and Auditing:
-
Accountant
-
Auditor (Internal or External)
-
Tax Consultant
-
Forensic Accountant
-
Cost Accountant
-
Marketing and Advertising:
-
Marketing Manager
-
Brand Manager
-
Advertising Executive
-
Market Research Analyst
-
Digital Marketing Specialist
-
Sales and Retail:
-
Sales Executive
-
Retail Manager
-
Customer Relationship Manager
-
Sales Analyst
-
Business Development Representative
-
Human Resources:
-
Human Resource Manager
-
Recruitment Specialist
-
Training and Development Coordinator
-
Compensation and Benefits Analyst
-
Business Consulting:
-
Management Consultant
-
Strategy Analyst
-
Business Process Analyst
-
Change Management Specialist
-
Entrepreneurship and Startups:
-
Business Owner
-
Startup Founder
-
Small Business Manager
-
Entrepreneurial Consultant
-
Information Technology (IT) and Business Analytics:
-
Business Analyst
-
Data Analyst
-
IT Consultant
-
Systems Analyst
-
Business Intelligence Analyst
-
Supply Chain and Logistics:
-
Supply Chain Manager
-
Logistics Coordinator
-
Procurement Specialist
-
Operations Analyst
-
Public Sector and Government:
-
Government Financial Officer
-
Budget Analyst
-
Taxation Officer
-
Customs Inspector
-
Nonprofit and NGOs:
-
Program Coordinator
-
Fundraising Manager
-
Grant Writer
-
NGO Financial Analyst
-
Insurance and Risk Management:
-
Insurance Underwriter
-
Risk Manager
-
Claims Analyst
-
Insurance Broker
-
Real Estate and Property Management:
-
Real Estate Agent
-
Property Manager
-
Real Estate Analyst
-
Real Estate Developer
-
Media and Entertainment:
-
Media Planner
-
Entertainment Manager
-
Public Relations Specialist
-
Event Coordinator
-
Healthcare Administration:
-
Healthcare Administrator
-
Medical Practice Manager
-
Health Services Manager
-
E-commerce and Retail Management:
-
E-commerce Manager
-
Online Retail Specialist
-
E-commerce Analyst
-
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
-
CSR Manager
-
Sustainability Consultant
-
Social Impact Analyst
-
Higher Education and Academia:
-
Academic Researcher
-
Lecturer or Professor
Remember, the sectors mentioned above are just a snapshot of the possibilities available to BCom graduates. The skills and knowledge gained during your BCom studies can be applied across industries, making your career choices highly versatile. It's important to explore your interests, strengths, and aspirations to find the sector that aligns best with your goals.
Courses after BCom
After completing a Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) degree, you have a variety of options for further education to enhance your skills, specialize in a particular field, or broaden your career opportunities. Here are some courses and paths you might consider pursuing after your BCom:
-
Master of Business Administration (MBA):
-
An MBA program provides advanced knowledge in business management and leadership skills, preparing you for executive-level roles.
-
Specializations might include Marketing, Finance, Human Resources, Operations, or Entrepreneurship.
-
Master of Commerce (MCom):
-
An MCom program delves deeper into subjects covered in your BCom, offering advanced knowledge in accounting, finance, economics, and management.
-
Master of Finance (MFin):
-
This program is ideal for those looking to specialize in finance, investment banking, portfolio management, and financial analysis.
-
Master of Marketing (MMkt):
-
This program focuses on advanced marketing strategies, consumer behavior, brand management, and digital marketing.
-
Master of Human Resource Management (MHRM):
-
If you're interested in HR, this program can help you specialize in areas like talent management, organizational behavior, and employee relations.
-
Master of Data Analytics:
-
As data becomes increasingly important, this program equips you with skills in data analysis, data mining, and business intelligence.
-
Master of International Business (MIB):
-
For those interested in global business, this program provides insights into international trade, cross-cultural management, and global economics.
-
Chartered Accountancy (CA):
-
Becoming a Chartered Accountant involves further studies and rigorous exams. It opens up opportunities in accounting, auditing, taxation, and financial management.
-
Certified Management Accountant (CMA):
-
Similar to CA, CMA focuses on management accounting and strategic financial management.
-
Certified Financial Planner (CFP):
-
If you're interested in personal financial planning, this certification can provide specialized skills in investment planning, retirement planning, and risk management.
-
Certified Public Accountant (CPA):
-
A CPA qualification is recognized globally and offers expertise in accounting, auditing, taxation, and financial reporting.
-
Digital Marketing Certification:
-
If you're interested in marketing, digital marketing certifications can enhance your skills in areas like SEO, social media, and online advertising.
-
Project Management Certification (PMP):
-
This certification is valuable for roles that involve managing projects, teams, and resources.
-
Data Science Bootcamps:
-
Short-term intensive programs that focus on data science skills, including programming, statistics, and machine learning.
-
Entrepreneurship and Innovation Programs:
-
These programs are designed for aspiring entrepreneurs, helping you develop business ideas and strategies.
-
Law Degree (LLB):
-
Combining a BCom with an LLB can open up opportunities in corporate law, mergers and acquisitions, and contract law.
-
Master's in Public Administration (MPA) or Public Policy (MPP):
-
For those interested in public service, these programs provide insights into policy analysis, public administration, and governance.
-
Professional Certifications:
-
Depending on your field of interest, there are various professional certifications available, such as Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP), Certified Fraud Examiner (CFE), or Professional in Human Resources (PHR).
Consider your career goals, interests, and strengths when deciding which course or certification to pursue. Further education can provide a significant boost to your career prospects and help you stand out in a competitive job market.
Corporate Job Options after BCom
After completing a Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) degree, there are numerous corporate job options available across various departments and roles within companies. Here are some corporate job options that BCom graduates can consider:
-
Financial Analyst:
-
Analyzing financial data, preparing reports, and providing insights for investment decisions.
-
Accountant:
-
Managing financial records, preparing financial statements, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
-
Auditor (Internal or External):
-
Reviewing financial records, internal controls, and processes to ensure accuracy and compliance.
-
Investment Banker:
-
Advising clients on financial transactions, mergers and acquisitions, and capital raising.
-
Marketing Manager:
-
Developing marketing strategies, managing campaigns, and analyzing market trends.
-
Sales Executive:
-
Identifying potential clients, selling products or services, and building client relationships.
-
Human Resources (HR) Manager:
-
Managing employee recruitment, training, benefits, and performance evaluations.
-
Operations Manager:
-
Overseeing day-to-day operations, optimizing processes, and ensuring efficiency.
-
Business Analyst:
-
Analyzing business processes, identifying areas for improvement, and proposing solutions.
-
Supply Chain Manager:
-
Managing the end-to-end supply chain, including procurement, logistics, and inventory management.
-
Management Consultant:
-
Providing expert advice to organizations on improving operations, efficiency, and strategy.
-
Risk Manager:
-
Identifying and assessing potential risks to the organization and implementing risk mitigation strategies.
-
Treasury Analyst:
-
Managing a company's financial assets, cash flow, and investments.
-
Tax Consultant:
-
Advising individuals and businesses on tax planning, compliance, and strategies.
-
Business Development Manager:
-
Identifying growth opportunities, developing partnerships, and expanding market presence.
-
Financial Planner:
-
Assisting clients in managing their finances, investments, and retirement planning.
-
Corporate Communications Specialist:
-
Managing internal and external communications, public relations, and media relations.
-
Digital Marketing Specialist:
-
Developing and executing digital marketing campaigns across various online platforms.
-
E-commerce Manager:
-
Overseeing online sales platforms, managing product listings, and optimizing user experience.
-
Real Estate Analyst:
-
Analyzing real estate market trends, property valuation, and investment opportunities.
-
Data Analyst:
-
Collecting, interpreting, and analyzing data to provide insights for business decisions.
-
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Manager:
-
Developing and implementing CSR initiatives and sustainability strategies.
-
Quality Control Analyst:
-
Monitoring and maintaining quality standards for products or services.
-
Business Intelligence Analyst:
-
Extracting insights from data to support strategic decision-making and business growth.
-
IT Project Manager:
-
Leading and managing technology-related projects within the organization.
These are just a few examples of the corporate job options available to BCom graduates. Depending on your interests, strengths, and the industry you're drawn to, you can explore various roles that align with your career aspirations. It's important to research and understand the requirements and responsibilities of each role to make an informed decision about your career path.
Some Competitive Exams for BCom Graduates
BCom graduates have the option to take various competitive exams to enhance their qualifications, skills, and career prospects. Here are some competitive exams that BCom graduates can consider:
-
Common Admission Test (CAT):
-
For admission to prestigious MBA programs in India, including the Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs).
-
Xavier Aptitude Test (XAT):
-
Accepted by many management institutes for admission to MBA programs.
-
Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT):
-
Widely recognized for admission to MBA and other business-related graduate programs globally.
-
Symbiosis National Aptitude Test (SNAP):
-
Conducted by Symbiosis International University for admission to various MBA programs in their affiliated institutes.
-
National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) Entrance Exam:
-
For admission to undergraduate and postgraduate fashion and design programs.
-
Company Secretary (CS) Entrance Exam:
-
For becoming a qualified Company Secretary, which involves corporate governance and legal compliance.
-
Chartered Accountant (CA) Examinations:
-
A series of exams to become a qualified Chartered Accountant, with opportunities in accounting, auditing, and taxation.
-
Certified Management Accountant (CMA) Examinations:
-
For becoming a Certified Management Accountant, focusing on management accounting and financial management.
-
Certified Public Accountant (CPA) Exam:
-
For becoming a Certified Public Accountant, recognized internationally for accounting and auditing roles.
-
Bank Probationary Officer (PO) Exams:
-
Exams conducted by various banks for recruitment as Probationary Officers in banking sector.
-
Staff Selection Commission (SSC) Exams:
-
Various SSC exams for recruitment to government jobs in different departments.
-
Insurance Exams (LIC, NIACL, UIIC, etc.):
-
For recruitment to positions in insurance companies.
-
Railway Recruitment Exams:
-
For positions in the Indian Railways.
-
UPSC Civil Services Exam:
-
For recruitment to prestigious government services like IAS, IPS, IFS, and more.
-
State Public Service Commission Exams:
-
State-level exams for recruitment to administrative, police, and other government positions.
-
Central Teacher Eligibility Test (CTET):
-
For those interested in becoming school teachers.
-
State Eligibility Test (SET/NET):
-
For eligibility as Assistant Professor in universities and colleges.
-
Defense Exams (CDS, AFCAT, NDA, etc.):
-
For recruitment to defense services like Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force.
-
RBI Grade B Officer Exam:
-
For recruitment to officer positions in the Reserve Bank of India.
-
NABARD Grade A and B Officer Exams:
-
For recruitment to officer positions in the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development.
Before appearing for any competitive exam, it's essential to thoroughly research the exam pattern, syllabus, eligibility criteria, and preparation strategies. Determine which exams align with your career goals and interests to make an informed decision about the exams you should focus on.
Career Switch options in Tech and Business (Influence KH career options)
Switching careers from one field to another, especially between technology and business, can be both challenging and rewarding. Here are some career switch options in the tech and business sectors, influenced by Influence KH's journey:
-
Digital Marketing Specialist:
-
Leverage your business acumen to specialize in digital marketing strategies, including social media marketing, content creation, and online advertising.
-
Product Manager:
-
Combine your tech knowledge with business insights to oversee the development and management of digital products or software applications.
-
Business Analyst for Tech Companies:
-
Utilize your understanding of both technology and business to analyze market trends, customer needs, and business requirements for tech companies.
-
IT Project Manager:
-
Use your leadership skills to manage and oversee the execution of technology projects within organizations.
-
E-commerce Manager:
-
Capitalize on your business background to manage and optimize online sales platforms and e-commerce operations.
-
Tech Entrepreneur:
-
Apply your tech skills and business mindset to start your own tech-related venture, such as a software startup or an e-commerce platform.
-
Business Intelligence Analyst:
-
Blend your business knowledge with data analytics skills to extract valuable insights and drive strategic decision-making.
-
IT Consulting:
-
Combine your tech expertise with business insights to offer consulting services to companies seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure and operations.
-
Digital Transformation Specialist:
-
Help organizations integrate technology into their business processes to achieve efficiency, innovation, and growth.
-
Data Science and Analytics Manager:
-
Combine your tech and business skills to lead data-driven initiatives, turning raw data into actionable insights for business strategies.
-
Tech Sales and Marketing:
-
Leverage your business acumen to sell and market tech products and services to clients, translating technical features into business benefits.
-
Tech Product Marketing Manager:
-
Utilize your tech knowledge to develop marketing strategies for tech products, translating their technical value into customer benefits.
-
Cybersecurity Analyst with Business Focus:
-
Combine your tech skills with a business perspective to analyze cybersecurity threats and their potential impact on business operations.
-
Technology Investment Analyst:
-
Use your business acumen to analyze tech companies and startups for investment opportunities in the venture capital or private equity sectors.
-
Business Development in Tech Startups:
-
Apply your business skills to identify growth opportunities, partnerships, and market expansion strategies for tech startups.
-
Tech Policy Analyst:
-
Combine your understanding of technology and its impact on business to analyze and formulate policies that address tech-related challenges.
-
Educator in Tech Business:
-
Share your combined tech and business knowledge by becoming an educator, teaching courses that bridge the gap between these two fields.
Influence KH's journey showcases the potential of successfully combining skills and experiences from both the tech and business sectors. Consider your own strengths, interests, and the skills you've acquired to determine the best career switch option for you. Transitioning between these two sectors can provide you with a unique advantage and open doors to exciting opportunities. Remember that a well-thought-out plan, continuous learning, and adaptability are key to a successful career switch.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of career options after a BCom degree is wide and diverse, offering a plethora of pathways for growth and success. As you stand at the threshold of your post-graduation journey, remember that your BCom degree equips you with a versatile skill set that can be applied across industries and sectors. The evolving job market calls for adaptability, continuous learning, and the ability to blend traditional business knowledge with emerging technologies.
Whether you choose to embark on a traditional career path in finance, accounting, or marketing, or opt for newer fields like digital marketing, fintech, or data analytics, the key lies in aligning your interests, strengths, and aspirations with the opportunities that resonate with you. Embrace the evolving landscape of business, where technology and innovation are driving transformations at an unprecedented pace.
Keep in mind that the pursuit of knowledge doesn't end with your degree. Lifelong learning, professional development, and staying updated with industry trends will be essential to thriving in your chosen career. Networking, both online and offline, will help you build meaningful connections that could lead to collaborations, mentorships, and job opportunities.
As you take your next steps after BCom, be open to exploring new paths, taking calculated risks, and stepping out of your comfort zone. Your journey might involve ups and downs, but each experience will contribute to your growth and resilience. Remember that success is not solely defined by the title of your job, but by the fulfillment you find in contributing to your field and making a positive impact on the world around you.
Whether you're drawn to traditional business roles, emerging tech-driven positions, or a blend of both, the future is bright for BCom graduates who are ready to seize the opportunities that await them. Your education, skills, and determination will be your compass as you navigate through a dynamic and ever-evolving professional landscape. So, go forth with confidence, curiosity, and a commitment to lifelong learning, and make your mark in the exciting world of post-BCom career possibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a BCom degree? A BCom degree, or Bachelor of Commerce, is an undergraduate academic program that provides a comprehensive education in various business-related disciplines, including finance, accounting, marketing, economics, and management.
2. What career options are available after completing a BCom degree? BCom graduates can pursue careers in fields such as finance, accounting, marketing, human resources, consulting, entrepreneurship, business analytics, and more. The degree's versatility allows graduates to explore various industries and job roles.
3. Can I switch to a tech-related career after completing a BCom degree? Yes, many tech-related career options are accessible to BCom graduates, especially with the integration of technology into various industries. By acquiring additional tech skills or certifications, you can transition to roles like data analyst, digital marketer, IT project manager, and more.
4. How can I specialize within my BCom degree for better career prospects? You can specialize by taking elective courses in specific areas during your BCom program. Specializations such as accounting, finance, marketing, entrepreneurship, and business analytics can enhance your expertise and open doors to relevant career opportunities.
5. Is further education necessary after a BCom degree? Further education, such as pursuing a master's degree, MBA, or professional certifications, can enhance your skills, qualifications, and career prospects. However, it's not mandatory, and career success can be achieved through a combination of education, skills, and experience.
6. How important is networking for post-BCom career success? Networking is crucial for career growth. Building professional relationships, attending industry events, and connecting with professionals in your desired field can lead to job opportunities, collaborations, and mentorships.
7. Can I start my own business after a BCom degree? Yes, a BCom degree equips you with fundamental business knowledge that can be valuable when starting your own business. Entrepreneurship is a viable path, but it requires careful planning, market research, and the ability to adapt to challenges.
8. What are the advantages of pursuing a career in tech with a BCom background? Combining a BCom background with tech skills offers a unique blend of business acumen and technological understanding, which is highly sought after in today's tech-driven world. It can open doors to roles that require a deep understanding of both business operations and technology.
9. How can I determine the right career path after BCom? Assess your interests, strengths, and values. Research different industries and job roles to understand their requirements and prospects. Seek advice from professionals in the field and consider seeking career counseling to make an informed decision.
10. What skills should I focus on developing after a BCom degree? Soft skills such as communication, leadership, problem-solving, and adaptability are crucial. Additionally, honing technical skills like data analysis, digital marketing, coding, and project management can make you more competitive in the job market.
Read More
In the dynamic landscape of career choices post-BCom, navigating the path to success requires both strategic thinking and informed decisions. As the year 2023 unfolds, opportunities abound for BCom graduates seeking to elevate their professional trajectories. With the convergence of business acumen and emerging technologies, this pivotal juncture presents a multitude of options that extend far beyond traditional boundaries.
In this pursuit, Icert Global offers courses such as CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional), CCBA (Certification of Capability in Business Analysis), and ECBA (Entry Certificate in Business Analysis) can be a transformative step. These courses serve as catalysts, equipping graduates with a refined skill set that bridges the gap between the business realm and the rapidly evolving tech landscape.
As we delve into the realm of "2023 Career Options: Your Next Steps After BCom," we'll explore how the symbiosis of your BCom foundation and these specialized courses can shape an exciting and impactful journey. From unleashing the power of data analysis to charting strategic business solutions, this exploration will illuminate the myriad possibilities that await, propelling BCom graduates towards the forefront of innovation and success.
In this article
-
Why Should You Pursue a BCom Degree?
-
Scope of BCom Degree
-
Career after BCom (Sectors)
-
Courses after BCom
-
Corporate Job Options after BCom
-
Some Competitive Exams for BCom Graduates
-
Career Switch options in Tech and Business (Influence KH career options)
-
Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why Should You Pursue a BCom Degree?
Pursuing a Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) degree can offer numerous advantages and open up a wide array of opportunities. Here are some compelling reasons why you should consider pursuing a BCom degree:
-
Versatile Skill Set: BCom programs provide a well-rounded education in various business disciplines, including accounting, finance, marketing, management, economics, and more. This versatile skill set prepares you for a range of roles across different industries.
-
Strong Foundation: A BCom degree lays a solid foundation in business concepts and principles. This knowledge is essential whether you plan to work in a corporate environment, start your own business, or pursue further education.
-
Diverse Career Paths: The skills gained through a BCom degree can lead to a diverse range of career paths. Whether you're interested in finance, marketing, entrepreneurship, consulting, or even public administration, a BCom degree equips you with the knowledge needed to excel in these areas.
-
High Demand: Businesses of all sizes require individuals with business acumen to handle various aspects of their operations. BCom graduates are in high demand across industries, making it easier to secure job opportunities upon graduation.
-
Adaptability: The business landscape is constantly evolving. A BCom degree teaches you how to adapt to change, think critically, and solve complex problems—skills that are crucial in a dynamic business world.
-
Networking Opportunities: University programs often provide opportunities to network with professors, fellow students, and industry professionals. These connections can be invaluable for future career growth and job opportunities.
-
Entrepreneurship: If you aspire to start your own business, a BCom degree can provide you with the foundational knowledge to understand market trends, manage finances, and develop effective business strategies.
-
Higher Earning Potential: On average, individuals with a BCom degree tend to earn higher salaries compared to those without a degree. As you progress in your career, your earning potential is likely to increase.
-
Global Opportunities: The principles learned in a BCom program are applicable worldwide. This opens up opportunities for international careers and the chance to work with multinational companies.
-
Preparation for Advanced Studies: If you're considering pursuing a master's degree or further education, a BCom degree can serve as a strong foundation. Many specialized fields, such as finance or business analytics, require a solid understanding of business concepts.
-
Analytical Skills: BCom programs emphasize data analysis, problem-solving, and critical thinking. These skills are highly transferable and can be applied to various aspects of both professional and personal life.
-
Career Progression: Many leadership roles within organizations require a deep understanding of business operations, strategy, and management. A BCom degree can help fast-track your career progression into such roles.
-
Contribution to Society: Businesses play a crucial role in shaping economies and societies. With a BCom degree, you have the opportunity to contribute positively to both business growth and community development.
In conclusion, pursuing a BCom degree can provide you with a strong educational foundation, a broad skill set, and a pathway to a fulfilling and successful career. Whether you're interested in working for established corporations, launching your own startup, or contributing to public sector initiatives, a BCom degree equips you with the tools you need to excel in various professional pursuits.
Scope of BCom Degree
The scope of a Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) degree is extensive and offers graduates a wide range of career opportunities across various industries. Here's an overview of the scope of a BCom degree:
-
Business Management and Administration:
-
Graduates can work in roles such as business managers, operations managers, and general managers, overseeing various aspects of company operations.
-
-
Finance and Accounting:
-
Opportunities exist in areas like corporate finance, investment banking, financial analysis, auditing, and accounting.
-
BCom graduates can become financial analysts, accountants, tax consultants, auditors, or even certified public accountants (CPAs).
-
-
Marketing and Sales:
-
BCom graduates can pursue careers in marketing, advertising, public relations, and sales.
-
Roles like marketing managers, brand managers, digital marketers, and sales executives are common.
-
-
E-commerce and Retail:
-
With the growth of online shopping, BCom graduates can excel in roles related to e-commerce management, online retail, and supply chain management.
-
-
Human Resources:
-
Graduates can work in HR roles, including human resource management, recruitment, training, and employee relations.
-
-
Entrepreneurship:
-
BCom graduates with an entrepreneurial spirit can start their own businesses or startups, using their business knowledge to create and manage successful ventures.
-
-
Consulting:
-
Graduates can become management consultants, offering expert advice to businesses on improving efficiency, strategy, and operations.
-
-
Business Analytics:
-
The increasing importance of data-driven decision-making has created a demand for business analysts who can interpret and analyze data to drive business strategies.
-
-
Public Sector and Government Jobs:
-
BCom graduates can work in government departments, public administration, and agencies, handling financial management, budgeting, and policy analysis.
-
-
International Business:
-
The global nature of business means that BCom graduates can find opportunities in international trade, export-import management, and global supply chain management.
-
-
Financial Technology (Fintech):
-
The integration of finance and technology has led to roles like fintech analysts, blockchain specialists, and payment system managers.
-
-
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
-
Graduates can work in CSR roles, helping companies implement socially responsible practices and sustainable business strategies.
-
-
Nonprofit and NGO Sector:
-
BCom graduates can contribute to nonprofit organizations and NGOs in areas such as finance management, fundraising, and program coordination.
-
-
Supply Chain Management:
-
Graduates can manage the end-to-end supply chain, ensuring efficient movement of goods and services from suppliers to customers.
-
-
Risk Management and Insurance:
-
Opportunities exist in roles related to risk assessment, insurance underwriting, and claims management.
-
-
Real Estate and Property Management:
-
BCom graduates can work in real estate, property management, and real estate development, handling transactions and investments.
-
-
Higher Education and Academia:
-
Some graduates choose to pursue advanced degrees and become educators, teaching business-related courses at universities and colleges.
-
-
Media and Entertainment Industry:
-
BCom graduates can work in media management, advertising, public relations, and entertainment business roles.
-
The scope of a BCom degree is not limited to any single industry, making it a versatile choice that can lead to a fulfilling and successful career in various fields. The key lies in identifying your strengths, interests, and career goals and aligning them with the diverse opportunities that a BCom degree offers.
Career after BCom (Sectors)
After completing a Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) degree, you'll have a wide range of career options across various sectors. Here are some of the prominent sectors where BCom graduates can find rewarding careers:
-
Finance and Banking:
-
Financial Analyst
-
Investment Banker
-
Wealth Manager
-
Credit Analyst
-
Retail or Commercial Banker
-
Financial Planner
-
-
Accounting and Auditing:
-
Accountant
-
Auditor (Internal or External)
-
Tax Consultant
-
Forensic Accountant
-
Cost Accountant
-
-
Marketing and Advertising:
-
Marketing Manager
-
Brand Manager
-
Advertising Executive
-
Market Research Analyst
-
Digital Marketing Specialist
-
-
Sales and Retail:
-
Sales Executive
-
Retail Manager
-
Customer Relationship Manager
-
Sales Analyst
-
Business Development Representative
-
-
Human Resources:
-
Human Resource Manager
-
Recruitment Specialist
-
Training and Development Coordinator
-
Compensation and Benefits Analyst
-
-
Business Consulting:
-
Management Consultant
-
Strategy Analyst
-
Business Process Analyst
-
Change Management Specialist
-
-
Entrepreneurship and Startups:
-
Business Owner
-
Startup Founder
-
Small Business Manager
-
Entrepreneurial Consultant
-
-
Information Technology (IT) and Business Analytics:
-
Business Analyst
-
Data Analyst
-
IT Consultant
-
Systems Analyst
-
Business Intelligence Analyst
-
-
Supply Chain and Logistics:
-
Supply Chain Manager
-
Logistics Coordinator
-
Procurement Specialist
-
Operations Analyst
-
-
Public Sector and Government:
-
Government Financial Officer
-
Budget Analyst
-
Taxation Officer
-
Customs Inspector
-
-
Nonprofit and NGOs:
-
Program Coordinator
-
Fundraising Manager
-
Grant Writer
-
NGO Financial Analyst
-
-
Insurance and Risk Management:
-
Insurance Underwriter
-
Risk Manager
-
Claims Analyst
-
Insurance Broker
-
-
Real Estate and Property Management:
-
Real Estate Agent
-
Property Manager
-
Real Estate Analyst
-
Real Estate Developer
-
-
Media and Entertainment:
-
Media Planner
-
Entertainment Manager
-
Public Relations Specialist
-
Event Coordinator
-
-
Healthcare Administration:
-
Healthcare Administrator
-
Medical Practice Manager
-
Health Services Manager
-
-
E-commerce and Retail Management:
-
E-commerce Manager
-
Online Retail Specialist
-
E-commerce Analyst
-
-
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
-
CSR Manager
-
Sustainability Consultant
-
Social Impact Analyst
-
-
Higher Education and Academia:
-
Academic Researcher
-
Lecturer or Professor
-
Remember, the sectors mentioned above are just a snapshot of the possibilities available to BCom graduates. The skills and knowledge gained during your BCom studies can be applied across industries, making your career choices highly versatile. It's important to explore your interests, strengths, and aspirations to find the sector that aligns best with your goals.
Courses after BCom
After completing a Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) degree, you have a variety of options for further education to enhance your skills, specialize in a particular field, or broaden your career opportunities. Here are some courses and paths you might consider pursuing after your BCom:
-
Master of Business Administration (MBA):
-
An MBA program provides advanced knowledge in business management and leadership skills, preparing you for executive-level roles.
-
Specializations might include Marketing, Finance, Human Resources, Operations, or Entrepreneurship.
-
-
Master of Commerce (MCom):
-
An MCom program delves deeper into subjects covered in your BCom, offering advanced knowledge in accounting, finance, economics, and management.
-
-
Master of Finance (MFin):
-
This program is ideal for those looking to specialize in finance, investment banking, portfolio management, and financial analysis.
-
-
Master of Marketing (MMkt):
-
This program focuses on advanced marketing strategies, consumer behavior, brand management, and digital marketing.
-
-
Master of Human Resource Management (MHRM):
-
If you're interested in HR, this program can help you specialize in areas like talent management, organizational behavior, and employee relations.
-
-
Master of Data Analytics:
-
As data becomes increasingly important, this program equips you with skills in data analysis, data mining, and business intelligence.
-
-
Master of International Business (MIB):
-
For those interested in global business, this program provides insights into international trade, cross-cultural management, and global economics.
-
-
Chartered Accountancy (CA):
-
Becoming a Chartered Accountant involves further studies and rigorous exams. It opens up opportunities in accounting, auditing, taxation, and financial management.
-
-
Certified Management Accountant (CMA):
-
Similar to CA, CMA focuses on management accounting and strategic financial management.
-
-
Certified Financial Planner (CFP):
-
If you're interested in personal financial planning, this certification can provide specialized skills in investment planning, retirement planning, and risk management.
-
-
Certified Public Accountant (CPA):
-
A CPA qualification is recognized globally and offers expertise in accounting, auditing, taxation, and financial reporting.
-
-
Digital Marketing Certification:
-
If you're interested in marketing, digital marketing certifications can enhance your skills in areas like SEO, social media, and online advertising.
-
-
Project Management Certification (PMP):
-
This certification is valuable for roles that involve managing projects, teams, and resources.
-
-
Data Science Bootcamps:
-
Short-term intensive programs that focus on data science skills, including programming, statistics, and machine learning.
-
-
Entrepreneurship and Innovation Programs:
-
These programs are designed for aspiring entrepreneurs, helping you develop business ideas and strategies.
-
-
Law Degree (LLB):
-
Combining a BCom with an LLB can open up opportunities in corporate law, mergers and acquisitions, and contract law.
-
-
Master's in Public Administration (MPA) or Public Policy (MPP):
-
For those interested in public service, these programs provide insights into policy analysis, public administration, and governance.
-
-
Professional Certifications:
-
Depending on your field of interest, there are various professional certifications available, such as Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP), Certified Fraud Examiner (CFE), or Professional in Human Resources (PHR).
-
Consider your career goals, interests, and strengths when deciding which course or certification to pursue. Further education can provide a significant boost to your career prospects and help you stand out in a competitive job market.
Corporate Job Options after BCom
After completing a Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) degree, there are numerous corporate job options available across various departments and roles within companies. Here are some corporate job options that BCom graduates can consider:
-
Financial Analyst:
-
Analyzing financial data, preparing reports, and providing insights for investment decisions.
-
-
Accountant:
-
Managing financial records, preparing financial statements, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
-
-
Auditor (Internal or External):
-
Reviewing financial records, internal controls, and processes to ensure accuracy and compliance.
-
-
Investment Banker:
-
Advising clients on financial transactions, mergers and acquisitions, and capital raising.
-
-
Marketing Manager:
-
Developing marketing strategies, managing campaigns, and analyzing market trends.
-
-
Sales Executive:
-
Identifying potential clients, selling products or services, and building client relationships.
-
-
Human Resources (HR) Manager:
-
Managing employee recruitment, training, benefits, and performance evaluations.
-
-
Operations Manager:
-
Overseeing day-to-day operations, optimizing processes, and ensuring efficiency.
-
-
Business Analyst:
-
Analyzing business processes, identifying areas for improvement, and proposing solutions.
-
-
Supply Chain Manager:
-
Managing the end-to-end supply chain, including procurement, logistics, and inventory management.
-
-
Management Consultant:
-
Providing expert advice to organizations on improving operations, efficiency, and strategy.
-
-
Risk Manager:
-
Identifying and assessing potential risks to the organization and implementing risk mitigation strategies.
-
-
Treasury Analyst:
-
Managing a company's financial assets, cash flow, and investments.
-
-
Tax Consultant:
-
Advising individuals and businesses on tax planning, compliance, and strategies.
-
-
Business Development Manager:
-
Identifying growth opportunities, developing partnerships, and expanding market presence.
-
-
Financial Planner:
-
Assisting clients in managing their finances, investments, and retirement planning.
-
-
Corporate Communications Specialist:
-
Managing internal and external communications, public relations, and media relations.
-
-
Digital Marketing Specialist:
-
Developing and executing digital marketing campaigns across various online platforms.
-
-
E-commerce Manager:
-
Overseeing online sales platforms, managing product listings, and optimizing user experience.
-
-
Real Estate Analyst:
-
Analyzing real estate market trends, property valuation, and investment opportunities.
-
-
Data Analyst:
-
Collecting, interpreting, and analyzing data to provide insights for business decisions.
-
-
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Manager:
-
Developing and implementing CSR initiatives and sustainability strategies.
-
-
Quality Control Analyst:
-
Monitoring and maintaining quality standards for products or services.
-
-
Business Intelligence Analyst:
-
Extracting insights from data to support strategic decision-making and business growth.
-
-
IT Project Manager:
-
Leading and managing technology-related projects within the organization.
-
These are just a few examples of the corporate job options available to BCom graduates. Depending on your interests, strengths, and the industry you're drawn to, you can explore various roles that align with your career aspirations. It's important to research and understand the requirements and responsibilities of each role to make an informed decision about your career path.
Some Competitive Exams for BCom Graduates
BCom graduates have the option to take various competitive exams to enhance their qualifications, skills, and career prospects. Here are some competitive exams that BCom graduates can consider:
-
Common Admission Test (CAT):
-
For admission to prestigious MBA programs in India, including the Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs).
-
-
Xavier Aptitude Test (XAT):
-
Accepted by many management institutes for admission to MBA programs.
-
-
Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT):
-
Widely recognized for admission to MBA and other business-related graduate programs globally.
-
-
Symbiosis National Aptitude Test (SNAP):
-
Conducted by Symbiosis International University for admission to various MBA programs in their affiliated institutes.
-
-
National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) Entrance Exam:
-
For admission to undergraduate and postgraduate fashion and design programs.
-
-
Company Secretary (CS) Entrance Exam:
-
For becoming a qualified Company Secretary, which involves corporate governance and legal compliance.
-
-
Chartered Accountant (CA) Examinations:
-
A series of exams to become a qualified Chartered Accountant, with opportunities in accounting, auditing, and taxation.
-
-
Certified Management Accountant (CMA) Examinations:
-
For becoming a Certified Management Accountant, focusing on management accounting and financial management.
-
-
Certified Public Accountant (CPA) Exam:
-
For becoming a Certified Public Accountant, recognized internationally for accounting and auditing roles.
-
-
Bank Probationary Officer (PO) Exams:
-
Exams conducted by various banks for recruitment as Probationary Officers in banking sector.
-
-
Staff Selection Commission (SSC) Exams:
-
Various SSC exams for recruitment to government jobs in different departments.
-
-
Insurance Exams (LIC, NIACL, UIIC, etc.):
-
For recruitment to positions in insurance companies.
-
-
Railway Recruitment Exams:
-
For positions in the Indian Railways.
-
-
UPSC Civil Services Exam:
-
For recruitment to prestigious government services like IAS, IPS, IFS, and more.
-
-
State Public Service Commission Exams:
-
State-level exams for recruitment to administrative, police, and other government positions.
-
-
Central Teacher Eligibility Test (CTET):
-
For those interested in becoming school teachers.
-
-
State Eligibility Test (SET/NET):
-
For eligibility as Assistant Professor in universities and colleges.
-
-
Defense Exams (CDS, AFCAT, NDA, etc.):
-
For recruitment to defense services like Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force.
-
-
RBI Grade B Officer Exam:
-
For recruitment to officer positions in the Reserve Bank of India.
-
-
NABARD Grade A and B Officer Exams:
-
For recruitment to officer positions in the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development.
-
Before appearing for any competitive exam, it's essential to thoroughly research the exam pattern, syllabus, eligibility criteria, and preparation strategies. Determine which exams align with your career goals and interests to make an informed decision about the exams you should focus on.
Career Switch options in Tech and Business (Influence KH career options)
Switching careers from one field to another, especially between technology and business, can be both challenging and rewarding. Here are some career switch options in the tech and business sectors, influenced by Influence KH's journey:
-
Digital Marketing Specialist:
-
Leverage your business acumen to specialize in digital marketing strategies, including social media marketing, content creation, and online advertising.
-
-
Product Manager:
-
Combine your tech knowledge with business insights to oversee the development and management of digital products or software applications.
-
-
Business Analyst for Tech Companies:
-
Utilize your understanding of both technology and business to analyze market trends, customer needs, and business requirements for tech companies.
-
-
IT Project Manager:
-
Use your leadership skills to manage and oversee the execution of technology projects within organizations.
-
-
E-commerce Manager:
-
Capitalize on your business background to manage and optimize online sales platforms and e-commerce operations.
-
-
Tech Entrepreneur:
-
Apply your tech skills and business mindset to start your own tech-related venture, such as a software startup or an e-commerce platform.
-
-
Business Intelligence Analyst:
-
Blend your business knowledge with data analytics skills to extract valuable insights and drive strategic decision-making.
-
-
IT Consulting:
-
Combine your tech expertise with business insights to offer consulting services to companies seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure and operations.
-
-
Digital Transformation Specialist:
-
Help organizations integrate technology into their business processes to achieve efficiency, innovation, and growth.
-
-
Data Science and Analytics Manager:
-
Combine your tech and business skills to lead data-driven initiatives, turning raw data into actionable insights for business strategies.
-
-
Tech Sales and Marketing:
-
Leverage your business acumen to sell and market tech products and services to clients, translating technical features into business benefits.
-
-
Tech Product Marketing Manager:
-
Utilize your tech knowledge to develop marketing strategies for tech products, translating their technical value into customer benefits.
-
-
Cybersecurity Analyst with Business Focus:
-
Combine your tech skills with a business perspective to analyze cybersecurity threats and their potential impact on business operations.
-
-
Technology Investment Analyst:
-
Use your business acumen to analyze tech companies and startups for investment opportunities in the venture capital or private equity sectors.
-
-
Business Development in Tech Startups:
-
Apply your business skills to identify growth opportunities, partnerships, and market expansion strategies for tech startups.
-
-
Tech Policy Analyst:
-
Combine your understanding of technology and its impact on business to analyze and formulate policies that address tech-related challenges.
-
-
Educator in Tech Business:
-
Share your combined tech and business knowledge by becoming an educator, teaching courses that bridge the gap between these two fields.
-
Influence KH's journey showcases the potential of successfully combining skills and experiences from both the tech and business sectors. Consider your own strengths, interests, and the skills you've acquired to determine the best career switch option for you. Transitioning between these two sectors can provide you with a unique advantage and open doors to exciting opportunities. Remember that a well-thought-out plan, continuous learning, and adaptability are key to a successful career switch.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of career options after a BCom degree is wide and diverse, offering a plethora of pathways for growth and success. As you stand at the threshold of your post-graduation journey, remember that your BCom degree equips you with a versatile skill set that can be applied across industries and sectors. The evolving job market calls for adaptability, continuous learning, and the ability to blend traditional business knowledge with emerging technologies.
Whether you choose to embark on a traditional career path in finance, accounting, or marketing, or opt for newer fields like digital marketing, fintech, or data analytics, the key lies in aligning your interests, strengths, and aspirations with the opportunities that resonate with you. Embrace the evolving landscape of business, where technology and innovation are driving transformations at an unprecedented pace.
Keep in mind that the pursuit of knowledge doesn't end with your degree. Lifelong learning, professional development, and staying updated with industry trends will be essential to thriving in your chosen career. Networking, both online and offline, will help you build meaningful connections that could lead to collaborations, mentorships, and job opportunities.
As you take your next steps after BCom, be open to exploring new paths, taking calculated risks, and stepping out of your comfort zone. Your journey might involve ups and downs, but each experience will contribute to your growth and resilience. Remember that success is not solely defined by the title of your job, but by the fulfillment you find in contributing to your field and making a positive impact on the world around you.
Whether you're drawn to traditional business roles, emerging tech-driven positions, or a blend of both, the future is bright for BCom graduates who are ready to seize the opportunities that await them. Your education, skills, and determination will be your compass as you navigate through a dynamic and ever-evolving professional landscape. So, go forth with confidence, curiosity, and a commitment to lifelong learning, and make your mark in the exciting world of post-BCom career possibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a BCom degree? A BCom degree, or Bachelor of Commerce, is an undergraduate academic program that provides a comprehensive education in various business-related disciplines, including finance, accounting, marketing, economics, and management.
2. What career options are available after completing a BCom degree? BCom graduates can pursue careers in fields such as finance, accounting, marketing, human resources, consulting, entrepreneurship, business analytics, and more. The degree's versatility allows graduates to explore various industries and job roles.
3. Can I switch to a tech-related career after completing a BCom degree? Yes, many tech-related career options are accessible to BCom graduates, especially with the integration of technology into various industries. By acquiring additional tech skills or certifications, you can transition to roles like data analyst, digital marketer, IT project manager, and more.
4. How can I specialize within my BCom degree for better career prospects? You can specialize by taking elective courses in specific areas during your BCom program. Specializations such as accounting, finance, marketing, entrepreneurship, and business analytics can enhance your expertise and open doors to relevant career opportunities.
5. Is further education necessary after a BCom degree? Further education, such as pursuing a master's degree, MBA, or professional certifications, can enhance your skills, qualifications, and career prospects. However, it's not mandatory, and career success can be achieved through a combination of education, skills, and experience.
6. How important is networking for post-BCom career success? Networking is crucial for career growth. Building professional relationships, attending industry events, and connecting with professionals in your desired field can lead to job opportunities, collaborations, and mentorships.
7. Can I start my own business after a BCom degree? Yes, a BCom degree equips you with fundamental business knowledge that can be valuable when starting your own business. Entrepreneurship is a viable path, but it requires careful planning, market research, and the ability to adapt to challenges.
8. What are the advantages of pursuing a career in tech with a BCom background? Combining a BCom background with tech skills offers a unique blend of business acumen and technological understanding, which is highly sought after in today's tech-driven world. It can open doors to roles that require a deep understanding of both business operations and technology.
9. How can I determine the right career path after BCom? Assess your interests, strengths, and values. Research different industries and job roles to understand their requirements and prospects. Seek advice from professionals in the field and consider seeking career counseling to make an informed decision.
10. What skills should I focus on developing after a BCom degree? Soft skills such as communication, leadership, problem-solving, and adaptability are crucial. Additionally, honing technical skills like data analysis, digital marketing, coding, and project management can make you more competitive in the job market.
Decision Making in Management: Importance, Types & Process
In the dynamic realm of modern business, decision making stands as a cornerstone of effective management. Every organization, regardless of its size or industry, encounters a multitude of choices that shape its trajectory, influence its success, and define its identity. From strategic crossroads to day-to-day operations, the decisions made by managers play a pivotal role in steering the organization toward its goals. The intricate interplay of factors, ranging from limited resources and uncertain environments to diverse stakeholder interests, underscores the complexity of decision making in management.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the multifaceted world of decision making within the management sphere. We delve into the significance of decision making, understanding the varied types that managers encounter, and dissecting the step-by-step process that underpins sound choices. We'll navigate through the intricate tapestry of methodologies and techniques that managers employ to address challenges, seize opportunities, and chart the course for their organizations. Through an exploration of the interplay between strategic, tactical, operational, and ethical considerations, this discussion sheds light on the art and science of effective decision making in the realm of management.
In this article
-
What is Decision Making in Management?
-
Characteristics of Decision Making
-
What is Decision Making Process?
-
Decision Making Process in Management with Example
-
Decision Making Styles
-
Techniques of Decision Making
-
Types of Decision Making in Management
-
Difficulties in Decision Making Process
-
Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs )
What is Decision Making in Management?
Decision making in management refers to the process of selecting the best course of action from available alternatives to achieve organizational goals and objectives. It is a crucial aspect of managerial and leadership roles as it involves evaluating various choices and choosing the one that aligns most effectively with the organization's strategic direction and desired outcomes.
In essence, decision making in management involves assessing complex situations, considering various factors and constraints, and then arriving at a choice that optimally utilizes resources while minimizing risks and uncertainties. This process is not limited to high-level executives; decision making occurs at all levels of an organization, from top management to front-line supervisors.
Effective decision making is essential for the successful functioning of an organization as it impacts:
-
Resource Allocation: Decisions determine how resources such as finances, personnel, and time are allocated to different activities or projects.
-
Goal Achievement: Decisions contribute to achieving short-term and long-term goals set by the organization.
-
Problem Solving: Decision making is crucial for identifying and resolving challenges or problems that arise in the course of operations.
-
Innovation: Decisions can lead to innovative approaches and the adoption of new technologies, processes, or strategies.
-
Competitive Advantage: Strategic decisions can provide an organization with a competitive edge in the marketplace.
-
Adaptation to Change: Effective decision making allows an organization to respond to changes in the business environment promptly.
-
Stakeholder Satisfaction: Decisions that consider the interests of stakeholders such as employees, customers, and investors can lead to greater satisfaction.
-
Risk Management: Decisions involve assessing and managing risks associated with different choices.
-
Organizational Culture: The decision-making process can shape the culture and values of an organization.
-
Long-Term Viability: Sound decisions contribute to the organization's sustainability and growth over time.
In summary, decision making in management involves a systematic approach to evaluating alternatives, considering various factors, and selecting the most appropriate option to achieve organizational objectives. It requires a combination of analytical thinking, critical judgment, creativity, and an understanding of both internal and external factors affecting the organization.
Characteristics of Decision Making
Decision making is a complex process that involves a variety of characteristics and considerations. Here are some key characteristics of decision making:
-
Rationality: Rational decision making involves evaluating options based on objective information, logical analysis, and a systematic approach. It aims to select the option that maximizes benefits or achieves goals.
-
Objective: Decisions should be based on facts, data, and information rather than personal biases or emotions. Objectivity ensures that decisions are grounded in reality and have a higher likelihood of success.
-
Subjectivity: While objectivity is important, some decisions may involve subjective elements, especially when dealing with uncertain or ambiguous situations. Balancing objectivity and subjectivity is essential.
-
Trade-offs: Decisions often require weighing the pros and cons of different options. Trade-offs involve giving up certain benefits to gain others and are inherent in decision making.
-
Uncertainty: Many decisions are made in environments with incomplete or uncertain information. Decision makers must assess risks and potential outcomes even when information is lacking.
-
Risk: Every decision carries some level of risk. Decision makers must evaluate the potential consequences of each option and choose one that aligns with their risk tolerance and organizational goals.
-
Time Constraints: Decisions are often made within specific timeframes. The urgency of a decision can influence the depth of analysis and the available options.
-
Information Overload: In today's information-rich world, decision makers may face an overwhelming amount of data. The challenge is to sift through the information to identify relevant and actionable insights.
-
Group Dynamics: Group decisions involve collaboration and negotiation among team members. Group dynamics, including communication, power dynamics, and consensus-building, play a significant role.
-
Ethical Considerations: Ethical principles guide decision making, ensuring that choices are aligned with moral values, social responsibility, and legal obligations.
-
Cognitive Biases: Decision makers are subject to cognitive biases—systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality— that can influence their judgment and lead to suboptimal decisions.
-
Intuition: Intuitive decision making involves relying on gut feelings and instincts. While it can be useful in certain situations, it also carries the risk of bias and error.
-
Involvement of Emotions: Emotions can impact decision making by influencing perceptions, preferences, and risk assessment. Being aware of emotional influences is crucial for making sound decisions.
-
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Orientation: Some decisions focus on immediate gains, while others prioritize long-term benefits. Balancing short-term needs with long-term strategic goals is important.
-
Feedback Loop: Effective decision making involves evaluating the outcomes of previous decisions and using this feedback to improve future decisions. This iterative process contributes to organizational learning.
-
Communication: Clear and effective communication of decisions is vital for implementation and alignment within the organization. Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings and resistance.
-
Stakeholder Consideration: Decision makers must take into account the interests and concerns of various stakeholders, including employees, customers, investors, and the community.
Understanding these characteristics can help decision makers navigate the complexities of the decision-making process and make more informed and effective choices.
What is Decision Making Process?
The decision-making process is a systematic sequence of steps that individuals or groups follow to identify a problem or opportunity, gather relevant information, evaluate alternative courses of action, and ultimately choose the best option to address the situation. While there are various models of the decision-making process, a commonly used framework involves the following steps:
-
Identifying the Problem or Opportunity:
-
Recognize the need for a decision, which could arise from a problem that needs solving or an opportunity that can be seized.
-
Clearly define the issue at hand to ensure a focused decision-making process.
-
Gathering Information:
-
Collect relevant data, facts, and information related to the problem or opportunity.
-
This step involves researching, consulting experts, analyzing historical data, and understanding the context.
-
Generating Alternative Solutions:
-
Brainstorm and develop a range of possible solutions or courses of action to address the identified problem or opportunity.
-
Encourage creativity and consider different perspectives during this stage.
-
Evaluating Alternatives:
-
Assess the pros and cons of each alternative solution against predetermined criteria and objectives.
-
Consider the potential outcomes, risks, costs, benefits, and feasibility of each option.
-
Making a Decision:
-
Based on the evaluation, select the most suitable solution that aligns with the organization's goals and objectives.
-
The decision might involve a single choice or a combination of options.
-
Implementing the Decision:
-
Develop an action plan that outlines the steps required to put the chosen solution into effect.
-
Allocate resources, assign responsibilities, and set timelines for implementation.
-
Monitoring and Evaluation:
-
Track the implementation progress to ensure that the decision is being executed as planned.
-
Continuously monitor outcomes and compare them to the expected results.
-
Feedback and Adjustments:
-
Based on the monitoring and evaluation, gather feedback about the outcomes and effectiveness of the decision.
-
If necessary, make adjustments to the implementation strategy to achieve desired results.
It's important to note that decision making is not always a linear process, and there may be iterations, adjustments, and revisions at various stages. Additionally, the complexity of the process can vary based on factors such as the nature of the decision, the level of uncertainty, and the involvement of multiple stakeholders.
Different decision-making models, such as the rational model, the bounded rationality model, and the incremental model, offer alternative perspectives on how decisions are made. Organizations may adapt and customize these models to suit their specific needs and circumstances.
Successful decision making requires a combination of analytical thinking, critical judgment, effective communication, and consideration of ethical and moral implications. Additionally, learning from both successes and failures contributes to the refinement of decision-making skills over time.
Decision Making Process in Management with Example
let's walk through the decision-making process in management using a hypothetical example:
Scenario: Imagine you are a manager in a retail company that sells electronics. The company is considering whether to introduce a new line of smart home devices to its product offerings. You've been tasked with leading the decision-making process.
1. Identifying the Problem or Opportunity: You recognize the opportunity to expand the company's product range and potentially increase revenue by introducing smart home devices. However, you also need to consider the potential risks and challenges associated with entering a new market segment.
2. Gathering Information: You gather data on the current market trends for smart home devices, including consumer demand, competition, pricing, and potential suppliers. You also collect information on the company's capabilities, resources, and potential challenges in entering this market.
3. Generating Alternative Solutions: You brainstorm several options:
-
Option A: Introduce a limited range of popular smart home devices initially.
-
Option B: Collaborate with a well-known technology brand to co-brand the smart home devices.
-
Option C: Conduct a market research study to gather more data before making a decision.
4. Evaluating Alternatives:
-
Option A: You consider the potential demand for these devices and assess whether the company's current resources can handle the new product line. You weigh the potential benefits of immediate entry into the market against the risk of not offering a comprehensive range.
-
Option B: You evaluate the potential benefits of leveraging an established brand's reputation. You also assess the possible challenges of negotiations, branding alignment, and resource allocation.
-
Option C: You analyze the costs and benefits of conducting market research, including time, resources, and potential delay in market entry.
5. Making a Decision: After careful evaluation, you decide to proceed with Option A: Introduce a limited range of popular smart home devices. This decision aligns with the company's growth goals while minimizing the risk of overextending resources.
6. Implementing the Decision: You develop an implementation plan that outlines the product selection process, supplier negotiations, marketing strategies, and distribution channels. You allocate a dedicated team to handle this project.
7. Monitoring and Evaluation: As the smart home devices are introduced to the market, you monitor sales data, customer feedback, and any unexpected challenges that arise. You regularly communicate with your team to ensure that the plan is being executed as intended.
8. Feedback and Adjustments: After a few months, you gather feedback from customers and review sales performance. You identify that certain devices are particularly popular, while others are underperforming. Based on this feedback, you decide to expand the range of popular devices and discontinue the underperforming ones.
In this example, the decision-making process involved identifying an opportunity, gathering relevant information, generating alternative solutions, evaluating those alternatives, making a decision, implementing the plan, monitoring outcomes, and making adjustments based on feedback. This process enables the company to enter a new market segment strategically and adapt its approach based on real-world results.
Decision Making Styles
Decision-making styles refer to the different approaches individuals or groups use when making choices. These styles are influenced by personal preferences, cognitive processes, and situational factors. Here are some common decision-making styles:
-
Rational Decision Making: This style involves a systematic, logical, and analytical approach. Decision makers gather relevant information, weigh pros and cons, and choose the option that maximizes benefits and aligns with objectives. It's often used in structured and well-defined situations.
-
Intuitive Decision Making: Intuitive decision makers rely on their instincts, feelings, and hunches to make choices. They quickly assess situations based on their past experiences and accumulated knowledge. This style is useful in situations with limited time for analysis.
-
Directive Decision Making: Directive decision makers are action-oriented and focus on efficiency. They prefer to make quick decisions with minimal information and follow established rules and procedures. This style works well in situations that require immediate action.
-
Analytical Decision Making: Analytical decision makers thoroughly analyze information, considering all available data and options. They are detail-oriented and tend to avoid risks. They often seek out more information even when it might not be necessary.
-
Conceptual Decision Making: Conceptual decision makers are creative and value innovative solutions. They consider abstract concepts, possibilities, and long-term consequences. They are willing to take calculated risks to achieve innovative outcomes.
-
Behavioral Decision Making: Behavioral decision makers prioritize collaboration and people's concerns. They focus on building consensus and fostering a positive working environment. They consider how decisions will impact individuals and group dynamics.
-
Autocratic Decision Making: In this style, decisions are made by a single individual or a small group at the top of the hierarchy. This approach is efficient but may not always consider input from others.
-
Consultative Decision Making: Decision makers seek input and suggestions from relevant stakeholders before making a choice. This style promotes engagement and may lead to better-informed decisions.
-
Participative Decision Making: Participative decision makers involve a broader group of stakeholders in the decision-making process. This style encourages collaboration, diversity of perspectives, and shared ownership of outcomes.
-
Delegative Decision Making: In this style, decision makers delegate the decision-making authority to others, often subordinates. It empowers individuals to make choices within their areas of expertise.
-
Group Decision Making: Group decision making involves a team or committee working together to arrive at a consensus. This style can result in more comprehensive solutions but may take longer due to discussions and negotiations.
It's important to note that individuals may use a combination of these styles depending on the situation, their role, and their personality. Effective decision makers are adaptable and capable of using different styles when appropriate. The choice of style should also consider the organization's culture, goals, and the complexity of the decision at hand.
Techniques of Decision Making
There are several techniques and tools that individuals and groups can use to facilitate the decision-making process. These techniques help structure thinking, analyze options, and make more informed choices. Here are some common techniques:
-
SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats): SWOT analysis helps assess the internal strengths and weaknesses of an organization along with external opportunities and threats. It provides a holistic view of the situation and aids in identifying strategic options.
-
Cost-Benefit Analysis: This technique involves evaluating the costs associated with each option against the potential benefits or gains. It helps quantify and compare the pros and cons of different alternatives.
-
Decision Trees: Decision trees visually represent choices and their potential outcomes in a branching format. This tool is particularly useful for analyzing complex decisions with multiple possible pathways and associated probabilities.
-
Pareto Analysis: Also known as the 80/20 rule, Pareto analysis focuses on identifying and prioritizing the most significant factors or issues contributing to a problem. It helps allocate resources effectively by addressing the most critical issues first.
-
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA): MCDA involves evaluating options against multiple criteria or factors. Weighted scores are assigned to each criterion, and the option with the highest overall score is selected. This technique helps account for the relative importance of different factors.
-
Force Field Analysis: This technique assesses the driving forces that support a decision and the restraining forces that oppose it. By analyzing these forces, decision makers can identify potential obstacles and ways to overcome them.
-
Scenario Planning: Scenario planning involves creating multiple possible future scenarios based on different assumptions. Decision makers can then assess the potential impacts of their choices under various circumstances.
-
Brainstorming: Brainstorming encourages creative thinking by generating a wide range of ideas without judgment. This technique is particularly useful for generating innovative solutions and alternatives.
-
Nominal Group Technique: This structured group technique allows participants to generate ideas individually, then share and discuss them as a group. It ensures that everyone's input is considered without the influence of dominant personalities.
-
Delphi Method: The Delphi method involves obtaining input from a panel of experts anonymously. The responses are compiled and shared with the group, and further iterations occur until a consensus is reached.
-
Six Thinking Hats: Developed by Edward de Bono, this technique assigns different "hats" to participants, representing different perspectives (e.g., logical, emotional, creative). It encourages well-rounded thinking and minimizes biases.
-
Pros and Cons Lists: A simple technique involving listing the advantages (pros) and disadvantages (cons) of each option. This helps decision makers visually compare the benefits and drawbacks of each choice.
-
Critical Path Analysis: Often used in project management, critical path analysis identifies the sequence of tasks and dependencies necessary to complete a project. It helps identify the most time-critical tasks and potential bottlenecks.
-
Decision Support Systems (DSS): DSS are computer-based tools that assist decision makers by providing data analysis, simulation, and modeling capabilities. They help structure complex decisions and provide data-driven insights.
The choice of technique depends on the complexity of the decision, the available resources, and the preferences of the decision makers. Some decisions may require a combination of techniques to thoroughly analyze the options and their potential outcomes.
Types of Decision Making in Management
In management, decision making can be categorized into various types based on different criteria, such as the level of impact, the level of structure, and the frequency of occurrence. Here are some common types of decision making in management:
-
Programmed Decisions: These are routine, repetitive decisions that follow established rules, procedures, or guidelines. They are typically made in response to well-defined and recurring situations. For example, approving employee vacation requests or reordering office supplies.
-
Non-Programmed Decisions: Non-programmed decisions are unique and require a more individualized approach. They are often made in response to complex and novel situations that lack predetermined solutions. Strategic decisions, mergers and acquisitions, and crisis management are examples of non-programmed decisions.
-
Strategic Decisions: Strategic decisions are high-level choices that have a long-term impact on the organization. They involve setting the organization's direction, goals, and strategies. Examples include entering new markets, developing new products, and making major investments.
-
Tactical Decisions: Tactical decisions are medium-term choices that focus on implementing the strategies defined in strategic decisions. They involve resource allocation, coordination of activities, and adjusting tactics based on changing circumstances. Budget allocation, workforce planning, and supply chain management are tactical decisions.
-
Operational Decisions: Operational decisions are short-term choices made at the operational level of an organization. They involve day-to-day activities, processes, and tasks. Scheduling shifts, managing inventory, and resolving customer complaints are examples of operational decisions.
-
Individual Decisions: Individual decisions are made by a single person within the organization. These decisions might involve personal tasks, individual responsibilities, or small-scale matters.
-
Group Decisions: Group decisions involve a team or committee working together to arrive at a consensus. Group decisions can leverage diverse perspectives and lead to more comprehensive solutions, but they can also take longer due to discussions and negotiations.
-
Routine Decisions: Routine decisions are those that are made frequently and have become part of the regular workflow. They are usually low in significance and can be automated or handled with minimal analysis.
-
Policy Decisions: Policy decisions establish guidelines or principles that guide future decisions and actions within an organization. They help maintain consistency and alignment with organizational goals.
-
Procedural Decisions: Procedural decisions involve choosing a specific method or process for accomplishing a task or achieving an objective. They provide a structured approach to tasks and operations.
-
Crisis Decisions: Crisis decisions are made in response to unexpected and urgent situations that require immediate action. Crisis management involves making decisions under pressure to minimize damage and restore normalcy.
-
Rational Decisions: Rational decisions are based on careful analysis, logic, and a systematic evaluation of alternatives. They aim to maximize benefits and achieve objectives with the available information.
-
Intuitive Decisions: Intuitive decisions rely on instinct, feelings, and personal experiences. These decisions are made quickly and might not involve extensive analysis.
-
Ethical Decisions: Ethical decisions involve assessing the moral implications of choices. Decision makers consider the impact on stakeholders and adhere to ethical principles.
-
Operative Decisions: Operative decisions involve selecting the most appropriate method or action to execute tasks efficiently. They are closely related to the day-to-day activities of an organization.
It's important to recognize that these types of decision making are not mutually exclusive and can overlap in practice. Managers often need to use a combination of these decision-making approaches based on the nature of the situation, the level of complexity, and the urgency of the decision.
Difficulties in Decision Making Process
The decision-making process can be challenging and complex due to various factors that can create difficulties and obstacles. Some of the common difficulties in decision making include:
-
Limited Information: Insufficient or incomplete information can make it difficult to thoroughly assess alternatives and predict outcomes accurately. Decisions made with inadequate information can lead to undesirable results.
-
Uncertainty: Many decisions are made in environments characterized by uncertainty, where outcomes are unpredictable due to factors such as changing market conditions, technological advancements, and unforeseen events.
-
Complexity: Complex decisions involve multiple variables, interdependencies, and potential consequences. Managing this complexity can be overwhelming and may require in-depth analysis.
-
Conflicting Objectives: Different stakeholders may have conflicting goals and interests, making it challenging to find a solution that satisfies everyone. Balancing competing objectives can be difficult.
-
Risk: All decisions involve some level of risk, and assessing potential risks accurately can be challenging. Making decisions with significant consequences can be daunting due to the fear of making the wrong choice.
-
Cognitive Biases: Cognitive biases are inherent mental shortcuts and patterns that can lead to irrational decision making. Biases such as confirmation bias, anchoring, and overconfidence can cloud judgment.
-
Time Constraints: Some decisions need to be made quickly due to deadlines or changing circumstances. Time constraints may limit the amount of research, analysis, and consultation that can be conducted.
-
Emotional Influences: Emotions can impact decision making by clouding judgment and leading to impulsive choices. Fear, excitement, and personal attachments can affect decision outcomes.
-
Group Dynamics: Group decision making can be challenging due to power dynamics, conflicts, and challenges in reaching consensus. Groupthink, where members prioritize harmony over critical thinking, can also hinder effective decisions.
-
Overanalysis Paralysis: Overanalyzing choices can lead to indecision, as decision makers become overwhelmed by the abundance of information and potential outcomes.
-
Lack of Experience: Inexperienced decision makers may struggle with making choices in unfamiliar situations, as they may not have encountered similar scenarios before.
-
Resistance to Change: Decisions that involve significant changes can face resistance from individuals or groups who are comfortable with the status quo. Overcoming resistance requires effective communication and change management strategies.
-
Ethical Dilemmas: Ethical decisions involve considering moral principles and values. Determining the right course of action in morally complex situations can be challenging.
-
Resource Constraints: Limited resources, such as time, budget, and manpower, can impact the feasibility of implementing certain decisions.
-
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Trade-offs: Balancing short-term gains with long-term benefits can be challenging. Immediate rewards might conflict with more sustainable strategies.
-
External Pressures: Pressure from external sources, such as stakeholders, competitors, or regulatory bodies, can influence decision making and create difficulties.
-
Unforeseen Consequences: Decisions can have unintended consequences that were not anticipated during the decision-making process.
Overcoming these difficulties requires a combination of critical thinking, analytical skills, collaboration, and self-awareness. Effective decision makers acknowledge these challenges and use appropriate techniques, tools, and strategies to mitigate their impact.
Conclusion
The process of decision making in management is a vital and complex aspect that influences the success and direction of organizations. It encompasses a series of steps aimed at identifying problems, evaluating options, and selecting the best course of action. Throughout this journey, various factors come into play, from the information available to the personal preferences of decision makers. Understanding the importance of decision making, the types of decisions, and the techniques involved contributes to effective leadership and organizational growth.
Effective decision making is the cornerstone of successful management. It impacts resource allocation, goal achievement, innovation, and adaptation to changing environments. The ability to make informed and strategic choices is a hallmark of effective leaders who guide their organizations toward sustainable success.
The types of decisions, ranging from routine and programmed choices to strategic and non-programmed ones, highlight the diverse nature of decision making. These decisions span the entire spectrum of organizational activities, from day-to-day operations to long-term planning, and they require tailored approaches and methodologies.
Techniques such as SWOT analysis, cost-benefit analysis, and decision trees provide structured frameworks for evaluating alternatives and making well-informed choices. These techniques empower decision makers to navigate the complexities of decision making and minimize the impact of cognitive biases and uncertainties.
However, decision making is not without challenges. Limited information, cognitive biases, time constraints, and conflicting objectives are among the difficulties decision makers encounter. Overcoming these challenges demands a blend of analytical thinking, effective communication, collaboration, and adaptability.
In the ever-evolving landscape of management, refining decision-making skills is an ongoing journey. Continuous improvement, learning from both successes and failures, and staying attuned to ethical considerations contribute to honing these skills.
In essence, decision making is the compass that guides organizations through the maze of possibilities. It's the art of translating information into action, transforming uncertainties into opportunities, and steering the course toward a prosperous future. By embracing the principles of effective decision making, management can chart a path toward sustainable growth, innovation, and success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs )
1. Why is decision making important in management? Effective decision making is crucial for achieving organizational goals, allocating resources, adapting to change, and maintaining a competitive edge. It shapes the direction and success of the organization.
2. What are the types of decisions made in management? Decision making in management involves various types, including strategic, tactical, operational, programmed, non-programmed, individual, group, ethical, and more. The type of decision depends on factors like scope and impact.
3. What are the steps in the decision-making process? The decision-making process typically includes identifying the problem or opportunity, gathering information, generating alternative solutions, evaluating options, making a decision, implementing the plan, monitoring outcomes, and making adjustments based on feedback.
4. What are some challenges in the decision-making process? Common challenges include limited information, uncertainty, cognitive biases, time constraints, conflicting objectives, and the complexity of choices. These challenges can impact the quality of decisions.
5. How can cognitive biases affect decision making? Cognitive biases are mental shortcuts that can lead to irrational decision making. They include confirmation bias, overconfidence, and anchoring, among others. Being aware of these biases is essential for making objective decisions.
6. What techniques can be used to facilitate decision making? Techniques like SWOT analysis, cost-benefit analysis, decision trees, brainstorming, and scenario planning can help structure thinking, analyze options, and make informed choices.
7. How do individuals balance short-term and long-term considerations in decision making? Balancing short-term gains with long-term benefits requires considering the potential consequences of decisions over time. This involves evaluating immediate rewards against sustainable strategies.
8. What is the role of ethical considerations in decision making? Ethical considerations guide decision making to ensure choices align with moral values, legal obligations, and social responsibility. Ethical decisions take into account the impact on stakeholders and society.
9. Can technology assist in decision making? Yes, technology like Decision Support Systems (DSS) can provide data analysis, simulation, and modeling capabilities. These tools aid decision makers in structuring complex decisions and deriving insights from data.
10. How does group decision making differ from individual decision making? Group decision making involves collaboration, diverse perspectives, and potential consensus. Individual decision making relies on the judgment of a single person. Group decisions can be more comprehensive but might take longer due to discussions.
Read More
In the dynamic realm of modern business, decision making stands as a cornerstone of effective management. Every organization, regardless of its size or industry, encounters a multitude of choices that shape its trajectory, influence its success, and define its identity. From strategic crossroads to day-to-day operations, the decisions made by managers play a pivotal role in steering the organization toward its goals. The intricate interplay of factors, ranging from limited resources and uncertain environments to diverse stakeholder interests, underscores the complexity of decision making in management.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the multifaceted world of decision making within the management sphere. We delve into the significance of decision making, understanding the varied types that managers encounter, and dissecting the step-by-step process that underpins sound choices. We'll navigate through the intricate tapestry of methodologies and techniques that managers employ to address challenges, seize opportunities, and chart the course for their organizations. Through an exploration of the interplay between strategic, tactical, operational, and ethical considerations, this discussion sheds light on the art and science of effective decision making in the realm of management.
In this article
-
What is Decision Making in Management?
-
Characteristics of Decision Making
-
What is Decision Making Process?
-
Decision Making Process in Management with Example
-
Decision Making Styles
-
Techniques of Decision Making
-
Types of Decision Making in Management
-
Difficulties in Decision Making Process
-
Conclusion
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs )
What is Decision Making in Management?
Decision making in management refers to the process of selecting the best course of action from available alternatives to achieve organizational goals and objectives. It is a crucial aspect of managerial and leadership roles as it involves evaluating various choices and choosing the one that aligns most effectively with the organization's strategic direction and desired outcomes.
In essence, decision making in management involves assessing complex situations, considering various factors and constraints, and then arriving at a choice that optimally utilizes resources while minimizing risks and uncertainties. This process is not limited to high-level executives; decision making occurs at all levels of an organization, from top management to front-line supervisors.
Effective decision making is essential for the successful functioning of an organization as it impacts:
-
Resource Allocation: Decisions determine how resources such as finances, personnel, and time are allocated to different activities or projects.
-
Goal Achievement: Decisions contribute to achieving short-term and long-term goals set by the organization.
-
Problem Solving: Decision making is crucial for identifying and resolving challenges or problems that arise in the course of operations.
-
Innovation: Decisions can lead to innovative approaches and the adoption of new technologies, processes, or strategies.
-
Competitive Advantage: Strategic decisions can provide an organization with a competitive edge in the marketplace.
-
Adaptation to Change: Effective decision making allows an organization to respond to changes in the business environment promptly.
-
Stakeholder Satisfaction: Decisions that consider the interests of stakeholders such as employees, customers, and investors can lead to greater satisfaction.
-
Risk Management: Decisions involve assessing and managing risks associated with different choices.
-
Organizational Culture: The decision-making process can shape the culture and values of an organization.
-
Long-Term Viability: Sound decisions contribute to the organization's sustainability and growth over time.
In summary, decision making in management involves a systematic approach to evaluating alternatives, considering various factors, and selecting the most appropriate option to achieve organizational objectives. It requires a combination of analytical thinking, critical judgment, creativity, and an understanding of both internal and external factors affecting the organization.
Characteristics of Decision Making
Decision making is a complex process that involves a variety of characteristics and considerations. Here are some key characteristics of decision making:
-
Rationality: Rational decision making involves evaluating options based on objective information, logical analysis, and a systematic approach. It aims to select the option that maximizes benefits or achieves goals.
-
Objective: Decisions should be based on facts, data, and information rather than personal biases or emotions. Objectivity ensures that decisions are grounded in reality and have a higher likelihood of success.
-
Subjectivity: While objectivity is important, some decisions may involve subjective elements, especially when dealing with uncertain or ambiguous situations. Balancing objectivity and subjectivity is essential.
-
Trade-offs: Decisions often require weighing the pros and cons of different options. Trade-offs involve giving up certain benefits to gain others and are inherent in decision making.
-
Uncertainty: Many decisions are made in environments with incomplete or uncertain information. Decision makers must assess risks and potential outcomes even when information is lacking.
-
Risk: Every decision carries some level of risk. Decision makers must evaluate the potential consequences of each option and choose one that aligns with their risk tolerance and organizational goals.
-
Time Constraints: Decisions are often made within specific timeframes. The urgency of a decision can influence the depth of analysis and the available options.
-
Information Overload: In today's information-rich world, decision makers may face an overwhelming amount of data. The challenge is to sift through the information to identify relevant and actionable insights.
-
Group Dynamics: Group decisions involve collaboration and negotiation among team members. Group dynamics, including communication, power dynamics, and consensus-building, play a significant role.
-
Ethical Considerations: Ethical principles guide decision making, ensuring that choices are aligned with moral values, social responsibility, and legal obligations.
-
Cognitive Biases: Decision makers are subject to cognitive biases—systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality— that can influence their judgment and lead to suboptimal decisions.
-
Intuition: Intuitive decision making involves relying on gut feelings and instincts. While it can be useful in certain situations, it also carries the risk of bias and error.
-
Involvement of Emotions: Emotions can impact decision making by influencing perceptions, preferences, and risk assessment. Being aware of emotional influences is crucial for making sound decisions.
-
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Orientation: Some decisions focus on immediate gains, while others prioritize long-term benefits. Balancing short-term needs with long-term strategic goals is important.
-
Feedback Loop: Effective decision making involves evaluating the outcomes of previous decisions and using this feedback to improve future decisions. This iterative process contributes to organizational learning.
-
Communication: Clear and effective communication of decisions is vital for implementation and alignment within the organization. Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings and resistance.
-
Stakeholder Consideration: Decision makers must take into account the interests and concerns of various stakeholders, including employees, customers, investors, and the community.
Understanding these characteristics can help decision makers navigate the complexities of the decision-making process and make more informed and effective choices.
What is Decision Making Process?
The decision-making process is a systematic sequence of steps that individuals or groups follow to identify a problem or opportunity, gather relevant information, evaluate alternative courses of action, and ultimately choose the best option to address the situation. While there are various models of the decision-making process, a commonly used framework involves the following steps:
-
Identifying the Problem or Opportunity:
-
Recognize the need for a decision, which could arise from a problem that needs solving or an opportunity that can be seized.
-
Clearly define the issue at hand to ensure a focused decision-making process.
-
-
Gathering Information:
-
Collect relevant data, facts, and information related to the problem or opportunity.
-
This step involves researching, consulting experts, analyzing historical data, and understanding the context.
-
-
Generating Alternative Solutions:
-
Brainstorm and develop a range of possible solutions or courses of action to address the identified problem or opportunity.
-
Encourage creativity and consider different perspectives during this stage.
-
-
Evaluating Alternatives:
-
Assess the pros and cons of each alternative solution against predetermined criteria and objectives.
-
Consider the potential outcomes, risks, costs, benefits, and feasibility of each option.
-
-
Making a Decision:
-
Based on the evaluation, select the most suitable solution that aligns with the organization's goals and objectives.
-
The decision might involve a single choice or a combination of options.
-
-
Implementing the Decision:
-
Develop an action plan that outlines the steps required to put the chosen solution into effect.
-
Allocate resources, assign responsibilities, and set timelines for implementation.
-
-
Monitoring and Evaluation:
-
Track the implementation progress to ensure that the decision is being executed as planned.
-
Continuously monitor outcomes and compare them to the expected results.
-
-
Feedback and Adjustments:
-
Based on the monitoring and evaluation, gather feedback about the outcomes and effectiveness of the decision.
-
If necessary, make adjustments to the implementation strategy to achieve desired results.
-
It's important to note that decision making is not always a linear process, and there may be iterations, adjustments, and revisions at various stages. Additionally, the complexity of the process can vary based on factors such as the nature of the decision, the level of uncertainty, and the involvement of multiple stakeholders.
Different decision-making models, such as the rational model, the bounded rationality model, and the incremental model, offer alternative perspectives on how decisions are made. Organizations may adapt and customize these models to suit their specific needs and circumstances.
Successful decision making requires a combination of analytical thinking, critical judgment, effective communication, and consideration of ethical and moral implications. Additionally, learning from both successes and failures contributes to the refinement of decision-making skills over time.
Decision Making Process in Management with Example
let's walk through the decision-making process in management using a hypothetical example:
Scenario: Imagine you are a manager in a retail company that sells electronics. The company is considering whether to introduce a new line of smart home devices to its product offerings. You've been tasked with leading the decision-making process.
1. Identifying the Problem or Opportunity: You recognize the opportunity to expand the company's product range and potentially increase revenue by introducing smart home devices. However, you also need to consider the potential risks and challenges associated with entering a new market segment.
2. Gathering Information: You gather data on the current market trends for smart home devices, including consumer demand, competition, pricing, and potential suppliers. You also collect information on the company's capabilities, resources, and potential challenges in entering this market.
3. Generating Alternative Solutions: You brainstorm several options:
-
Option A: Introduce a limited range of popular smart home devices initially.
-
Option B: Collaborate with a well-known technology brand to co-brand the smart home devices.
-
Option C: Conduct a market research study to gather more data before making a decision.
4. Evaluating Alternatives:
-
Option A: You consider the potential demand for these devices and assess whether the company's current resources can handle the new product line. You weigh the potential benefits of immediate entry into the market against the risk of not offering a comprehensive range.
-
Option B: You evaluate the potential benefits of leveraging an established brand's reputation. You also assess the possible challenges of negotiations, branding alignment, and resource allocation.
-
Option C: You analyze the costs and benefits of conducting market research, including time, resources, and potential delay in market entry.
5. Making a Decision: After careful evaluation, you decide to proceed with Option A: Introduce a limited range of popular smart home devices. This decision aligns with the company's growth goals while minimizing the risk of overextending resources.
6. Implementing the Decision: You develop an implementation plan that outlines the product selection process, supplier negotiations, marketing strategies, and distribution channels. You allocate a dedicated team to handle this project.
7. Monitoring and Evaluation: As the smart home devices are introduced to the market, you monitor sales data, customer feedback, and any unexpected challenges that arise. You regularly communicate with your team to ensure that the plan is being executed as intended.
8. Feedback and Adjustments: After a few months, you gather feedback from customers and review sales performance. You identify that certain devices are particularly popular, while others are underperforming. Based on this feedback, you decide to expand the range of popular devices and discontinue the underperforming ones.
In this example, the decision-making process involved identifying an opportunity, gathering relevant information, generating alternative solutions, evaluating those alternatives, making a decision, implementing the plan, monitoring outcomes, and making adjustments based on feedback. This process enables the company to enter a new market segment strategically and adapt its approach based on real-world results.
Decision Making Styles
Decision-making styles refer to the different approaches individuals or groups use when making choices. These styles are influenced by personal preferences, cognitive processes, and situational factors. Here are some common decision-making styles:
-
Rational Decision Making: This style involves a systematic, logical, and analytical approach. Decision makers gather relevant information, weigh pros and cons, and choose the option that maximizes benefits and aligns with objectives. It's often used in structured and well-defined situations.
-
Intuitive Decision Making: Intuitive decision makers rely on their instincts, feelings, and hunches to make choices. They quickly assess situations based on their past experiences and accumulated knowledge. This style is useful in situations with limited time for analysis.
-
Directive Decision Making: Directive decision makers are action-oriented and focus on efficiency. They prefer to make quick decisions with minimal information and follow established rules and procedures. This style works well in situations that require immediate action.
-
Analytical Decision Making: Analytical decision makers thoroughly analyze information, considering all available data and options. They are detail-oriented and tend to avoid risks. They often seek out more information even when it might not be necessary.
-
Conceptual Decision Making: Conceptual decision makers are creative and value innovative solutions. They consider abstract concepts, possibilities, and long-term consequences. They are willing to take calculated risks to achieve innovative outcomes.
-
Behavioral Decision Making: Behavioral decision makers prioritize collaboration and people's concerns. They focus on building consensus and fostering a positive working environment. They consider how decisions will impact individuals and group dynamics.
-
Autocratic Decision Making: In this style, decisions are made by a single individual or a small group at the top of the hierarchy. This approach is efficient but may not always consider input from others.
-
Consultative Decision Making: Decision makers seek input and suggestions from relevant stakeholders before making a choice. This style promotes engagement and may lead to better-informed decisions.
-
Participative Decision Making: Participative decision makers involve a broader group of stakeholders in the decision-making process. This style encourages collaboration, diversity of perspectives, and shared ownership of outcomes.
-
Delegative Decision Making: In this style, decision makers delegate the decision-making authority to others, often subordinates. It empowers individuals to make choices within their areas of expertise.
-
Group Decision Making: Group decision making involves a team or committee working together to arrive at a consensus. This style can result in more comprehensive solutions but may take longer due to discussions and negotiations.
It's important to note that individuals may use a combination of these styles depending on the situation, their role, and their personality. Effective decision makers are adaptable and capable of using different styles when appropriate. The choice of style should also consider the organization's culture, goals, and the complexity of the decision at hand.
Techniques of Decision Making
There are several techniques and tools that individuals and groups can use to facilitate the decision-making process. These techniques help structure thinking, analyze options, and make more informed choices. Here are some common techniques:
-
SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats): SWOT analysis helps assess the internal strengths and weaknesses of an organization along with external opportunities and threats. It provides a holistic view of the situation and aids in identifying strategic options.
-
Cost-Benefit Analysis: This technique involves evaluating the costs associated with each option against the potential benefits or gains. It helps quantify and compare the pros and cons of different alternatives.
-
Decision Trees: Decision trees visually represent choices and their potential outcomes in a branching format. This tool is particularly useful for analyzing complex decisions with multiple possible pathways and associated probabilities.
-
Pareto Analysis: Also known as the 80/20 rule, Pareto analysis focuses on identifying and prioritizing the most significant factors or issues contributing to a problem. It helps allocate resources effectively by addressing the most critical issues first.
-
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA): MCDA involves evaluating options against multiple criteria or factors. Weighted scores are assigned to each criterion, and the option with the highest overall score is selected. This technique helps account for the relative importance of different factors.
-
Force Field Analysis: This technique assesses the driving forces that support a decision and the restraining forces that oppose it. By analyzing these forces, decision makers can identify potential obstacles and ways to overcome them.
-
Scenario Planning: Scenario planning involves creating multiple possible future scenarios based on different assumptions. Decision makers can then assess the potential impacts of their choices under various circumstances.
-
Brainstorming: Brainstorming encourages creative thinking by generating a wide range of ideas without judgment. This technique is particularly useful for generating innovative solutions and alternatives.
-
Nominal Group Technique: This structured group technique allows participants to generate ideas individually, then share and discuss them as a group. It ensures that everyone's input is considered without the influence of dominant personalities.
-
Delphi Method: The Delphi method involves obtaining input from a panel of experts anonymously. The responses are compiled and shared with the group, and further iterations occur until a consensus is reached.
-
Six Thinking Hats: Developed by Edward de Bono, this technique assigns different "hats" to participants, representing different perspectives (e.g., logical, emotional, creative). It encourages well-rounded thinking and minimizes biases.
-
Pros and Cons Lists: A simple technique involving listing the advantages (pros) and disadvantages (cons) of each option. This helps decision makers visually compare the benefits and drawbacks of each choice.
-
Critical Path Analysis: Often used in project management, critical path analysis identifies the sequence of tasks and dependencies necessary to complete a project. It helps identify the most time-critical tasks and potential bottlenecks.
-
Decision Support Systems (DSS): DSS are computer-based tools that assist decision makers by providing data analysis, simulation, and modeling capabilities. They help structure complex decisions and provide data-driven insights.
The choice of technique depends on the complexity of the decision, the available resources, and the preferences of the decision makers. Some decisions may require a combination of techniques to thoroughly analyze the options and their potential outcomes.
Types of Decision Making in Management
In management, decision making can be categorized into various types based on different criteria, such as the level of impact, the level of structure, and the frequency of occurrence. Here are some common types of decision making in management:
-
Programmed Decisions: These are routine, repetitive decisions that follow established rules, procedures, or guidelines. They are typically made in response to well-defined and recurring situations. For example, approving employee vacation requests or reordering office supplies.
-
Non-Programmed Decisions: Non-programmed decisions are unique and require a more individualized approach. They are often made in response to complex and novel situations that lack predetermined solutions. Strategic decisions, mergers and acquisitions, and crisis management are examples of non-programmed decisions.
-
Strategic Decisions: Strategic decisions are high-level choices that have a long-term impact on the organization. They involve setting the organization's direction, goals, and strategies. Examples include entering new markets, developing new products, and making major investments.
-
Tactical Decisions: Tactical decisions are medium-term choices that focus on implementing the strategies defined in strategic decisions. They involve resource allocation, coordination of activities, and adjusting tactics based on changing circumstances. Budget allocation, workforce planning, and supply chain management are tactical decisions.
-
Operational Decisions: Operational decisions are short-term choices made at the operational level of an organization. They involve day-to-day activities, processes, and tasks. Scheduling shifts, managing inventory, and resolving customer complaints are examples of operational decisions.
-
Individual Decisions: Individual decisions are made by a single person within the organization. These decisions might involve personal tasks, individual responsibilities, or small-scale matters.
-
Group Decisions: Group decisions involve a team or committee working together to arrive at a consensus. Group decisions can leverage diverse perspectives and lead to more comprehensive solutions, but they can also take longer due to discussions and negotiations.
-
Routine Decisions: Routine decisions are those that are made frequently and have become part of the regular workflow. They are usually low in significance and can be automated or handled with minimal analysis.
-
Policy Decisions: Policy decisions establish guidelines or principles that guide future decisions and actions within an organization. They help maintain consistency and alignment with organizational goals.
-
Procedural Decisions: Procedural decisions involve choosing a specific method or process for accomplishing a task or achieving an objective. They provide a structured approach to tasks and operations.
-
Crisis Decisions: Crisis decisions are made in response to unexpected and urgent situations that require immediate action. Crisis management involves making decisions under pressure to minimize damage and restore normalcy.
-
Rational Decisions: Rational decisions are based on careful analysis, logic, and a systematic evaluation of alternatives. They aim to maximize benefits and achieve objectives with the available information.
-
Intuitive Decisions: Intuitive decisions rely on instinct, feelings, and personal experiences. These decisions are made quickly and might not involve extensive analysis.
-
Ethical Decisions: Ethical decisions involve assessing the moral implications of choices. Decision makers consider the impact on stakeholders and adhere to ethical principles.
-
Operative Decisions: Operative decisions involve selecting the most appropriate method or action to execute tasks efficiently. They are closely related to the day-to-day activities of an organization.
It's important to recognize that these types of decision making are not mutually exclusive and can overlap in practice. Managers often need to use a combination of these decision-making approaches based on the nature of the situation, the level of complexity, and the urgency of the decision.
Difficulties in Decision Making Process
The decision-making process can be challenging and complex due to various factors that can create difficulties and obstacles. Some of the common difficulties in decision making include:
-
Limited Information: Insufficient or incomplete information can make it difficult to thoroughly assess alternatives and predict outcomes accurately. Decisions made with inadequate information can lead to undesirable results.
-
Uncertainty: Many decisions are made in environments characterized by uncertainty, where outcomes are unpredictable due to factors such as changing market conditions, technological advancements, and unforeseen events.
-
Complexity: Complex decisions involve multiple variables, interdependencies, and potential consequences. Managing this complexity can be overwhelming and may require in-depth analysis.
-
Conflicting Objectives: Different stakeholders may have conflicting goals and interests, making it challenging to find a solution that satisfies everyone. Balancing competing objectives can be difficult.
-
Risk: All decisions involve some level of risk, and assessing potential risks accurately can be challenging. Making decisions with significant consequences can be daunting due to the fear of making the wrong choice.
-
Cognitive Biases: Cognitive biases are inherent mental shortcuts and patterns that can lead to irrational decision making. Biases such as confirmation bias, anchoring, and overconfidence can cloud judgment.
-
Time Constraints: Some decisions need to be made quickly due to deadlines or changing circumstances. Time constraints may limit the amount of research, analysis, and consultation that can be conducted.
-
Emotional Influences: Emotions can impact decision making by clouding judgment and leading to impulsive choices. Fear, excitement, and personal attachments can affect decision outcomes.
-
Group Dynamics: Group decision making can be challenging due to power dynamics, conflicts, and challenges in reaching consensus. Groupthink, where members prioritize harmony over critical thinking, can also hinder effective decisions.
-
Overanalysis Paralysis: Overanalyzing choices can lead to indecision, as decision makers become overwhelmed by the abundance of information and potential outcomes.
-
Lack of Experience: Inexperienced decision makers may struggle with making choices in unfamiliar situations, as they may not have encountered similar scenarios before.
-
Resistance to Change: Decisions that involve significant changes can face resistance from individuals or groups who are comfortable with the status quo. Overcoming resistance requires effective communication and change management strategies.
-
Ethical Dilemmas: Ethical decisions involve considering moral principles and values. Determining the right course of action in morally complex situations can be challenging.
-
Resource Constraints: Limited resources, such as time, budget, and manpower, can impact the feasibility of implementing certain decisions.
-
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Trade-offs: Balancing short-term gains with long-term benefits can be challenging. Immediate rewards might conflict with more sustainable strategies.
-
External Pressures: Pressure from external sources, such as stakeholders, competitors, or regulatory bodies, can influence decision making and create difficulties.
-
Unforeseen Consequences: Decisions can have unintended consequences that were not anticipated during the decision-making process.
Overcoming these difficulties requires a combination of critical thinking, analytical skills, collaboration, and self-awareness. Effective decision makers acknowledge these challenges and use appropriate techniques, tools, and strategies to mitigate their impact.
Conclusion
The process of decision making in management is a vital and complex aspect that influences the success and direction of organizations. It encompasses a series of steps aimed at identifying problems, evaluating options, and selecting the best course of action. Throughout this journey, various factors come into play, from the information available to the personal preferences of decision makers. Understanding the importance of decision making, the types of decisions, and the techniques involved contributes to effective leadership and organizational growth.
Effective decision making is the cornerstone of successful management. It impacts resource allocation, goal achievement, innovation, and adaptation to changing environments. The ability to make informed and strategic choices is a hallmark of effective leaders who guide their organizations toward sustainable success.
The types of decisions, ranging from routine and programmed choices to strategic and non-programmed ones, highlight the diverse nature of decision making. These decisions span the entire spectrum of organizational activities, from day-to-day operations to long-term planning, and they require tailored approaches and methodologies.
Techniques such as SWOT analysis, cost-benefit analysis, and decision trees provide structured frameworks for evaluating alternatives and making well-informed choices. These techniques empower decision makers to navigate the complexities of decision making and minimize the impact of cognitive biases and uncertainties.
However, decision making is not without challenges. Limited information, cognitive biases, time constraints, and conflicting objectives are among the difficulties decision makers encounter. Overcoming these challenges demands a blend of analytical thinking, effective communication, collaboration, and adaptability.
In the ever-evolving landscape of management, refining decision-making skills is an ongoing journey. Continuous improvement, learning from both successes and failures, and staying attuned to ethical considerations contribute to honing these skills.
In essence, decision making is the compass that guides organizations through the maze of possibilities. It's the art of translating information into action, transforming uncertainties into opportunities, and steering the course toward a prosperous future. By embracing the principles of effective decision making, management can chart a path toward sustainable growth, innovation, and success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs )
1. Why is decision making important in management? Effective decision making is crucial for achieving organizational goals, allocating resources, adapting to change, and maintaining a competitive edge. It shapes the direction and success of the organization.
2. What are the types of decisions made in management? Decision making in management involves various types, including strategic, tactical, operational, programmed, non-programmed, individual, group, ethical, and more. The type of decision depends on factors like scope and impact.
3. What are the steps in the decision-making process? The decision-making process typically includes identifying the problem or opportunity, gathering information, generating alternative solutions, evaluating options, making a decision, implementing the plan, monitoring outcomes, and making adjustments based on feedback.
4. What are some challenges in the decision-making process? Common challenges include limited information, uncertainty, cognitive biases, time constraints, conflicting objectives, and the complexity of choices. These challenges can impact the quality of decisions.
5. How can cognitive biases affect decision making? Cognitive biases are mental shortcuts that can lead to irrational decision making. They include confirmation bias, overconfidence, and anchoring, among others. Being aware of these biases is essential for making objective decisions.
6. What techniques can be used to facilitate decision making? Techniques like SWOT analysis, cost-benefit analysis, decision trees, brainstorming, and scenario planning can help structure thinking, analyze options, and make informed choices.
7. How do individuals balance short-term and long-term considerations in decision making? Balancing short-term gains with long-term benefits requires considering the potential consequences of decisions over time. This involves evaluating immediate rewards against sustainable strategies.
8. What is the role of ethical considerations in decision making? Ethical considerations guide decision making to ensure choices align with moral values, legal obligations, and social responsibility. Ethical decisions take into account the impact on stakeholders and society.
9. Can technology assist in decision making? Yes, technology like Decision Support Systems (DSS) can provide data analysis, simulation, and modeling capabilities. These tools aid decision makers in structuring complex decisions and deriving insights from data.
10. How does group decision making differ from individual decision making? Group decision making involves collaboration, diverse perspectives, and potential consensus. Individual decision making relies on the judgment of a single person. Group decisions can be more comprehensive but might take longer due to discussions.
Cisco UCS Admin Certification: Expert Guide for Success.
Cisco UCS (Unified Computing System) is a popular data center solution that offers an innovative architecture for deploying and managing complex computing environments. It is designed to help organizations achieve better scalability, agility, and efficiency in their data center operations. The Cisco UCS Administration Certification is a professional-level certification that validates the expertise of individuals in managing and administering Cisco UCS environments. It demonstrates the ability to deploy, configure, manage, and troubleshoot Cisco UCS solutions. Obtaining this certification can open up numerous career opportunities in the field of data center administration and networking. In this blog, we will dive deep into the various aspects of Cisco UCS Administration Certification, including its importance, exam requirements, benefits, and the knowledge and skills required to earn this certification. We will also discuss some of the subtopics related to Cisco UCS administration, such as UCS Manager and UCS Central, configuring UCS infrastructure, deploying and managing service profiles, backup and disaster recovery, troubleshooting UCS issues, and UCS integration with other technologies.
Table of contents
-
Introduction to Cisco UCS:
-
Benefits of Cisco UCS Certification:
-
Different Cisco UCS Certifications:
-
Prerequisites for Cisco UCS Certification:
-
Exam Details and Topics:
-
Study Resources and Preparation:
-
Career Pathways and Growth:
-
Tips for Exam Success:
-
Continuing Education and Recertification:
-
Conclusion
Introduction to Cisco UCS
Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) is a data center architecture that integrates computing, networking, and storage resources into a single, cohesive system. It is designed to help organizations streamline their data center operations by simplifying infrastructure management, increasing agility, and reducing costs. The UCS architecture is based on a blade server platform that is highly scalable and adaptable, allowing organizations to easily expand their computing resources as needed. The system is managed through a single pane of glass, called the UCS Manager, which provides a unified view of the entire data center infrastructure.
UCS consists of several components, including the Fabric Interconnects, which provide connectivity between the servers, storage, and network, and the UCS Manager, which serves as the centralized management tool for the entire system. The UCS platform also includes service profiles, which are templates that define the configuration of a server, allowing for rapid deployment and consistent management across multiple servers.
One of the key advantages of UCS is its ability to integrate with other Cisco products and technologies, such as Cisco Nexus switches and Cisco ACI (Application Centric Infrastructure), providing a highly customizable and flexible infrastructure for modern data centers. Additionally, UCS offers a range of features and capabilities that enable organizations to achieve high levels of performance, reliability, and security, making it a popular choice for many enterprises around the world.
Benefits of Cisco UCS Certification
Obtaining a Cisco UCS certification comes with several benefits that can positively impact your career and professional growth. Here are some key benefits you can highlight in your blog:
-
Enhanced Career Opportunities: Cisco UCS certifications are recognized globally and are highly respected in the IT industry. Having a certification demonstrates your expertise and commitment to mastering Cisco's data center technologies, making you a valuable asset to potential employers.
-
Increased Earning Potential: Certified professionals often command higher salaries compared to their non-certified counterparts. Cisco UCS certifications validate your skills, giving you leverage when negotiating compensation packages.
-
Industry Recognition: Being certified by Cisco, a prominent leader in networking and IT solutions, adds credibility to your resume. Employers and colleagues will acknowledge your proficiency and knowledge in UCS administration.
-
Job Roles and Specializations: Cisco UCS certifications open doors to various job roles, such as Data Center Administrator, Network Engineer, Systems Engineer, and Cloud Infrastructure Specialist. Depending on the level of certification, you can specialize in different aspects of data center operations.
-
Competitive Advantage: In today's competitive job market, a Cisco UCS certification sets you apart from others. It can be the factor that pushes your resume to the top of the pile and lands you an interview.
-
Skill Validation: Cisco UCS certifications are not easy to obtain. Earning a certification demonstrates your dedication to learning and your ability to master complex technologies, which can boost your confidence in your skills.
-
Networking Opportunities: Pursuing a Cisco UCS certification connects you with a community of like-minded professionals. This network can provide insights, guidance, and potential collaborations in the future.
-
Hands-On Experience: The certification process often involves hands-on lab work and practical exercises. This experience equips you with real-world skills that are directly applicable to your job.
-
Knowledge Enhancement: The certification process encourages in-depth learning about Cisco UCS technologies and data center architecture. This knowledge can be applied not only to certification exams but also to real-world scenarios.
-
Career Progression: Cisco offers a tiered certification structure, allowing you to start with foundational certifications and progress to more advanced levels. This path enables you to continually grow your skills and advance your career.
-
Employer Confidence: Employers are more likely to trust certified professionals to handle critical infrastructure and projects. Having certified UCS administrators can contribute to the stability and efficiency of the organization's data center operations.
-
Global Recognition: Cisco UCS certifications are recognized internationally. This can be especially beneficial if you're considering working in different regions or countries.
-
Continuous Learning: Cisco's technology landscape is always evolving. Maintaining your certification requires staying up-to-date with the latest advancements, encouraging continuous learning throughout your career.
-
Job Satisfaction: Mastering Cisco UCS technologies can be intellectually rewarding. Seeing the impact of your skills on data center operations can provide a sense of accomplishment and job satisfaction.
Different Cisco UCS Certifications
Certainly, Cisco offers a range of Unified Computing System (UCS) certifications tailored to different skill levels and roles. Here's an overview of the different Cisco UCS certifications that you can include in your blog:
-
Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Data Center:
-
This entry-level certification is designed for individuals who are new to data center technologies.
-
It covers foundational topics related to data center networking, virtualization, storage, and Cisco UCS architecture.
-
CCNA Data Center provides a solid understanding of basic data center concepts and prepares candidates for more advanced certifications.
-
Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Data Center:
-
The CCNP Data Center certification is aimed at IT professionals who want to specialize in data center technologies.
-
It consists of a series of exams that cover various aspects of data center design, implementation, and troubleshooting.
-
CCNP Data Center covers advanced topics like implementing Cisco UCS infrastructure, data center automation, and implementing storage networking solutions.
-
Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert (CCIE) Data Center:
-
CCIE Data Center is the expert-level certification for individuals seeking mastery in data center technologies.
-
It requires both written and practical lab exams to demonstrate comprehensive knowledge and hands-on skills.
-
CCIE Data Center covers complex topics such as data center infrastructure design, application-centric infrastructure (ACI), and network services.
-
Cisco Certified Specialist - Data Center Unified Computing:
-
This specialist certification focuses specifically on Cisco UCS technologies.
-
It covers topics such as configuring, deploying, and managing Cisco UCS servers and equipment.
-
The certification validates expertise in UCS architecture, server provisioning, and maintenance.
-
Cisco Certified Specialist - Data Center Unified Computing Design:
-
This specialist certification is aimed at professionals involved in designing Cisco UCS solutions.
-
It covers design considerations for Cisco UCS deployments, including scalability, performance, and high availability.
-
Cisco Certified Specialist - Data Center Unified Computing Implementation:
-
This certification focuses on the implementation and deployment of Cisco UCS solutions.
-
It covers topics such as server installation, initial setup, firmware upgrades, and integration with other data center components.
-
Cisco Certified Specialist - Data Center Unified Computing Support:
-
This certification is tailored for individuals responsible for supporting and troubleshooting Cisco UCS environments.
-
It covers topics related to diagnosing and resolving common issues in UCS deployments.
-
Cisco Certified Specialist - Data Center Unified Fabric:
-
While not exclusively UCS-focused, this certification covers data center fabric technologies that are closely related to UCS deployments.
-
It encompasses topics like Cisco Nexus switches, data center networking, and unified fabric architectures.
Prerequisites for Cisco UCS Certification
Obtaining a Cisco UCS certification requires a certain level of knowledge, experience, and skills. While specific prerequisites can vary depending on the certification level, here are some general prerequisites you might encounter when pursuing a Cisco UCS certification:
-
Basic Networking Knowledge:
-
A foundational understanding of networking concepts, including TCP/IP, subnets, routing, and switching, is often required. This knowledge serves as a basis for understanding data center networking in the context of Cisco UCS.
-
Familiarity with Data Center Concepts:
-
A grasp of basic data center concepts such as virtualization, storage, and server architecture is important. This knowledge will help you understand how Cisco UCS fits into the larger data center environment.
-
Experience with Cisco Technologies:
-
Familiarity with Cisco networking technologies is beneficial. If you're pursuing a higher-level certification, having a Cisco CCNA or CCNP certification (or equivalent knowledge) can provide a strong foundation.
-
Hands-On Experience:
-
Practical experience with data center equipment and technologies, including server hardware, switches, and storage systems, is essential. Many Cisco UCS certifications emphasize hands-on skills.
-
Previous IT Experience:
-
For more advanced certifications, such as CCNP Data Center or CCIE Data Center, having a certain amount of professional IT experience is often recommended. This experience helps contextualize the concepts covered in the certification.
-
Study Resources:
-
While not a formal prerequisite, having access to Cisco's official study materials, practice exams, and recommended reading can greatly assist in exam preparation.
-
Training Courses:
-
Cisco often provides training courses specifically designed to prepare candidates for their certifications. While not always mandatory, these courses can provide in-depth knowledge and hands-on labs.
-
Problem-Solving Skills:
-
Cisco UCS certifications may include scenario-based questions or simulations that test your ability to troubleshoot and solve complex problems. Developing strong analytical and problem-solving skills is crucial.
-
Foundation in Server Administration:
-
Depending on the certification, having a background in server administration can be helpful. This includes knowledge of server operating systems, server hardware components, and server virtualization.
-
Commitment to Learning:
-
Pursuing a Cisco UCS certification requires dedication to learning and staying updated with the latest technologies. Being committed to ongoing education is essential.
Exam Details and Topics
Certainly, understanding the details and topics covered in the Cisco UCS certification exams is essential for effective exam preparation. While the specifics can vary depending on the certification level, here's a general overview of what you might expect in terms of exam details and topics:
-
Exam Format:
-
Most Cisco certification exams are computer-based and consist of a combination of question types, including multiple-choice, drag-and-drop, simulation-based, and scenario-based questions.
-
The number of questions and the time allotted for the exam can vary based on the certification level.
-
Passing Score:
-
Cisco certification exams typically require a passing score of around 800 out of 1000 points. However, passing scores can differ between exams, so it's important to check the specific requirements for the certification you're pursuing.
-
Exam Topics:
-
The topics covered in Cisco UCS certification exams are closely aligned with the skills and knowledge required for effective administration of Cisco UCS solutions. Here are some general categories of exam topics you might encounter:
a. Introduction to Cisco UCS:
-
-
Overview of Cisco UCS components, architecture, and benefits.
-
Understanding service profiles, templates, and pools.
b. Server Deployment and Configuration:
-
-
Installing and configuring Cisco UCS servers.
-
Creating service profiles and templates.
-
Understanding server pools and policies.
c. Networking in Cisco UCS:
-
-
Configuring Ethernet and Fibre Channel connectivity.
-
Implementing VLANs and fabric interconnects.
-
Understanding Cisco UCS networking concepts and features.
d. Storage in Cisco UCS:
-
-
Configuring storage connectivity, including SAN zoning.
-
Implementing storage policies and profiles.
-
Understanding storage concepts and protocols.
e. Cisco UCS Management:
-
-
Using UCS Manager for system management and monitoring.
-
Administering firmware upgrades and backups.
-
Troubleshooting common issues.
f. Automation and Orchestration:
-
-
Implementing automation using UCS Manager XML API.
-
Understanding scripting and programmability in Cisco UCS.
g. Integration with Virtualization:
-
-
Integrating Cisco UCS with virtualization platforms like VMware and Hyper-V.
-
Understanding virtual networking and storage.
h. Security and Access Control:
-
-
Implementing security features such as role-based access control.
-
Configuring authentication and authorization in UCS.
i. High Availability and Redundancy:
-
-
Configuring redundancy and failover in Cisco UCS.
-
Implementing fault tolerance and high availability.
j. Monitoring and Troubleshooting:
-
-
Diagnosing and resolving common issues in Cisco UCS environments.
-
Using logging and monitoring tools for troubleshooting.
Remember that the above topics are general guidelines and can vary based on the specific Cisco UCS certification you're pursuing. It's crucial to review the official exam blueprint provided by Cisco for each certification to get a detailed breakdown of the topics and subtopics that will be covered in the exam. This will help you focus your study efforts effectively and ensure that you're well-prepared for success on exam day.
Study Resources and Preparation
Preparing for a Cisco UCS certification requires effective study strategies and the right resources. Here's a guide to help you plan your study approach and identify useful study resources:
-
Official Cisco Study Materials:
-
Cisco's official certification website is a valuable resource. It provides exam blueprints, official study guides, and sample questions for each certification.
-
Review the official certification exam topics and objectives to ensure your study materials align with the content.
-
Cisco Learning Network:
-
The Cisco Learning Network is an online community where you can connect with other candidates, ask questions, and access study materials, including videos, discussions, and blogs.
-
Training Courses:
-
Cisco offers instructor-led training courses that cover the exam topics in-depth. These courses include hands-on labs and insights from experienced instructors.
-
Check Cisco's official training portal for available courses related to your certification.
-
Books and Ebooks:
-
There are many books and ebooks available that focus on Cisco UCS technologies and certification exam preparation. Look for reputable authors and publications.
-
Practice Exams:
-
Practice exams are crucial for assessing your knowledge and identifying areas where you need further study.
-
Cisco provides official practice exams, and you can also find third-party practice exam providers.
-
Hands-On Labs:
-
Hands-on experience is essential for mastering Cisco UCS technologies. If possible, set up a lab environment to practice configuring, managing, and troubleshooting UCS components.
-
Online Forums and Communities:
-
Online forums like Reddit, Stack Exchange, and Cisco support communities can provide valuable insights, tips, and answers to your questions.
-
Video Courses and Tutorials:
-
iCert Global and YouTube host video courses and tutorials that cover Cisco UCS concepts and exam preparation.
-
Flashcards and Note-Taking:
-
Create flashcards to review key concepts and definitions. Summarize your notes as you study to reinforce your understanding.
-
Time Management:
-
Create a study schedule that allocates time for each exam topic. Consistent, focused study sessions are more effective than cramming.
-
Practice Time Management:
-
Cisco exams often have time constraints. When taking practice exams, practice managing your time effectively to complete all questions within the allotted time.
-
Hands-On Practice:
-
Whenever possible, apply theoretical knowledge in a hands-on lab environment. This reinforces your understanding and helps you become comfortable with actual configurations.
-
Review and Revision:
-
Regularly review your notes, practice exams, and study resources to reinforce your memory and understanding of key concepts.
-
Stay Updated:
-
Stay current with any updates or changes to the exam objectives or topics by checking Cisco's official certification website.
Career Pathways and Growth
Earning a Cisco UCS Administration certification can lead to exciting career opportunities and growth within the IT and data center fields. Here are some potential career pathways and growth opportunities for individuals who hold Cisco UCS certifications:
-
Data Center Administrator:
-
Cisco UCS certifications provide a strong foundation for working as a data center administrator. You'll be responsible for managing and maintaining data center infrastructure, including servers, networking, and storage.
-
Network Engineer:
-
With a focus on Cisco UCS networking components, you can pursue roles as a network engineer, where you design, implement, and manage data center networks.
-
Systems Engineer:
-
Systems engineers leverage their Cisco UCS skills to design and deploy integrated data center solutions, ensuring seamless operations between servers, storage, and networking components.
-
Cloud Infrastructure Specialist:
-
As cloud computing continues to grow, having expertise in Cisco UCS can be valuable for roles involving cloud infrastructure design and management.
-
Virtualization Specialist:
-
Cisco UCS certifications align well with virtualization technologies. You can specialize in managing virtual environments, working with platforms like VMware or Hyper-V.
-
Data Center Architect:
-
With advanced Cisco UCS certifications, you can transition into data center architecture roles, designing complex, scalable, and efficient data center solutions.
-
IT Consultant:
-
Cisco UCS certifications are highly respected by clients seeking IT consulting services for their data center needs. Consultants provide expert advice and solutions.
-
IT Manager or Director:
-
As you accumulate experience and expertise, you can move into management roles overseeing data center operations, infrastructure, and teams.
-
Specialization in Hybrid Cloud:
-
With the integration of on-premises data centers and cloud solutions, professionals with Cisco UCS skills can specialize in hybrid cloud architecture and management.
-
Security Analyst:
-
Cisco UCS certifications can complement a career in security by providing insights into securing data center infrastructure and protecting critical assets.
-
Training and Education:
-
As a certified UCS administrator, you can share your knowledge by becoming an instructor, developing training materials, or delivering workshops.
-
Vendor Solutions Engineer:
-
Cisco UCS expertise is valuable to technology vendors. You could work as a pre-sales engineer, demonstrating how your vendor's solutions integrate with Cisco UCS environments.
-
Career Progression:
-
Cisco offers a tiered certification structure, allowing you to advance from associate to professional to expert levels. This progression demonstrates continuous growth and expertise.
-
Entrepreneurship:
-
Armed with in-depth knowledge of Cisco UCS, you might explore entrepreneurial opportunities, such as starting a consulting firm or offering specialized services to businesses.
Tips for Exam Success
Preparing for and taking a Cisco UCS certification exam requires a focused and strategic approach. Here are some valuable tips to help you achieve success on your exam day:
-
Understand Exam Objectives:
-
Familiarize yourself with the official exam blueprint or objectives provided by Cisco. This will guide your study plan and ensure you cover all required topics.
-
Create a Study Plan:
-
Develop a structured study plan that allocates sufficient time to each exam topic. Consistency is key to effective learning.
-
Use Official Study Materials:
-
Rely on Cisco's official study guides, practice exams, and resources. These materials are aligned with the exam content and provide accurate information.
-
Practice Regularly:
-
Regular practice with practice exams and hands-on labs helps reinforce your knowledge and build confidence.
-
Focus on Hands-On Experience:
-
Cisco exams often test practical skills. Spend ample time working in a lab environment to gain hands-on experience with Cisco UCS technologies.
-
Time Management Practice:
-
During practice exams, practice time management to ensure you can complete all questions within the allotted time.
-
Review and Revise:
-
Regularly review your study materials and notes to reinforce your understanding of key concepts.
-
Use Multiple Resources:
-
Supplement official materials with other resources like books, online tutorials, and videos to gain a well-rounded understanding.
-
Join Study Groups:
-
Engage with study groups or online forums to discuss concepts, share insights, and ask questions.
-
Simulate Exam Conditions:
-
When taking practice exams, simulate exam conditions by minimizing distractions and adhering to time limits.
-
Identify Weak Areas:
-
Use practice exams to identify areas where you need more focus. Spend extra time studying topics that challenge you.
-
Stay Calm and Confident:
-
On the exam day, remain calm and confident in your preparation. Positive thinking can have a significant impact on your performance.
-
Read Questions Carefully:
-
Take your time to read each question carefully and fully understand what is being asked before selecting an answer.
-
Eliminate Wrong Answers:
-
If you're unsure about an answer, eliminate obviously incorrect options to improve your chances of selecting the correct one.
-
Flag and Manage:
-
If allowed, flag questions you're unsure about and return to them later. Prioritize questions you're more confident about.
-
Answer All Questions:
-
Never leave questions unanswered. Even if you're unsure, make an educated guess.
-
Check Before Submitting:
-
If time allows, review your answers before submitting the exam to catch any errors or oversights.
-
Stay Hydrated and Relaxed:
-
On the exam day, stay hydrated and get a good night's sleep to ensure you're mentally alert and focused.
-
Arrive Early:
-
If the exam is in a physical testing center, arrive early to ensure a smooth check-in process.
-
Believe in Yourself:
-
Trust in your preparation and believe in your abilities. Confidence can make a significant difference in your performance.
Continuing Education and Recertification
Continuing education and recertification are important aspects of maintaining your Cisco UCS certification and staying current in the rapidly evolving IT industry. Here's what you need to know about these processes:
Continuing Education:
-
Stay Updated: Technology is constantly evolving. Stay current with the latest developments in Cisco UCS technologies, data center trends, and related fields.
-
Read Documentation: Regularly review Cisco's official documentation, whitepapers, and tech blogs to stay informed about new features, updates, and best practices.
-
Attend Webinars and Conferences: Participate in webinars, workshops, and industry conferences focused on data center technologies and Cisco UCS. These events offer insights from experts and networking opportunities.
-
Online Courses: Enroll in online courses or platforms that offer continuous learning in areas related to your certification.
-
Blogs and Forums: Follow industry blogs, online forums, and social media accounts that discuss Cisco UCS and data center topics. Engaging in discussions can broaden your understanding.
Recertification:
-
Certification Expiry: Cisco certifications are valid for a certain period (e.g., three years). After this time, your certification becomes inactive.
-
Recertification Options: To keep your certification active, you can choose from several recertification options:
a. Pass a Higher-Level Exam: You can recertify by passing a higher-level exam in the same technology track. b. Pass the Same Exam Again: Re-taking the same exam also recertifies your current certification. c. Earn Continuing Education Credits: Accumulate a certain number of Continuing Education (CE) credits through activities like training, attending seminars, or contributing to the community.
-
CE Credits: Cisco offers a Continuing Education program that allows you to earn CE credits for various activities. These credits help you recertify without retaking exams.
-
Track Your Progress: Use Cisco's recertification tracker tool to monitor your progress and plan your recertification strategy.
-
Prepare in Advance: Start planning for recertification well before your certification's expiration date. This gives you ample time to choose the best recertification option for your career goals.
-
Stay Informed: Cisco periodically updates its recertification policies. Stay informed about any changes to ensure you're following the correct recertification process.
-
Recertification Exams: If you choose to take a recertification exam, ensure you review the latest exam blueprint and study materials to align your preparation with the updated content.
-
Stay Engaged: Even after obtaining a certification, stay active in Cisco's online communities, contribute to discussions, and keep learning to maintain your expertise.
Maintaining your certification through continuing education and recertification showcases your commitment to staying relevant in the field and provides evidence of your ongoing expertise. By adopting a mindset of lifelong learning, you'll be better equipped to adapt to new technologies and advancements in the data center domain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a Cisco UCS Administration certification offers a gateway to a thriving career in the dynamic realm of data center technologies. With benefits ranging from increased earning potential and industry recognition to a spectrum of specialized roles, this certification validates expertise in Cisco UCS architecture and administration. By diligently preparing through official study materials, practical labs, and thorough review, aspiring professionals can confidently navigate the certification exams. Beyond certification, the commitment to continuous learning, coupled with timely recertification, ensures a lasting impact and success in an ever-evolving IT landscape, making the journey towards Cisco UCS proficiency an investment in both personal growth and professional achievement.
Read More
Cisco UCS (Unified Computing System) is a popular data center solution that offers an innovative architecture for deploying and managing complex computing environments. It is designed to help organizations achieve better scalability, agility, and efficiency in their data center operations. The Cisco UCS Administration Certification is a professional-level certification that validates the expertise of individuals in managing and administering Cisco UCS environments. It demonstrates the ability to deploy, configure, manage, and troubleshoot Cisco UCS solutions. Obtaining this certification can open up numerous career opportunities in the field of data center administration and networking. In this blog, we will dive deep into the various aspects of Cisco UCS Administration Certification, including its importance, exam requirements, benefits, and the knowledge and skills required to earn this certification. We will also discuss some of the subtopics related to Cisco UCS administration, such as UCS Manager and UCS Central, configuring UCS infrastructure, deploying and managing service profiles, backup and disaster recovery, troubleshooting UCS issues, and UCS integration with other technologies.
Table of contents
-
Introduction to Cisco UCS:
-
Benefits of Cisco UCS Certification:
-
Different Cisco UCS Certifications:
-
Prerequisites for Cisco UCS Certification:
-
Exam Details and Topics:
-
Study Resources and Preparation:
-
Career Pathways and Growth:
-
Tips for Exam Success:
-
Continuing Education and Recertification:
-
Conclusion
Introduction to Cisco UCS
Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) is a data center architecture that integrates computing, networking, and storage resources into a single, cohesive system. It is designed to help organizations streamline their data center operations by simplifying infrastructure management, increasing agility, and reducing costs. The UCS architecture is based on a blade server platform that is highly scalable and adaptable, allowing organizations to easily expand their computing resources as needed. The system is managed through a single pane of glass, called the UCS Manager, which provides a unified view of the entire data center infrastructure.
UCS consists of several components, including the Fabric Interconnects, which provide connectivity between the servers, storage, and network, and the UCS Manager, which serves as the centralized management tool for the entire system. The UCS platform also includes service profiles, which are templates that define the configuration of a server, allowing for rapid deployment and consistent management across multiple servers.
One of the key advantages of UCS is its ability to integrate with other Cisco products and technologies, such as Cisco Nexus switches and Cisco ACI (Application Centric Infrastructure), providing a highly customizable and flexible infrastructure for modern data centers. Additionally, UCS offers a range of features and capabilities that enable organizations to achieve high levels of performance, reliability, and security, making it a popular choice for many enterprises around the world.
Benefits of Cisco UCS Certification
Obtaining a Cisco UCS certification comes with several benefits that can positively impact your career and professional growth. Here are some key benefits you can highlight in your blog:
-
Enhanced Career Opportunities: Cisco UCS certifications are recognized globally and are highly respected in the IT industry. Having a certification demonstrates your expertise and commitment to mastering Cisco's data center technologies, making you a valuable asset to potential employers.
-
Increased Earning Potential: Certified professionals often command higher salaries compared to their non-certified counterparts. Cisco UCS certifications validate your skills, giving you leverage when negotiating compensation packages.
-
Industry Recognition: Being certified by Cisco, a prominent leader in networking and IT solutions, adds credibility to your resume. Employers and colleagues will acknowledge your proficiency and knowledge in UCS administration.
-
Job Roles and Specializations: Cisco UCS certifications open doors to various job roles, such as Data Center Administrator, Network Engineer, Systems Engineer, and Cloud Infrastructure Specialist. Depending on the level of certification, you can specialize in different aspects of data center operations.
-
Competitive Advantage: In today's competitive job market, a Cisco UCS certification sets you apart from others. It can be the factor that pushes your resume to the top of the pile and lands you an interview.
-
Skill Validation: Cisco UCS certifications are not easy to obtain. Earning a certification demonstrates your dedication to learning and your ability to master complex technologies, which can boost your confidence in your skills.
-
Networking Opportunities: Pursuing a Cisco UCS certification connects you with a community of like-minded professionals. This network can provide insights, guidance, and potential collaborations in the future.
-
Hands-On Experience: The certification process often involves hands-on lab work and practical exercises. This experience equips you with real-world skills that are directly applicable to your job.
-
Knowledge Enhancement: The certification process encourages in-depth learning about Cisco UCS technologies and data center architecture. This knowledge can be applied not only to certification exams but also to real-world scenarios.
-
Career Progression: Cisco offers a tiered certification structure, allowing you to start with foundational certifications and progress to more advanced levels. This path enables you to continually grow your skills and advance your career.
-
Employer Confidence: Employers are more likely to trust certified professionals to handle critical infrastructure and projects. Having certified UCS administrators can contribute to the stability and efficiency of the organization's data center operations.
-
Global Recognition: Cisco UCS certifications are recognized internationally. This can be especially beneficial if you're considering working in different regions or countries.
-
Continuous Learning: Cisco's technology landscape is always evolving. Maintaining your certification requires staying up-to-date with the latest advancements, encouraging continuous learning throughout your career.
-
Job Satisfaction: Mastering Cisco UCS technologies can be intellectually rewarding. Seeing the impact of your skills on data center operations can provide a sense of accomplishment and job satisfaction.
Different Cisco UCS Certifications
Certainly, Cisco offers a range of Unified Computing System (UCS) certifications tailored to different skill levels and roles. Here's an overview of the different Cisco UCS certifications that you can include in your blog:
-
Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Data Center:
-
This entry-level certification is designed for individuals who are new to data center technologies.
-
It covers foundational topics related to data center networking, virtualization, storage, and Cisco UCS architecture.
-
CCNA Data Center provides a solid understanding of basic data center concepts and prepares candidates for more advanced certifications.
-
-
Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Data Center:
-
The CCNP Data Center certification is aimed at IT professionals who want to specialize in data center technologies.
-
It consists of a series of exams that cover various aspects of data center design, implementation, and troubleshooting.
-
CCNP Data Center covers advanced topics like implementing Cisco UCS infrastructure, data center automation, and implementing storage networking solutions.
-
-
Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert (CCIE) Data Center:
-
CCIE Data Center is the expert-level certification for individuals seeking mastery in data center technologies.
-
It requires both written and practical lab exams to demonstrate comprehensive knowledge and hands-on skills.
-
CCIE Data Center covers complex topics such as data center infrastructure design, application-centric infrastructure (ACI), and network services.
-
-
Cisco Certified Specialist - Data Center Unified Computing:
-
This specialist certification focuses specifically on Cisco UCS technologies.
-
It covers topics such as configuring, deploying, and managing Cisco UCS servers and equipment.
-
The certification validates expertise in UCS architecture, server provisioning, and maintenance.
-
-
Cisco Certified Specialist - Data Center Unified Computing Design:
-
This specialist certification is aimed at professionals involved in designing Cisco UCS solutions.
-
It covers design considerations for Cisco UCS deployments, including scalability, performance, and high availability.
-
-
Cisco Certified Specialist - Data Center Unified Computing Implementation:
-
This certification focuses on the implementation and deployment of Cisco UCS solutions.
-
It covers topics such as server installation, initial setup, firmware upgrades, and integration with other data center components.
-
-
Cisco Certified Specialist - Data Center Unified Computing Support:
-
This certification is tailored for individuals responsible for supporting and troubleshooting Cisco UCS environments.
-
It covers topics related to diagnosing and resolving common issues in UCS deployments.
-
-
Cisco Certified Specialist - Data Center Unified Fabric:
-
While not exclusively UCS-focused, this certification covers data center fabric technologies that are closely related to UCS deployments.
-
It encompasses topics like Cisco Nexus switches, data center networking, and unified fabric architectures.
-
Prerequisites for Cisco UCS Certification
Obtaining a Cisco UCS certification requires a certain level of knowledge, experience, and skills. While specific prerequisites can vary depending on the certification level, here are some general prerequisites you might encounter when pursuing a Cisco UCS certification:
-
Basic Networking Knowledge:
-
A foundational understanding of networking concepts, including TCP/IP, subnets, routing, and switching, is often required. This knowledge serves as a basis for understanding data center networking in the context of Cisco UCS.
-
-
Familiarity with Data Center Concepts:
-
A grasp of basic data center concepts such as virtualization, storage, and server architecture is important. This knowledge will help you understand how Cisco UCS fits into the larger data center environment.
-
-
Experience with Cisco Technologies:
-
Familiarity with Cisco networking technologies is beneficial. If you're pursuing a higher-level certification, having a Cisco CCNA or CCNP certification (or equivalent knowledge) can provide a strong foundation.
-
-
Hands-On Experience:
-
Practical experience with data center equipment and technologies, including server hardware, switches, and storage systems, is essential. Many Cisco UCS certifications emphasize hands-on skills.
-
-
Previous IT Experience:
-
For more advanced certifications, such as CCNP Data Center or CCIE Data Center, having a certain amount of professional IT experience is often recommended. This experience helps contextualize the concepts covered in the certification.
-
-
Study Resources:
-
While not a formal prerequisite, having access to Cisco's official study materials, practice exams, and recommended reading can greatly assist in exam preparation.
-
-
Training Courses:
-
Cisco often provides training courses specifically designed to prepare candidates for their certifications. While not always mandatory, these courses can provide in-depth knowledge and hands-on labs.
-
-
Problem-Solving Skills:
-
Cisco UCS certifications may include scenario-based questions or simulations that test your ability to troubleshoot and solve complex problems. Developing strong analytical and problem-solving skills is crucial.
-
-
Foundation in Server Administration:
-
Depending on the certification, having a background in server administration can be helpful. This includes knowledge of server operating systems, server hardware components, and server virtualization.
-
-
Commitment to Learning:
-
Pursuing a Cisco UCS certification requires dedication to learning and staying updated with the latest technologies. Being committed to ongoing education is essential.
-
Exam Details and Topics
Certainly, understanding the details and topics covered in the Cisco UCS certification exams is essential for effective exam preparation. While the specifics can vary depending on the certification level, here's a general overview of what you might expect in terms of exam details and topics:
-
Exam Format:
-
Most Cisco certification exams are computer-based and consist of a combination of question types, including multiple-choice, drag-and-drop, simulation-based, and scenario-based questions.
-
The number of questions and the time allotted for the exam can vary based on the certification level.
-
-
Passing Score:
-
Cisco certification exams typically require a passing score of around 800 out of 1000 points. However, passing scores can differ between exams, so it's important to check the specific requirements for the certification you're pursuing.
-
-
Exam Topics:
-
The topics covered in Cisco UCS certification exams are closely aligned with the skills and knowledge required for effective administration of Cisco UCS solutions. Here are some general categories of exam topics you might encounter:
-
a. Introduction to Cisco UCS:
-
-
Overview of Cisco UCS components, architecture, and benefits.
-
Understanding service profiles, templates, and pools.
-
b. Server Deployment and Configuration:
-
-
Installing and configuring Cisco UCS servers.
-
Creating service profiles and templates.
-
Understanding server pools and policies.
-
c. Networking in Cisco UCS:
-
-
Configuring Ethernet and Fibre Channel connectivity.
-
Implementing VLANs and fabric interconnects.
-
Understanding Cisco UCS networking concepts and features.
-
d. Storage in Cisco UCS:
-
-
Configuring storage connectivity, including SAN zoning.
-
Implementing storage policies and profiles.
-
Understanding storage concepts and protocols.
-
e. Cisco UCS Management:
-
-
Using UCS Manager for system management and monitoring.
-
Administering firmware upgrades and backups.
-
Troubleshooting common issues.
-
f. Automation and Orchestration:
-
-
Implementing automation using UCS Manager XML API.
-
Understanding scripting and programmability in Cisco UCS.
-
g. Integration with Virtualization:
-
-
Integrating Cisco UCS with virtualization platforms like VMware and Hyper-V.
-
Understanding virtual networking and storage.
-
h. Security and Access Control:
-
-
Implementing security features such as role-based access control.
-
Configuring authentication and authorization in UCS.
-
i. High Availability and Redundancy:
-
-
Configuring redundancy and failover in Cisco UCS.
-
Implementing fault tolerance and high availability.
-
j. Monitoring and Troubleshooting:
-
-
Diagnosing and resolving common issues in Cisco UCS environments.
-
Using logging and monitoring tools for troubleshooting.
-
Remember that the above topics are general guidelines and can vary based on the specific Cisco UCS certification you're pursuing. It's crucial to review the official exam blueprint provided by Cisco for each certification to get a detailed breakdown of the topics and subtopics that will be covered in the exam. This will help you focus your study efforts effectively and ensure that you're well-prepared for success on exam day.
Study Resources and Preparation
Preparing for a Cisco UCS certification requires effective study strategies and the right resources. Here's a guide to help you plan your study approach and identify useful study resources:
-
Official Cisco Study Materials:
-
Cisco's official certification website is a valuable resource. It provides exam blueprints, official study guides, and sample questions for each certification.
-
Review the official certification exam topics and objectives to ensure your study materials align with the content.
-
-
Cisco Learning Network:
-
The Cisco Learning Network is an online community where you can connect with other candidates, ask questions, and access study materials, including videos, discussions, and blogs.
-
-
Training Courses:
-
Cisco offers instructor-led training courses that cover the exam topics in-depth. These courses include hands-on labs and insights from experienced instructors.
-
Check Cisco's official training portal for available courses related to your certification.
-
-
Books and Ebooks:
-
There are many books and ebooks available that focus on Cisco UCS technologies and certification exam preparation. Look for reputable authors and publications.
-
-
Practice Exams:
-
Practice exams are crucial for assessing your knowledge and identifying areas where you need further study.
-
Cisco provides official practice exams, and you can also find third-party practice exam providers.
-
-
Hands-On Labs:
-
Hands-on experience is essential for mastering Cisco UCS technologies. If possible, set up a lab environment to practice configuring, managing, and troubleshooting UCS components.
-
-
Online Forums and Communities:
-
Online forums like Reddit, Stack Exchange, and Cisco support communities can provide valuable insights, tips, and answers to your questions.
-
-
Video Courses and Tutorials:
-
iCert Global and YouTube host video courses and tutorials that cover Cisco UCS concepts and exam preparation.
-
-
Flashcards and Note-Taking:
-
Create flashcards to review key concepts and definitions. Summarize your notes as you study to reinforce your understanding.
-
-
Time Management:
-
Create a study schedule that allocates time for each exam topic. Consistent, focused study sessions are more effective than cramming.
-
-
Practice Time Management:
-
Cisco exams often have time constraints. When taking practice exams, practice managing your time effectively to complete all questions within the allotted time.
-
-
Hands-On Practice:
-
Whenever possible, apply theoretical knowledge in a hands-on lab environment. This reinforces your understanding and helps you become comfortable with actual configurations.
-
-
Review and Revision:
-
Regularly review your notes, practice exams, and study resources to reinforce your memory and understanding of key concepts.
-
-
Stay Updated:
-
Stay current with any updates or changes to the exam objectives or topics by checking Cisco's official certification website.
-
Career Pathways and Growth
Earning a Cisco UCS Administration certification can lead to exciting career opportunities and growth within the IT and data center fields. Here are some potential career pathways and growth opportunities for individuals who hold Cisco UCS certifications:
-
Data Center Administrator:
-
Cisco UCS certifications provide a strong foundation for working as a data center administrator. You'll be responsible for managing and maintaining data center infrastructure, including servers, networking, and storage.
-
-
Network Engineer:
-
With a focus on Cisco UCS networking components, you can pursue roles as a network engineer, where you design, implement, and manage data center networks.
-
-
Systems Engineer:
-
Systems engineers leverage their Cisco UCS skills to design and deploy integrated data center solutions, ensuring seamless operations between servers, storage, and networking components.
-
-
Cloud Infrastructure Specialist:
-
As cloud computing continues to grow, having expertise in Cisco UCS can be valuable for roles involving cloud infrastructure design and management.
-
-
Virtualization Specialist:
-
Cisco UCS certifications align well with virtualization technologies. You can specialize in managing virtual environments, working with platforms like VMware or Hyper-V.
-
-
Data Center Architect:
-
With advanced Cisco UCS certifications, you can transition into data center architecture roles, designing complex, scalable, and efficient data center solutions.
-
-
IT Consultant:
-
Cisco UCS certifications are highly respected by clients seeking IT consulting services for their data center needs. Consultants provide expert advice and solutions.
-
-
IT Manager or Director:
-
As you accumulate experience and expertise, you can move into management roles overseeing data center operations, infrastructure, and teams.
-
-
Specialization in Hybrid Cloud:
-
With the integration of on-premises data centers and cloud solutions, professionals with Cisco UCS skills can specialize in hybrid cloud architecture and management.
-
-
Security Analyst:
-
Cisco UCS certifications can complement a career in security by providing insights into securing data center infrastructure and protecting critical assets.
-
-
Training and Education:
-
As a certified UCS administrator, you can share your knowledge by becoming an instructor, developing training materials, or delivering workshops.
-
-
Vendor Solutions Engineer:
-
Cisco UCS expertise is valuable to technology vendors. You could work as a pre-sales engineer, demonstrating how your vendor's solutions integrate with Cisco UCS environments.
-
-
Career Progression:
-
Cisco offers a tiered certification structure, allowing you to advance from associate to professional to expert levels. This progression demonstrates continuous growth and expertise.
-
-
Entrepreneurship:
-
Armed with in-depth knowledge of Cisco UCS, you might explore entrepreneurial opportunities, such as starting a consulting firm or offering specialized services to businesses.
-
Tips for Exam Success
Preparing for and taking a Cisco UCS certification exam requires a focused and strategic approach. Here are some valuable tips to help you achieve success on your exam day:
-
Understand Exam Objectives:
-
Familiarize yourself with the official exam blueprint or objectives provided by Cisco. This will guide your study plan and ensure you cover all required topics.
-
-
Create a Study Plan:
-
Develop a structured study plan that allocates sufficient time to each exam topic. Consistency is key to effective learning.
-
-
Use Official Study Materials:
-
Rely on Cisco's official study guides, practice exams, and resources. These materials are aligned with the exam content and provide accurate information.
-
-
Practice Regularly:
-
Regular practice with practice exams and hands-on labs helps reinforce your knowledge and build confidence.
-
-
Focus on Hands-On Experience:
-
Cisco exams often test practical skills. Spend ample time working in a lab environment to gain hands-on experience with Cisco UCS technologies.
-
-
Time Management Practice:
-
During practice exams, practice time management to ensure you can complete all questions within the allotted time.
-
-
Review and Revise:
-
Regularly review your study materials and notes to reinforce your understanding of key concepts.
-
-
Use Multiple Resources:
-
Supplement official materials with other resources like books, online tutorials, and videos to gain a well-rounded understanding.
-
-
Join Study Groups:
-
Engage with study groups or online forums to discuss concepts, share insights, and ask questions.
-
-
Simulate Exam Conditions:
-
When taking practice exams, simulate exam conditions by minimizing distractions and adhering to time limits.
-
-
Identify Weak Areas:
-
Use practice exams to identify areas where you need more focus. Spend extra time studying topics that challenge you.
-
-
Stay Calm and Confident:
-
On the exam day, remain calm and confident in your preparation. Positive thinking can have a significant impact on your performance.
-
-
Read Questions Carefully:
-
Take your time to read each question carefully and fully understand what is being asked before selecting an answer.
-
-
Eliminate Wrong Answers:
-
If you're unsure about an answer, eliminate obviously incorrect options to improve your chances of selecting the correct one.
-
-
Flag and Manage:
-
If allowed, flag questions you're unsure about and return to them later. Prioritize questions you're more confident about.
-
-
Answer All Questions:
-
Never leave questions unanswered. Even if you're unsure, make an educated guess.
-
-
Check Before Submitting:
-
If time allows, review your answers before submitting the exam to catch any errors or oversights.
-
-
Stay Hydrated and Relaxed:
-
On the exam day, stay hydrated and get a good night's sleep to ensure you're mentally alert and focused.
-
-
Arrive Early:
-
If the exam is in a physical testing center, arrive early to ensure a smooth check-in process.
-
-
Believe in Yourself:
-
Trust in your preparation and believe in your abilities. Confidence can make a significant difference in your performance.
-
Continuing Education and Recertification
Continuing education and recertification are important aspects of maintaining your Cisco UCS certification and staying current in the rapidly evolving IT industry. Here's what you need to know about these processes:
Continuing Education:
-
Stay Updated: Technology is constantly evolving. Stay current with the latest developments in Cisco UCS technologies, data center trends, and related fields.
-
Read Documentation: Regularly review Cisco's official documentation, whitepapers, and tech blogs to stay informed about new features, updates, and best practices.
-
Attend Webinars and Conferences: Participate in webinars, workshops, and industry conferences focused on data center technologies and Cisco UCS. These events offer insights from experts and networking opportunities.
-
Online Courses: Enroll in online courses or platforms that offer continuous learning in areas related to your certification.
-
Blogs and Forums: Follow industry blogs, online forums, and social media accounts that discuss Cisco UCS and data center topics. Engaging in discussions can broaden your understanding.
Recertification:
-
Certification Expiry: Cisco certifications are valid for a certain period (e.g., three years). After this time, your certification becomes inactive.
-
Recertification Options: To keep your certification active, you can choose from several recertification options:
a. Pass a Higher-Level Exam: You can recertify by passing a higher-level exam in the same technology track. b. Pass the Same Exam Again: Re-taking the same exam also recertifies your current certification. c. Earn Continuing Education Credits: Accumulate a certain number of Continuing Education (CE) credits through activities like training, attending seminars, or contributing to the community.
-
CE Credits: Cisco offers a Continuing Education program that allows you to earn CE credits for various activities. These credits help you recertify without retaking exams.
-
Track Your Progress: Use Cisco's recertification tracker tool to monitor your progress and plan your recertification strategy.
-
Prepare in Advance: Start planning for recertification well before your certification's expiration date. This gives you ample time to choose the best recertification option for your career goals.
-
Stay Informed: Cisco periodically updates its recertification policies. Stay informed about any changes to ensure you're following the correct recertification process.
-
Recertification Exams: If you choose to take a recertification exam, ensure you review the latest exam blueprint and study materials to align your preparation with the updated content.
-
Stay Engaged: Even after obtaining a certification, stay active in Cisco's online communities, contribute to discussions, and keep learning to maintain your expertise.
Maintaining your certification through continuing education and recertification showcases your commitment to staying relevant in the field and provides evidence of your ongoing expertise. By adopting a mindset of lifelong learning, you'll be better equipped to adapt to new technologies and advancements in the data center domain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a Cisco UCS Administration certification offers a gateway to a thriving career in the dynamic realm of data center technologies. With benefits ranging from increased earning potential and industry recognition to a spectrum of specialized roles, this certification validates expertise in Cisco UCS architecture and administration. By diligently preparing through official study materials, practical labs, and thorough review, aspiring professionals can confidently navigate the certification exams. Beyond certification, the commitment to continuous learning, coupled with timely recertification, ensures a lasting impact and success in an ever-evolving IT landscape, making the journey towards Cisco UCS proficiency an investment in both personal growth and professional achievement.
Complete Guide to Cisco Certified Network Professional,CCNP
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Certification. In today's dynamic digital world, CCNP stands as a testament to networking expertise, validating skills in designing, implementing, and managing intricate network solutions. Whether you're an aspiring network engineer or an IT professional, this guide will navigate you through CCNP's significance, exam structures, preparation strategies, and the array of career opportunities it unlocks. Join us to explore the realm of Cisco's networking technology and harness the benefits of CCNP certification for your professional growth.
Table of contents
-
Introduction to CCNP Certification
-
CCNP Certification Tracks
-
CCNP Certification Exam Format
-
CCNP Exam Preparation Tips
-
CCNP Enterprise Certification
-
CCNP Security Certification
-
CCNP Data Center Certification
-
CCNP Certification Exam Tips
-
CCNP Certification Renewal
-
Conclusion
Introduction to CCNP Certification
Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) is a professional-level certification offered by Cisco Systems, a leading provider of networking equipment and solutions. The CCNP certification is designed for network engineers, administrators, and technicians who want to advance their skills and knowledge in networking and enhance their career prospects.
To earn the CCNP certification, candidates must pass a series of exams that cover advanced networking concepts and technologies. These exams are designed to test the candidate's ability to design, implement, manage, and troubleshoot complex networks and infrastructure.
The CCNP certification program offers several tracks, each of which focuses on a specific area of networking. These tracks include Enterprise, Security, Data Center, Collaboration, Service Provider, and DevNet. Each track has its own set of exams and requirements, but they all share a common goal of helping professionals become experts in their chosen field of networking.
CCNP certification provides numerous benefits to professionals, including increased job opportunities, higher salaries, and recognition of their expertise in the industry. It also serves as a stepping stone towards achieving higher-level certifications, such as the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert (CCIE).
Overall, CCNP certification is an excellent way for networking professionals to validate their skills and knowledge, enhance their career prospects, and stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and trends in the networking industry.
CCNP Certification Tracks
Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification offers several tracks, each of which focuses on a specific area of networking. The following are the six CCNP certification tracks:
-
CCNP Enterprise: The CCNP Enterprise certification track focuses on designing, deploying, and managing enterprise-level networks. The track covers topics such as advanced routing and switching, network design, security, wireless, and automation.
-
CCNP Security: The CCNP Security certification track focuses on designing, implementing, and maintaining secure network infrastructure. The track covers topics such as network security, identity management, VPN, and firewall technologies.
-
CCNP Data Center: The CCNP Data Center certification track focuses on designing, deploying, and managing data center infrastructure. The track covers topics such as data center networking, storage networking, virtualization, and automation.
-
CCNP Collaboration: The CCNP Collaboration certification track focuses on designing, deploying, and managing collaboration solutions such as voice, video, and messaging. The track covers topics such as collaboration applications, endpoint configuration, call control, and messaging.
-
CCNP Service Provider: The CCNP Service Provider certification track focuses on designing, implementing, and maintaining service provider networks. The track covers topics such as service provider architecture, advanced routing and switching, and network automation.
-
CCNP DevNet: The CCNP DevNet certification track focuses on developing and maintaining applications that run on Cisco platforms. The track covers topics such as software development, automation, and infrastructure as code.
Each of these tracks includes a set of exams that candidates must pass to earn the CCNP certification in that track. The exams cover both theoretical knowledge and hands-on skills, ensuring that certified professionals are capable of designing, deploying, and maintaining complex networks and infrastructure in their chosen field of networking.
CCNP Certification Exam Format
The Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification exams vary in format, depending on the specific certification track and exam being taken. However, most CCNP exams share some common characteristics. Here are some typical features of CCNP certification exams:
-
Exam Type: Most CCNP exams are computer-based exams (CBE), which means that they are taken on a computer rather than on paper.
-
Exam Duration: The exam duration varies from exam to exam but typically ranges from 120 to 180 minutes.
-
Exam Questions: The exam questions may include multiple-choice questions, drag-and-drop questions, simulation questions, and other types of questions.
-
Exam Content: The exam content is based on the specific certification track and covers advanced networking concepts and technologies. The exams are designed to test the candidate's ability to design, implement, manage, and troubleshoot complex networks and infrastructure.
-
Exam Prerequisites: Some CCNP exams may have prerequisites, such as passing a lower-level certification exam or having a certain amount of work experience in the field.
-
Passing Score: The passing score for CCNP exams is typically 750 out of 1000 points.
-
Exam Availability: CCNP exams are available at Pearson VUE test centers worldwide.
-
Exam Cost: The cost of each CCNP exam varies by country and region, but typically ranges from $300 to $500 USD per exam.
It's important to note that the exam format and content may change over time as new technologies and concepts emerge in the networking industry. Therefore, it's important to stay up-to-date with the latest exam requirements and study materials.
CCNP Exam Preparation Tips
Preparing for a Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification exam requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience. Here are some tips to help you prepare for CCNP exams:
-
Understand the Exam Objectives: Before you start studying, it's important to understand the exam objectives and content. Review the exam blueprint and study materials provided by Cisco to get a clear understanding of what topics and concepts the exam will cover.
-
Create a Study Plan: Once you understand the exam objectives, create a study plan that works for you. Set a realistic timeline and allocate time for both theoretical study and hands-on practice.
-
Study the Theory: Study the theory behind the topics and concepts covered in the exam. Use study materials such as books, videos, and online resources to gain a deep understanding of the concepts.
-
Practice Hands-on Labs: Hands-on practice is essential to prepare for CCNP exams. Use virtual labs or real equipment to gain practical experience with the technologies and concepts covered in the exam.
-
Join Study Groups: Joining a study group can be helpful for preparing for CCNP exams. You can discuss topics and concepts with other professionals preparing for the same exam, share knowledge, and learn from each other.
-
Take Practice Tests: Take practice tests to gauge your understanding of the exam content and identify areas that require further study. Use Cisco's official practice tests and study materials or third-party practice tests.
-
Review Your Mistakes: After taking practice tests, review your mistakes and areas of weakness. Focus on studying those areas in-depth to improve your understanding.
-
Stay Up-to-date with Industry Trends: Stay up-to-date with the latest networking technologies and trends in the industry. Attend conferences, read blogs, and follow industry experts to stay informed.
By following these tips, you can prepare effectively for CCNP certification exams and increase your chances of passing the exam.
CCNP Enterprise Certification
The Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Enterprise certification is designed for network professionals who want to specialize in enterprise networking technologies. It focuses on designing, deploying, and managing enterprise-level networks. Here are some key details about the CCNP Enterprise certification:
-
Certification Exams: To earn the CCNP Enterprise certification, you must pass two exams: a core exam and a concentration exam. The core exam is the 350-401 ENCOR (Implementing and Operating Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies) exam, which covers advanced enterprise networking concepts and technologies. The concentration exam can be selected from a list of available concentration exams, such as the 300-410 ENARSI (Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services) exam.
-
Exam Format: The CCNP Enterprise exams are computer-based exams (CBE) and consist of multiple-choice questions, drag-and-drop questions, simulation questions, and other types of questions. The exam duration is 120 minutes for the core exam and 90 minutes for the concentration exam.
-
Exam Preparation: To prepare for the CCNP Enterprise exams, you should have a good understanding of networking concepts and technologies covered in the exam blueprint. Cisco provides official study materials, such as books, videos, and online resources, to help you prepare for the exam. Additionally, you should gain hands-on experience with enterprise-level networking technologies by using virtual labs or real equipment.
-
Recertification: CCNP Enterprise certification is valid for three years. To maintain your certification, you must pass one qualifying exam or earn a higher-level certification before the certification expiration date.
-
Career Opportunities: CCNP Enterprise certification can open up many career opportunities in enterprise-level networking. It can help you to land a job as a network engineer, network architect, network administrator, or other related positions. Additionally, CCNP Enterprise certification can lead to higher salaries, as it demonstrates a high level of expertise in enterprise networking technologies.
Overall, the CCNP Enterprise certification is an excellent choice for network professionals who want to specialize in enterprise-level networking and demonstrate their expertise to potential employers.
CCNP Security Certification
The Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Security certification is designed for network security professionals who want to specialize in security technologies and solutions. It focuses on designing, deploying, and managing security solutions in enterprise-level networks. Here are some key details about the CCNP Security certification:
-
Certification Exams: To earn the CCNP Security certification, you must pass four exams: a core exam and three concentration exams. The core exam is the 350-701 SCOR (Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies) exam, which covers advanced security concepts and technologies. The concentration exams can be selected from a list of available exams, such as the 300-710 SNCF (Securing Networks with Cisco Firepower) exam.
-
Exam Format: The CCNP Security exams are computer-based exams (CBE) and consist of multiple-choice questions, drag-and-drop questions, simulation questions, and other types of questions. The exam duration is 120 minutes for the core exam and 90 minutes for the concentration exams.
-
Exam Preparation: To prepare for the CCNP Security exams, you should have a good understanding of security concepts and technologies covered in the exam blueprint. Cisco provides official study materials, such as books, videos, and online resources, to help you prepare for the exam. Additionally, you should gain hands-on experience with security technologies by using virtual labs or real equipment.
-
Recertification: CCNP Security certification is valid for three years. To maintain your certification, you must pass one qualifying exam or earn a higher-level certification before the certification expiration date.
-
Career Opportunities: CCNP Security certification can open up many career opportunities in network security. It can help you to land a job as a network security engineer, security analyst, security architect, or other related positions. Additionally, CCNP Security certification can lead to higher salaries, as it demonstrates a high level of expertise in security technologies and solutions.
Overall, the CCNP Security certification is an excellent choice for network security professionals who want to specialize in security technologies and demonstrate their expertise to potential employers.
CCNP Data Center Certification
The Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Data Center certification is designed for network professionals who want to specialize in data center technologies. It focuses on designing, deploying, and managing data center infrastructure and technologies. Here are some key details about the CCNP Data Center certification:
-
Certification Exams: To earn the CCNP Data Center certification, you must pass two exams: a core exam and a concentration exam. The core exam is the 350-601 DCCOR (Implementing Cisco Data Center Core Technologies) exam, which covers advanced data center networking concepts and technologies. The concentration exam can be selected from a list of available exams, such as the 300-615 DCIT (Implementing Cisco Data Center Infrastructure) exam.
-
Exam Format: The CCNP Data Center exams are computer-based exams (CBE) and consist of multiple-choice questions, drag-and-drop questions, simulation questions, and other types of questions. The exam duration is 120 minutes for the core exam and 90 minutes for the concentration exam.
-
Exam Preparation: To prepare for the CCNP Data Center exams, you should have a good understanding of data center concepts and technologies covered in the exam blueprint. Cisco provides official study materials, such as books, videos, and online resources, to help you prepare for the exam. Additionally, you should gain hands-on experience with data center technologies by using virtual labs or real equipment.
-
Recertification: CCNP Data Center certification is valid for three years. To maintain your certification, you must pass one qualifying exam or earn a higher-level certification before the certification expiration date.
-
Career Opportunities: CCNP Data Center certification can open up many career opportunities in data center networking. It can help you to land a job as a data center engineer, data center architect, data center administrator, or other related positions. Additionally, CCNP Data Center certification can lead to higher salaries, as it demonstrates a high level of expertise in data center technologies and infrastructure.
Overall, the CCNP Data Center certification is an excellent choice for network professionals who want to specialize in data center technologies and infrastructure and demonstrate their expertise to potential employers.
CCNP Certification Exam Tips
Here are some exam tips to help you prepare for the Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification exams:
-
Understand the Exam Blueprint: Before you start studying for the exam, make sure you understand the exam blueprint. The exam blueprint outlines the topics and subtopics covered on the exam, as well as the percentage of questions dedicated to each topic. Use the blueprint as a guide for your study plan.
-
Study Official Materials: Use official study materials provided by Cisco, such as books, videos, and online resources. These materials are designed to align with the exam blueprint and provide a comprehensive understanding of the topics covered on the exam.
-
Practice with Hands-On Labs: Gain hands-on experience with the technologies and concepts covered on the exam by using virtual labs or real equipment. This will help you to understand how the technologies work in real-world scenarios and prepare you for simulation questions on the exam.
-
Join Study Groups: Join online study groups or forums to connect with other exam candidates. Discussing the exam topics with others can help you to understand difficult concepts and gain new perspectives on the materials.
-
Take Practice Exams: Take practice exams to assess your knowledge and identify areas where you need more study. Cisco provides official practice exams, as well as third-party practice exams, that simulate the format and difficulty of the real exam.
-
Manage Your Time: During the exam, manage your time wisely. Read each question carefully and avoid spending too much time on difficult questions. If you get stuck on a question, mark it and move on. You can come back to it later if you have time.
-
Practice Good Exam Habits: Practice good exam habits, such as getting a good night's sleep before the exam, eating a healthy meal, arriving at the testing center early, and bringing all necessary identification and materials.
By following these exam tips, you can improve your chances of passing the CCNP certification exams and achieving your career goals.
CCNP Certification Renewal
To maintain your Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification, you must renew it before it expires. Here are some details on how to renew your CCNP certification:
-
Renewal Period: CCNP certifications are valid for three years. You should aim to renew your certification at least six months before it expires.
-
Qualifying Exams: To renew your CCNP certification, you can pass one qualifying exam from the list of available exams. The qualifying exam can be a core exam from the CCNP track you are certified in or a concentration exam from any CCNP track. For example, if you are certified in CCNP Enterprise, you can pass the 350-401 ENCOR exam or any of the concentration exams from the CCNP Enterprise track to renew your certification.
-
Higher-Level Certification: Alternatively, you can earn a higher-level certification, such as CCIE or Cisco Certified Architect (CCAr), to renew your CCNP certification. Higher-level certifications demonstrate a higher level of expertise and can help you advance your career.
-
Continuing Education: Another way to renew your CCNP certification is to earn Continuing Education (CE) credits. CE credits can be earned by completing eligible training courses, attending Cisco Live events, or participating in other eligible activities. You can earn CE credits by participating in Cisco's Continuing Education Program.
-
Recertification Exam: If your CCNP certification has already expired, you can still renew it by passing a recertification exam. The recertification exam is the same as the qualifying exam and can be a core exam or a concentration exam from any CCNP track.
Renewing your CCNP certification demonstrates your commitment to ongoing professional development and keeps your skills up to date. By renewing your CCNP certification, you can continue to advance your career and stay competitive in the job market.
How to obtain CCNP Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Power BI Certification
-
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
-
Cisco : CCNP Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification is a highly regarded and respected certification that demonstrates your knowledge and expertise in networking technologies. The CCNP certification offers different tracks, including Enterprise, Security, Data Center, Collaboration, Service Provider, and DevNet, each with its own set of exams and requirements.
To earn the CCNP certification, you must pass the required exams and demonstrate a deep understanding of networking concepts and technologies. Exam preparation should include studying official materials, practicing with hands-on labs, taking practice exams, and managing your time wisely during the actual exam.
To maintain your CCNP certification, you must renew it before it expires. You can renew your certification by passing a qualifying exam, earning a higher-level certification, earning Continuing Education credits, or passing a recertification exam.
Overall, the CCNP certification is a valuable asset for networking professionals seeking to advance their careers, expand their knowledge, and stay current with the latest technologies and best practices in the networking industry.
Read More
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Certification. In today's dynamic digital world, CCNP stands as a testament to networking expertise, validating skills in designing, implementing, and managing intricate network solutions. Whether you're an aspiring network engineer or an IT professional, this guide will navigate you through CCNP's significance, exam structures, preparation strategies, and the array of career opportunities it unlocks. Join us to explore the realm of Cisco's networking technology and harness the benefits of CCNP certification for your professional growth.
Table of contents
-
Introduction to CCNP Certification
-
CCNP Certification Tracks
-
CCNP Certification Exam Format
-
CCNP Exam Preparation Tips
-
CCNP Enterprise Certification
-
CCNP Security Certification
-
CCNP Data Center Certification
-
CCNP Certification Exam Tips
-
CCNP Certification Renewal
-
Conclusion
Introduction to CCNP Certification
Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) is a professional-level certification offered by Cisco Systems, a leading provider of networking equipment and solutions. The CCNP certification is designed for network engineers, administrators, and technicians who want to advance their skills and knowledge in networking and enhance their career prospects.
To earn the CCNP certification, candidates must pass a series of exams that cover advanced networking concepts and technologies. These exams are designed to test the candidate's ability to design, implement, manage, and troubleshoot complex networks and infrastructure.
The CCNP certification program offers several tracks, each of which focuses on a specific area of networking. These tracks include Enterprise, Security, Data Center, Collaboration, Service Provider, and DevNet. Each track has its own set of exams and requirements, but they all share a common goal of helping professionals become experts in their chosen field of networking.
CCNP certification provides numerous benefits to professionals, including increased job opportunities, higher salaries, and recognition of their expertise in the industry. It also serves as a stepping stone towards achieving higher-level certifications, such as the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert (CCIE).
Overall, CCNP certification is an excellent way for networking professionals to validate their skills and knowledge, enhance their career prospects, and stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and trends in the networking industry.
CCNP Certification Tracks
Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification offers several tracks, each of which focuses on a specific area of networking. The following are the six CCNP certification tracks:
-
CCNP Enterprise: The CCNP Enterprise certification track focuses on designing, deploying, and managing enterprise-level networks. The track covers topics such as advanced routing and switching, network design, security, wireless, and automation.
-
CCNP Security: The CCNP Security certification track focuses on designing, implementing, and maintaining secure network infrastructure. The track covers topics such as network security, identity management, VPN, and firewall technologies.
-
CCNP Data Center: The CCNP Data Center certification track focuses on designing, deploying, and managing data center infrastructure. The track covers topics such as data center networking, storage networking, virtualization, and automation.
-
CCNP Collaboration: The CCNP Collaboration certification track focuses on designing, deploying, and managing collaboration solutions such as voice, video, and messaging. The track covers topics such as collaboration applications, endpoint configuration, call control, and messaging.
-
CCNP Service Provider: The CCNP Service Provider certification track focuses on designing, implementing, and maintaining service provider networks. The track covers topics such as service provider architecture, advanced routing and switching, and network automation.
-
CCNP DevNet: The CCNP DevNet certification track focuses on developing and maintaining applications that run on Cisco platforms. The track covers topics such as software development, automation, and infrastructure as code.
Each of these tracks includes a set of exams that candidates must pass to earn the CCNP certification in that track. The exams cover both theoretical knowledge and hands-on skills, ensuring that certified professionals are capable of designing, deploying, and maintaining complex networks and infrastructure in their chosen field of networking.
CCNP Certification Exam Format
The Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification exams vary in format, depending on the specific certification track and exam being taken. However, most CCNP exams share some common characteristics. Here are some typical features of CCNP certification exams:
-
Exam Type: Most CCNP exams are computer-based exams (CBE), which means that they are taken on a computer rather than on paper.
-
Exam Duration: The exam duration varies from exam to exam but typically ranges from 120 to 180 minutes.
-
Exam Questions: The exam questions may include multiple-choice questions, drag-and-drop questions, simulation questions, and other types of questions.
-
Exam Content: The exam content is based on the specific certification track and covers advanced networking concepts and technologies. The exams are designed to test the candidate's ability to design, implement, manage, and troubleshoot complex networks and infrastructure.
-
Exam Prerequisites: Some CCNP exams may have prerequisites, such as passing a lower-level certification exam or having a certain amount of work experience in the field.
-
Passing Score: The passing score for CCNP exams is typically 750 out of 1000 points.
-
Exam Availability: CCNP exams are available at Pearson VUE test centers worldwide.
-
Exam Cost: The cost of each CCNP exam varies by country and region, but typically ranges from $300 to $500 USD per exam.
It's important to note that the exam format and content may change over time as new technologies and concepts emerge in the networking industry. Therefore, it's important to stay up-to-date with the latest exam requirements and study materials.
CCNP Exam Preparation Tips
Preparing for a Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification exam requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience. Here are some tips to help you prepare for CCNP exams:
-
Understand the Exam Objectives: Before you start studying, it's important to understand the exam objectives and content. Review the exam blueprint and study materials provided by Cisco to get a clear understanding of what topics and concepts the exam will cover.
-
Create a Study Plan: Once you understand the exam objectives, create a study plan that works for you. Set a realistic timeline and allocate time for both theoretical study and hands-on practice.
-
Study the Theory: Study the theory behind the topics and concepts covered in the exam. Use study materials such as books, videos, and online resources to gain a deep understanding of the concepts.
-
Practice Hands-on Labs: Hands-on practice is essential to prepare for CCNP exams. Use virtual labs or real equipment to gain practical experience with the technologies and concepts covered in the exam.
-
Join Study Groups: Joining a study group can be helpful for preparing for CCNP exams. You can discuss topics and concepts with other professionals preparing for the same exam, share knowledge, and learn from each other.
-
Take Practice Tests: Take practice tests to gauge your understanding of the exam content and identify areas that require further study. Use Cisco's official practice tests and study materials or third-party practice tests.
-
Review Your Mistakes: After taking practice tests, review your mistakes and areas of weakness. Focus on studying those areas in-depth to improve your understanding.
-
Stay Up-to-date with Industry Trends: Stay up-to-date with the latest networking technologies and trends in the industry. Attend conferences, read blogs, and follow industry experts to stay informed.
By following these tips, you can prepare effectively for CCNP certification exams and increase your chances of passing the exam.
CCNP Enterprise Certification
The Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Enterprise certification is designed for network professionals who want to specialize in enterprise networking technologies. It focuses on designing, deploying, and managing enterprise-level networks. Here are some key details about the CCNP Enterprise certification:
-
Certification Exams: To earn the CCNP Enterprise certification, you must pass two exams: a core exam and a concentration exam. The core exam is the 350-401 ENCOR (Implementing and Operating Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies) exam, which covers advanced enterprise networking concepts and technologies. The concentration exam can be selected from a list of available concentration exams, such as the 300-410 ENARSI (Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services) exam.
-
Exam Format: The CCNP Enterprise exams are computer-based exams (CBE) and consist of multiple-choice questions, drag-and-drop questions, simulation questions, and other types of questions. The exam duration is 120 minutes for the core exam and 90 minutes for the concentration exam.
-
Exam Preparation: To prepare for the CCNP Enterprise exams, you should have a good understanding of networking concepts and technologies covered in the exam blueprint. Cisco provides official study materials, such as books, videos, and online resources, to help you prepare for the exam. Additionally, you should gain hands-on experience with enterprise-level networking technologies by using virtual labs or real equipment.
-
Recertification: CCNP Enterprise certification is valid for three years. To maintain your certification, you must pass one qualifying exam or earn a higher-level certification before the certification expiration date.
-
Career Opportunities: CCNP Enterprise certification can open up many career opportunities in enterprise-level networking. It can help you to land a job as a network engineer, network architect, network administrator, or other related positions. Additionally, CCNP Enterprise certification can lead to higher salaries, as it demonstrates a high level of expertise in enterprise networking technologies.
Overall, the CCNP Enterprise certification is an excellent choice for network professionals who want to specialize in enterprise-level networking and demonstrate their expertise to potential employers.
CCNP Security Certification
The Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Security certification is designed for network security professionals who want to specialize in security technologies and solutions. It focuses on designing, deploying, and managing security solutions in enterprise-level networks. Here are some key details about the CCNP Security certification:
-
Certification Exams: To earn the CCNP Security certification, you must pass four exams: a core exam and three concentration exams. The core exam is the 350-701 SCOR (Implementing and Operating Cisco Security Core Technologies) exam, which covers advanced security concepts and technologies. The concentration exams can be selected from a list of available exams, such as the 300-710 SNCF (Securing Networks with Cisco Firepower) exam.
-
Exam Format: The CCNP Security exams are computer-based exams (CBE) and consist of multiple-choice questions, drag-and-drop questions, simulation questions, and other types of questions. The exam duration is 120 minutes for the core exam and 90 minutes for the concentration exams.
-
Exam Preparation: To prepare for the CCNP Security exams, you should have a good understanding of security concepts and technologies covered in the exam blueprint. Cisco provides official study materials, such as books, videos, and online resources, to help you prepare for the exam. Additionally, you should gain hands-on experience with security technologies by using virtual labs or real equipment.
-
Recertification: CCNP Security certification is valid for three years. To maintain your certification, you must pass one qualifying exam or earn a higher-level certification before the certification expiration date.
-
Career Opportunities: CCNP Security certification can open up many career opportunities in network security. It can help you to land a job as a network security engineer, security analyst, security architect, or other related positions. Additionally, CCNP Security certification can lead to higher salaries, as it demonstrates a high level of expertise in security technologies and solutions.
Overall, the CCNP Security certification is an excellent choice for network security professionals who want to specialize in security technologies and demonstrate their expertise to potential employers.
CCNP Data Center Certification
The Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Data Center certification is designed for network professionals who want to specialize in data center technologies. It focuses on designing, deploying, and managing data center infrastructure and technologies. Here are some key details about the CCNP Data Center certification:
-
Certification Exams: To earn the CCNP Data Center certification, you must pass two exams: a core exam and a concentration exam. The core exam is the 350-601 DCCOR (Implementing Cisco Data Center Core Technologies) exam, which covers advanced data center networking concepts and technologies. The concentration exam can be selected from a list of available exams, such as the 300-615 DCIT (Implementing Cisco Data Center Infrastructure) exam.
-
Exam Format: The CCNP Data Center exams are computer-based exams (CBE) and consist of multiple-choice questions, drag-and-drop questions, simulation questions, and other types of questions. The exam duration is 120 minutes for the core exam and 90 minutes for the concentration exam.
-
Exam Preparation: To prepare for the CCNP Data Center exams, you should have a good understanding of data center concepts and technologies covered in the exam blueprint. Cisco provides official study materials, such as books, videos, and online resources, to help you prepare for the exam. Additionally, you should gain hands-on experience with data center technologies by using virtual labs or real equipment.
-
Recertification: CCNP Data Center certification is valid for three years. To maintain your certification, you must pass one qualifying exam or earn a higher-level certification before the certification expiration date.
-
Career Opportunities: CCNP Data Center certification can open up many career opportunities in data center networking. It can help you to land a job as a data center engineer, data center architect, data center administrator, or other related positions. Additionally, CCNP Data Center certification can lead to higher salaries, as it demonstrates a high level of expertise in data center technologies and infrastructure.
Overall, the CCNP Data Center certification is an excellent choice for network professionals who want to specialize in data center technologies and infrastructure and demonstrate their expertise to potential employers.
CCNP Certification Exam Tips
Here are some exam tips to help you prepare for the Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification exams:
-
Understand the Exam Blueprint: Before you start studying for the exam, make sure you understand the exam blueprint. The exam blueprint outlines the topics and subtopics covered on the exam, as well as the percentage of questions dedicated to each topic. Use the blueprint as a guide for your study plan.
-
Study Official Materials: Use official study materials provided by Cisco, such as books, videos, and online resources. These materials are designed to align with the exam blueprint and provide a comprehensive understanding of the topics covered on the exam.
-
Practice with Hands-On Labs: Gain hands-on experience with the technologies and concepts covered on the exam by using virtual labs or real equipment. This will help you to understand how the technologies work in real-world scenarios and prepare you for simulation questions on the exam.
-
Join Study Groups: Join online study groups or forums to connect with other exam candidates. Discussing the exam topics with others can help you to understand difficult concepts and gain new perspectives on the materials.
-
Take Practice Exams: Take practice exams to assess your knowledge and identify areas where you need more study. Cisco provides official practice exams, as well as third-party practice exams, that simulate the format and difficulty of the real exam.
-
Manage Your Time: During the exam, manage your time wisely. Read each question carefully and avoid spending too much time on difficult questions. If you get stuck on a question, mark it and move on. You can come back to it later if you have time.
-
Practice Good Exam Habits: Practice good exam habits, such as getting a good night's sleep before the exam, eating a healthy meal, arriving at the testing center early, and bringing all necessary identification and materials.
By following these exam tips, you can improve your chances of passing the CCNP certification exams and achieving your career goals.
CCNP Certification Renewal
To maintain your Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification, you must renew it before it expires. Here are some details on how to renew your CCNP certification:
-
Renewal Period: CCNP certifications are valid for three years. You should aim to renew your certification at least six months before it expires.
-
Qualifying Exams: To renew your CCNP certification, you can pass one qualifying exam from the list of available exams. The qualifying exam can be a core exam from the CCNP track you are certified in or a concentration exam from any CCNP track. For example, if you are certified in CCNP Enterprise, you can pass the 350-401 ENCOR exam or any of the concentration exams from the CCNP Enterprise track to renew your certification.
-
Higher-Level Certification: Alternatively, you can earn a higher-level certification, such as CCIE or Cisco Certified Architect (CCAr), to renew your CCNP certification. Higher-level certifications demonstrate a higher level of expertise and can help you advance your career.
-
Continuing Education: Another way to renew your CCNP certification is to earn Continuing Education (CE) credits. CE credits can be earned by completing eligible training courses, attending Cisco Live events, or participating in other eligible activities. You can earn CE credits by participating in Cisco's Continuing Education Program.
-
Recertification Exam: If your CCNP certification has already expired, you can still renew it by passing a recertification exam. The recertification exam is the same as the qualifying exam and can be a core exam or a concentration exam from any CCNP track.
Renewing your CCNP certification demonstrates your commitment to ongoing professional development and keeps your skills up to date. By renewing your CCNP certification, you can continue to advance your career and stay competitive in the job market.
How to obtain CCNP Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Power BI Certification
-
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
-
Cisco : CCNP Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) certification is a highly regarded and respected certification that demonstrates your knowledge and expertise in networking technologies. The CCNP certification offers different tracks, including Enterprise, Security, Data Center, Collaboration, Service Provider, and DevNet, each with its own set of exams and requirements.
To earn the CCNP certification, you must pass the required exams and demonstrate a deep understanding of networking concepts and technologies. Exam preparation should include studying official materials, practicing with hands-on labs, taking practice exams, and managing your time wisely during the actual exam.
To maintain your CCNP certification, you must renew it before it expires. You can renew your certification by passing a qualifying exam, earning a higher-level certification, earning Continuing Education credits, or passing a recertification exam.
Overall, the CCNP certification is a valuable asset for networking professionals seeking to advance their careers, expand their knowledge, and stay current with the latest technologies and best practices in the networking industry.
The Essential Guide to Cisco Certified Network Associate.
Welcome to "The Essential Guide to Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Certification." In this comprehensive guide, we will navigate the intricate world of networking, providing aspiring and seasoned IT professionals alike with a clear understanding of the CCNA certification. From deciphering networking concepts to mastering Cisco technologies, you will gain the knowledge and skills needed to excel in designing, implementing, and troubleshooting networks. Join us on this transformative journey towards network expertise and open the door to a world of exciting career opportunities and technical innovation.
Table of contents
Introduction to CCNA Certification and its significance in the IT industry
Overview of the CCNA Exam
Preparing for the CCNA Exam
The Benefits of CCNA Certification
CCNA Certification Exam Tracks and Specializations
The Future of CCNA Certification and its evolution in line with changing industry requirements and advancements
Insights from CCNA Certified Professionals
Tips for Exam Day
Conclusion
Introduction to CCNA Certification and its significance in the IT industry
Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) is an entry-level certification program offered by Cisco Systems, a multinational technology company that specializes in networking, cybersecurity, and telecommunications solutions. CCNA certification validates an individual's skills and knowledge in networking fundamentals, network access, IP connectivity, IP services, security fundamentals, and automation and programmability.
CCNA certification holds significant value in the IT industry, as it is a globally recognized credential that demonstrates an individual's competence in designing, implementing, and managing small to medium-sized enterprise networks. CCNA certification is widely recognized by organizations across the globe, and individuals holding this certification are in high demand.
Some of the key benefits of CCNA certification in the IT industry are:
Improved Career Opportunities: CCNA certification enhances an individual's employability, as it demonstrates their technical skills and proficiency in networking. CCNA certified professionals can pursue career paths such as Network Engineer, Network Administrator, IT Manager, and more.
Salary Advancement: CCNA certification opens up the possibility of higher salaries, as it demonstrates an individual's expertise and knowledge in networking. According to Payscale, the average salary of a CCNA certified professional in the United States is $78,000 per annum.
Competitive Edge: In a highly competitive IT industry, CCNA certification provides individuals with a competitive edge over others who lack this credential. CCNA certification serves as a differentiator and helps individuals stand out in the job market.
Overview of the CCNA Exam
The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) exam is a comprehensive certification exam that tests an individual's skills and knowledge in networking fundamentals, network access, IP connectivity, IP services, security fundamentals, and automation and programmability. The exam is designed to validate an individual's ability to design, implement, and manage small to medium-sized enterprise networks.
Here is an overview of the CCNA exam:
Exam format: The CCNA exam is a computer-based exam that includes multiple-choice, drag and drop, and simulation questions. The exam is available in multiple languages, including English, Japanese, Chinese, French, and Spanish.
Exam duration: The exam duration is 120 minutes (2 hours).
Number of Questions: The exam contains 100-120 questions.
Exam fee: The exam fee varies by country, but it typically ranges from $300 to $325.
Exam topics: The CCNA exam covers the following topics:
Network fundamentals
Network access
IP connectivity
IP services
Security fundamentals
Exam preparation: Cisco provides study materials, such as official certification guides, practice exams, and training courses to help individuals prepare for the CCNA exam. Additionally, there are many online resources and study groups available for CCNA exam preparation.
Passing score: The passing score for the CCNA exam is determined by Cisco and is not disclosed to the public. However, it is generally considered to be around 825-850 out of 1000.
Exam retake policy: Individuals who fail the CCNA exam can retake the exam after a waiting period of 5 calendar days. There is no limit to the number of times an individual can retake the exam.
Preparing for the CCNA Exam
Preparing for the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) exam requires a significant amount of effort, dedication, and preparation. Here are some tips and resources to help you prepare for the CCNA exam:
Understand the Exam Topics: The first step in preparing for the CCNA exam is to familiarize yourself with the exam topics. Cisco provides an exam blueprint that outlines the exam topics and subtopics. Use this blueprint to create a study plan and focus your efforts on the topics that you need to improve upon.
Study Materials: Cisco provides official certification guides, practice exams, and training courses to help individuals prepare for the CCNA exam. The official certification guides are an excellent resource for understanding the exam topics in-depth and preparing for the exam. The practice exams can help you identify areas where you need to improve your knowledge and skills. Additionally, there are many online resources, such as blogs, forums, and study groups, that can provide additional study materials and support.
Hands-on Experience: It's essential to have hands-on experience in configuring and managing network devices to pass the CCNA exam. Consider setting up a lab environment with routers and switches to practice configuring and troubleshooting network devices. Many online resources offer free lab exercises and simulations, such as Cisco Packet Tracer, that can help you gain hands-on experience.
Time Management: The CCNA exam is a timed exam, and time management is critical to passing the exam. Practice taking practice exams and simulating exam conditions to improve your time management skills.
Take Practice Tests: Taking practice tests is an excellent way to prepare for the CCNA exam. Practice tests can help you identify areas where you need to improve your knowledge and skills and help you familiarize yourself with the exam format and structure.
Join Study Groups: Joining study groups is an excellent way to connect with other individuals preparing for the CCNA exam. Study groups provide a forum for sharing knowledge and experiences, asking questions, and getting support from other individuals preparing for the exam.
The Benefits of CCNA Certification
The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification provides many benefits for individuals seeking to advance their careers in the IT industry. Here are some of the benefits of CCNA certification:
Career Advancement: CCNA certification is a valuable asset for individuals seeking to advance their careers in the IT industry. The certification demonstrates an individual's expertise and knowledge in networking, which can lead to career advancement opportunities and higher salaries.
Industry Recognition: CCNA certification is recognized globally as a standard of excellence in networking. The certification demonstrates an individual's commitment to professional development and expertise in networking.
Competitive Advantage: CCNA certification provides a competitive advantage in the job market. Employers often prefer candidates with CCNA certification because it demonstrates their expertise and knowledge in networking.
Enhanced Knowledge and Skills: Preparing for the CCNA certification exam requires significant effort and dedication. The process of studying for the exam enhances an individual's knowledge and skills in networking, which can be applied to real-world scenarios.
Access to Cisco Resources: CCNA certification provides access to Cisco resources, including technical support, online communities, and training materials. These resources can help individuals stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies in networking.
Professional Networking: CCNA certification provides opportunities for individuals to network with other IT professionals and experts in the field. Networking can lead to new job opportunities, collaborations, and professional development.
CCNA Certification Exam Tracks and Specializations
Cisco offers various tracks and specializations for the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification. Here are some of the CCNA certification exam tracks and specializations:
CCNA Routing and Switching: The CCNA Routing and Switching track is the most popular track for the CCNA certification. This track covers networking concepts, routing protocols, switching technologies, and WAN technologies.
CCNA Security: The CCNA Security specialization focuses on network security technologies and concepts, including firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
CCNA Cloud: The CCNA Cloud specialization focuses on cloud computing technologies and concepts, including cloud infrastructure, deployment models, and virtualization.
CCNA Collaboration: The CCNA Collaboration specialization focuses on collaboration technologies and concepts, including voice and video technologies, Cisco Unified Communications Manager, and Cisco Unity Connection.
CCNA Data Center: The CCNA Data Center specialization focuses on data center technologies and concepts, including data center networking, storage networking, and network virtualization.
CCNA Wireless: The CCNA Wireless specialization focuses on wireless networking technologies and concepts, including wireless LANs, wireless security, and wireless site surveys.
CCNA Industrial: The CCNA Industrial specialization focuses on networking technologies and concepts for industrial environments, including manufacturing, oil and gas, and transportation.
CCNA Service Provider: The CCNA Service Provider specialization focuses on networking technologies and concepts for service provider environments, including carrier-grade infrastructure, service provider network architectures, and IP NGN (Next-Generation Networks).
The Future of CCNA Certification and its evolution in line with changing industry requirements and advancements
The CCNA certification has evolved over the years in line with changing industry requirements and advancements in technology. As the IT industry continues to evolve, the CCNA certification is expected to evolve to keep pace with these changes. Here are some trends that are likely to shape the future of the CCNA certification:
Emerging Technologies: Emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML), are expected to drive the future of the IT industry. The CCNA certification is likely to evolve to cover these technologies and their impact on network infrastructure.
Network Automation: Network automation is becoming increasingly important as organizations look to improve network performance, reduce downtime, and increase efficiency. The CCNA certification is likely to evolve to cover network automation technologies and tools.
Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity threats are becoming more sophisticated and frequent, making it essential for organizations to have strong security measures in place. The CCNA certification is likely to evolve to cover cybersecurity technologies and concepts in more depth.
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing is becoming increasingly popular as organizations look to reduce costs and improve scalability. The CCNA certification is likely to evolve to cover cloud computing technologies and their impact on network infrastructure.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN is becoming increasingly important as organizations look to improve network agility and flexibility. The CCNA certification is likely to evolve to cover SDN technologies and their impact on network infrastructure.
Specializations: The CCNA certification may continue to evolve to include more specializations that focus on specific technologies and industries, such as cybersecurity, data center networking, and wireless networking.
Insights from CCNA Certified Professionals
CCNA certified professionals have valuable insights and experiences that can be helpful for others who are preparing for the CCNA certification exam or are considering pursuing a career in network infrastructure. Here are some insights from CCNA certified professionals:
The CCNA certification is a solid foundation for a career in network infrastructure: CCNA certified professionals emphasize the importance of the CCNA certification as a foundation for a career in network infrastructure. They note that the certification provides a strong understanding of networking concepts, protocols, and technologies, which is essential for success in this field.
Practical experience is important: CCNA certified professionals emphasize the importance of practical experience in network infrastructure. They note that hands-on experience with network devices and tools is essential for developing a deep understanding of networking concepts and troubleshooting skills.
Continual learning is essential: CCNA certified professionals note that the IT industry is constantly evolving, and professionals need to continually learn and stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and trends. They emphasize the importance of pursuing additional certifications, attending industry conferences, and staying engaged with the networking community to stay current.
Soft skills are important: CCNA certified professionals emphasize the importance of soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving skills, in addition to technical skills. They note that these skills are essential for success in network infrastructure, as professionals need to work effectively with others and communicate technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
Networking is a growing and in-demand field: CCNA certified professionals note that networking is a growing and in-demand field, with many opportunities for career growth and advancement. They note that the demand for skilled networking professionals is likely to continue to grow, making the CCNA certification a valuable investment in a career in IT.
Tips for Exam Day
Here are some tips to help you prepare for the CCNA exam day:
Get a good night's sleep: Make sure to get a good night's sleep before the exam. This will help you stay alert and focused during the exam.
Arrive early: Arrive at the exam center early to allow yourself enough time to check in and get settled.
Bring two forms of identification: Bring two forms of identification, such as a driver's license and passport, to the exam center. This is required for identification verification.
Don't cram the night before: Don't try to cram all the material the night before the exam. Instead, take some time to relax and review your notes.
Read the questions carefully: Read each question carefully before answering. Make sure you understand what the question is asking before selecting your answer.
Manage your time: Manage your time during the exam. If you get stuck on a question, move on to the next one and come back to it later.
Use scratch paper: Use scratch paper to work out problems and keep track of important information.
Don't rush: Don't rush through the exam. Take your time and make sure you understand each question before answering.
Review your answers: Review your answers before submitting the exam. Make sure you have answered each question and check for any errors.
Stay calm and confident: Stay calm and confident during the exam. Remember that you have prepared for this and you are ready to pass the exam.
How to obtain CISCO Certified Network Associate Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CRISC Certification
CISCO Certification : CISCO Certified Network Associate Certification
Conclusion
The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification is a crucial milestone for aspiring IT professionals, providing a solid foundation and validation of essential networking skills. With expertise in designing, implementing, managing, and troubleshooting network infrastructures, CCNA holders gain a deep understanding of routing, switching technologies, and network security principles. Widely recognized in the industry, the CCNA certification enhances job prospects and earning potential, opening doors to specialization and career advancement. As technology becomes increasingly reliant on robust networks, CCNA-certified professionals are well-positioned to play pivotal roles in ensuring connectivity, data integrity, and contributing to the future of information technology.
Read More
Welcome to "The Essential Guide to Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Certification." In this comprehensive guide, we will navigate the intricate world of networking, providing aspiring and seasoned IT professionals alike with a clear understanding of the CCNA certification. From deciphering networking concepts to mastering Cisco technologies, you will gain the knowledge and skills needed to excel in designing, implementing, and troubleshooting networks. Join us on this transformative journey towards network expertise and open the door to a world of exciting career opportunities and technical innovation.
Table of contents
Introduction to CCNA Certification and its significance in the IT industry
Overview of the CCNA Exam
Preparing for the CCNA Exam
The Benefits of CCNA Certification
CCNA Certification Exam Tracks and Specializations
The Future of CCNA Certification and its evolution in line with changing industry requirements and advancements
Insights from CCNA Certified Professionals
Tips for Exam Day
Conclusion
Introduction to CCNA Certification and its significance in the IT industry
Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) is an entry-level certification program offered by Cisco Systems, a multinational technology company that specializes in networking, cybersecurity, and telecommunications solutions. CCNA certification validates an individual's skills and knowledge in networking fundamentals, network access, IP connectivity, IP services, security fundamentals, and automation and programmability.
CCNA certification holds significant value in the IT industry, as it is a globally recognized credential that demonstrates an individual's competence in designing, implementing, and managing small to medium-sized enterprise networks. CCNA certification is widely recognized by organizations across the globe, and individuals holding this certification are in high demand.
Some of the key benefits of CCNA certification in the IT industry are:
Improved Career Opportunities: CCNA certification enhances an individual's employability, as it demonstrates their technical skills and proficiency in networking. CCNA certified professionals can pursue career paths such as Network Engineer, Network Administrator, IT Manager, and more.
Salary Advancement: CCNA certification opens up the possibility of higher salaries, as it demonstrates an individual's expertise and knowledge in networking. According to Payscale, the average salary of a CCNA certified professional in the United States is $78,000 per annum.
Competitive Edge: In a highly competitive IT industry, CCNA certification provides individuals with a competitive edge over others who lack this credential. CCNA certification serves as a differentiator and helps individuals stand out in the job market.
Overview of the CCNA Exam
The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) exam is a comprehensive certification exam that tests an individual's skills and knowledge in networking fundamentals, network access, IP connectivity, IP services, security fundamentals, and automation and programmability. The exam is designed to validate an individual's ability to design, implement, and manage small to medium-sized enterprise networks.
Here is an overview of the CCNA exam:
Exam format: The CCNA exam is a computer-based exam that includes multiple-choice, drag and drop, and simulation questions. The exam is available in multiple languages, including English, Japanese, Chinese, French, and Spanish.
Exam duration: The exam duration is 120 minutes (2 hours).
Number of Questions: The exam contains 100-120 questions.
Exam fee: The exam fee varies by country, but it typically ranges from $300 to $325.
Exam topics: The CCNA exam covers the following topics:
Network fundamentals
Network access
IP connectivity
IP services
Security fundamentals
Exam preparation: Cisco provides study materials, such as official certification guides, practice exams, and training courses to help individuals prepare for the CCNA exam. Additionally, there are many online resources and study groups available for CCNA exam preparation.
Passing score: The passing score for the CCNA exam is determined by Cisco and is not disclosed to the public. However, it is generally considered to be around 825-850 out of 1000.
Exam retake policy: Individuals who fail the CCNA exam can retake the exam after a waiting period of 5 calendar days. There is no limit to the number of times an individual can retake the exam.
Preparing for the CCNA Exam
Preparing for the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) exam requires a significant amount of effort, dedication, and preparation. Here are some tips and resources to help you prepare for the CCNA exam:
Understand the Exam Topics: The first step in preparing for the CCNA exam is to familiarize yourself with the exam topics. Cisco provides an exam blueprint that outlines the exam topics and subtopics. Use this blueprint to create a study plan and focus your efforts on the topics that you need to improve upon.
Study Materials: Cisco provides official certification guides, practice exams, and training courses to help individuals prepare for the CCNA exam. The official certification guides are an excellent resource for understanding the exam topics in-depth and preparing for the exam. The practice exams can help you identify areas where you need to improve your knowledge and skills. Additionally, there are many online resources, such as blogs, forums, and study groups, that can provide additional study materials and support.
Hands-on Experience: It's essential to have hands-on experience in configuring and managing network devices to pass the CCNA exam. Consider setting up a lab environment with routers and switches to practice configuring and troubleshooting network devices. Many online resources offer free lab exercises and simulations, such as Cisco Packet Tracer, that can help you gain hands-on experience.
Time Management: The CCNA exam is a timed exam, and time management is critical to passing the exam. Practice taking practice exams and simulating exam conditions to improve your time management skills.
Take Practice Tests: Taking practice tests is an excellent way to prepare for the CCNA exam. Practice tests can help you identify areas where you need to improve your knowledge and skills and help you familiarize yourself with the exam format and structure.
Join Study Groups: Joining study groups is an excellent way to connect with other individuals preparing for the CCNA exam. Study groups provide a forum for sharing knowledge and experiences, asking questions, and getting support from other individuals preparing for the exam.
The Benefits of CCNA Certification
The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification provides many benefits for individuals seeking to advance their careers in the IT industry. Here are some of the benefits of CCNA certification:
Career Advancement: CCNA certification is a valuable asset for individuals seeking to advance their careers in the IT industry. The certification demonstrates an individual's expertise and knowledge in networking, which can lead to career advancement opportunities and higher salaries.
Industry Recognition: CCNA certification is recognized globally as a standard of excellence in networking. The certification demonstrates an individual's commitment to professional development and expertise in networking.
Competitive Advantage: CCNA certification provides a competitive advantage in the job market. Employers often prefer candidates with CCNA certification because it demonstrates their expertise and knowledge in networking.
Enhanced Knowledge and Skills: Preparing for the CCNA certification exam requires significant effort and dedication. The process of studying for the exam enhances an individual's knowledge and skills in networking, which can be applied to real-world scenarios.
Access to Cisco Resources: CCNA certification provides access to Cisco resources, including technical support, online communities, and training materials. These resources can help individuals stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies in networking.
Professional Networking: CCNA certification provides opportunities for individuals to network with other IT professionals and experts in the field. Networking can lead to new job opportunities, collaborations, and professional development.
CCNA Certification Exam Tracks and Specializations
Cisco offers various tracks and specializations for the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification. Here are some of the CCNA certification exam tracks and specializations:
CCNA Routing and Switching: The CCNA Routing and Switching track is the most popular track for the CCNA certification. This track covers networking concepts, routing protocols, switching technologies, and WAN technologies.
CCNA Security: The CCNA Security specialization focuses on network security technologies and concepts, including firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
CCNA Cloud: The CCNA Cloud specialization focuses on cloud computing technologies and concepts, including cloud infrastructure, deployment models, and virtualization.
CCNA Collaboration: The CCNA Collaboration specialization focuses on collaboration technologies and concepts, including voice and video technologies, Cisco Unified Communications Manager, and Cisco Unity Connection.
CCNA Data Center: The CCNA Data Center specialization focuses on data center technologies and concepts, including data center networking, storage networking, and network virtualization.
CCNA Wireless: The CCNA Wireless specialization focuses on wireless networking technologies and concepts, including wireless LANs, wireless security, and wireless site surveys.
CCNA Industrial: The CCNA Industrial specialization focuses on networking technologies and concepts for industrial environments, including manufacturing, oil and gas, and transportation.
CCNA Service Provider: The CCNA Service Provider specialization focuses on networking technologies and concepts for service provider environments, including carrier-grade infrastructure, service provider network architectures, and IP NGN (Next-Generation Networks).
The Future of CCNA Certification and its evolution in line with changing industry requirements and advancements
The CCNA certification has evolved over the years in line with changing industry requirements and advancements in technology. As the IT industry continues to evolve, the CCNA certification is expected to evolve to keep pace with these changes. Here are some trends that are likely to shape the future of the CCNA certification:
Emerging Technologies: Emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML), are expected to drive the future of the IT industry. The CCNA certification is likely to evolve to cover these technologies and their impact on network infrastructure.
Network Automation: Network automation is becoming increasingly important as organizations look to improve network performance, reduce downtime, and increase efficiency. The CCNA certification is likely to evolve to cover network automation technologies and tools.
Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity threats are becoming more sophisticated and frequent, making it essential for organizations to have strong security measures in place. The CCNA certification is likely to evolve to cover cybersecurity technologies and concepts in more depth.
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing is becoming increasingly popular as organizations look to reduce costs and improve scalability. The CCNA certification is likely to evolve to cover cloud computing technologies and their impact on network infrastructure.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN is becoming increasingly important as organizations look to improve network agility and flexibility. The CCNA certification is likely to evolve to cover SDN technologies and their impact on network infrastructure.
Specializations: The CCNA certification may continue to evolve to include more specializations that focus on specific technologies and industries, such as cybersecurity, data center networking, and wireless networking.
Insights from CCNA Certified Professionals
CCNA certified professionals have valuable insights and experiences that can be helpful for others who are preparing for the CCNA certification exam or are considering pursuing a career in network infrastructure. Here are some insights from CCNA certified professionals:
The CCNA certification is a solid foundation for a career in network infrastructure: CCNA certified professionals emphasize the importance of the CCNA certification as a foundation for a career in network infrastructure. They note that the certification provides a strong understanding of networking concepts, protocols, and technologies, which is essential for success in this field.
Practical experience is important: CCNA certified professionals emphasize the importance of practical experience in network infrastructure. They note that hands-on experience with network devices and tools is essential for developing a deep understanding of networking concepts and troubleshooting skills.
Continual learning is essential: CCNA certified professionals note that the IT industry is constantly evolving, and professionals need to continually learn and stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and trends. They emphasize the importance of pursuing additional certifications, attending industry conferences, and staying engaged with the networking community to stay current.
Soft skills are important: CCNA certified professionals emphasize the importance of soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving skills, in addition to technical skills. They note that these skills are essential for success in network infrastructure, as professionals need to work effectively with others and communicate technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
Networking is a growing and in-demand field: CCNA certified professionals note that networking is a growing and in-demand field, with many opportunities for career growth and advancement. They note that the demand for skilled networking professionals is likely to continue to grow, making the CCNA certification a valuable investment in a career in IT.
Tips for Exam Day
Here are some tips to help you prepare for the CCNA exam day:
Get a good night's sleep: Make sure to get a good night's sleep before the exam. This will help you stay alert and focused during the exam.
Arrive early: Arrive at the exam center early to allow yourself enough time to check in and get settled.
Bring two forms of identification: Bring two forms of identification, such as a driver's license and passport, to the exam center. This is required for identification verification.
Don't cram the night before: Don't try to cram all the material the night before the exam. Instead, take some time to relax and review your notes.
Read the questions carefully: Read each question carefully before answering. Make sure you understand what the question is asking before selecting your answer.
Manage your time: Manage your time during the exam. If you get stuck on a question, move on to the next one and come back to it later.
Use scratch paper: Use scratch paper to work out problems and keep track of important information.
Don't rush: Don't rush through the exam. Take your time and make sure you understand each question before answering.
Review your answers: Review your answers before submitting the exam. Make sure you have answered each question and check for any errors.
Stay calm and confident: Stay calm and confident during the exam. Remember that you have prepared for this and you are ready to pass the exam.
How to obtain CISCO Certified Network Associate Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CRISC Certification
CISCO Certification : CISCO Certified Network Associate Certification
Conclusion
The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification is a crucial milestone for aspiring IT professionals, providing a solid foundation and validation of essential networking skills. With expertise in designing, implementing, managing, and troubleshooting network infrastructures, CCNA holders gain a deep understanding of routing, switching technologies, and network security principles. Widely recognized in the industry, the CCNA certification enhances job prospects and earning potential, opening doors to specialization and career advancement. As technology becomes increasingly reliant on robust networks, CCNA-certified professionals are well-positioned to play pivotal roles in ensuring connectivity, data integrity, and contributing to the future of information technology.
SAS Base Programmer Certification: What You Need to Know
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the SAS Base Programmer Certification: What You Need to Know. In today's data-centric world, where information is a prized asset, the ability to manipulate, analyze, and extract insights from data is invaluable. The SAS Base Programmer Certification stands as a testament to your proficiency in using SAS software for data analysis and programming. Whether you're an aspiring data analyst, a seasoned programmer expanding your skill set, or a professional seeking to validate your expertise, this guide will provide you with a clear roadmap to understand the intricacies of the SAS Base Programmer Certification. From its significance in the industry to the skills it evaluates and the resources available for preparation, we'll cover all the essential aspects to help you embark on your certification journey with confidence. Let's dive into the world of SAS certification and equip you with the knowledge you need to excel in the field of data analysis and programming.
Table of Contents
What is SAS Base Programmer certification?
Benefits of SAS Base Programmer certification.
How to prepare for SAS Base Programmer certification?
Overview of SAS programming concepts tested in the certification exam.
Best practices for programming in SAS.
Tips for passing the SAS Base Programmer certification exam.
Differences between SAS Base Programmer and Advanced Programmer certifications.
Career opportunities after SAS Base Programmer certification.
Comparison between SAS and other programming languages.
Conclusion
What is SAS Base Programmer certification?
SAS Base Programmer certification is a professional certification program offered by SAS Institute, a leading provider of business analytics software and services. It is designed for individuals who want to demonstrate their proficiency in SAS programming skills and knowledge.
The SAS Base Programmer certification exam tests an individual's knowledge of SAS programming concepts such as data manipulation, data analysis, data reporting, and SAS programming essentials. The certification is internationally recognized and is a valuable credential for individuals who work in data analysis, business intelligence, and other related fields.
To earn the SAS Base Programmer certification, candidates must pass a comprehensive exam that covers topics such as SAS data sets, data manipulation techniques, and basic programming concepts. The exam consists of multiple-choice questions, short-answer questions, and coding tasks.
The SAS Base Programmer certification is suitable for individuals who are new to SAS programming as well as those who have some experience in SAS programming. It is a prerequisite for advanced-level certifications such as SAS Certified Advanced Programmer and SAS Certified Data Scientist.
Benefits of SAS Base Programmer certification
There are several benefits of earning the SAS Base Programmer certification, including:
Enhanced Career Opportunities: SAS Base Programmer certification demonstrates your proficiency in SAS programming skills, which can help you stand out in the job market. Employers often prefer candidates with SAS certification, and the certification can lead to better job opportunities and higher salaries.
Validation of SAS Programming Skills: SAS Base Programmer certification validates your knowledge and skills in SAS programming. This can help you gain credibility among your peers and establish yourself as an expert in the field.
Improved Data Analysis: SAS Base Programmer certification equips you with the knowledge and skills to effectively analyze and manipulate data using SAS. This can help you make better decisions, improve processes, and identify new opportunities for your organization.
Access to SAS Resources: SAS Base Programmer certification provides access to a wealth of resources, including SAS software, documentation, and support. This can help you stay up-to-date with the latest developments in SAS technology and improve your skills and knowledge.
Path to Advanced Certifications: SAS Base Programmer certification is a prerequisite for advanced-level certifications such as SAS Certified Advanced Programmer and SAS Certified Data Scientist. Earning the SAS Base Programmer certification can help you build a solid foundation for your career in data analysis and provide a path to advanced certifications.
How to prepare for SAS Base Programmer certification?
Preparing for the SAS Base Programmer certification requires a combination of knowledge, skills, and preparation. Here are some steps you can take to prepare for the certification exam:
Familiarize Yourself with SAS: To pass the SAS Base Programmer certification, you need to have a strong understanding of SAS programming concepts and techniques. Start by familiarizing yourself with SAS software and learning the basics of SAS programming.
Review SAS Programming Concepts: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS programming concepts such as data manipulation, data analysis, and data reporting. Reviewing these concepts will help you prepare for the exam.
Practice with SAS Software: The SAS Base Programmer certification exam includes coding tasks that require you to write SAS programs. Practicing with SAS software will help you become more familiar with the programming environment and improve your programming skills.
Use SAS Documentation: SAS provides comprehensive documentation that covers all aspects of SAS programming. Use these resources to deepen your understanding of SAS programming concepts and techniques.
Take Practice Tests: Practice tests are a great way to prepare for the SAS Base Programmer certification exam. They allow you to test your knowledge, identify areas of weakness, and become more familiar with the exam format.
Join SAS Community: Joining the SAS community can provide you with access to SAS experts, tips, and tricks. It is a great way to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in SAS technology and improve your skills.
Attend SAS Training: SAS offers training courses that cover all aspects of SAS programming. Attending these courses can help you develop your skills and prepare for the SAS Base Programmer certification exam.
Overview of SAS programming concepts tested in the certification exam
The SAS Base Programmer certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS programming concepts, including data manipulation, data analysis, data reporting, and SAS programming essentials. Here is an overview of the key concepts tested in the exam:
SAS Data Sets: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS data sets, including how to create, access, and modify data sets. You need to know how to read data from external files, manipulate data using SAS functions, and subset data using WHERE and IF statements.
Data Manipulation Techniques: The certification exam tests your knowledge of data manipulation techniques such as merging and appending data sets, sorting data, and using conditional logic in SAS programming.
SAS Procedures: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS procedures such as PROC SORT, PROC MEANS, PROC FREQ, and PROC PRINT. You need to know how to use these procedures to analyze and report data.
SAS Programming Essentials: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS programming essentials, including programming statements, syntax, and data step processing. You need to know how to write SAS programs, debug code, and troubleshoot errors.
SAS Macro Language: The certification exam tests your knowledge of the SAS macro language, including how to define and use macros in SAS programming.
SAS Graphics: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS graphics, including how to create and modify graphs using SAS procedures and the SAS/GRAPH software.
SAS Formats and Informats: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS formats and informats, including how to convert data types, manipulate data formats, and use SAS formats to customize data display.
Best practices for programming in SAS
Programming in SAS requires following best practices to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of SAS programs. Here are some best practices for programming in SAS:
Comment Your Code: Commenting your code is essential to make your code more readable and understandable. Use comments to explain your code, provide context, and make it easier for others to follow.
Use Meaningful Variable Names: Use descriptive and meaningful variable names to make your code more readable and understandable. Avoid using short and cryptic names that are difficult to understand.
Use Data Step Options: Use data step options to improve the efficiency of your code. Options such as OBS, FIRSTOBS, and DROP can help you subset data, improve performance, and reduce the size of your output.
Use SAS Functions: Use SAS functions to simplify your code and perform complex operations. Functions such as SUM, MEAN, and COUNT can help you calculate statistics, while functions such as SUBSTR and SCAN can help you manipulate character data.
Use SAS Procedures: Use SAS procedures to analyze and report data. Procedures such as PROC SORT, PROC MEANS, and PROC FREQ can help you summarize and analyze data, while procedures such as PROC PRINT and PROC REPORT can help you create reports.
Use Macros: Use SAS macros to automate tasks and simplify your code. Macros can help you generate code dynamically, automate repetitive tasks, and improve code readability.
Check for Errors: Check your code for errors and debug it to ensure that it produces the expected results. Use the SAS log to identify errors and troubleshoot problems.
Use Version Control: Use version control to manage your SAS code and track changes. Version control can help you collaborate with others, track changes, and maintain a history of your code.
Tips for passing the SAS Base Programmer certification exam
Passing the SAS Base Programmer certification exam requires a thorough understanding of SAS programming concepts and careful preparation. Here are some tips that can help you pass the exam:
Understand the Exam Format: The SAS Base Programmer certification exam consists of multiple-choice questions and has a time limit of 105 minutes. Familiarize yourself with the exam format, timing, and number of questions to help you manage your time effectively.
Study the Exam Objectives: The SAS Base Programmer certification exam covers a range of SAS programming concepts, including data manipulation, data analysis, data reporting, SAS programming essentials, and the SAS macro language. Study the exam objectives and make sure you understand each concept.
Practice with Sample Questions: Practice with sample questions to help you prepare for the exam. SAS provides sample questions and practice exams that you can use to test your knowledge and identify areas where you need to improve.
Use SAS Documentation: SAS provides comprehensive documentation for its software. Use the SAS documentation to help you understand SAS programming concepts, syntax, and functions.
Take a SAS Programming Course: Consider taking a SAS programming course to help you prepare for the exam. SAS offers courses that cover SAS programming concepts, data manipulation, and data analysis.
Join SAS Communities: Join SAS communities, such as SAS Support Communities, SAS Communities, and SAS Users Groups, to network with other SAS programmers, learn from their experiences, and get help with SAS programming.
Manage Your Time Effectively: Manage your time effectively during the exam. Read each question carefully, eliminate obviously incorrect answers, and answer the questions you know first.
Differences between SAS Base Programmer and Advanced Programmer certifications
SAS offers two levels of programming certifications: SAS Base Programmer and SAS Advanced Programmer. Here are the main differences between these two certifications:
Exam Content: The SAS Base Programmer certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS programming concepts such as data manipulation, data analysis, data reporting, SAS programming essentials, and the SAS macro language. The SAS Advanced Programmer certification exam tests your knowledge of advanced SAS programming concepts such as advanced data manipulation, efficiency techniques, debugging, and advanced macro processing.
Exam Difficulty: The SAS Advanced Programmer certification exam is more difficult than the SAS Base Programmer certification exam. The questions are more complex, and the passing score is higher.
Prerequisites: To earn the SAS Base Programmer certification, you do not need any prerequisites. To earn the SAS Advanced Programmer certification, you need to have earned the SAS Base Programmer certification.
Recognition: The SAS Base Programmer certification is a prerequisite for many SAS-related job positions, and it demonstrates your proficiency in SAS programming concepts. The SAS Advanced Programmer certification is a higher-level certification and demonstrates your advanced skills in SAS programming.
Job Opportunities: Having both the SAS Base Programmer and SAS Advanced Programmer certifications can help you stand out in the job market. The SAS Advanced Programmer certification can lead to more advanced job opportunities, such as SAS consultant or SAS programmer analyst.
Career opportunities after SAS Base Programmer certification.
Earning a SAS Base Programmer certification can open up various career opportunities for individuals in the field of data analytics. Here are some career opportunities that are available for individuals who hold a SAS Base Programmer certification:
SAS Programmer: SAS programmers write and maintain SAS code to manage, analyze, and report data. They are responsible for cleaning and manipulating data, generating reports, and creating custom programs to meet specific business requirements.
Data Analyst: Data analysts use SAS programming to analyze and interpret large volumes of data. They are responsible for designing and implementing data collection systems, creating reports and dashboards, and identifying trends and insights.
Data Manager: Data managers are responsible for overseeing the collection, storage, and maintenance of data. They ensure that data is accurate, complete, and secure. They may also work on projects to improve data quality and develop data management policies and procedures.
Business Analyst: Business analysts use data to inform business decisions. They work with stakeholders to understand business requirements, identify data sources, and develop reports and dashboards. They may also perform data modeling and forecasting to help organizations make informed decisions.
Consultant: SAS consultants work with clients to design and implement SAS-based solutions. They may work on projects related to data management, data analysis, or custom programming. They are responsible for managing project timelines, communicating with clients, and delivering high-quality solutions.
How to obtain SAS Base Programmer Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Development : SAS Base Programmer Certification
Comparison between SAS and other programming languages
SAS is a proprietary software suite that is primarily used for data management, analytics, and business intelligence. Here are some key differences between SAS and other programming languages:
Ease of Use: SAS is designed to be user-friendly and easy to use, with a point-and-click interface that makes it easy to navigate. Other programming languages, such as Python and R, may have a steeper learning curve for beginners.
Data Handling: SAS is particularly strong in handling large datasets and performing data manipulation tasks, such as merging datasets and transforming variables. Other programming languages, such as Python and R, also have strong data handling capabilities, but may require additional packages or libraries to achieve the same functionality.
Statistical Analysis: SAS is known for its powerful statistical analysis capabilities and is often used in research and academia. Other programming languages, such as Python and R, also have strong statistical analysis capabilities, with the added advantage of being open-source and having a larger community of users contributing to their development.
Cost: SAS is a proprietary software, which means that users must pay for licenses to use the software. Other programming languages, such as Python and R, are open-source and free to use, which makes them more accessible to users who may not have the budget for proprietary software.
Community Support: While SAS has a large community of users and developers, the community for other programming languages, such as Python and R, is much larger. This means that users of Python and R have access to a wider range of resources, including online forums, tutorials, and open-source libraries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, obtaining the SAS Base Programmer Certification can be a pivotal step in your career journey, opening doors to a world of opportunities in the realm of data analysis and programming. Throughout this guide, we've explored the key aspects of this certification, from its benefits in enhancing your skill set and boosting your professional credibility, to understanding the core concepts that the exam covers. By delving into this certification, you're not only validating your expertise in SAS programming but also positioning yourself as a valuable asset in today's data-driven industries. As you embark on your certification journey, remember that preparation, practice, and a solid understanding of the foundational concepts will be your allies. Best of luck on your path to becoming a certified SAS Base Programmer, and may your newly acquired skills propel you toward a successful and fulfilling career in the dynamic world of data analysis and programming.
Read More
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the SAS Base Programmer Certification: What You Need to Know. In today's data-centric world, where information is a prized asset, the ability to manipulate, analyze, and extract insights from data is invaluable. The SAS Base Programmer Certification stands as a testament to your proficiency in using SAS software for data analysis and programming. Whether you're an aspiring data analyst, a seasoned programmer expanding your skill set, or a professional seeking to validate your expertise, this guide will provide you with a clear roadmap to understand the intricacies of the SAS Base Programmer Certification. From its significance in the industry to the skills it evaluates and the resources available for preparation, we'll cover all the essential aspects to help you embark on your certification journey with confidence. Let's dive into the world of SAS certification and equip you with the knowledge you need to excel in the field of data analysis and programming.
Table of Contents
What is SAS Base Programmer certification?
Benefits of SAS Base Programmer certification.
How to prepare for SAS Base Programmer certification?
Overview of SAS programming concepts tested in the certification exam.
Best practices for programming in SAS.
Tips for passing the SAS Base Programmer certification exam.
Differences between SAS Base Programmer and Advanced Programmer certifications.
Career opportunities after SAS Base Programmer certification.
Comparison between SAS and other programming languages.
Conclusion
What is SAS Base Programmer certification?
SAS Base Programmer certification is a professional certification program offered by SAS Institute, a leading provider of business analytics software and services. It is designed for individuals who want to demonstrate their proficiency in SAS programming skills and knowledge.
The SAS Base Programmer certification exam tests an individual's knowledge of SAS programming concepts such as data manipulation, data analysis, data reporting, and SAS programming essentials. The certification is internationally recognized and is a valuable credential for individuals who work in data analysis, business intelligence, and other related fields.
To earn the SAS Base Programmer certification, candidates must pass a comprehensive exam that covers topics such as SAS data sets, data manipulation techniques, and basic programming concepts. The exam consists of multiple-choice questions, short-answer questions, and coding tasks.
The SAS Base Programmer certification is suitable for individuals who are new to SAS programming as well as those who have some experience in SAS programming. It is a prerequisite for advanced-level certifications such as SAS Certified Advanced Programmer and SAS Certified Data Scientist.
Benefits of SAS Base Programmer certification
There are several benefits of earning the SAS Base Programmer certification, including:
Enhanced Career Opportunities: SAS Base Programmer certification demonstrates your proficiency in SAS programming skills, which can help you stand out in the job market. Employers often prefer candidates with SAS certification, and the certification can lead to better job opportunities and higher salaries.
Validation of SAS Programming Skills: SAS Base Programmer certification validates your knowledge and skills in SAS programming. This can help you gain credibility among your peers and establish yourself as an expert in the field.
Improved Data Analysis: SAS Base Programmer certification equips you with the knowledge and skills to effectively analyze and manipulate data using SAS. This can help you make better decisions, improve processes, and identify new opportunities for your organization.
Access to SAS Resources: SAS Base Programmer certification provides access to a wealth of resources, including SAS software, documentation, and support. This can help you stay up-to-date with the latest developments in SAS technology and improve your skills and knowledge.
Path to Advanced Certifications: SAS Base Programmer certification is a prerequisite for advanced-level certifications such as SAS Certified Advanced Programmer and SAS Certified Data Scientist. Earning the SAS Base Programmer certification can help you build a solid foundation for your career in data analysis and provide a path to advanced certifications.
How to prepare for SAS Base Programmer certification?
Preparing for the SAS Base Programmer certification requires a combination of knowledge, skills, and preparation. Here are some steps you can take to prepare for the certification exam:
Familiarize Yourself with SAS: To pass the SAS Base Programmer certification, you need to have a strong understanding of SAS programming concepts and techniques. Start by familiarizing yourself with SAS software and learning the basics of SAS programming.
Review SAS Programming Concepts: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS programming concepts such as data manipulation, data analysis, and data reporting. Reviewing these concepts will help you prepare for the exam.
Practice with SAS Software: The SAS Base Programmer certification exam includes coding tasks that require you to write SAS programs. Practicing with SAS software will help you become more familiar with the programming environment and improve your programming skills.
Use SAS Documentation: SAS provides comprehensive documentation that covers all aspects of SAS programming. Use these resources to deepen your understanding of SAS programming concepts and techniques.
Take Practice Tests: Practice tests are a great way to prepare for the SAS Base Programmer certification exam. They allow you to test your knowledge, identify areas of weakness, and become more familiar with the exam format.
Join SAS Community: Joining the SAS community can provide you with access to SAS experts, tips, and tricks. It is a great way to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in SAS technology and improve your skills.
Attend SAS Training: SAS offers training courses that cover all aspects of SAS programming. Attending these courses can help you develop your skills and prepare for the SAS Base Programmer certification exam.
Overview of SAS programming concepts tested in the certification exam
The SAS Base Programmer certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS programming concepts, including data manipulation, data analysis, data reporting, and SAS programming essentials. Here is an overview of the key concepts tested in the exam:
SAS Data Sets: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS data sets, including how to create, access, and modify data sets. You need to know how to read data from external files, manipulate data using SAS functions, and subset data using WHERE and IF statements.
Data Manipulation Techniques: The certification exam tests your knowledge of data manipulation techniques such as merging and appending data sets, sorting data, and using conditional logic in SAS programming.
SAS Procedures: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS procedures such as PROC SORT, PROC MEANS, PROC FREQ, and PROC PRINT. You need to know how to use these procedures to analyze and report data.
SAS Programming Essentials: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS programming essentials, including programming statements, syntax, and data step processing. You need to know how to write SAS programs, debug code, and troubleshoot errors.
SAS Macro Language: The certification exam tests your knowledge of the SAS macro language, including how to define and use macros in SAS programming.
SAS Graphics: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS graphics, including how to create and modify graphs using SAS procedures and the SAS/GRAPH software.
SAS Formats and Informats: The certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS formats and informats, including how to convert data types, manipulate data formats, and use SAS formats to customize data display.
Best practices for programming in SAS
Programming in SAS requires following best practices to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of SAS programs. Here are some best practices for programming in SAS:
Comment Your Code: Commenting your code is essential to make your code more readable and understandable. Use comments to explain your code, provide context, and make it easier for others to follow.
Use Meaningful Variable Names: Use descriptive and meaningful variable names to make your code more readable and understandable. Avoid using short and cryptic names that are difficult to understand.
Use Data Step Options: Use data step options to improve the efficiency of your code. Options such as OBS, FIRSTOBS, and DROP can help you subset data, improve performance, and reduce the size of your output.
Use SAS Functions: Use SAS functions to simplify your code and perform complex operations. Functions such as SUM, MEAN, and COUNT can help you calculate statistics, while functions such as SUBSTR and SCAN can help you manipulate character data.
Use SAS Procedures: Use SAS procedures to analyze and report data. Procedures such as PROC SORT, PROC MEANS, and PROC FREQ can help you summarize and analyze data, while procedures such as PROC PRINT and PROC REPORT can help you create reports.
Use Macros: Use SAS macros to automate tasks and simplify your code. Macros can help you generate code dynamically, automate repetitive tasks, and improve code readability.
Check for Errors: Check your code for errors and debug it to ensure that it produces the expected results. Use the SAS log to identify errors and troubleshoot problems.
Use Version Control: Use version control to manage your SAS code and track changes. Version control can help you collaborate with others, track changes, and maintain a history of your code.
Tips for passing the SAS Base Programmer certification exam
Passing the SAS Base Programmer certification exam requires a thorough understanding of SAS programming concepts and careful preparation. Here are some tips that can help you pass the exam:
Understand the Exam Format: The SAS Base Programmer certification exam consists of multiple-choice questions and has a time limit of 105 minutes. Familiarize yourself with the exam format, timing, and number of questions to help you manage your time effectively.
Study the Exam Objectives: The SAS Base Programmer certification exam covers a range of SAS programming concepts, including data manipulation, data analysis, data reporting, SAS programming essentials, and the SAS macro language. Study the exam objectives and make sure you understand each concept.
Practice with Sample Questions: Practice with sample questions to help you prepare for the exam. SAS provides sample questions and practice exams that you can use to test your knowledge and identify areas where you need to improve.
Use SAS Documentation: SAS provides comprehensive documentation for its software. Use the SAS documentation to help you understand SAS programming concepts, syntax, and functions.
Take a SAS Programming Course: Consider taking a SAS programming course to help you prepare for the exam. SAS offers courses that cover SAS programming concepts, data manipulation, and data analysis.
Join SAS Communities: Join SAS communities, such as SAS Support Communities, SAS Communities, and SAS Users Groups, to network with other SAS programmers, learn from their experiences, and get help with SAS programming.
Manage Your Time Effectively: Manage your time effectively during the exam. Read each question carefully, eliminate obviously incorrect answers, and answer the questions you know first.
Differences between SAS Base Programmer and Advanced Programmer certifications
SAS offers two levels of programming certifications: SAS Base Programmer and SAS Advanced Programmer. Here are the main differences between these two certifications:
Exam Content: The SAS Base Programmer certification exam tests your knowledge of SAS programming concepts such as data manipulation, data analysis, data reporting, SAS programming essentials, and the SAS macro language. The SAS Advanced Programmer certification exam tests your knowledge of advanced SAS programming concepts such as advanced data manipulation, efficiency techniques, debugging, and advanced macro processing.
Exam Difficulty: The SAS Advanced Programmer certification exam is more difficult than the SAS Base Programmer certification exam. The questions are more complex, and the passing score is higher.
Prerequisites: To earn the SAS Base Programmer certification, you do not need any prerequisites. To earn the SAS Advanced Programmer certification, you need to have earned the SAS Base Programmer certification.
Recognition: The SAS Base Programmer certification is a prerequisite for many SAS-related job positions, and it demonstrates your proficiency in SAS programming concepts. The SAS Advanced Programmer certification is a higher-level certification and demonstrates your advanced skills in SAS programming.
Job Opportunities: Having both the SAS Base Programmer and SAS Advanced Programmer certifications can help you stand out in the job market. The SAS Advanced Programmer certification can lead to more advanced job opportunities, such as SAS consultant or SAS programmer analyst.
Career opportunities after SAS Base Programmer certification.
Earning a SAS Base Programmer certification can open up various career opportunities for individuals in the field of data analytics. Here are some career opportunities that are available for individuals who hold a SAS Base Programmer certification:
SAS Programmer: SAS programmers write and maintain SAS code to manage, analyze, and report data. They are responsible for cleaning and manipulating data, generating reports, and creating custom programs to meet specific business requirements.
Data Analyst: Data analysts use SAS programming to analyze and interpret large volumes of data. They are responsible for designing and implementing data collection systems, creating reports and dashboards, and identifying trends and insights.
Data Manager: Data managers are responsible for overseeing the collection, storage, and maintenance of data. They ensure that data is accurate, complete, and secure. They may also work on projects to improve data quality and develop data management policies and procedures.
Business Analyst: Business analysts use data to inform business decisions. They work with stakeholders to understand business requirements, identify data sources, and develop reports and dashboards. They may also perform data modeling and forecasting to help organizations make informed decisions.
Consultant: SAS consultants work with clients to design and implement SAS-based solutions. They may work on projects related to data management, data analysis, or custom programming. They are responsible for managing project timelines, communicating with clients, and delivering high-quality solutions.
How to obtain SAS Base Programmer Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Development : SAS Base Programmer Certification
Comparison between SAS and other programming languages
SAS is a proprietary software suite that is primarily used for data management, analytics, and business intelligence. Here are some key differences between SAS and other programming languages:
Ease of Use: SAS is designed to be user-friendly and easy to use, with a point-and-click interface that makes it easy to navigate. Other programming languages, such as Python and R, may have a steeper learning curve for beginners.
Data Handling: SAS is particularly strong in handling large datasets and performing data manipulation tasks, such as merging datasets and transforming variables. Other programming languages, such as Python and R, also have strong data handling capabilities, but may require additional packages or libraries to achieve the same functionality.
Statistical Analysis: SAS is known for its powerful statistical analysis capabilities and is often used in research and academia. Other programming languages, such as Python and R, also have strong statistical analysis capabilities, with the added advantage of being open-source and having a larger community of users contributing to their development.
Cost: SAS is a proprietary software, which means that users must pay for licenses to use the software. Other programming languages, such as Python and R, are open-source and free to use, which makes them more accessible to users who may not have the budget for proprietary software.
Community Support: While SAS has a large community of users and developers, the community for other programming languages, such as Python and R, is much larger. This means that users of Python and R have access to a wider range of resources, including online forums, tutorials, and open-source libraries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, obtaining the SAS Base Programmer Certification can be a pivotal step in your career journey, opening doors to a world of opportunities in the realm of data analysis and programming. Throughout this guide, we've explored the key aspects of this certification, from its benefits in enhancing your skill set and boosting your professional credibility, to understanding the core concepts that the exam covers. By delving into this certification, you're not only validating your expertise in SAS programming but also positioning yourself as a valuable asset in today's data-driven industries. As you embark on your certification journey, remember that preparation, practice, and a solid understanding of the foundational concepts will be your allies. Best of luck on your path to becoming a certified SAS Base Programmer, and may your newly acquired skills propel you toward a successful and fulfilling career in the dynamic world of data analysis and programming.
Guide to Deep Learning Certification Training Courses!!
Welcome to "A Comprehensive Guide to Python Certification Training Courses"! This guide aims to be your ultimate companion in navigating the diverse landscape of Python certification programs. Whether you are a beginner taking your first steps into the world of Python or an experienced developer looking to enhance your skills, we have something for everyone. Through this guide, you will discover the benefits of Python certification, the skills you'll acquire, and the different certification levels available. We'll showcase some of the best online and in-person training platforms, renowned for their immersive and hands-on Python courses. No matter your background or experience, our goal is to equip you with the knowledge and confidence to embark on a transformative Python certification journey successfully. Let's unlock the doors to a bright and rewarding future in Python development together!
Table of contents
Introduction to Python Certification Training:
Benefits of Python Certification:
Different Python Certification Programs:
Prerequisites for Python Certification:
Preparation Strategies:
Exam Format and Structure:
Tips for Success in the Certification Exam:
Post-Certification Opportunities:
Conclusion:
Introduction to Python Certification Training
Python certification training is a program designed to equip learners with the knowledge and skills needed to become proficient in the Python programming language. Python is one of the most popular and widely used programming languages in the world, thanks to its simplicity, versatility, and ease of use. It has become the go-to language for web development, data science, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and other emerging technologies.
Python certification training programs are offered by various institutions, including universities, colleges, coding bootcamps, online learning platforms, and certification organizations. These programs provide learners with hands-on training and practical experience working with Python, as well as an opportunity to earn a recognized certification that validates their skills and knowledge.
Python certification training is suitable for individuals with different levels of experience, from beginners with little to no coding knowledge to experienced developers seeking to expand their skills and expertise. It offers a comprehensive curriculum covering core Python concepts, libraries, frameworks, databases, testing and debugging, web scraping, automation, and deployment.
In today's competitive job market, Python certification has become a valuable asset for job seekers, as it demonstrates to employers their proficiency in the language and their commitment to professional development. Python certified professionals can pursue a wide range of career paths, including software development, data analysis, data science, machine learning, artificial intelligence, web development, and more.
In summary, Python certification training is an excellent investment for individuals looking to enhance their programming skills and advance their careers in the tech industry. With the growing demand for Python developers and the increasing importance of data-driven technologies, Python certification has become an essential qualification for professionals in various fields.
Benefits of Python Certification
The benefits of obtaining a Python certification extend far beyond a simple acknowledgment of your skills. Here's a closer look at how a Python certification can positively impact your career and professional development:
- Validation of Expertise: Python certification serves as a tangible validation of your proficiency in the language. It demonstrates to employers, peers, and clients that you possess a solid foundation and understanding of Python programming.
- Career Advancement: A certification can accelerate your career growth by making you stand out in a competitive job market. It can lead to promotions, salary increases, and opportunities for more challenging roles.
- Enhanced Job Prospects: Certified Python professionals are in high demand across various industries. Holding a certification can open doors to a wide range of job opportunities, from web development and data analysis to artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Industry Recognition: Recognized by industry experts and employers, a Python certification reflects your commitment to staying current in your field. It demonstrates that you're aligning with industry standards and best practices.
- Credibility and Trustworthiness: Being certified establishes your credibility in the eyes of employers and clients. It instills confidence in your abilities and assures them that you possess the skills needed to excel in Python-related tasks.
- Skill Diversification: Python certification often covers a broad range of topics and applications. This diversifies your skill set, making you capable of tackling various projects and challenges across different domains.
- Networking Opportunities: Many certification programs come with access to exclusive communities, forums, and events. These platforms allow you to connect with fellow certified professionals, share insights, and build valuable industry relationships.
- Personal Satisfaction: Earning a certification can be personally fulfilling. It's a testament to your hard work, dedication, and the knowledge you've acquired. This sense of accomplishment can boost your confidence and motivation.
- Confidence Boost: Holding a certification can enhance your self-assurance when facing new projects or opportunities. You'll have a solid foundation to rely on, leading to more innovative and impactful contributions.
- Global Opportunities: Python's international popularity means that your certification is recognized worldwide. This opens doors to job opportunities not only in your local market but also in different countries.
- Stay Relevant in Tech: In the rapidly changing technology landscape, staying up-to-date is essential. A Python certification demonstrates your commitment to continuous learning, making you adaptable to new trends and developments.
- Differentiation: When competing against candidates without certifications, you'll have a distinctive advantage. Your certification showcases your commitment to professional growth and positions you as a proactive learner.
Different Python Certification Programs
- Python Institute Certifications: The Python Institute offers a series of certifications catering to different skill levels. These certifications include:
- PCAP (Certified Associate in Python Programming): A beginner-level certification focusing on foundational Python programming concepts and syntax.
- PCPP (Certified Professional in Python Programming): An intermediate-level certification that delves deeper into advanced Python programming techniques, algorithms, and problem-solving.
- PCAP-31-02: This certification is designed for educators who wish to teach Python programming effectively to their students.
- Microsoft Certified: Azure AI Engineer Associate: While not solely Python-focused, this certification demonstrates your ability to design, implement, and monitor AI solutions using various technologies, including Python. It showcases your proficiency in building machine learning models, deploying them on Azure, and integrating AI services into applications.
- Cisco Certified DevNet Professional: This certification is ideal for professionals who work with Cisco platforms and want to leverage Python for network automation, software-defined networking (SDN), and other software development aspects in networking. It demonstrates your ability to automate network tasks using programming skills, including Python.
- DataCamp Certifications: DataCamp offers certifications tailored to data science and analytics. Their certifications include tracks such as Data Scientist with Python, Python Programmer, and Data Analyst with Python. These certifications validate your practical skills in Python for data manipulation, analysis, and visualization.
- edX Python Certifications: edX hosts various Python-related certification courses from universities and institutions worldwide. These range from introductory courses to more specialized tracks like Python for Data Science or Python for Artificial Intelligence.
- Certified Python Programmer by The Open Group: This certification is vendor-neutral and focuses on assessing your skills as a programmer using the Python language. It tests your understanding of Python syntax, data structures, and problem-solving techniques.
- IBM Data Science Professional Certificate: While not exclusively Python-centric, this program offered on platforms in Online Websites focuses on data science skills, including Python programming for data analysis, visualization, and machine learning.
Prerequisites for Python Certification
The prerequisites for Python certification can vary depending on the specific certification program and its level of difficulty. However, here are some general prerequisites you might encounter when pursuing a Python certification:
- Basic Programming Knowledge: Most Python certification programs assume that you have a basic understanding of programming concepts, regardless of the language. Familiarity with variables, loops, conditionals, and functions will provide a solid foundation for learning Python.
- Fundamental Python Proficiency: For entry-level certifications, having a grasp of Python's basic syntax, data types, operators, and control structures is essential. You should be comfortable writing simple Python programs and solving elementary programming challenges.
- Mathematics and Logic: Depending on the certification level, you might need a basic understanding of mathematical concepts like algebra, statistics, and logic. This is particularly relevant for certifications in fields like data science and machine learning.
- Computer Science Fundamentals: Some advanced certifications might assume knowledge of computer science principles, such as algorithms, data structures, and object-oriented programming. These concepts are crucial for building more complex Python applications.
- Experience with Libraries and Frameworks: If the certification focuses on a specific domain like web development, data analysis, or machine learning, having experience with relevant Python libraries and frameworks (e.g., Django, NumPy, Pandas, TensorFlow) could be beneficial.
- Previous Programming Experience: While not always a strict requirement, having prior programming experience in any language can help you adapt to Python's syntax and concepts more quickly.
- Educational Background: Some advanced certifications, particularly those in specialized domains like AI or network programming, might require a relevant educational background or work experience.
- Enthusiasm for Learning: Above all, a willingness to learn, practice, and dedicate time to mastering Python is essential for any certification journey.
Preparation Strategies:
Effective preparation is key to succeeding in a Python certification exam. Here are some preparation strategies to help you make the most of your study time:
- Understand the Exam Format: Familiarize yourself with the exam's structure, types of questions, time limits, and scoring. This will help you plan your study approach accordingly.
- Assess Your Knowledge: Start by evaluating your current Python skills and identifying areas that need improvement. This will help you create a focused study plan.
- Set Clear Goals and Deadlines: Define specific goals for each study session and set deadlines for completing topics. This will keep you on track and prevent procrastination.
- Create a Study Schedule: Design a study schedule that allocates time for reviewing different topics, practicing exercises, and taking mock exams. Consistency is key.
- Use Multiple Resources: Utilize a combination of textbooks, online courses, video tutorials, and practice exams. Diverse resources can provide different perspectives on the same topics.
- Hands-on Practice: Python is best learned through hands-on coding. Work on coding exercises, projects, and real-world scenarios to solidify your understanding.
- Practice Exams and Mock Tests: Take practice exams and mock tests regularly to simulate the actual exam environment. Analyze your performance and focus on weak areas.
- Review and Refine: After each study session, review your notes and revise concepts you've learned. Address any doubts or uncertainties immediately.
- Join Study Groups or Forums: Engage with fellow learners in study groups or online forums. Discussing concepts and problem-solving together can enhance your understanding.
- Breaks and Self-Care: Include short breaks in your study schedule to prevent burnout. Proper rest and self-care are essential for effective learning.
- Use Flashcards and Summaries: Create flashcards for key concepts, formulas, and syntax rules. Summarize complex topics in your own words to reinforce understanding.
- Teach Someone Else: Teaching a concept to someone else can reinforce your own understanding. Explain complex ideas in simple terms to ensure clarity.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with any updates in Python or the certification program. New versions or changes could impact the exam content.
- Time Management in Exams: During the actual exam, manage your time wisely. Allocate more time to questions you're confident about and revisit challenging ones.
- Stay Positive and Confident: Believe in your preparation and abilities. Positive self-talk and confidence can significantly impact your exam performance.
Exam Format and Structure
Understanding the exam format and structure is crucial for preparing effectively and performing well in your Python certification exam. While the specifics can vary based on the certification program, here's a general overview of what you might expect:
- Question Types:
- Multiple-Choice Questions: These require you to select the correct answer from a list of options.
- Code Writing or Coding Challenges: You might be asked to write code that solves a specific problem or meets certain criteria.
- Scenario-based Questions: These present real-world scenarios where you need to apply Python knowledge to solve problems.
- Time Limits:
- The exam will have a predetermined time limit that varies depending on the complexity and number of questions.
- Number of Questions:
- The number of questions can vary widely, from a few dozen to over a hundred, depending on the certification level.
- Scoring:
- Different questions might carry different weights. Some questions could be worth more points than others.
- The total points earned are usually converted into a final scaled score for easy comparison across different exam versions.
- Passing Score:
- The passing score can also vary. It's the minimum score you need to achieve to earn the certification.
- Exam Environment:
- Certification exams are typically proctored, meaning they're monitored to ensure fairness and prevent cheating.
- Some exams might be taken in-person at a testing center, while others could be online and remotely proctored.
- Allowed Resources:
- The exam might restrict the use of certain resources, like external websites, reference materials, or calculators.
- Use of Python Interpreter:
- Some exams allow you to use a Python interpreter to run and test your code.
- Real-world Applications:
- Many certification exams focus on practical application rather than rote memorization. You'll be tested on your ability to solve problems and write functional code.
- Adaptive Testing (Possibly):
- Some certification exams use adaptive testing, where the difficulty of questions adjusts based on your previous answers. This ensures a tailored experience but can be more challenging.
- Review and Navigation:
- Most exams allow you to navigate back and forth between questions, review and change answers before submitting.
- Exam Rules and Policies:
- Familiarize yourself with the specific rules and policies of the certification program. This might include rules about breaks, ID requirements, and behavior during the exam.
Tips for Success in the Certification Exam
Achieving success in a Python certification exam requires a combination of effective preparation, strategic approach, and confidence. Here are some tips to help you excel on exam day:
- Know the Exam Content:
- Familiarize yourself with the exam objectives and content domains outlined in the official certification documentation. Focus your preparation on these areas.
- Master the Fundamentals:
- Ensure you have a solid grasp of Python fundamentals, including syntax, data types, control structures, and basic algorithms. Strong fundamentals form the basis for more advanced concepts.
- Practice Coding Challenges:
- Practice coding exercises and challenges similar to those you might encounter in the exam. This will improve your problem-solving skills and coding efficiency.
- Review Mock Exams:
- Take multiple mock exams under timed conditions to simulate the real exam environment. Analyze your performance and identify areas needing improvement.
- Time Management:
- Allocate appropriate time to each question based on its complexity. Don't get stuck on a single question for too long; move on and return later if needed.
- Read Questions Carefully:
- Pay close attention to the wording of questions and instructions. Misunderstanding a question can lead to incorrect answers.
- Answer Confidently:
- If you're confident in your answer, trust your instincts and move on. Overthinking can lead to doubt and potentially changing correct answers.
- Eliminate Wrong Answers:
- In multiple-choice questions, eliminate obviously incorrect answers to narrow down your choices, increasing the likelihood of choosing the right one.
- Manage Nervousness:
- Feeling nervous is normal. Deep breaths and positive self-talk can help calm your nerves and keep your focus.
- Prioritize Strong Areas:
- Start with the questions you're most comfortable with. This builds confidence and saves time for more challenging questions later.
- Skip and Return:
- If you encounter a difficult question, skip it and return later if you have time remaining. Answering easier questions first can boost your confidence.
- Double-Check Answers:
- If time allows, review your answers before submitting. Check for typos, logic errors, and ensure you've answered as accurately as possible.
- Use Scratch Paper:
- If permitted, jot down notes, code snippets, or key concepts on scratch paper. This can help you organize your thoughts and solve problems more effectively.
- Stay Hydrated and Rested:
- Prioritize sleep the night before the exam and stay hydrated on exam day. A well-rested mind performs better.
- Stay Positive:
- Maintain a positive attitude and believe in your preparation. Self-confidence can positively impact your performance.
Post-Certification Opportunities:
Earning a Python certification opens the door to a world of exciting opportunities and career advancements. Here's a glimpse into the post-certification landscape:
- Career Advancement:
- A Python certification showcases your dedication and expertise, positioning you for promotions, raises, and advanced roles within your current organization.
- Job Opportunities:
- Your certification sets you apart in the job market, increasing your chances of landing coveted positions in various industries that require Python skills.
- Salary Boost:
- Certified professionals often command higher salaries than their non-certified counterparts. Employers recognize the value of certified individuals and are willing to compensate accordingly.
- Expanded Skill Set:
- Through your certification journey, you've likely acquired a deeper understanding of Python and related technologies. This expanded skill set opens doors to tackle more complex projects.
- Specialization Pathways:
- Some certifications act as stepping stones to specialized fields like data science, machine learning, web development, or network programming, allowing you to focus on areas that align with your interests.
- Networking Opportunities:
- Certification programs often have associated communities and forums where certified professionals can connect, share insights, and collaborate on projects.
- Consulting and Freelancing:
- Armed with certification, you can offer your expertise as a consultant or freelancer. Many businesses seek certified professionals for short-term projects.
- Personal Branding:
- Displaying your certification on your resume, LinkedIn profile, and other professional platforms enhances your personal brand and credibility.
- Career Transition:
- If you're transitioning into a new career, a Python certification can help bridge the gap and showcase your transferable skills.
- Continuous Learning:
- Certification is just one milestone in your learning journey. Stay up-to-date with Python's evolving landscape and consider pursuing more advanced certifications as you grow.
- Innovation and Creativity:
- Armed with a solid foundation in Python, you'll be better equipped to innovate and create solutions to real-world problems.
- Recognition and Respect:
- Colleagues, employers, and peers often admire certified professionals for their dedication and the effort they've put into skill development.
- Global Opportunities:
- Python's universal applicability means that your certification can open doors to opportunities not only in your country but also internationally.
- Contributions to Open Source:
- With advanced Python knowledge, you might contribute to open-source projects, giving back to the community and enhancing your portfolio.
- Lifelong Learning Journey:
- Your certification is not the end; it's a launchpad for a lifelong journey of continuous learning and growth in the dynamic world of technology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, embarking on a Python certification training journey is a strategic move towards personal and professional growth in the ever-evolving world of technology. Through this comprehensive exploration, we've uncovered the multifaceted benefits of Python certification, delved into the various certification programs available, and dissected the essential components of successful preparation and exam execution.
A Python certification is more than just a credential; it's a testament to your dedication, proficiency, and commitment to mastering a versatile programming language. As you traverse the diverse subtopics we've covered, from understanding prerequisites to mastering coding challenges, you're equipping yourself with the tools to excel in both certification exams and real-world scenarios.
Armed with insights into the exam's structure, time-tested tips for success, and a vision of post-certification horizons, you're ready to navigate the challenging but rewarding journey towards certification. Whether you're aspiring to step into a new realm of opportunities or seeking to enhance your existing skills, Python certification offers a roadmap to a brighter and more promising future.
So, as you venture forth, remember that the journey is as important as the destination. Embrace the learning, relish the challenges, and celebrate your achievements along the way. With the world of Python at your fingertips and a certification as your compass, the possibilities are limitless. Let this blog be your guide as you embark on your remarkable journey of Python certification training.
Read More
Welcome to "A Comprehensive Guide to Python Certification Training Courses"! This guide aims to be your ultimate companion in navigating the diverse landscape of Python certification programs. Whether you are a beginner taking your first steps into the world of Python or an experienced developer looking to enhance your skills, we have something for everyone. Through this guide, you will discover the benefits of Python certification, the skills you'll acquire, and the different certification levels available. We'll showcase some of the best online and in-person training platforms, renowned for their immersive and hands-on Python courses. No matter your background or experience, our goal is to equip you with the knowledge and confidence to embark on a transformative Python certification journey successfully. Let's unlock the doors to a bright and rewarding future in Python development together!
Table of contents
Introduction to Python Certification Training:
Benefits of Python Certification:
Different Python Certification Programs:
Prerequisites for Python Certification:
Preparation Strategies:
Exam Format and Structure:
Tips for Success in the Certification Exam:
Post-Certification Opportunities:
Conclusion:
Introduction to Python Certification Training
Python certification training is a program designed to equip learners with the knowledge and skills needed to become proficient in the Python programming language. Python is one of the most popular and widely used programming languages in the world, thanks to its simplicity, versatility, and ease of use. It has become the go-to language for web development, data science, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and other emerging technologies.
Python certification training programs are offered by various institutions, including universities, colleges, coding bootcamps, online learning platforms, and certification organizations. These programs provide learners with hands-on training and practical experience working with Python, as well as an opportunity to earn a recognized certification that validates their skills and knowledge.
Python certification training is suitable for individuals with different levels of experience, from beginners with little to no coding knowledge to experienced developers seeking to expand their skills and expertise. It offers a comprehensive curriculum covering core Python concepts, libraries, frameworks, databases, testing and debugging, web scraping, automation, and deployment.
In today's competitive job market, Python certification has become a valuable asset for job seekers, as it demonstrates to employers their proficiency in the language and their commitment to professional development. Python certified professionals can pursue a wide range of career paths, including software development, data analysis, data science, machine learning, artificial intelligence, web development, and more.
In summary, Python certification training is an excellent investment for individuals looking to enhance their programming skills and advance their careers in the tech industry. With the growing demand for Python developers and the increasing importance of data-driven technologies, Python certification has become an essential qualification for professionals in various fields.
Benefits of Python Certification
The benefits of obtaining a Python certification extend far beyond a simple acknowledgment of your skills. Here's a closer look at how a Python certification can positively impact your career and professional development:
- Validation of Expertise: Python certification serves as a tangible validation of your proficiency in the language. It demonstrates to employers, peers, and clients that you possess a solid foundation and understanding of Python programming.
- Career Advancement: A certification can accelerate your career growth by making you stand out in a competitive job market. It can lead to promotions, salary increases, and opportunities for more challenging roles.
- Enhanced Job Prospects: Certified Python professionals are in high demand across various industries. Holding a certification can open doors to a wide range of job opportunities, from web development and data analysis to artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Industry Recognition: Recognized by industry experts and employers, a Python certification reflects your commitment to staying current in your field. It demonstrates that you're aligning with industry standards and best practices.
- Credibility and Trustworthiness: Being certified establishes your credibility in the eyes of employers and clients. It instills confidence in your abilities and assures them that you possess the skills needed to excel in Python-related tasks.
- Skill Diversification: Python certification often covers a broad range of topics and applications. This diversifies your skill set, making you capable of tackling various projects and challenges across different domains.
- Networking Opportunities: Many certification programs come with access to exclusive communities, forums, and events. These platforms allow you to connect with fellow certified professionals, share insights, and build valuable industry relationships.
- Personal Satisfaction: Earning a certification can be personally fulfilling. It's a testament to your hard work, dedication, and the knowledge you've acquired. This sense of accomplishment can boost your confidence and motivation.
- Confidence Boost: Holding a certification can enhance your self-assurance when facing new projects or opportunities. You'll have a solid foundation to rely on, leading to more innovative and impactful contributions.
- Global Opportunities: Python's international popularity means that your certification is recognized worldwide. This opens doors to job opportunities not only in your local market but also in different countries.
- Stay Relevant in Tech: In the rapidly changing technology landscape, staying up-to-date is essential. A Python certification demonstrates your commitment to continuous learning, making you adaptable to new trends and developments.
- Differentiation: When competing against candidates without certifications, you'll have a distinctive advantage. Your certification showcases your commitment to professional growth and positions you as a proactive learner.
Different Python Certification Programs
- Python Institute Certifications: The Python Institute offers a series of certifications catering to different skill levels. These certifications include:
- PCAP (Certified Associate in Python Programming): A beginner-level certification focusing on foundational Python programming concepts and syntax.
- PCPP (Certified Professional in Python Programming): An intermediate-level certification that delves deeper into advanced Python programming techniques, algorithms, and problem-solving.
- PCAP-31-02: This certification is designed for educators who wish to teach Python programming effectively to their students.
- Microsoft Certified: Azure AI Engineer Associate: While not solely Python-focused, this certification demonstrates your ability to design, implement, and monitor AI solutions using various technologies, including Python. It showcases your proficiency in building machine learning models, deploying them on Azure, and integrating AI services into applications.
- Cisco Certified DevNet Professional: This certification is ideal for professionals who work with Cisco platforms and want to leverage Python for network automation, software-defined networking (SDN), and other software development aspects in networking. It demonstrates your ability to automate network tasks using programming skills, including Python.
- DataCamp Certifications: DataCamp offers certifications tailored to data science and analytics. Their certifications include tracks such as Data Scientist with Python, Python Programmer, and Data Analyst with Python. These certifications validate your practical skills in Python for data manipulation, analysis, and visualization.
- edX Python Certifications: edX hosts various Python-related certification courses from universities and institutions worldwide. These range from introductory courses to more specialized tracks like Python for Data Science or Python for Artificial Intelligence.
- Certified Python Programmer by The Open Group: This certification is vendor-neutral and focuses on assessing your skills as a programmer using the Python language. It tests your understanding of Python syntax, data structures, and problem-solving techniques.
- IBM Data Science Professional Certificate: While not exclusively Python-centric, this program offered on platforms in Online Websites focuses on data science skills, including Python programming for data analysis, visualization, and machine learning.
Prerequisites for Python Certification
The prerequisites for Python certification can vary depending on the specific certification program and its level of difficulty. However, here are some general prerequisites you might encounter when pursuing a Python certification:
- Basic Programming Knowledge: Most Python certification programs assume that you have a basic understanding of programming concepts, regardless of the language. Familiarity with variables, loops, conditionals, and functions will provide a solid foundation for learning Python.
- Fundamental Python Proficiency: For entry-level certifications, having a grasp of Python's basic syntax, data types, operators, and control structures is essential. You should be comfortable writing simple Python programs and solving elementary programming challenges.
- Mathematics and Logic: Depending on the certification level, you might need a basic understanding of mathematical concepts like algebra, statistics, and logic. This is particularly relevant for certifications in fields like data science and machine learning.
- Computer Science Fundamentals: Some advanced certifications might assume knowledge of computer science principles, such as algorithms, data structures, and object-oriented programming. These concepts are crucial for building more complex Python applications.
- Experience with Libraries and Frameworks: If the certification focuses on a specific domain like web development, data analysis, or machine learning, having experience with relevant Python libraries and frameworks (e.g., Django, NumPy, Pandas, TensorFlow) could be beneficial.
- Previous Programming Experience: While not always a strict requirement, having prior programming experience in any language can help you adapt to Python's syntax and concepts more quickly.
- Educational Background: Some advanced certifications, particularly those in specialized domains like AI or network programming, might require a relevant educational background or work experience.
- Enthusiasm for Learning: Above all, a willingness to learn, practice, and dedicate time to mastering Python is essential for any certification journey.
Preparation Strategies:
Effective preparation is key to succeeding in a Python certification exam. Here are some preparation strategies to help you make the most of your study time:
- Understand the Exam Format: Familiarize yourself with the exam's structure, types of questions, time limits, and scoring. This will help you plan your study approach accordingly.
- Assess Your Knowledge: Start by evaluating your current Python skills and identifying areas that need improvement. This will help you create a focused study plan.
- Set Clear Goals and Deadlines: Define specific goals for each study session and set deadlines for completing topics. This will keep you on track and prevent procrastination.
- Create a Study Schedule: Design a study schedule that allocates time for reviewing different topics, practicing exercises, and taking mock exams. Consistency is key.
- Use Multiple Resources: Utilize a combination of textbooks, online courses, video tutorials, and practice exams. Diverse resources can provide different perspectives on the same topics.
- Hands-on Practice: Python is best learned through hands-on coding. Work on coding exercises, projects, and real-world scenarios to solidify your understanding.
- Practice Exams and Mock Tests: Take practice exams and mock tests regularly to simulate the actual exam environment. Analyze your performance and focus on weak areas.
- Review and Refine: After each study session, review your notes and revise concepts you've learned. Address any doubts or uncertainties immediately.
- Join Study Groups or Forums: Engage with fellow learners in study groups or online forums. Discussing concepts and problem-solving together can enhance your understanding.
- Breaks and Self-Care: Include short breaks in your study schedule to prevent burnout. Proper rest and self-care are essential for effective learning.
- Use Flashcards and Summaries: Create flashcards for key concepts, formulas, and syntax rules. Summarize complex topics in your own words to reinforce understanding.
- Teach Someone Else: Teaching a concept to someone else can reinforce your own understanding. Explain complex ideas in simple terms to ensure clarity.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with any updates in Python or the certification program. New versions or changes could impact the exam content.
- Time Management in Exams: During the actual exam, manage your time wisely. Allocate more time to questions you're confident about and revisit challenging ones.
- Stay Positive and Confident: Believe in your preparation and abilities. Positive self-talk and confidence can significantly impact your exam performance.
Exam Format and Structure
Understanding the exam format and structure is crucial for preparing effectively and performing well in your Python certification exam. While the specifics can vary based on the certification program, here's a general overview of what you might expect:
- Question Types:
- Multiple-Choice Questions: These require you to select the correct answer from a list of options.
- Code Writing or Coding Challenges: You might be asked to write code that solves a specific problem or meets certain criteria.
- Scenario-based Questions: These present real-world scenarios where you need to apply Python knowledge to solve problems.
- Time Limits:
- The exam will have a predetermined time limit that varies depending on the complexity and number of questions.
- Number of Questions:
- The number of questions can vary widely, from a few dozen to over a hundred, depending on the certification level.
- Scoring:
- Different questions might carry different weights. Some questions could be worth more points than others.
- The total points earned are usually converted into a final scaled score for easy comparison across different exam versions.
- Passing Score:
- The passing score can also vary. It's the minimum score you need to achieve to earn the certification.
- Exam Environment:
- Certification exams are typically proctored, meaning they're monitored to ensure fairness and prevent cheating.
- Some exams might be taken in-person at a testing center, while others could be online and remotely proctored.
- Allowed Resources:
- The exam might restrict the use of certain resources, like external websites, reference materials, or calculators.
- Use of Python Interpreter:
- Some exams allow you to use a Python interpreter to run and test your code.
- Real-world Applications:
- Many certification exams focus on practical application rather than rote memorization. You'll be tested on your ability to solve problems and write functional code.
- Adaptive Testing (Possibly):
- Some certification exams use adaptive testing, where the difficulty of questions adjusts based on your previous answers. This ensures a tailored experience but can be more challenging.
- Review and Navigation:
- Most exams allow you to navigate back and forth between questions, review and change answers before submitting.
- Exam Rules and Policies:
- Familiarize yourself with the specific rules and policies of the certification program. This might include rules about breaks, ID requirements, and behavior during the exam.
Tips for Success in the Certification Exam
Achieving success in a Python certification exam requires a combination of effective preparation, strategic approach, and confidence. Here are some tips to help you excel on exam day:
- Know the Exam Content:
- Familiarize yourself with the exam objectives and content domains outlined in the official certification documentation. Focus your preparation on these areas.
- Master the Fundamentals:
- Ensure you have a solid grasp of Python fundamentals, including syntax, data types, control structures, and basic algorithms. Strong fundamentals form the basis for more advanced concepts.
- Practice Coding Challenges:
- Practice coding exercises and challenges similar to those you might encounter in the exam. This will improve your problem-solving skills and coding efficiency.
- Review Mock Exams:
- Take multiple mock exams under timed conditions to simulate the real exam environment. Analyze your performance and identify areas needing improvement.
- Time Management:
- Allocate appropriate time to each question based on its complexity. Don't get stuck on a single question for too long; move on and return later if needed.
- Read Questions Carefully:
- Pay close attention to the wording of questions and instructions. Misunderstanding a question can lead to incorrect answers.
- Answer Confidently:
- If you're confident in your answer, trust your instincts and move on. Overthinking can lead to doubt and potentially changing correct answers.
- Eliminate Wrong Answers:
- In multiple-choice questions, eliminate obviously incorrect answers to narrow down your choices, increasing the likelihood of choosing the right one.
- Manage Nervousness:
- Feeling nervous is normal. Deep breaths and positive self-talk can help calm your nerves and keep your focus.
- Prioritize Strong Areas:
- Start with the questions you're most comfortable with. This builds confidence and saves time for more challenging questions later.
- Skip and Return:
- If you encounter a difficult question, skip it and return later if you have time remaining. Answering easier questions first can boost your confidence.
- Double-Check Answers:
- If time allows, review your answers before submitting. Check for typos, logic errors, and ensure you've answered as accurately as possible.
- Use Scratch Paper:
- If permitted, jot down notes, code snippets, or key concepts on scratch paper. This can help you organize your thoughts and solve problems more effectively.
- Stay Hydrated and Rested:
- Prioritize sleep the night before the exam and stay hydrated on exam day. A well-rested mind performs better.
- Stay Positive:
- Maintain a positive attitude and believe in your preparation. Self-confidence can positively impact your performance.
Post-Certification Opportunities:
Earning a Python certification opens the door to a world of exciting opportunities and career advancements. Here's a glimpse into the post-certification landscape:
- Career Advancement:
- A Python certification showcases your dedication and expertise, positioning you for promotions, raises, and advanced roles within your current organization.
- Job Opportunities:
- Your certification sets you apart in the job market, increasing your chances of landing coveted positions in various industries that require Python skills.
- Salary Boost:
- Certified professionals often command higher salaries than their non-certified counterparts. Employers recognize the value of certified individuals and are willing to compensate accordingly.
- Expanded Skill Set:
- Through your certification journey, you've likely acquired a deeper understanding of Python and related technologies. This expanded skill set opens doors to tackle more complex projects.
- Specialization Pathways:
- Some certifications act as stepping stones to specialized fields like data science, machine learning, web development, or network programming, allowing you to focus on areas that align with your interests.
- Networking Opportunities:
- Certification programs often have associated communities and forums where certified professionals can connect, share insights, and collaborate on projects.
- Consulting and Freelancing:
- Armed with certification, you can offer your expertise as a consultant or freelancer. Many businesses seek certified professionals for short-term projects.
- Personal Branding:
- Displaying your certification on your resume, LinkedIn profile, and other professional platforms enhances your personal brand and credibility.
- Career Transition:
- If you're transitioning into a new career, a Python certification can help bridge the gap and showcase your transferable skills.
- Continuous Learning:
- Certification is just one milestone in your learning journey. Stay up-to-date with Python's evolving landscape and consider pursuing more advanced certifications as you grow.
- Innovation and Creativity:
- Armed with a solid foundation in Python, you'll be better equipped to innovate and create solutions to real-world problems.
- Recognition and Respect:
- Colleagues, employers, and peers often admire certified professionals for their dedication and the effort they've put into skill development.
- Global Opportunities:
- Python's universal applicability means that your certification can open doors to opportunities not only in your country but also internationally.
- Contributions to Open Source:
- With advanced Python knowledge, you might contribute to open-source projects, giving back to the community and enhancing your portfolio.
- Lifelong Learning Journey:
- Your certification is not the end; it's a launchpad for a lifelong journey of continuous learning and growth in the dynamic world of technology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, embarking on a Python certification training journey is a strategic move towards personal and professional growth in the ever-evolving world of technology. Through this comprehensive exploration, we've uncovered the multifaceted benefits of Python certification, delved into the various certification programs available, and dissected the essential components of successful preparation and exam execution.
A Python certification is more than just a credential; it's a testament to your dedication, proficiency, and commitment to mastering a versatile programming language. As you traverse the diverse subtopics we've covered, from understanding prerequisites to mastering coding challenges, you're equipping yourself with the tools to excel in both certification exams and real-world scenarios.
Armed with insights into the exam's structure, time-tested tips for success, and a vision of post-certification horizons, you're ready to navigate the challenging but rewarding journey towards certification. Whether you're aspiring to step into a new realm of opportunities or seeking to enhance your existing skills, Python certification offers a roadmap to a brighter and more promising future.
So, as you venture forth, remember that the journey is as important as the destination. Embrace the learning, relish the challenges, and celebrate your achievements along the way. With the world of Python at your fingertips and a certification as your compass, the possibilities are limitless. Let this blog be your guide as you embark on your remarkable journey of Python certification training.
Java Certification Training Course: A Step-by-Step Guide
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on the "Java Certification Training Course: A Step-by-Step Guide." In today's fast-paced and ever-evolving technological landscape, mastering a programming language like Java is a crucial step towards a successful career in software development. This guide will navigate you through the intricacies of the Java Certification Training Course, offering a detailed roadmap to help you acquire a deep understanding of Java's core concepts, libraries, and real-world applications. Whether you're an aspiring programmer or a seasoned developer looking to expand your skill set, this guide will provide you with insights into the structured learning journey, hands-on exercises, and practical examples that will empower you to confidently navigate the world of Java programming and attain a recognized certification. Let's embark on this enriching educational journey together.
Table of contents
Introduction to Java Certification
Choosing the Right Java Certification
Preparing for the Java Certification Exam
Core Java Concepts and Topics
Java APIs and Libraries
Java Development Tools and Environments
Java Best Practices and Design Patterns
Exam Tips and Strategies
Beyond Certification: Advancing Your Java Skills
Conclusion
Introduction to Java Certification
Java certification is a validation of an individual's knowledge and skills in the Java programming language. It is a globally recognized credential that demonstrates expertise and proficiency in Java development. Java certifications are offered by Oracle, the company behind Java, and are widely respected in the software industry.
Importance and Benefits of Java Certification
Professional Credibility: Obtaining a Java certification enhances your professional credibility and validates your skills in the Java programming language. It demonstrates to employers and clients that you have the necessary knowledge and expertise to develop Java applications.
Career Advancement: Java certifications can open doors to new career opportunities and advancement within the software development industry. Employers often prefer candidates with certifications as they provide assurance of their competency.
Industry Recognition: Java certifications are widely recognized and respected in the industry. They are acknowledged as a standard benchmark of Java proficiency and can give you an edge over other candidates during job interviews.
Skill Validation: Going through the process of preparing for a Java certification exam allows you to deepen your understanding of the Java language and its core concepts. It ensures that you have a comprehensive knowledge of Java, including its syntax, libraries, APIs, and best practices.
Different Java Certification Levels and Tracks
Oracle Certified Associate (OCA): The OCA certification is the entry-level certification in Java. It validates your foundational knowledge of Java and is a stepping stone towards more advanced certifications.
Oracle Certified Professional (OCP): The OCP certification is the next level of certification after OCA. It is designed for experienced Java developers and demonstrates a deeper understanding of Java programming, APIs, and best practices.
Oracle Certified Expert (OCE): The OCE certifications focus on specialized areas of Java development, such as Java EE, Java Persistence API, or Java Web Services. These certifications showcase your expertise in specific domains.
Oracle Certified Master (OCM): The OCM certification is the highest level of Java certification. It is a prestigious designation that demonstrates advanced skills and knowledge in Java development. OCM certifications are available in specific areas, such as Java EE or Java SE.
It's important to note that Oracle regularly updates its certification program, so it's advisable to visit the official Oracle Certification website to stay updated on the latest certifications, tracks, and requirements.
Choosing the Right Java Certification
Choosing the right Java certification is an important decision that can impact your career as a Java developer. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a Java certification:
Professional Goals and Interests: Consider your career goals and the areas of Java development that interest you the most. Determine whether you want to specialize in a particular domain, such as Java EE, or if you prefer a broader certification that covers the fundamentals of Java programming.
Skill Level and Experience: Assess your current skill level and experience in Java. If you are new to Java, starting with an entry-level certification like the Oracle Certified Associate (OCA) can provide a solid foundation. If you have several years of experience, you may consider pursuing a more advanced certification like the Oracle Certified Professional (OCP) or an expert-level certification.
Job Market Demand: Research the job market to understand which certifications are in demand by employers. Look for certifications that are frequently mentioned in job postings or preferred by companies in your desired industry. This can increase your chances of landing a job or advancing in your current role.
Certification Prerequisites: Check the prerequisites for each certification to ensure you meet the requirements. Some certifications may require you to hold a previous certification or have a specific level of experience. Make sure you fulfill these prerequisites before pursuing a particular certification.
Certification Tracks: Explore the different certification tracks offered by Oracle. These tracks cater to different areas of Java development, such as Java SE, Java EE, or specialized topics like Java Web Services or Java Persistence API. Choose a track that aligns with your interests and career goals.
Exam Difficulty and Preparation Effort: Consider the difficulty level of the certification exams and the amount of preparation effort required. Some certifications may have more rigorous exams and demand extensive study and hands-on practice. Assess your commitment and availability to dedicate time and effort to prepare for the certification.
Personal Learning Style: Reflect on your preferred learning style. Some individuals excel in self-study environments, while others benefit from instructor-led training programs. Choose a certification that offers learning resources and study materials that align with your learning preferences.
Certification Validity and Maintenance: Check the validity period of the certification and any requirements for maintaining it. Some certifications may require you to recertify periodically or earn continuing education credits. Consider the long-term commitment and investment required to maintain the certification.
Industry Reputation: Take into account the reputation and recognition of the certification within the industry. Research the opinions and experiences of other professionals who have pursued the certification. Seek feedback from colleagues, mentors, or online communities to gain insights into the value and reputation of the certification.
Preparing for the Java Certification Exam
Preparing for a Java certification exam requires dedication, effort, and a structured study plan. Here are some tips to help you prepare effectively for the exam:
Understand the Exam Objectives: Review the exam objectives outlined by Oracle for the specific certification you are pursuing. Understand the topics covered and the skills required to pass the exam.
Choose Study Materials: Select study materials that align with your learning style and preferences. Oracle offers official study guides, practice exams, and training courses. You can also find third-party study materials, such as books, online courses, and video tutorials.
Practice with Hands-on Exercises: Java certification exams typically involve coding exercises that test your practical skills. Practice coding exercises and hands-on projects to deepen your understanding of Java programming concepts and develop your problem-solving skills.
Use Practice Exams: Practice exams are an excellent tool to simulate the exam environment and assess your readiness. Take advantage of the official practice exams offered by Oracle, or look for third-party practice exams. Analyze your performance and identify areas that need improvement.
Join Study Groups and Communities: Join study groups and online communities to connect with other individuals pursuing the same certification. Exchange tips, share resources, and collaborate on coding projects. This can help you stay motivated and accountable during the preparation process.
Attend Instructor-led Training: Consider attending instructor-led training programs that offer structured learning and personalized feedback. Oracle offers training courses, workshops, and boot camps that cover the exam objectives and provide hands-on practice.
Manage Your Time Effectively: Create a study schedule that accommodates your daily routine and allows you to dedicate sufficient time to exam preparation. Break down the study material into manageable chunks and allocate time for practice exercises and review.
Take Care of Your Physical and Mental Health: Exam preparation can be stressful, so make sure to prioritize your physical and mental well-being. Get enough sleep, exercise regularly, and eat a healthy diet. Take breaks and engage in activities that help you relax and reduce stress.
Review Exam Day Policies and Procedures: Review the exam day policies and procedures, such as the check-in process, ID requirements, and exam rules. Familiarize yourself with the exam interface and the time limits for each section.
Core Java Concepts and Topics
To excel in the Java certification exam, it's crucial to have a strong understanding of core Java concepts and topics. Here are some essential concepts and topics you should be familiar with:
Java Basics:
Java programming language history and features
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) and bytecode
Java development environment setup
Variables, Data Types, and Operators:
Primitive data types (int, double, boolean, etc.)
Reference data types (classes, interfaces, arrays)
Variable declaration, initialization, and scope
Arithmetic, assignment, comparison, and logical operators
Control Flow Statements:
Conditional statements (if-else, switch-case)
Looping statements (for, while, do-while)
Branching statements (break, continue, return)
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts:
Classes, objects, and methods
Constructors and method overloading
Inheritance, interfaces, and polymorphism
Encapsulation, abstraction, and access modifiers
Arrays and Strings:
Single-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays
Array manipulation (traversing, sorting, searching)
String manipulation, concatenation, and comparison
Exception Handling:
Try-catch blocks and exception types
Throwing and catching exceptions
Exception propagation and handling best practices
Input/Output (I/O) Operations:
Reading from and writing to files
Using streams (byte stream and character stream)
Serialization and deserialization of objects
Generics and Collections:
Generics and type parameterization
Working with Java collections (List, Set, Map)
Iterating over collections and using iterators
Java APIs and Libraries:
java.lang package (String, StringBuilder, etc.)
java.util package (ArrayList, HashMap, etc.)
java.io package (File, BufferedReader, etc.)
java.time package (Date, LocalDate, etc.)
Multithreading and Concurrency:
Creating and running threads
Thread synchronization and locks
Concurrent data structures and utilities
Thread pools and executors
Java Development Tools:
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) like Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA
Build tools like Apache Maven or Gradle
Debugging techniques and tools
Version control systems like Git
Java APIs and Libraries
Java provides a vast array of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and libraries that offer pre-built functionality and components to simplify and enhance Java application development. Here are some important Java APIs and libraries you should be familiar with:
java.lang package:
String: Manipulating and working with strings.
Object: The root class of all Java classes.
Math: Mathematical operations and functions.
StringBuilder and StringBuffer: Efficient manipulation of string data.
java.util package:
Collection framework: Provides interfaces and classes for managing and manipulating groups of objects, such as ArrayList, LinkedList, HashSet, and TreeSet.
Map interface and implementations: Key-value pair data structures, such as HashMap, TreeMap, and LinkedHashMap.
Iterator and Iterable interfaces: Enables traversing collections.
Date and Time API: Introduced in Java 8, it provides classes like LocalDate, LocalDateTime, Instant, and Duration for handling date and time operations.
java.io package:
File and File I/O: Reading from and writing to files, working with directories, and file manipulation.
BufferedReader and BufferedWriter: Efficiently reading and writing character streams.
Object Serialization: Converting Java objects into a stream of bytes for storage or transmission.
java.net package:
Networking: Classes and interfaces for networking operations, including socket programming, URLs, and HTTP connections.
InetAddress: Representing IP addresses and DNS resolution.
HttpURLConnection: Performing HTTP requests and handling responses.
java.awt and javax.swing packages:
Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT): Basic GUI components for creating desktop applications.
Swing: Extended GUI components and a more sophisticated framework for building graphical user interfaces.
java.util.concurrent package:
Concurrency utilities: Classes for concurrent programming, such as Executor, ThreadPoolExecutor, and ConcurrentCollections.
Locks: ReentrantLock, ReadWriteLock, and related classes for managing thread synchronization.
java.sql package:
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity): API for connecting to relational databases, executing SQL queries, and managing database operations.
java.nio package:
New I/O (NIO): Provides a non-blocking I/O model and supports high-performance I/O operations.
java.security package:
Security and cryptography: Classes for encryption, digital signatures, key management, and secure communication.
Third-Party Libraries: Java has a rich ecosystem of third-party libraries and frameworks that provide additional functionality and simplify specific tasks. Examples include:
Apache Commons: A collection of reusable Java components for various purposes, such as handling collections, file operations, and networking.
Google Guava: A library that provides utility classes, collections, caching, and functional programming support.
Jackson or Gson: Libraries for JSON parsing and serialization.
Spring Framework: A popular framework for building Java enterprise applications, providing comprehensive features for dependency injection, MVC, and more.
Java Development Tools and Environments
Java offers a range of development tools and environments that facilitate the creation, testing, and debugging of Java applications. These tools enhance productivity, provide code editing features, offer build and deployment options, and aid in diagnosing and fixing issues. Here are some essential Java development tools and environments:
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs):
Eclipse: A popular open-source IDE with a rich set of features for Java development, including code editing, debugging, refactoring, and plug-in support.
IntelliJ IDEA: A powerful commercial IDE that provides advanced code analysis, intelligent code completion, and productivity features. It offers a free Community Edition and a more comprehensive Ultimate Edition.
NetBeans: An open-source IDE with a user-friendly interface, providing a wide range of tools for Java development, including GUI design, profiling, and version control integration.
Build Tools:
Apache Maven: A widely used build automation tool that manages dependencies, compiles source code, and generates artifacts like JAR files. It uses XML-based project configurations and promotes project consistency and reusability.
Gradle: A flexible build automation tool that supports multiple programming languages, including Java. It uses Groovy or Kotlin-based scripts for defining build configurations and provides a powerful dependency management system.
Version Control Systems:
Git: A distributed version control system that allows you to track changes to your codebase, collaborate with others, and manage code branches effectively. Popular Git hosting platforms include GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket.
Subversion (SVN): A centralized version control system that tracks changes and manages source code repositories. It offers features like branching, merging, and tagging.
Debugging Tools:
Debugging in IDEs: IDEs like Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, and NetBeans provide comprehensive debugging features, such as breakpoints, variable inspection, step-by-step execution, and exception tracing.
Java Debugger (jdb): A command-line tool bundled with the Java Development Kit (JDK) that allows manual debugging of Java applications. It provides basic debugging functionalities for examining variables, setting breakpoints, and stepping through code.
Profiling Tools:
Java VisualVM: A profiling tool included with the JDK that provides detailed insights into the performance of Java applications. It offers features like CPU and memory profiling, thread analysis, and monitoring of Java Virtual Machine (JVM) metrics.
YourKit Java Profiler: A commercial profiling tool that helps identify performance bottlenecks, memory leaks, and CPU utilization issues. It offers advanced profiling capabilities and integration with popular IDEs.
Testing Frameworks:
JUnit: A widely-used testing framework for writing unit tests in Java. It provides annotations, assertions, and test runners to simplify test creation and execution.
TestNG: An alternative testing framework that offers advanced features such as data-driven testing, parallel test execution, and test configuration flexibility.
Continuous Integration and Deployment:
Jenkins: An open-source automation server that supports continuous integration and deployment. It can be configured to build, test, and deploy Java applications automatically based on predefined pipelines or triggers.
Travis CI: A cloud-based continuous integration platform that integrates with Git repositories. It builds and tests Java applications automatically upon code changes or pull requests.
Java Best Practices and Design Patterns
To write efficient, maintainable, and scalable Java code, it is important to follow best practices and utilize design patterns. Here are some Java best practices and commonly used design patterns:
Java Best Practices:
Follow Naming Conventions:
Use meaningful and descriptive names for variables, methods, classes, and packages.
Follow the camelCase convention for variables and methods, and use PascalCase for class names.
Use Proper Indentation and Formatting:
Maintain consistent indentation to enhance code readability.
Use whitespace, line breaks, and comments effectively to make your code more readable and understandable.
Encapsulate Data:
Use private access modifiers for class members and provide public getter and setter methods for data access.
Follow the principle of encapsulation to protect internal state and provide controlled access to class members.
Use Exception Handling:
Handle exceptions appropriately using try-catch blocks to provide graceful error handling and prevent application crashes.
Use specific exception types that accurately describe the nature of the exception.
Avoid Magic Numbers and Strings:
Assign meaningful constants or variables instead of hard-coding numbers or strings throughout your code.
Use constants or enumerations to represent fixed values.
Optimize Loops:
Minimize unnecessary iterations in loops by optimizing loop conditions and terminating conditions.
Avoid performing heavy computations within loops if possible.
Implement Object Equality Correctly:
Override the equals() method when comparing object equality based on custom criteria.
Implement the hashCode() method consistently with the equals() method to ensure proper usage in data structures like HashMap and HashSet.
Use Interfaces and Abstract Classes:
Utilize interfaces to define contracts and provide abstraction for classes implementing them.
Abstract classes can provide a common base for related classes, defining common behavior and leaving specific implementation to subclasses.
Java Design Patterns:
Creational Patterns:
Singleton: Ensures a class has only one instance and provides a global access point to it.
Factory Method: Provides an interface for creating objects, allowing subclasses to decide which class to instantiate.
Builder: Simplifies the creation of complex objects by separating the construction process from its representation.
Structural Patterns:
Adapter: Converts the interface of a class into another interface clients expect, enabling classes to work together that otherwise couldn't due to incompatible interfaces.
Decorator: Dynamically adds behavior to an object at runtime without modifying its existing structure.
Facade: Provides a simplified interface to a complex subsystem, making it easier to use and understand.
Behavioral Patterns:
Observer: Defines a one-to-many dependency between objects, ensuring that changes in one object trigger updates to its dependents.
Strategy: Enables the selection of an algorithm at runtime, encapsulating it in a separate class and allowing interchangeable implementations.
Template Method: Defines the skeleton of an algorithm in a base class while allowing subclasses to provide certain steps of the algorithm.
Architectural Patterns:
Model-View-Controller (MVC): Separates the presentation, business logic, and data layers to achieve modularity and maintainability.
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA): Organizes functionality into loosely coupled, reusable services that communicate with each other over a network.
Exam Tips and Strategies for Java Certification
Preparing for a Java certification exam requires a systematic approach and effective strategies to maximize your chances of success. Here are some tips and strategies to help you excel in your Java certification exam:
Understand the Exam Format:
Familiarize yourself with the exam structure, duration, and the types of questions (multiple-choice, coding exercises, etc.).
Read the official exam documentation to understand the objectives and topics covered in the exam.
Review the Exam Syllabus:
Study the exam syllabus or content outline provided by the certification body. Ensure you have a solid understanding of each topic mentioned.
Create a Study Plan:
Develop a study plan based on the exam syllabus, allocating sufficient time to cover each topic.
Break down the study plan into smaller tasks, such as reviewing specific concepts, practicing coding exercises, and taking mock exams.
Gain Hands-on Experience:
Practice coding and implementing Java concepts by working on small projects or exercises.
Write and execute Java programs to reinforce your understanding of core concepts.
Utilize Official Study Resources:
Use official study guides, textbooks, and documentation provided by the certification body.
Take advantage of any sample questions or practice exams available from the official sources.
Take Mock Exams:
Practice with mock exams to simulate the actual exam environment and assess your readiness.
Analyze your performance, identify weak areas, and focus on improving your knowledge in those areas.
Join Study Groups or Forums:
Engage in discussions with fellow exam takers or Java enthusiasts to exchange knowledge, clarify doubts, and learn from their experiences.
Participate in online forums, developer communities, or social media groups dedicated to Java certification.
Read Documentation and Specifications:
Go through relevant Java documentation, such as the Java API documentation, to understand the details of classes, methods, and their usage.
Study Java language specifications to gain a deeper understanding of the language rules and features.
Practice Time Management:
Allocate specific time slots for each section of the exam during your practice sessions.
Develop time management skills to ensure you can answer all questions within the allocated time during the actual exam.
Stay Calm and Confident:
On the day of the exam, stay calm and confident. Trust in your preparation and abilities.
Read each question carefully and manage your time effectively to answer all questions.
Review and Revise:
Set aside time for revision a few days before the exam. Review key concepts, notes, and any weak areas you identified during your preparation.
Get Adequate Rest:
Prioritize your well-being and ensure you get enough rest and sleep before the exam day.
Being well-rested will help you stay focused and alert during the exam.
How to obtain Java Developer Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Microsoft : Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification
Development : Java Certification
Beyond Certification: Advancing Your Java Skills
Obtaining a Java certification is a significant achievement that demonstrates your knowledge and expertise in the language. However, to further advance your Java skills and stay relevant in a rapidly evolving industry, it's important to continue learning and exploring new areas. Here are some suggestions for advancing your Java skills beyond certification:
Explore Advanced Java Concepts:
Dive deeper into advanced Java topics such as multithreading, concurrency, design patterns, data structures, and algorithms.
Study the Java Memory Model and learn about JVM internals, garbage collection, and performance optimization techniques.
Learn Java Frameworks and Libraries:
Expand your knowledge by exploring popular Java frameworks and libraries like Spring, Hibernate, JavaFX, Apache Kafka, and Apache Spark.
Understand how these frameworks and libraries can simplify and enhance your development process.
Master Java 8+ Features:
Java has evolved significantly in recent versions. Familiarize yourself with new features introduced in Java 8 and subsequent releases.
Learn about functional programming concepts, lambda expressions, Stream API, Date and Time API, and other enhancements.
Build Real-World Projects:
Apply your Java skills to real-world projects that align with your interests or professional goals.
Develop web applications, mobile apps, or desktop applications using Java and related technologies.
Contribute to Open-Source Projects:
Participate in open-source projects written in Java. It allows you to collaborate with experienced developers and gain exposure to industry best practices.
Contribute code, report issues, and learn from the feedback and code reviews of the project's community.
Attend Java Conferences and Meetups:
Attend Java conferences, workshops, and meetups to network with professionals, learn about the latest trends, and gain insights from industry experts.
Engage in discussions, ask questions, and share your knowledge with others.
Read Books and Blogs:
Read books and blogs written by renowned Java experts to deepen your understanding of specific Java topics.
Stay updated with the latest trends, best practices, and emerging technologies in the Java ecosystem.
Take Online Courses and Tutorials:
Enroll in online courses or tutorials to learn advanced Java concepts, frameworks, and tools.
Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Pluralsight offer a wide range of Java courses taught by industry professionals.
Practice Continuous Learning:
Treat learning as an ongoing process. Dedicate time regularly to expand your Java knowledge and explore new technologies and techniques.
Stay curious, experiment with new ideas, and embrace continuous improvement.
Collaborate and Mentor Others:
Engage in developer communities, forums, or social media groups to share your knowledge and learn from others.
Mentor aspiring Java developers and help them navigate their learning journey.
Conclusion
In summary, the Java Certification Training Course, outlined in this step-by-step guide, presents a comprehensive and hands-on approach to mastering the Java programming language, equipping learners with both fundamental concepts and advanced skills. By blending theoretical knowledge with practical application and interactive assessments, this course not only fosters a deep understanding of Java but also nurtures problem-solving abilities and industry best practices. Ultimately, obtaining the Java certification through this training not only signifies technical proficiency but also a commitment to professional growth, making it an invaluable asset for aspiring and experienced developers seeking to excel in the dynamic landscape of software development.
Read More
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on the "Java Certification Training Course: A Step-by-Step Guide." In today's fast-paced and ever-evolving technological landscape, mastering a programming language like Java is a crucial step towards a successful career in software development. This guide will navigate you through the intricacies of the Java Certification Training Course, offering a detailed roadmap to help you acquire a deep understanding of Java's core concepts, libraries, and real-world applications. Whether you're an aspiring programmer or a seasoned developer looking to expand your skill set, this guide will provide you with insights into the structured learning journey, hands-on exercises, and practical examples that will empower you to confidently navigate the world of Java programming and attain a recognized certification. Let's embark on this enriching educational journey together.
Table of contents
Introduction to Java Certification
Choosing the Right Java Certification
Preparing for the Java Certification Exam
Core Java Concepts and Topics
Java APIs and Libraries
Java Development Tools and Environments
Java Best Practices and Design Patterns
Exam Tips and Strategies
Beyond Certification: Advancing Your Java Skills
Conclusion
Introduction to Java Certification
Java certification is a validation of an individual's knowledge and skills in the Java programming language. It is a globally recognized credential that demonstrates expertise and proficiency in Java development. Java certifications are offered by Oracle, the company behind Java, and are widely respected in the software industry.
Importance and Benefits of Java Certification
Professional Credibility: Obtaining a Java certification enhances your professional credibility and validates your skills in the Java programming language. It demonstrates to employers and clients that you have the necessary knowledge and expertise to develop Java applications.
Career Advancement: Java certifications can open doors to new career opportunities and advancement within the software development industry. Employers often prefer candidates with certifications as they provide assurance of their competency.
Industry Recognition: Java certifications are widely recognized and respected in the industry. They are acknowledged as a standard benchmark of Java proficiency and can give you an edge over other candidates during job interviews.
Skill Validation: Going through the process of preparing for a Java certification exam allows you to deepen your understanding of the Java language and its core concepts. It ensures that you have a comprehensive knowledge of Java, including its syntax, libraries, APIs, and best practices.
Different Java Certification Levels and Tracks
Oracle Certified Associate (OCA): The OCA certification is the entry-level certification in Java. It validates your foundational knowledge of Java and is a stepping stone towards more advanced certifications.
Oracle Certified Professional (OCP): The OCP certification is the next level of certification after OCA. It is designed for experienced Java developers and demonstrates a deeper understanding of Java programming, APIs, and best practices.
Oracle Certified Expert (OCE): The OCE certifications focus on specialized areas of Java development, such as Java EE, Java Persistence API, or Java Web Services. These certifications showcase your expertise in specific domains.
Oracle Certified Master (OCM): The OCM certification is the highest level of Java certification. It is a prestigious designation that demonstrates advanced skills and knowledge in Java development. OCM certifications are available in specific areas, such as Java EE or Java SE.
It's important to note that Oracle regularly updates its certification program, so it's advisable to visit the official Oracle Certification website to stay updated on the latest certifications, tracks, and requirements.
Choosing the Right Java Certification
Choosing the right Java certification is an important decision that can impact your career as a Java developer. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a Java certification:
Professional Goals and Interests: Consider your career goals and the areas of Java development that interest you the most. Determine whether you want to specialize in a particular domain, such as Java EE, or if you prefer a broader certification that covers the fundamentals of Java programming.
Skill Level and Experience: Assess your current skill level and experience in Java. If you are new to Java, starting with an entry-level certification like the Oracle Certified Associate (OCA) can provide a solid foundation. If you have several years of experience, you may consider pursuing a more advanced certification like the Oracle Certified Professional (OCP) or an expert-level certification.
Job Market Demand: Research the job market to understand which certifications are in demand by employers. Look for certifications that are frequently mentioned in job postings or preferred by companies in your desired industry. This can increase your chances of landing a job or advancing in your current role.
Certification Prerequisites: Check the prerequisites for each certification to ensure you meet the requirements. Some certifications may require you to hold a previous certification or have a specific level of experience. Make sure you fulfill these prerequisites before pursuing a particular certification.
Certification Tracks: Explore the different certification tracks offered by Oracle. These tracks cater to different areas of Java development, such as Java SE, Java EE, or specialized topics like Java Web Services or Java Persistence API. Choose a track that aligns with your interests and career goals.
Exam Difficulty and Preparation Effort: Consider the difficulty level of the certification exams and the amount of preparation effort required. Some certifications may have more rigorous exams and demand extensive study and hands-on practice. Assess your commitment and availability to dedicate time and effort to prepare for the certification.
Personal Learning Style: Reflect on your preferred learning style. Some individuals excel in self-study environments, while others benefit from instructor-led training programs. Choose a certification that offers learning resources and study materials that align with your learning preferences.
Certification Validity and Maintenance: Check the validity period of the certification and any requirements for maintaining it. Some certifications may require you to recertify periodically or earn continuing education credits. Consider the long-term commitment and investment required to maintain the certification.
Industry Reputation: Take into account the reputation and recognition of the certification within the industry. Research the opinions and experiences of other professionals who have pursued the certification. Seek feedback from colleagues, mentors, or online communities to gain insights into the value and reputation of the certification.
Preparing for the Java Certification Exam
Preparing for a Java certification exam requires dedication, effort, and a structured study plan. Here are some tips to help you prepare effectively for the exam:
Understand the Exam Objectives: Review the exam objectives outlined by Oracle for the specific certification you are pursuing. Understand the topics covered and the skills required to pass the exam.
Choose Study Materials: Select study materials that align with your learning style and preferences. Oracle offers official study guides, practice exams, and training courses. You can also find third-party study materials, such as books, online courses, and video tutorials.
Practice with Hands-on Exercises: Java certification exams typically involve coding exercises that test your practical skills. Practice coding exercises and hands-on projects to deepen your understanding of Java programming concepts and develop your problem-solving skills.
Use Practice Exams: Practice exams are an excellent tool to simulate the exam environment and assess your readiness. Take advantage of the official practice exams offered by Oracle, or look for third-party practice exams. Analyze your performance and identify areas that need improvement.
Join Study Groups and Communities: Join study groups and online communities to connect with other individuals pursuing the same certification. Exchange tips, share resources, and collaborate on coding projects. This can help you stay motivated and accountable during the preparation process.
Attend Instructor-led Training: Consider attending instructor-led training programs that offer structured learning and personalized feedback. Oracle offers training courses, workshops, and boot camps that cover the exam objectives and provide hands-on practice.
Manage Your Time Effectively: Create a study schedule that accommodates your daily routine and allows you to dedicate sufficient time to exam preparation. Break down the study material into manageable chunks and allocate time for practice exercises and review.
Take Care of Your Physical and Mental Health: Exam preparation can be stressful, so make sure to prioritize your physical and mental well-being. Get enough sleep, exercise regularly, and eat a healthy diet. Take breaks and engage in activities that help you relax and reduce stress.
Review Exam Day Policies and Procedures: Review the exam day policies and procedures, such as the check-in process, ID requirements, and exam rules. Familiarize yourself with the exam interface and the time limits for each section.
Core Java Concepts and Topics
To excel in the Java certification exam, it's crucial to have a strong understanding of core Java concepts and topics. Here are some essential concepts and topics you should be familiar with:
Java Basics:
Java programming language history and features
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) and bytecode
Java development environment setup
Variables, Data Types, and Operators:
Primitive data types (int, double, boolean, etc.)
Reference data types (classes, interfaces, arrays)
Variable declaration, initialization, and scope
Arithmetic, assignment, comparison, and logical operators
Control Flow Statements:
Conditional statements (if-else, switch-case)
Looping statements (for, while, do-while)
Branching statements (break, continue, return)
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts:
Classes, objects, and methods
Constructors and method overloading
Inheritance, interfaces, and polymorphism
Encapsulation, abstraction, and access modifiers
Arrays and Strings:
Single-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays
Array manipulation (traversing, sorting, searching)
String manipulation, concatenation, and comparison
Exception Handling:
Try-catch blocks and exception types
Throwing and catching exceptions
Exception propagation and handling best practices
Input/Output (I/O) Operations:
Reading from and writing to files
Using streams (byte stream and character stream)
Serialization and deserialization of objects
Generics and Collections:
Generics and type parameterization
Working with Java collections (List, Set, Map)
Iterating over collections and using iterators
Java APIs and Libraries:
java.lang package (String, StringBuilder, etc.)
java.util package (ArrayList, HashMap, etc.)
java.io package (File, BufferedReader, etc.)
java.time package (Date, LocalDate, etc.)
Multithreading and Concurrency:
Creating and running threads
Thread synchronization and locks
Concurrent data structures and utilities
Thread pools and executors
Java Development Tools:
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) like Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA
Build tools like Apache Maven or Gradle
Debugging techniques and tools
Version control systems like Git
Java APIs and Libraries
Java provides a vast array of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and libraries that offer pre-built functionality and components to simplify and enhance Java application development. Here are some important Java APIs and libraries you should be familiar with:
java.lang package:
String: Manipulating and working with strings.
Object: The root class of all Java classes.
Math: Mathematical operations and functions.
StringBuilder and StringBuffer: Efficient manipulation of string data.
java.util package:
Collection framework: Provides interfaces and classes for managing and manipulating groups of objects, such as ArrayList, LinkedList, HashSet, and TreeSet.
Map interface and implementations: Key-value pair data structures, such as HashMap, TreeMap, and LinkedHashMap.
Iterator and Iterable interfaces: Enables traversing collections.
Date and Time API: Introduced in Java 8, it provides classes like LocalDate, LocalDateTime, Instant, and Duration for handling date and time operations.
java.io package:
File and File I/O: Reading from and writing to files, working with directories, and file manipulation.
BufferedReader and BufferedWriter: Efficiently reading and writing character streams.
Object Serialization: Converting Java objects into a stream of bytes for storage or transmission.
java.net package:
Networking: Classes and interfaces for networking operations, including socket programming, URLs, and HTTP connections.
InetAddress: Representing IP addresses and DNS resolution.
HttpURLConnection: Performing HTTP requests and handling responses.
java.awt and javax.swing packages:
Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT): Basic GUI components for creating desktop applications.
Swing: Extended GUI components and a more sophisticated framework for building graphical user interfaces.
java.util.concurrent package:
Concurrency utilities: Classes for concurrent programming, such as Executor, ThreadPoolExecutor, and ConcurrentCollections.
Locks: ReentrantLock, ReadWriteLock, and related classes for managing thread synchronization.
java.sql package:
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity): API for connecting to relational databases, executing SQL queries, and managing database operations.
java.nio package:
New I/O (NIO): Provides a non-blocking I/O model and supports high-performance I/O operations.
java.security package:
Security and cryptography: Classes for encryption, digital signatures, key management, and secure communication.
Third-Party Libraries: Java has a rich ecosystem of third-party libraries and frameworks that provide additional functionality and simplify specific tasks. Examples include:
Apache Commons: A collection of reusable Java components for various purposes, such as handling collections, file operations, and networking.
Google Guava: A library that provides utility classes, collections, caching, and functional programming support.
Jackson or Gson: Libraries for JSON parsing and serialization.
Spring Framework: A popular framework for building Java enterprise applications, providing comprehensive features for dependency injection, MVC, and more.
Java Development Tools and Environments
Java offers a range of development tools and environments that facilitate the creation, testing, and debugging of Java applications. These tools enhance productivity, provide code editing features, offer build and deployment options, and aid in diagnosing and fixing issues. Here are some essential Java development tools and environments:
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs):
Eclipse: A popular open-source IDE with a rich set of features for Java development, including code editing, debugging, refactoring, and plug-in support.
IntelliJ IDEA: A powerful commercial IDE that provides advanced code analysis, intelligent code completion, and productivity features. It offers a free Community Edition and a more comprehensive Ultimate Edition.
NetBeans: An open-source IDE with a user-friendly interface, providing a wide range of tools for Java development, including GUI design, profiling, and version control integration.
Build Tools:
Apache Maven: A widely used build automation tool that manages dependencies, compiles source code, and generates artifacts like JAR files. It uses XML-based project configurations and promotes project consistency and reusability.
Gradle: A flexible build automation tool that supports multiple programming languages, including Java. It uses Groovy or Kotlin-based scripts for defining build configurations and provides a powerful dependency management system.
Version Control Systems:
Git: A distributed version control system that allows you to track changes to your codebase, collaborate with others, and manage code branches effectively. Popular Git hosting platforms include GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket.
Subversion (SVN): A centralized version control system that tracks changes and manages source code repositories. It offers features like branching, merging, and tagging.
Debugging Tools:
Debugging in IDEs: IDEs like Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, and NetBeans provide comprehensive debugging features, such as breakpoints, variable inspection, step-by-step execution, and exception tracing.
Java Debugger (jdb): A command-line tool bundled with the Java Development Kit (JDK) that allows manual debugging of Java applications. It provides basic debugging functionalities for examining variables, setting breakpoints, and stepping through code.
Profiling Tools:
Java VisualVM: A profiling tool included with the JDK that provides detailed insights into the performance of Java applications. It offers features like CPU and memory profiling, thread analysis, and monitoring of Java Virtual Machine (JVM) metrics.
YourKit Java Profiler: A commercial profiling tool that helps identify performance bottlenecks, memory leaks, and CPU utilization issues. It offers advanced profiling capabilities and integration with popular IDEs.
Testing Frameworks:
JUnit: A widely-used testing framework for writing unit tests in Java. It provides annotations, assertions, and test runners to simplify test creation and execution.
TestNG: An alternative testing framework that offers advanced features such as data-driven testing, parallel test execution, and test configuration flexibility.
Continuous Integration and Deployment:
Jenkins: An open-source automation server that supports continuous integration and deployment. It can be configured to build, test, and deploy Java applications automatically based on predefined pipelines or triggers.
Travis CI: A cloud-based continuous integration platform that integrates with Git repositories. It builds and tests Java applications automatically upon code changes or pull requests.
Java Best Practices and Design Patterns
To write efficient, maintainable, and scalable Java code, it is important to follow best practices and utilize design patterns. Here are some Java best practices and commonly used design patterns:
Java Best Practices:
Follow Naming Conventions:
Use meaningful and descriptive names for variables, methods, classes, and packages.
Follow the camelCase convention for variables and methods, and use PascalCase for class names.
Use Proper Indentation and Formatting:
Maintain consistent indentation to enhance code readability.
Use whitespace, line breaks, and comments effectively to make your code more readable and understandable.
Encapsulate Data:
Use private access modifiers for class members and provide public getter and setter methods for data access.
Follow the principle of encapsulation to protect internal state and provide controlled access to class members.
Use Exception Handling:
Handle exceptions appropriately using try-catch blocks to provide graceful error handling and prevent application crashes.
Use specific exception types that accurately describe the nature of the exception.
Avoid Magic Numbers and Strings:
Assign meaningful constants or variables instead of hard-coding numbers or strings throughout your code.
Use constants or enumerations to represent fixed values.
Optimize Loops:
Minimize unnecessary iterations in loops by optimizing loop conditions and terminating conditions.
Avoid performing heavy computations within loops if possible.
Implement Object Equality Correctly:
Override the equals() method when comparing object equality based on custom criteria.
Implement the hashCode() method consistently with the equals() method to ensure proper usage in data structures like HashMap and HashSet.
Use Interfaces and Abstract Classes:
Utilize interfaces to define contracts and provide abstraction for classes implementing them.
Abstract classes can provide a common base for related classes, defining common behavior and leaving specific implementation to subclasses.
Java Design Patterns:
Creational Patterns:
Singleton: Ensures a class has only one instance and provides a global access point to it.
Factory Method: Provides an interface for creating objects, allowing subclasses to decide which class to instantiate.
Builder: Simplifies the creation of complex objects by separating the construction process from its representation.
Structural Patterns:
Adapter: Converts the interface of a class into another interface clients expect, enabling classes to work together that otherwise couldn't due to incompatible interfaces.
Decorator: Dynamically adds behavior to an object at runtime without modifying its existing structure.
Facade: Provides a simplified interface to a complex subsystem, making it easier to use and understand.
Behavioral Patterns:
Observer: Defines a one-to-many dependency between objects, ensuring that changes in one object trigger updates to its dependents.
Strategy: Enables the selection of an algorithm at runtime, encapsulating it in a separate class and allowing interchangeable implementations.
Template Method: Defines the skeleton of an algorithm in a base class while allowing subclasses to provide certain steps of the algorithm.
Architectural Patterns:
Model-View-Controller (MVC): Separates the presentation, business logic, and data layers to achieve modularity and maintainability.
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA): Organizes functionality into loosely coupled, reusable services that communicate with each other over a network.
Exam Tips and Strategies for Java Certification
Preparing for a Java certification exam requires a systematic approach and effective strategies to maximize your chances of success. Here are some tips and strategies to help you excel in your Java certification exam:
Understand the Exam Format:
Familiarize yourself with the exam structure, duration, and the types of questions (multiple-choice, coding exercises, etc.).
Read the official exam documentation to understand the objectives and topics covered in the exam.
Review the Exam Syllabus:
Study the exam syllabus or content outline provided by the certification body. Ensure you have a solid understanding of each topic mentioned.
Create a Study Plan:
Develop a study plan based on the exam syllabus, allocating sufficient time to cover each topic.
Break down the study plan into smaller tasks, such as reviewing specific concepts, practicing coding exercises, and taking mock exams.
Gain Hands-on Experience:
Practice coding and implementing Java concepts by working on small projects or exercises.
Write and execute Java programs to reinforce your understanding of core concepts.
Utilize Official Study Resources:
Use official study guides, textbooks, and documentation provided by the certification body.
Take advantage of any sample questions or practice exams available from the official sources.
Take Mock Exams:
Practice with mock exams to simulate the actual exam environment and assess your readiness.
Analyze your performance, identify weak areas, and focus on improving your knowledge in those areas.
Join Study Groups or Forums:
Engage in discussions with fellow exam takers or Java enthusiasts to exchange knowledge, clarify doubts, and learn from their experiences.
Participate in online forums, developer communities, or social media groups dedicated to Java certification.
Read Documentation and Specifications:
Go through relevant Java documentation, such as the Java API documentation, to understand the details of classes, methods, and their usage.
Study Java language specifications to gain a deeper understanding of the language rules and features.
Practice Time Management:
Allocate specific time slots for each section of the exam during your practice sessions.
Develop time management skills to ensure you can answer all questions within the allocated time during the actual exam.
Stay Calm and Confident:
On the day of the exam, stay calm and confident. Trust in your preparation and abilities.
Read each question carefully and manage your time effectively to answer all questions.
Review and Revise:
Set aside time for revision a few days before the exam. Review key concepts, notes, and any weak areas you identified during your preparation.
Get Adequate Rest:
Prioritize your well-being and ensure you get enough rest and sleep before the exam day.
Being well-rested will help you stay focused and alert during the exam.
How to obtain Java Developer Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Microsoft : Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification
Development : Java Certification
Beyond Certification: Advancing Your Java Skills
Obtaining a Java certification is a significant achievement that demonstrates your knowledge and expertise in the language. However, to further advance your Java skills and stay relevant in a rapidly evolving industry, it's important to continue learning and exploring new areas. Here are some suggestions for advancing your Java skills beyond certification:
Explore Advanced Java Concepts:
Dive deeper into advanced Java topics such as multithreading, concurrency, design patterns, data structures, and algorithms.
Study the Java Memory Model and learn about JVM internals, garbage collection, and performance optimization techniques.
Learn Java Frameworks and Libraries:
Expand your knowledge by exploring popular Java frameworks and libraries like Spring, Hibernate, JavaFX, Apache Kafka, and Apache Spark.
Understand how these frameworks and libraries can simplify and enhance your development process.
Master Java 8+ Features:
Java has evolved significantly in recent versions. Familiarize yourself with new features introduced in Java 8 and subsequent releases.
Learn about functional programming concepts, lambda expressions, Stream API, Date and Time API, and other enhancements.
Build Real-World Projects:
Apply your Java skills to real-world projects that align with your interests or professional goals.
Develop web applications, mobile apps, or desktop applications using Java and related technologies.
Contribute to Open-Source Projects:
Participate in open-source projects written in Java. It allows you to collaborate with experienced developers and gain exposure to industry best practices.
Contribute code, report issues, and learn from the feedback and code reviews of the project's community.
Attend Java Conferences and Meetups:
Attend Java conferences, workshops, and meetups to network with professionals, learn about the latest trends, and gain insights from industry experts.
Engage in discussions, ask questions, and share your knowledge with others.
Read Books and Blogs:
Read books and blogs written by renowned Java experts to deepen your understanding of specific Java topics.
Stay updated with the latest trends, best practices, and emerging technologies in the Java ecosystem.
Take Online Courses and Tutorials:
Enroll in online courses or tutorials to learn advanced Java concepts, frameworks, and tools.
Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Pluralsight offer a wide range of Java courses taught by industry professionals.
Practice Continuous Learning:
Treat learning as an ongoing process. Dedicate time regularly to expand your Java knowledge and explore new technologies and techniques.
Stay curious, experiment with new ideas, and embrace continuous improvement.
Collaborate and Mentor Others:
Engage in developer communities, forums, or social media groups to share your knowledge and learn from others.
Mentor aspiring Java developers and help them navigate their learning journey.
Conclusion
In summary, the Java Certification Training Course, outlined in this step-by-step guide, presents a comprehensive and hands-on approach to mastering the Java programming language, equipping learners with both fundamental concepts and advanced skills. By blending theoretical knowledge with practical application and interactive assessments, this course not only fosters a deep understanding of Java but also nurtures problem-solving abilities and industry best practices. Ultimately, obtaining the Java certification through this training not only signifies technical proficiency but also a commitment to professional growth, making it an invaluable asset for aspiring and experienced developers seeking to excel in the dynamic landscape of software development.
Mongo Developer & Admin Certification: Unlock Potential.
Welcome to the world of opportunities and innovation in database management with the "Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification: Unlocking Your Professional Potential." This comprehensive program equips you with the skills to excel as a MongoDB Developer and Administrator, mastering data modeling, schema design, query optimization, and administration techniques. Seamlessly integrating MongoDB into applications, ensuring performance, scalability, and security, you'll tackle real-world challenges and open doors to exciting career prospects. Join us on this transformative journey towards unlocking your true professional potential in the realm of data innovation. Your future starts here.
Table of contents
What is Mongo Certification and Why is it Important?
Mongo Developer Certification
Mongo Administrator Certification
Requirements for Mongo Certification
Job Opportunities for Mongo Certified Professionals
Preparation Resources
Tips for Exam Success
Continuing Professional Development
Conclusion and Next Steps
What is Mongo Certification and Why is it Important?
Mongo Certification is a program that offers credentials for individuals who have demonstrated proficiency in using the Mongo platform. Mongo is a business intelligence and analytics platform that helps organizations to make data-driven decisions by providing powerful data analysis and visualization tools.
Mongo Certification is important for a number of reasons. Firstly, it provides a standardized way for employers to assess the proficiency of potential hires or current employees who are using the Mongo platform. This helps employers to identify skilled professionals who have the knowledge and skills required to use the platform effectively.
Additionally, Mongo Certification provides professionals with a competitive advantage in the job market. By earning a Mongo Certification, professionals demonstrate their commitment to staying up-to-date with the latest technology and their dedication to continuous learning and improvement. This can help them to stand out from other candidates who do not have the same level of certification or experience.
Finally, Mongo Certification can also lead to increased earning potential. Certified professionals are often able to command higher salaries than those who are not certified, as they are seen as more valuable to employers due to their demonstrated expertise in the Mongo platform.
Mongo Developer Certification
Mongo Developer Certification is a program that provides credentials for individuals who have demonstrated proficiency in developing solutions using the Mongo platform. The certification program is designed for developers who work with Mongo to create custom applications, dashboards, reports, and other solutions.
To become Mongo Developer certified, individuals must pass a certification exam that tests their knowledge and skills in several areas, including:
Mongo Data Modeling - This section tests the candidate's ability to create and optimize data models in Mongo.
Data Integration - This section tests the candidate's knowledge of how to connect Mongo to various data sources and integrate them into Mongo solutions.
Application Development - This section tests the candidate's ability to design and develop custom applications using Mongo APIs and SDKs.
Dashboard Development - This section tests the candidate's ability to create and customize dashboards in Mongo.
Report Development - This section tests the candidate's ability to create and customize reports in Mongo.
To prepare for the Mongo Developer certification exam, candidates can take advantage of the official Mongo Developer Certification study materials and resources, including online training courses, documentation, and community support.
Mongo Administrator Certification
Mongo Administrator Certification is a program that provides credentials for individuals who have demonstrated proficiency in administering and managing the Mongo platform. The certification program is designed for administrators who are responsible for deploying, configuring, and maintaining Mongo systems.
To become Mongo Administrator certified, individuals must pass a certification exam that tests their knowledge and skills in several areas, including:
Mongo Installation and Configuration - This section tests the candidate's ability to install, configure, and upgrade Mongo systems.
User Management - This section tests the candidate's ability to manage user accounts, permissions, and security settings in Mongo.
Backup and Recovery - This section tests the candidate's knowledge of how to perform backups, restore data, and manage disaster recovery in Mongo.
Performance Optimization - This section tests the candidate's ability to optimize Mongo systems for performance, including configuring caching, tuning database settings, and monitoring system performance.
Security and Compliance - This section tests the candidate's knowledge of security best practices and compliance requirements for Mongo systems.
To prepare for the Mongo Administrator certification exam, candidates can take advantage of the official Mongo Administrator Certification study materials and resources, including online training courses, documentation, and community support.
Requirements for Mongo Certification
To become Mongo certified, individuals must meet certain requirements, including:
Prerequisites - For Mongo Developer certification, candidates should have experience developing solutions using the Mongo platform and have a basic understanding of data modeling, data integration, and dashboard and report development. For Mongo Administrator certification, candidates should have experience administering and managing Mongo systems and have a basic understanding of Mongo installation, configuration, security, and performance optimization.
Mongo Certification Exam - To become certified, individuals must pass a certification exam that tests their knowledge and skills in the relevant Mongo certification areas. The certification exam is administered online and consists of multiple-choice questions.
Certification Renewal - Mongo certifications are valid for a period of two years. To maintain their certification, individuals must complete the Mongo Certification Renewal Program, which includes continuing education, participation in online forums and events, and the completion of a renewal exam.
It's important to note that while Mongo recommends certain prerequisites for certification, there are no strict requirements for taking the certification exams. Anyone with an interest in becoming Mongo certified can take the exams, but individuals who do not meet the prerequisites may need to spend additional time preparing for the exam.
Job Opportunities for Mongo Certified Professionals
There are several job opportunities available for Mongo certified professionals, including:
Mongo Developer - As a Mongo Developer, certified professionals can work with clients to develop custom applications, dashboards, and reports using Mongo APIs and SDKs.
Mongo Administrator - As a Mongo Administrator, certified professionals can be responsible for deploying, configuring, and maintaining Mongo systems, managing users and permissions, and ensuring the security and compliance of the system.
Business Intelligence Analyst - Mongo certified professionals can work as a business intelligence analyst, analyzing data and creating reports and dashboards to help businesses make informed decisions.
Data Engineer - Mongo certified professionals can work as data engineers, designing and building data pipelines to integrate and transform data from various sources.
Data Architect - Mongo certified professionals can work as data architects, designing and implementing data models and data structures to optimize data management and analytics.
Preparation Resources
Official Documentation: Start by referring to the official documentation provided by Mongo. This documentation usually includes user guides, tutorials, and reference materials that cover various aspects of the Mongo platform.
Online Courses and Training Programs:
Mongo University: Mongo offers its own training programs and courses designed to prepare individuals for the certification exam. These courses cover topics such as data modeling, building applications, analytics, and administration. Check their website for available courses.
Third-party Training Providers: Look for reputable training providers that offer specific Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification courses. These providers may offer comprehensive training materials, video tutorials, practice exams, and hands-on exercises.
Practice Exams and Mock Tests:
Mongo Certification Exam Simulator: Look for mock tests or practice exams specifically designed for the Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification. These resources can help you familiarize yourself with the exam format, types of questions, and time management.
Online Platforms: Explore online platforms that offer practice exams and quizzes related to Mongo and its functionalities. These platforms may have user-contributed content and can help you assess your knowledge and identify areas for improvement.
Online Communities and Forums:
Mongo Community: Join the Mongo community forums or discussion groups where you can interact with other Mongo users, including certified professionals. Engaging in discussions and asking questions can provide valuable insights and tips for the certification exam.
Stack Overflow: Look for Mongo-related questions and discussions on Stack Overflow, a popular community platform for developers. This platform often has threads related to Mongo development and administration, where you can learn from experienced professionals.
Hands-on Experience:
Practice with Mongo: Gain hands-on experience by working on real-world scenarios using the Mongo platform. The more you experiment and build applications, the better you will understand the platform and its functionalities.
Personal Projects: Undertake personal projects where you can apply Mongo for data modeling, analytics, and administration. This practical experience will strengthen your skills and help you prepare for the certification exam.
Tips for Exam Success
Understand the Exam Format and Syllabus: Familiarize yourself with the exam structure, duration, and the topics that will be covered. Review the official exam syllabus and make sure you have a clear understanding of the areas you need to focus on during your preparation.
Create a Study Plan: Develop a study plan that outlines your preparation schedule leading up to the exam. Break down the topics into manageable chunks and allocate specific time slots for studying each topic. This will help you stay organized and ensure you cover all the necessary material.
Utilize Official Documentation: Make use of the official documentation provided by Mongo. Thoroughly study the user guides, tutorials, and reference materials to gain a comprehensive understanding of the Mongo platform and its functionalities.
Practice Hands-on Exercises: Engage in hands-on practice by building applications, working with data models, and exploring the various features of Mongo. Practical experience will help reinforce your understanding of the concepts and enhance your problem-solving skills.
Take Mock Exams: Practice with mock exams and sample questions to familiarize yourself with the exam format and assess your knowledge. This will help you get comfortable with the types of questions that may be asked and improve your time management skills.
Identify Weak Areas: Regularly assess your knowledge and identify any weak areas where you need to put in extra effort. Focus on understanding these topics in depth and seek additional resources or guidance if needed.
Join Study Groups or Communities: Connect with other individuals preparing for the same certification or certified professionals in Mongo-related communities or forums. Engaging in discussions, sharing insights, and seeking guidance from others can provide valuable support and help you gain new perspectives.
Time Management during the Exam: During the exam, manage your time wisely. Read the instructions carefully, allocate appropriate time to each question, and avoid spending too much time on a single question. If you get stuck on a question, make a note and come back to it later.
Stay Calm and Confident: Maintain a positive mindset and stay calm during the exam. Don't panic if you encounter challenging questions. Trust in your preparation and focus on answering the questions to the best of your ability.
Review and Revise: Set aside time for revision before the exam. Review the key concepts, important formulas, and any notes you have taken during your preparation. Consolidate your knowledge and ensure you have a solid understanding of the material.
Continuing Professional Development
Importance of CPD: CPD ensures that professionals stay up-to-date with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices in their field. It helps them maintain and improve their competence, enabling them to deliver high-quality work and provide value to their organizations and clients.
Ongoing Learning Opportunities: CPD provides various avenues for professionals to engage in continuous learning. These opportunities may include attending conferences, workshops, seminars, webinars, and industry-specific events. It also involves reading industry publications, research papers, and staying updated with relevant news and developments.
Skill Enhancement: CPD allows professionals to broaden their skill set and acquire new competencies. It may involve learning new programming languages, tools, methodologies, or gaining expertise in specific areas of their profession. This continuous learning ensures professionals can tackle new challenges and take on more complex projects.
Professional Certifications: Pursuing additional professional certifications is an important aspect of CPD. These certifications validate and recognize a professional's expertise in a particular domain. They demonstrate commitment to professional growth and can enhance career prospects.
Networking and Collaboration: CPD activities often provide opportunities to network and collaborate with peers and industry experts. Engaging with like-minded professionals can foster knowledge sharing, idea exchange, and potential collaborations on projects or research initiatives.
Reflective Practice: CPD involves reflective practice, which encourages professionals to evaluate their own work, identify areas for improvement, and set goals for their professional development. Reflecting on past experiences helps in recognizing strengths and weaknesses and guides the focus of future learning efforts.
Industry Associations and Communities: Joining industry associations and professional communities is a valuable way to engage in CPD. These organizations offer access to resources, events, discussion forums, and networking opportunities specifically tailored to a profession or industry.
Online Learning Platforms: Utilize online learning platforms that offer a wide range of courses, tutorials, and educational resources. These platforms often provide flexibility in terms of timing and content selection, allowing professionals to learn at their own pace and convenience.
Mentorship and Coaching: Engaging in mentorship or coaching relationships can greatly contribute to CPD. Experienced mentors or coaches provide guidance, advice, and support based on their expertise and can help professionals navigate challenges and accelerate their learning journey.
Setting Personal Development Goals: As part of CPD, professionals should set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for their personal development. These goals can focus on acquiring new skills, gaining industry-specific knowledge, or achieving specific milestones in their careers.
How to obtain Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Development : Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, Mongo Certification is a valuable program that provides credentials for individuals who have demonstrated proficiency in developing and administering Mongo solutions. The Mongo Developer Certification is designed for professionals who develop solutions using the Mongo platform, while the Mongo Administrator Certification is designed for professionals who administer and manage Mongo systems.
By becoming Mongo certified, professionals can demonstrate their expertise in Mongo development or administration, which can lead to increased job opportunities, higher salaries, and career advancement. Additionally, Mongo certification provides professionals with a recognized standard of proficiency in Mongo, which can help them to stand out in the job market and demonstrate their commitment to continuous learning and professional development.
If you are interested in becoming Mongo certified, your next steps should include reviewing the certification requirements and prerequisites, preparing for the certification exam using official study materials and resources, and scheduling and taking the certification exam. Once you have become Mongo certified, you should also make sure to maintain your certification by completing the renewal process every two years.
Read More
Welcome to the world of opportunities and innovation in database management with the "Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification: Unlocking Your Professional Potential." This comprehensive program equips you with the skills to excel as a MongoDB Developer and Administrator, mastering data modeling, schema design, query optimization, and administration techniques. Seamlessly integrating MongoDB into applications, ensuring performance, scalability, and security, you'll tackle real-world challenges and open doors to exciting career prospects. Join us on this transformative journey towards unlocking your true professional potential in the realm of data innovation. Your future starts here.
Table of contents
What is Mongo Certification and Why is it Important?
Mongo Developer Certification
Mongo Administrator Certification
Requirements for Mongo Certification
Job Opportunities for Mongo Certified Professionals
Preparation Resources
Tips for Exam Success
Continuing Professional Development
Conclusion and Next Steps
What is Mongo Certification and Why is it Important?
Mongo Certification is a program that offers credentials for individuals who have demonstrated proficiency in using the Mongo platform. Mongo is a business intelligence and analytics platform that helps organizations to make data-driven decisions by providing powerful data analysis and visualization tools.
Mongo Certification is important for a number of reasons. Firstly, it provides a standardized way for employers to assess the proficiency of potential hires or current employees who are using the Mongo platform. This helps employers to identify skilled professionals who have the knowledge and skills required to use the platform effectively.
Additionally, Mongo Certification provides professionals with a competitive advantage in the job market. By earning a Mongo Certification, professionals demonstrate their commitment to staying up-to-date with the latest technology and their dedication to continuous learning and improvement. This can help them to stand out from other candidates who do not have the same level of certification or experience.
Finally, Mongo Certification can also lead to increased earning potential. Certified professionals are often able to command higher salaries than those who are not certified, as they are seen as more valuable to employers due to their demonstrated expertise in the Mongo platform.
Mongo Developer Certification
Mongo Developer Certification is a program that provides credentials for individuals who have demonstrated proficiency in developing solutions using the Mongo platform. The certification program is designed for developers who work with Mongo to create custom applications, dashboards, reports, and other solutions.
To become Mongo Developer certified, individuals must pass a certification exam that tests their knowledge and skills in several areas, including:
Mongo Data Modeling - This section tests the candidate's ability to create and optimize data models in Mongo.
Data Integration - This section tests the candidate's knowledge of how to connect Mongo to various data sources and integrate them into Mongo solutions.
Application Development - This section tests the candidate's ability to design and develop custom applications using Mongo APIs and SDKs.
Dashboard Development - This section tests the candidate's ability to create and customize dashboards in Mongo.
Report Development - This section tests the candidate's ability to create and customize reports in Mongo.
To prepare for the Mongo Developer certification exam, candidates can take advantage of the official Mongo Developer Certification study materials and resources, including online training courses, documentation, and community support.
Mongo Administrator Certification
Mongo Administrator Certification is a program that provides credentials for individuals who have demonstrated proficiency in administering and managing the Mongo platform. The certification program is designed for administrators who are responsible for deploying, configuring, and maintaining Mongo systems.
To become Mongo Administrator certified, individuals must pass a certification exam that tests their knowledge and skills in several areas, including:
Mongo Installation and Configuration - This section tests the candidate's ability to install, configure, and upgrade Mongo systems.
User Management - This section tests the candidate's ability to manage user accounts, permissions, and security settings in Mongo.
Backup and Recovery - This section tests the candidate's knowledge of how to perform backups, restore data, and manage disaster recovery in Mongo.
Performance Optimization - This section tests the candidate's ability to optimize Mongo systems for performance, including configuring caching, tuning database settings, and monitoring system performance.
Security and Compliance - This section tests the candidate's knowledge of security best practices and compliance requirements for Mongo systems.
To prepare for the Mongo Administrator certification exam, candidates can take advantage of the official Mongo Administrator Certification study materials and resources, including online training courses, documentation, and community support.
Requirements for Mongo Certification
To become Mongo certified, individuals must meet certain requirements, including:
Prerequisites - For Mongo Developer certification, candidates should have experience developing solutions using the Mongo platform and have a basic understanding of data modeling, data integration, and dashboard and report development. For Mongo Administrator certification, candidates should have experience administering and managing Mongo systems and have a basic understanding of Mongo installation, configuration, security, and performance optimization.
Mongo Certification Exam - To become certified, individuals must pass a certification exam that tests their knowledge and skills in the relevant Mongo certification areas. The certification exam is administered online and consists of multiple-choice questions.
Certification Renewal - Mongo certifications are valid for a period of two years. To maintain their certification, individuals must complete the Mongo Certification Renewal Program, which includes continuing education, participation in online forums and events, and the completion of a renewal exam.
It's important to note that while Mongo recommends certain prerequisites for certification, there are no strict requirements for taking the certification exams. Anyone with an interest in becoming Mongo certified can take the exams, but individuals who do not meet the prerequisites may need to spend additional time preparing for the exam.
Job Opportunities for Mongo Certified Professionals
There are several job opportunities available for Mongo certified professionals, including:
Mongo Developer - As a Mongo Developer, certified professionals can work with clients to develop custom applications, dashboards, and reports using Mongo APIs and SDKs.
Mongo Administrator - As a Mongo Administrator, certified professionals can be responsible for deploying, configuring, and maintaining Mongo systems, managing users and permissions, and ensuring the security and compliance of the system.
Business Intelligence Analyst - Mongo certified professionals can work as a business intelligence analyst, analyzing data and creating reports and dashboards to help businesses make informed decisions.
Data Engineer - Mongo certified professionals can work as data engineers, designing and building data pipelines to integrate and transform data from various sources.
Data Architect - Mongo certified professionals can work as data architects, designing and implementing data models and data structures to optimize data management and analytics.
Preparation Resources
Official Documentation: Start by referring to the official documentation provided by Mongo. This documentation usually includes user guides, tutorials, and reference materials that cover various aspects of the Mongo platform.
Online Courses and Training Programs:
Mongo University: Mongo offers its own training programs and courses designed to prepare individuals for the certification exam. These courses cover topics such as data modeling, building applications, analytics, and administration. Check their website for available courses.
Third-party Training Providers: Look for reputable training providers that offer specific Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification courses. These providers may offer comprehensive training materials, video tutorials, practice exams, and hands-on exercises.
Practice Exams and Mock Tests:
Mongo Certification Exam Simulator: Look for mock tests or practice exams specifically designed for the Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification. These resources can help you familiarize yourself with the exam format, types of questions, and time management.
Online Platforms: Explore online platforms that offer practice exams and quizzes related to Mongo and its functionalities. These platforms may have user-contributed content and can help you assess your knowledge and identify areas for improvement.
Online Communities and Forums:
Mongo Community: Join the Mongo community forums or discussion groups where you can interact with other Mongo users, including certified professionals. Engaging in discussions and asking questions can provide valuable insights and tips for the certification exam.
Stack Overflow: Look for Mongo-related questions and discussions on Stack Overflow, a popular community platform for developers. This platform often has threads related to Mongo development and administration, where you can learn from experienced professionals.
Hands-on Experience:
Practice with Mongo: Gain hands-on experience by working on real-world scenarios using the Mongo platform. The more you experiment and build applications, the better you will understand the platform and its functionalities.
Personal Projects: Undertake personal projects where you can apply Mongo for data modeling, analytics, and administration. This practical experience will strengthen your skills and help you prepare for the certification exam.
Tips for Exam Success
Understand the Exam Format and Syllabus: Familiarize yourself with the exam structure, duration, and the topics that will be covered. Review the official exam syllabus and make sure you have a clear understanding of the areas you need to focus on during your preparation.
Create a Study Plan: Develop a study plan that outlines your preparation schedule leading up to the exam. Break down the topics into manageable chunks and allocate specific time slots for studying each topic. This will help you stay organized and ensure you cover all the necessary material.
Utilize Official Documentation: Make use of the official documentation provided by Mongo. Thoroughly study the user guides, tutorials, and reference materials to gain a comprehensive understanding of the Mongo platform and its functionalities.
Practice Hands-on Exercises: Engage in hands-on practice by building applications, working with data models, and exploring the various features of Mongo. Practical experience will help reinforce your understanding of the concepts and enhance your problem-solving skills.
Take Mock Exams: Practice with mock exams and sample questions to familiarize yourself with the exam format and assess your knowledge. This will help you get comfortable with the types of questions that may be asked and improve your time management skills.
Identify Weak Areas: Regularly assess your knowledge and identify any weak areas where you need to put in extra effort. Focus on understanding these topics in depth and seek additional resources or guidance if needed.
Join Study Groups or Communities: Connect with other individuals preparing for the same certification or certified professionals in Mongo-related communities or forums. Engaging in discussions, sharing insights, and seeking guidance from others can provide valuable support and help you gain new perspectives.
Time Management during the Exam: During the exam, manage your time wisely. Read the instructions carefully, allocate appropriate time to each question, and avoid spending too much time on a single question. If you get stuck on a question, make a note and come back to it later.
Stay Calm and Confident: Maintain a positive mindset and stay calm during the exam. Don't panic if you encounter challenging questions. Trust in your preparation and focus on answering the questions to the best of your ability.
Review and Revise: Set aside time for revision before the exam. Review the key concepts, important formulas, and any notes you have taken during your preparation. Consolidate your knowledge and ensure you have a solid understanding of the material.
Continuing Professional Development
Importance of CPD: CPD ensures that professionals stay up-to-date with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices in their field. It helps them maintain and improve their competence, enabling them to deliver high-quality work and provide value to their organizations and clients.
Ongoing Learning Opportunities: CPD provides various avenues for professionals to engage in continuous learning. These opportunities may include attending conferences, workshops, seminars, webinars, and industry-specific events. It also involves reading industry publications, research papers, and staying updated with relevant news and developments.
Skill Enhancement: CPD allows professionals to broaden their skill set and acquire new competencies. It may involve learning new programming languages, tools, methodologies, or gaining expertise in specific areas of their profession. This continuous learning ensures professionals can tackle new challenges and take on more complex projects.
Professional Certifications: Pursuing additional professional certifications is an important aspect of CPD. These certifications validate and recognize a professional's expertise in a particular domain. They demonstrate commitment to professional growth and can enhance career prospects.
Networking and Collaboration: CPD activities often provide opportunities to network and collaborate with peers and industry experts. Engaging with like-minded professionals can foster knowledge sharing, idea exchange, and potential collaborations on projects or research initiatives.
Reflective Practice: CPD involves reflective practice, which encourages professionals to evaluate their own work, identify areas for improvement, and set goals for their professional development. Reflecting on past experiences helps in recognizing strengths and weaknesses and guides the focus of future learning efforts.
Industry Associations and Communities: Joining industry associations and professional communities is a valuable way to engage in CPD. These organizations offer access to resources, events, discussion forums, and networking opportunities specifically tailored to a profession or industry.
Online Learning Platforms: Utilize online learning platforms that offer a wide range of courses, tutorials, and educational resources. These platforms often provide flexibility in terms of timing and content selection, allowing professionals to learn at their own pace and convenience.
Mentorship and Coaching: Engaging in mentorship or coaching relationships can greatly contribute to CPD. Experienced mentors or coaches provide guidance, advice, and support based on their expertise and can help professionals navigate challenges and accelerate their learning journey.
Setting Personal Development Goals: As part of CPD, professionals should set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for their personal development. These goals can focus on acquiring new skills, gaining industry-specific knowledge, or achieving specific milestones in their careers.
How to obtain Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Development : Mongo Developer and Administrator Certification
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, Mongo Certification is a valuable program that provides credentials for individuals who have demonstrated proficiency in developing and administering Mongo solutions. The Mongo Developer Certification is designed for professionals who develop solutions using the Mongo platform, while the Mongo Administrator Certification is designed for professionals who administer and manage Mongo systems.
By becoming Mongo certified, professionals can demonstrate their expertise in Mongo development or administration, which can lead to increased job opportunities, higher salaries, and career advancement. Additionally, Mongo certification provides professionals with a recognized standard of proficiency in Mongo, which can help them to stand out in the job market and demonstrate their commitment to continuous learning and professional development.
If you are interested in becoming Mongo certified, your next steps should include reviewing the certification requirements and prerequisites, preparing for the certification exam using official study materials and resources, and scheduling and taking the certification exam. Once you have become Mongo certified, you should also make sure to maintain your certification by completing the renewal process every two years.
A Comprehensive Guide to Angular 4 Training Certification
Welcome to "A Comprehensive Guide to Angular 4 Training Certification." In this all-encompassing resource, we will explore the ins and outs of Angular 4, the dynamic JavaScript framework revolutionizing web development. From grasping fundamental concepts to mastering advanced functionalities, we'll empower you to build dynamic and responsive user interfaces, streamline data management, and elevate your web development skills. Moreover, we'll guide you on the path to obtaining an Angular 4 training certification, providing expert insights and hands-on exercises to ensure you're well-equipped to showcase your expertise and excel in your web development journey. Embark on this enlightening expedition and kickstart your career as a certified Angular 4 developer today.
Table of contents
Introduction to Angular 4
Benefits of Angular 4 Certification
Angular 4 Training Programs
Training Duration and Modes
Exam Preparation Strategies
Benefits of Certification for Employers
Success Stories
Continuing Education and Beyond
Conclusion
Introduction to Angular 4
Angular 4 is a popular and widely used JavaScript framework for building dynamic web applications. It is the successor to AngularJS (Angular 1.x) and is known for its powerful features, performance improvements, and enhanced developer experience. Released in March 2017, Angular 4 brought several significant updates and enhancements to its predecessor, making it a preferred choice for modern web development.
Key Features of Angular 4:
TypeScript: Angular 4 is built with TypeScript, a statically-typed superset of JavaScript. TypeScript offers enhanced tooling, better code organization, and improved maintainability by providing features like static typing, classes, modules, and interfaces.
Component-Based Architecture: Angular 4 follows a component-based architecture, where the application is built by combining reusable and independent components. Components encapsulate the application's logic, structure, and presentation, making it easier to manage and maintain the codebase.
Reactive Programming: Angular 4 leverages the power of reactive programming through its built-in support for Reactive Extensions (RxJS). Reactive programming enables efficient handling of asynchronous events, such as user interactions and data streams, by utilizing observables and operators.
Enhanced Performance: Angular 4 introduced several optimizations that improved the framework's performance. These optimizations include faster view rendering, reduced bundle sizes, improved change detection mechanisms, and enhanced tree shaking for more efficient production builds.
Angular CLI: Angular 4 introduced the Angular Command Line Interface (CLI), a powerful tool that simplifies the development process. The CLI provides commands for generating components, services, modules, and other artifacts, as well as features like code scaffolding, testing utilities, and build optimization.
Improved Template Syntax: Angular 4 introduced a streamlined template syntax that offers a more concise and expressive way to write templates. It introduced the "ngIf" and "ngFor" structural directives with enhanced capabilities, making it easier to conditionally render elements and iterate over collections.
Dependency Injection: Angular 4 includes a robust dependency injection (DI) system that helps manage the application's components and their dependencies. DI allows for loosely coupled and reusable code, promoting modularity and testability.
Mobile Development: Angular 4 provides extensive support for building mobile applications. It includes features like responsive design capabilities, touch gestures, and performance optimizations for mobile devices.
Seamless Upgrading: Angular 4 was designed to facilitate a smooth upgrade path for developers using AngularJS or older versions of Angular. The Angular team provided tools and guidelines to help migrate existing applications to Angular 4, making the transition easier
Benefits of Angular 4 Certification
Obtaining an Angular 4 certification can bring several benefits to both individual developers and organizations. Here are some key advantages of Angular 4 certification:
Validation of Skills: Angular 4 certification serves as a validation of your skills and expertise in using the framework. It demonstrates to potential employers or clients that you possess the necessary knowledge and proficiency to develop high-quality Angular applications.
Career Advancement: Having an Angular 4 certification can significantly enhance your career prospects. It can open up new job opportunities and increase your marketability as Angular 4 is widely used in the industry. Certified professionals often have a competitive edge over non-certified candidates in the job market.
Industry Recognition: Angular 4 certification is typically provided by reputable organizations or the official Angular team. Being certified by recognized entities adds credibility to your profile and showcases your commitment to professional growth and excellence in Angular development.
Enhanced Skill Set: The process of preparing for an Angular 4 certification exam requires in-depth learning and understanding of the framework. It enables you to gain a comprehensive knowledge of Angular 4 concepts, best practices, and advanced features. This expanded skill set can make you more versatile and proficient in developing complex Angular applications.
Keeping Up with Latest Updates: Angular is a rapidly evolving framework, and new versions and updates are released regularly. By pursuing an Angular 4 certification, you stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in Angular development. It ensures that you are knowledgeable about the features and improvements introduced in Angular 4 and can effectively utilize them in your projects.
Networking Opportunities: Certification programs often provide opportunities to connect and interact with a community of Angular developers. This networking can lead to valuable professional connections, collaboration, and knowledge sharing. It allows you to engage with experts, mentors, and like-minded individuals who can support your growth in the Angular ecosystem.
Confidence and Trust: Earning an Angular 4 certification boosts your confidence in your abilities as a developer. It gives you the assurance that you have acquired the necessary skills to tackle complex Angular projects successfully. Clients and employers also tend to have more trust in certified professionals, as they demonstrate a higher level of expertise and competence.
Organizational Benefits: Organizations that employ Angular 4 certified professionals can experience several advantages. Certified developers bring a deep understanding of Angular best practices, which can result in more efficient development processes, improved code quality, and reduced maintenance efforts. Angular 4 certification can also be beneficial for organizations when bidding on projects or acquiring new clients, as it showcases the expertise and competency of their development team.
Angular 4 Training Programs
When it comes to Angular 4 training programs, there are various options available to suit different learning preferences and schedules. Here are some common types of Angular 4 training programs:
Online Courses: Online courses provide the flexibility to learn Angular 4 at your own pace and convenience. These courses typically consist of video lectures, coding exercises, quizzes, and assignments. They may also include access to a community or instructor support. Website like iCert Global offer a wide range of Angular 4 online courses.
Instructor-Led Live Online Training: Live online training programs provide a structured learning experience with real-time interaction with instructors. These programs usually involve scheduled classes conducted through video conferencing tools. Participants can ask questions, participate in discussions, and receive guidance from experienced instructors. Platforms like edX, Simplilearn, and BitDegree offer instructor-led live online training for Angular 4.
Bootcamps: Angular 4 bootcamps are intensive, short-term training programs designed to quickly immerse participants in Angular development. These programs are usually full-time and offer an immersive learning experience with hands-on projects and practical exercises. Bootcamps often focus on rapid skill acquisition and may include career support services. Some well-known Angular bootcamps include Le Wagon, General Assembly, and Ironhack.
Workshops and Webinars: Angular 4 workshops and webinars are shorter, focused training sessions that cover specific topics or aspects of Angular 4. These programs are often conducted by industry experts or organizations and may be offered as standalone sessions or as part of conferences or events. Workshops and webinars provide an opportunity to learn from experts, gain practical insights, and ask specific questions related to Angular 4.
In-Person Classroom Training: In-person classroom training programs allow participants to attend physical training sessions conducted by instructors at training centers or educational institutions. These programs provide a structured learning environment with hands-on exercises, group discussions, and real-time interaction with instructors. In-person training may be suitable for those who prefer face-to-face interaction and structured learning.
Training Duration and Modes
The duration and modes of Angular 4 training programs can vary depending on the training provider, the level of the program, and the specific learning objectives. Here are some common training durations and modes for Angular 4 training:
Full-Time Intensive Training: Full-time Angular 4 training programs are immersive and intensive, typically lasting between 2 to 12 weeks. These programs require a full-time commitment from participants, usually from Monday to Friday, with several hours of instruction and hands-on exercises each day. Full-time training programs are suitable for individuals who can dedicate their time solely to the training and want to learn Angular 4 quickly.
Part-Time Training: Part-time Angular 4 training programs are designed for individuals who may have other commitments such as work or studies. These programs usually have flexible schedules, with classes conducted in the evenings or on weekends. The duration of part-time training can range from a few weeks to a few months, depending on the program. Part-time training allows participants to learn Angular 4 at a slower pace while balancing their other responsibilities.
Self-Paced Learning: Some Angular 4 training programs offer self-paced learning options, allowing participants to learn at their own convenience. These programs provide access to pre-recorded video lectures, tutorials, and learning resources that participants can access and progress through at their own pace. Self-paced learning is ideal for individuals who prefer flexibility in their learning schedule and want to learn Angular 4 at their own speed.
Blended Learning: Blended learning combines online and in-person components to provide a flexible and interactive learning experience. It may involve a combination of online video lectures and assignments, along with periodic in-person workshops or mentoring sessions. Blended learning programs offer the benefits of both online and in-person training, providing flexibility while also allowing for face-to-face interaction and guidance.
Obtaining an industry-recognized certification in Angular 4 demonstrates your proficiency and expertise in the framework. While there are no specific certification exams exclusively for Angular 4, there are some certifications that cover Angular and web development in general. Here are a few industry-recognized certification exams that can validate your Angular 4 skills:
Microsoft Certified: Azure Developer Associate: This certification validates the skills and knowledge required to develop and deploy applications on Microsoft Azure. It includes topics such as creating and managing Azure App Service resources, implementing authentication and securing data, and integrating with Azure services. Since Angular can be used in conjunction with Azure for web application development, this certification can be valuable for Angular developers.
Oracle Certified Professional, Java SE 8 Programmer: While this certification focuses on Java programming, it is relevant to Angular development as Angular is often used in conjunction with Java for building enterprise applications. This certification validates your understanding of Java programming concepts and techniques, which are beneficial for Angular development.
AWS Certified Developer - Associate: This certification is for developers who work with Amazon Web Services (AWS) and demonstrates proficiency in designing, developing, and deploying applications on the AWS platform. As Angular applications can be hosted and deployed on AWS, this certification can be valuable for Angular developers working in AWS environments.
Google Cloud Certified - Professional Cloud Developer: This certification validates the skills and knowledge required to develop and deploy applications on the Google Cloud Platform (GCP). While not specifically focused on Angular, it covers topics such as application development, deploying applications, integrating Google Cloud services, and working with APIs, which can be relevant to Angular developers using GCP.
It's important to note that while these certifications may not be Angular-specific, they can still provide valuable recognition of your skills and knowledge in web development and related technologies. Additionally, the Angular team and Google do not currently offer official certifications specifically for Angular 4 or later versions. However, they provide learning resources, documentation, and tutorials that can help you gain expertise in Angular development.
Exam Preparation Strategies
Preparing for an exam, including Angular 4-related certifications, requires a systematic approach and effective study strategies. Here are some exam preparation strategies to help you maximize your chances of success:
Understand the Exam Objectives: Familiarize yourself with the exam objectives and topics outlined by the certification program. This will help you understand what areas to focus on during your preparation and ensure you cover all the necessary content.
Create a Study Plan: Develop a study plan that outlines your study schedule, including specific topics to cover and milestones to achieve. Break down your study sessions into manageable chunks and allocate time for reviewing and practicing.
Gather Study Materials: Gather relevant study materials, such as textbooks, online resources, tutorials, practice exams, and official documentation. Ensure that the resources you choose cover the exam objectives and provide comprehensive coverage of Angular 4 concepts.
Hands-on Practice: Angular 4 is best learned through hands-on practice. Allocate time for practical coding exercises and projects to reinforce your understanding of Angular concepts. Implement different features and functionalities using Angular 4 to gain practical experience.
Review Documentation and Official Guides: Explore the official Angular documentation and guides provided by the Angular team. These resources offer in-depth explanations, examples, and best practices. Understanding the official documentation can help you solidify your knowledge and ensure you are following recommended approaches.
Take Practice Exams: Practice exams are valuable in familiarizing yourself with the exam format and assessing your knowledge. Look for sample exams or practice tests specifically designed for Angular 4 or related certifications. Analyze your performance, identify areas of weakness, and focus on improving those areas through further study and practice.
Join Study Groups or Forums: Engage in study groups or online forums where you can discuss concepts, ask questions, and learn from others preparing for the same exam. Sharing knowledge and collaborating with peers can enhance your understanding and provide additional insights.
Review and Reinforce Weak Areas: Continuously evaluate your progress and identify areas where you need further reinforcement. Spend extra time reviewing and practicing topics that you find challenging. Focus on understanding the underlying principles and practice applying them in different scenarios.
Simulate Exam Conditions: Prior to the actual exam, simulate exam conditions during your practice sessions. Set a timer, create a quiet and focused environment, and attempt practice exams or sample questions under timed conditions. This will help you develop time management skills and build confidence in your ability to complete the exam within the given time frame.
Stay Calm and Rest: As the exam day approaches, make sure to get adequate rest and manage your stress levels. Being well-rested and maintaining a calm mindset can improve your concentration and performance during the exam.
Benefits of Certification for Employers
Certifications in Angular 4 can offer several benefits to employers who are looking to hire skilled Angular developers or build a team with expertise in the framework. Here are some benefits of Angular 4 certifications for employers:
Assurance of Skills and Expertise: Angular 4 certifications provide employers with assurance that candidates possess the necessary skills and expertise in Angular development. Certified professionals have demonstrated their understanding of Angular 4 concepts, best practices, and industry-standard techniques. This helps employers ensure that their development team has the required knowledge to effectively work with Angular 4.
Improved Development Quality: Hiring certified Angular 4 professionals can contribute to improved development quality. Certified individuals have a deeper understanding of Angular's architecture, design patterns, and development principles. They are more likely to adhere to best practices, resulting in well-structured, maintainable, and scalable Angular applications.
Up-to-Date Knowledge: Angular certifications often require candidates to demonstrate knowledge of the latest version of Angular. By hiring certified professionals, employers can ensure that their development team is up to date with the latest features, enhancements, and best practices in Angular 4. This enables the team to leverage new functionalities and deliver cutting-edge solutions.
Time and Cost Savings: Certified Angular 4 professionals are equipped with the skills and knowledge to efficiently develop Angular applications. Their expertise can help streamline development processes, reduce coding errors, and optimize application performance. This can lead to time and cost savings for employers by accelerating project delivery and minimizing rework.
Enhanced Team Collaboration: Certifications provide a common language and framework for communication within the development team. Certified professionals share a standardized understanding of Angular 4 concepts, which facilitates collaboration, code reviews, and knowledge sharing among team members. This results in improved teamwork and more effective cooperation on Angular projects.
Competitive Advantage: Hiring certified Angular 4 professionals can give employers a competitive edge in the market. It demonstrates the organization's commitment to quality and technical excellence. Clients and stakeholders are more likely to trust an organization that has a team of certified Angular developers, which can enhance the organization's reputation and attract more business opportunities.
Professional Development Opportunities: Certifications often require ongoing professional development to maintain and renew the certification. This ensures that certified professionals stay updated with the latest advancements in Angular development. Employers can support their employees' professional growth by encouraging them to pursue certifications and providing resources for continuous learning.
Success Stories
Certainly! Here are a few success stories of individuals who have benefited from Angular 4 training and certification:
Sarah, a Front-End Developer: Sarah had a background in front-end development and wanted to enhance her skills in Angular. She enrolled in an Angular 4 training program and obtained certification. The certification helped her secure a new job as an Angular Developer at a leading tech company. With her Angular 4 knowledge, she contributed to the development of complex web applications and was recognized for her expertise in Angular. The certification boosted her career and opened up new opportunities for growth.
John, a Freelancer: John was a freelance web developer with experience in various frameworks. He decided to specialize in Angular 4 to attract more clients and work on larger-scale projects. After completing an Angular 4 training program and earning certification, John showcased his credentials on his freelance profile and updated his portfolio with Angular projects. As a result, he attracted higher-paying clients and was able to take on more challenging Angular development projects. The certification helped him establish credibility and build a successful freelance career focused on Angular 4.
Emily, a Career Switcher: Emily had a background in a non-technical field but was passionate about web development. She wanted to transition into a career as a web developer, with a focus on Angular. Emily enrolled in an intensive Angular 4 training program that provided hands-on projects and mentorship. After completing the program and obtaining certification, she started applying for entry-level Angular developer positions. The certification served as evidence of her commitment and proficiency in Angular 4, and she landed a job at a software development company. The certification played a crucial role in her successful career transition.
Mark, an Entrepreneur: Mark had an entrepreneurial spirit and wanted to start his own web development agency. He recognized the growing demand for Angular development and decided to invest in his skills. Mark enrolled in an Angular 4 training program and obtained certification. Armed with his Angular 4 knowledge, he established his web development agency and promoted his expertise in Angular. The certification helped him win clients and build a reputation for delivering high-quality Angular applications. Today, his agency is thriving, and he continues to expand his team of Angular developers.
Continuing Education and Beyond
Continuing education is crucial for professionals in the field of Angular development to stay updated with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices. Beyond Angular 4, there have been subsequent versions released, and it's important to keep learning and adapting to the evolving Angular ecosystem. Here are some options for continuing education and further career growth in Angular development:
Angular Updates and Documentation: Stay updated with the latest versions of Angular by regularly exploring the official Angular documentation and release notes. The Angular team continuously enhances and introduces new features, improvements, and updates. Understanding these updates and how they affect your development workflow is essential for staying current in Angular development.
Angular Conferences and Events: Attend Angular conferences, meetups, and workshops to learn from industry experts, hear about the latest Angular trends, and network with fellow developers. These events provide valuable insights, practical tips, and opportunities to connect with the Angular community. Examples of notable Angular conferences include ng-conf and AngularConnect.
Online Courses and Tutorials: Explore online platforms that offer Angular courses and tutorials. Websites like iCert Global offer a wide range of Angular courses taught by experienced instructors. These courses can help you deepen your knowledge, learn advanced techniques, and gain expertise in specific Angular topics such as Angular Material, performance optimization, or advanced routing.
Angular Certification Programs: Keep an eye out for any new Angular certification programs that may be introduced in the future. As the Angular ecosystem evolves, certification programs may be updated to cover newer versions and advanced concepts. Earning additional certifications can validate your expertise and demonstrate your commitment to continuous learning.
Open Source Contributions: Contribute to open source Angular projects to expand your skills and gain practical experience. Engaging with the Angular community through open source projects allows you to collaborate with other developers, learn from their expertise, and contribute to the improvement of Angular tools and libraries.
Personal Projects and Side Projects: Undertake personal projects or side projects that allow you to experiment with new Angular features or explore specific areas of interest. Building real-world applications on your own can provide hands-on experience and help you stay engaged with Angular development.
Blogging and Sharing Knowledge: Share your knowledge and experiences by writing blog posts, creating tutorials, or contributing to technical publications. This not only helps the Angular community but also allows you to solidify your understanding of Angular concepts by explaining them to others.
Continuous Professional Development: Stay curious and be open to learning new technologies and complementary skills. Angular development often goes hand-in-hand with technologies such as TypeScript, RxJS, and testing frameworks like Jasmine or Karma. Investing time in learning these related technologies can enhance your overall expertise and make you a well-rounded Angular developer.
How to obtain Angular4 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Development : Angular 4 Training Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, Angular 4 training and certification can be highly beneficial for individuals and organizations in the field of web development. By obtaining certification in Angular 4, developers can showcase their proficiency in the framework, enhance their career prospects, and open up new opportunities for growth.
Angular 4 certification provides individuals with a solid understanding of the framework's concepts, best practices, and development techniques. It demonstrates their ability to design, build, and maintain Angular 4 applications effectively. Employers can benefit from hiring certified Angular 4 professionals as they bring expertise, improved development quality, and up-to-date knowledge to their teams.
The success stories of professionals who have completed Angular 4 training and obtained certification highlight the positive impact it can have on their careers. They have experienced career advancements, higher earnings, and opportunities to work on exciting projects. Whether it's through securing new job roles, freelancing opportunities, career transitions, or entrepreneurial ventures, Angular 4 certification has empowered individuals to achieve their goals.
Continuing education and staying updated with the latest developments in Angular development is essential beyond Angular 4. Professionals should embrace ongoing learning through resources such as documentation updates, conferences, online courses, personal projects, open-source contributions, and continuous professional development. By doing so, they can stay competitive, adapt to the evolving Angular ecosystem, and continue to excel in their careers.
Read More
Welcome to "A Comprehensive Guide to Angular 4 Training Certification." In this all-encompassing resource, we will explore the ins and outs of Angular 4, the dynamic JavaScript framework revolutionizing web development. From grasping fundamental concepts to mastering advanced functionalities, we'll empower you to build dynamic and responsive user interfaces, streamline data management, and elevate your web development skills. Moreover, we'll guide you on the path to obtaining an Angular 4 training certification, providing expert insights and hands-on exercises to ensure you're well-equipped to showcase your expertise and excel in your web development journey. Embark on this enlightening expedition and kickstart your career as a certified Angular 4 developer today.
Table of contents
Introduction to Angular 4
Benefits of Angular 4 Certification
Angular 4 Training Programs
Training Duration and Modes
Exam Preparation Strategies
Benefits of Certification for Employers
Success Stories
Continuing Education and Beyond
Conclusion
Introduction to Angular 4
Angular 4 is a popular and widely used JavaScript framework for building dynamic web applications. It is the successor to AngularJS (Angular 1.x) and is known for its powerful features, performance improvements, and enhanced developer experience. Released in March 2017, Angular 4 brought several significant updates and enhancements to its predecessor, making it a preferred choice for modern web development.
Key Features of Angular 4:
TypeScript: Angular 4 is built with TypeScript, a statically-typed superset of JavaScript. TypeScript offers enhanced tooling, better code organization, and improved maintainability by providing features like static typing, classes, modules, and interfaces.
Component-Based Architecture: Angular 4 follows a component-based architecture, where the application is built by combining reusable and independent components. Components encapsulate the application's logic, structure, and presentation, making it easier to manage and maintain the codebase.
Reactive Programming: Angular 4 leverages the power of reactive programming through its built-in support for Reactive Extensions (RxJS). Reactive programming enables efficient handling of asynchronous events, such as user interactions and data streams, by utilizing observables and operators.
Enhanced Performance: Angular 4 introduced several optimizations that improved the framework's performance. These optimizations include faster view rendering, reduced bundle sizes, improved change detection mechanisms, and enhanced tree shaking for more efficient production builds.
Angular CLI: Angular 4 introduced the Angular Command Line Interface (CLI), a powerful tool that simplifies the development process. The CLI provides commands for generating components, services, modules, and other artifacts, as well as features like code scaffolding, testing utilities, and build optimization.
Improved Template Syntax: Angular 4 introduced a streamlined template syntax that offers a more concise and expressive way to write templates. It introduced the "ngIf" and "ngFor" structural directives with enhanced capabilities, making it easier to conditionally render elements and iterate over collections.
Dependency Injection: Angular 4 includes a robust dependency injection (DI) system that helps manage the application's components and their dependencies. DI allows for loosely coupled and reusable code, promoting modularity and testability.
Mobile Development: Angular 4 provides extensive support for building mobile applications. It includes features like responsive design capabilities, touch gestures, and performance optimizations for mobile devices.
Seamless Upgrading: Angular 4 was designed to facilitate a smooth upgrade path for developers using AngularJS or older versions of Angular. The Angular team provided tools and guidelines to help migrate existing applications to Angular 4, making the transition easier
Benefits of Angular 4 Certification
Obtaining an Angular 4 certification can bring several benefits to both individual developers and organizations. Here are some key advantages of Angular 4 certification:
Validation of Skills: Angular 4 certification serves as a validation of your skills and expertise in using the framework. It demonstrates to potential employers or clients that you possess the necessary knowledge and proficiency to develop high-quality Angular applications.
Career Advancement: Having an Angular 4 certification can significantly enhance your career prospects. It can open up new job opportunities and increase your marketability as Angular 4 is widely used in the industry. Certified professionals often have a competitive edge over non-certified candidates in the job market.
Industry Recognition: Angular 4 certification is typically provided by reputable organizations or the official Angular team. Being certified by recognized entities adds credibility to your profile and showcases your commitment to professional growth and excellence in Angular development.
Enhanced Skill Set: The process of preparing for an Angular 4 certification exam requires in-depth learning and understanding of the framework. It enables you to gain a comprehensive knowledge of Angular 4 concepts, best practices, and advanced features. This expanded skill set can make you more versatile and proficient in developing complex Angular applications.
Keeping Up with Latest Updates: Angular is a rapidly evolving framework, and new versions and updates are released regularly. By pursuing an Angular 4 certification, you stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in Angular development. It ensures that you are knowledgeable about the features and improvements introduced in Angular 4 and can effectively utilize them in your projects.
Networking Opportunities: Certification programs often provide opportunities to connect and interact with a community of Angular developers. This networking can lead to valuable professional connections, collaboration, and knowledge sharing. It allows you to engage with experts, mentors, and like-minded individuals who can support your growth in the Angular ecosystem.
Confidence and Trust: Earning an Angular 4 certification boosts your confidence in your abilities as a developer. It gives you the assurance that you have acquired the necessary skills to tackle complex Angular projects successfully. Clients and employers also tend to have more trust in certified professionals, as they demonstrate a higher level of expertise and competence.
Organizational Benefits: Organizations that employ Angular 4 certified professionals can experience several advantages. Certified developers bring a deep understanding of Angular best practices, which can result in more efficient development processes, improved code quality, and reduced maintenance efforts. Angular 4 certification can also be beneficial for organizations when bidding on projects or acquiring new clients, as it showcases the expertise and competency of their development team.
Angular 4 Training Programs
When it comes to Angular 4 training programs, there are various options available to suit different learning preferences and schedules. Here are some common types of Angular 4 training programs:
Online Courses: Online courses provide the flexibility to learn Angular 4 at your own pace and convenience. These courses typically consist of video lectures, coding exercises, quizzes, and assignments. They may also include access to a community or instructor support. Website like iCert Global offer a wide range of Angular 4 online courses.
Instructor-Led Live Online Training: Live online training programs provide a structured learning experience with real-time interaction with instructors. These programs usually involve scheduled classes conducted through video conferencing tools. Participants can ask questions, participate in discussions, and receive guidance from experienced instructors. Platforms like edX, Simplilearn, and BitDegree offer instructor-led live online training for Angular 4.
Bootcamps: Angular 4 bootcamps are intensive, short-term training programs designed to quickly immerse participants in Angular development. These programs are usually full-time and offer an immersive learning experience with hands-on projects and practical exercises. Bootcamps often focus on rapid skill acquisition and may include career support services. Some well-known Angular bootcamps include Le Wagon, General Assembly, and Ironhack.
Workshops and Webinars: Angular 4 workshops and webinars are shorter, focused training sessions that cover specific topics or aspects of Angular 4. These programs are often conducted by industry experts or organizations and may be offered as standalone sessions or as part of conferences or events. Workshops and webinars provide an opportunity to learn from experts, gain practical insights, and ask specific questions related to Angular 4.
In-Person Classroom Training: In-person classroom training programs allow participants to attend physical training sessions conducted by instructors at training centers or educational institutions. These programs provide a structured learning environment with hands-on exercises, group discussions, and real-time interaction with instructors. In-person training may be suitable for those who prefer face-to-face interaction and structured learning.
Training Duration and Modes
The duration and modes of Angular 4 training programs can vary depending on the training provider, the level of the program, and the specific learning objectives. Here are some common training durations and modes for Angular 4 training:
Full-Time Intensive Training: Full-time Angular 4 training programs are immersive and intensive, typically lasting between 2 to 12 weeks. These programs require a full-time commitment from participants, usually from Monday to Friday, with several hours of instruction and hands-on exercises each day. Full-time training programs are suitable for individuals who can dedicate their time solely to the training and want to learn Angular 4 quickly.
Part-Time Training: Part-time Angular 4 training programs are designed for individuals who may have other commitments such as work or studies. These programs usually have flexible schedules, with classes conducted in the evenings or on weekends. The duration of part-time training can range from a few weeks to a few months, depending on the program. Part-time training allows participants to learn Angular 4 at a slower pace while balancing their other responsibilities.
Self-Paced Learning: Some Angular 4 training programs offer self-paced learning options, allowing participants to learn at their own convenience. These programs provide access to pre-recorded video lectures, tutorials, and learning resources that participants can access and progress through at their own pace. Self-paced learning is ideal for individuals who prefer flexibility in their learning schedule and want to learn Angular 4 at their own speed.
Blended Learning: Blended learning combines online and in-person components to provide a flexible and interactive learning experience. It may involve a combination of online video lectures and assignments, along with periodic in-person workshops or mentoring sessions. Blended learning programs offer the benefits of both online and in-person training, providing flexibility while also allowing for face-to-face interaction and guidance.
Obtaining an industry-recognized certification in Angular 4 demonstrates your proficiency and expertise in the framework. While there are no specific certification exams exclusively for Angular 4, there are some certifications that cover Angular and web development in general. Here are a few industry-recognized certification exams that can validate your Angular 4 skills:
Microsoft Certified: Azure Developer Associate: This certification validates the skills and knowledge required to develop and deploy applications on Microsoft Azure. It includes topics such as creating and managing Azure App Service resources, implementing authentication and securing data, and integrating with Azure services. Since Angular can be used in conjunction with Azure for web application development, this certification can be valuable for Angular developers.
Oracle Certified Professional, Java SE 8 Programmer: While this certification focuses on Java programming, it is relevant to Angular development as Angular is often used in conjunction with Java for building enterprise applications. This certification validates your understanding of Java programming concepts and techniques, which are beneficial for Angular development.
AWS Certified Developer - Associate: This certification is for developers who work with Amazon Web Services (AWS) and demonstrates proficiency in designing, developing, and deploying applications on the AWS platform. As Angular applications can be hosted and deployed on AWS, this certification can be valuable for Angular developers working in AWS environments.
Google Cloud Certified - Professional Cloud Developer: This certification validates the skills and knowledge required to develop and deploy applications on the Google Cloud Platform (GCP). While not specifically focused on Angular, it covers topics such as application development, deploying applications, integrating Google Cloud services, and working with APIs, which can be relevant to Angular developers using GCP.
It's important to note that while these certifications may not be Angular-specific, they can still provide valuable recognition of your skills and knowledge in web development and related technologies. Additionally, the Angular team and Google do not currently offer official certifications specifically for Angular 4 or later versions. However, they provide learning resources, documentation, and tutorials that can help you gain expertise in Angular development.
Exam Preparation Strategies
Preparing for an exam, including Angular 4-related certifications, requires a systematic approach and effective study strategies. Here are some exam preparation strategies to help you maximize your chances of success:
Understand the Exam Objectives: Familiarize yourself with the exam objectives and topics outlined by the certification program. This will help you understand what areas to focus on during your preparation and ensure you cover all the necessary content.
Create a Study Plan: Develop a study plan that outlines your study schedule, including specific topics to cover and milestones to achieve. Break down your study sessions into manageable chunks and allocate time for reviewing and practicing.
Gather Study Materials: Gather relevant study materials, such as textbooks, online resources, tutorials, practice exams, and official documentation. Ensure that the resources you choose cover the exam objectives and provide comprehensive coverage of Angular 4 concepts.
Hands-on Practice: Angular 4 is best learned through hands-on practice. Allocate time for practical coding exercises and projects to reinforce your understanding of Angular concepts. Implement different features and functionalities using Angular 4 to gain practical experience.
Review Documentation and Official Guides: Explore the official Angular documentation and guides provided by the Angular team. These resources offer in-depth explanations, examples, and best practices. Understanding the official documentation can help you solidify your knowledge and ensure you are following recommended approaches.
Take Practice Exams: Practice exams are valuable in familiarizing yourself with the exam format and assessing your knowledge. Look for sample exams or practice tests specifically designed for Angular 4 or related certifications. Analyze your performance, identify areas of weakness, and focus on improving those areas through further study and practice.
Join Study Groups or Forums: Engage in study groups or online forums where you can discuss concepts, ask questions, and learn from others preparing for the same exam. Sharing knowledge and collaborating with peers can enhance your understanding and provide additional insights.
Review and Reinforce Weak Areas: Continuously evaluate your progress and identify areas where you need further reinforcement. Spend extra time reviewing and practicing topics that you find challenging. Focus on understanding the underlying principles and practice applying them in different scenarios.
Simulate Exam Conditions: Prior to the actual exam, simulate exam conditions during your practice sessions. Set a timer, create a quiet and focused environment, and attempt practice exams or sample questions under timed conditions. This will help you develop time management skills and build confidence in your ability to complete the exam within the given time frame.
Stay Calm and Rest: As the exam day approaches, make sure to get adequate rest and manage your stress levels. Being well-rested and maintaining a calm mindset can improve your concentration and performance during the exam.
Benefits of Certification for Employers
Certifications in Angular 4 can offer several benefits to employers who are looking to hire skilled Angular developers or build a team with expertise in the framework. Here are some benefits of Angular 4 certifications for employers:
Assurance of Skills and Expertise: Angular 4 certifications provide employers with assurance that candidates possess the necessary skills and expertise in Angular development. Certified professionals have demonstrated their understanding of Angular 4 concepts, best practices, and industry-standard techniques. This helps employers ensure that their development team has the required knowledge to effectively work with Angular 4.
Improved Development Quality: Hiring certified Angular 4 professionals can contribute to improved development quality. Certified individuals have a deeper understanding of Angular's architecture, design patterns, and development principles. They are more likely to adhere to best practices, resulting in well-structured, maintainable, and scalable Angular applications.
Up-to-Date Knowledge: Angular certifications often require candidates to demonstrate knowledge of the latest version of Angular. By hiring certified professionals, employers can ensure that their development team is up to date with the latest features, enhancements, and best practices in Angular 4. This enables the team to leverage new functionalities and deliver cutting-edge solutions.
Time and Cost Savings: Certified Angular 4 professionals are equipped with the skills and knowledge to efficiently develop Angular applications. Their expertise can help streamline development processes, reduce coding errors, and optimize application performance. This can lead to time and cost savings for employers by accelerating project delivery and minimizing rework.
Enhanced Team Collaboration: Certifications provide a common language and framework for communication within the development team. Certified professionals share a standardized understanding of Angular 4 concepts, which facilitates collaboration, code reviews, and knowledge sharing among team members. This results in improved teamwork and more effective cooperation on Angular projects.
Competitive Advantage: Hiring certified Angular 4 professionals can give employers a competitive edge in the market. It demonstrates the organization's commitment to quality and technical excellence. Clients and stakeholders are more likely to trust an organization that has a team of certified Angular developers, which can enhance the organization's reputation and attract more business opportunities.
Professional Development Opportunities: Certifications often require ongoing professional development to maintain and renew the certification. This ensures that certified professionals stay updated with the latest advancements in Angular development. Employers can support their employees' professional growth by encouraging them to pursue certifications and providing resources for continuous learning.
Success Stories
Certainly! Here are a few success stories of individuals who have benefited from Angular 4 training and certification:
Sarah, a Front-End Developer: Sarah had a background in front-end development and wanted to enhance her skills in Angular. She enrolled in an Angular 4 training program and obtained certification. The certification helped her secure a new job as an Angular Developer at a leading tech company. With her Angular 4 knowledge, she contributed to the development of complex web applications and was recognized for her expertise in Angular. The certification boosted her career and opened up new opportunities for growth.
John, a Freelancer: John was a freelance web developer with experience in various frameworks. He decided to specialize in Angular 4 to attract more clients and work on larger-scale projects. After completing an Angular 4 training program and earning certification, John showcased his credentials on his freelance profile and updated his portfolio with Angular projects. As a result, he attracted higher-paying clients and was able to take on more challenging Angular development projects. The certification helped him establish credibility and build a successful freelance career focused on Angular 4.
Emily, a Career Switcher: Emily had a background in a non-technical field but was passionate about web development. She wanted to transition into a career as a web developer, with a focus on Angular. Emily enrolled in an intensive Angular 4 training program that provided hands-on projects and mentorship. After completing the program and obtaining certification, she started applying for entry-level Angular developer positions. The certification served as evidence of her commitment and proficiency in Angular 4, and she landed a job at a software development company. The certification played a crucial role in her successful career transition.
Mark, an Entrepreneur: Mark had an entrepreneurial spirit and wanted to start his own web development agency. He recognized the growing demand for Angular development and decided to invest in his skills. Mark enrolled in an Angular 4 training program and obtained certification. Armed with his Angular 4 knowledge, he established his web development agency and promoted his expertise in Angular. The certification helped him win clients and build a reputation for delivering high-quality Angular applications. Today, his agency is thriving, and he continues to expand his team of Angular developers.
Continuing Education and Beyond
Continuing education is crucial for professionals in the field of Angular development to stay updated with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices. Beyond Angular 4, there have been subsequent versions released, and it's important to keep learning and adapting to the evolving Angular ecosystem. Here are some options for continuing education and further career growth in Angular development:
Angular Updates and Documentation: Stay updated with the latest versions of Angular by regularly exploring the official Angular documentation and release notes. The Angular team continuously enhances and introduces new features, improvements, and updates. Understanding these updates and how they affect your development workflow is essential for staying current in Angular development.
Angular Conferences and Events: Attend Angular conferences, meetups, and workshops to learn from industry experts, hear about the latest Angular trends, and network with fellow developers. These events provide valuable insights, practical tips, and opportunities to connect with the Angular community. Examples of notable Angular conferences include ng-conf and AngularConnect.
Online Courses and Tutorials: Explore online platforms that offer Angular courses and tutorials. Websites like iCert Global offer a wide range of Angular courses taught by experienced instructors. These courses can help you deepen your knowledge, learn advanced techniques, and gain expertise in specific Angular topics such as Angular Material, performance optimization, or advanced routing.
Angular Certification Programs: Keep an eye out for any new Angular certification programs that may be introduced in the future. As the Angular ecosystem evolves, certification programs may be updated to cover newer versions and advanced concepts. Earning additional certifications can validate your expertise and demonstrate your commitment to continuous learning.
Open Source Contributions: Contribute to open source Angular projects to expand your skills and gain practical experience. Engaging with the Angular community through open source projects allows you to collaborate with other developers, learn from their expertise, and contribute to the improvement of Angular tools and libraries.
Personal Projects and Side Projects: Undertake personal projects or side projects that allow you to experiment with new Angular features or explore specific areas of interest. Building real-world applications on your own can provide hands-on experience and help you stay engaged with Angular development.
Blogging and Sharing Knowledge: Share your knowledge and experiences by writing blog posts, creating tutorials, or contributing to technical publications. This not only helps the Angular community but also allows you to solidify your understanding of Angular concepts by explaining them to others.
Continuous Professional Development: Stay curious and be open to learning new technologies and complementary skills. Angular development often goes hand-in-hand with technologies such as TypeScript, RxJS, and testing frameworks like Jasmine or Karma. Investing time in learning these related technologies can enhance your overall expertise and make you a well-rounded Angular developer.
How to obtain Angular4 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Development : Angular 4 Training Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, Angular 4 training and certification can be highly beneficial for individuals and organizations in the field of web development. By obtaining certification in Angular 4, developers can showcase their proficiency in the framework, enhance their career prospects, and open up new opportunities for growth.
Angular 4 certification provides individuals with a solid understanding of the framework's concepts, best practices, and development techniques. It demonstrates their ability to design, build, and maintain Angular 4 applications effectively. Employers can benefit from hiring certified Angular 4 professionals as they bring expertise, improved development quality, and up-to-date knowledge to their teams.
The success stories of professionals who have completed Angular 4 training and obtained certification highlight the positive impact it can have on their careers. They have experienced career advancements, higher earnings, and opportunities to work on exciting projects. Whether it's through securing new job roles, freelancing opportunities, career transitions, or entrepreneurial ventures, Angular 4 certification has empowered individuals to achieve their goals.
Continuing education and staying updated with the latest developments in Angular development is essential beyond Angular 4. Professionals should embrace ongoing learning through resources such as documentation updates, conferences, online courses, personal projects, open-source contributions, and continuous professional development. By doing so, they can stay competitive, adapt to the evolving Angular ecosystem, and continue to excel in their careers.
Microsoft Project 2013 Certification: Achieving Your Goals
Embark on a transformative journey of professional growth with the "Microsoft Project 2013 Certification: Achieving Your Goals" program. Designed to equip you with the essential skills of project management and the technical prowess of Microsoft Project 2013, this certification offers a comprehensive understanding of efficient resource allocation, streamlined communication, and timely goal achievement. Discover the art of orchestrating tasks, managing timelines, and inspiring teams, while mastering the strategic insights needed to excel in today's dynamic business landscape. Your commitment to this certification reflects your dedication to personal and professional advancement, propelling you towards a future defined by success and accomplishment
Table of Contents
What is Microsoft Project 2013 Certification?
Benefits of getting certified in Microsoft Project 2013.
How to prepare for the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam?
Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam format and structure.
Overview of Microsoft Project 2013 features and functionalities.
Tips and tricks for using Microsoft Project 2013.
Understanding project management principles and their application in Microsoft Project 2013.
Microsoft Project 2013 certification levels and their differences.
Career opportunities for Microsoft Project 2013 certified professionals.
Comparison between Microsoft Project 2013 and other project management tools.
Conclusion
What is Microsoft Project 2013 Certification?
Microsoft Project 2013 Certification is a professional certification program offered by Microsoft that validates an individual's knowledge and expertise in using Microsoft Project 2013, which is a popular project management software. The certification program is designed to test an individual's ability to effectively use Microsoft Project 2013 to plan, manage, and execute projects, as well as to provide an understanding of project management concepts and principles.
To obtain the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification, candidates must pass an exam that assesses their knowledge of Microsoft Project 2013. The exam covers various topics such as project planning and scheduling, resource management, task management, budgeting, and reporting. The exam is available in multiple languages and can be taken online or at a testing center.
The Microsoft Project 2013 Certification program offers different levels of certification, including the Microsoft Certified Professional (MCP) certification, the Microsoft Specialist certification, and the Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE) certification. Each certification level requires passing a different set of exams, and the requirements for each certification level vary.
Obtaining the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification can help individuals enhance their career prospects and demonstrate their expertise in project management. It can also provide an advantage when applying for jobs that require knowledge and proficiency in Microsoft Project 2013.
Benefits of getting certified in Microsoft Project 2013
There are several benefits of obtaining the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification:
Enhanced skills and knowledge: The certification program provides individuals with a comprehensive understanding of project management principles and techniques using Microsoft Project 2013. This knowledge can help individuals to effectively plan, manage, and execute projects, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
Increased career opportunities: The certification demonstrates an individual's proficiency in using Microsoft Project 2013 and project management concepts, which can help open up new career opportunities. Many companies prefer to hire individuals who are certified in Microsoft Project 2013, as it indicates a high level of skill and knowledge.
Competitive edge: The certification can provide an edge over non-certified candidates in a competitive job market. It can also help individuals negotiate better salaries and benefits.
Professional credibility: The Microsoft Project 2013 Certification is recognized globally and is a widely respected certification in the field of project management. It can provide individuals with professional credibility and demonstrate their commitment to their field.
Increased productivity: The certification can help individuals work more efficiently and effectively, as they will be able to utilize Microsoft Project 2013 to its full potential. This can lead to increased productivity and improved project outcomes.
Professional development: The certification program provides individuals with ongoing professional development opportunities, as they can continue to learn and develop their skills through advanced-level certification programs and training courses.
How to prepare for the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam?
Preparing for the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam requires a combination of studying and hands-on experience with the software. Here are some tips to help you prepare:
Familiarize yourself with the exam format: Understand the structure of the exam, the types of questions, and the amount of time provided. Microsoft offers a variety of resources to help you understand the exam format.
Understand the exam objectives: Review the exam objectives to understand what topics are covered. Microsoft provides an exam preparation guide that outlines the topics and skills measured in the exam.
Use official Microsoft study materials: Microsoft provides study materials such as books, online courses, and practice exams. Use these materials to prepare for the exam and reinforce your understanding of the topics.
Practice with Microsoft Project 2013: Gain hands-on experience with Microsoft Project 2013 by working on projects and using the software to perform tasks related to the exam objectives. Microsoft offers a trial version of the software that you can use to practice.
Join a study group: Consider joining a study group or online forum where you can connect with other individuals who are preparing for the same exam. This can provide a supportive environment for asking questions and sharing tips.
Take practice exams: Microsoft provides official practice exams that can help you understand the types of questions you may encounter and assess your readiness for the exam.
Time management: Make a study schedule and plan your study sessions. Utilize study breaks to maintain focus. Allocate more time to difficult areas.
Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam format and structure
The Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam format and structure include the following:
Exam format: The exam is a computer-based test that consists of multiple-choice questions. The exam is timed, and the time allotted varies depending on the specific exam.
Number of questions: The number of questions in the exam varies, but typically ranges between 40 to 60 questions.
Passing score: To pass the exam, you must achieve a minimum passing score. The passing score varies depending on the specific exam.
Exam duration: The duration of the exam varies depending on the specific exam. The time allotted for the exam ranges from 120 minutes to 180 minutes.
Exam topics: The exam covers a range of topics related to Microsoft Project 2013, including project planning and scheduling, resource management, task management, budgeting, and reporting.
Exam difficulty level: The exam is designed to test an individual's knowledge and expertise in using Microsoft Project 2013 and project management concepts. The exam difficulty level varies depending on the specific exam.
Exam prerequisites: There are no prerequisites for the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam. However, it is recommended that candidates have a basic understanding of project management principles and some experience using Microsoft Project 2013 before taking the exam.
Overview of Microsoft Project 2013 features and functionalities
Microsoft Project 2013 is a project management software that helps individuals and organizations plan, manage, and execute projects. The software offers a range of features and functionalities that allow users to manage all aspects of their projects, from scheduling and resource management to budgeting and reporting. Here is an overview of some of the key features and functionalities of Microsoft Project 2013:
Project planning and scheduling: Microsoft Project 2013 offers tools for project planning and scheduling, including the ability to create project timelines, assign tasks and deadlines, and track progress.
Resource management: The software allows users to manage project resources, including people, equipment, and materials. Users can assign resources to tasks, monitor resource usage, and make adjustments as needed.
Budgeting: Microsoft Project 2013 allows users to create project budgets, track project expenses, and forecast project costs. The software offers tools for managing project budgets, including cost tracking and analysis.
Reporting: The software offers a range of reporting options, including Gantt charts, task lists, and custom reports. Users can generate reports to track project progress, analyze project data, and communicate project status to stakeholders.
Collaboration: Microsoft Project 2013 allows users to collaborate with team members and stakeholders, including the ability to share project information and communicate with team members in real-time.
Integration with other Microsoft products: Microsoft Project 2013 integrates with other Microsoft products, including Microsoft Excel and SharePoint. This allows users to import and export data, and collaborate with team members using these products.
Customization: The software offers a range of customization options, including the ability to customize project templates, create custom views and reports, and automate repetitive tasks using macros.
Tips and tricks for using Microsoft Project 2013
Here are some tips and tricks for using Microsoft Project 2013:
Start with a plan: Before you start using Microsoft Project 2013, make sure you have a clear plan in place. This includes defining project goals, creating a project schedule, and identifying project resources.
Use templates: Microsoft Project 2013 offers a range of templates that can help you get started with your project. These templates include pre-defined tasks, schedules, and resource assignments.
Customize views: Microsoft Project 2013 allows you to customize views to fit your specific needs. This includes adding or removing columns, changing the order of columns, and filtering data.
Use the timeline view: The timeline view in Microsoft Project 2013 allows you to see a high-level view of your project schedule. This can be helpful for communicating project progress to stakeholders.
Use the critical path: The critical path in Microsoft Project 2013 is the sequence of tasks that must be completed on time for the project to be completed on schedule. Use the critical path view to identify tasks that are critical to the project timeline.
Use constraints sparingly: Constraints in Microsoft Project 2013 can be helpful for ensuring that tasks are completed on time, but they can also limit flexibility in the project schedule. Use constraints sparingly and only when necessary.
Use resource leveling: Resource leveling in Microsoft Project 2013 helps you balance resource assignments to ensure that resources are not over-allocated. This can help prevent delays in the project schedule.
Use the tracking tools: Microsoft Project 2013 offers tools for tracking project progress, including the ability to track task completion and resource usage. Use these tools to monitor project progress and make adjustments as needed.
Use the collaboration tools: Microsoft Project 2013 offers a range of collaboration tools, including the ability to share project information and communicate with team members in real-time. Use these tools to keep team members informed and engaged.
Learn keyboard shortcuts: Microsoft Project 2013 offers a range of keyboard shortcuts that can help you work more efficiently. Take the time to learn these shortcuts to save time and improve your productivity.
Understanding project management principles and their application in Microsoft Project 2013
Microsoft Project 2013 is a powerful project management tool that allows users to apply a range of project management principles to their projects. Here are some key project management principles and how they can be applied in Microsoft Project 2013:
Planning: Planning is a critical project management principle that involves defining project goals, creating a project schedule, and identifying project resources. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Gantt chart view to create and manage project schedules. They can also use the resource management tools to assign resources to tasks and monitor resource usage.
Risk management: Risk management involves identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Risk Management feature to identify potential risks and develop contingency plans.
Budgeting: Budgeting is a key project management principle that involves creating and managing project budgets. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Budget Overview feature to track project expenses and compare them to the project budget.
Communication: Communication is a critical project management principle that involves keeping team members and stakeholders informed about project progress. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Report feature to generate reports that communicate project progress and status.
Resource management: Resource management is a key project management principle that involves managing project resources, including people, equipment, and materials. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Resource Management feature to assign resources to tasks and monitor resource usage.
Time management: Time management is a critical project management principle that involves managing project schedules and timelines. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Gantt chart view to create and manage project schedules, and use the Timeline view to visualize the project schedule.
Scope management: Scope management involves defining and managing the project scope, or the work that needs to be completed to achieve project goals. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Task List view to manage project tasks and ensure that they are aligned with project goals.
Microsoft Project 2013 certification levels and their differences
There are three levels of Microsoft Project 2013 certifications, each with different requirements and objectives. These levels include:
Microsoft Specialist: Microsoft Project 2013: The Microsoft Specialist certification is the entry-level certification for Microsoft Project 2013. This certification is designed for individuals who have a basic understanding of project management principles and are familiar with the features and functionality of Microsoft Project 2013. To earn this certification, candidates must pass the Microsoft Project 2013 exam.
Microsoft Certified: Microsoft Project 2013: The Microsoft Certified certification is the intermediate-level certification for Microsoft Project 2013. This certification is designed for individuals who have a more advanced understanding of project management principles and are able to apply those principles using Microsoft Project 2013. To earn this certification, candidates must pass the Microsoft Project 2013 exam and an additional elective exam.
Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE): Project Management: The MCSE certification is the highest-level certification for Microsoft Project 2013. This certification is designed for individuals who have an expert-level understanding of project management principles and are able to design and implement project management solutions using Microsoft Project 2013. To earn this certification, candidates must pass the Microsoft Project 2013 exam, an additional elective exam, and a design exam.
Career opportunities for Microsoft Project 2013 certified professionals.
Microsoft Project 2013 certification can open up a range of career opportunities for professionals in project management and related fields. Here are some of the career opportunities for Microsoft Project 2013 certified professionals:
Project Manager: Microsoft Project 2013 certification can be a valuable credential for professionals seeking to become project managers. With this certification, professionals can demonstrate their expertise in project management principles and their ability to effectively use Microsoft Project 2013 to manage projects.
Project Coordinator: Microsoft Project 2013 certification can also be useful for professionals seeking to become project coordinators. In this role, professionals are responsible for supporting project managers and ensuring that projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the desired quality standards. Microsoft Project 2013 certification can help professionals in this role effectively support project managers and contribute to project success.
Program Manager: Program managers are responsible for overseeing a portfolio of related projects and ensuring that they are aligned with organizational goals and objectives. Microsoft Project 2013 certification can be a valuable credential for professionals seeking to become program managers, as it demonstrates their expertise in project management principles and their ability to effectively manage complex projects.
Business Analyst: Business analysts are responsible for analyzing business processes, identifying areas for improvement, and developing solutions to address those areas. Microsoft Project 2013 certification can be useful for business analysts who work on projects, as it demonstrates their ability to effectively use Microsoft Project 2013 to manage project schedules and resources.
Consultant: Microsoft Project 2013 certified professionals can also work as consultants, providing project management expertise and guidance to organizations. In this role, professionals may help organizations implement Microsoft Project 2013, develop project management processes and procedures, or manage projects on behalf of clients.
Comparison between Microsoft Project 2013 and other project management tools
Microsoft Project 2013 is a widely used project management tool, but it's not the only tool available. Here's a comparison between Microsoft Project 2013 and some other popular project management tools:
Trello: Trello is a visual project management tool that uses boards, lists, and cards to help teams organize and manage tasks. While Microsoft Project 2013 is more focused on project scheduling and resource management, Trello is more flexible and allows teams to manage projects in a more visual and collaborative way.
Asana: Asana is another popular project management tool that allows teams to manage tasks, projects, and workflows. While Asana is more focused on team collaboration and communication, Microsoft Project 2013 is more focused on project planning and tracking.
Basecamp: Basecamp is a project management tool that combines project management, team collaboration, and communication features in one platform. While Basecamp is more focused on team collaboration and communication, Microsoft Project 2013 is more focused on project planning and scheduling.
Smartsheet: Smartsheet is a project management tool that combines project management, collaboration, and automation features in one platform. While Smartsheet is more flexible and allows teams to manage projects in a more visual and collaborative way, Microsoft Project 2013 is more focused on project planning and scheduling.
How to obtain Microsoft Project 2013 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Microsoft : Microsoft Project 2013 Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, obtaining a Microsoft Project 2013 Certification can be a significant step towards achieving your professional goals. This certification demonstrates your expertise and proficiency in effectively utilizing the Microsoft Project 2013 software, a valuable skillset in today's competitive job market. By becoming certified, you not only enhance your credibility and marketability but also open doors to new career opportunities and advancement. The certification validates your ability to plan, execute, monitor, and control projects using the Microsoft Project 2013 tool, enabling you to deliver successful projects on time and within budget. Moreover, the knowledge and techniques gained through the certification process can be applied to various industries and sectors, making you a versatile project manager. Whether you are looking to boost your career prospects, improve your project management skills, or enhance your professional standing, earning a Microsoft Project 2013 Certification is a worthwhile investment that can propel you towards your goals. So, seize the opportunity, dedicate yourself to the certification process, and unlock a world of possibilities in the project management domain.
Read More
Embark on a transformative journey of professional growth with the "Microsoft Project 2013 Certification: Achieving Your Goals" program. Designed to equip you with the essential skills of project management and the technical prowess of Microsoft Project 2013, this certification offers a comprehensive understanding of efficient resource allocation, streamlined communication, and timely goal achievement. Discover the art of orchestrating tasks, managing timelines, and inspiring teams, while mastering the strategic insights needed to excel in today's dynamic business landscape. Your commitment to this certification reflects your dedication to personal and professional advancement, propelling you towards a future defined by success and accomplishment
Table of Contents
What is Microsoft Project 2013 Certification?
Benefits of getting certified in Microsoft Project 2013.
How to prepare for the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam?
Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam format and structure.
Overview of Microsoft Project 2013 features and functionalities.
Tips and tricks for using Microsoft Project 2013.
Understanding project management principles and their application in Microsoft Project 2013.
Microsoft Project 2013 certification levels and their differences.
Career opportunities for Microsoft Project 2013 certified professionals.
Comparison between Microsoft Project 2013 and other project management tools.
Conclusion
What is Microsoft Project 2013 Certification?
Microsoft Project 2013 Certification is a professional certification program offered by Microsoft that validates an individual's knowledge and expertise in using Microsoft Project 2013, which is a popular project management software. The certification program is designed to test an individual's ability to effectively use Microsoft Project 2013 to plan, manage, and execute projects, as well as to provide an understanding of project management concepts and principles.
To obtain the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification, candidates must pass an exam that assesses their knowledge of Microsoft Project 2013. The exam covers various topics such as project planning and scheduling, resource management, task management, budgeting, and reporting. The exam is available in multiple languages and can be taken online or at a testing center.
The Microsoft Project 2013 Certification program offers different levels of certification, including the Microsoft Certified Professional (MCP) certification, the Microsoft Specialist certification, and the Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE) certification. Each certification level requires passing a different set of exams, and the requirements for each certification level vary.
Obtaining the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification can help individuals enhance their career prospects and demonstrate their expertise in project management. It can also provide an advantage when applying for jobs that require knowledge and proficiency in Microsoft Project 2013.
Benefits of getting certified in Microsoft Project 2013
There are several benefits of obtaining the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification:
Enhanced skills and knowledge: The certification program provides individuals with a comprehensive understanding of project management principles and techniques using Microsoft Project 2013. This knowledge can help individuals to effectively plan, manage, and execute projects, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
Increased career opportunities: The certification demonstrates an individual's proficiency in using Microsoft Project 2013 and project management concepts, which can help open up new career opportunities. Many companies prefer to hire individuals who are certified in Microsoft Project 2013, as it indicates a high level of skill and knowledge.
Competitive edge: The certification can provide an edge over non-certified candidates in a competitive job market. It can also help individuals negotiate better salaries and benefits.
Professional credibility: The Microsoft Project 2013 Certification is recognized globally and is a widely respected certification in the field of project management. It can provide individuals with professional credibility and demonstrate their commitment to their field.
Increased productivity: The certification can help individuals work more efficiently and effectively, as they will be able to utilize Microsoft Project 2013 to its full potential. This can lead to increased productivity and improved project outcomes.
Professional development: The certification program provides individuals with ongoing professional development opportunities, as they can continue to learn and develop their skills through advanced-level certification programs and training courses.
How to prepare for the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam?
Preparing for the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam requires a combination of studying and hands-on experience with the software. Here are some tips to help you prepare:
Familiarize yourself with the exam format: Understand the structure of the exam, the types of questions, and the amount of time provided. Microsoft offers a variety of resources to help you understand the exam format.
Understand the exam objectives: Review the exam objectives to understand what topics are covered. Microsoft provides an exam preparation guide that outlines the topics and skills measured in the exam.
Use official Microsoft study materials: Microsoft provides study materials such as books, online courses, and practice exams. Use these materials to prepare for the exam and reinforce your understanding of the topics.
Practice with Microsoft Project 2013: Gain hands-on experience with Microsoft Project 2013 by working on projects and using the software to perform tasks related to the exam objectives. Microsoft offers a trial version of the software that you can use to practice.
Join a study group: Consider joining a study group or online forum where you can connect with other individuals who are preparing for the same exam. This can provide a supportive environment for asking questions and sharing tips.
Take practice exams: Microsoft provides official practice exams that can help you understand the types of questions you may encounter and assess your readiness for the exam.
Time management: Make a study schedule and plan your study sessions. Utilize study breaks to maintain focus. Allocate more time to difficult areas.
Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam format and structure
The Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam format and structure include the following:
Exam format: The exam is a computer-based test that consists of multiple-choice questions. The exam is timed, and the time allotted varies depending on the specific exam.
Number of questions: The number of questions in the exam varies, but typically ranges between 40 to 60 questions.
Passing score: To pass the exam, you must achieve a minimum passing score. The passing score varies depending on the specific exam.
Exam duration: The duration of the exam varies depending on the specific exam. The time allotted for the exam ranges from 120 minutes to 180 minutes.
Exam topics: The exam covers a range of topics related to Microsoft Project 2013, including project planning and scheduling, resource management, task management, budgeting, and reporting.
Exam difficulty level: The exam is designed to test an individual's knowledge and expertise in using Microsoft Project 2013 and project management concepts. The exam difficulty level varies depending on the specific exam.
Exam prerequisites: There are no prerequisites for the Microsoft Project 2013 Certification Exam. However, it is recommended that candidates have a basic understanding of project management principles and some experience using Microsoft Project 2013 before taking the exam.
Overview of Microsoft Project 2013 features and functionalities
Microsoft Project 2013 is a project management software that helps individuals and organizations plan, manage, and execute projects. The software offers a range of features and functionalities that allow users to manage all aspects of their projects, from scheduling and resource management to budgeting and reporting. Here is an overview of some of the key features and functionalities of Microsoft Project 2013:
Project planning and scheduling: Microsoft Project 2013 offers tools for project planning and scheduling, including the ability to create project timelines, assign tasks and deadlines, and track progress.
Resource management: The software allows users to manage project resources, including people, equipment, and materials. Users can assign resources to tasks, monitor resource usage, and make adjustments as needed.
Budgeting: Microsoft Project 2013 allows users to create project budgets, track project expenses, and forecast project costs. The software offers tools for managing project budgets, including cost tracking and analysis.
Reporting: The software offers a range of reporting options, including Gantt charts, task lists, and custom reports. Users can generate reports to track project progress, analyze project data, and communicate project status to stakeholders.
Collaboration: Microsoft Project 2013 allows users to collaborate with team members and stakeholders, including the ability to share project information and communicate with team members in real-time.
Integration with other Microsoft products: Microsoft Project 2013 integrates with other Microsoft products, including Microsoft Excel and SharePoint. This allows users to import and export data, and collaborate with team members using these products.
Customization: The software offers a range of customization options, including the ability to customize project templates, create custom views and reports, and automate repetitive tasks using macros.
Tips and tricks for using Microsoft Project 2013
Here are some tips and tricks for using Microsoft Project 2013:
Start with a plan: Before you start using Microsoft Project 2013, make sure you have a clear plan in place. This includes defining project goals, creating a project schedule, and identifying project resources.
Use templates: Microsoft Project 2013 offers a range of templates that can help you get started with your project. These templates include pre-defined tasks, schedules, and resource assignments.
Customize views: Microsoft Project 2013 allows you to customize views to fit your specific needs. This includes adding or removing columns, changing the order of columns, and filtering data.
Use the timeline view: The timeline view in Microsoft Project 2013 allows you to see a high-level view of your project schedule. This can be helpful for communicating project progress to stakeholders.
Use the critical path: The critical path in Microsoft Project 2013 is the sequence of tasks that must be completed on time for the project to be completed on schedule. Use the critical path view to identify tasks that are critical to the project timeline.
Use constraints sparingly: Constraints in Microsoft Project 2013 can be helpful for ensuring that tasks are completed on time, but they can also limit flexibility in the project schedule. Use constraints sparingly and only when necessary.
Use resource leveling: Resource leveling in Microsoft Project 2013 helps you balance resource assignments to ensure that resources are not over-allocated. This can help prevent delays in the project schedule.
Use the tracking tools: Microsoft Project 2013 offers tools for tracking project progress, including the ability to track task completion and resource usage. Use these tools to monitor project progress and make adjustments as needed.
Use the collaboration tools: Microsoft Project 2013 offers a range of collaboration tools, including the ability to share project information and communicate with team members in real-time. Use these tools to keep team members informed and engaged.
Learn keyboard shortcuts: Microsoft Project 2013 offers a range of keyboard shortcuts that can help you work more efficiently. Take the time to learn these shortcuts to save time and improve your productivity.
Understanding project management principles and their application in Microsoft Project 2013
Microsoft Project 2013 is a powerful project management tool that allows users to apply a range of project management principles to their projects. Here are some key project management principles and how they can be applied in Microsoft Project 2013:
Planning: Planning is a critical project management principle that involves defining project goals, creating a project schedule, and identifying project resources. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Gantt chart view to create and manage project schedules. They can also use the resource management tools to assign resources to tasks and monitor resource usage.
Risk management: Risk management involves identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Risk Management feature to identify potential risks and develop contingency plans.
Budgeting: Budgeting is a key project management principle that involves creating and managing project budgets. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Budget Overview feature to track project expenses and compare them to the project budget.
Communication: Communication is a critical project management principle that involves keeping team members and stakeholders informed about project progress. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Report feature to generate reports that communicate project progress and status.
Resource management: Resource management is a key project management principle that involves managing project resources, including people, equipment, and materials. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Resource Management feature to assign resources to tasks and monitor resource usage.
Time management: Time management is a critical project management principle that involves managing project schedules and timelines. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Gantt chart view to create and manage project schedules, and use the Timeline view to visualize the project schedule.
Scope management: Scope management involves defining and managing the project scope, or the work that needs to be completed to achieve project goals. In Microsoft Project 2013, users can use the Task List view to manage project tasks and ensure that they are aligned with project goals.
Microsoft Project 2013 certification levels and their differences
There are three levels of Microsoft Project 2013 certifications, each with different requirements and objectives. These levels include:
Microsoft Specialist: Microsoft Project 2013: The Microsoft Specialist certification is the entry-level certification for Microsoft Project 2013. This certification is designed for individuals who have a basic understanding of project management principles and are familiar with the features and functionality of Microsoft Project 2013. To earn this certification, candidates must pass the Microsoft Project 2013 exam.
Microsoft Certified: Microsoft Project 2013: The Microsoft Certified certification is the intermediate-level certification for Microsoft Project 2013. This certification is designed for individuals who have a more advanced understanding of project management principles and are able to apply those principles using Microsoft Project 2013. To earn this certification, candidates must pass the Microsoft Project 2013 exam and an additional elective exam.
Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE): Project Management: The MCSE certification is the highest-level certification for Microsoft Project 2013. This certification is designed for individuals who have an expert-level understanding of project management principles and are able to design and implement project management solutions using Microsoft Project 2013. To earn this certification, candidates must pass the Microsoft Project 2013 exam, an additional elective exam, and a design exam.
Career opportunities for Microsoft Project 2013 certified professionals.
Microsoft Project 2013 certification can open up a range of career opportunities for professionals in project management and related fields. Here are some of the career opportunities for Microsoft Project 2013 certified professionals:
Project Manager: Microsoft Project 2013 certification can be a valuable credential for professionals seeking to become project managers. With this certification, professionals can demonstrate their expertise in project management principles and their ability to effectively use Microsoft Project 2013 to manage projects.
Project Coordinator: Microsoft Project 2013 certification can also be useful for professionals seeking to become project coordinators. In this role, professionals are responsible for supporting project managers and ensuring that projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the desired quality standards. Microsoft Project 2013 certification can help professionals in this role effectively support project managers and contribute to project success.
Program Manager: Program managers are responsible for overseeing a portfolio of related projects and ensuring that they are aligned with organizational goals and objectives. Microsoft Project 2013 certification can be a valuable credential for professionals seeking to become program managers, as it demonstrates their expertise in project management principles and their ability to effectively manage complex projects.
Business Analyst: Business analysts are responsible for analyzing business processes, identifying areas for improvement, and developing solutions to address those areas. Microsoft Project 2013 certification can be useful for business analysts who work on projects, as it demonstrates their ability to effectively use Microsoft Project 2013 to manage project schedules and resources.
Consultant: Microsoft Project 2013 certified professionals can also work as consultants, providing project management expertise and guidance to organizations. In this role, professionals may help organizations implement Microsoft Project 2013, develop project management processes and procedures, or manage projects on behalf of clients.
Comparison between Microsoft Project 2013 and other project management tools
Microsoft Project 2013 is a widely used project management tool, but it's not the only tool available. Here's a comparison between Microsoft Project 2013 and some other popular project management tools:
Trello: Trello is a visual project management tool that uses boards, lists, and cards to help teams organize and manage tasks. While Microsoft Project 2013 is more focused on project scheduling and resource management, Trello is more flexible and allows teams to manage projects in a more visual and collaborative way.
Asana: Asana is another popular project management tool that allows teams to manage tasks, projects, and workflows. While Asana is more focused on team collaboration and communication, Microsoft Project 2013 is more focused on project planning and tracking.
Basecamp: Basecamp is a project management tool that combines project management, team collaboration, and communication features in one platform. While Basecamp is more focused on team collaboration and communication, Microsoft Project 2013 is more focused on project planning and scheduling.
Smartsheet: Smartsheet is a project management tool that combines project management, collaboration, and automation features in one platform. While Smartsheet is more flexible and allows teams to manage projects in a more visual and collaborative way, Microsoft Project 2013 is more focused on project planning and scheduling.
How to obtain Microsoft Project 2013 Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Microsoft : Microsoft Project 2013 Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, obtaining a Microsoft Project 2013 Certification can be a significant step towards achieving your professional goals. This certification demonstrates your expertise and proficiency in effectively utilizing the Microsoft Project 2013 software, a valuable skillset in today's competitive job market. By becoming certified, you not only enhance your credibility and marketability but also open doors to new career opportunities and advancement. The certification validates your ability to plan, execute, monitor, and control projects using the Microsoft Project 2013 tool, enabling you to deliver successful projects on time and within budget. Moreover, the knowledge and techniques gained through the certification process can be applied to various industries and sectors, making you a versatile project manager. Whether you are looking to boost your career prospects, improve your project management skills, or enhance your professional standing, earning a Microsoft Project 2013 Certification is a worthwhile investment that can propel you towards your goals. So, seize the opportunity, dedicate yourself to the certification process, and unlock a world of possibilities in the project management domain.
Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification: Key Information
Unlock the potential of your spreadsheet prowess with our comprehensive guide to the "Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification: What You Need to Know." In an increasingly data-driven world, this guide illuminates the significance of mastering Excel's advanced features and empowers you to navigate the certification journey with confidence. Delve into intricate data manipulation, advanced formulae, and dynamic data visualization techniques as we demystify the certification process, highlighting its career-boosting benefits and the expertise it confers. Whether you're a proficient Excel user or a newcomer to advanced spreadsheet applications, this guide equips you to excel in the realm of Microsoft Excel 2013 and attain a coveted certification that amplifies your professional potential.
Table of contents
Overview of Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Benefits of getting certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Exam format and requirements for Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam
Tips and tricks for passing the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam
Common topics covered in the exam, including advanced formulas and functions, data analysis tools, and pivot tables
Real-world applications of Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification skills in various industries, such as finance, marketing, and business analytics
Career opportunities for individuals who hold the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
How to showcase your Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification on your resume and LinkedIn profile
Future trends in Microsoft Excel and the importance of staying up-to-date with the latest developments.
Conclusion
Overview of Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification is a professional certification offered by Microsoft that validates an individual's advanced skills and knowledge in using Microsoft Excel 2013. It is designed for individuals who are seeking to demonstrate their proficiency in using Excel for complex data analysis and modeling tasks.
To earn the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification, individuals must pass the Microsoft Office Specialist (MOS) Excel 2013 Expert Part 1 and Part 2 exams. The MOS certification program is globally recognized as a standard for demonstrating proficiency in Microsoft Office products.
The certification exam consists of hands-on tasks that simulate real-world scenarios. It covers advanced topics such as working with multiple worksheets and workbooks, using advanced formulas and functions, creating and modifying charts and tables, analyzing data with pivot tables and pivot charts, and creating macros.
Individuals who pass the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam can use their certification as a credential to demonstrate their skills and knowledge to potential employers. It can help them stand out in a competitive job market and increase their earning potential.
Overall, the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification is a valuable credential for individuals who use Excel extensively in their jobs, including data analysts, financial analysts, accountants, and business professionals. It provides a standard for measuring advanced Excel skills and knowledge and helps individuals to differentiate themselves in the job market.
Benefits of getting certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
There are several benefits to getting certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification, including:
Validation of advanced Excel skills: The certification demonstrates that an individual has advanced skills and knowledge in using Excel, including complex data analysis and modeling tasks.
Increased employability: The certification can make an individual more attractive to potential employers who are looking for candidates with advanced Excel skills.
Career advancement: Certified professionals may have access to higher-paying job opportunities and career advancement within their current organizations.
Competitive edge: The certification can give an individual a competitive edge over other candidates who may not have the same level of Excel skills.
Personal satisfaction: Earning the certification can provide a sense of personal achievement and satisfaction.
Industry recognition: The Microsoft Office Specialist certification program is globally recognized as a standard for demonstrating proficiency in Microsoft Office products, which can help to boost an individual's credibility in their industry.
Improved productivity: Advanced Excel skills can help individuals to work more efficiently and effectively, which can lead to improved productivity and better business outcomes.
Exam format and requirements for Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam is a performance-based exam that measures an individual's ability to use Microsoft Excel 2013 to complete complex data analysis and modeling tasks. The exam consists of two parts: Part 1 and Part 2.
Part 1 of the exam focuses on advanced Excel skills related to managing and analyzing data, including:
Managing workbooks and worksheets
Applying custom formats and layouts
Creating advanced formulas and functions
Creating advanced charts and tables
Part 2 of the exam focuses on advanced Excel skills related to analyzing and presenting data, including:
Analyzing data with pivot tables and pivot charts
Creating and manipulating data models
Creating macros and other custom tools
Collaborating and securing data
The exam format for both parts is the same. The exam consists of several performance-based tasks that simulate real-world scenarios. The tasks are designed to test an individual's ability to complete complex Excel tasks using various tools and features.
The exam is timed, and individuals are given a set amount of time to complete the tasks. The passing score for each part of the exam is 700 out of a possible 1000 points.
To take the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam, individuals must first have a solid understanding of basic Excel skills and have experience using Excel for complex data analysis and modeling tasks. They must also have access to a computer with Microsoft Excel 2013 installed and have a valid Microsoft Office Specialist certification ID.
Preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam
Preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam requires a solid understanding of advanced Excel skills and knowledge. Here are some tips for preparing for the exam:
Review the exam objectives: The Microsoft website provides detailed exam objectives for each part of the exam. Reviewing these objectives can help individuals to focus their study efforts and ensure they are covering all the necessary topics.
Use Microsoft training resources: Microsoft offers a variety of training resources for Excel, including online courses, videos, and practice exams. These resources can help individuals to develop their Excel skills and prepare for the exam.
Practice using Excel: One of the best ways to prepare for the exam is to practice using Excel to complete complex data analysis and modeling tasks. Individuals can create practice scenarios that simulate the types of tasks they will encounter on the exam.
Use study guides and reference materials: There are several study guides and reference materials available for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam. These resources can help individuals to reinforce their knowledge of advanced Excel concepts and techniques.
Take practice exams: Microsoft offers practice exams for the Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam. Taking these exams can help individuals to assess their knowledge and identify areas where they need to focus their study efforts.
Get hands-on experience: Individuals can also gain valuable hands-on experience by working on real-world Excel projects or volunteering to help with Excel-related tasks in their current job.
Tips and tricks for passing the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam
Passing the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam requires a combination of advanced Excel skills and knowledge, as well as effective test-taking strategies. Here are some tips and tricks to help individuals pass the exam:
Understand the exam format: The exam is a performance-based exam that consists of several tasks that simulate real-world scenarios. Understanding the format of the exam and the types of tasks that will be included can help individuals to prepare effectively.
Manage your time effectively: The exam is timed, so it is important to manage your time effectively. Read each task carefully, and prioritize tasks based on their complexity and point value. Don't spend too much time on any one task, as this can prevent you from completing other tasks.
Use Excel shortcuts and functions: Knowing Excel shortcuts and functions can help you complete tasks more quickly and efficiently. Make sure you are familiar with commonly used shortcuts and functions, such as Ctrl+C and SUMIF.
Check your work: Before submitting your exam, take the time to review your work carefully. Check for errors and make sure you have completed all the required tasks.
Practice with sample exams: Microsoft provides practice exams that simulate the real exam. Practicing with these exams can help you get familiar with the format of the exam and identify areas where you may need to focus your study efforts.
Take breaks: The exam can be long and challenging, so it is important to take breaks and give your brain a rest. Stand up, stretch, and take a short walk to help refresh your mind and improve your concentration.
Stay calm and focused: Finally, it is important to stay calm and focused during the exam. Don't let anxiety or stress distract you from the task at hand. Take a deep breath, and stay focused on completing each task to the best of your ability.
Common topics covered in the exam, including advanced formulas and functions, data analysis tools, and pivot tables
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam covers a wide range of advanced topics related to data analysis, modeling, and reporting. Here are some of the common topics covered in the exam:
Advanced formulas and functions: The exam tests individuals on their ability to use advanced formulas and functions, such as array formulas, conditional formulas, and nested functions.
Data analysis tools: The exam also covers advanced data analysis tools, such as data validation, sorting, filtering, and subtotals. Individuals may also be tested on their ability to use advanced analysis tools, such as Goal Seek and Solver.
Pivot tables: Pivot tables are a key feature of Excel, and the exam tests individuals on their ability to create and modify pivot tables, as well as use them for data analysis and reporting.
Charts and graphs: The exam may also test individuals on their ability to create and modify charts and graphs, as well as use them for data visualization and reporting.
Macros and VBA: The exam may include questions related to macros and Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Individuals may be tested on their ability to create and edit macros, as well as write and modify VBA code.
Collaboration and sharing: The exam may also test individuals on their ability to collaborate and share Excel workbooks, including using features such as comments, protection, and sharing options.
Real-world applications of Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification skills in various industries, such as finance, marketing, and business analytics
Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification skills are valuable in a wide range of industries, including finance, marketing, and business analytics. Here are some real-world applications of these skills in various industries:
Finance: In finance, Excel skills are critical for financial analysis, forecasting, and reporting. Advanced Excel skills, such as pivot tables, financial modeling, and data visualization, are particularly valuable for financial professionals. For example, financial analysts may use Excel to analyze financial statements, build financial models, and create charts and graphs to visualize financial data.
Marketing: In marketing, Excel skills are essential for data analysis and reporting. Advanced Excel skills, such as using macros and pivot tables, can help marketers to analyze marketing campaigns, track customer behavior, and create reports to inform marketing strategies. For example, marketers may use Excel to analyze website traffic, track social media engagement, and create reports on marketing campaign performance.
Business analytics: In business analytics, Excel skills are critical for data modeling, data visualization, and data analysis. Advanced Excel skills, such as using Power Query and Power Pivot, can help analysts to import and transform data, build data models, and create interactive dashboards to visualize data. For example, business analysts may use Excel to analyze customer data, build predictive models, and create dashboards to track business performance.
Operations: In operations, Excel skills are essential for inventory management, production planning, and supply chain analysis. Advanced Excel skills, such as using data validation and conditional formatting, can help operations professionals to manage inventory levels, plan production schedules, and analyze supply chain performance. For example, operations managers may use Excel to track inventory levels, plan production schedules, and analyze supplier performance.
Career opportunities for individuals who hold the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Individuals who hold the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification have a range of career opportunities available to them. Here are some examples of career paths and positions that may benefit from this certification:
Financial Analyst: Financial analysts use Excel extensively for financial modeling, forecasting, and analysis. Having an Excel certification can demonstrate proficiency in these skills and increase the likelihood of being hired for a financial analyst position.
Data Analyst: Data analysts use Excel to analyze and interpret large amounts of data. An Excel certification can demonstrate the ability to use advanced Excel features, such as pivot tables and data visualization, which are critical for data analysis.
Business Analyst: Business analysts use Excel to analyze data and create reports to inform business decisions. An Excel certification can demonstrate the ability to use Excel effectively for data analysis and reporting, which is essential for a business analyst position.
Operations Manager: Operations managers use Excel for inventory management, production planning, and supply chain analysis. An Excel certification can demonstrate the ability to use advanced Excel features, such as data validation and conditional formatting, which are critical for operations management.
Marketing Analyst: Marketing analysts use Excel for data analysis and reporting to track marketing campaign performance and customer behavior. An Excel certification can demonstrate the ability to use advanced Excel features, such as macros and pivot tables, which are essential for marketing analytics.
How to showcase your Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification on your resume and LinkedIn profile
If you have achieved the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification, it is important to showcase this accomplishment on your resume and LinkedIn profile. Here are some tips on how to do this effectively:
Include the certification in the Education or Certification section of your resume. List the certification name, the organization that issued it (Microsoft), and the date you received it.
Highlight your Excel skills in the Skills section of your resume. Use bullet points to list specific Excel skills you have, such as pivot tables, macros, and advanced formulas.
Include the certification logo on your LinkedIn profile. You can download the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification logo from the Microsoft website and upload it to your LinkedIn profile under the Licenses & Certifications section.
Add the certification to your LinkedIn headline and summary. Including the certification in your headline and summary can help catch the attention of recruiters and hiring managers.
Showcase your Excel skills in your LinkedIn profile. Use the Projects or Experience section of your LinkedIn profile to highlight specific projects or accomplishments that showcase your Excel skills.
Provide specific examples of how you have used Excel in your professional experience. This can help demonstrate your Excel proficiency to potential employers.
Future trends in Microsoft Excel and the importance of staying up-to-date with the latest developments
Microsoft Excel has been a staple of the business world for over three decades, and it continues to evolve and improve. Staying up-to-date with the latest developments in Excel is essential for anyone who uses the software regularly. Here are some future trends in Excel and the importance of staying up-to-date with them:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Excel is expected to incorporate more AI and machine learning capabilities, which will enable users to perform more complex data analysis and automate routine tasks. Staying up-to-date with these developments can help users become more efficient and effective in their work.
Cloud-Based Collaboration: Microsoft has been emphasizing cloud-based collaboration with Excel, which allows users to collaborate on spreadsheets in real-time. Staying up-to-date with these developments can help users work more efficiently with colleagues, even if they are not in the same physical location.
Mobile Access: With the rise of mobile devices, Microsoft has been working to make Excel more accessible on smartphones and tablets. Staying up-to-date with these developments can enable users to work on their spreadsheets while on-the-go.
Visualizations and Data Visualization Tools: Excel has been expanding its capabilities in data visualization, which allows users to create more visually compelling charts and graphs. Staying up-to-date with these developments can help users create more engaging and informative reports.
Integration with other Software: Excel is integrating with other software and services such as Power BI, Azure Machine Learning, and Dynamics 365. Staying up-to-date with these developments can help users leverage Excel's capabilities in conjunction with other software to create more powerful solutions.
How to obtain Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Microsoft : Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification is a significant achievement that can greatly enhance your career prospects and demonstrate your advanced skills in Excel. By obtaining this certification, you showcase your ability to leverage the full potential of Excel's advanced features and functionalities to solve complex business problems and drive data-driven decision-making.
Throughout this article, we have explored the key benefits of acquiring the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification. We have discussed how this credential can help you stand out in the job market, validate your expertise, and open doors to new opportunities. We have also examined the specific topics covered in the certification exam, ranging from advanced formulas and data analysis techniques to collaboration features and data visualization tools.
Furthermore, we have highlighted the resources available to help you prepare for the certification exam, including official study guides, practice tests, and online training courses. These resources can provide you with the knowledge and practice necessary to excel in the exam and ensure that you are well-prepared to tackle real-world Excel challenges.
By investing the time and effort into acquiring the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification, you are not only expanding your technical skills but also demonstrating your commitment to professional growth and continuous learning. This certification is a testament to your dedication and sets you apart as a competent and proficient Excel user.
In today's data-driven business environment, Excel skills are in high demand, and the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification equips you with the expertise needed to excel in various roles, including data analysis, finance, project management, and more. It is a valuable asset that can enhance your employability, increase your earning potential, and give you a competitive advantage in your career.
So, if you're looking to take your Excel skills to the next level and differentiate yourself in the job market, consider pursuing the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification. It is a worthwhile investment that can unlock new opportunities and propel your career forward in the ever-evolving world of data analysis and business intelligence.
Read More
Unlock the potential of your spreadsheet prowess with our comprehensive guide to the "Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification: What You Need to Know." In an increasingly data-driven world, this guide illuminates the significance of mastering Excel's advanced features and empowers you to navigate the certification journey with confidence. Delve into intricate data manipulation, advanced formulae, and dynamic data visualization techniques as we demystify the certification process, highlighting its career-boosting benefits and the expertise it confers. Whether you're a proficient Excel user or a newcomer to advanced spreadsheet applications, this guide equips you to excel in the realm of Microsoft Excel 2013 and attain a coveted certification that amplifies your professional potential.
Table of contents
Overview of Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Benefits of getting certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Exam format and requirements for Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam
Tips and tricks for passing the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam
Common topics covered in the exam, including advanced formulas and functions, data analysis tools, and pivot tables
Real-world applications of Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification skills in various industries, such as finance, marketing, and business analytics
Career opportunities for individuals who hold the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
How to showcase your Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification on your resume and LinkedIn profile
Future trends in Microsoft Excel and the importance of staying up-to-date with the latest developments.
Conclusion
Overview of Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification is a professional certification offered by Microsoft that validates an individual's advanced skills and knowledge in using Microsoft Excel 2013. It is designed for individuals who are seeking to demonstrate their proficiency in using Excel for complex data analysis and modeling tasks.
To earn the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification, individuals must pass the Microsoft Office Specialist (MOS) Excel 2013 Expert Part 1 and Part 2 exams. The MOS certification program is globally recognized as a standard for demonstrating proficiency in Microsoft Office products.
The certification exam consists of hands-on tasks that simulate real-world scenarios. It covers advanced topics such as working with multiple worksheets and workbooks, using advanced formulas and functions, creating and modifying charts and tables, analyzing data with pivot tables and pivot charts, and creating macros.
Individuals who pass the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam can use their certification as a credential to demonstrate their skills and knowledge to potential employers. It can help them stand out in a competitive job market and increase their earning potential.
Overall, the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification is a valuable credential for individuals who use Excel extensively in their jobs, including data analysts, financial analysts, accountants, and business professionals. It provides a standard for measuring advanced Excel skills and knowledge and helps individuals to differentiate themselves in the job market.
Benefits of getting certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
There are several benefits to getting certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification, including:
Validation of advanced Excel skills: The certification demonstrates that an individual has advanced skills and knowledge in using Excel, including complex data analysis and modeling tasks.
Increased employability: The certification can make an individual more attractive to potential employers who are looking for candidates with advanced Excel skills.
Career advancement: Certified professionals may have access to higher-paying job opportunities and career advancement within their current organizations.
Competitive edge: The certification can give an individual a competitive edge over other candidates who may not have the same level of Excel skills.
Personal satisfaction: Earning the certification can provide a sense of personal achievement and satisfaction.
Industry recognition: The Microsoft Office Specialist certification program is globally recognized as a standard for demonstrating proficiency in Microsoft Office products, which can help to boost an individual's credibility in their industry.
Improved productivity: Advanced Excel skills can help individuals to work more efficiently and effectively, which can lead to improved productivity and better business outcomes.
Exam format and requirements for Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam is a performance-based exam that measures an individual's ability to use Microsoft Excel 2013 to complete complex data analysis and modeling tasks. The exam consists of two parts: Part 1 and Part 2.
Part 1 of the exam focuses on advanced Excel skills related to managing and analyzing data, including:
Managing workbooks and worksheets
Applying custom formats and layouts
Creating advanced formulas and functions
Creating advanced charts and tables
Part 2 of the exam focuses on advanced Excel skills related to analyzing and presenting data, including:
Analyzing data with pivot tables and pivot charts
Creating and manipulating data models
Creating macros and other custom tools
Collaborating and securing data
The exam format for both parts is the same. The exam consists of several performance-based tasks that simulate real-world scenarios. The tasks are designed to test an individual's ability to complete complex Excel tasks using various tools and features.
The exam is timed, and individuals are given a set amount of time to complete the tasks. The passing score for each part of the exam is 700 out of a possible 1000 points.
To take the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam, individuals must first have a solid understanding of basic Excel skills and have experience using Excel for complex data analysis and modeling tasks. They must also have access to a computer with Microsoft Excel 2013 installed and have a valid Microsoft Office Specialist certification ID.
Preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam
Preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam requires a solid understanding of advanced Excel skills and knowledge. Here are some tips for preparing for the exam:
Review the exam objectives: The Microsoft website provides detailed exam objectives for each part of the exam. Reviewing these objectives can help individuals to focus their study efforts and ensure they are covering all the necessary topics.
Use Microsoft training resources: Microsoft offers a variety of training resources for Excel, including online courses, videos, and practice exams. These resources can help individuals to develop their Excel skills and prepare for the exam.
Practice using Excel: One of the best ways to prepare for the exam is to practice using Excel to complete complex data analysis and modeling tasks. Individuals can create practice scenarios that simulate the types of tasks they will encounter on the exam.
Use study guides and reference materials: There are several study guides and reference materials available for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam. These resources can help individuals to reinforce their knowledge of advanced Excel concepts and techniques.
Take practice exams: Microsoft offers practice exams for the Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam. Taking these exams can help individuals to assess their knowledge and identify areas where they need to focus their study efforts.
Get hands-on experience: Individuals can also gain valuable hands-on experience by working on real-world Excel projects or volunteering to help with Excel-related tasks in their current job.
Tips and tricks for passing the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam
Passing the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam requires a combination of advanced Excel skills and knowledge, as well as effective test-taking strategies. Here are some tips and tricks to help individuals pass the exam:
Understand the exam format: The exam is a performance-based exam that consists of several tasks that simulate real-world scenarios. Understanding the format of the exam and the types of tasks that will be included can help individuals to prepare effectively.
Manage your time effectively: The exam is timed, so it is important to manage your time effectively. Read each task carefully, and prioritize tasks based on their complexity and point value. Don't spend too much time on any one task, as this can prevent you from completing other tasks.
Use Excel shortcuts and functions: Knowing Excel shortcuts and functions can help you complete tasks more quickly and efficiently. Make sure you are familiar with commonly used shortcuts and functions, such as Ctrl+C and SUMIF.
Check your work: Before submitting your exam, take the time to review your work carefully. Check for errors and make sure you have completed all the required tasks.
Practice with sample exams: Microsoft provides practice exams that simulate the real exam. Practicing with these exams can help you get familiar with the format of the exam and identify areas where you may need to focus your study efforts.
Take breaks: The exam can be long and challenging, so it is important to take breaks and give your brain a rest. Stand up, stretch, and take a short walk to help refresh your mind and improve your concentration.
Stay calm and focused: Finally, it is important to stay calm and focused during the exam. Don't let anxiety or stress distract you from the task at hand. Take a deep breath, and stay focused on completing each task to the best of your ability.
Common topics covered in the exam, including advanced formulas and functions, data analysis tools, and pivot tables
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification exam covers a wide range of advanced topics related to data analysis, modeling, and reporting. Here are some of the common topics covered in the exam:
Advanced formulas and functions: The exam tests individuals on their ability to use advanced formulas and functions, such as array formulas, conditional formulas, and nested functions.
Data analysis tools: The exam also covers advanced data analysis tools, such as data validation, sorting, filtering, and subtotals. Individuals may also be tested on their ability to use advanced analysis tools, such as Goal Seek and Solver.
Pivot tables: Pivot tables are a key feature of Excel, and the exam tests individuals on their ability to create and modify pivot tables, as well as use them for data analysis and reporting.
Charts and graphs: The exam may also test individuals on their ability to create and modify charts and graphs, as well as use them for data visualization and reporting.
Macros and VBA: The exam may include questions related to macros and Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Individuals may be tested on their ability to create and edit macros, as well as write and modify VBA code.
Collaboration and sharing: The exam may also test individuals on their ability to collaborate and share Excel workbooks, including using features such as comments, protection, and sharing options.
Real-world applications of Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification skills in various industries, such as finance, marketing, and business analytics
Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification skills are valuable in a wide range of industries, including finance, marketing, and business analytics. Here are some real-world applications of these skills in various industries:
Finance: In finance, Excel skills are critical for financial analysis, forecasting, and reporting. Advanced Excel skills, such as pivot tables, financial modeling, and data visualization, are particularly valuable for financial professionals. For example, financial analysts may use Excel to analyze financial statements, build financial models, and create charts and graphs to visualize financial data.
Marketing: In marketing, Excel skills are essential for data analysis and reporting. Advanced Excel skills, such as using macros and pivot tables, can help marketers to analyze marketing campaigns, track customer behavior, and create reports to inform marketing strategies. For example, marketers may use Excel to analyze website traffic, track social media engagement, and create reports on marketing campaign performance.
Business analytics: In business analytics, Excel skills are critical for data modeling, data visualization, and data analysis. Advanced Excel skills, such as using Power Query and Power Pivot, can help analysts to import and transform data, build data models, and create interactive dashboards to visualize data. For example, business analysts may use Excel to analyze customer data, build predictive models, and create dashboards to track business performance.
Operations: In operations, Excel skills are essential for inventory management, production planning, and supply chain analysis. Advanced Excel skills, such as using data validation and conditional formatting, can help operations professionals to manage inventory levels, plan production schedules, and analyze supply chain performance. For example, operations managers may use Excel to track inventory levels, plan production schedules, and analyze supplier performance.
Career opportunities for individuals who hold the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Individuals who hold the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification have a range of career opportunities available to them. Here are some examples of career paths and positions that may benefit from this certification:
Financial Analyst: Financial analysts use Excel extensively for financial modeling, forecasting, and analysis. Having an Excel certification can demonstrate proficiency in these skills and increase the likelihood of being hired for a financial analyst position.
Data Analyst: Data analysts use Excel to analyze and interpret large amounts of data. An Excel certification can demonstrate the ability to use advanced Excel features, such as pivot tables and data visualization, which are critical for data analysis.
Business Analyst: Business analysts use Excel to analyze data and create reports to inform business decisions. An Excel certification can demonstrate the ability to use Excel effectively for data analysis and reporting, which is essential for a business analyst position.
Operations Manager: Operations managers use Excel for inventory management, production planning, and supply chain analysis. An Excel certification can demonstrate the ability to use advanced Excel features, such as data validation and conditional formatting, which are critical for operations management.
Marketing Analyst: Marketing analysts use Excel for data analysis and reporting to track marketing campaign performance and customer behavior. An Excel certification can demonstrate the ability to use advanced Excel features, such as macros and pivot tables, which are essential for marketing analytics.
How to showcase your Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification on your resume and LinkedIn profile
If you have achieved the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification, it is important to showcase this accomplishment on your resume and LinkedIn profile. Here are some tips on how to do this effectively:
Include the certification in the Education or Certification section of your resume. List the certification name, the organization that issued it (Microsoft), and the date you received it.
Highlight your Excel skills in the Skills section of your resume. Use bullet points to list specific Excel skills you have, such as pivot tables, macros, and advanced formulas.
Include the certification logo on your LinkedIn profile. You can download the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification logo from the Microsoft website and upload it to your LinkedIn profile under the Licenses & Certifications section.
Add the certification to your LinkedIn headline and summary. Including the certification in your headline and summary can help catch the attention of recruiters and hiring managers.
Showcase your Excel skills in your LinkedIn profile. Use the Projects or Experience section of your LinkedIn profile to highlight specific projects or accomplishments that showcase your Excel skills.
Provide specific examples of how you have used Excel in your professional experience. This can help demonstrate your Excel proficiency to potential employers.
Future trends in Microsoft Excel and the importance of staying up-to-date with the latest developments
Microsoft Excel has been a staple of the business world for over three decades, and it continues to evolve and improve. Staying up-to-date with the latest developments in Excel is essential for anyone who uses the software regularly. Here are some future trends in Excel and the importance of staying up-to-date with them:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Excel is expected to incorporate more AI and machine learning capabilities, which will enable users to perform more complex data analysis and automate routine tasks. Staying up-to-date with these developments can help users become more efficient and effective in their work.
Cloud-Based Collaboration: Microsoft has been emphasizing cloud-based collaboration with Excel, which allows users to collaborate on spreadsheets in real-time. Staying up-to-date with these developments can help users work more efficiently with colleagues, even if they are not in the same physical location.
Mobile Access: With the rise of mobile devices, Microsoft has been working to make Excel more accessible on smartphones and tablets. Staying up-to-date with these developments can enable users to work on their spreadsheets while on-the-go.
Visualizations and Data Visualization Tools: Excel has been expanding its capabilities in data visualization, which allows users to create more visually compelling charts and graphs. Staying up-to-date with these developments can help users create more engaging and informative reports.
Integration with other Software: Excel is integrating with other software and services such as Power BI, Azure Machine Learning, and Dynamics 365. Staying up-to-date with these developments can help users leverage Excel's capabilities in conjunction with other software to create more powerful solutions.
How to obtain Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Microsoft : Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification is a significant achievement that can greatly enhance your career prospects and demonstrate your advanced skills in Excel. By obtaining this certification, you showcase your ability to leverage the full potential of Excel's advanced features and functionalities to solve complex business problems and drive data-driven decision-making.
Throughout this article, we have explored the key benefits of acquiring the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification. We have discussed how this credential can help you stand out in the job market, validate your expertise, and open doors to new opportunities. We have also examined the specific topics covered in the certification exam, ranging from advanced formulas and data analysis techniques to collaboration features and data visualization tools.
Furthermore, we have highlighted the resources available to help you prepare for the certification exam, including official study guides, practice tests, and online training courses. These resources can provide you with the knowledge and practice necessary to excel in the exam and ensure that you are well-prepared to tackle real-world Excel challenges.
By investing the time and effort into acquiring the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification, you are not only expanding your technical skills but also demonstrating your commitment to professional growth and continuous learning. This certification is a testament to your dedication and sets you apart as a competent and proficient Excel user.
In today's data-driven business environment, Excel skills are in high demand, and the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification equips you with the expertise needed to excel in various roles, including data analysis, finance, project management, and more. It is a valuable asset that can enhance your employability, increase your earning potential, and give you a competitive advantage in your career.
So, if you're looking to take your Excel skills to the next level and differentiate yourself in the job market, consider pursuing the Microsoft Excel 2013 Advanced Certification. It is a worthwhile investment that can unlock new opportunities and propel your career forward in the ever-evolving world of data analysis and business intelligence.
The Ultimate Guide to Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Cert
Welcome to "The Ultimate Guide to Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification"! This comprehensive guide is designed to take you on a transformative journey through the world of Microsoft Excel 2013's intermediate features. From advanced formulas and functions to pivot tables and data analysis, each chapter provides step-by-step instructions and practical examples, empowering you to not only understand the concepts but also apply them confidently in real-world scenarios. Whether you're a student, a professional, or an aspiring data enthusiast, this resource will equip you with the knowledge and expertise to conquer the Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification, unlock the full potential of Excel, and elevate your productivity to new heights. Let's dive in and become an Excel maestro!
Table of contents
What is Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification?
Benefits of obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification
Prerequisites for taking the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam
Exam format and structure
Tips for preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam
Common topics covered in the exam, such as working with formulas and functions, sorting and filtering data, and creating charts and graphs
Overview of the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam objectives
Review of Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification study materials and resources
Potential career opportunities and job roles that may require or benefit from the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification
Conclusion
What is Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification?
Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification is a professional credential that validates an individual's proficiency in using Microsoft Excel 2013 at an intermediate level. It is designed to demonstrate a user's knowledge and skills in creating and manipulating worksheets and workbooks, managing data, formatting cells and ranges, working with tables and charts, and using advanced formulas and functions.
Earning the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification indicates that a user has a strong understanding of Excel and can work more efficiently with complex data. It demonstrates to employers that an individual has the knowledge and skills necessary to perform intermediate-level tasks in Excel, making them more marketable in today's competitive job market.
To obtain the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification, individuals must pass a certification exam, which assesses their knowledge and skills in various Excel concepts and features. The certification is issued by Microsoft, a globally recognized technology company, and is widely accepted by employers and organizations worldwide.
Benefits of obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification
Obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can offer several benefits, including:
Enhanced Excel skills: The certification process includes preparation for the exam, which can help users develop a deeper understanding of Excel features and functions, and become more proficient in using the software.
Career advancement: Earning the certification can demonstrate to current or potential employers that an individual has the skills and knowledge necessary to perform intermediate-level tasks in Excel, which can lead to increased job responsibilities, promotions, or new job opportunities.
Increased earning potential: Individuals who earn the certification may have a competitive advantage in the job market and may be able to negotiate higher salaries or hourly rates.
Professional recognition: Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification is a globally recognized credential that demonstrates an individual's expertise in Excel. It can enhance the credibility and reputation of individuals who work in finance, accounting, data analysis, or other fields that require Excel proficiency.
Access to resources and community: Microsoft offers resources and a community for individuals who have earned their certification, including access to exclusive webinars, training materials, and networking opportunities.
Prerequisites for taking the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam
Before taking the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam, there are a few prerequisites that individuals should be aware of.
Intermediate Excel skills: The exam is designed for individuals who have a good understanding of Excel at an intermediate level. It is recommended that individuals have at least six months to one year of experience using Excel to prepare for the exam.
Basic computer skills: The certification exam is administered on a computer, so individuals should have basic computer skills, such as the ability to use a mouse and keyboard and navigate computer programs.
Familiarity with Microsoft Excel 2013: The exam is specifically designed for Excel 2013, so individuals should have a working knowledge of this version of the software.
Microsoft account: Individuals will need to create a Microsoft account in order to register for the certification exam and access study materials.
Registration fee: There is a fee to take the certification exam, which varies by location. Individuals should be prepared to pay this fee before registering for the exam.
Exam format and structure
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam is a computer-based test that assesses an individual's proficiency in using Excel 2013 at an intermediate level. The exam is timed and consists of a series of multiple-choice questions.
Here are the details of the exam format and structure:
Number of questions: The exam consists of 40 to 60 questions.
Time limit: The exam has a time limit of 50 minutes.
Exam content: The exam covers a range of topics, including creating and manipulating worksheets and workbooks, managing data, formatting cells and ranges, working with tables and charts, and using advanced formulas and functions.
Question types: The exam includes multiple-choice questions with a single correct answer, as well as multiple-choice questions with multiple correct answers.
Passing score: The passing score for the exam is 700 out of 1,000 points.
Exam delivery: The exam is delivered through Microsoft's testing partner, Certiport, and can be taken at authorized testing centers worldwide.
Tips for preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam
Here are some tips to help individuals prepare for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam:
Familiarize yourself with the exam content: The exam covers a range of topics, so it's important to review and practice using the relevant Excel features and functions. Microsoft offers study materials and practice exams to help individuals prepare for the exam.
Take advantage of online resources: There are many online resources available that can help individuals prepare for the exam, such as video tutorials, blogs, and forums. These resources can provide additional explanations and examples to reinforce learning.
Practice with real-world examples: Practicing using Excel with real-world examples can help individuals better understand how to apply Excel features and functions in different scenarios.
Take practice exams: Taking practice exams can help individuals get a sense of the exam format and structure, as well as identify areas where they need additional practice.
Use Excel regularly: Using Excel regularly can help individuals build proficiency and familiarity with the software, making it easier to apply concepts during the exam.
Manage your time effectively: The exam has a time limit, so it's important to manage your time effectively during the exam. Practice answering questions quickly and efficiently, and don't spend too much time on any one question.
Stay calm and focused during the exam: Taking deep breaths and staying focused during the exam can help individuals remain calm and reduce test anxiety.
Common topics covered in the exam, such as working with formulas and functions, sorting and filtering data, and creating charts and graphs
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam covers a range of topics related to using Excel 2013 at an intermediate level. Here are some of the common topics that individuals can expect to see on the exam:
Working with formulas and functions: The exam may test individuals' knowledge of creating and using basic and advanced formulas and functions, such as SUM, AVERAGE, IF, COUNTIF, and VLOOKUP.
Sorting and filtering data: The exam may test individuals' ability to sort and filter data in a worksheet based on specific criteria, as well as their knowledge of using custom sorts and filters.
Creating charts and graphs: The exam may test individuals' ability to create and customize various types of charts and graphs, including pie charts, bar charts, and line charts.
Formatting cells and ranges: The exam may test individuals' ability to format cells and ranges, including changing font styles and sizes, applying borders and shading, and using conditional formatting.
Managing worksheets and workbooks: The exam may test individuals' knowledge of managing multiple worksheets and workbooks, including copying, moving, and linking data between worksheets and workbooks.
Using advanced features: The exam may test individuals' knowledge of using advanced Excel features, such as PivotTables, macros, and data validation.
Overview of the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam objectives
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam objectives are organized into the following categories:
Managing worksheets and workbooks: This objective measures an individual's ability to create, navigate, and manage worksheets and workbooks in Excel 2013. This includes creating, copying, and moving worksheets, as well as managing workbook properties and options.
Data entry and manipulation: This objective measures an individual's ability to enter and manipulate data in Excel 2013. This includes entering data into cells, using autofill to complete a series of data, and editing and deleting data.
Formatting cells and ranges: This objective measures an individual's ability to format cells and ranges in Excel 2013. This includes applying font styles and sizes, borders and shading, and conditional formatting.
Charts and objects: This objective measures an individual's ability to create, format, and modify charts and objects in Excel 2013. This includes creating various types of charts and graphs, modifying chart elements, and adding and formatting objects such as shapes and pictures.
Advanced formulas and functions: This objective measures an individual's ability to use advanced formulas and functions in Excel 2013. This includes using functions such as VLOOKUP, IF, and COUNTIF, as well as creating and using named ranges.
PivotTables and PivotCharts: This objective measures an individual's ability to create and modify PivotTables and PivotCharts in Excel 2013. This includes creating PivotTables from data, grouping and ungrouping data, and formatting PivotCharts.
Data analysis: This objective measures an individual's ability to analyze data in Excel 2013. This includes using sorting and filtering tools, as well as using data validation to control data entry.
Review of Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification study materials and resources
There are several study materials and resources available to prepare for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam. Here are some of the most popular options:
Official Microsoft training courses: Microsoft offers a range of training courses designed specifically for the Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam. These courses cover all the topics and objectives included in the exam and provide hands-on training using Excel 2013.
Microsoft Excel 2013 textbooks: Several textbooks are available that cover all the topics and objectives included in the Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam. These textbooks provide comprehensive coverage of the material and often include practice exercises and sample questions.
Online tutorials and videos: There are many online tutorials and videos available that cover specific topics related to Excel 2013. These can be especially helpful for individuals who prefer a more visual learning experience.
Practice exams: Many practice exams are available that simulate the actual Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam. These practice exams can be useful for identifying areas where an individual may need additional study and for gaining familiarity with the exam format.
Excel 2013 user community forums: There are several online user community forums where individuals can connect with other Excel users and ask questions or seek advice related to the Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam.
Potential career opportunities and job roles that may require or benefit from the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can open up a variety of career opportunities and job roles, as it demonstrates a strong proficiency in one of the most widely used data analysis tools. Here are some potential career opportunities and job roles that may require or benefit from the certification:
Data Analyst: Data analysts use Excel to collect, process, and analyze large amounts of data to inform business decisions. The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can demonstrate a strong foundation in data analysis and management, making it a valuable credential for this role.
Financial Analyst: Financial analysts use Excel to create financial models and analyze financial data to inform investment decisions. The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can demonstrate a strong understanding of financial functions and formulas in Excel, making it a valuable credential for this role.
Operations Manager: Operations managers use Excel to track and manage inventory, monitor productivity, and analyze sales data. The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can demonstrate a strong foundation in data management and analysis, making it a valuable credential for this role.
Marketing Analyst: Marketing analysts use Excel to analyze customer data and develop marketing strategies. The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can demonstrate a strong understanding of data analysis and visualization in Excel, making it a valuable credential for this role.
Human Resources Specialist: Human resources specialists use Excel to manage employee data, track performance metrics, and analyze employee demographics. The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can demonstrate a strong foundation in data management and analysis, making it a valuable credential for this role.
How to obtain Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Microsoft : Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification is a valuable achievement for individuals looking to enhance their skills and proficiency in using Excel. This ultimate guide has provided comprehensive and practical insights into the intermediate level features and functionalities of Excel 2013.
By following this guide, learners have gained a solid foundation in various topics, including data analysis, advanced formulas, chart creation, and data manipulation. The guide has presented clear explanations, step-by-step instructions, and real-world examples, making it accessible for users of all levels of experience.
The certification not only validates one's expertise in Excel 2013 but also opens up numerous career opportunities. As Excel is widely used in various industries, having an intermediate-level certification demonstrates a high level of proficiency and increases employability. It showcases an individual's ability to handle complex data analysis tasks, automate processes, and make informed decisions using Excel.
Moreover, this guide has equipped learners with the necessary knowledge and skills to excel in their professional roles. Whether it be in finance, marketing, human resources, or any other field that requires data management, the Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification serves as a testament to one's commitment to continuous learning and professional growth.
In a world driven by data, mastering Excel is essential for both personal and professional success. This guide has provided learners with the tools and techniques needed to become proficient Excel users, giving them a competitive edge in the digital age.
In summary, the Ultimate Guide to Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification has empowered individuals to unlock the full potential of Excel 2013 and gain recognition for their skills. With this certification, learners are well-positioned to excel in their careers, tackle complex data challenges, and contribute effectively to their organizations.
Read More
Welcome to "The Ultimate Guide to Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification"! This comprehensive guide is designed to take you on a transformative journey through the world of Microsoft Excel 2013's intermediate features. From advanced formulas and functions to pivot tables and data analysis, each chapter provides step-by-step instructions and practical examples, empowering you to not only understand the concepts but also apply them confidently in real-world scenarios. Whether you're a student, a professional, or an aspiring data enthusiast, this resource will equip you with the knowledge and expertise to conquer the Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification, unlock the full potential of Excel, and elevate your productivity to new heights. Let's dive in and become an Excel maestro!
Table of contents
What is Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification?
Benefits of obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification
Prerequisites for taking the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam
Exam format and structure
Tips for preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam
Common topics covered in the exam, such as working with formulas and functions, sorting and filtering data, and creating charts and graphs
Overview of the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam objectives
Review of Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification study materials and resources
Potential career opportunities and job roles that may require or benefit from the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification
Conclusion
What is Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification?
Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification is a professional credential that validates an individual's proficiency in using Microsoft Excel 2013 at an intermediate level. It is designed to demonstrate a user's knowledge and skills in creating and manipulating worksheets and workbooks, managing data, formatting cells and ranges, working with tables and charts, and using advanced formulas and functions.
Earning the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification indicates that a user has a strong understanding of Excel and can work more efficiently with complex data. It demonstrates to employers that an individual has the knowledge and skills necessary to perform intermediate-level tasks in Excel, making them more marketable in today's competitive job market.
To obtain the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification, individuals must pass a certification exam, which assesses their knowledge and skills in various Excel concepts and features. The certification is issued by Microsoft, a globally recognized technology company, and is widely accepted by employers and organizations worldwide.
Benefits of obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification
Obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can offer several benefits, including:
Enhanced Excel skills: The certification process includes preparation for the exam, which can help users develop a deeper understanding of Excel features and functions, and become more proficient in using the software.
Career advancement: Earning the certification can demonstrate to current or potential employers that an individual has the skills and knowledge necessary to perform intermediate-level tasks in Excel, which can lead to increased job responsibilities, promotions, or new job opportunities.
Increased earning potential: Individuals who earn the certification may have a competitive advantage in the job market and may be able to negotiate higher salaries or hourly rates.
Professional recognition: Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification is a globally recognized credential that demonstrates an individual's expertise in Excel. It can enhance the credibility and reputation of individuals who work in finance, accounting, data analysis, or other fields that require Excel proficiency.
Access to resources and community: Microsoft offers resources and a community for individuals who have earned their certification, including access to exclusive webinars, training materials, and networking opportunities.
Prerequisites for taking the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam
Before taking the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam, there are a few prerequisites that individuals should be aware of.
Intermediate Excel skills: The exam is designed for individuals who have a good understanding of Excel at an intermediate level. It is recommended that individuals have at least six months to one year of experience using Excel to prepare for the exam.
Basic computer skills: The certification exam is administered on a computer, so individuals should have basic computer skills, such as the ability to use a mouse and keyboard and navigate computer programs.
Familiarity with Microsoft Excel 2013: The exam is specifically designed for Excel 2013, so individuals should have a working knowledge of this version of the software.
Microsoft account: Individuals will need to create a Microsoft account in order to register for the certification exam and access study materials.
Registration fee: There is a fee to take the certification exam, which varies by location. Individuals should be prepared to pay this fee before registering for the exam.
Exam format and structure
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam is a computer-based test that assesses an individual's proficiency in using Excel 2013 at an intermediate level. The exam is timed and consists of a series of multiple-choice questions.
Here are the details of the exam format and structure:
Number of questions: The exam consists of 40 to 60 questions.
Time limit: The exam has a time limit of 50 minutes.
Exam content: The exam covers a range of topics, including creating and manipulating worksheets and workbooks, managing data, formatting cells and ranges, working with tables and charts, and using advanced formulas and functions.
Question types: The exam includes multiple-choice questions with a single correct answer, as well as multiple-choice questions with multiple correct answers.
Passing score: The passing score for the exam is 700 out of 1,000 points.
Exam delivery: The exam is delivered through Microsoft's testing partner, Certiport, and can be taken at authorized testing centers worldwide.
Tips for preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam
Here are some tips to help individuals prepare for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam:
Familiarize yourself with the exam content: The exam covers a range of topics, so it's important to review and practice using the relevant Excel features and functions. Microsoft offers study materials and practice exams to help individuals prepare for the exam.
Take advantage of online resources: There are many online resources available that can help individuals prepare for the exam, such as video tutorials, blogs, and forums. These resources can provide additional explanations and examples to reinforce learning.
Practice with real-world examples: Practicing using Excel with real-world examples can help individuals better understand how to apply Excel features and functions in different scenarios.
Take practice exams: Taking practice exams can help individuals get a sense of the exam format and structure, as well as identify areas where they need additional practice.
Use Excel regularly: Using Excel regularly can help individuals build proficiency and familiarity with the software, making it easier to apply concepts during the exam.
Manage your time effectively: The exam has a time limit, so it's important to manage your time effectively during the exam. Practice answering questions quickly and efficiently, and don't spend too much time on any one question.
Stay calm and focused during the exam: Taking deep breaths and staying focused during the exam can help individuals remain calm and reduce test anxiety.
Common topics covered in the exam, such as working with formulas and functions, sorting and filtering data, and creating charts and graphs
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam covers a range of topics related to using Excel 2013 at an intermediate level. Here are some of the common topics that individuals can expect to see on the exam:
Working with formulas and functions: The exam may test individuals' knowledge of creating and using basic and advanced formulas and functions, such as SUM, AVERAGE, IF, COUNTIF, and VLOOKUP.
Sorting and filtering data: The exam may test individuals' ability to sort and filter data in a worksheet based on specific criteria, as well as their knowledge of using custom sorts and filters.
Creating charts and graphs: The exam may test individuals' ability to create and customize various types of charts and graphs, including pie charts, bar charts, and line charts.
Formatting cells and ranges: The exam may test individuals' ability to format cells and ranges, including changing font styles and sizes, applying borders and shading, and using conditional formatting.
Managing worksheets and workbooks: The exam may test individuals' knowledge of managing multiple worksheets and workbooks, including copying, moving, and linking data between worksheets and workbooks.
Using advanced features: The exam may test individuals' knowledge of using advanced Excel features, such as PivotTables, macros, and data validation.
Overview of the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam objectives
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam objectives are organized into the following categories:
Managing worksheets and workbooks: This objective measures an individual's ability to create, navigate, and manage worksheets and workbooks in Excel 2013. This includes creating, copying, and moving worksheets, as well as managing workbook properties and options.
Data entry and manipulation: This objective measures an individual's ability to enter and manipulate data in Excel 2013. This includes entering data into cells, using autofill to complete a series of data, and editing and deleting data.
Formatting cells and ranges: This objective measures an individual's ability to format cells and ranges in Excel 2013. This includes applying font styles and sizes, borders and shading, and conditional formatting.
Charts and objects: This objective measures an individual's ability to create, format, and modify charts and objects in Excel 2013. This includes creating various types of charts and graphs, modifying chart elements, and adding and formatting objects such as shapes and pictures.
Advanced formulas and functions: This objective measures an individual's ability to use advanced formulas and functions in Excel 2013. This includes using functions such as VLOOKUP, IF, and COUNTIF, as well as creating and using named ranges.
PivotTables and PivotCharts: This objective measures an individual's ability to create and modify PivotTables and PivotCharts in Excel 2013. This includes creating PivotTables from data, grouping and ungrouping data, and formatting PivotCharts.
Data analysis: This objective measures an individual's ability to analyze data in Excel 2013. This includes using sorting and filtering tools, as well as using data validation to control data entry.
Review of Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification study materials and resources
There are several study materials and resources available to prepare for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam. Here are some of the most popular options:
Official Microsoft training courses: Microsoft offers a range of training courses designed specifically for the Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam. These courses cover all the topics and objectives included in the exam and provide hands-on training using Excel 2013.
Microsoft Excel 2013 textbooks: Several textbooks are available that cover all the topics and objectives included in the Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam. These textbooks provide comprehensive coverage of the material and often include practice exercises and sample questions.
Online tutorials and videos: There are many online tutorials and videos available that cover specific topics related to Excel 2013. These can be especially helpful for individuals who prefer a more visual learning experience.
Practice exams: Many practice exams are available that simulate the actual Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam. These practice exams can be useful for identifying areas where an individual may need additional study and for gaining familiarity with the exam format.
Excel 2013 user community forums: There are several online user community forums where individuals can connect with other Excel users and ask questions or seek advice related to the Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification exam.
Potential career opportunities and job roles that may require or benefit from the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can open up a variety of career opportunities and job roles, as it demonstrates a strong proficiency in one of the most widely used data analysis tools. Here are some potential career opportunities and job roles that may require or benefit from the certification:
Data Analyst: Data analysts use Excel to collect, process, and analyze large amounts of data to inform business decisions. The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can demonstrate a strong foundation in data analysis and management, making it a valuable credential for this role.
Financial Analyst: Financial analysts use Excel to create financial models and analyze financial data to inform investment decisions. The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can demonstrate a strong understanding of financial functions and formulas in Excel, making it a valuable credential for this role.
Operations Manager: Operations managers use Excel to track and manage inventory, monitor productivity, and analyze sales data. The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can demonstrate a strong foundation in data management and analysis, making it a valuable credential for this role.
Marketing Analyst: Marketing analysts use Excel to analyze customer data and develop marketing strategies. The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can demonstrate a strong understanding of data analysis and visualization in Excel, making it a valuable credential for this role.
Human Resources Specialist: Human resources specialists use Excel to manage employee data, track performance metrics, and analyze employee demographics. The Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification can demonstrate a strong foundation in data management and analysis, making it a valuable credential for this role.
How to obtain Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Microsoft : Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification is a valuable achievement for individuals looking to enhance their skills and proficiency in using Excel. This ultimate guide has provided comprehensive and practical insights into the intermediate level features and functionalities of Excel 2013.
By following this guide, learners have gained a solid foundation in various topics, including data analysis, advanced formulas, chart creation, and data manipulation. The guide has presented clear explanations, step-by-step instructions, and real-world examples, making it accessible for users of all levels of experience.
The certification not only validates one's expertise in Excel 2013 but also opens up numerous career opportunities. As Excel is widely used in various industries, having an intermediate-level certification demonstrates a high level of proficiency and increases employability. It showcases an individual's ability to handle complex data analysis tasks, automate processes, and make informed decisions using Excel.
Moreover, this guide has equipped learners with the necessary knowledge and skills to excel in their professional roles. Whether it be in finance, marketing, human resources, or any other field that requires data management, the Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification serves as a testament to one's commitment to continuous learning and professional growth.
In a world driven by data, mastering Excel is essential for both personal and professional success. This guide has provided learners with the tools and techniques needed to become proficient Excel users, giving them a competitive edge in the digital age.
In summary, the Ultimate Guide to Microsoft Excel 2013 Intermediate Certification has empowered individuals to unlock the full potential of Excel 2013 and gain recognition for their skills. With this certification, learners are well-positioned to excel in their careers, tackle complex data challenges, and contribute effectively to their organizations.
MS Excel 2013 Certification: Professional Development Guide
Welcome to "Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification: A Guide to Professional Development"! This comprehensive guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and expertise required to earn the esteemed Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification. Whether you're a novice looking to build a strong foundation or a seasoned user seeking to refine your skills and gain formal recognition, our step-by-step tutorials, practical exercises, and real-world examples will provide you with hands-on experience, ensuring that you not only grasp the concepts but also understand how to apply them effectively in your daily tasks. So, whether you are an ambitious student, a working professional, or an aspiring entrepreneur, let's embark on this learning journey together, mastering the art of data manipulation and analysis, and elevating your career to new heights with confidence!
Table of contents
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2013
Why should you get certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation?
What are the prerequisites for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification?
Overview of the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam:
Exam topics covered in the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification:
How to prepare for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification:
Tips and tricks to pass the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam
Benefits of obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification
Conclusion
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2013
Microsoft Excel 2013 is a spreadsheet software developed by Microsoft Corporation, used for data analysis, organizing, and managing large amounts of data. Excel 2013 comes with a wide range of features and functions that make it an essential tool for businesses, students, and professionals across various industries.
Excel 2013 has a user-friendly interface that allows users to enter, manipulate and analyze data easily. It supports various data formats like text, numbers, dates, and more. Excel 2013 is equipped with several advanced features, including powerful formulas and functions, charts and graphs, conditional formatting, pivot tables, data validation, and more.
Excel 2013 also offers a variety of customization options to make your spreadsheet look more professional, such as adjusting cell sizes, colors, fonts, and borders. Excel's extensive functionality makes it a versatile tool for a wide range of tasks, from basic calculations to complex data analysis.
One of the benefits of Excel 2013 is that it provides users with the ability to collaborate with others, allowing multiple users to work on a single spreadsheet simultaneously. This feature makes it easier to share information and ensures that everyone is working on the same up-to-date data.
Why should you get certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation?
Getting certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation can offer many benefits to individuals looking to enhance their professional skills and advance their careers. Here are some reasons why you should consider getting certified in Excel 2013 Foundation:
Validation of your skills: Excel 2013 Foundation Certification validates your skills and knowledge in using Excel 2013. It serves as proof to employers that you have a solid understanding of Excel's fundamental features and functions.
Enhanced job opportunities: Excel skills are in high demand in today's job market, and having an Excel 2013 Foundation Certification can significantly enhance your job opportunities. Many job postings require candidates to have Excel skills, and being certified can make you stand out from other candidates.
Increased earning potential: According to a survey conducted by Global Knowledge, individuals who hold a Microsoft certification earn an average of 15% more than those who are not certified. Having an Excel 2013 Foundation Certification can potentially increase your earning potential in your current job or when applying for a new one.
Professional development: Obtaining an Excel 2013 Foundation Certification demonstrates your commitment to professional development and continuous learning. It shows that you are willing to invest time and effort into developing your skills and knowledge in using Excel 2013.
Competitive advantage: In today's highly competitive job market, having an Excel 2013 Foundation Certification can give you a competitive advantage over other candidates who do not have this certification. It can make you a more attractive candidate to potential employers and increase your chances of being hired.
What are the prerequisites for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification?
To obtain the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification, there are no specific prerequisites. However, Microsoft recommends that candidates have a basic understanding of Microsoft Office and Excel, as well as some experience working with spreadsheets and formulas.
It is important to note that while there are no prerequisites for the certification, candidates should be familiar with the topics covered in the exam. These include creating and managing worksheets and workbooks, formatting cells and data, creating formulas and functions, and working with charts and tables.
Microsoft provides study materials, training courses, and practice exams to help candidates prepare for the Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam. These resources can help candidates develop the necessary skills and knowledge to pass the exam successfully.
In summary, while there are no specific prerequisites for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification, candidates should have some basic experience working with spreadsheets and formulas and be familiar with the topics covered in the exam. Microsoft provides study materials and training courses to help candidates prepare for the certification exam.
Overview of the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam is designed to test the candidate's skills and knowledge in using Microsoft Excel 2013. Here is an overview of the format, duration, and number of questions for the certification exam:
Format: The Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam consists of multiple-choice questions and simulations. The multiple-choice questions test the candidate's knowledge of Excel concepts and features, while the simulations test the candidate's ability to perform tasks using Excel 2013.
Duration: The exam is timed and lasts for 50 minutes. However, some exams may have extra time added for non-native speakers.
Number of Questions: The exam contains between 30 and 35 questions, although Microsoft does not disclose the exact number of questions in the exam. The number of questions may vary slightly as Microsoft updates the exam periodically.
Passing Score: To pass the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam, candidates must achieve a minimum score of 700 out of 1000.
Topics Covered: The exam covers a range of topics, including creating and managing worksheets and workbooks, formatting cells and data, creating formulas and functions, and working with charts and tables. Microsoft provides a detailed exam guide outlining the topics and skills that candidates should master before taking the exam.
In conclusion, the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam consists of multiple-choice questions and simulations and lasts for 50 minutes. The exam covers various topics related to Excel 2013, including creating and managing worksheets, formatting cells, creating formulas and functions, and working with charts and tables. Candidates must achieve a minimum score of 700 out of 1000 to pass the exam and earn the certification.
Exam topics covered in the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam covers a range of topics related to using Microsoft Excel 2013. Here is an overview of the key topics covered in the exam:
Creating and Managing Worksheets and Workbooks:
Creating new workbooks
Navigating and selecting cells, ranges, and worksheets
Inserting and deleting data, rows, and columns
Managing multiple worksheets
Formatting Cells and Data:
Formatting cells and data using fonts, colors, and borders
Applying number and date formatting
Using conditional formatting to highlight data
Creating Formulas and Functions:
Creating and editing formulas
Using built-in functions such as SUM, AVERAGE, and COUNT
Using absolute and relative references in formulas
Working with Charts and Tables:
Creating and formatting charts and graphs
Using chart and graph elements such as legends and titles
Creating and formatting tables
Data Analysis:
Sorting and filtering data
Using Excel's data analysis tools such as Goal Seek and Solver
Creating and using PivotTables and PivotCharts
Collaborating with Others:
Protecting and sharing workbooks
Adding comments and notes
Using Excel's collaboration features such as sharing and co-authoring
How to prepare for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification
Preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam requires a combination of study materials, practice exams, and training courses. Here are some steps that candidates can take to prepare for the exam:
Review the Exam Guide: Microsoft provides a detailed exam guide that outlines the topics and skills that candidates should master before taking the exam. Reviewing this guide can help candidates identify areas where they need to focus their study efforts.
Use Study Materials: Microsoft offers study materials such as books, online courses, and tutorials to help candidates prepare for the exam. These materials cover the key topics and skills needed to pass the exam and provide practice exercises to reinforce learning.
Take Practice Exams: Taking practice exams can help candidates familiarize themselves with the format and style of the exam questions. Microsoft offers official practice exams that closely simulate the actual exam.
Attend Training Courses: Microsoft offers training courses led by certified instructors to help candidates prepare for the exam. These courses cover the key topics and skills needed to pass the exam and provide hands-on practice exercises.
Use Excel Regularly: Practicing using Excel regularly can help candidates develop the skills and knowledge needed to pass the exam. Candidates can create spreadsheets and work on projects that simulate real-world scenarios to build their confidence and proficiency in using Excel.
Join Online Communities: Joining online communities and forums dedicated to Excel can provide candidates with a wealth of knowledge and resources. These communities can help candidates connect with other Excel users and experts, ask questions, and share tips and tricks.
Tips and tricks to pass the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam
Passing the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam requires more than just knowledge of the subject matter. Here are some tips and tricks that can help candidates pass the exam:
Manage your Time: The exam has a time limit, so it's important to manage your time effectively. Allocate time for each question and stick to your plan. Don't spend too much time on any one question and make sure you answer all questions before time runs out.
Read the Questions Carefully: Carefully read each question and understand what is being asked before answering. Ensure you understand the requirements and don't make assumptions about what is being asked.
Know the Exam Format: Familiarize yourself with the exam format and structure before taking the exam. Know how many questions are on the exam, the time limit, and the types of questions that may be asked.
Practice with Sample Questions: Practice with sample questions to get a sense of the exam format and the types of questions that may be asked. This can help you feel more comfortable and confident on exam day.
Use the Highlighting Feature: Excel provides a highlighting feature that can help you mark important information in the questions and identify the key points you need to address in your answer.
Understand the Scoring: Know how the exam is scored and the minimum passing score required. This can help you understand how many questions you need to answer correctly to pass the exam.
Stay Focused and Confident: Stay focused and confident throughout the exam. Don't panic if you encounter difficult questions, and don't rush through questions too quickly. Take your time, stay calm, and do your best.
Benefits of obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification
Obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification can provide several benefits for professionals. Here are some of the key benefits:
Career Advancement: The certification can demonstrate a candidate's proficiency in using Microsoft Excel, which can help them stand out in job interviews and advance their careers. Employers may prefer candidates who are certified, as it indicates that they have the knowledge and skills needed to use Excel effectively.
Salary Increase: Certified professionals may be eligible for higher salaries and bonuses compared to non-certified professionals. Employers may be willing to pay a premium for certified professionals, as they can bring added value to the organization.
Professional Recognition: The certification is recognized globally and can provide professionals with recognition for their skills and expertise in Microsoft Excel. Being certified can enhance a professional's reputation and credibility in the industry.
Improved Productivity: The certification can help professionals use Excel more efficiently and effectively, which can lead to improved productivity and better results. Certified professionals can use Excel's advanced features and tools to complete tasks more quickly and accurately, saving time and reducing errors.
Continuing Education: Microsoft's certification program requires certified professionals to maintain their knowledge and skills through ongoing training and education. This can help professionals stay up-to-date with the latest features and tools in Excel, which can improve their performance and effectiveness in the workplace.
How to obtain Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Microsoft : Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification
Conclusion
In today's job market, proficiency in Microsoft Excel has become a fundamental skill that employers look for in candidates across various industries. With the increasing amount of data being generated and analyzed, it has become critical for professionals to have a good grasp of Excel and its advanced features to effectively process and interpret data.
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification is a globally recognized credential that can demonstrate your proficiency in using Excel and help you stand out in a competitive job market. With the certification, you can showcase your expertise in data analysis, formatting, charting, and more, which can help you advance in your career and achieve your professional goals.
The certification offers several benefits, including career advancement, salary increase, professional recognition, improved productivity, and continuing education. By preparing and passing the certification exam, you can show potential employers that you have the necessary skills and knowledge to use Excel effectively, making you a valuable asset to any organization.
In conclusion, the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification can significantly boost your career prospects and open doors to new opportunities in a range of industries. By investing in your Excel skills and obtaining this certification, you can take your career to the next level and achieve success in your professional journey.
Read More
Welcome to "Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification: A Guide to Professional Development"! This comprehensive guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and expertise required to earn the esteemed Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification. Whether you're a novice looking to build a strong foundation or a seasoned user seeking to refine your skills and gain formal recognition, our step-by-step tutorials, practical exercises, and real-world examples will provide you with hands-on experience, ensuring that you not only grasp the concepts but also understand how to apply them effectively in your daily tasks. So, whether you are an ambitious student, a working professional, or an aspiring entrepreneur, let's embark on this learning journey together, mastering the art of data manipulation and analysis, and elevating your career to new heights with confidence!
Table of contents
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2013
Why should you get certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation?
What are the prerequisites for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification?
Overview of the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam:
Exam topics covered in the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification:
How to prepare for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification:
Tips and tricks to pass the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam
Benefits of obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification
Conclusion
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2013
Microsoft Excel 2013 is a spreadsheet software developed by Microsoft Corporation, used for data analysis, organizing, and managing large amounts of data. Excel 2013 comes with a wide range of features and functions that make it an essential tool for businesses, students, and professionals across various industries.
Excel 2013 has a user-friendly interface that allows users to enter, manipulate and analyze data easily. It supports various data formats like text, numbers, dates, and more. Excel 2013 is equipped with several advanced features, including powerful formulas and functions, charts and graphs, conditional formatting, pivot tables, data validation, and more.
Excel 2013 also offers a variety of customization options to make your spreadsheet look more professional, such as adjusting cell sizes, colors, fonts, and borders. Excel's extensive functionality makes it a versatile tool for a wide range of tasks, from basic calculations to complex data analysis.
One of the benefits of Excel 2013 is that it provides users with the ability to collaborate with others, allowing multiple users to work on a single spreadsheet simultaneously. This feature makes it easier to share information and ensures that everyone is working on the same up-to-date data.
Why should you get certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation?
Getting certified in Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation can offer many benefits to individuals looking to enhance their professional skills and advance their careers. Here are some reasons why you should consider getting certified in Excel 2013 Foundation:
Validation of your skills: Excel 2013 Foundation Certification validates your skills and knowledge in using Excel 2013. It serves as proof to employers that you have a solid understanding of Excel's fundamental features and functions.
Enhanced job opportunities: Excel skills are in high demand in today's job market, and having an Excel 2013 Foundation Certification can significantly enhance your job opportunities. Many job postings require candidates to have Excel skills, and being certified can make you stand out from other candidates.
Increased earning potential: According to a survey conducted by Global Knowledge, individuals who hold a Microsoft certification earn an average of 15% more than those who are not certified. Having an Excel 2013 Foundation Certification can potentially increase your earning potential in your current job or when applying for a new one.
Professional development: Obtaining an Excel 2013 Foundation Certification demonstrates your commitment to professional development and continuous learning. It shows that you are willing to invest time and effort into developing your skills and knowledge in using Excel 2013.
Competitive advantage: In today's highly competitive job market, having an Excel 2013 Foundation Certification can give you a competitive advantage over other candidates who do not have this certification. It can make you a more attractive candidate to potential employers and increase your chances of being hired.
What are the prerequisites for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification?
To obtain the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification, there are no specific prerequisites. However, Microsoft recommends that candidates have a basic understanding of Microsoft Office and Excel, as well as some experience working with spreadsheets and formulas.
It is important to note that while there are no prerequisites for the certification, candidates should be familiar with the topics covered in the exam. These include creating and managing worksheets and workbooks, formatting cells and data, creating formulas and functions, and working with charts and tables.
Microsoft provides study materials, training courses, and practice exams to help candidates prepare for the Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam. These resources can help candidates develop the necessary skills and knowledge to pass the exam successfully.
In summary, while there are no specific prerequisites for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification, candidates should have some basic experience working with spreadsheets and formulas and be familiar with the topics covered in the exam. Microsoft provides study materials and training courses to help candidates prepare for the certification exam.
Overview of the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam is designed to test the candidate's skills and knowledge in using Microsoft Excel 2013. Here is an overview of the format, duration, and number of questions for the certification exam:
Format: The Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam consists of multiple-choice questions and simulations. The multiple-choice questions test the candidate's knowledge of Excel concepts and features, while the simulations test the candidate's ability to perform tasks using Excel 2013.
Duration: The exam is timed and lasts for 50 minutes. However, some exams may have extra time added for non-native speakers.
Number of Questions: The exam contains between 30 and 35 questions, although Microsoft does not disclose the exact number of questions in the exam. The number of questions may vary slightly as Microsoft updates the exam periodically.
Passing Score: To pass the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam, candidates must achieve a minimum score of 700 out of 1000.
Topics Covered: The exam covers a range of topics, including creating and managing worksheets and workbooks, formatting cells and data, creating formulas and functions, and working with charts and tables. Microsoft provides a detailed exam guide outlining the topics and skills that candidates should master before taking the exam.
In conclusion, the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam consists of multiple-choice questions and simulations and lasts for 50 minutes. The exam covers various topics related to Excel 2013, including creating and managing worksheets, formatting cells, creating formulas and functions, and working with charts and tables. Candidates must achieve a minimum score of 700 out of 1000 to pass the exam and earn the certification.
Exam topics covered in the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam covers a range of topics related to using Microsoft Excel 2013. Here is an overview of the key topics covered in the exam:
Creating and Managing Worksheets and Workbooks:
Creating new workbooks
Navigating and selecting cells, ranges, and worksheets
Inserting and deleting data, rows, and columns
Managing multiple worksheets
Formatting Cells and Data:
Formatting cells and data using fonts, colors, and borders
Applying number and date formatting
Using conditional formatting to highlight data
Creating Formulas and Functions:
Creating and editing formulas
Using built-in functions such as SUM, AVERAGE, and COUNT
Using absolute and relative references in formulas
Working with Charts and Tables:
Creating and formatting charts and graphs
Using chart and graph elements such as legends and titles
Creating and formatting tables
Data Analysis:
Sorting and filtering data
Using Excel's data analysis tools such as Goal Seek and Solver
Creating and using PivotTables and PivotCharts
Collaborating with Others:
Protecting and sharing workbooks
Adding comments and notes
Using Excel's collaboration features such as sharing and co-authoring
How to prepare for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification
Preparing for the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam requires a combination of study materials, practice exams, and training courses. Here are some steps that candidates can take to prepare for the exam:
Review the Exam Guide: Microsoft provides a detailed exam guide that outlines the topics and skills that candidates should master before taking the exam. Reviewing this guide can help candidates identify areas where they need to focus their study efforts.
Use Study Materials: Microsoft offers study materials such as books, online courses, and tutorials to help candidates prepare for the exam. These materials cover the key topics and skills needed to pass the exam and provide practice exercises to reinforce learning.
Take Practice Exams: Taking practice exams can help candidates familiarize themselves with the format and style of the exam questions. Microsoft offers official practice exams that closely simulate the actual exam.
Attend Training Courses: Microsoft offers training courses led by certified instructors to help candidates prepare for the exam. These courses cover the key topics and skills needed to pass the exam and provide hands-on practice exercises.
Use Excel Regularly: Practicing using Excel regularly can help candidates develop the skills and knowledge needed to pass the exam. Candidates can create spreadsheets and work on projects that simulate real-world scenarios to build their confidence and proficiency in using Excel.
Join Online Communities: Joining online communities and forums dedicated to Excel can provide candidates with a wealth of knowledge and resources. These communities can help candidates connect with other Excel users and experts, ask questions, and share tips and tricks.
Tips and tricks to pass the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam
Passing the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification exam requires more than just knowledge of the subject matter. Here are some tips and tricks that can help candidates pass the exam:
Manage your Time: The exam has a time limit, so it's important to manage your time effectively. Allocate time for each question and stick to your plan. Don't spend too much time on any one question and make sure you answer all questions before time runs out.
Read the Questions Carefully: Carefully read each question and understand what is being asked before answering. Ensure you understand the requirements and don't make assumptions about what is being asked.
Know the Exam Format: Familiarize yourself with the exam format and structure before taking the exam. Know how many questions are on the exam, the time limit, and the types of questions that may be asked.
Practice with Sample Questions: Practice with sample questions to get a sense of the exam format and the types of questions that may be asked. This can help you feel more comfortable and confident on exam day.
Use the Highlighting Feature: Excel provides a highlighting feature that can help you mark important information in the questions and identify the key points you need to address in your answer.
Understand the Scoring: Know how the exam is scored and the minimum passing score required. This can help you understand how many questions you need to answer correctly to pass the exam.
Stay Focused and Confident: Stay focused and confident throughout the exam. Don't panic if you encounter difficult questions, and don't rush through questions too quickly. Take your time, stay calm, and do your best.
Benefits of obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification
Obtaining the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification can provide several benefits for professionals. Here are some of the key benefits:
Career Advancement: The certification can demonstrate a candidate's proficiency in using Microsoft Excel, which can help them stand out in job interviews and advance their careers. Employers may prefer candidates who are certified, as it indicates that they have the knowledge and skills needed to use Excel effectively.
Salary Increase: Certified professionals may be eligible for higher salaries and bonuses compared to non-certified professionals. Employers may be willing to pay a premium for certified professionals, as they can bring added value to the organization.
Professional Recognition: The certification is recognized globally and can provide professionals with recognition for their skills and expertise in Microsoft Excel. Being certified can enhance a professional's reputation and credibility in the industry.
Improved Productivity: The certification can help professionals use Excel more efficiently and effectively, which can lead to improved productivity and better results. Certified professionals can use Excel's advanced features and tools to complete tasks more quickly and accurately, saving time and reducing errors.
Continuing Education: Microsoft's certification program requires certified professionals to maintain their knowledge and skills through ongoing training and education. This can help professionals stay up-to-date with the latest features and tools in Excel, which can improve their performance and effectiveness in the workplace.
How to obtain Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop
Microsoft : Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification
Conclusion
In today's job market, proficiency in Microsoft Excel has become a fundamental skill that employers look for in candidates across various industries. With the increasing amount of data being generated and analyzed, it has become critical for professionals to have a good grasp of Excel and its advanced features to effectively process and interpret data.
The Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification is a globally recognized credential that can demonstrate your proficiency in using Excel and help you stand out in a competitive job market. With the certification, you can showcase your expertise in data analysis, formatting, charting, and more, which can help you advance in your career and achieve your professional goals.
The certification offers several benefits, including career advancement, salary increase, professional recognition, improved productivity, and continuing education. By preparing and passing the certification exam, you can show potential employers that you have the necessary skills and knowledge to use Excel effectively, making you a valuable asset to any organization.
In conclusion, the Microsoft Excel 2013 Foundation Certification can significantly boost your career prospects and open doors to new opportunities in a range of industries. By investing in your Excel skills and obtaining this certification, you can take your career to the next level and achieve success in your professional journey.
The Essential Guide to Salesforce Admin Certification!!
Welcome to "The Essential Guide to Salesforce Administration Certification"! This comprehensive resource is designed to equip both seasoned professionals and newcomers with the knowledge, skills, and best practices needed to become proficient Salesforce administrators and pass the coveted Salesforce Administration Certification exam. From mastering the platform's fundamentals and data model to tackling user management, security settings, workflow automation, and insightful reporting, this guide provides expert advice and exam-specific tips, empowering you to confidently navigate the certification journey and open doors to a rewarding career in Salesforce administration. Let's embark on this transformative learning experience together and unlock the boundless opportunities that Salesforce has to offer.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Salesforce Administration Certification
Eligibility and Requirements for Salesforce Administration Certification
Benefits of Salesforce Administration Certification
Exam Format and Structure of Salesforce Administration Certification
Tips for Preparing and Passing the Salesforce Administration Certification Exam
Understanding Salesforce Data Management
Managing Users, Roles, and Permissions in Salesforce
Best Practices for Salesforce Administration
Continuing Education and Professional Development for Salesforce Administrators
Conclusion
Introduction to Salesforce Administration Certification
Salesforce Administration Certification is a professional credential that validates an individual's knowledge and skills in Salesforce administration. Salesforce is a leading customer relationship management (CRM) platform that helps businesses manage their customer data, sales processes, and customer interactions. Salesforce administrators play a critical role in configuring, customizing, and maintaining the Salesforce platform to meet their organization's specific needs.
The Salesforce Administration Certification is offered by Salesforce.com and demonstrates an individual's proficiency in various areas of Salesforce administration. This certification is widely recognized and highly regarded in the industry, as it signifies a person's expertise in implementing and managing Salesforce solutions effectively.
To earn the Salesforce Administration Certification, candidates must pass the Salesforce Certified Administrator exam. This exam assesses a candidate's knowledge of Salesforce features, functionality, and best practices related to user management, data management, security, automation, customization, and analytics. It also evaluates their understanding of the Salesforce Lightning Experience interface and the declarative development tools available within the platform.
Preparing for the Salesforce Certified Administrator exam usually involves studying Salesforce's official study materials, such as trailhead modules, documentation, and online resources. Candidates may also benefit from attending training courses or joining study groups to enhance their understanding of Salesforce administration concepts.
By achieving the Salesforce Administration Certification, professionals can demonstrate their proficiency and dedication to Salesforce administration, making them highly valuable to employers and organizations utilizing Salesforce as their CRM system. It opens up opportunities for career advancement, such as becoming a Salesforce administrator, consultant, or analyst, and may lead to increased job responsibilities and higher earning potential.
It's important to note that Salesforce regularly updates its platform and introduces new features and functionalities. Therefore, maintaining the certification requires staying up to date with these changes and periodically completing maintenance exams or earning additional certifications, such as the Salesforce Advanced Administrator Certification or specialized certifications in areas like Sales Cloud or Service Cloud.
Overall, Salesforce Administration Certification is an industry-recognized credential that validates an individual's expertise in Salesforce administration, enabling them to drive business success and optimize Salesforce implementations for their organizations.
Eligibility and Requirements for Salesforce Administration Certification
To be eligible for Salesforce Administration Certification, candidates must meet certain requirements and prerequisites. Here are the typical eligibility and requirements for Salesforce Administration Certification:
Experience: Candidates should have experience working with Salesforce and should have a good understanding of its various features and functionalities. For the Salesforce Certified Administrator certification, candidates should have at least 6 months to 1 year of experience using Salesforce. For the Salesforce Certified Advanced Administrator certification, candidates should have at least 2 years of experience using Salesforce.
Training: Candidates are recommended to complete the Salesforce Administration Essentials for New Admins course or have equivalent knowledge and experience.
Exam: Candidates must pass a proctored multiple-choice exam that tests their knowledge of Salesforce Administration. The exam covers various topics, including data management, security, automation, user management, and customization.
Payment: Candidates must pay a fee to register for the exam.
It is important to note that these eligibility and requirements may vary depending on the specific Salesforce Administration Certification level. For example, the Salesforce Certified Platform App Builder certification requires candidates to have experience in designing, building, and implementing custom applications on the Salesforce platform.
Benefits of Salesforce Administration Certification
Salesforce Administration Certification offers several benefits to individuals and organizations alike. Here are some of the key benefits of obtaining Salesforce Administration Certification:
Improved Job Opportunities: Salesforce is one of the most popular and widely-used CRM platforms in the world. Obtaining Salesforce Administration Certification can increase job opportunities for individuals, as many companies require professionals with Salesforce expertise. This certification validates an individual's knowledge and skills in Salesforce administration and makes them a more attractive candidate for job openings.
Increased Earning Potential: Salesforce professionals with certification are typically paid more than those without certification. According to a survey by Salesforce, Certified Salesforce Administrators earn an average of $89,000 per year, while Certified Advanced Administrators earn an average of $107,000 per year. This higher salary is due to the high demand for professionals with Salesforce expertise.
Enhanced Credibility: Salesforce Administration Certification demonstrates an individual's knowledge and expertise in Salesforce administration. This certification is recognized globally and enhances an individual's credibility as a Salesforce professional. It also helps individuals gain respect and trust from colleagues and employers.
Better Career Growth: Obtaining Salesforce Administration Certification can help individuals to advance their careers. This certification provides individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to manage and customize Salesforce for their organization. This can lead to career growth opportunities such as promotions, leadership roles, and higher-level positions within the organization.
Improved Salesforce Implementation: Salesforce Administration Certification ensures that an individual has a deep understanding of Salesforce administration. This can help organizations to implement Salesforce more effectively, resulting in improved business processes, better customer management, and increased productivity.
Exam Format and Structure of Salesforce Administration Certification
The Salesforce Administration Certification exam is a proctored multiple-choice exam that tests candidates' knowledge of Salesforce Administration. The exam format and structure may vary depending on the specific certification level, but here is an overview of the typical exam format and structure for the Salesforce Certified Administrator certification:
Exam Format: The Salesforce Certified Administrator exam is a computer-based exam that consists of 60 multiple-choice questions. Candidates have 105 minutes to complete the exam.
Exam Content: The Salesforce Certified Administrator exam covers various topics, including data management, security, automation, user management, and customization. The exam questions are designed to test candidates' knowledge of Salesforce Administration best practices, concepts, and features.
Passing Score: Candidates must achieve a passing score of 65% or higher to pass the exam and obtain certification.
Retake Policy: If a candidate fails the exam, they can retake the exam after 15 days. However, candidates can only take the exam a maximum of 10 times per year.
Exam Fee: Candidates must pay a fee to register for the exam.
It is important for candidates to prepare adequately for the exam to increase their chances of passing. Salesforce offers study resources, including study guides, practice exams, and online training courses, to help candidates prepare for the exam.
In addition, candidates should ensure that they have a good understanding of Salesforce Administration best practices, concepts, and features. They should also be familiar with the exam format and structure, and practice answering multiple-choice questions to get familiar with the exam format.
Tips for Preparing and Passing the Salesforce Administration Certification Exam
Here are some tips for preparing and passing the Salesforce Administration Certification Exam:
Study the Exam Guide: The Salesforce Administration Certification Exam Guide provides an overview of the topics covered on the exam and the weightage assigned to each topic. Read the guide thoroughly to understand the exam format, topics, and level of difficulty.
Use Trailhead: Salesforce's Trailhead provides free learning modules, projects, and quizzes to help prepare for the exam. Use Trailhead to reinforce your knowledge and gain hands-on experience with Salesforce.
Take Practice Exams: Salesforce offers practice exams that simulate the actual exam environment and provide feedback on your performance. Take multiple practice exams to identify areas of weakness and focus on those areas.
Join Study Groups: Joining study groups can provide a collaborative learning environment and offer different perspectives on the topics covered on the exam. Look for study groups on Salesforce user groups or communities.
Get Hands-on Experience: Hands-on experience with Salesforce is essential for passing the exam. Work on real-world projects or create your own projects to gain practical experience with Salesforce.
Focus on Key Topics: Focus on the key topics outlined in the exam guide, such as data management, security and access management, automation, and reporting and analytics. Develop a study plan that prioritizes these topics.
Manage Your Time: Manage your time during the exam carefully. The exam is timed, and you will not have enough time to review each question in detail. Answer the questions you know first and come back to the ones you are unsure about later.
Relax and Stay Confident: Finally, relax and stay confident during the exam. Take deep breaths, read each question carefully, and trust in your preparation. Remember, you can retake the exam if needed.
Understanding Salesforce Data Management
Salesforce Data Management refers to the process of organizing, storing, and maintaining data within Salesforce. It involves managing the lifecycle of data, from data entry to archiving, and ensuring data quality, accuracy, and consistency.
Here are some key concepts to understand when it comes to Salesforce Data Management:
Objects: Salesforce objects are database tables that store specific types of data. For example, the Account object stores information about a customer account, while the Opportunity object stores information about a potential sales opportunity.
Fields: Fields are the individual data elements within an object. For example, an Account object might have fields for the account name, billing address, and phone number.
Records: Records are the individual instances of an object. For example, an Account record represents a specific customer account with its unique information.
Relationships: Relationships define how objects are related to one another in Salesforce. For example, an Account object might have a relationship to the Contact object, which stores information about individuals associated with that account.
Data Importing and Exporting: Salesforce provides several tools for importing and exporting data, including the Data Loader and Data Import Wizard. These tools enable administrators to quickly and easily import and export large amounts of data.
Data Quality: Maintaining data quality is critical for effective data management. Salesforce provides tools for ensuring data accuracy and consistency, such as validation rules, data cleansing, and duplicate management.
Data Security: Data security is also important for data management. Salesforce provides a range of security features to control access to data, including role-based access control, field-level security, and object-level security.
Managing Users, Roles, and Permissions in Salesforce
Managing users, roles, and permissions in Salesforce is an essential part of Salesforce administration. Here are some key concepts to understand:
User Management: Salesforce allows you to create and manage user accounts for your organization. User accounts can be assigned to specific roles and given permissions to access and modify data within Salesforce.
Role Hierarchy: Salesforce uses a role hierarchy to control access to data. The hierarchy defines a series of roles, with higher-level roles having access to data owned by lower-level roles.
Profiles: Profiles define the level of access and permissions that users have in Salesforce. You can customize profiles to restrict access to certain features or data based on a user's role in the organization.
Permission Sets: Permission sets are used to grant additional permissions to users beyond what is defined in their profile. You can use permission sets to grant temporary or additional permissions to users based on their specific needs.
Sharing Settings: Sharing settings control how data is shared between users in Salesforce. You can configure sharing settings to restrict or allow access to certain types of data based on user roles or other criteria.
Single Sign-On (SSO): SSO allows users to log in to Salesforce using their existing credentials from an external system, such as Active Directory. SSO can simplify user management and improve security.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA provides an extra layer of security for user accounts by requiring users to provide a second form of identification, such as a code sent to their phone, in addition to their password.
Best Practices for Salesforce Administration
Here are some best practices for Salesforce administration:
Stay up-to-date with new features and releases: Salesforce releases updates three times a year, and it's important to stay up-to-date with new features and functionality. This can help you take advantage of new tools and improve efficiency.
Maintain data quality: Data quality is essential for accurate reporting and analytics. Administrators should implement data validation rules, maintain clean data, and establish data ownership and sharing rules.
Use a sandbox environment: Sandbox environments allow you to test changes and updates before implementing them in your production environment. This can help minimize errors and ensure that changes are functioning correctly.
Establish user roles and permissions: Establishing user roles and permissions is crucial for ensuring data security and preventing unauthorized access. Administrators should regularly review and update user permissions to ensure that they align with business needs.
Automate workflows: Automating workflows can help streamline business processes and improve efficiency. Administrators should identify repetitive tasks and create workflows to automate them.
Customize Salesforce to meet business needs: Customizing Salesforce to meet business needs can help improve efficiency and productivity. Administrators should work closely with business stakeholders to identify areas where customization can improve business processes.
Provide training and support: Providing training and support to users can help ensure that they are using Salesforce effectively and efficiently. Administrators should create documentation, conduct training sessions, and provide ongoing support to users.
Continuing Education and Professional Development for Salesforce Administrators
Continuing education and professional development are essential for Salesforce administrators to stay current with new technologies, best practices, and industry trends. Here are some options for continuing education and professional development for Salesforce administrators:
Trailhead: Trailhead is Salesforce's free online learning platform that offers a variety of courses, modules, and projects for all skill levels. Administrators can earn badges and certifications to demonstrate their expertise and keep their skills up-to-date.
Salesforce Certifications: Salesforce offers a range of certifications for administrators, developers, architects, and consultants. These certifications demonstrate proficiency in specific areas of Salesforce and can help administrators advance their careers.
User Groups and Communities: User groups and communities provide opportunities for administrators to network with peers, share best practices, and learn from others' experiences. Salesforce has an active community of users, and there are many local and virtual user groups that administrators can join.
Conferences and Events: Conferences and events provide opportunities to learn about new technologies, best practices, and industry trends. Salesforce hosts several annual events, including Dreamforce and TrailheaDX, as well as many regional events and meetups.
Online Training Programs: Online training programs provide structured learning experiences with a focus on specific areas of Salesforce. These programs can be self-paced or instructor-led and may offer certifications upon completion.
On-the-Job Training and Mentoring: On-the-job training and mentoring provide opportunities for administrators to learn from more experienced colleagues. Administrators can seek out mentors within their organization or participate in mentoring programs offered by user groups or communities.
How to obtain Salesforce Administration Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Blockchain Certification
Salesforce : Salesforce Administration Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, Salesforce Administration Certification is a valuable credential for professionals in the field of Salesforce administration. It demonstrates an individual's knowledge and skills in configuring, customizing, and maintaining Salesforce solutions to meet the unique needs of organizations. By earning this certification, individuals can enhance their career prospects, open up new opportunities, and showcase their expertise in Salesforce administration.
Salesforce is a widely used CRM platform, and organizations across various industries rely on it to manage their customer data and streamline their sales processes. As a result, skilled Salesforce administrators are in high demand, and the certification serves as a validation of their abilities to effectively leverage the platform.
To achieve Salesforce Administration Certification, candidates must pass the Salesforce Certified Administrator exam, which assesses their knowledge of various Salesforce features and functionalities. Preparation for the exam typically involves studying Salesforce's official materials and utilizing online resources and training courses.
It is important to note that maintaining the certification requires staying updated with Salesforce platform changes and advancements. This may involve completing maintenance exams or pursuing additional certifications to deepen knowledge in specialized areas.
Overall, Salesforce Administration Certification offers numerous benefits to professionals, including increased career opportunities, recognition, and the ability to contribute to the success of organizations by optimizing Salesforce implementations.
Read More
Welcome to "The Essential Guide to Salesforce Administration Certification"! This comprehensive resource is designed to equip both seasoned professionals and newcomers with the knowledge, skills, and best practices needed to become proficient Salesforce administrators and pass the coveted Salesforce Administration Certification exam. From mastering the platform's fundamentals and data model to tackling user management, security settings, workflow automation, and insightful reporting, this guide provides expert advice and exam-specific tips, empowering you to confidently navigate the certification journey and open doors to a rewarding career in Salesforce administration. Let's embark on this transformative learning experience together and unlock the boundless opportunities that Salesforce has to offer.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Salesforce Administration Certification
Eligibility and Requirements for Salesforce Administration Certification
Benefits of Salesforce Administration Certification
Exam Format and Structure of Salesforce Administration Certification
Tips for Preparing and Passing the Salesforce Administration Certification Exam
Understanding Salesforce Data Management
Managing Users, Roles, and Permissions in Salesforce
Best Practices for Salesforce Administration
Continuing Education and Professional Development for Salesforce Administrators
Conclusion
Introduction to Salesforce Administration Certification
Salesforce Administration Certification is a professional credential that validates an individual's knowledge and skills in Salesforce administration. Salesforce is a leading customer relationship management (CRM) platform that helps businesses manage their customer data, sales processes, and customer interactions. Salesforce administrators play a critical role in configuring, customizing, and maintaining the Salesforce platform to meet their organization's specific needs.
The Salesforce Administration Certification is offered by Salesforce.com and demonstrates an individual's proficiency in various areas of Salesforce administration. This certification is widely recognized and highly regarded in the industry, as it signifies a person's expertise in implementing and managing Salesforce solutions effectively.
To earn the Salesforce Administration Certification, candidates must pass the Salesforce Certified Administrator exam. This exam assesses a candidate's knowledge of Salesforce features, functionality, and best practices related to user management, data management, security, automation, customization, and analytics. It also evaluates their understanding of the Salesforce Lightning Experience interface and the declarative development tools available within the platform.
Preparing for the Salesforce Certified Administrator exam usually involves studying Salesforce's official study materials, such as trailhead modules, documentation, and online resources. Candidates may also benefit from attending training courses or joining study groups to enhance their understanding of Salesforce administration concepts.
By achieving the Salesforce Administration Certification, professionals can demonstrate their proficiency and dedication to Salesforce administration, making them highly valuable to employers and organizations utilizing Salesforce as their CRM system. It opens up opportunities for career advancement, such as becoming a Salesforce administrator, consultant, or analyst, and may lead to increased job responsibilities and higher earning potential.
It's important to note that Salesforce regularly updates its platform and introduces new features and functionalities. Therefore, maintaining the certification requires staying up to date with these changes and periodically completing maintenance exams or earning additional certifications, such as the Salesforce Advanced Administrator Certification or specialized certifications in areas like Sales Cloud or Service Cloud.
Overall, Salesforce Administration Certification is an industry-recognized credential that validates an individual's expertise in Salesforce administration, enabling them to drive business success and optimize Salesforce implementations for their organizations.
Eligibility and Requirements for Salesforce Administration Certification
To be eligible for Salesforce Administration Certification, candidates must meet certain requirements and prerequisites. Here are the typical eligibility and requirements for Salesforce Administration Certification:
Experience: Candidates should have experience working with Salesforce and should have a good understanding of its various features and functionalities. For the Salesforce Certified Administrator certification, candidates should have at least 6 months to 1 year of experience using Salesforce. For the Salesforce Certified Advanced Administrator certification, candidates should have at least 2 years of experience using Salesforce.
Training: Candidates are recommended to complete the Salesforce Administration Essentials for New Admins course or have equivalent knowledge and experience.
Exam: Candidates must pass a proctored multiple-choice exam that tests their knowledge of Salesforce Administration. The exam covers various topics, including data management, security, automation, user management, and customization.
Payment: Candidates must pay a fee to register for the exam.
It is important to note that these eligibility and requirements may vary depending on the specific Salesforce Administration Certification level. For example, the Salesforce Certified Platform App Builder certification requires candidates to have experience in designing, building, and implementing custom applications on the Salesforce platform.
Benefits of Salesforce Administration Certification
Salesforce Administration Certification offers several benefits to individuals and organizations alike. Here are some of the key benefits of obtaining Salesforce Administration Certification:
Improved Job Opportunities: Salesforce is one of the most popular and widely-used CRM platforms in the world. Obtaining Salesforce Administration Certification can increase job opportunities for individuals, as many companies require professionals with Salesforce expertise. This certification validates an individual's knowledge and skills in Salesforce administration and makes them a more attractive candidate for job openings.
Increased Earning Potential: Salesforce professionals with certification are typically paid more than those without certification. According to a survey by Salesforce, Certified Salesforce Administrators earn an average of $89,000 per year, while Certified Advanced Administrators earn an average of $107,000 per year. This higher salary is due to the high demand for professionals with Salesforce expertise.
Enhanced Credibility: Salesforce Administration Certification demonstrates an individual's knowledge and expertise in Salesforce administration. This certification is recognized globally and enhances an individual's credibility as a Salesforce professional. It also helps individuals gain respect and trust from colleagues and employers.
Better Career Growth: Obtaining Salesforce Administration Certification can help individuals to advance their careers. This certification provides individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to manage and customize Salesforce for their organization. This can lead to career growth opportunities such as promotions, leadership roles, and higher-level positions within the organization.
Improved Salesforce Implementation: Salesforce Administration Certification ensures that an individual has a deep understanding of Salesforce administration. This can help organizations to implement Salesforce more effectively, resulting in improved business processes, better customer management, and increased productivity.
Exam Format and Structure of Salesforce Administration Certification
The Salesforce Administration Certification exam is a proctored multiple-choice exam that tests candidates' knowledge of Salesforce Administration. The exam format and structure may vary depending on the specific certification level, but here is an overview of the typical exam format and structure for the Salesforce Certified Administrator certification:
Exam Format: The Salesforce Certified Administrator exam is a computer-based exam that consists of 60 multiple-choice questions. Candidates have 105 minutes to complete the exam.
Exam Content: The Salesforce Certified Administrator exam covers various topics, including data management, security, automation, user management, and customization. The exam questions are designed to test candidates' knowledge of Salesforce Administration best practices, concepts, and features.
Passing Score: Candidates must achieve a passing score of 65% or higher to pass the exam and obtain certification.
Retake Policy: If a candidate fails the exam, they can retake the exam after 15 days. However, candidates can only take the exam a maximum of 10 times per year.
Exam Fee: Candidates must pay a fee to register for the exam.
It is important for candidates to prepare adequately for the exam to increase their chances of passing. Salesforce offers study resources, including study guides, practice exams, and online training courses, to help candidates prepare for the exam.
In addition, candidates should ensure that they have a good understanding of Salesforce Administration best practices, concepts, and features. They should also be familiar with the exam format and structure, and practice answering multiple-choice questions to get familiar with the exam format.
Tips for Preparing and Passing the Salesforce Administration Certification Exam
Here are some tips for preparing and passing the Salesforce Administration Certification Exam:
Study the Exam Guide: The Salesforce Administration Certification Exam Guide provides an overview of the topics covered on the exam and the weightage assigned to each topic. Read the guide thoroughly to understand the exam format, topics, and level of difficulty.
Use Trailhead: Salesforce's Trailhead provides free learning modules, projects, and quizzes to help prepare for the exam. Use Trailhead to reinforce your knowledge and gain hands-on experience with Salesforce.
Take Practice Exams: Salesforce offers practice exams that simulate the actual exam environment and provide feedback on your performance. Take multiple practice exams to identify areas of weakness and focus on those areas.
Join Study Groups: Joining study groups can provide a collaborative learning environment and offer different perspectives on the topics covered on the exam. Look for study groups on Salesforce user groups or communities.
Get Hands-on Experience: Hands-on experience with Salesforce is essential for passing the exam. Work on real-world projects or create your own projects to gain practical experience with Salesforce.
Focus on Key Topics: Focus on the key topics outlined in the exam guide, such as data management, security and access management, automation, and reporting and analytics. Develop a study plan that prioritizes these topics.
Manage Your Time: Manage your time during the exam carefully. The exam is timed, and you will not have enough time to review each question in detail. Answer the questions you know first and come back to the ones you are unsure about later.
Relax and Stay Confident: Finally, relax and stay confident during the exam. Take deep breaths, read each question carefully, and trust in your preparation. Remember, you can retake the exam if needed.
Understanding Salesforce Data Management
Salesforce Data Management refers to the process of organizing, storing, and maintaining data within Salesforce. It involves managing the lifecycle of data, from data entry to archiving, and ensuring data quality, accuracy, and consistency.
Here are some key concepts to understand when it comes to Salesforce Data Management:
Objects: Salesforce objects are database tables that store specific types of data. For example, the Account object stores information about a customer account, while the Opportunity object stores information about a potential sales opportunity.
Fields: Fields are the individual data elements within an object. For example, an Account object might have fields for the account name, billing address, and phone number.
Records: Records are the individual instances of an object. For example, an Account record represents a specific customer account with its unique information.
Relationships: Relationships define how objects are related to one another in Salesforce. For example, an Account object might have a relationship to the Contact object, which stores information about individuals associated with that account.
Data Importing and Exporting: Salesforce provides several tools for importing and exporting data, including the Data Loader and Data Import Wizard. These tools enable administrators to quickly and easily import and export large amounts of data.
Data Quality: Maintaining data quality is critical for effective data management. Salesforce provides tools for ensuring data accuracy and consistency, such as validation rules, data cleansing, and duplicate management.
Data Security: Data security is also important for data management. Salesforce provides a range of security features to control access to data, including role-based access control, field-level security, and object-level security.
Managing Users, Roles, and Permissions in Salesforce
Managing users, roles, and permissions in Salesforce is an essential part of Salesforce administration. Here are some key concepts to understand:
User Management: Salesforce allows you to create and manage user accounts for your organization. User accounts can be assigned to specific roles and given permissions to access and modify data within Salesforce.
Role Hierarchy: Salesforce uses a role hierarchy to control access to data. The hierarchy defines a series of roles, with higher-level roles having access to data owned by lower-level roles.
Profiles: Profiles define the level of access and permissions that users have in Salesforce. You can customize profiles to restrict access to certain features or data based on a user's role in the organization.
Permission Sets: Permission sets are used to grant additional permissions to users beyond what is defined in their profile. You can use permission sets to grant temporary or additional permissions to users based on their specific needs.
Sharing Settings: Sharing settings control how data is shared between users in Salesforce. You can configure sharing settings to restrict or allow access to certain types of data based on user roles or other criteria.
Single Sign-On (SSO): SSO allows users to log in to Salesforce using their existing credentials from an external system, such as Active Directory. SSO can simplify user management and improve security.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA provides an extra layer of security for user accounts by requiring users to provide a second form of identification, such as a code sent to their phone, in addition to their password.
Best Practices for Salesforce Administration
Here are some best practices for Salesforce administration:
Stay up-to-date with new features and releases: Salesforce releases updates three times a year, and it's important to stay up-to-date with new features and functionality. This can help you take advantage of new tools and improve efficiency.
Maintain data quality: Data quality is essential for accurate reporting and analytics. Administrators should implement data validation rules, maintain clean data, and establish data ownership and sharing rules.
Use a sandbox environment: Sandbox environments allow you to test changes and updates before implementing them in your production environment. This can help minimize errors and ensure that changes are functioning correctly.
Establish user roles and permissions: Establishing user roles and permissions is crucial for ensuring data security and preventing unauthorized access. Administrators should regularly review and update user permissions to ensure that they align with business needs.
Automate workflows: Automating workflows can help streamline business processes and improve efficiency. Administrators should identify repetitive tasks and create workflows to automate them.
Customize Salesforce to meet business needs: Customizing Salesforce to meet business needs can help improve efficiency and productivity. Administrators should work closely with business stakeholders to identify areas where customization can improve business processes.
Provide training and support: Providing training and support to users can help ensure that they are using Salesforce effectively and efficiently. Administrators should create documentation, conduct training sessions, and provide ongoing support to users.
Continuing Education and Professional Development for Salesforce Administrators
Continuing education and professional development are essential for Salesforce administrators to stay current with new technologies, best practices, and industry trends. Here are some options for continuing education and professional development for Salesforce administrators:
Trailhead: Trailhead is Salesforce's free online learning platform that offers a variety of courses, modules, and projects for all skill levels. Administrators can earn badges and certifications to demonstrate their expertise and keep their skills up-to-date.
Salesforce Certifications: Salesforce offers a range of certifications for administrators, developers, architects, and consultants. These certifications demonstrate proficiency in specific areas of Salesforce and can help administrators advance their careers.
User Groups and Communities: User groups and communities provide opportunities for administrators to network with peers, share best practices, and learn from others' experiences. Salesforce has an active community of users, and there are many local and virtual user groups that administrators can join.
Conferences and Events: Conferences and events provide opportunities to learn about new technologies, best practices, and industry trends. Salesforce hosts several annual events, including Dreamforce and TrailheaDX, as well as many regional events and meetups.
Online Training Programs: Online training programs provide structured learning experiences with a focus on specific areas of Salesforce. These programs can be self-paced or instructor-led and may offer certifications upon completion.
On-the-Job Training and Mentoring: On-the-job training and mentoring provide opportunities for administrators to learn from more experienced colleagues. Administrators can seek out mentors within their organization or participate in mentoring programs offered by user groups or communities.
How to obtain Salesforce Administration Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
DevOps
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Blockchain Certification
Salesforce : Salesforce Administration Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, Salesforce Administration Certification is a valuable credential for professionals in the field of Salesforce administration. It demonstrates an individual's knowledge and skills in configuring, customizing, and maintaining Salesforce solutions to meet the unique needs of organizations. By earning this certification, individuals can enhance their career prospects, open up new opportunities, and showcase their expertise in Salesforce administration.
Salesforce is a widely used CRM platform, and organizations across various industries rely on it to manage their customer data and streamline their sales processes. As a result, skilled Salesforce administrators are in high demand, and the certification serves as a validation of their abilities to effectively leverage the platform.
To achieve Salesforce Administration Certification, candidates must pass the Salesforce Certified Administrator exam, which assesses their knowledge of various Salesforce features and functionalities. Preparation for the exam typically involves studying Salesforce's official materials and utilizing online resources and training courses.
It is important to note that maintaining the certification requires staying updated with Salesforce platform changes and advancements. This may involve completing maintenance exams or pursuing additional certifications to deepen knowledge in specialized areas.
Overall, Salesforce Administration Certification offers numerous benefits to professionals, including increased career opportunities, recognition, and the ability to contribute to the success of organizations by optimizing Salesforce implementations.
Salesforce Platform Developer Certification: A Guide!!!
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on "Everything You Need to Know About Salesforce Platform Developer Certification." This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to become a skilled Salesforce developer or enhance your expertise in the Salesforce ecosystem. We'll explore the significance of the certification, the skills it validates, the certification process, and valuable tips to excel in the exam. Whether you're new to Salesforce development or an experienced professional, this guide will prepare you to create innovative solutions for diverse business needs and unlock the vast potential that the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification offers. Let's dive in and discover all you need to know to succeed in your Salesforce developer journey.
Table of contents
- Overview of the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam
- Benefits of obtaining the certification
- Study resources and tips for passing the exam
- Understanding the Salesforce Platform and its capabilities
- Customizing and developing on the Salesforce Platform using Apex and Visualforce
- Best practices for designing and building scalable applications on the Salesforce Platform
- Integrating external systems with the Salesforce Platform
- Using declarative tools like Process Builder and Flow to automate business processes
- Managing data and data models in Salesforce
- Conclusion
Overview of the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam
The Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam is designed for individuals who have experience developing and deploying custom applications on the Salesforce Platform. The certification validates your knowledge and skills in designing, building, and implementing custom applications using Apex and Visualforce, and also covers various other topics related to the Salesforce Platform.
The exam is a proctored, multiple-choice exam that consists of 60 questions and is 105 minutes long. The passing score for the exam is 65%, which means that you need to correctly answer at least 39 questions out of 60 to pass the exam. The exam is available in various languages, including English, Spanish, French, German, Portuguese, and Japanese.
To take the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam, you must have a solid understanding of programming concepts and knowledge of the Salesforce Platform, including its architecture, data model, and security features. You should also have experience developing custom applications on the Salesforce Platform using Apex and Visualforce.
Before taking the exam, it's recommended that you study and prepare using official study materials and resources, such as the Salesforce Platform Developer I Certification Exam Guide, Trailhead modules, and other training materials. Additionally, you can take practice exams to test your knowledge and identify areas where you need to improve.
Obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification can help you demonstrate your expertise in developing custom applications on the Salesforce Platform and increase your job opportunities and earning potential.
Benefits of obtaining the certification
Validation of Skills: Obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification validates your skills and knowledge of the Salesforce Platform, including its architecture, data model, and security features. It demonstrates to potential employers or clients that you have the necessary skills to develop and deploy custom applications on the Salesforce Platform.
Competitive Advantage: As the Salesforce Platform continues to grow in popularity, obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification can give you a competitive advantage in the job market. It can make you stand out among other candidates who do not have the certification and increase your chances of being hired.
Increased Earning Potential: Having the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification can lead to higher pay and more job opportunities. According to the 2021 Salesforce Salary Survey, certified Salesforce professionals earn on average 25% more than their non-certified peers.
Continued Professional Development: The Salesforce Platform is constantly evolving, and obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification demonstrates your commitment to continuing your professional development and staying up-to-date with the latest technology trends and best practices.
Community Recognition: Obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification can also lead to community recognition and networking opportunities. You can connect with other certified professionals and engage in discussions about the latest Salesforce trends and developments, as well as attend events and conferences for professional development.
Study resources and tips for passing the exam
Official Study Materials: The Salesforce Platform Developer Certification Exam Guide is the official study guide provided by Salesforce. It outlines the exam's content and structure, provides sample questions, and offers helpful tips and resources for exam preparation. You can also check out other official Salesforce resources such as Trailhead modules, developer documentation, and webinars.
Practice Exams: Taking practice exams can help you gauge your knowledge and identify areas where you need to improve. There are many resources available, including official Salesforce practice exams, as well as third-party practice exams from companies such as Focus on Force or Quizlet.
Hands-On Experience: Hands-on experience with the Salesforce Platform is crucial for passing the exam. You should practice developing and deploying custom applications using Apex and Visualforce, as well as other technologies like Lightning Components and APIs. You can also work on sample projects and use cases to gain practical experience.
Join Study Groups: Joining a study group can help you connect with other individuals preparing for the exam, share resources and tips, and get feedback on your progress. You can join online communities such as the Salesforce Trailblazer Community or LinkedIn groups, or form your own study group with friends or colleagues.
Time Management: The Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam is 105 minutes long, and you'll need to manage your time wisely to answer all the questions. Make sure you understand the content and structure of the exam, and allocate your time appropriately to ensure you have enough time to answer all the questions.
Stay Calm and Confident: Finally, it's important to stay calm and confident during the exam. Read each question carefully, eliminate any obviously wrong answers, and take your time to select the best answer. Don't get discouraged if you encounter difficult questions, and remember that you have prepared well for the exam. With the right preparation and mindset, you can pass the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam.
Understanding the Salesforce Platform and its capabilities
Salesforce is a cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) platform that allows businesses to manage their customer interactions, sales, marketing, and customer service operations in one place. The Salesforce Platform is the foundation of the Salesforce CRM and provides a powerful suite of tools and capabilities for developers to build custom applications on top of the platform.
The Salesforce Platform includes the following capabilities:
Custom Objects: The Salesforce Platform allows developers to create custom objects to store and manage data specific to their business requirements. Custom objects can be related to standard objects such as Accounts, Contacts, and Opportunities.
Apex: Apex is a programming language used to write custom business logic on the Salesforce Platform. Developers can use Apex to create custom triggers, workflows, and classes to automate processes and extend the functionality of the Salesforce Platform.
Visualforce: Visualforce is a framework used to build custom user interfaces on the Salesforce Platform. Developers can use Visualforce to create custom pages, components, and apps that can be integrated into the Salesforce CRM.
Lightning Components: Lightning Components is a modern UI framework that enables developers to build responsive, interactive, and customizable user interfaces on the Salesforce Platform. Lightning Components can be used to build custom apps, dashboards, and pages that can be accessed on desktop and mobile devices.
APIs: The Salesforce Platform provides a rich set of APIs that enable developers to integrate with external systems and build custom integrations. The APIs include SOAP, REST, Bulk, Streaming, and Metadata APIs.
AppExchange: AppExchange is the Salesforce marketplace where developers can publish and sell their custom apps and components to other Salesforce users. AppExchange includes thousands of apps and components that can be used to extend the functionality of the Salesforce Platform.
Customizing and developing on the Salesforce Platform using Apex and Visualforce
Apex is a programming language used to write custom business logic on the Salesforce Platform. Apex code runs on the Salesforce servers, and can be used to create custom triggers, workflows, and classes to automate processes and extend the functionality of the Salesforce Platform. Visualforce is a framework used to build custom user interfaces on the Salesforce Platform. Developers can use Visualforce to create custom pages, components, and apps that can be integrated into the Salesforce CRM.
Here are some steps to follow for customizing and developing on the Salesforce Platform using Apex and Visualforce:
Define Business Requirements: Before starting development, it's important to clearly define the business requirements and use cases for the custom application. This will help you determine what data needs to be stored, what processes need to be automated, and what user interfaces need to be built.
Create Custom Objects: Using the Salesforce Object Manager, create custom objects to store and manage data specific to your business requirements. Custom objects can be related to standard objects such as Accounts, Contacts, and Opportunities.
Write Apex Code: Write Apex code to create custom triggers, classes, and workflows to automate processes and extend the functionality of the Salesforce Platform. Apex code can be written in the Developer Console, a web-based integrated development environment (IDE) provided by Salesforce.
Build Visualforce Pages: Use the Visualforce framework to build custom pages, components, and apps that can be integrated into the Salesforce CRM. Visualforce pages can be created using a combination of HTML, CSS, and Apex code.
Test and Debug: Once you have developed the custom application, it's important to test and debug it thoroughly to ensure it meets the business requirements and works as expected. You can use the Apex Test Runner to run unit tests on your Apex code, and the Visualforce Previewer to preview your Visualforce pages.
Deploy the Custom Application: Once the custom application has been tested and debugged, it can be deployed to a production environment using the Salesforce Metadata API or the Force.com IDE.
Best practices for designing and building scalable applications on the Salesforce Platform
Define Business Requirements: Before starting development, it's important to clearly define the business requirements and use cases for the custom application. This will help you determine what data needs to be stored, what processes need to be automated, and what user interfaces need to be built.
Use Custom Indexes: Create custom indexes on fields that are frequently used in queries or where clauses to improve query performance and reduce execution time.
Avoid Large Data Sets: Try to avoid querying or manipulating large data sets in a single transaction as it can cause performance issues. Instead, use batch processing or asynchronous processing to handle large data sets.
Design Custom Objects Carefully: Carefully design custom objects and their relationships with other objects to ensure scalability. Avoid creating too many custom objects or having too many fields on a single object.
Use Bulk APIs: Use Bulk APIs instead of REST APIs when performing operations on large data sets to improve performance.
Use Governor Limits: Understand the governor limits in the Salesforce Platform and design your custom application to work within these limits. Avoid hitting governor limit exceptions as it can cause performance issues.
Implement Caching: Implement caching to improve performance and reduce the number of requests to the Salesforce Platform. Use caching for frequently accessed data and avoid caching large data sets.
Monitor Performance: Monitor the performance of your custom application and use Salesforce's monitoring tools to identify bottlenecks and performance issues. Optimize your code and design based on the results of performance monitoring.
Document Your Design: Document your design and architecture to make it easy for other developers to understand and maintain the custom application. Use standard design patterns and best practices to ensure scalability and maintainability.
Integrating external systems with the Salesforce Platform
Determine Integration Requirements: The first step in integrating external systems with Salesforce is to determine the integration requirements. Identify the systems that need to be integrated and the data that needs to be shared between them. Define the integration endpoints and data mapping requirements.
Choose the Integration Method: Choose the integration method based on the requirements. There are several integration methods available in Salesforce, including REST API, SOAP API, Bulk API, Streaming API, and Outbound Messaging. Choose the method that best suits your requirements.
Develop Integration Code: Develop integration code to handle data mapping, data transformation, and integration logic. Use the appropriate API to integrate with the external system. The integration code can be developed using programming languages like Java, .NET, or PHP.
Test the Integration: Once the integration code is developed, test it thoroughly to ensure it meets the integration requirements. Use tools like Postman, SOAPUI, or Apex Test Classes to test the integration code.
Configure Security and Authentication: Configure security and authentication settings for the integration. Use OAuth or Salesforce Connect to authenticate external systems and ensure secure communication between the systems.
Monitor and Maintain Integration: Monitor the integration to ensure it's working as expected. Use Salesforce's monitoring tools like Event Monitoring, Debug Logs, and System Logs to identify issues and fix them. Maintain the integration code to keep it up-to-date with the latest changes in Salesforce.
Using declarative tools like Process Builder and Flow to automate business processes
Identify Business Process: The first step in automating business processes is to identify the process that needs to be automated. Identify the process steps, data flow, and business rules.
Choose Declarative Tool: Choose the appropriate declarative tool to automate the business process. Salesforce provides several declarative tools like Process Builder, Flow, Workflow Rules, and Approval Processes. Choose the tool that best suits the business requirements.
Build the Process: Build the process using the chosen declarative tool. Use the drag-and-drop interface to define the process steps, data flow, and business rules. Configure the process to trigger based on specific events or criteria.
Test the Process: Once the process is built, test it thoroughly to ensure it meets the business requirements. Use test data to test the process and validate the output.
Deploy the Process: After testing, deploy the process to the production environment. Monitor the process to ensure it's working as expected.
Maintain the Process: Maintain the process to keep it up-to-date with the changing business requirements. Update the process steps and business rules as needed.
Managing data and data models in Salesforce
Salesforce provides a powerful data model that allows businesses to store and manage their data in a structured and organized way. Here are some key concepts to keep in mind when it comes to managing data and data models in Salesforce:
Objects: Objects are the basic building blocks of Salesforce's data model. Objects represent things like accounts, contacts, and opportunities, and each object contains a set of fields that define the data that can be stored within it.
Fields: Fields are the individual pieces of data that can be stored within an object. Fields can be of various data types, such as text, number, date, or picklist.
Relationships: Relationships define how objects are related to each other. There are three types of relationships in Salesforce: one-to-many, many-to-many, and lookup.
Data Import and Export: Salesforce provides tools for importing and exporting data, allowing businesses to move data in and out of the system as needed.
Data Quality: Salesforce provides tools for managing data quality, such as duplicate management and data validation rules.
Data Security: As mentioned in the previous section, Salesforce provides a robust security model that helps businesses protect their data and ensure that only authorized users can access it.
How to obtain Salesforce Platform Developer Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Blockchain Certification
Salesforce : Salesforce Platform Developer Certification
Conclusion
Certainly! Here's a sample conclusion for your blog on Salesforce Platform Developer Certification:
"In conclusion, obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification is a significant milestone for any aspiring Salesforce developer. It demonstrates your expertise in designing and developing custom applications on the Salesforce platform, showcasing your ability to create innovative solutions to address complex business requirements.
Throughout this blog, we have explored various subtopics related to the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification. We discussed the exam details, essential programming languages like Apex, and user interface development with Visualforce and Lightning Components. We also delved into data management, integration, testing, security, and advanced development concepts.
By investing time and effort into studying and preparing for the certification exam, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the Salesforce platform's capabilities and best practices for developing robust applications. This certification not only validates your skills and knowledge but also opens up new career opportunities in the Salesforce ecosystem.
However, it is important to remember that learning does not stop with certification. The Salesforce platform evolves continuously, with new features and enhancements introduced in each release. Therefore, it is crucial to engage in continuous learning and stay updated with the latest advancements to remain at the forefront of Salesforce development.
Maintaining and renewing your Salesforce certifications is equally important. This can be achieved through ongoing education, attending webinars and events, participating in the Salesforce Trailhead learning platform, and exploring additional certifications that align with your career goals.
As a Salesforce Platform Developer, you possess a valuable skill set that is in high demand in today's job market. With the ability to create custom solutions and integrate Salesforce with external systems, you can contribute to the success of organizations across various industries.
So, embark on your journey to become a Salesforce Platform Developer, unlock new opportunities, and make a significant impact in the world of Salesforce development. Start by preparing for the certification exam, honing your skills, and embracing a mindset of continuous learning. Remember, with dedication and perseverance, you can achieve your goals and thrive in the dynamic Salesforce ecosystem.
Best of luck on your path to becoming a Salesforce Platform Developer!
Read More
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on "Everything You Need to Know About Salesforce Platform Developer Certification." This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to become a skilled Salesforce developer or enhance your expertise in the Salesforce ecosystem. We'll explore the significance of the certification, the skills it validates, the certification process, and valuable tips to excel in the exam. Whether you're new to Salesforce development or an experienced professional, this guide will prepare you to create innovative solutions for diverse business needs and unlock the vast potential that the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification offers. Let's dive in and discover all you need to know to succeed in your Salesforce developer journey.
Table of contents
- Overview of the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam
- Benefits of obtaining the certification
- Study resources and tips for passing the exam
- Understanding the Salesforce Platform and its capabilities
- Customizing and developing on the Salesforce Platform using Apex and Visualforce
- Best practices for designing and building scalable applications on the Salesforce Platform
- Integrating external systems with the Salesforce Platform
- Using declarative tools like Process Builder and Flow to automate business processes
- Managing data and data models in Salesforce
- Conclusion
Overview of the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam
The Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam is designed for individuals who have experience developing and deploying custom applications on the Salesforce Platform. The certification validates your knowledge and skills in designing, building, and implementing custom applications using Apex and Visualforce, and also covers various other topics related to the Salesforce Platform.
The exam is a proctored, multiple-choice exam that consists of 60 questions and is 105 minutes long. The passing score for the exam is 65%, which means that you need to correctly answer at least 39 questions out of 60 to pass the exam. The exam is available in various languages, including English, Spanish, French, German, Portuguese, and Japanese.
To take the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam, you must have a solid understanding of programming concepts and knowledge of the Salesforce Platform, including its architecture, data model, and security features. You should also have experience developing custom applications on the Salesforce Platform using Apex and Visualforce.
Before taking the exam, it's recommended that you study and prepare using official study materials and resources, such as the Salesforce Platform Developer I Certification Exam Guide, Trailhead modules, and other training materials. Additionally, you can take practice exams to test your knowledge and identify areas where you need to improve.
Obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification can help you demonstrate your expertise in developing custom applications on the Salesforce Platform and increase your job opportunities and earning potential.
Benefits of obtaining the certification
Validation of Skills: Obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification validates your skills and knowledge of the Salesforce Platform, including its architecture, data model, and security features. It demonstrates to potential employers or clients that you have the necessary skills to develop and deploy custom applications on the Salesforce Platform.
Competitive Advantage: As the Salesforce Platform continues to grow in popularity, obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification can give you a competitive advantage in the job market. It can make you stand out among other candidates who do not have the certification and increase your chances of being hired.
Increased Earning Potential: Having the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification can lead to higher pay and more job opportunities. According to the 2021 Salesforce Salary Survey, certified Salesforce professionals earn on average 25% more than their non-certified peers.
Continued Professional Development: The Salesforce Platform is constantly evolving, and obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification demonstrates your commitment to continuing your professional development and staying up-to-date with the latest technology trends and best practices.
Community Recognition: Obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification can also lead to community recognition and networking opportunities. You can connect with other certified professionals and engage in discussions about the latest Salesforce trends and developments, as well as attend events and conferences for professional development.
Study resources and tips for passing the exam
Official Study Materials: The Salesforce Platform Developer Certification Exam Guide is the official study guide provided by Salesforce. It outlines the exam's content and structure, provides sample questions, and offers helpful tips and resources for exam preparation. You can also check out other official Salesforce resources such as Trailhead modules, developer documentation, and webinars.
Practice Exams: Taking practice exams can help you gauge your knowledge and identify areas where you need to improve. There are many resources available, including official Salesforce practice exams, as well as third-party practice exams from companies such as Focus on Force or Quizlet.
Hands-On Experience: Hands-on experience with the Salesforce Platform is crucial for passing the exam. You should practice developing and deploying custom applications using Apex and Visualforce, as well as other technologies like Lightning Components and APIs. You can also work on sample projects and use cases to gain practical experience.
Join Study Groups: Joining a study group can help you connect with other individuals preparing for the exam, share resources and tips, and get feedback on your progress. You can join online communities such as the Salesforce Trailblazer Community or LinkedIn groups, or form your own study group with friends or colleagues.
Time Management: The Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam is 105 minutes long, and you'll need to manage your time wisely to answer all the questions. Make sure you understand the content and structure of the exam, and allocate your time appropriately to ensure you have enough time to answer all the questions.
Stay Calm and Confident: Finally, it's important to stay calm and confident during the exam. Read each question carefully, eliminate any obviously wrong answers, and take your time to select the best answer. Don't get discouraged if you encounter difficult questions, and remember that you have prepared well for the exam. With the right preparation and mindset, you can pass the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification exam.
Understanding the Salesforce Platform and its capabilities
Salesforce is a cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) platform that allows businesses to manage their customer interactions, sales, marketing, and customer service operations in one place. The Salesforce Platform is the foundation of the Salesforce CRM and provides a powerful suite of tools and capabilities for developers to build custom applications on top of the platform.
The Salesforce Platform includes the following capabilities:
Custom Objects: The Salesforce Platform allows developers to create custom objects to store and manage data specific to their business requirements. Custom objects can be related to standard objects such as Accounts, Contacts, and Opportunities.
Apex: Apex is a programming language used to write custom business logic on the Salesforce Platform. Developers can use Apex to create custom triggers, workflows, and classes to automate processes and extend the functionality of the Salesforce Platform.
Visualforce: Visualforce is a framework used to build custom user interfaces on the Salesforce Platform. Developers can use Visualforce to create custom pages, components, and apps that can be integrated into the Salesforce CRM.
Lightning Components: Lightning Components is a modern UI framework that enables developers to build responsive, interactive, and customizable user interfaces on the Salesforce Platform. Lightning Components can be used to build custom apps, dashboards, and pages that can be accessed on desktop and mobile devices.
APIs: The Salesforce Platform provides a rich set of APIs that enable developers to integrate with external systems and build custom integrations. The APIs include SOAP, REST, Bulk, Streaming, and Metadata APIs.
AppExchange: AppExchange is the Salesforce marketplace where developers can publish and sell their custom apps and components to other Salesforce users. AppExchange includes thousands of apps and components that can be used to extend the functionality of the Salesforce Platform.
Customizing and developing on the Salesforce Platform using Apex and Visualforce
Apex is a programming language used to write custom business logic on the Salesforce Platform. Apex code runs on the Salesforce servers, and can be used to create custom triggers, workflows, and classes to automate processes and extend the functionality of the Salesforce Platform. Visualforce is a framework used to build custom user interfaces on the Salesforce Platform. Developers can use Visualforce to create custom pages, components, and apps that can be integrated into the Salesforce CRM.
Here are some steps to follow for customizing and developing on the Salesforce Platform using Apex and Visualforce:
Define Business Requirements: Before starting development, it's important to clearly define the business requirements and use cases for the custom application. This will help you determine what data needs to be stored, what processes need to be automated, and what user interfaces need to be built.
Create Custom Objects: Using the Salesforce Object Manager, create custom objects to store and manage data specific to your business requirements. Custom objects can be related to standard objects such as Accounts, Contacts, and Opportunities.
Write Apex Code: Write Apex code to create custom triggers, classes, and workflows to automate processes and extend the functionality of the Salesforce Platform. Apex code can be written in the Developer Console, a web-based integrated development environment (IDE) provided by Salesforce.
Build Visualforce Pages: Use the Visualforce framework to build custom pages, components, and apps that can be integrated into the Salesforce CRM. Visualforce pages can be created using a combination of HTML, CSS, and Apex code.
Test and Debug: Once you have developed the custom application, it's important to test and debug it thoroughly to ensure it meets the business requirements and works as expected. You can use the Apex Test Runner to run unit tests on your Apex code, and the Visualforce Previewer to preview your Visualforce pages.
Deploy the Custom Application: Once the custom application has been tested and debugged, it can be deployed to a production environment using the Salesforce Metadata API or the Force.com IDE.
Best practices for designing and building scalable applications on the Salesforce Platform
Define Business Requirements: Before starting development, it's important to clearly define the business requirements and use cases for the custom application. This will help you determine what data needs to be stored, what processes need to be automated, and what user interfaces need to be built.
Use Custom Indexes: Create custom indexes on fields that are frequently used in queries or where clauses to improve query performance and reduce execution time.
Avoid Large Data Sets: Try to avoid querying or manipulating large data sets in a single transaction as it can cause performance issues. Instead, use batch processing or asynchronous processing to handle large data sets.
Design Custom Objects Carefully: Carefully design custom objects and their relationships with other objects to ensure scalability. Avoid creating too many custom objects or having too many fields on a single object.
Use Bulk APIs: Use Bulk APIs instead of REST APIs when performing operations on large data sets to improve performance.
Use Governor Limits: Understand the governor limits in the Salesforce Platform and design your custom application to work within these limits. Avoid hitting governor limit exceptions as it can cause performance issues.
Implement Caching: Implement caching to improve performance and reduce the number of requests to the Salesforce Platform. Use caching for frequently accessed data and avoid caching large data sets.
Monitor Performance: Monitor the performance of your custom application and use Salesforce's monitoring tools to identify bottlenecks and performance issues. Optimize your code and design based on the results of performance monitoring.
Document Your Design: Document your design and architecture to make it easy for other developers to understand and maintain the custom application. Use standard design patterns and best practices to ensure scalability and maintainability.
Integrating external systems with the Salesforce Platform
Determine Integration Requirements: The first step in integrating external systems with Salesforce is to determine the integration requirements. Identify the systems that need to be integrated and the data that needs to be shared between them. Define the integration endpoints and data mapping requirements.
Choose the Integration Method: Choose the integration method based on the requirements. There are several integration methods available in Salesforce, including REST API, SOAP API, Bulk API, Streaming API, and Outbound Messaging. Choose the method that best suits your requirements.
Develop Integration Code: Develop integration code to handle data mapping, data transformation, and integration logic. Use the appropriate API to integrate with the external system. The integration code can be developed using programming languages like Java, .NET, or PHP.
Test the Integration: Once the integration code is developed, test it thoroughly to ensure it meets the integration requirements. Use tools like Postman, SOAPUI, or Apex Test Classes to test the integration code.
Configure Security and Authentication: Configure security and authentication settings for the integration. Use OAuth or Salesforce Connect to authenticate external systems and ensure secure communication between the systems.
Monitor and Maintain Integration: Monitor the integration to ensure it's working as expected. Use Salesforce's monitoring tools like Event Monitoring, Debug Logs, and System Logs to identify issues and fix them. Maintain the integration code to keep it up-to-date with the latest changes in Salesforce.
Using declarative tools like Process Builder and Flow to automate business processes
Identify Business Process: The first step in automating business processes is to identify the process that needs to be automated. Identify the process steps, data flow, and business rules.
Choose Declarative Tool: Choose the appropriate declarative tool to automate the business process. Salesforce provides several declarative tools like Process Builder, Flow, Workflow Rules, and Approval Processes. Choose the tool that best suits the business requirements.
Build the Process: Build the process using the chosen declarative tool. Use the drag-and-drop interface to define the process steps, data flow, and business rules. Configure the process to trigger based on specific events or criteria.
Test the Process: Once the process is built, test it thoroughly to ensure it meets the business requirements. Use test data to test the process and validate the output.
Deploy the Process: After testing, deploy the process to the production environment. Monitor the process to ensure it's working as expected.
Maintain the Process: Maintain the process to keep it up-to-date with the changing business requirements. Update the process steps and business rules as needed.
Managing data and data models in Salesforce
Salesforce provides a powerful data model that allows businesses to store and manage their data in a structured and organized way. Here are some key concepts to keep in mind when it comes to managing data and data models in Salesforce:
Objects: Objects are the basic building blocks of Salesforce's data model. Objects represent things like accounts, contacts, and opportunities, and each object contains a set of fields that define the data that can be stored within it.
Fields: Fields are the individual pieces of data that can be stored within an object. Fields can be of various data types, such as text, number, date, or picklist.
Relationships: Relationships define how objects are related to each other. There are three types of relationships in Salesforce: one-to-many, many-to-many, and lookup.
Data Import and Export: Salesforce provides tools for importing and exporting data, allowing businesses to move data in and out of the system as needed.
Data Quality: Salesforce provides tools for managing data quality, such as duplicate management and data validation rules.
Data Security: As mentioned in the previous section, Salesforce provides a robust security model that helps businesses protect their data and ensure that only authorized users can access it.
How to obtain Salesforce Platform Developer Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
Scrum Training: CSM
Program Management: PgMP
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
Data Science : Power BI Certification
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
Emerging Technologies : Blockchain Certification
Salesforce : Salesforce Platform Developer Certification
Conclusion
Certainly! Here's a sample conclusion for your blog on Salesforce Platform Developer Certification:
"In conclusion, obtaining the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification is a significant milestone for any aspiring Salesforce developer. It demonstrates your expertise in designing and developing custom applications on the Salesforce platform, showcasing your ability to create innovative solutions to address complex business requirements.
Throughout this blog, we have explored various subtopics related to the Salesforce Platform Developer Certification. We discussed the exam details, essential programming languages like Apex, and user interface development with Visualforce and Lightning Components. We also delved into data management, integration, testing, security, and advanced development concepts.
By investing time and effort into studying and preparing for the certification exam, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the Salesforce platform's capabilities and best practices for developing robust applications. This certification not only validates your skills and knowledge but also opens up new career opportunities in the Salesforce ecosystem.
However, it is important to remember that learning does not stop with certification. The Salesforce platform evolves continuously, with new features and enhancements introduced in each release. Therefore, it is crucial to engage in continuous learning and stay updated with the latest advancements to remain at the forefront of Salesforce development.
Maintaining and renewing your Salesforce certifications is equally important. This can be achieved through ongoing education, attending webinars and events, participating in the Salesforce Trailhead learning platform, and exploring additional certifications that align with your career goals.
As a Salesforce Platform Developer, you possess a valuable skill set that is in high demand in today's job market. With the ability to create custom solutions and integrate Salesforce with external systems, you can contribute to the success of organizations across various industries.
So, embark on your journey to become a Salesforce Platform Developer, unlock new opportunities, and make a significant impact in the world of Salesforce development. Start by preparing for the certification exam, honing your skills, and embracing a mindset of continuous learning. Remember, with dedication and perseverance, you can achieve your goals and thrive in the dynamic Salesforce ecosystem.
Best of luck on your path to becoming a Salesforce Platform Developer!
The Essential Guide to Salesforce Admin & App Builder Cert
Welcome to "The Essential Guide to Salesforce Administrator and App Builder Certification"! This comprehensive guide is your gateway to a rewarding career in the world of Salesforce. Whether you're an aspiring Salesforce professional or an IT expert looking to expand your skill set, we'll equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to pursue two essential certifications: Salesforce Administrator and Salesforce App Builder. From fundamental concepts to exam preparation tips and study resources, join us on this journey to streamline processes, create custom applications, and optimize user experiences, ultimately enhancing your career prospects in the dynamic realm of Salesforce. Let's unlock a world of opportunities together!
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Salesforce Certifications:
- Salesforce Administrator Certification:
- Salesforce App Builder Certification:
- Prerequisites and Eligibility:
- Exam Preparation Strategies:
- Maintaining and Renewing Certifications:
- Tips for a Successful Exam Day:
- Conclusion
Introduction to Salesforce Certifications
Salesforce certifications have become essential in the Salesforce ecosystem, validating professionals' knowledge and skills in leveraging the platform. These certifications are available for various roles and proficiency levels, such as administrators, app builders, consultants, and developers. They provide a standardized benchmark for employers and clients to evaluate expertise and commitment to staying updated with Salesforce technologies and best practices. By obtaining Salesforce certifications, professionals enhance their career prospects, gain a competitive edge in the job market, and increase their job security.
Certifications offer a structured learning path, enabling individuals to master the intricacies of the Salesforce platform. Through the certification journey, professionals gain in-depth knowledge of features, functionality, and best practices, equipping them with the skills to solve complex business challenges using Salesforce. Additionally, certified individuals gain access to a supportive community of Salesforce professionals, facilitating networking opportunities, knowledge sharing, and collaboration. Overall, Salesforce certifications are instrumental in establishing credibility, showcasing expertise, and unlocking career opportunities in the Salesforce ecosystem.
Salesforce Administrator Certification
The Salesforce Administrator Certification is a highly sought-after credential that validates a professional's knowledge and expertise in administering Salesforce. This certification is designed for individuals who are responsible for managing, configuring, and maintaining Salesforce implementations within an organization.
To obtain the Salesforce Administrator Certification, candidates must pass a comprehensive exam that covers various topics, including data management, security and access, automation, and reporting. The exam consists of multiple-choice questions, scenario-based questions, and may include hands-on exercises to evaluate practical application skills.
By earning the Salesforce Administrator Certification, professionals demonstrate their proficiency in effectively managing Salesforce orgs, maintaining data integrity, setting up user access and permissions, designing and implementing automation processes, and generating meaningful reports and dashboards. This certification serves as a testament to one's ability to optimize and maximize the benefits of Salesforce for their organization.
The Salesforce Administrator Certification offers several benefits to certified professionals. It enhances career prospects, as employers recognize the value of certified administrators who can efficiently leverage Salesforce to drive business success. Certified administrators are often preferred during the hiring process and may have access to a wider range of job opportunities. Moreover, the certification provides a competitive edge by showcasing expertise and a commitment to ongoing professional development.
To prepare for the Salesforce Administrator Certification, candidates can utilize official Salesforce study materials, online training modules, practice exams, and resources provided by Salesforce. It is important to create a study plan, focus on understanding the key concepts and best practices, and gain hands-on experience with Salesforce to reinforce learning.
Overall, the Salesforce Administrator Certification is a valuable credential that validates a professional's ability to effectively administer Salesforce and adds credibility to their profile. It opens up new career opportunities, demonstrates expertise, and serves as a foundation for further Salesforce certifications and specialization tracks.
Salesforce App Builder Certification
The Salesforce App Builder Certification is a prestigious credential that validates a professional's proficiency in designing, building, and implementing custom applications using the Salesforce platform. This certification is tailored for individuals who are involved in creating custom solutions and extending the capabilities of Salesforce to meet specific business needs.
To earn the Salesforce App Builder Certification, candidates must pass an exam that evaluates their knowledge and skills in various areas, including data modeling, user interface customization, business logic implementation, and deployment strategies. The exam includes multiple-choice questions and scenario-based questions that assess a candidate's ability to design and build scalable and efficient Salesforce applications.
By obtaining the Salesforce App Builder Certification, professionals demonstrate their expertise in leveraging declarative features and tools to create custom objects, fields, and relationships. They are adept at designing intuitive user interfaces using Lightning App Builder, configuring automation through workflows and process builders, and implementing effective security and data access controls. This certification showcases their ability to create robust and customized Salesforce applications that align with specific business requirements.
The Salesforce App Builder Certification offers several advantages to certified professionals. It enhances career prospects by highlighting one's skills in designing and building custom applications on the Salesforce platform. Employers recognize the value of certified app builders who can create tailored solutions to streamline processes, enhance user experience, and drive business growth. Additionally, the certification provides a competitive advantage, setting certified professionals apart from others in the job market.
To prepare for the Salesforce App Builder Certification, candidates can utilize official Salesforce study materials, online training modules, practice exams, and other resources provided by Salesforce. It is important to focus on understanding the key concepts and best practices related to app building on the Salesforce platform. Hands-on experience with Salesforce, particularly in designing and configuring custom applications, is crucial for success in the exam.
In conclusion, the Salesforce App Builder Certification is a prestigious credential that validates a professional's ability to design and build custom applications on the Salesforce platform. It offers career advancement opportunities, demonstrates expertise in Salesforce app development, and adds credibility to one's profile. By obtaining this certification, professionals showcase their skills in creating tailored solutions that drive business success using Salesforce.
Prerequisites and Eligibility
To pursue Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certifications, there are certain prerequisites and eligibility criteria that candidates should be aware of. Here are the general guidelines:
- Experience: While there are no strict experience requirements for these certifications, it is recommended to have some practical experience working with the Salesforce platform. This experience helps in understanding the concepts and applying them effectively during the certification exams.
- Knowledge: Candidates should have a solid understanding of the Salesforce platform, its features, and functionality. Familiarity with Salesforce terminology, data model, user interface, and basic administration tasks is important. Salesforce provides study resources and training materials to help candidates acquire the necessary knowledge.
- Training and Learning Paths: Salesforce offers various training options, including online courses, instructor-led classes, and self-study materials, to help candidates prepare for the certification exams. While not mandatory, completing training courses specific to the Administrator and App Builder certifications can greatly enhance your understanding and exam readiness.
- Prerequisite Certifications: The Salesforce Administrator Certification does not have any specific prerequisite certifications. However, for the Salesforce App Builder Certification, it is recommended (but not mandatory) to have the Salesforce Administrator Certification as a foundation. The knowledge and skills gained from the Administrator certification serve as a solid basis for pursuing the App Builder certification.
- Trailhead Badges: Salesforce's Trailhead is an online learning platform that offers a wealth of interactive and self-paced modules to learn Salesforce. While not mandatory, completing relevant Trailhead modules and earning badges can provide valuable hands-on experience and knowledge to support your certification journey.
Exam Preparation Strategies
Preparing for the Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certification exams requires a systematic approach and effective study strategies. Here are some exam preparation strategies to help you succeed:
- Understand the Exam Blueprint: Familiarize yourself with the exam blueprint provided by Salesforce. It outlines the topics and percentage weightage for each section of the exam. This will help you prioritize your study efforts and allocate more time to areas with higher weightage.
- Utilize Official Salesforce Study Materials: Salesforce provides official study guides, documentation, and resources specific to each certification. These materials cover the exam objectives and provide valuable insights into Salesforce concepts and best practices. Make sure to thoroughly review and understand these resources.
- Hands-on Experience: Practice using Salesforce and work on real-life scenarios to gain practical experience. The more hands-on experience you have with the platform, the better you'll understand its functionality and be able to apply it during the exam. Create a Salesforce Developer Edition or use a Trailhead Playground to practice building and configuring Salesforce components.
- Take Advantage of Trailhead: Salesforce's Trailhead platform offers interactive modules, trails, and projects that can significantly enhance your understanding of Salesforce concepts. Complete relevant Trailhead modules and earn badges to reinforce your knowledge and gain practical experience.
- Join Study Groups or Communities: Engage with other individuals preparing for the same certification exam. Join study groups, forums, or online communities dedicated to Salesforce certifications. These platforms allow you to ask questions, share insights, and learn from the experiences of others. Collaboration and knowledge sharing can greatly benefit your preparation.
- Practice with Sample Exams: Salesforce provides official sample exams and practice tests that simulate the format and difficulty level of the actual exams. Take advantage of these resources to familiarize yourself with the exam structure, time constraints, and question types. Review your results and focus on areas where you need improvement.
- Create a Study Plan: Develop a study plan that outlines your study schedule, goals, and milestones. Set aside dedicated study time and break down the topics into manageable chunks. This will help you stay organized, track your progress, and ensure comprehensive coverage of all exam objectives.
- Review Documentation and Release Notes: Stay updated with the latest Salesforce features, enhancements, and changes by reviewing official documentation and release notes. Salesforce regularly updates its platform, and being aware of new features can be beneficial during the exam.
- Seek Additional Resources: Explore additional study materials, blogs, tutorials, and videos available online. There are numerous blogs, YouTube channels, and online courses that offer valuable insights and exam preparation tips from experienced Salesforce professionals.
- Manage Exam Day: Familiarize yourself with the exam logistics, such as exam duration, rules, and requirements. Plan ahead to ensure a calm and distraction-free environment during the exam. Take breaks, stay hydrated, and get a good night's sleep before the exam day to optimize your performance.
Maintaining and Renewing Certifications
Once you have earned your Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certifications, it's important to maintain and renew them to demonstrate ongoing expertise and stay current with the evolving Salesforce platform. Here are some key points to consider for maintaining and renewing your certifications:
- Stay Updated with Release Updates: Salesforce regularly introduces new features, enhancements, and updates to its platform. It's crucial to stay informed about these changes by regularly reviewing official documentation, release notes, and participating in webinars or events hosted by Salesforce. This will ensure that you are up-to-date with the latest Salesforce capabilities and best practices.
- Complete Trailhead Modules and Superbadges: Salesforce's Trailhead offers a wide range of modules, trails, and superbadges that cover various topics and help you expand your knowledge and skills. Completing relevant modules and earning superbadges not only reinforces your understanding but also contributes to maintaining your certifications. Salesforce provides a Maintenance Exam option for some certifications, which can be fulfilled by completing specified Trailhead content.
- Attend Salesforce Events and Webinars: Salesforce organizes events, webinars, and user group meetings where you can connect with fellow professionals, learn about new features, and engage in discussions. Participating in these events allows you to expand your network, exchange insights, and stay informed about industry trends.
- Earn Continuing Education Units (CEUs): Salesforce requires certified professionals to earn a specific number of Continuing Education Units (CEUs) to renew their certifications. CEUs can be earned through a variety of activities, such as attending training sessions, completing Trailhead modules, presenting at conferences, or participating in relevant Salesforce-related volunteer work. The number of CEUs required may vary depending on the certification.
- Recertify at Regular Intervals: Salesforce certifications typically have a validity period, after which you need to recertify to maintain your credential. Stay aware of the expiration date of your certifications and make a plan to recertify well in advance. This may involve taking the updated version of the certification exam or fulfilling specific requirements, such as completing a maintenance exam or earning a designated number of CEUs.
- Leverage Salesforce Help and Support: Salesforce provides support resources, forums, and a knowledge base to help certified professionals with questions, issues, or clarification on specific topics. Utilize these resources to enhance your understanding and address any challenges you may encounter during your certification maintenance journey.
- Stay Engaged with the Salesforce Community: Engage with the larger Salesforce community through online forums, social media groups, and user group meetings. Connect with other certified professionals, participate in discussions, and share your experiences. This active involvement helps you stay connected, gain insights, and stay motivated in maintaining your certifications.
Tips for a Successful Exam Day
Preparing for the Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certification exams is crucial, but it's equally important to have a successful exam day experience. Here are some tips to help you perform your best on the day of the exam:
- Review Exam Logistics: Familiarize yourself with the exam logistics, such as the duration of the exam, number of questions, and passing score requirements. Understand any specific rules or restrictions, such as the use of scratch paper or breaks during the exam. Knowing what to expect will help you feel more confident and prepared.
- Get a Good Night's Sleep: Ensure you get a good night's sleep before the exam day. A well-rested mind performs better and is more capable of focusing and retaining information. Avoid last-minute cramming and allow your brain to rest and recharge for optimal performance.
- Start the Day with a Positive Mindset: Begin your day with a positive mindset and believe in your ability to succeed. Encourage yourself and visualize a successful outcome. Positive thinking can help alleviate stress and boost your confidence, leading to better performance during the exam.
- Have a Nutritious Meal: Prioritize a healthy and nutritious meal before the exam. Fueling your body with nutritious food will provide you with sustained energy and help you stay focused throughout the exam. Avoid heavy meals that may cause drowsiness or discomfort.
- Arrive Early and Be Prepared: Plan to arrive at the exam center or your chosen exam location early. Give yourself ample time to check-in, complete any necessary paperwork, and get settled. Ensure you have all the required identification and any permitted resources, such as a calculator or notepad, if allowed.
- Take Deep Breaths and Relax: Before starting the exam, take a few deep breaths to calm your nerves and relax your mind. Deep breathing helps reduce stress and anxiety, allowing you to approach the exam with a clear and focused mindset. Take a moment to center yourself and visualize success.
- Read Questions Carefully: During the exam, read each question carefully to understand the requirements and any specific details. Pay attention to keywords and ensure you're addressing what is being asked. Take your time and avoid rushing through the questions.
- Manage Time Effectively: Keep an eye on the time throughout the exam to ensure you're progressing at a reasonable pace. If you encounter challenging questions, don't dwell on them for too long. Mark them for review and move on. Allocate time wisely to maximize your chances of completing all questions within the allotted time.
- Answer with Confidence: Trust your preparation and answer each question to the best of your ability. Avoid second-guessing yourself excessively. Trust your instincts and select the option that you believe is most accurate. Maintain confidence in your knowledge and decision-making skills.
- Review and Validate Answers: If time permits, review your answers before submitting the exam. Use this time to double-check your responses, verify that you have addressed all requirements, and correct any errors or oversights. Be mindful of the time remaining and make strategic choices about where to focus your review.
How to obtain Salesforce Administrator and App Builder Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
- Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
- Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
- Data Science : Power BI Certification
- Cyber Security : CISA Certification
- Emerging Technologies : Blockchain Certification
- Salesforce : Salesforce Administrator and App Builder Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, pursuing the Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certifications can greatly enhance your skills and career prospects within the Salesforce ecosystem. These certifications validate your knowledge, expertise, and ability to effectively administer and develop applications on the Salesforce platform.
The Salesforce Administrator Certification focuses on managing and configuring Salesforce implementations, ensuring data integrity, and maximizing the platform's capabilities. It showcases your proficiency in handling user access, security, automation, and reporting, making you a valuable asset to any organization leveraging Salesforce.
On the other hand, the Salesforce App Builder Certification recognizes your skills in designing and building custom applications that meet specific business requirements. It demonstrates your ability to leverage declarative features, design intuitive user interfaces, implement automation, and deploy scalable applications on the Salesforce platform.
To successfully pursue these certifications, it's essential to understand the prerequisites and eligibility criteria, engage in comprehensive exam preparation, and stay updated with the latest Salesforce features and best practices. Utilizing official study materials, practicing with sample exams, gaining hands-on experience, and participating in the Salesforce community are key strategies for success.
Once certified, maintaining and renewing your credentials require ongoing learning, staying informed about Salesforce releases, earning Continuing Education Units (CEUs), and actively participating in the Salesforce community. By staying committed to professional development and remaining engaged, you can continuously showcase your expertise and keep your certifications up to date.
Earning the Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certifications demonstrates your dedication to excellence, positions you as a trusted Salesforce professional, and opens doors to new career opportunities. Whether you are an aspiring administrator or an application developer, these certifications serve as valuable assets in your Salesforce journey.
Read More
Welcome to "The Essential Guide to Salesforce Administrator and App Builder Certification"! This comprehensive guide is your gateway to a rewarding career in the world of Salesforce. Whether you're an aspiring Salesforce professional or an IT expert looking to expand your skill set, we'll equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to pursue two essential certifications: Salesforce Administrator and Salesforce App Builder. From fundamental concepts to exam preparation tips and study resources, join us on this journey to streamline processes, create custom applications, and optimize user experiences, ultimately enhancing your career prospects in the dynamic realm of Salesforce. Let's unlock a world of opportunities together!
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Salesforce Certifications:
- Salesforce Administrator Certification:
- Salesforce App Builder Certification:
- Prerequisites and Eligibility:
- Exam Preparation Strategies:
- Maintaining and Renewing Certifications:
- Tips for a Successful Exam Day:
- Conclusion
Introduction to Salesforce Certifications
Salesforce certifications have become essential in the Salesforce ecosystem, validating professionals' knowledge and skills in leveraging the platform. These certifications are available for various roles and proficiency levels, such as administrators, app builders, consultants, and developers. They provide a standardized benchmark for employers and clients to evaluate expertise and commitment to staying updated with Salesforce technologies and best practices. By obtaining Salesforce certifications, professionals enhance their career prospects, gain a competitive edge in the job market, and increase their job security.
Certifications offer a structured learning path, enabling individuals to master the intricacies of the Salesforce platform. Through the certification journey, professionals gain in-depth knowledge of features, functionality, and best practices, equipping them with the skills to solve complex business challenges using Salesforce. Additionally, certified individuals gain access to a supportive community of Salesforce professionals, facilitating networking opportunities, knowledge sharing, and collaboration. Overall, Salesforce certifications are instrumental in establishing credibility, showcasing expertise, and unlocking career opportunities in the Salesforce ecosystem.
Salesforce Administrator Certification
The Salesforce Administrator Certification is a highly sought-after credential that validates a professional's knowledge and expertise in administering Salesforce. This certification is designed for individuals who are responsible for managing, configuring, and maintaining Salesforce implementations within an organization.
To obtain the Salesforce Administrator Certification, candidates must pass a comprehensive exam that covers various topics, including data management, security and access, automation, and reporting. The exam consists of multiple-choice questions, scenario-based questions, and may include hands-on exercises to evaluate practical application skills.
By earning the Salesforce Administrator Certification, professionals demonstrate their proficiency in effectively managing Salesforce orgs, maintaining data integrity, setting up user access and permissions, designing and implementing automation processes, and generating meaningful reports and dashboards. This certification serves as a testament to one's ability to optimize and maximize the benefits of Salesforce for their organization.
The Salesforce Administrator Certification offers several benefits to certified professionals. It enhances career prospects, as employers recognize the value of certified administrators who can efficiently leverage Salesforce to drive business success. Certified administrators are often preferred during the hiring process and may have access to a wider range of job opportunities. Moreover, the certification provides a competitive edge by showcasing expertise and a commitment to ongoing professional development.
To prepare for the Salesforce Administrator Certification, candidates can utilize official Salesforce study materials, online training modules, practice exams, and resources provided by Salesforce. It is important to create a study plan, focus on understanding the key concepts and best practices, and gain hands-on experience with Salesforce to reinforce learning.
Overall, the Salesforce Administrator Certification is a valuable credential that validates a professional's ability to effectively administer Salesforce and adds credibility to their profile. It opens up new career opportunities, demonstrates expertise, and serves as a foundation for further Salesforce certifications and specialization tracks.
Salesforce App Builder Certification
The Salesforce App Builder Certification is a prestigious credential that validates a professional's proficiency in designing, building, and implementing custom applications using the Salesforce platform. This certification is tailored for individuals who are involved in creating custom solutions and extending the capabilities of Salesforce to meet specific business needs.
To earn the Salesforce App Builder Certification, candidates must pass an exam that evaluates their knowledge and skills in various areas, including data modeling, user interface customization, business logic implementation, and deployment strategies. The exam includes multiple-choice questions and scenario-based questions that assess a candidate's ability to design and build scalable and efficient Salesforce applications.
By obtaining the Salesforce App Builder Certification, professionals demonstrate their expertise in leveraging declarative features and tools to create custom objects, fields, and relationships. They are adept at designing intuitive user interfaces using Lightning App Builder, configuring automation through workflows and process builders, and implementing effective security and data access controls. This certification showcases their ability to create robust and customized Salesforce applications that align with specific business requirements.
The Salesforce App Builder Certification offers several advantages to certified professionals. It enhances career prospects by highlighting one's skills in designing and building custom applications on the Salesforce platform. Employers recognize the value of certified app builders who can create tailored solutions to streamline processes, enhance user experience, and drive business growth. Additionally, the certification provides a competitive advantage, setting certified professionals apart from others in the job market.
To prepare for the Salesforce App Builder Certification, candidates can utilize official Salesforce study materials, online training modules, practice exams, and other resources provided by Salesforce. It is important to focus on understanding the key concepts and best practices related to app building on the Salesforce platform. Hands-on experience with Salesforce, particularly in designing and configuring custom applications, is crucial for success in the exam.
In conclusion, the Salesforce App Builder Certification is a prestigious credential that validates a professional's ability to design and build custom applications on the Salesforce platform. It offers career advancement opportunities, demonstrates expertise in Salesforce app development, and adds credibility to one's profile. By obtaining this certification, professionals showcase their skills in creating tailored solutions that drive business success using Salesforce.
Prerequisites and Eligibility
To pursue Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certifications, there are certain prerequisites and eligibility criteria that candidates should be aware of. Here are the general guidelines:
- Experience: While there are no strict experience requirements for these certifications, it is recommended to have some practical experience working with the Salesforce platform. This experience helps in understanding the concepts and applying them effectively during the certification exams.
- Knowledge: Candidates should have a solid understanding of the Salesforce platform, its features, and functionality. Familiarity with Salesforce terminology, data model, user interface, and basic administration tasks is important. Salesforce provides study resources and training materials to help candidates acquire the necessary knowledge.
- Training and Learning Paths: Salesforce offers various training options, including online courses, instructor-led classes, and self-study materials, to help candidates prepare for the certification exams. While not mandatory, completing training courses specific to the Administrator and App Builder certifications can greatly enhance your understanding and exam readiness.
- Prerequisite Certifications: The Salesforce Administrator Certification does not have any specific prerequisite certifications. However, for the Salesforce App Builder Certification, it is recommended (but not mandatory) to have the Salesforce Administrator Certification as a foundation. The knowledge and skills gained from the Administrator certification serve as a solid basis for pursuing the App Builder certification.
- Trailhead Badges: Salesforce's Trailhead is an online learning platform that offers a wealth of interactive and self-paced modules to learn Salesforce. While not mandatory, completing relevant Trailhead modules and earning badges can provide valuable hands-on experience and knowledge to support your certification journey.
Exam Preparation Strategies
Preparing for the Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certification exams requires a systematic approach and effective study strategies. Here are some exam preparation strategies to help you succeed:
- Understand the Exam Blueprint: Familiarize yourself with the exam blueprint provided by Salesforce. It outlines the topics and percentage weightage for each section of the exam. This will help you prioritize your study efforts and allocate more time to areas with higher weightage.
- Utilize Official Salesforce Study Materials: Salesforce provides official study guides, documentation, and resources specific to each certification. These materials cover the exam objectives and provide valuable insights into Salesforce concepts and best practices. Make sure to thoroughly review and understand these resources.
- Hands-on Experience: Practice using Salesforce and work on real-life scenarios to gain practical experience. The more hands-on experience you have with the platform, the better you'll understand its functionality and be able to apply it during the exam. Create a Salesforce Developer Edition or use a Trailhead Playground to practice building and configuring Salesforce components.
- Take Advantage of Trailhead: Salesforce's Trailhead platform offers interactive modules, trails, and projects that can significantly enhance your understanding of Salesforce concepts. Complete relevant Trailhead modules and earn badges to reinforce your knowledge and gain practical experience.
- Join Study Groups or Communities: Engage with other individuals preparing for the same certification exam. Join study groups, forums, or online communities dedicated to Salesforce certifications. These platforms allow you to ask questions, share insights, and learn from the experiences of others. Collaboration and knowledge sharing can greatly benefit your preparation.
- Practice with Sample Exams: Salesforce provides official sample exams and practice tests that simulate the format and difficulty level of the actual exams. Take advantage of these resources to familiarize yourself with the exam structure, time constraints, and question types. Review your results and focus on areas where you need improvement.
- Create a Study Plan: Develop a study plan that outlines your study schedule, goals, and milestones. Set aside dedicated study time and break down the topics into manageable chunks. This will help you stay organized, track your progress, and ensure comprehensive coverage of all exam objectives.
- Review Documentation and Release Notes: Stay updated with the latest Salesforce features, enhancements, and changes by reviewing official documentation and release notes. Salesforce regularly updates its platform, and being aware of new features can be beneficial during the exam.
- Seek Additional Resources: Explore additional study materials, blogs, tutorials, and videos available online. There are numerous blogs, YouTube channels, and online courses that offer valuable insights and exam preparation tips from experienced Salesforce professionals.
- Manage Exam Day: Familiarize yourself with the exam logistics, such as exam duration, rules, and requirements. Plan ahead to ensure a calm and distraction-free environment during the exam. Take breaks, stay hydrated, and get a good night's sleep before the exam day to optimize your performance.
Maintaining and Renewing Certifications
Once you have earned your Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certifications, it's important to maintain and renew them to demonstrate ongoing expertise and stay current with the evolving Salesforce platform. Here are some key points to consider for maintaining and renewing your certifications:
- Stay Updated with Release Updates: Salesforce regularly introduces new features, enhancements, and updates to its platform. It's crucial to stay informed about these changes by regularly reviewing official documentation, release notes, and participating in webinars or events hosted by Salesforce. This will ensure that you are up-to-date with the latest Salesforce capabilities and best practices.
- Complete Trailhead Modules and Superbadges: Salesforce's Trailhead offers a wide range of modules, trails, and superbadges that cover various topics and help you expand your knowledge and skills. Completing relevant modules and earning superbadges not only reinforces your understanding but also contributes to maintaining your certifications. Salesforce provides a Maintenance Exam option for some certifications, which can be fulfilled by completing specified Trailhead content.
- Attend Salesforce Events and Webinars: Salesforce organizes events, webinars, and user group meetings where you can connect with fellow professionals, learn about new features, and engage in discussions. Participating in these events allows you to expand your network, exchange insights, and stay informed about industry trends.
- Earn Continuing Education Units (CEUs): Salesforce requires certified professionals to earn a specific number of Continuing Education Units (CEUs) to renew their certifications. CEUs can be earned through a variety of activities, such as attending training sessions, completing Trailhead modules, presenting at conferences, or participating in relevant Salesforce-related volunteer work. The number of CEUs required may vary depending on the certification.
- Recertify at Regular Intervals: Salesforce certifications typically have a validity period, after which you need to recertify to maintain your credential. Stay aware of the expiration date of your certifications and make a plan to recertify well in advance. This may involve taking the updated version of the certification exam or fulfilling specific requirements, such as completing a maintenance exam or earning a designated number of CEUs.
- Leverage Salesforce Help and Support: Salesforce provides support resources, forums, and a knowledge base to help certified professionals with questions, issues, or clarification on specific topics. Utilize these resources to enhance your understanding and address any challenges you may encounter during your certification maintenance journey.
- Stay Engaged with the Salesforce Community: Engage with the larger Salesforce community through online forums, social media groups, and user group meetings. Connect with other certified professionals, participate in discussions, and share your experiences. This active involvement helps you stay connected, gain insights, and stay motivated in maintaining your certifications.
Tips for a Successful Exam Day
Preparing for the Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certification exams is crucial, but it's equally important to have a successful exam day experience. Here are some tips to help you perform your best on the day of the exam:
- Review Exam Logistics: Familiarize yourself with the exam logistics, such as the duration of the exam, number of questions, and passing score requirements. Understand any specific rules or restrictions, such as the use of scratch paper or breaks during the exam. Knowing what to expect will help you feel more confident and prepared.
- Get a Good Night's Sleep: Ensure you get a good night's sleep before the exam day. A well-rested mind performs better and is more capable of focusing and retaining information. Avoid last-minute cramming and allow your brain to rest and recharge for optimal performance.
- Start the Day with a Positive Mindset: Begin your day with a positive mindset and believe in your ability to succeed. Encourage yourself and visualize a successful outcome. Positive thinking can help alleviate stress and boost your confidence, leading to better performance during the exam.
- Have a Nutritious Meal: Prioritize a healthy and nutritious meal before the exam. Fueling your body with nutritious food will provide you with sustained energy and help you stay focused throughout the exam. Avoid heavy meals that may cause drowsiness or discomfort.
- Arrive Early and Be Prepared: Plan to arrive at the exam center or your chosen exam location early. Give yourself ample time to check-in, complete any necessary paperwork, and get settled. Ensure you have all the required identification and any permitted resources, such as a calculator or notepad, if allowed.
- Take Deep Breaths and Relax: Before starting the exam, take a few deep breaths to calm your nerves and relax your mind. Deep breathing helps reduce stress and anxiety, allowing you to approach the exam with a clear and focused mindset. Take a moment to center yourself and visualize success.
- Read Questions Carefully: During the exam, read each question carefully to understand the requirements and any specific details. Pay attention to keywords and ensure you're addressing what is being asked. Take your time and avoid rushing through the questions.
- Manage Time Effectively: Keep an eye on the time throughout the exam to ensure you're progressing at a reasonable pace. If you encounter challenging questions, don't dwell on them for too long. Mark them for review and move on. Allocate time wisely to maximize your chances of completing all questions within the allotted time.
- Answer with Confidence: Trust your preparation and answer each question to the best of your ability. Avoid second-guessing yourself excessively. Trust your instincts and select the option that you believe is most accurate. Maintain confidence in your knowledge and decision-making skills.
- Review and Validate Answers: If time permits, review your answers before submitting the exam. Use this time to double-check your responses, verify that you have addressed all requirements, and correct any errors or oversights. Be mindful of the time remaining and make strategic choices about where to focus your review.
How to obtain Salesforce Administrator and App Builder Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
- Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
- Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
- Data Science : Power BI Certification
- Cyber Security : CISA Certification
- Emerging Technologies : Blockchain Certification
- Salesforce : Salesforce Administrator and App Builder Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, pursuing the Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certifications can greatly enhance your skills and career prospects within the Salesforce ecosystem. These certifications validate your knowledge, expertise, and ability to effectively administer and develop applications on the Salesforce platform.
The Salesforce Administrator Certification focuses on managing and configuring Salesforce implementations, ensuring data integrity, and maximizing the platform's capabilities. It showcases your proficiency in handling user access, security, automation, and reporting, making you a valuable asset to any organization leveraging Salesforce.
On the other hand, the Salesforce App Builder Certification recognizes your skills in designing and building custom applications that meet specific business requirements. It demonstrates your ability to leverage declarative features, design intuitive user interfaces, implement automation, and deploy scalable applications on the Salesforce platform.
To successfully pursue these certifications, it's essential to understand the prerequisites and eligibility criteria, engage in comprehensive exam preparation, and stay updated with the latest Salesforce features and best practices. Utilizing official study materials, practicing with sample exams, gaining hands-on experience, and participating in the Salesforce community are key strategies for success.
Once certified, maintaining and renewing your credentials require ongoing learning, staying informed about Salesforce releases, earning Continuing Education Units (CEUs), and actively participating in the Salesforce community. By staying committed to professional development and remaining engaged, you can continuously showcase your expertise and keep your certifications up to date.
Earning the Salesforce Administrator and App Builder certifications demonstrates your dedication to excellence, positions you as a trusted Salesforce professional, and opens doors to new career opportunities. Whether you are an aspiring administrator or an application developer, these certifications serve as valuable assets in your Salesforce journey.
Comprehensive Guide to Blockchain Certification Training
Welcome to our "Blockchain Certification Training Course: A Step-by-Step Guide," where you'll discover the revolutionary potential of blockchain technology. Whether you're new to this innovative field or seeking to deepen your understanding, our comprehensive course offers a transformative learning experience. Dive into the core principles of blockchain, explore cryptographic hashing, consensus algorithms, and real-world applications. Through hands-on exercises and simulations, you'll gain practical expertise in creating blockchain applications and understanding smart contracts. Whether your goal is to become a blockchain developer, integrate blockchain solutions in your business, or simply explore this cutting-edge technology, our course is your gateway to embracing the future of blockchain. Let's embark on this journey together and unlock the limitless possibilities of blockchain technology.
Table of contents
-
Introduction to Blockchain Technology
-
Importance of Blockchain Certification
-
Popular Blockchain Certifications
-
Blockchain Fundamentals
-
Cryptography and Blockchain
-
Blockchain Networks
-
Smart Contracts and Solidity
-
Future Trends in Blockchain
-
Conclusion
Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary concept that has the potential to transform various industries. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and transparent digital ledger that enables secure and immutable record-keeping of transactions. Originally introduced as the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has since gained recognition for its wide-ranging applications beyond digital currencies.
The fundamental concept of blockchain revolves around creating a decentralized network of computers, known as nodes, that work together to validate, record, and store transactions. Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single authority maintains control, blockchain distributes this responsibility across multiple participants, ensuring transparency, security, and resilience.
Key Principles of Blockchain:
-
Decentralization: Blockchain eliminates the need for a central authority, such as a bank or government, by distributing control among multiple participants in the network. This decentralization enhances trust and removes the reliance on intermediaries.
-
Transparency: Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is visible to all participants in the network. This transparency increases accountability and reduces the risk of fraud or manipulation.
-
Security: Blockchain utilizes cryptographic techniques to ensure the integrity and security of data. Transactions are cryptographically linked, making it extremely difficult to alter or tamper with the information stored in the blockchain.
-
Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes a permanent and unchangeable part of the ledger. This immutability ensures the integrity of the data and provides an auditable trail of events.
-
Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain employs consensus algorithms to achieve agreement among network participants regarding the validity of transactions. Popular consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), among others.
Importance of Blockchain Certification
The importance of blockchain certification has grown significantly as blockchain technology continues to gain prominence across industries. Blockchain certification validates an individual's knowledge and skills in understanding and implementing blockchain solutions, making it a valuable asset in today's job market. Here are several reasons why blockchain certification holds significance:
-
Demonstrates Expertise: Blockchain certification serves as tangible proof that an individual possesses a deep understanding of blockchain technology, its principles, and its applications. It demonstrates their expertise in areas such as blockchain architecture, smart contract development, cryptography, consensus mechanisms, and more. This expertise can open doors to exciting career opportunities in blockchain development, consulting, project management, and other related roles.
-
Competitive Advantage: In a rapidly evolving job market, blockchain certification sets candidates apart from their peers. It showcases their commitment to continuous learning and staying updated with the latest advancements in blockchain technology. Employers value certified professionals as they bring specialized knowledge and skills to the table, giving them a competitive advantage when seeking employment or career advancement.
-
Industry Recognition: Receiving a blockchain certification from a reputable certification provider brings industry recognition and credibility. Employers, clients, and colleagues recognize the value of certifications from established organizations, as they signify a certain level of expertise and adherence to industry standards. Blockchain certification can enhance an individual's professional reputation and make them a sought-after resource in the field.
-
Expanded Career Opportunities: The demand for blockchain professionals is growing rapidly across industries such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, government, and more. Blockchain certification equips individuals with the necessary skills to explore diverse job roles, including blockchain developer, blockchain architect, blockchain consultant, blockchain project manager, and blockchain analyst. It widens the scope for career growth and increases the chances of landing lucrative positions in emerging and high-demand fields.
-
Entrepreneurial Pursuits: Blockchain certification not only benefits individuals seeking employment but also aspiring entrepreneurs. With a solid understanding of blockchain technology and its applications, certified individuals can explore entrepreneurial opportunities in developing blockchain-based solutions, launching startups focused on blockchain innovations, or advising businesses on blockchain integration strategies. Certification provides a strong foundation for success in the rapidly evolving blockchain ecosystem.
-
Networking and Collaboration: Obtaining blockchain certification often involves participating in training programs, workshops, and communities dedicated to blockchain education. These platforms provide opportunities to network and collaborate with like-minded professionals, industry experts, and thought leaders. Building connections in the blockchain community can lead to collaborations, mentorship, and exposure to new ideas and opportunities.
Popular Blockchain Certifications
There are several reputable and popular blockchain certifications available today. These certifications validate an individual's knowledge and skills in blockchain technology, helping them stand out in the job market. Here are some well-known blockchain certifications:
-
Certified Blockchain Developer (CBD) by Blockchain Training Alliance: The CBD certification is designed for developers who want to demonstrate their proficiency in developing blockchain applications. It covers topics such as blockchain architecture, smart contract development, tokenization, and security. The certification is recognized globally and highly regarded in the blockchain industry.
-
Certified Blockchain Professional (CBP) by EC-Council: The CBP certification is offered by EC-Council, a leading provider of cybersecurity certifications. It covers blockchain fundamentals, cryptocurrency concepts, smart contracts, and blockchain security. The certification is suitable for professionals looking to enhance their knowledge and skills in blockchain technology.
-
Certified Blockchain Expert (CBE) by Blockchain Council: The CBE certification is a comprehensive program that covers various aspects of blockchain technology, including blockchain basics, cryptocurrency, smart contracts, consensus mechanisms, and decentralized applications. It is suitable for professionals aiming to become blockchain experts across different domains.
-
Certified Blockchain Solution Architect (CBSA) by Blockchain Training Alliance: The CBSA certification focuses on blockchain architecture and design principles. It covers topics such as network topology, consensus algorithms, privacy, and scalability. The certification is designed for architects, developers, and technical professionals involved in designing and implementing blockchain solutions.
-
Certified Blockchain Business Foundations (CBBF) by Blockchain Training Alliance: The CBBF certification is aimed at business professionals who want to gain a foundational understanding of blockchain technology and its business applications. It covers blockchain basics, use cases, smart contracts, and regulatory considerations. This certification is suitable for individuals interested in exploring blockchain's potential impact on various industries.
-
Certified Ethereum Developer (CED) by ConsenSys Academy: The CED certification focuses on Ethereum, one of the most popular blockchain platforms. It covers Solidity programming, smart contract development, and decentralized application (DApp) development. The certification is suitable for developers looking to specialize in Ethereum-based blockchain solutions.
-
Hyperledger Certified Administrator (HCA) by The Linux Foundation: The HCA certification focuses on Hyperledger, an open-source blockchain framework. It covers Hyperledger Fabric and Hyperledger Sawtooth platforms, network setup and administration, and chaincode development. The certification is suitable for professionals interested in working with enterprise-grade blockchain solutions.
Blockchain Fundamentals
Blockchain fundamentals encompass the core concepts and principles that underpin blockchain technology. Understanding these fundamentals is essential for anyone looking to delve into the world of blockchain. Here are some key aspects of blockchain fundamentals:
-
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology. A distributed ledger is a database that is maintained across multiple network participants or nodes. Each participant has a copy of the entire ledger, and updates are achieved through a consensus mechanism.
-
Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems where a central authority controls data and transactions, blockchain operates in a decentralized manner. It eliminates the need for intermediaries by distributing control and decision-making among participants in the network.
-
Blocks and Transactions: A blockchain consists of a series of blocks, with each block containing a set of transactions. Transactions represent the transfer of assets or information on the blockchain. Blocks serve as containers for these transactions and are linked together using cryptographic hashes.
-
Cryptographic Hash Functions: Blockchain uses cryptographic hash functions to secure and verify data integrity. A hash function takes an input (such as a block or transaction) and produces a fixed-size output, which is unique to that input. Any change in the input data will result in a completely different hash value, making it easy to detect tampering or modifications.
-
Consensus Mechanisms: Consensus mechanisms are protocols that ensure agreement and validation of transactions within a blockchain network. They enable network participants to reach a consensus on the validity and ordering of transactions. Examples of consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT).
-
Immutable and Append-Only Structure: Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or tampered with. The append-only nature of the blockchain ensures that new transactions are added in a sequential and chronological order, creating a transparent and auditable record of events.
-
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions encoded into the blockchain. They automatically execute and enforce contractual agreements when specified conditions are met. Smart contracts can facilitate complex transactions, automate processes, and enhance trust and transparency.
-
Public and Private Blockchains: Public blockchains are open to anyone and allow anyone to participate in the network, read the data, and validate transactions. Private blockchains, on the other hand, are restricted to a specific group of participants, granting them control over access and governance.
-
Security and Consensus: Blockchain technology ensures security through the use of cryptographic algorithms, immutability, and consensus mechanisms. The decentralized nature of blockchain reduces the risk of a single point of failure and makes it resistant to hacking and data manipulation.
-
Transparency and Privacy: Blockchain provides transparency by allowing all participants to view and validate transactions. However, it also offers privacy features through techniques like encryption, zero-knowledge proofs, and selective disclosure, enabling participants to protect sensitive data while maintaining the integrity of the blockchain.
Cryptography and Blockchain
Cryptography plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of blockchain technology. It provides the underlying mechanisms that protect the confidentiality, authenticity, and immutability of data stored on the blockchain. Here are some key aspects of the relationship between cryptography and blockchain:
-
Secure Hash Functions: Cryptographic hash functions are an integral part of blockchain technology. They are used to generate a unique fixed-length string of characters, called a hash, from any input data. Hash functions have several important properties for blockchain, including collision resistance (the difficulty of finding two different inputs with the same hash) and preimage resistance (the inability to determine the original input from its hash). These properties help ensure data integrity and prevent tampering with the information stored on the blockchain.
-
Digital Signatures: Digital signatures are a cryptographic technique used in blockchain to provide authenticity and non-repudiation of transactions. A digital signature involves the use of asymmetric key pairs, consisting of a private key and a corresponding public key. The sender of a transaction uses their private key to create a unique digital signature, which can be verified by anyone using the corresponding public key. This ensures that transactions on the blockchain are securely associated with their respective senders and cannot be altered or repudiated.
-
Public-Key Cryptography: Public-key cryptography, also known as asymmetric cryptography, is a cryptographic system that uses pairs of public and private keys. Public keys are widely distributed and used to encrypt data, while private keys are kept secret and used to decrypt the encrypted data. Blockchain utilizes public-key cryptography for various purposes, including generating addresses for cryptocurrency wallets, verifying digital signatures, and enabling secure peer-to-peer communication between participants.
-
Encryption: Encryption is the process of transforming plaintext into ciphertext using cryptographic algorithms and a secret key. In the context of blockchain, encryption can be used to protect the privacy and confidentiality of sensitive data, such as personal information stored on the blockchain. Encryption ensures that only authorized parties with the corresponding decryption key can access and understand the encrypted data.
-
Merkle Trees: Merkle trees, or hash trees, are a data structure used in blockchain to efficiently verify the integrity of large sets of data. A Merkle tree organizes data into a hierarchical structure, where each leaf node represents a piece of data, and each non-leaf node represents the hash of its child nodes. By recursively hashing the data and combining the hashes, it becomes possible to efficiently verify the integrity of large datasets without needing to examine each individual piece of data.
Blockchain Networks
Blockchain networks are the underlying infrastructure that enables the functioning and operation of blockchain technology. These networks consist of interconnected nodes that collaborate to maintain the distributed ledger and validate transactions. Here are the key types of blockchain networks:
-
Public Blockchain: Public blockchains are open and permissionless networks that allow anyone to participate, read the data, and validate transactions. These networks are decentralized and provide a high level of transparency, as anyone can view the entire transaction history and the current state of the blockchain. Examples of public blockchains include Bitcoin and Ethereum.
-
Private Blockchain: Private blockchains are restricted to a specific group of participants who have been granted access and permission to participate in the network. These networks are often used by organizations to maintain control over the blockchain and ensure privacy among participants. Private blockchains are more centralized compared to public blockchains and are commonly used in enterprise settings for various applications, such as supply chain management and intercompany transactions.
-
Consortium Blockchain: Consortium blockchains are a hybrid model that combines elements of both public and private blockchains. In a consortium blockchain, a group of pre-selected nodes or organizations come together to maintain the blockchain network. Consortium blockchains provide a higher degree of decentralization and security compared to private blockchains while allowing for more efficient consensus mechanisms and faster transaction processing.
-
Permissioned Blockchain: Permissioned blockchains require participants to obtain explicit permission or credentials to join the network and contribute to the consensus process. Permissioned blockchains are commonly used in enterprise environments where privacy, compliance, and data access control are critical. Participants in permissioned blockchains typically have defined roles and responsibilities within the network.
-
Hybrid Blockchain: Hybrid blockchains combine elements of different types of blockchain networks to leverage the benefits of both public and private blockchains. They enable controlled transparency and public participation for certain aspects of the blockchain while maintaining privacy and confidentiality for sensitive data. Hybrid blockchains are designed to provide flexibility and cater to specific use cases that require a combination of public and private elements.
Smart Contracts and Solidity
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. They automatically execute and enforce the agreed-upon rules and conditions when specific conditions are met. Smart contracts are a fundamental feature of blockchain technology, enabling the automation and trustless execution of transactions and agreements.
Solidity is a high-level programming language used for writing smart contracts on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. It is specifically designed for the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and is the most popular language for developing smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Here are some key aspects of smart contracts and Solidity:
-
Automation and Self-Execution: Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries by automating the execution of contractual agreements. Once deployed on the blockchain, smart contracts autonomously execute the predefined functions and logic when triggered by specific events or conditions, without requiring manual intervention or intermediaries.
-
Decentralized Trust: Smart contracts leverage the decentralized nature of blockchain technology to provide trust and transparency. The execution of smart contracts is verified and validated by multiple nodes in the network, ensuring that the contract's execution follows the rules and conditions encoded in the contract code. This decentralized trust mechanism eliminates the need for relying on a central authority or third-party intermediaries.
-
Solidity Programming Language: Solidity is a statically-typed, contract-oriented programming language used for writing smart contracts on the Ethereum platform. It is similar to JavaScript in terms of syntax and is designed to facilitate secure and efficient smart contract development. Solidity provides features such as inheritance, libraries, modifiers, and events to enable developers to build complex and robust smart contracts.
-
Contract Deployment and Execution: Smart contracts written in Solidity are compiled into bytecode, which can then be deployed onto the Ethereum blockchain. Once deployed, the smart contract is assigned a unique address on the blockchain and becomes an immutable and tamper-proof entity. Users can interact with the smart contract by sending transactions to its address, triggering the execution of its functions and altering its state.
-
Security Considerations: Writing secure smart contracts is crucial to avoid vulnerabilities and potential exploits. Solidity provides various security features and best practices to help developers mitigate risks, such as preventing reentrancy attacks, handling exception cases, avoiding integer overflow and underflow, and implementing proper access control mechanisms. Auditing tools and code review processes are commonly employed to identify and fix potential security issues in smart contracts.
-
Ecosystem and Tooling: Solidity has a vibrant ecosystem with a wide range of developer tools, frameworks, and libraries that simplify smart contract development. These include development frameworks like Truffle and Hardhat, testing frameworks like Mocha and Chai, and libraries such as OpenZeppelin for reusable smart contract components. These tools and resources aid in writing, testing, deploying, and managing Solidity-based smart contracts efficiently.
Future Trends in Blockchain
The field of blockchain technology continues to evolve rapidly, with several emerging trends that have the potential to shape its future. Here are some key trends to watch out for in the blockchain space:
-
Interoperability and Cross-Chain Solutions: As different blockchain networks and platforms emerge, there is a growing need for interoperability between them. Interoperability solutions aim to enable seamless communication and data exchange between different blockchains, allowing for increased connectivity and collaboration. Cross-chain technologies and protocols, such as Polkadot, Cosmos, and interoperability-focused projects like Chainlink and Aion, are working towards creating a connected blockchain ecosystem.
-
Scalability and Performance Enhancements: Scalability has been a significant challenge for blockchain networks, particularly for public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum. To handle a higher volume of transactions and support widespread adoption, scalability solutions are being explored. Layer 2 solutions like payment channels (Lightning Network) and sidechains, as well as novel consensus mechanisms (Proof of Stake, Proof of Authority), are being developed to improve blockchain performance, throughput, and transaction speeds.
-
Enterprise Blockchain Adoption: Blockchain technology is gaining traction among enterprises across various industries, including finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more. Enterprises are exploring blockchain solutions to enhance transparency, traceability, and efficiency in their operations. Consortium and private blockchains are particularly being leveraged to address industry-specific challenges, compliance requirements, and data privacy concerns.
-
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi has emerged as a significant use case for blockchain technology, enabling financial applications to be built on open and decentralized networks. DeFi protocols offer services such as lending, borrowing, decentralized exchanges, and yield farming. DeFi has gained significant attention and investment, and it has the potential to revolutionize traditional finance by removing intermediaries and providing greater financial inclusivity.
-
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs have gained immense popularity, enabling the ownership and trading of unique digital assets on the blockchain. NFTs have been primarily associated with digital art, collectibles, and gaming, but their potential extends to areas like real estate, intellectual property, and identity verification. The NFT market has witnessed significant growth and innovation, with artists, creators, and brands exploring new avenues for tokenizing and monetizing digital assets.
-
Enhanced Privacy and Confidentiality: While blockchain offers transparency and immutability, privacy and confidentiality of data remain important considerations, especially in enterprise and government use cases. Privacy-focused blockchain solutions, such as zero-knowledge proofs, homomorphic encryption, and privacy-preserving protocols like Zcash and Monero, are being developed to address these concerns while preserving the security and integrity of the underlying blockchain.
-
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: The energy consumption associated with blockchain mining and transaction processing has raised concerns about its environmental impact. As the industry grows, there is a focus on developing more sustainable and energy-efficient consensus algorithms and infrastructure solutions. Projects are exploring proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanisms, energy-efficient consensus protocols, and renewable energy integration to reduce the carbon footprint of blockchain networks.
How to obtain Blockchain Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Power BI Certification
-
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
-
Emerging Technologies : Blockchain Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology continues to make significant strides and has the potential to revolutionize various industries and sectors. Its core principles of decentralization, transparency, security, and immutability offer numerous benefits and opportunities for innovation. As blockchain evolves, it is important to keep an eye on the emerging trends shaping its future.
Interoperability and cross-chain solutions aim to connect different blockchain networks, fostering collaboration and expanding the possibilities of decentralized applications. Scalability and performance enhancements are crucial for blockchain's widespread adoption, with various solutions and consensus mechanisms being explored to improve transaction speeds and throughput.
Enterprise adoption of blockchain is growing, with organizations recognizing its potential to enhance transparency, efficiency, and security in their operations. DeFi and NFTs have emerged as prominent use cases, revolutionizing finance and digital asset ownership. Privacy and confidentiality are being addressed through the development of privacy-focused protocols and technologies.
Read More
Welcome to our "Blockchain Certification Training Course: A Step-by-Step Guide," where you'll discover the revolutionary potential of blockchain technology. Whether you're new to this innovative field or seeking to deepen your understanding, our comprehensive course offers a transformative learning experience. Dive into the core principles of blockchain, explore cryptographic hashing, consensus algorithms, and real-world applications. Through hands-on exercises and simulations, you'll gain practical expertise in creating blockchain applications and understanding smart contracts. Whether your goal is to become a blockchain developer, integrate blockchain solutions in your business, or simply explore this cutting-edge technology, our course is your gateway to embracing the future of blockchain. Let's embark on this journey together and unlock the limitless possibilities of blockchain technology.
Table of contents
-
Introduction to Blockchain Technology
-
Importance of Blockchain Certification
-
Popular Blockchain Certifications
-
Blockchain Fundamentals
-
Cryptography and Blockchain
-
Blockchain Networks
-
Smart Contracts and Solidity
-
Future Trends in Blockchain
-
Conclusion
Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary concept that has the potential to transform various industries. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and transparent digital ledger that enables secure and immutable record-keeping of transactions. Originally introduced as the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has since gained recognition for its wide-ranging applications beyond digital currencies.
The fundamental concept of blockchain revolves around creating a decentralized network of computers, known as nodes, that work together to validate, record, and store transactions. Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single authority maintains control, blockchain distributes this responsibility across multiple participants, ensuring transparency, security, and resilience.
Key Principles of Blockchain:
-
Decentralization: Blockchain eliminates the need for a central authority, such as a bank or government, by distributing control among multiple participants in the network. This decentralization enhances trust and removes the reliance on intermediaries.
-
Transparency: Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is visible to all participants in the network. This transparency increases accountability and reduces the risk of fraud or manipulation.
-
Security: Blockchain utilizes cryptographic techniques to ensure the integrity and security of data. Transactions are cryptographically linked, making it extremely difficult to alter or tamper with the information stored in the blockchain.
-
Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes a permanent and unchangeable part of the ledger. This immutability ensures the integrity of the data and provides an auditable trail of events.
-
Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain employs consensus algorithms to achieve agreement among network participants regarding the validity of transactions. Popular consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), among others.
Importance of Blockchain Certification
The importance of blockchain certification has grown significantly as blockchain technology continues to gain prominence across industries. Blockchain certification validates an individual's knowledge and skills in understanding and implementing blockchain solutions, making it a valuable asset in today's job market. Here are several reasons why blockchain certification holds significance:
-
Demonstrates Expertise: Blockchain certification serves as tangible proof that an individual possesses a deep understanding of blockchain technology, its principles, and its applications. It demonstrates their expertise in areas such as blockchain architecture, smart contract development, cryptography, consensus mechanisms, and more. This expertise can open doors to exciting career opportunities in blockchain development, consulting, project management, and other related roles.
-
Competitive Advantage: In a rapidly evolving job market, blockchain certification sets candidates apart from their peers. It showcases their commitment to continuous learning and staying updated with the latest advancements in blockchain technology. Employers value certified professionals as they bring specialized knowledge and skills to the table, giving them a competitive advantage when seeking employment or career advancement.
-
Industry Recognition: Receiving a blockchain certification from a reputable certification provider brings industry recognition and credibility. Employers, clients, and colleagues recognize the value of certifications from established organizations, as they signify a certain level of expertise and adherence to industry standards. Blockchain certification can enhance an individual's professional reputation and make them a sought-after resource in the field.
-
Expanded Career Opportunities: The demand for blockchain professionals is growing rapidly across industries such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, government, and more. Blockchain certification equips individuals with the necessary skills to explore diverse job roles, including blockchain developer, blockchain architect, blockchain consultant, blockchain project manager, and blockchain analyst. It widens the scope for career growth and increases the chances of landing lucrative positions in emerging and high-demand fields.
-
Entrepreneurial Pursuits: Blockchain certification not only benefits individuals seeking employment but also aspiring entrepreneurs. With a solid understanding of blockchain technology and its applications, certified individuals can explore entrepreneurial opportunities in developing blockchain-based solutions, launching startups focused on blockchain innovations, or advising businesses on blockchain integration strategies. Certification provides a strong foundation for success in the rapidly evolving blockchain ecosystem.
-
Networking and Collaboration: Obtaining blockchain certification often involves participating in training programs, workshops, and communities dedicated to blockchain education. These platforms provide opportunities to network and collaborate with like-minded professionals, industry experts, and thought leaders. Building connections in the blockchain community can lead to collaborations, mentorship, and exposure to new ideas and opportunities.
Popular Blockchain Certifications
There are several reputable and popular blockchain certifications available today. These certifications validate an individual's knowledge and skills in blockchain technology, helping them stand out in the job market. Here are some well-known blockchain certifications:
-
Certified Blockchain Developer (CBD) by Blockchain Training Alliance: The CBD certification is designed for developers who want to demonstrate their proficiency in developing blockchain applications. It covers topics such as blockchain architecture, smart contract development, tokenization, and security. The certification is recognized globally and highly regarded in the blockchain industry.
-
Certified Blockchain Professional (CBP) by EC-Council: The CBP certification is offered by EC-Council, a leading provider of cybersecurity certifications. It covers blockchain fundamentals, cryptocurrency concepts, smart contracts, and blockchain security. The certification is suitable for professionals looking to enhance their knowledge and skills in blockchain technology.
-
Certified Blockchain Expert (CBE) by Blockchain Council: The CBE certification is a comprehensive program that covers various aspects of blockchain technology, including blockchain basics, cryptocurrency, smart contracts, consensus mechanisms, and decentralized applications. It is suitable for professionals aiming to become blockchain experts across different domains.
-
Certified Blockchain Solution Architect (CBSA) by Blockchain Training Alliance: The CBSA certification focuses on blockchain architecture and design principles. It covers topics such as network topology, consensus algorithms, privacy, and scalability. The certification is designed for architects, developers, and technical professionals involved in designing and implementing blockchain solutions.
-
Certified Blockchain Business Foundations (CBBF) by Blockchain Training Alliance: The CBBF certification is aimed at business professionals who want to gain a foundational understanding of blockchain technology and its business applications. It covers blockchain basics, use cases, smart contracts, and regulatory considerations. This certification is suitable for individuals interested in exploring blockchain's potential impact on various industries.
-
Certified Ethereum Developer (CED) by ConsenSys Academy: The CED certification focuses on Ethereum, one of the most popular blockchain platforms. It covers Solidity programming, smart contract development, and decentralized application (DApp) development. The certification is suitable for developers looking to specialize in Ethereum-based blockchain solutions.
-
Hyperledger Certified Administrator (HCA) by The Linux Foundation: The HCA certification focuses on Hyperledger, an open-source blockchain framework. It covers Hyperledger Fabric and Hyperledger Sawtooth platforms, network setup and administration, and chaincode development. The certification is suitable for professionals interested in working with enterprise-grade blockchain solutions.
Blockchain Fundamentals
Blockchain fundamentals encompass the core concepts and principles that underpin blockchain technology. Understanding these fundamentals is essential for anyone looking to delve into the world of blockchain. Here are some key aspects of blockchain fundamentals:
-
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology. A distributed ledger is a database that is maintained across multiple network participants or nodes. Each participant has a copy of the entire ledger, and updates are achieved through a consensus mechanism.
-
Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems where a central authority controls data and transactions, blockchain operates in a decentralized manner. It eliminates the need for intermediaries by distributing control and decision-making among participants in the network.
-
Blocks and Transactions: A blockchain consists of a series of blocks, with each block containing a set of transactions. Transactions represent the transfer of assets or information on the blockchain. Blocks serve as containers for these transactions and are linked together using cryptographic hashes.
-
Cryptographic Hash Functions: Blockchain uses cryptographic hash functions to secure and verify data integrity. A hash function takes an input (such as a block or transaction) and produces a fixed-size output, which is unique to that input. Any change in the input data will result in a completely different hash value, making it easy to detect tampering or modifications.
-
Consensus Mechanisms: Consensus mechanisms are protocols that ensure agreement and validation of transactions within a blockchain network. They enable network participants to reach a consensus on the validity and ordering of transactions. Examples of consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT).
-
Immutable and Append-Only Structure: Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or tampered with. The append-only nature of the blockchain ensures that new transactions are added in a sequential and chronological order, creating a transparent and auditable record of events.
-
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions encoded into the blockchain. They automatically execute and enforce contractual agreements when specified conditions are met. Smart contracts can facilitate complex transactions, automate processes, and enhance trust and transparency.
-
Public and Private Blockchains: Public blockchains are open to anyone and allow anyone to participate in the network, read the data, and validate transactions. Private blockchains, on the other hand, are restricted to a specific group of participants, granting them control over access and governance.
-
Security and Consensus: Blockchain technology ensures security through the use of cryptographic algorithms, immutability, and consensus mechanisms. The decentralized nature of blockchain reduces the risk of a single point of failure and makes it resistant to hacking and data manipulation.
-
Transparency and Privacy: Blockchain provides transparency by allowing all participants to view and validate transactions. However, it also offers privacy features through techniques like encryption, zero-knowledge proofs, and selective disclosure, enabling participants to protect sensitive data while maintaining the integrity of the blockchain.
Cryptography and Blockchain
Cryptography plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of blockchain technology. It provides the underlying mechanisms that protect the confidentiality, authenticity, and immutability of data stored on the blockchain. Here are some key aspects of the relationship between cryptography and blockchain:
-
Secure Hash Functions: Cryptographic hash functions are an integral part of blockchain technology. They are used to generate a unique fixed-length string of characters, called a hash, from any input data. Hash functions have several important properties for blockchain, including collision resistance (the difficulty of finding two different inputs with the same hash) and preimage resistance (the inability to determine the original input from its hash). These properties help ensure data integrity and prevent tampering with the information stored on the blockchain.
-
Digital Signatures: Digital signatures are a cryptographic technique used in blockchain to provide authenticity and non-repudiation of transactions. A digital signature involves the use of asymmetric key pairs, consisting of a private key and a corresponding public key. The sender of a transaction uses their private key to create a unique digital signature, which can be verified by anyone using the corresponding public key. This ensures that transactions on the blockchain are securely associated with their respective senders and cannot be altered or repudiated.
-
Public-Key Cryptography: Public-key cryptography, also known as asymmetric cryptography, is a cryptographic system that uses pairs of public and private keys. Public keys are widely distributed and used to encrypt data, while private keys are kept secret and used to decrypt the encrypted data. Blockchain utilizes public-key cryptography for various purposes, including generating addresses for cryptocurrency wallets, verifying digital signatures, and enabling secure peer-to-peer communication between participants.
-
Encryption: Encryption is the process of transforming plaintext into ciphertext using cryptographic algorithms and a secret key. In the context of blockchain, encryption can be used to protect the privacy and confidentiality of sensitive data, such as personal information stored on the blockchain. Encryption ensures that only authorized parties with the corresponding decryption key can access and understand the encrypted data.
-
Merkle Trees: Merkle trees, or hash trees, are a data structure used in blockchain to efficiently verify the integrity of large sets of data. A Merkle tree organizes data into a hierarchical structure, where each leaf node represents a piece of data, and each non-leaf node represents the hash of its child nodes. By recursively hashing the data and combining the hashes, it becomes possible to efficiently verify the integrity of large datasets without needing to examine each individual piece of data.
Blockchain Networks
Blockchain networks are the underlying infrastructure that enables the functioning and operation of blockchain technology. These networks consist of interconnected nodes that collaborate to maintain the distributed ledger and validate transactions. Here are the key types of blockchain networks:
-
Public Blockchain: Public blockchains are open and permissionless networks that allow anyone to participate, read the data, and validate transactions. These networks are decentralized and provide a high level of transparency, as anyone can view the entire transaction history and the current state of the blockchain. Examples of public blockchains include Bitcoin and Ethereum.
-
Private Blockchain: Private blockchains are restricted to a specific group of participants who have been granted access and permission to participate in the network. These networks are often used by organizations to maintain control over the blockchain and ensure privacy among participants. Private blockchains are more centralized compared to public blockchains and are commonly used in enterprise settings for various applications, such as supply chain management and intercompany transactions.
-
Consortium Blockchain: Consortium blockchains are a hybrid model that combines elements of both public and private blockchains. In a consortium blockchain, a group of pre-selected nodes or organizations come together to maintain the blockchain network. Consortium blockchains provide a higher degree of decentralization and security compared to private blockchains while allowing for more efficient consensus mechanisms and faster transaction processing.
-
Permissioned Blockchain: Permissioned blockchains require participants to obtain explicit permission or credentials to join the network and contribute to the consensus process. Permissioned blockchains are commonly used in enterprise environments where privacy, compliance, and data access control are critical. Participants in permissioned blockchains typically have defined roles and responsibilities within the network.
-
Hybrid Blockchain: Hybrid blockchains combine elements of different types of blockchain networks to leverage the benefits of both public and private blockchains. They enable controlled transparency and public participation for certain aspects of the blockchain while maintaining privacy and confidentiality for sensitive data. Hybrid blockchains are designed to provide flexibility and cater to specific use cases that require a combination of public and private elements.
Smart Contracts and Solidity
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. They automatically execute and enforce the agreed-upon rules and conditions when specific conditions are met. Smart contracts are a fundamental feature of blockchain technology, enabling the automation and trustless execution of transactions and agreements.
Solidity is a high-level programming language used for writing smart contracts on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. It is specifically designed for the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and is the most popular language for developing smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Here are some key aspects of smart contracts and Solidity:
-
Automation and Self-Execution: Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries by automating the execution of contractual agreements. Once deployed on the blockchain, smart contracts autonomously execute the predefined functions and logic when triggered by specific events or conditions, without requiring manual intervention or intermediaries.
-
Decentralized Trust: Smart contracts leverage the decentralized nature of blockchain technology to provide trust and transparency. The execution of smart contracts is verified and validated by multiple nodes in the network, ensuring that the contract's execution follows the rules and conditions encoded in the contract code. This decentralized trust mechanism eliminates the need for relying on a central authority or third-party intermediaries.
-
Solidity Programming Language: Solidity is a statically-typed, contract-oriented programming language used for writing smart contracts on the Ethereum platform. It is similar to JavaScript in terms of syntax and is designed to facilitate secure and efficient smart contract development. Solidity provides features such as inheritance, libraries, modifiers, and events to enable developers to build complex and robust smart contracts.
-
Contract Deployment and Execution: Smart contracts written in Solidity are compiled into bytecode, which can then be deployed onto the Ethereum blockchain. Once deployed, the smart contract is assigned a unique address on the blockchain and becomes an immutable and tamper-proof entity. Users can interact with the smart contract by sending transactions to its address, triggering the execution of its functions and altering its state.
-
Security Considerations: Writing secure smart contracts is crucial to avoid vulnerabilities and potential exploits. Solidity provides various security features and best practices to help developers mitigate risks, such as preventing reentrancy attacks, handling exception cases, avoiding integer overflow and underflow, and implementing proper access control mechanisms. Auditing tools and code review processes are commonly employed to identify and fix potential security issues in smart contracts.
-
Ecosystem and Tooling: Solidity has a vibrant ecosystem with a wide range of developer tools, frameworks, and libraries that simplify smart contract development. These include development frameworks like Truffle and Hardhat, testing frameworks like Mocha and Chai, and libraries such as OpenZeppelin for reusable smart contract components. These tools and resources aid in writing, testing, deploying, and managing Solidity-based smart contracts efficiently.
Future Trends in Blockchain
The field of blockchain technology continues to evolve rapidly, with several emerging trends that have the potential to shape its future. Here are some key trends to watch out for in the blockchain space:
-
Interoperability and Cross-Chain Solutions: As different blockchain networks and platforms emerge, there is a growing need for interoperability between them. Interoperability solutions aim to enable seamless communication and data exchange between different blockchains, allowing for increased connectivity and collaboration. Cross-chain technologies and protocols, such as Polkadot, Cosmos, and interoperability-focused projects like Chainlink and Aion, are working towards creating a connected blockchain ecosystem.
-
Scalability and Performance Enhancements: Scalability has been a significant challenge for blockchain networks, particularly for public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum. To handle a higher volume of transactions and support widespread adoption, scalability solutions are being explored. Layer 2 solutions like payment channels (Lightning Network) and sidechains, as well as novel consensus mechanisms (Proof of Stake, Proof of Authority), are being developed to improve blockchain performance, throughput, and transaction speeds.
-
Enterprise Blockchain Adoption: Blockchain technology is gaining traction among enterprises across various industries, including finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more. Enterprises are exploring blockchain solutions to enhance transparency, traceability, and efficiency in their operations. Consortium and private blockchains are particularly being leveraged to address industry-specific challenges, compliance requirements, and data privacy concerns.
-
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi has emerged as a significant use case for blockchain technology, enabling financial applications to be built on open and decentralized networks. DeFi protocols offer services such as lending, borrowing, decentralized exchanges, and yield farming. DeFi has gained significant attention and investment, and it has the potential to revolutionize traditional finance by removing intermediaries and providing greater financial inclusivity.
-
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs have gained immense popularity, enabling the ownership and trading of unique digital assets on the blockchain. NFTs have been primarily associated with digital art, collectibles, and gaming, but their potential extends to areas like real estate, intellectual property, and identity verification. The NFT market has witnessed significant growth and innovation, with artists, creators, and brands exploring new avenues for tokenizing and monetizing digital assets.
-
Enhanced Privacy and Confidentiality: While blockchain offers transparency and immutability, privacy and confidentiality of data remain important considerations, especially in enterprise and government use cases. Privacy-focused blockchain solutions, such as zero-knowledge proofs, homomorphic encryption, and privacy-preserving protocols like Zcash and Monero, are being developed to address these concerns while preserving the security and integrity of the underlying blockchain.
-
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: The energy consumption associated with blockchain mining and transaction processing has raised concerns about its environmental impact. As the industry grows, there is a focus on developing more sustainable and energy-efficient consensus algorithms and infrastructure solutions. Projects are exploring proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanisms, energy-efficient consensus protocols, and renewable energy integration to reduce the carbon footprint of blockchain networks.
How to obtain Blockchain Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
-
Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
-
Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
-
Data Science : Power BI Certification
-
Cyber Security : CISA Certification
-
Emerging Technologies : Blockchain Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology continues to make significant strides and has the potential to revolutionize various industries and sectors. Its core principles of decentralization, transparency, security, and immutability offer numerous benefits and opportunities for innovation. As blockchain evolves, it is important to keep an eye on the emerging trends shaping its future.
Interoperability and cross-chain solutions aim to connect different blockchain networks, fostering collaboration and expanding the possibilities of decentralized applications. Scalability and performance enhancements are crucial for blockchain's widespread adoption, with various solutions and consensus mechanisms being explored to improve transaction speeds and throughput.
Enterprise adoption of blockchain is growing, with organizations recognizing its potential to enhance transparency, efficiency, and security in their operations. DeFi and NFTs have emerged as prominent use cases, revolutionizing finance and digital asset ownership. Privacy and confidentiality are being addressed through the development of privacy-focused protocols and technologies.
Guide to Deep Learning Certification Training Courses!!
Welcome to "A Comprehensive Guide to Deep Learning Certification Training Courses" . Deep learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that utilizes neural networks to mimic the human brain's ability to process and learn from vast amounts of data. It is a powerful technology that has enabled significant advancements in tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and decision-making systems. This extensive resource is your compass in navigating the exciting world of deep learning and its impact on artificial intelligence and machine learning. Whether you're a seasoned professional or a newcomer, our guide will introduce you to core concepts, applications, and the benefits of pursuing deep learning certification. Discover top learning platforms, institutes, and online resources offering in-depth courses to acquire essential skills and knowledge. Empowered with insights from industry experts and potential career opportunities, you'll be well-equipped to make informed decisions and excel in this ever-evolving field of deep learning. Let's embark on this enlightening expedition, where knowledge knows no bounds and possibilities are limitless.
Table of contents
- The Rise of Deep Learning: An Introduction to the Field
- Understanding Deep Learning: Concepts and Techniques
- Benefits of Deep Learning Certification
- Choosing the Right Deep Learning Certification Training Course
- Prerequisites for Deep Learning Certification Training
- Industry Recognition and Career Opportunities
- Beyond Certification: Continuous Learning and Community Involvement
- Conclusion
The Rise of Deep Learning: An Introduction to the Field
Deep learning has experienced a meteoric rise, revolutionizing the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and transforming various industries. With its ability to analyze large datasets and extract meaningful insights, deep learning has propelled AI to new heights. This subfield of machine learning is inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain, employing neural networks with multiple layers to learn and make predictions. The rise of deep learning can be attributed to key breakthroughs, such as the development of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image recognition and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for sequential data analysis. These advancements have paved the way for remarkable achievements in computer vision, natural language processing, and other AI applications. Deep learning's impact is evident in fields such as healthcare, finance, autonomous systems, and robotics, where it has enabled unprecedented advancements in medical diagnosis, financial analysis, self-driving cars, and more. As the availability of computational resources and data continues to increase, deep learning is poised to drive further innovation and shape the future of AI.
Understanding Deep Learning: Concepts and Techniques
Deep learning, a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI), encompasses a set of concepts and techniques that have revolutionized the way machines learn and make predictions. At the core of deep learning are neural networks, complex structures composed of interconnected nodes that mimic the human brain's functioning. Activation functions introduce non-linearity to neural networks, enabling them to model intricate relationships within data. The backpropagation algorithm plays a vital role in training deep learning models by adjusting network parameters based on the prediction errors. Various architectures, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for computer vision and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for sequential data analysis, have been developed to tackle specific tasks effectively. Optimization techniques, including stochastic gradient descent (SGD) and regularization methods like dropout and batch normalization, ensure efficient learning and prevent overfitting. Additionally, transfer learning and hyperparameter tuning are crucial strategies for leveraging pre-existing knowledge and fine-tuning models for specific tasks. Evaluating deep learning models using appropriate metrics and validating their performance with test sets further ensures their accuracy and effectiveness. Understanding these foundational concepts and techniques is pivotal in unlocking the full potential of deep learning and its applications in AI.
Benefits of Deep Learning Certification
Deep learning certification offers numerous advantages for individuals seeking to enhance their career prospects in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Here are some key benefits of obtaining a deep learning certification:
- Career Advancement Opportunities: Deep learning is a rapidly growing field with high demand for skilled professionals. By earning a certification, you demonstrate your expertise and dedication to staying updated with the latest advancements. This can open doors to new job opportunities and help you advance in your current role.
- Increased Earning Potential: Certified deep learning professionals often command higher salaries compared to their non-certified counterparts. The specialized skills and knowledge gained through certification can make you more valuable to employers, leading to better compensation packages and salary negotiations.
- Validation of Skills and Expertise: A deep learning certification serves as tangible proof of your skills and competence in the field. It validates your knowledge of key concepts, techniques, and best practices in deep learning, giving employers confidence in your abilities.
- Recognition by Employers and Industry Professionals: Certification from reputable organizations or institutions carries weight and credibility in the industry. It demonstrates that you have met rigorous standards and have been evaluated by experts. Employers often prioritize certified professionals when hiring for deep learning roles.
- Access to Specialized Roles: Deep learning certification can qualify you for specialized roles that require advanced knowledge in AI and machine learning. These roles may include deep learning engineer, data scientist, AI researcher, or computer vision specialist. Certification can give you a competitive edge in securing such positions.
- Stay Updated with Evolving Technologies: Deep learning certification programs typically cover the latest trends, tools, and techniques in the field. By enrolling in a certification course, you ensure that your knowledge remains current and aligned with industry developments. This enables you to apply cutting-edge techniques to real-world problems.
- Networking Opportunities: Certification programs often provide opportunities to connect with industry professionals, experts, and fellow learners. This networking can lead to collaborations, mentorships, and exposure to new career opportunities. Engaging with a community of like-minded individuals can enrich your learning journey.
- Professional Credibility and Trust: Certification adds credibility to your professional profile and builds trust with clients, employers, and colleagues. It demonstrates your commitment to continuous learning and professional growth, positioning you as a reliable and knowledgeable deep learning practitioner.
- International Recognition: Many deep learning certifications are recognized globally, which expands your career prospects beyond local boundaries. This recognition allows you to pursue opportunities in different countries and work on projects with international organizations.
- Lifelong Learning and Skill Development: Deep learning certification is a stepping stone in your learning journey. It encourages a mindset of continuous learning and motivates you to explore advanced concepts and specialized areas within deep learning. This ongoing skill development is crucial in a rapidly evolving field like AI.
Choosing the Right Deep Learning Certification Training Course
With the abundance of deep learning certification training courses available, it's important to make an informed decision when selecting the right one for your needs. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing a deep learning certification training course:
- Course Content and Curriculum: Evaluate the course content and curriculum to ensure it covers essential topics and concepts in deep learning. Look for courses that provide a comprehensive understanding of neural networks, deep learning architectures, optimization techniques, and practical applications. The curriculum should be up-to-date, relevant, and aligned with industry standards.
- Expert Instructors and Mentors: Research the qualifications and experience of the instructors and mentors delivering the course. Look for instructors who have expertise in deep learning and real-world experience in applying deep learning techniques. Their knowledge and guidance will significantly impact your learning experience and the quality of education you receive.
- Hands-on Projects and Practical Experience: Practical experience is crucial in deep learning. Look for courses that offer hands-on projects and exercises to reinforce theoretical concepts. Practical experience allows you to apply what you've learned, build a portfolio of projects, and gain confidence in implementing deep learning models.
- Industry Recognition and Accreditation: Consider certifications offered by reputable organizations or institutions that are recognized within the industry. Look for courses that have accreditation or partnerships with established AI and deep learning organizations. Certifications from recognized institutions carry more weight and credibility in the job market.
- Learning Resources and Support: Evaluate the learning resources and support provided by the course. Look for courses that offer comprehensive study materials, including video lectures, tutorials, code examples, and reference materials. Consider the availability of a support system such as discussion forums, dedicated mentors, or online communities to assist you throughout the learning process.
- Flexibility and Learning Format: Consider your learning preferences and availability. Assess whether the course offers flexibility in terms of learning format, such as self-paced online courses, blended learning, or in-person classes. Choose a format that aligns with your schedule and allows you to learn at your own pace.
- Reviews and Testimonials: Read reviews and testimonials from past participants to gauge their experiences with the course. Look for feedback regarding the course content, instructor effectiveness, project quality, and overall learning experience. Reviews can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the course.
- Career Support and Job Placement Assistance: Consider whether the course provides career support or job placement assistance. Some courses offer networking opportunities, career guidance, resume reviews, and connections to industry professionals, which can be valuable in your job search or career transition.
- Cost and Value for Money: Assess the cost of the course and evaluate it in terms of the value you will receive. Consider the course's reputation, content quality, and potential career benefits. While cost is a factor, prioritize the value and quality of the training over the price alone.
- Alumni Success and Industry Reputation: Research the success stories of alumni from the course and their accomplishments in the industry. Look for evidence of how the course has helped participants advance their careers or achieve notable achievements. A strong network of successful alumni and a positive industry reputation can indicate the quality of the training program.
Prerequisites for Deep Learning Certification Training
Deep learning is a complex field that requires a solid foundation in mathematics, programming, and machine learning. Before embarking on a deep learning certification training, it is beneficial to have the following prerequisites:
- Mathematics: Deep learning involves mathematical concepts and techniques, so a strong understanding of mathematics is essential. Familiarity with linear algebra, calculus, probability theory, and statistics will help you comprehend the underlying principles of deep learning algorithms and models. Key mathematical concepts include matrix operations, differentiation, optimization algorithms, and probability distributions.
- Programming Skills: Proficiency in programming is crucial for implementing deep learning models. Python is the most commonly used language in the deep learning community due to its rich ecosystem of libraries and frameworks, such as TensorFlow and PyTorch. Prior experience in Python programming, including knowledge of data structures, control flow, functions, and file handling, is highly recommended.
- Machine Learning Fundamentals: A solid understanding of machine learning concepts and techniques is necessary for deep learning. Familiarize yourself with supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms, feature engineering, model evaluation, and cross-validation. Understanding the basics of gradient descent, regularization, and overfitting will also be beneficial.
- Probability and Statistics: Deep learning models often rely on probabilistic reasoning and statistical analysis. Knowledge of probability theory, including concepts such as conditional probability, Bayes' theorem, and random variables, is essential. Understanding statistical measures, hypothesis testing, and confidence intervals will enable you to interpret and evaluate model performance.
- Linear Algebra: Deep learning heavily utilizes linear algebra for matrix operations, transformations, and vector spaces. Be comfortable with concepts such as vectors, matrices, matrix multiplication, eigenvectors, and eigenvalues. Knowledge of linear transformations, dot products, and matrix inverses will be helpful in understanding the mechanics of deep learning algorithms.
- Basic Knowledge of Neural Networks: Having a basic understanding of neural networks is beneficial before diving into deep learning. Familiarize yourself with the structure and functioning of neural networks, including feedforward networks, backpropagation, activation functions, and gradient descent. Knowledge of concepts such as weights, biases, and layers will provide a solid foundation for deep learning concepts.
Industry Recognition and Career Opportunities
Deep learning, with its wide-ranging applications and potential for breakthroughs in various fields, has gained significant industry recognition in recent years. The field continues to grow rapidly, offering numerous career opportunities for professionals with expertise in deep learning. Here are some key aspects of industry recognition and career opportunities in deep learning:
- High Demand for Deep Learning Professionals: The demand for deep learning professionals is consistently high across industries such as technology, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and more. Companies are increasingly relying on deep learning techniques to extract insights from complex datasets, improve decision-making processes, and develop innovative AI-powered products and services. This high demand translates into a wealth of career opportunities for individuals skilled in deep learning.
- Integration of Deep Learning in Various Domains: Deep learning has found applications in diverse domains, including computer vision, natural language processing, speech recognition, recommendation systems, autonomous vehicles, healthcare diagnostics, finance, and robotics. As deep learning techniques continue to advance, their integration into these domains is expected to accelerate, leading to an increasing need for professionals with expertise in applying deep learning in specific industries.
- Research and Development Opportunities: Deep learning is an active field of research, with ongoing advancements and breakthroughs. Pursuing a career in deep learning offers opportunities for involvement in cutting-edge research and development projects. This involvement can lead to contributions to the field, publications in renowned conferences or journals, and collaboration with leading researchers and institutions.
- Startups and Entrepreneurship: The rapid growth and innovation in deep learning have created a vibrant ecosystem of startups and entrepreneurial opportunities. Many startups are focused on applying deep learning techniques to address specific industry challenges or develop disruptive solutions. Joining a deep learning startup or starting your own venture can provide an exciting and dynamic career path.
- Industry-Recognized Certifications and Credentials: Deep learning certifications and credentials from reputable organizations or institutions carry significant industry recognition. Acquiring such certifications demonstrates your expertise, credibility, and commitment to the field. Industry-recognized certifications can enhance your resume, improve your chances of securing job opportunities, and open doors to specialized roles and projects.
- Collaboration with AI Professionals: Deep learning professionals often collaborate with other AI professionals, including data scientists, machine learning engineers, and domain experts. This collaboration fosters cross-functional learning, innovation, and the development of comprehensive AI solutions. Networking and collaborating with other AI professionals can provide valuable growth opportunities and broaden your skill set.
- Continuous Learning and Skill Development: Deep learning is a rapidly evolving field, and staying updated with the latest advancements and techniques is crucial for career growth. Deep learning professionals engage in continuous learning, attending conferences, workshops, and online courses, and participating in research communities. This commitment to lifelong learning ensures that professionals remain at the forefront of deep learning and continue to explore new career opportunities.
- Leadership and Management Roles: With experience and expertise in deep learning, professionals can advance into leadership and management roles. These roles involve overseeing teams, driving AI strategies, making informed decisions about project directions, and managing collaborations with stakeholders. Deep learning professionals who possess strong technical and leadership skills are highly sought after for these positions.
Beyond Certification: Continuous Learning and Community Involvement in Deep Learning
Obtaining a deep learning certification is an excellent way to validate your skills and expertise in the field. However, deep learning is a rapidly evolving domain, and to stay ahead, it is crucial to engage in continuous learning and actively participate in the deep learning community. Here are some key aspects of continuous learning and community involvement in deep learning:
- Stay Updated with Latest Research and Techniques: Deep learning research is constantly progressing, with new techniques, architectures, and algorithms emerging regularly. To remain at the forefront of the field, it is important to stay updated with the latest research papers, publications, and conference proceedings. Follow leading researchers, join relevant online forums, and participate in discussions to keep abreast of the cutting-edge advancements.
- Participate in Online Courses and Workshops: Continuous learning through online courses and workshops allows you to deepen your knowledge and explore specialized areas of deep learning. Platforms like iCert Global offer a wide range of courses covering advanced topics in deep learning. Participating in these courses enables you to learn from industry experts and gain hands-on experience through practical assignments and projects.
- Engage in Research Projects and Kaggle Competitions: Actively participating in research projects and Kaggle competitions provides valuable practical experience in solving real-world problems. These activities offer opportunities to apply deep learning techniques, collaborate with other professionals, and gain insights from experienced practitioners. Engaging in such projects enhances your problem-solving skills and exposes you to different domains and datasets.
- Contribute to Open-Source Projects: Contributing to open-source deep learning projects is a great way to enhance your skills, collaborate with other developers, and give back to the community. By contributing code, documentation, or bug fixes, you not only improve your technical abilities but also gain visibility among the deep learning community. Open-source projects provide a platform for knowledge exchange and foster innovation.
- Attend Deep Learning Conferences and Meetups: Deep learning conferences, such as NeurIPS, ICML, and CVPR, offer a wealth of knowledge-sharing and networking opportunities. Attending these conferences allows you to hear from leading researchers, learn about groundbreaking research, and connect with like-minded professionals. Additionally, local meetups and workshops provide a more accessible platform to meet and interact with experts and enthusiasts in your area.
- Join Deep Learning Communities and Forums: Engaging with deep learning communities and online forums is valuable for sharing ideas, seeking advice, and collaborating with fellow deep learning practitioners. Platforms like Reddit's r/MachineLearning, Stack Exchange's Artificial Intelligence forum, and LinkedIn groups dedicated to deep learning provide avenues to connect, learn, and grow. Actively participate by asking questions, answering queries, and sharing your experiences.
- Publish and Present Your Work: Sharing your work through publications, blog posts, or conference presentations enhances your professional profile and establishes you as a thought leader in the field. Contributing to the body of knowledge in deep learning through your insights, research findings, or innovative approaches can have a significant impact on the community. It also provides opportunities for collaboration and feedback from experts.
- Mentor and Teach Others: Once you have gained expertise in deep learning, consider mentoring or teaching others who are starting their journey. Sharing your knowledge and guiding aspiring deep learning practitioners not only contributes to the growth of the community but also reinforces your own understanding and mastery of the subject. Mentorship programs, online forums, or local meetups are excellent platforms to offer support and guidance to others.
How to obtain Deep Learning Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
- Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
- Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
- Data Science : Power BI Certification
- Cyber Security : CISA Certification
- Emerging Technologies Deep Learning Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, deep learning certification training is an excellent way to acquire the necessary skills and knowledge in this rapidly evolving field. However, the journey doesn't end with certification. To truly excel and stay ahead in deep learning, continuous learning and active community involvement are essential.
By staying updated with the latest research and techniques, participating in online courses and workshops, engaging in research projects and Kaggle competitions, contributing to open-source projects, attending conferences and meetups, joining deep learning communities and forums, publishing and presenting your work, and mentoring others, you can foster personal growth, expand your network, and contribute to the advancement of deep learning.
Deep learning is a field that thrives on collaboration, innovation, and sharing of knowledge. By embracing continuous learning and community involvement, you can leverage the collective wisdom and experiences of the deep learning community, stay abreast of emerging trends, and make meaningful contributions to the field.
Remember, deep learning is a journey that requires dedication, perseverance, and a commitment to lifelong learning. Embrace the opportunities for growth, push the boundaries of your knowledge, and make a positive impact in the exciting world of deep learning.
Read More
Welcome to "A Comprehensive Guide to Deep Learning Certification Training Courses" . Deep learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that utilizes neural networks to mimic the human brain's ability to process and learn from vast amounts of data. It is a powerful technology that has enabled significant advancements in tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and decision-making systems. This extensive resource is your compass in navigating the exciting world of deep learning and its impact on artificial intelligence and machine learning. Whether you're a seasoned professional or a newcomer, our guide will introduce you to core concepts, applications, and the benefits of pursuing deep learning certification. Discover top learning platforms, institutes, and online resources offering in-depth courses to acquire essential skills and knowledge. Empowered with insights from industry experts and potential career opportunities, you'll be well-equipped to make informed decisions and excel in this ever-evolving field of deep learning. Let's embark on this enlightening expedition, where knowledge knows no bounds and possibilities are limitless.
Table of contents
- The Rise of Deep Learning: An Introduction to the Field
- Understanding Deep Learning: Concepts and Techniques
- Benefits of Deep Learning Certification
- Choosing the Right Deep Learning Certification Training Course
- Prerequisites for Deep Learning Certification Training
- Industry Recognition and Career Opportunities
- Beyond Certification: Continuous Learning and Community Involvement
- Conclusion
The Rise of Deep Learning: An Introduction to the Field
Deep learning has experienced a meteoric rise, revolutionizing the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and transforming various industries. With its ability to analyze large datasets and extract meaningful insights, deep learning has propelled AI to new heights. This subfield of machine learning is inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain, employing neural networks with multiple layers to learn and make predictions. The rise of deep learning can be attributed to key breakthroughs, such as the development of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image recognition and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for sequential data analysis. These advancements have paved the way for remarkable achievements in computer vision, natural language processing, and other AI applications. Deep learning's impact is evident in fields such as healthcare, finance, autonomous systems, and robotics, where it has enabled unprecedented advancements in medical diagnosis, financial analysis, self-driving cars, and more. As the availability of computational resources and data continues to increase, deep learning is poised to drive further innovation and shape the future of AI.
Understanding Deep Learning: Concepts and Techniques
Deep learning, a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI), encompasses a set of concepts and techniques that have revolutionized the way machines learn and make predictions. At the core of deep learning are neural networks, complex structures composed of interconnected nodes that mimic the human brain's functioning. Activation functions introduce non-linearity to neural networks, enabling them to model intricate relationships within data. The backpropagation algorithm plays a vital role in training deep learning models by adjusting network parameters based on the prediction errors. Various architectures, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for computer vision and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for sequential data analysis, have been developed to tackle specific tasks effectively. Optimization techniques, including stochastic gradient descent (SGD) and regularization methods like dropout and batch normalization, ensure efficient learning and prevent overfitting. Additionally, transfer learning and hyperparameter tuning are crucial strategies for leveraging pre-existing knowledge and fine-tuning models for specific tasks. Evaluating deep learning models using appropriate metrics and validating their performance with test sets further ensures their accuracy and effectiveness. Understanding these foundational concepts and techniques is pivotal in unlocking the full potential of deep learning and its applications in AI.
Benefits of Deep Learning Certification
Deep learning certification offers numerous advantages for individuals seeking to enhance their career prospects in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Here are some key benefits of obtaining a deep learning certification:
- Career Advancement Opportunities: Deep learning is a rapidly growing field with high demand for skilled professionals. By earning a certification, you demonstrate your expertise and dedication to staying updated with the latest advancements. This can open doors to new job opportunities and help you advance in your current role.
- Increased Earning Potential: Certified deep learning professionals often command higher salaries compared to their non-certified counterparts. The specialized skills and knowledge gained through certification can make you more valuable to employers, leading to better compensation packages and salary negotiations.
- Validation of Skills and Expertise: A deep learning certification serves as tangible proof of your skills and competence in the field. It validates your knowledge of key concepts, techniques, and best practices in deep learning, giving employers confidence in your abilities.
- Recognition by Employers and Industry Professionals: Certification from reputable organizations or institutions carries weight and credibility in the industry. It demonstrates that you have met rigorous standards and have been evaluated by experts. Employers often prioritize certified professionals when hiring for deep learning roles.
- Access to Specialized Roles: Deep learning certification can qualify you for specialized roles that require advanced knowledge in AI and machine learning. These roles may include deep learning engineer, data scientist, AI researcher, or computer vision specialist. Certification can give you a competitive edge in securing such positions.
- Stay Updated with Evolving Technologies: Deep learning certification programs typically cover the latest trends, tools, and techniques in the field. By enrolling in a certification course, you ensure that your knowledge remains current and aligned with industry developments. This enables you to apply cutting-edge techniques to real-world problems.
- Networking Opportunities: Certification programs often provide opportunities to connect with industry professionals, experts, and fellow learners. This networking can lead to collaborations, mentorships, and exposure to new career opportunities. Engaging with a community of like-minded individuals can enrich your learning journey.
- Professional Credibility and Trust: Certification adds credibility to your professional profile and builds trust with clients, employers, and colleagues. It demonstrates your commitment to continuous learning and professional growth, positioning you as a reliable and knowledgeable deep learning practitioner.
- International Recognition: Many deep learning certifications are recognized globally, which expands your career prospects beyond local boundaries. This recognition allows you to pursue opportunities in different countries and work on projects with international organizations.
- Lifelong Learning and Skill Development: Deep learning certification is a stepping stone in your learning journey. It encourages a mindset of continuous learning and motivates you to explore advanced concepts and specialized areas within deep learning. This ongoing skill development is crucial in a rapidly evolving field like AI.
Choosing the Right Deep Learning Certification Training Course
With the abundance of deep learning certification training courses available, it's important to make an informed decision when selecting the right one for your needs. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing a deep learning certification training course:
- Course Content and Curriculum: Evaluate the course content and curriculum to ensure it covers essential topics and concepts in deep learning. Look for courses that provide a comprehensive understanding of neural networks, deep learning architectures, optimization techniques, and practical applications. The curriculum should be up-to-date, relevant, and aligned with industry standards.
- Expert Instructors and Mentors: Research the qualifications and experience of the instructors and mentors delivering the course. Look for instructors who have expertise in deep learning and real-world experience in applying deep learning techniques. Their knowledge and guidance will significantly impact your learning experience and the quality of education you receive.
- Hands-on Projects and Practical Experience: Practical experience is crucial in deep learning. Look for courses that offer hands-on projects and exercises to reinforce theoretical concepts. Practical experience allows you to apply what you've learned, build a portfolio of projects, and gain confidence in implementing deep learning models.
- Industry Recognition and Accreditation: Consider certifications offered by reputable organizations or institutions that are recognized within the industry. Look for courses that have accreditation or partnerships with established AI and deep learning organizations. Certifications from recognized institutions carry more weight and credibility in the job market.
- Learning Resources and Support: Evaluate the learning resources and support provided by the course. Look for courses that offer comprehensive study materials, including video lectures, tutorials, code examples, and reference materials. Consider the availability of a support system such as discussion forums, dedicated mentors, or online communities to assist you throughout the learning process.
- Flexibility and Learning Format: Consider your learning preferences and availability. Assess whether the course offers flexibility in terms of learning format, such as self-paced online courses, blended learning, or in-person classes. Choose a format that aligns with your schedule and allows you to learn at your own pace.
- Reviews and Testimonials: Read reviews and testimonials from past participants to gauge their experiences with the course. Look for feedback regarding the course content, instructor effectiveness, project quality, and overall learning experience. Reviews can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the course.
- Career Support and Job Placement Assistance: Consider whether the course provides career support or job placement assistance. Some courses offer networking opportunities, career guidance, resume reviews, and connections to industry professionals, which can be valuable in your job search or career transition.
- Cost and Value for Money: Assess the cost of the course and evaluate it in terms of the value you will receive. Consider the course's reputation, content quality, and potential career benefits. While cost is a factor, prioritize the value and quality of the training over the price alone.
- Alumni Success and Industry Reputation: Research the success stories of alumni from the course and their accomplishments in the industry. Look for evidence of how the course has helped participants advance their careers or achieve notable achievements. A strong network of successful alumni and a positive industry reputation can indicate the quality of the training program.
Prerequisites for Deep Learning Certification Training
Deep learning is a complex field that requires a solid foundation in mathematics, programming, and machine learning. Before embarking on a deep learning certification training, it is beneficial to have the following prerequisites:
- Mathematics: Deep learning involves mathematical concepts and techniques, so a strong understanding of mathematics is essential. Familiarity with linear algebra, calculus, probability theory, and statistics will help you comprehend the underlying principles of deep learning algorithms and models. Key mathematical concepts include matrix operations, differentiation, optimization algorithms, and probability distributions.
- Programming Skills: Proficiency in programming is crucial for implementing deep learning models. Python is the most commonly used language in the deep learning community due to its rich ecosystem of libraries and frameworks, such as TensorFlow and PyTorch. Prior experience in Python programming, including knowledge of data structures, control flow, functions, and file handling, is highly recommended.
- Machine Learning Fundamentals: A solid understanding of machine learning concepts and techniques is necessary for deep learning. Familiarize yourself with supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms, feature engineering, model evaluation, and cross-validation. Understanding the basics of gradient descent, regularization, and overfitting will also be beneficial.
- Probability and Statistics: Deep learning models often rely on probabilistic reasoning and statistical analysis. Knowledge of probability theory, including concepts such as conditional probability, Bayes' theorem, and random variables, is essential. Understanding statistical measures, hypothesis testing, and confidence intervals will enable you to interpret and evaluate model performance.
- Linear Algebra: Deep learning heavily utilizes linear algebra for matrix operations, transformations, and vector spaces. Be comfortable with concepts such as vectors, matrices, matrix multiplication, eigenvectors, and eigenvalues. Knowledge of linear transformations, dot products, and matrix inverses will be helpful in understanding the mechanics of deep learning algorithms.
- Basic Knowledge of Neural Networks: Having a basic understanding of neural networks is beneficial before diving into deep learning. Familiarize yourself with the structure and functioning of neural networks, including feedforward networks, backpropagation, activation functions, and gradient descent. Knowledge of concepts such as weights, biases, and layers will provide a solid foundation for deep learning concepts.
Industry Recognition and Career Opportunities
Deep learning, with its wide-ranging applications and potential for breakthroughs in various fields, has gained significant industry recognition in recent years. The field continues to grow rapidly, offering numerous career opportunities for professionals with expertise in deep learning. Here are some key aspects of industry recognition and career opportunities in deep learning:
- High Demand for Deep Learning Professionals: The demand for deep learning professionals is consistently high across industries such as technology, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and more. Companies are increasingly relying on deep learning techniques to extract insights from complex datasets, improve decision-making processes, and develop innovative AI-powered products and services. This high demand translates into a wealth of career opportunities for individuals skilled in deep learning.
- Integration of Deep Learning in Various Domains: Deep learning has found applications in diverse domains, including computer vision, natural language processing, speech recognition, recommendation systems, autonomous vehicles, healthcare diagnostics, finance, and robotics. As deep learning techniques continue to advance, their integration into these domains is expected to accelerate, leading to an increasing need for professionals with expertise in applying deep learning in specific industries.
- Research and Development Opportunities: Deep learning is an active field of research, with ongoing advancements and breakthroughs. Pursuing a career in deep learning offers opportunities for involvement in cutting-edge research and development projects. This involvement can lead to contributions to the field, publications in renowned conferences or journals, and collaboration with leading researchers and institutions.
- Startups and Entrepreneurship: The rapid growth and innovation in deep learning have created a vibrant ecosystem of startups and entrepreneurial opportunities. Many startups are focused on applying deep learning techniques to address specific industry challenges or develop disruptive solutions. Joining a deep learning startup or starting your own venture can provide an exciting and dynamic career path.
- Industry-Recognized Certifications and Credentials: Deep learning certifications and credentials from reputable organizations or institutions carry significant industry recognition. Acquiring such certifications demonstrates your expertise, credibility, and commitment to the field. Industry-recognized certifications can enhance your resume, improve your chances of securing job opportunities, and open doors to specialized roles and projects.
- Collaboration with AI Professionals: Deep learning professionals often collaborate with other AI professionals, including data scientists, machine learning engineers, and domain experts. This collaboration fosters cross-functional learning, innovation, and the development of comprehensive AI solutions. Networking and collaborating with other AI professionals can provide valuable growth opportunities and broaden your skill set.
- Continuous Learning and Skill Development: Deep learning is a rapidly evolving field, and staying updated with the latest advancements and techniques is crucial for career growth. Deep learning professionals engage in continuous learning, attending conferences, workshops, and online courses, and participating in research communities. This commitment to lifelong learning ensures that professionals remain at the forefront of deep learning and continue to explore new career opportunities.
- Leadership and Management Roles: With experience and expertise in deep learning, professionals can advance into leadership and management roles. These roles involve overseeing teams, driving AI strategies, making informed decisions about project directions, and managing collaborations with stakeholders. Deep learning professionals who possess strong technical and leadership skills are highly sought after for these positions.
Beyond Certification: Continuous Learning and Community Involvement in Deep Learning
Obtaining a deep learning certification is an excellent way to validate your skills and expertise in the field. However, deep learning is a rapidly evolving domain, and to stay ahead, it is crucial to engage in continuous learning and actively participate in the deep learning community. Here are some key aspects of continuous learning and community involvement in deep learning:
- Stay Updated with Latest Research and Techniques: Deep learning research is constantly progressing, with new techniques, architectures, and algorithms emerging regularly. To remain at the forefront of the field, it is important to stay updated with the latest research papers, publications, and conference proceedings. Follow leading researchers, join relevant online forums, and participate in discussions to keep abreast of the cutting-edge advancements.
- Participate in Online Courses and Workshops: Continuous learning through online courses and workshops allows you to deepen your knowledge and explore specialized areas of deep learning. Platforms like iCert Global offer a wide range of courses covering advanced topics in deep learning. Participating in these courses enables you to learn from industry experts and gain hands-on experience through practical assignments and projects.
- Engage in Research Projects and Kaggle Competitions: Actively participating in research projects and Kaggle competitions provides valuable practical experience in solving real-world problems. These activities offer opportunities to apply deep learning techniques, collaborate with other professionals, and gain insights from experienced practitioners. Engaging in such projects enhances your problem-solving skills and exposes you to different domains and datasets.
- Contribute to Open-Source Projects: Contributing to open-source deep learning projects is a great way to enhance your skills, collaborate with other developers, and give back to the community. By contributing code, documentation, or bug fixes, you not only improve your technical abilities but also gain visibility among the deep learning community. Open-source projects provide a platform for knowledge exchange and foster innovation.
- Attend Deep Learning Conferences and Meetups: Deep learning conferences, such as NeurIPS, ICML, and CVPR, offer a wealth of knowledge-sharing and networking opportunities. Attending these conferences allows you to hear from leading researchers, learn about groundbreaking research, and connect with like-minded professionals. Additionally, local meetups and workshops provide a more accessible platform to meet and interact with experts and enthusiasts in your area.
- Join Deep Learning Communities and Forums: Engaging with deep learning communities and online forums is valuable for sharing ideas, seeking advice, and collaborating with fellow deep learning practitioners. Platforms like Reddit's r/MachineLearning, Stack Exchange's Artificial Intelligence forum, and LinkedIn groups dedicated to deep learning provide avenues to connect, learn, and grow. Actively participate by asking questions, answering queries, and sharing your experiences.
- Publish and Present Your Work: Sharing your work through publications, blog posts, or conference presentations enhances your professional profile and establishes you as a thought leader in the field. Contributing to the body of knowledge in deep learning through your insights, research findings, or innovative approaches can have a significant impact on the community. It also provides opportunities for collaboration and feedback from experts.
- Mentor and Teach Others: Once you have gained expertise in deep learning, consider mentoring or teaching others who are starting their journey. Sharing your knowledge and guiding aspiring deep learning practitioners not only contributes to the growth of the community but also reinforces your own understanding and mastery of the subject. Mentorship programs, online forums, or local meetups are excellent platforms to offer support and guidance to others.
How to obtain Deep Learning Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: SMAC Certication
- Big Data: Big Data and Hadoop Administrator
- Digital Marketing : Digital Marketing Certification
- Data Science : Power BI Certification
- Cyber Security : CISA Certification
- Emerging Technologies Deep Learning Certification
Conclusion
In conclusion, deep learning certification training is an excellent way to acquire the necessary skills and knowledge in this rapidly evolving field. However, the journey doesn't end with certification. To truly excel and stay ahead in deep learning, continuous learning and active community involvement are essential.
By staying updated with the latest research and techniques, participating in online courses and workshops, engaging in research projects and Kaggle competitions, contributing to open-source projects, attending conferences and meetups, joining deep learning communities and forums, publishing and presenting your work, and mentoring others, you can foster personal growth, expand your network, and contribute to the advancement of deep learning.
Deep learning is a field that thrives on collaboration, innovation, and sharing of knowledge. By embracing continuous learning and community involvement, you can leverage the collective wisdom and experiences of the deep learning community, stay abreast of emerging trends, and make meaningful contributions to the field.
Remember, deep learning is a journey that requires dedication, perseverance, and a commitment to lifelong learning. Embrace the opportunities for growth, push the boundaries of your knowledge, and make a positive impact in the exciting world of deep learning.


.webp)
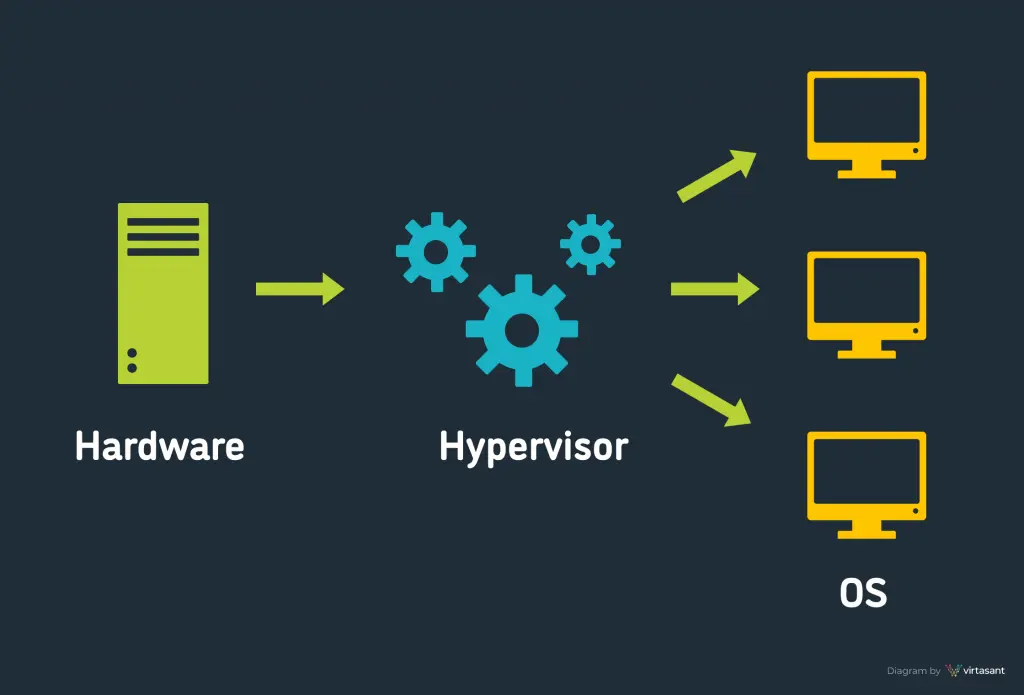

.jpg)
































.webp)
