Quick Enquiry Form
Categories
- Agile and Scrum (226)
- BigData (36)
- Business Analysis (94)
- Cirtix Client Administration (54)
- Cisco (63)
- Cloud Technology (96)
- Cyber Security (56)
- Data Science and Business Intelligence (54)
- Developement Courses (53)
- DevOps (16)
- Digital Marketing (58)
- Emerging Technology (198)
- IT Service Management (76)
- Microsoft (54)
- Other (395)
- Project Management (502)
- Quality Management (143)
- salesforce (67)
Latest posts
5 Types of Feasibility Studies..
The 5 Core Principles of..
Top 11 Statistical Tools for..
Free Resources
Subscribe to Newsletter
The Impact of DevOps on Software Delivery and Efficiency.
DevOps is a game-changer in the world of software development, revolutionizing the way teams collaborate, automate processes, and deliver high-quality software products. This article explores the significant impact of DevOps, its benefits, practices, tools, methodologies, and best practices that every organization should adopt.
The Impact of DevOps
Dev Ops bridges the gap between development and operations, enabling seamless collaboration between these two crucial teams. By breaking down silos and fostering a culture of collaboration and shared responsibility, DevOps significantly impacts the software development lifecycle. Here's how:
Enhanced Efficiency and Scalability
DevOps eliminates manual and time-consuming processes through automation, thereby increasing efficiency and scalability. By automating tasks such as code deployment, configuration management, and testing, developers can focus on innovation rather than repetitive tasks. This results in faster time-to-market and improved customer satisfaction.
Increased Agility and Productivity
With DevOps, organizations can respond quickly to changing business requirements. Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) practices enable frequent and smaller code releases, reducing the risk associated with large and infrequent deployments. Developers can iterate and enhance software features in real-time, leading to increased productivity and agility.
Improved Quality and Reliability
DevOps emphasizes automated testing and quality assurance throughout the development cycle. Continuous testing ensures that software meets the highest standards of quality, resulting in fewer unexpected bugs and issues in production. By catching and resolving issues early on, organizations can avoid costly downtime and customer dissatisfaction.
Culture of Collaboration and Communication
One of the core principles of DevOps is fostering collaboration and communication between teams. By encouraging cross-functional collaboration and shared goals, development, operations, and other stakeholders work together towards a common objective. This culture ensures transparency, improved decision-making, and a faster feedback loop.
DevOps Benefits and Importance
Implementing DevOps brings numerous benefits and is crucial for organizations looking to thrive in the rapidly evolving software development landscape. Some key benefits and importance of DevOps are:
Faster Time-to-Market
DevOps practices enable organizations to release software faster, reducing the time-gap between development and deployment. By automating processes and eliminating bottlenecks, teams can deliver new features and updates to customers rapidly, gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Enhanced Customer Experience
By focusing on continuous delivery and customer feedback, DevOps enables organizations to deliver software that meets the specific needs and expectations of customers. This customer-centric approach enhances user satisfaction, leading to increased loyalty and higher profitability.
Improved Collaboration and Teamwork
DevOps promotes a collaborative culture where developers, operations, and other stakeholders work together as a unified team. This collaboration enhances communication, knowledge sharing, and problem-solving, resulting in faster issue resolution and improved teamwork.
Reduced Risk and Downtime
With automated testing and deployment processes, DevOps minimizes the risk of human errors and ensures consistent and reliable software releases. By catching and resolving issues early in the development cycle, organizations can avoid costly downtime and negative impact on business operations.
Continuous Improvement and Innovation
DevOps embraces a culture of continuous improvement and encourages experimentation and innovation. By creating an environment where failure is seen as an opportunity to learn, organizations can drive innovation and foster a culture of continuous learning and growth.
DevOps Practices, Tools, and Methodologies
To effectively implement DevOps, organizations need to adopt specific practices, utilize the right tools, and follow proven methodologies. Here are some key aspects of DevOps implementation:
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
Continuous Integration (CI) involves merging code changes from multiple developers into a shared repository, followed by automated builds and tests. Continuous Delivery (CD) takes this a step further by automating the release process, ensuring that software is always in a deployable state. CI/CD practices enable faster and more reliable software development and deployment.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
DevOps encourages collaboration and knowledge sharing through tools like version control systems, chat platforms, and collaboration platforms. By centralizing communication and documentation, teams can effectively share information, resolve issues, and improve overall productivity.
Automation and Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Automation is at the core of DevOps. By using tools like configuration management and infrastructure as code, organizations can automate the provisioning, configuration, and management of infrastructure resources. This automation reduces manual errors, improves consistency, and enables faster deployments.
Metrics and Monitoring
DevOps emphasizes the importance of gathering metrics and monitoring system performance. Using tools for monitoring, logging, and analytics, organizations can gain valuable insights into the health and performance of their software, enabling proactive issue detection and resolution.
DevOps Transformation and Best Practices
Implementing DevOps requires a mindset shift and a well-defined strategy. Here are some key considerations for a successful DevOps transformation:
Cultivate a DevOps Culture
DevOps is not just about implementing tools and processes. It requires a cultural transformation where collaboration, communication, and shared responsibility are prioritized. Organizations should focus on building trust, promoting cross-functional collaboration, and encouraging continuous learning.
Start Small and Iterate
Rather than attempting a complete DevOps overhaul, organizations should start with small pilot projects and iterate based on feedback and lessons learned. This incremental approach allows for a smoother transition and helps identify potential challenges and roadblocks early on.
Embrace Continuous Learning and Improvement
DevOps is a journey, and organizations need to foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Encouraging employees to acquire new skills, experimenting with new tools and methodologies, and regularly reviewing and refining processes are essential for long-term success.
Measure Success Metrics
To gauge the effectiveness of DevOps implementation, organizations should define and track relevant success metrics. These could include deployment frequency, mean time to recover from incidents, customer satisfaction metrics, and employee engagement levels. Regularly reviewing these metrics helps identify areas for improvement and measure the impact of DevOps initiatives.
Foster Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Creating forums for collaboration and knowledge sharing, such as cross-functional team meetings, internal conferences, and online communities, promote a culture of learning and continuous improvement. Encouraging employees to share best practices and lessons learned contributes to the success of DevOps implementation.
How to obtain DevOps certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, DevOps has a transformative impact on software development by enhancing efficiency, productivity, and the overall quality of software products. By adopting DevOps practices, organizations can achieve faster time-to-market, improved customer experience, and seamless collaboration between development and operations teams. Successful DevOps implementation requires a cultural transformation, the right mix of tools and methodologies, and a continuous focus on learning and improvement. Embracing DevOps is essential for organizations looking to thrive in the dynamic and competitive software development landscape.
Read More
DevOps is a game-changer in the world of software development, revolutionizing the way teams collaborate, automate processes, and deliver high-quality software products. This article explores the significant impact of DevOps, its benefits, practices, tools, methodologies, and best practices that every organization should adopt.
The Impact of DevOps
Dev Ops bridges the gap between development and operations, enabling seamless collaboration between these two crucial teams. By breaking down silos and fostering a culture of collaboration and shared responsibility, DevOps significantly impacts the software development lifecycle. Here's how:
Enhanced Efficiency and Scalability
DevOps eliminates manual and time-consuming processes through automation, thereby increasing efficiency and scalability. By automating tasks such as code deployment, configuration management, and testing, developers can focus on innovation rather than repetitive tasks. This results in faster time-to-market and improved customer satisfaction.
Increased Agility and Productivity
With DevOps, organizations can respond quickly to changing business requirements. Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) practices enable frequent and smaller code releases, reducing the risk associated with large and infrequent deployments. Developers can iterate and enhance software features in real-time, leading to increased productivity and agility.
Improved Quality and Reliability
DevOps emphasizes automated testing and quality assurance throughout the development cycle. Continuous testing ensures that software meets the highest standards of quality, resulting in fewer unexpected bugs and issues in production. By catching and resolving issues early on, organizations can avoid costly downtime and customer dissatisfaction.
Culture of Collaboration and Communication
One of the core principles of DevOps is fostering collaboration and communication between teams. By encouraging cross-functional collaboration and shared goals, development, operations, and other stakeholders work together towards a common objective. This culture ensures transparency, improved decision-making, and a faster feedback loop.
DevOps Benefits and Importance
Implementing DevOps brings numerous benefits and is crucial for organizations looking to thrive in the rapidly evolving software development landscape. Some key benefits and importance of DevOps are:
Faster Time-to-Market
DevOps practices enable organizations to release software faster, reducing the time-gap between development and deployment. By automating processes and eliminating bottlenecks, teams can deliver new features and updates to customers rapidly, gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Enhanced Customer Experience
By focusing on continuous delivery and customer feedback, DevOps enables organizations to deliver software that meets the specific needs and expectations of customers. This customer-centric approach enhances user satisfaction, leading to increased loyalty and higher profitability.
Improved Collaboration and Teamwork
DevOps promotes a collaborative culture where developers, operations, and other stakeholders work together as a unified team. This collaboration enhances communication, knowledge sharing, and problem-solving, resulting in faster issue resolution and improved teamwork.
Reduced Risk and Downtime
With automated testing and deployment processes, DevOps minimizes the risk of human errors and ensures consistent and reliable software releases. By catching and resolving issues early in the development cycle, organizations can avoid costly downtime and negative impact on business operations.
Continuous Improvement and Innovation
DevOps embraces a culture of continuous improvement and encourages experimentation and innovation. By creating an environment where failure is seen as an opportunity to learn, organizations can drive innovation and foster a culture of continuous learning and growth.
DevOps Practices, Tools, and Methodologies
To effectively implement DevOps, organizations need to adopt specific practices, utilize the right tools, and follow proven methodologies. Here are some key aspects of DevOps implementation:
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
Continuous Integration (CI) involves merging code changes from multiple developers into a shared repository, followed by automated builds and tests. Continuous Delivery (CD) takes this a step further by automating the release process, ensuring that software is always in a deployable state. CI/CD practices enable faster and more reliable software development and deployment.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
DevOps encourages collaboration and knowledge sharing through tools like version control systems, chat platforms, and collaboration platforms. By centralizing communication and documentation, teams can effectively share information, resolve issues, and improve overall productivity.
Automation and Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Automation is at the core of DevOps. By using tools like configuration management and infrastructure as code, organizations can automate the provisioning, configuration, and management of infrastructure resources. This automation reduces manual errors, improves consistency, and enables faster deployments.
Metrics and Monitoring
DevOps emphasizes the importance of gathering metrics and monitoring system performance. Using tools for monitoring, logging, and analytics, organizations can gain valuable insights into the health and performance of their software, enabling proactive issue detection and resolution.
DevOps Transformation and Best Practices
Implementing DevOps requires a mindset shift and a well-defined strategy. Here are some key considerations for a successful DevOps transformation:
Cultivate a DevOps Culture
DevOps is not just about implementing tools and processes. It requires a cultural transformation where collaboration, communication, and shared responsibility are prioritized. Organizations should focus on building trust, promoting cross-functional collaboration, and encouraging continuous learning.
Start Small and Iterate
Rather than attempting a complete DevOps overhaul, organizations should start with small pilot projects and iterate based on feedback and lessons learned. This incremental approach allows for a smoother transition and helps identify potential challenges and roadblocks early on.
Embrace Continuous Learning and Improvement
DevOps is a journey, and organizations need to foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Encouraging employees to acquire new skills, experimenting with new tools and methodologies, and regularly reviewing and refining processes are essential for long-term success.
Measure Success Metrics
To gauge the effectiveness of DevOps implementation, organizations should define and track relevant success metrics. These could include deployment frequency, mean time to recover from incidents, customer satisfaction metrics, and employee engagement levels. Regularly reviewing these metrics helps identify areas for improvement and measure the impact of DevOps initiatives.
Foster Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Creating forums for collaboration and knowledge sharing, such as cross-functional team meetings, internal conferences, and online communities, promote a culture of learning and continuous improvement. Encouraging employees to share best practices and lessons learned contributes to the success of DevOps implementation.
How to obtain DevOps certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, DevOps has a transformative impact on software development by enhancing efficiency, productivity, and the overall quality of software products. By adopting DevOps practices, organizations can achieve faster time-to-market, improved customer experience, and seamless collaboration between development and operations teams. Successful DevOps implementation requires a cultural transformation, the right mix of tools and methodologies, and a continuous focus on learning and improvement. Embracing DevOps is essential for organizations looking to thrive in the dynamic and competitive software development landscape.
Agile ITSM: Adapting to Rapid Changes in Tech Support!!
In today's fast-paced world, traditional IT Service Management (ITSM) practices are no longer sufficient to meet the demands of modern businesses. With technology innovation happening at breakneck speed, organizations need to be responsive, efficient, and adaptable to stay ahead of the curve. This is where Agile ITSM comes into play, offering a more flexible and dynamic approach that allows businesses to quickly adapt to rapid changes in the IT landscape.
What is Agile ITSM?
Agile ITSM is a methodology that combines the principles of Agile software development with IT Service Management best practices. It focuses on delivering value to customers through iterative and incremental improvements, rather than following a rigid, linear process. By breaking down work into smaller, manageable chunks, Agile ITSM enables teams to respond quickly to changing requirements and priorities.
How does Agile ITSM differ from traditional ITSM?
Traditional ITSM is often characterized by strict processes and procedures that can be slow to adapt to changing circumstances. In contrast, Agile ITSM encourages collaboration, flexibility, and continuous improvement. Teams work together in cross-functional units, with a shared goal of delivering high-quality services that meet the needs of the business.
The Benefits of Agile ITSM
-
Increased Flexibility: Agile ITSM allows teams to respond quickly to changing requirements, ensuring that IT services remain aligned with business goals.
-
Faster Time to Market: By breaking work down into smaller increments, Agile ITSM enables organizations to deliver value to customers more quickly.
-
Improved Customer Satisfaction: Agile ITSM focuses on delivering value to customers, resulting in higher levels of satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: Agile ITSM encourages cross-functional teams to work together, fostering a culture of collaboration and innovation.
-
Continuous Improvement: Agile ITSM emphasizes the importance of learning from experience and making ongoing improvements to processes and services.
How to Implement Agile ITSM
-
Define Clear Goals: Start by setting clear goals and objectives for your Agile ITSM implementation. What do you hope to achieve? How will you measure success?
-
Build Cross-Functional Teams: Create cross-functional teams with the right mix of skills and expertise to deliver value to customers.
-
Implement Agile Practices: Adopt Agile practices such as Scrum, Kanban, and Lean to manage work effectively and efficiently.
-
Embrace a Culture of Collaboration: Encourage open communication, feedback, and collaboration among team members to drive innovation and continuous improvement.
-
Measure and Adapt: Continuously monitor and measure your progress, making adjustments as needed to ensure that you are meeting your goals.
How to obtain Agile & Scrum certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, Agile ITSM offers a more flexible and adaptable approach to IT Service Management, enabling organizations to respond quickly to rapid changes in technology and business requirements. By embracing Agile principles and practices, businesses can deliver value to customers more effectively, improve collaboration and innovation, and drive continuous improvement. Are you ready to take your ITSM practices to the next level with Agile?
Read More
In today's fast-paced world, traditional IT Service Management (ITSM) practices are no longer sufficient to meet the demands of modern businesses. With technology innovation happening at breakneck speed, organizations need to be responsive, efficient, and adaptable to stay ahead of the curve. This is where Agile ITSM comes into play, offering a more flexible and dynamic approach that allows businesses to quickly adapt to rapid changes in the IT landscape.
What is Agile ITSM?
Agile ITSM is a methodology that combines the principles of Agile software development with IT Service Management best practices. It focuses on delivering value to customers through iterative and incremental improvements, rather than following a rigid, linear process. By breaking down work into smaller, manageable chunks, Agile ITSM enables teams to respond quickly to changing requirements and priorities.
How does Agile ITSM differ from traditional ITSM?
Traditional ITSM is often characterized by strict processes and procedures that can be slow to adapt to changing circumstances. In contrast, Agile ITSM encourages collaboration, flexibility, and continuous improvement. Teams work together in cross-functional units, with a shared goal of delivering high-quality services that meet the needs of the business.
The Benefits of Agile ITSM
-
Increased Flexibility: Agile ITSM allows teams to respond quickly to changing requirements, ensuring that IT services remain aligned with business goals.
-
Faster Time to Market: By breaking work down into smaller increments, Agile ITSM enables organizations to deliver value to customers more quickly.
-
Improved Customer Satisfaction: Agile ITSM focuses on delivering value to customers, resulting in higher levels of satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: Agile ITSM encourages cross-functional teams to work together, fostering a culture of collaboration and innovation.
-
Continuous Improvement: Agile ITSM emphasizes the importance of learning from experience and making ongoing improvements to processes and services.
How to Implement Agile ITSM
-
Define Clear Goals: Start by setting clear goals and objectives for your Agile ITSM implementation. What do you hope to achieve? How will you measure success?
-
Build Cross-Functional Teams: Create cross-functional teams with the right mix of skills and expertise to deliver value to customers.
-
Implement Agile Practices: Adopt Agile practices such as Scrum, Kanban, and Lean to manage work effectively and efficiently.
-
Embrace a Culture of Collaboration: Encourage open communication, feedback, and collaboration among team members to drive innovation and continuous improvement.
-
Measure and Adapt: Continuously monitor and measure your progress, making adjustments as needed to ensure that you are meeting your goals.
How to obtain Agile & Scrum certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, Agile ITSM offers a more flexible and adaptable approach to IT Service Management, enabling organizations to respond quickly to rapid changes in technology and business requirements. By embracing Agile principles and practices, businesses can deliver value to customers more effectively, improve collaboration and innovation, and drive continuous improvement. Are you ready to take your ITSM practices to the next level with Agile?
How AI is Transforming Digital Marketing for Greater Success
In today's fast-paced digital world, technology continues to evolve and revolutionize how businesses market their products and services. One of the most significant advancements in recent years is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into digital marketing strategies. AI has become a game-changer for marketers, providing powerful tools and capabilities to optimize campaigns, analyze data, and personalize customer experiences like never before.
AI in Digital Marketing
Artificial intelligence technology is reshaping the landscape of digital marketing in various ways. From automation in marketing to machine learning algorithms, AI is empowering marketers to streamline processes, enhance decision-making, and deliver more targeted and personalized campaigns to their audiences. With AI, marketers can leverage predictive analytics to forecast trends, identify opportunities, and optimize their strategies for maximum impact.
Digital Marketing Trends
The use of AI in digital marketing has opened up new possibilities and trends that are shaping how businesses engage with their customers. From chatbots and personalized marketing to digital advertising and customer segmentation, AI-driven solutions are driving growth and innovation across industries. As businesses continue to invest in digital transformation, AI will play a crucial role in driving success and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Automation in Marketing
Automation has become a cornerstone of modern marketing strategies, allowing businesses to streamline processes and scale their efforts efficiently. AI-powered tools enable marketers to automate repetitive tasks, such as email marketing automation, targeted advertising, and social media management. By automating these processes, marketers can focus on higher-value tasks, such as creating compelling content and analyzing campaign performance.
Marketing Strategies
Artificial intelligence is redefining marketing strategies by providing insights and intelligence that help businesses make data-driven decisions. With AI, marketers can optimize online campaigns, analyze customer behavior, and measure the effectiveness of their marketing efforts in real-time. By leveraging AI-driven insights, businesses can adjust their strategies on-the-go, ensuring they stay relevant and engaging to their target audience.
Personalized Marketing
Personalization has become a critical component of successful marketing strategies, as customers demand more personalized experiences from brands. AI enables marketers to create tailored experiences for each customer, based on their preferences, behavior, and interactions with the brand. By delivering personalized content, recommendations, and offers, businesses can enhance customer engagement, drive loyalty, and increase conversions.
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is the process of integrating digital technologies into all aspects of a business, fundamentally changing how they operate and deliver value to customers. AI is at the forefront of this transformation, empowering businesses to leverage data analytics, marketing intelligence, and automation tools to drive growth and innovation. By embracing AI, businesses can stay ahead of the curve, adapt to changing market dynamics, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
How to obtain Emerging Technology certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, artificial intelligence is revolutionizing digital marketing by empowering businesses to leverage data, automation, and intelligence to optimize their strategies and engage with customers in more meaningful ways. As AI continues to evolve and advance, businesses that embrace this technology will have a competitive advantage, driving growth and success in the digital landscape.
Read More
In today's fast-paced digital world, technology continues to evolve and revolutionize how businesses market their products and services. One of the most significant advancements in recent years is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into digital marketing strategies. AI has become a game-changer for marketers, providing powerful tools and capabilities to optimize campaigns, analyze data, and personalize customer experiences like never before.
AI in Digital Marketing
Artificial intelligence technology is reshaping the landscape of digital marketing in various ways. From automation in marketing to machine learning algorithms, AI is empowering marketers to streamline processes, enhance decision-making, and deliver more targeted and personalized campaigns to their audiences. With AI, marketers can leverage predictive analytics to forecast trends, identify opportunities, and optimize their strategies for maximum impact.
Digital Marketing Trends
The use of AI in digital marketing has opened up new possibilities and trends that are shaping how businesses engage with their customers. From chatbots and personalized marketing to digital advertising and customer segmentation, AI-driven solutions are driving growth and innovation across industries. As businesses continue to invest in digital transformation, AI will play a crucial role in driving success and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Automation in Marketing
Automation has become a cornerstone of modern marketing strategies, allowing businesses to streamline processes and scale their efforts efficiently. AI-powered tools enable marketers to automate repetitive tasks, such as email marketing automation, targeted advertising, and social media management. By automating these processes, marketers can focus on higher-value tasks, such as creating compelling content and analyzing campaign performance.
Marketing Strategies
Artificial intelligence is redefining marketing strategies by providing insights and intelligence that help businesses make data-driven decisions. With AI, marketers can optimize online campaigns, analyze customer behavior, and measure the effectiveness of their marketing efforts in real-time. By leveraging AI-driven insights, businesses can adjust their strategies on-the-go, ensuring they stay relevant and engaging to their target audience.
Personalized Marketing
Personalization has become a critical component of successful marketing strategies, as customers demand more personalized experiences from brands. AI enables marketers to create tailored experiences for each customer, based on their preferences, behavior, and interactions with the brand. By delivering personalized content, recommendations, and offers, businesses can enhance customer engagement, drive loyalty, and increase conversions.
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is the process of integrating digital technologies into all aspects of a business, fundamentally changing how they operate and deliver value to customers. AI is at the forefront of this transformation, empowering businesses to leverage data analytics, marketing intelligence, and automation tools to drive growth and innovation. By embracing AI, businesses can stay ahead of the curve, adapt to changing market dynamics, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
How to obtain Emerging Technology certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, artificial intelligence is revolutionizing digital marketing by empowering businesses to leverage data, automation, and intelligence to optimize their strategies and engage with customers in more meaningful ways. As AI continues to evolve and advance, businesses that embrace this technology will have a competitive advantage, driving growth and success in the digital landscape.
Building a Culture of Service Excellence in IT Teams!!!
In today's fast-paced and competitive business environment, it is crucial for IT companies to prioritize service excellence. Building a culture of service excellence in IT can lead to increased customer satisfaction, improved employee morale, and ultimately, enhanced business growth. In this article, we will explore the importance of service excellence in the IT industry and provide valuable insights on how to cultivate a culture of service excellence within your organization.
Why is Service Excellence Important in IT?
Service excellence is essential in the IT industry as it allows companies to differentiate themselves from competitors and deliver exceptional value to customers. In a highly competitive market, providing outstanding service can be a key differentiator that sets your company apart and attracts new customers. Additionally, focusing on service excellence can help improve customer retention rates, increase customer loyalty, and drive repeat business.
How to Build a Culture of Service Excellence in IT
Lead by Example: Cultivating a culture of service excellence starts at the top. Leaders within the organization should demonstrate a commitment to providing exceptional service and set a positive example for their teams to follow.
Empower Employees: Empowering employees to take ownership of the customer experience can lead to improved service delivery. Provide training, resources, and support to help employees excel in their roles and deliver outstanding service to customers.
Foster a Customer-Centric Mindset: Encourage employees to always prioritize the needs and preferences of customers. By focusing on understanding and meeting customer expectations, employees can deliver personalized service that exceeds customer satisfaction.
Establish Clear Service Standards: Define clear service standards and expectations to guide employees in their interactions with customers. Regularly review and update these standards to ensure they align with the company's values and goals.
Encourage Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Create a culture of continuous improvement by actively seeking feedback from customers and employees. Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance the overall customer experience.
Benefits of Building a Culture of Service Excellence in IT
Increased Customer Satisfaction: By prioritizing service excellence, IT companies can enhance customer satisfaction levels and build strong relationships with their clients.
Improved Employee Morale: Employees who feel empowered to deliver exceptional service are more engaged, motivated, and satisfied in their roles.
Enhanced Business Growth: A culture of service excellence can drive business growth by attracting new customers, increasing customer loyalty, and generating positive word-of-mouth referrals.
How to obtain ITServices & Management certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Building a culture of service excellence in IT is essential for companies looking to thrive in today's competitive business landscape. By prioritizing service excellence, empowering employees, and fostering a customer-centric mindset, IT organizations can differentiate themselves from competitors, drive business growth, and create lasting customer relationships. Embrace service excellence as a core value within your organization and watch as it transforms the way you do business.
Read More
In today's fast-paced and competitive business environment, it is crucial for IT companies to prioritize service excellence. Building a culture of service excellence in IT can lead to increased customer satisfaction, improved employee morale, and ultimately, enhanced business growth. In this article, we will explore the importance of service excellence in the IT industry and provide valuable insights on how to cultivate a culture of service excellence within your organization.
Why is Service Excellence Important in IT?
Service excellence is essential in the IT industry as it allows companies to differentiate themselves from competitors and deliver exceptional value to customers. In a highly competitive market, providing outstanding service can be a key differentiator that sets your company apart and attracts new customers. Additionally, focusing on service excellence can help improve customer retention rates, increase customer loyalty, and drive repeat business.
How to Build a Culture of Service Excellence in IT
Lead by Example: Cultivating a culture of service excellence starts at the top. Leaders within the organization should demonstrate a commitment to providing exceptional service and set a positive example for their teams to follow.
Empower Employees: Empowering employees to take ownership of the customer experience can lead to improved service delivery. Provide training, resources, and support to help employees excel in their roles and deliver outstanding service to customers.
Foster a Customer-Centric Mindset: Encourage employees to always prioritize the needs and preferences of customers. By focusing on understanding and meeting customer expectations, employees can deliver personalized service that exceeds customer satisfaction.
Establish Clear Service Standards: Define clear service standards and expectations to guide employees in their interactions with customers. Regularly review and update these standards to ensure they align with the company's values and goals.
Encourage Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Create a culture of continuous improvement by actively seeking feedback from customers and employees. Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance the overall customer experience.
Benefits of Building a Culture of Service Excellence in IT
Increased Customer Satisfaction: By prioritizing service excellence, IT companies can enhance customer satisfaction levels and build strong relationships with their clients.
Improved Employee Morale: Employees who feel empowered to deliver exceptional service are more engaged, motivated, and satisfied in their roles.
Enhanced Business Growth: A culture of service excellence can drive business growth by attracting new customers, increasing customer loyalty, and generating positive word-of-mouth referrals.
How to obtain ITServices & Management certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Building a culture of service excellence in IT is essential for companies looking to thrive in today's competitive business landscape. By prioritizing service excellence, empowering employees, and fostering a customer-centric mindset, IT organizations can differentiate themselves from competitors, drive business growth, and create lasting customer relationships. Embrace service excellence as a core value within your organization and watch as it transforms the way you do business.
Top Cloud Computing Skills You Must Master in 2024: Go Now!
Are you looking to stay ahead of the curve in the rapidly evolving world of technology? If so, then understanding and acquiring the right cloud computing skills is essential. Cloud computing has become a game-changer in the IT industry, with companies of all sizes relying on cloud infrastructure to drive their operations. In this article, we will explore the top cloud computing skills that you need to know in 2024. So, let's dive in and future-proof your career!
The Importance of Cloud Computing Skills
Cloud computing skills have become increasingly valuable as businesses continue to migrate their operations to the cloud. According to Gartner, the worldwide public cloud services market is projected to grow to $397.4 billion by 2022, indicating the strong demand for cloud computing expertise. Whether you are an aspiring IT professional or a seasoned veteran, having the right cloud computing skills can open doors to exciting career opportunities.
Top Cloud Computing Skills for 2024
Cloud Security: With the increasing reliance on cloud technology, securing cloud environments has become crucial. In-demand cloud security skills include knowledge of encryption, access control, data governance, and threat intelligence. Obtaining certifications like Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) or Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) can enhance your credibility in this field.
Cloud Architecture: As organizations strive for efficient and scalable cloud infrastructure, having a strong grasp of cloud architecture is highly advantageous. Expertise in designing, implementing, and managing cloud solutions using popular platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is vital.
Cloud Networking: Understanding how to configure and optimize networking in a cloud environment is a valuable skill. Proficiency in Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and knowledge of network protocols, load balancers, and content delivery networks (CDNs) are essential. Networking certifications like AWS Certified Advanced Networking - Specialty can validate your expertise in this area.
DevOps: The integration of development and operations (DevOps) has become a significant trend in cloud computing. DevOps skills involve automating, managing, and monitoring cloud infrastructure and applications. Familiarity with tools such as Docker, Kubernetes, Jenkins, and Git is highly sought after by recruiters.
Data Management and Analytics: With the immense amount of data generated by cloud systems, skills in data management and analytics are invaluable. Proficiency in cloud-based databases, data warehousing, and data visualization tools like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, or Microsoft Power BI can give you a competitive edge.
Emerging Cloud Computing Skills
In addition to the top cloud computing skills mentioned above, several emerging skills are expected to gain prominence in the coming years. By staying ahead of the curve, you can position yourself as a valuable asset in the job market. Here are some examples:
Serverless Computing: Serverless architecture abstracts infrastructure management, allowing developers to focus solely on writing code. Familiarity with serverless computing frameworks like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions is crucial for building scalable and cost-effective applications.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): The intersection of cloud computing and AI/ML is revolutionizing various industries. Acquiring skills in areas like natural language processing, image recognition, or predictive analytics will be in high demand as organizations seek to leverage AI/ML capabilities in the cloud.
Internet of Things (IoT): As IoT devices continue to proliferate, knowledge of connecting, managing, and securing these devices in the cloud is becoming essential. Skills in IoT platforms like AWS IoT or Azure IoT Hub can open doors to exciting IoT-related projects.
How to obtain Cloud Computing Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud computing skills are an essential asset for IT professionals seeking a successful career in the ever-evolving technology landscape. By acquiring the top cloud computing skills for 2024, such as cloud security, cloud architecture, cloud networking, DevOps, and data management, you can position yourself as a highly sought-after professional. Additionally, keeping an eye on emerging skills like serverless computing, AI/ML, and IoT will ensure you stay ahead of the curve. So, invest in learning and mastering these skills today to secure a promising and prosperous future in cloud computing.
Read More
Are you looking to stay ahead of the curve in the rapidly evolving world of technology? If so, then understanding and acquiring the right cloud computing skills is essential. Cloud computing has become a game-changer in the IT industry, with companies of all sizes relying on cloud infrastructure to drive their operations. In this article, we will explore the top cloud computing skills that you need to know in 2024. So, let's dive in and future-proof your career!
The Importance of Cloud Computing Skills
Cloud computing skills have become increasingly valuable as businesses continue to migrate their operations to the cloud. According to Gartner, the worldwide public cloud services market is projected to grow to $397.4 billion by 2022, indicating the strong demand for cloud computing expertise. Whether you are an aspiring IT professional or a seasoned veteran, having the right cloud computing skills can open doors to exciting career opportunities.
Top Cloud Computing Skills for 2024
Cloud Security: With the increasing reliance on cloud technology, securing cloud environments has become crucial. In-demand cloud security skills include knowledge of encryption, access control, data governance, and threat intelligence. Obtaining certifications like Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) or Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) can enhance your credibility in this field.
Cloud Architecture: As organizations strive for efficient and scalable cloud infrastructure, having a strong grasp of cloud architecture is highly advantageous. Expertise in designing, implementing, and managing cloud solutions using popular platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is vital.
Cloud Networking: Understanding how to configure and optimize networking in a cloud environment is a valuable skill. Proficiency in Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and knowledge of network protocols, load balancers, and content delivery networks (CDNs) are essential. Networking certifications like AWS Certified Advanced Networking - Specialty can validate your expertise in this area.
DevOps: The integration of development and operations (DevOps) has become a significant trend in cloud computing. DevOps skills involve automating, managing, and monitoring cloud infrastructure and applications. Familiarity with tools such as Docker, Kubernetes, Jenkins, and Git is highly sought after by recruiters.
Data Management and Analytics: With the immense amount of data generated by cloud systems, skills in data management and analytics are invaluable. Proficiency in cloud-based databases, data warehousing, and data visualization tools like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, or Microsoft Power BI can give you a competitive edge.
Emerging Cloud Computing Skills
In addition to the top cloud computing skills mentioned above, several emerging skills are expected to gain prominence in the coming years. By staying ahead of the curve, you can position yourself as a valuable asset in the job market. Here are some examples:
Serverless Computing: Serverless architecture abstracts infrastructure management, allowing developers to focus solely on writing code. Familiarity with serverless computing frameworks like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions is crucial for building scalable and cost-effective applications.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): The intersection of cloud computing and AI/ML is revolutionizing various industries. Acquiring skills in areas like natural language processing, image recognition, or predictive analytics will be in high demand as organizations seek to leverage AI/ML capabilities in the cloud.
Internet of Things (IoT): As IoT devices continue to proliferate, knowledge of connecting, managing, and securing these devices in the cloud is becoming essential. Skills in IoT platforms like AWS IoT or Azure IoT Hub can open doors to exciting IoT-related projects.
How to obtain Cloud Computing Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud computing skills are an essential asset for IT professionals seeking a successful career in the ever-evolving technology landscape. By acquiring the top cloud computing skills for 2024, such as cloud security, cloud architecture, cloud networking, DevOps, and data management, you can position yourself as a highly sought-after professional. Additionally, keeping an eye on emerging skills like serverless computing, AI/ML, and IoT will ensure you stay ahead of the curve. So, invest in learning and mastering these skills today to secure a promising and prosperous future in cloud computing.
Next-Generation Software Development: Key Insights & Trends
In the dynamic landscape of technology, the realm of software development is undergoing a profound transformation, giving rise to what is now commonly referred to as Next-Generation Software Development. As the demand for innovative and efficient solutions escalates, software engineers and development companies find themselves at the forefront of a paradigm shift. This evolution encompasses various facets, from the methodologies employed, such as Agile Software Development, to the tools leveraged, including app development software and full-stack web development frameworks.
Next-Generation Software Development is not merely a chronological successor; it encapsulates a strategic blend of cutting-edge technologies, collaborative approaches, and adaptive methodologies. In this era, software development companies are not confined to traditional practices but are venturing into realms like custom software development and app building software to meet the diverse and evolving needs of clients.
Moreover, the landscape of software development outsourcing is witnessing a surge, with a multitude of outsourcing software development companies emerging as key players. This trend enables organizations to harness global expertise, providing them with access to a vast pool of talented software developers, whether it be custom software development experts or those specializing in app development.
As businesses seek to stay ahead in the competitive market, the emphasis on Next-Generation Software Development becomes paramount. Whether it's staying agile, exploring custom solutions, or collaborating with software development experts near and far, this paradigm shift is reshaping the very core of software engineering. Join us on a journey into the future, where the lines between software development and innovation blur, and the possibilities are as limitless as the ever-expanding digital landscape.
Agile Methodologies in Next-Generation Software Development
In the realm of Next-Generation Software Development, Agile methodologies stand out as a cornerstone, driving a fundamental shift in the way software is conceptualized, developed, and delivered. Agile methodologies are characterized by their iterative and collaborative approach, emphasizing adaptability and customer-centricity. In this paradigm, software development is no longer a linear process but rather an ongoing series of iterations, allowing teams to respond swiftly to changing requirements and priorities. The principles of Agile, as outlined in the Agile Manifesto, prioritize individuals and interactions, working solutions, and customer collaboration over rigid processes and exhaustive documentation. Teams practicing Agile embrace flexibility and continuous improvement, fostering a dynamic and responsive environment that aligns seamlessly with the fast-paced demands of the digital era. As organizations increasingly adopt Agile methodologies, the next generation of software development is marked by enhanced efficiency, reduced time-to-market, and a heightened ability to meet evolving user expectations through iterative development cycles.
Emerging Technologies Driving Next-Generation Software Development
The landscape of Next-Generation Software Development is profoundly influenced by a wave of emerging technologies that are reshaping the very fabric of the industry. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, and other cutting-edge innovations are serving as catalysts for unprecedented advancements in software engineering. These technologies are not merely augmenting existing processes but fundamentally transforming the way software is conceptualized and developed. Artificial intelligence, for instance, is revolutionizing tasks such as automated testing, predictive analytics, and natural language processing, enhancing the intelligence and efficiency of software applications. Machine learning algorithms are empowering software to evolve and adapt autonomously based on patterns and data insights. The integration of blockchain technology is fostering enhanced security and transparency in software systems. As software development embraces these technologies, the next generation is marked by a convergence of intelligence, automation, and decentralized architectures, unlocking new possibilities and paving the way for innovative solutions across various industry domains. The continuous evolution of these emerging technologies promises to redefine the boundaries of what is achievable in the dynamic landscape of software development.
Custom Software Development: Tailoring Solutions for the Future
Custom Software Development has emerged as a linchpin in the future of software engineering, offering a departure from off-the-shelf solutions to provide tailor-made applications that precisely align with unique business needs. In an era marked by diverse requirements and evolving market dynamics, businesses are increasingly recognizing the value of bespoke software designed to address specific challenges and opportunities. Custom solutions empower organizations to move beyond the constraints of standardized applications, enabling them to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and achieve a competitive edge. While off-the-shelf software may offer general functionalities, custom software development tailors solutions to fit seamlessly into existing workflows, ensuring optimal performance and scalability. This approach not only caters to immediate needs but also allows for future adaptability and growth. However, the journey of custom software development is not without its challenges, and understanding the nuances of client requirements is paramount. As businesses seek to navigate the intricacies of their unique landscapes, the trend towards custom software development emerges as a pivotal force, shaping the software landscape of the future.
Global Collaboration and Software Outsourcing Trends
In the dynamic landscape of Next-Generation Software Development, global collaboration and outsourcing have become instrumental trends reshaping the industry. Businesses are increasingly recognizing the advantages of tapping into a global pool of talent, enabling them to harness specialized expertise and foster innovation. Software development outsourcing has evolved beyond cost efficiency, becoming a strategic choice for companies seeking access to diverse skill sets and accelerating time-to-market. Collaborating with software development partners across geographical borders allows organizations to leverage the strengths of distributed teams, providing 24/7 development cycles and overcoming challenges associated with talent scarcity. However, this trend comes with its own set of considerations, including cultural nuances, communication challenges, and the need for robust project management. As organizations navigate this paradigm shift, the global collaboration and outsourcing trends in software development represent a pivotal step towards building dynamic, scalable, and globally competitive solutions in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Full Stack Web Development: Unveiling the Comprehensive Approach
In the realm of Next-Generation Software Development, Full Stack Web Development has emerged as a comprehensive and integral approach, reshaping the way modern web applications are conceptualized and built. A full stack developer possesses proficiency not only in the frontend, dealing with user interfaces and experiences, but also in the backend, managing server-side logic and databases. This holistic expertise allows developers to seamlessly navigate the entire software stack, fostering a more integrated and efficient development process. Full stack web development facilitates the creation of cohesive and responsive web applications, as developers can bridge the gap between client-side and server-side functionalities with a deep understanding of both. This approach not only streamlines the development cycle but also promotes versatility and adaptability. Full stack developers are equipped to handle the complexities of modern web development frameworks, ensuring that the resulting applications are not only visually appealing but also robust, scalable, and capable of meeting the dynamic demands of the digital era. As the industry gravitates towards this comprehensive approach, Full Stack Web Development stands out as a cornerstone in the evolution of software engineering, promising a more cohesive and efficient future for web application development.
How to obtain Development certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, the landscape of Next-Generation Software Development is characterized by a confluence of transformative trends, each playing a crucial role in reshaping the industry. From the adoption of Agile methodologies, emphasizing flexibility and customer collaboration, to the integration of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and blockchain, the software development process is evolving at an unprecedented pace. The rise of custom software development signifies a departure from one-size-fits-all solutions, empowering businesses to address unique challenges and seize opportunities in their specific domains. Simultaneously, the trends of global collaboration and outsourcing underscore the importance of tapping into a global talent pool, fostering innovation, and overcoming geographical constraints. Lastly, Full Stack Web Development emerges as a comprehensive approach, bridging the gap between frontend and backend expertise, ensuring the creation of robust and adaptable web applications.
As we navigate this transformative era, the future of software development lies in embracing adaptability, innovation, and a deep understanding of evolving technologies. The amalgamation of these trends not only enhances the efficiency of software development processes but also paves the way for groundbreaking solutions that meet the dynamic needs of businesses and users alike. In the journey towards Next-Generation Software Development, the industry finds itself at the intersection of collaboration, customization, and cutting-edge technologies, promising a future where software engineering continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in the digital age.
Read More
In the dynamic landscape of technology, the realm of software development is undergoing a profound transformation, giving rise to what is now commonly referred to as Next-Generation Software Development. As the demand for innovative and efficient solutions escalates, software engineers and development companies find themselves at the forefront of a paradigm shift. This evolution encompasses various facets, from the methodologies employed, such as Agile Software Development, to the tools leveraged, including app development software and full-stack web development frameworks.
Next-Generation Software Development is not merely a chronological successor; it encapsulates a strategic blend of cutting-edge technologies, collaborative approaches, and adaptive methodologies. In this era, software development companies are not confined to traditional practices but are venturing into realms like custom software development and app building software to meet the diverse and evolving needs of clients.
Moreover, the landscape of software development outsourcing is witnessing a surge, with a multitude of outsourcing software development companies emerging as key players. This trend enables organizations to harness global expertise, providing them with access to a vast pool of talented software developers, whether it be custom software development experts or those specializing in app development.
As businesses seek to stay ahead in the competitive market, the emphasis on Next-Generation Software Development becomes paramount. Whether it's staying agile, exploring custom solutions, or collaborating with software development experts near and far, this paradigm shift is reshaping the very core of software engineering. Join us on a journey into the future, where the lines between software development and innovation blur, and the possibilities are as limitless as the ever-expanding digital landscape.
Agile Methodologies in Next-Generation Software Development
In the realm of Next-Generation Software Development, Agile methodologies stand out as a cornerstone, driving a fundamental shift in the way software is conceptualized, developed, and delivered. Agile methodologies are characterized by their iterative and collaborative approach, emphasizing adaptability and customer-centricity. In this paradigm, software development is no longer a linear process but rather an ongoing series of iterations, allowing teams to respond swiftly to changing requirements and priorities. The principles of Agile, as outlined in the Agile Manifesto, prioritize individuals and interactions, working solutions, and customer collaboration over rigid processes and exhaustive documentation. Teams practicing Agile embrace flexibility and continuous improvement, fostering a dynamic and responsive environment that aligns seamlessly with the fast-paced demands of the digital era. As organizations increasingly adopt Agile methodologies, the next generation of software development is marked by enhanced efficiency, reduced time-to-market, and a heightened ability to meet evolving user expectations through iterative development cycles.
Emerging Technologies Driving Next-Generation Software Development
The landscape of Next-Generation Software Development is profoundly influenced by a wave of emerging technologies that are reshaping the very fabric of the industry. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, and other cutting-edge innovations are serving as catalysts for unprecedented advancements in software engineering. These technologies are not merely augmenting existing processes but fundamentally transforming the way software is conceptualized and developed. Artificial intelligence, for instance, is revolutionizing tasks such as automated testing, predictive analytics, and natural language processing, enhancing the intelligence and efficiency of software applications. Machine learning algorithms are empowering software to evolve and adapt autonomously based on patterns and data insights. The integration of blockchain technology is fostering enhanced security and transparency in software systems. As software development embraces these technologies, the next generation is marked by a convergence of intelligence, automation, and decentralized architectures, unlocking new possibilities and paving the way for innovative solutions across various industry domains. The continuous evolution of these emerging technologies promises to redefine the boundaries of what is achievable in the dynamic landscape of software development.
Custom Software Development: Tailoring Solutions for the Future
Custom Software Development has emerged as a linchpin in the future of software engineering, offering a departure from off-the-shelf solutions to provide tailor-made applications that precisely align with unique business needs. In an era marked by diverse requirements and evolving market dynamics, businesses are increasingly recognizing the value of bespoke software designed to address specific challenges and opportunities. Custom solutions empower organizations to move beyond the constraints of standardized applications, enabling them to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and achieve a competitive edge. While off-the-shelf software may offer general functionalities, custom software development tailors solutions to fit seamlessly into existing workflows, ensuring optimal performance and scalability. This approach not only caters to immediate needs but also allows for future adaptability and growth. However, the journey of custom software development is not without its challenges, and understanding the nuances of client requirements is paramount. As businesses seek to navigate the intricacies of their unique landscapes, the trend towards custom software development emerges as a pivotal force, shaping the software landscape of the future.
Global Collaboration and Software Outsourcing Trends
In the dynamic landscape of Next-Generation Software Development, global collaboration and outsourcing have become instrumental trends reshaping the industry. Businesses are increasingly recognizing the advantages of tapping into a global pool of talent, enabling them to harness specialized expertise and foster innovation. Software development outsourcing has evolved beyond cost efficiency, becoming a strategic choice for companies seeking access to diverse skill sets and accelerating time-to-market. Collaborating with software development partners across geographical borders allows organizations to leverage the strengths of distributed teams, providing 24/7 development cycles and overcoming challenges associated with talent scarcity. However, this trend comes with its own set of considerations, including cultural nuances, communication challenges, and the need for robust project management. As organizations navigate this paradigm shift, the global collaboration and outsourcing trends in software development represent a pivotal step towards building dynamic, scalable, and globally competitive solutions in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Full Stack Web Development: Unveiling the Comprehensive Approach
In the realm of Next-Generation Software Development, Full Stack Web Development has emerged as a comprehensive and integral approach, reshaping the way modern web applications are conceptualized and built. A full stack developer possesses proficiency not only in the frontend, dealing with user interfaces and experiences, but also in the backend, managing server-side logic and databases. This holistic expertise allows developers to seamlessly navigate the entire software stack, fostering a more integrated and efficient development process. Full stack web development facilitates the creation of cohesive and responsive web applications, as developers can bridge the gap between client-side and server-side functionalities with a deep understanding of both. This approach not only streamlines the development cycle but also promotes versatility and adaptability. Full stack developers are equipped to handle the complexities of modern web development frameworks, ensuring that the resulting applications are not only visually appealing but also robust, scalable, and capable of meeting the dynamic demands of the digital era. As the industry gravitates towards this comprehensive approach, Full Stack Web Development stands out as a cornerstone in the evolution of software engineering, promising a more cohesive and efficient future for web application development.
How to obtain Development certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, the landscape of Next-Generation Software Development is characterized by a confluence of transformative trends, each playing a crucial role in reshaping the industry. From the adoption of Agile methodologies, emphasizing flexibility and customer collaboration, to the integration of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and blockchain, the software development process is evolving at an unprecedented pace. The rise of custom software development signifies a departure from one-size-fits-all solutions, empowering businesses to address unique challenges and seize opportunities in their specific domains. Simultaneously, the trends of global collaboration and outsourcing underscore the importance of tapping into a global talent pool, fostering innovation, and overcoming geographical constraints. Lastly, Full Stack Web Development emerges as a comprehensive approach, bridging the gap between frontend and backend expertise, ensuring the creation of robust and adaptable web applications.
As we navigate this transformative era, the future of software development lies in embracing adaptability, innovation, and a deep understanding of evolving technologies. The amalgamation of these trends not only enhances the efficiency of software development processes but also paves the way for groundbreaking solutions that meet the dynamic needs of businesses and users alike. In the journey towards Next-Generation Software Development, the industry finds itself at the intersection of collaboration, customization, and cutting-edge technologies, promising a future where software engineering continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in the digital age.
The impact of clean data on business intelligence outcomes
In today's data-driven world, businesses rely heavily on business intelligence to make informed decisions and drive growth. But the success of business intelligence initiatives hinges on the quality of the data being utilized. Clean data plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate and reliable business intelligence outcomes. In this article, we will explore the impact of clean data on business intelligence outcomes and the benefits it brings to organizations.
The Importance of Clean Data:
Clean data refers to data that is accurate, consistent, complete, and up-to-date. It is free from errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies, making it reliable and trustworthy for analysis. When businesses have clean data at their disposal, they can be confident in the insights and recommendations derived from their business intelligence processes. Clean data forms the foundation of effective decision-making and strategic planning.
How Clean Data Impacts Business Intelligence Outcomes:
Improved Accuracy: Clean data leads to more accurate business intelligence outcomes. By eliminating errors and inconsistencies, businesses can trust the insights generated from their data analytics. This, in turn, enables organizations to make informed decisions based on reliable information.
Enhanced Efficiency: Clean data streamlines the data analysis process, saving time and resources for businesses. With clean data, analysts can focus on interpreting the data rather than cleaning it, leading to more efficient and effective business intelligence outcomes.
Better Insights: Clean data ensures that businesses are working with the most relevant and up-to-date information. This results in deeper insights and a better understanding of market trends, customer behavior, and business performance. With clean data, organizations can uncover valuable opportunities for growth and optimization.
Elevated Data Management: Clean data promotes good data management practices within organizations. Businesses with clean data are better equipped to organize, store, and maintain their data effectively. This leads to optimized data processes and improved data governance, enhancing overall business intelligence outcomes.
Informed Decision-Making: Clean data empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions with confidence. With accurate and reliable information at their fingertips, organizations can make strategic choices that drive business growth and success. Clean data forms the basis for smart decision-making and ensures that businesses are operating with a competitive edge.
The Benefits of Clean Data for Business Growth:
-
Increased trust in data quality
-
Enhanced reporting and visualization capabilities
-
Better customer segmentation and targeting
-
Improved operational efficiency
-
Facilitates regulatory compliance
-
Enables proactive risk management
How to obtain Business Intelligence certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion:
The impact of clean data on business intelligence outcomes cannot be overstated. Clean data is the key to unlocking the full potential of business intelligence, driving accurate insights, informed decision-making, and sustainable business growth. Organizations that prioritize data quality and invest in data management will undoubtedly reap the benefits of clean data in their business intelligence initiatives.
Read More
In today's data-driven world, businesses rely heavily on business intelligence to make informed decisions and drive growth. But the success of business intelligence initiatives hinges on the quality of the data being utilized. Clean data plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate and reliable business intelligence outcomes. In this article, we will explore the impact of clean data on business intelligence outcomes and the benefits it brings to organizations.
The Importance of Clean Data:
Clean data refers to data that is accurate, consistent, complete, and up-to-date. It is free from errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies, making it reliable and trustworthy for analysis. When businesses have clean data at their disposal, they can be confident in the insights and recommendations derived from their business intelligence processes. Clean data forms the foundation of effective decision-making and strategic planning.
How Clean Data Impacts Business Intelligence Outcomes:
Improved Accuracy: Clean data leads to more accurate business intelligence outcomes. By eliminating errors and inconsistencies, businesses can trust the insights generated from their data analytics. This, in turn, enables organizations to make informed decisions based on reliable information.
Enhanced Efficiency: Clean data streamlines the data analysis process, saving time and resources for businesses. With clean data, analysts can focus on interpreting the data rather than cleaning it, leading to more efficient and effective business intelligence outcomes.
Better Insights: Clean data ensures that businesses are working with the most relevant and up-to-date information. This results in deeper insights and a better understanding of market trends, customer behavior, and business performance. With clean data, organizations can uncover valuable opportunities for growth and optimization.
Elevated Data Management: Clean data promotes good data management practices within organizations. Businesses with clean data are better equipped to organize, store, and maintain their data effectively. This leads to optimized data processes and improved data governance, enhancing overall business intelligence outcomes.
Informed Decision-Making: Clean data empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions with confidence. With accurate and reliable information at their fingertips, organizations can make strategic choices that drive business growth and success. Clean data forms the basis for smart decision-making and ensures that businesses are operating with a competitive edge.
The Benefits of Clean Data for Business Growth:
-
Increased trust in data quality
-
Enhanced reporting and visualization capabilities
-
Better customer segmentation and targeting
-
Improved operational efficiency
-
Facilitates regulatory compliance
-
Enables proactive risk management
How to obtain Business Intelligence certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion:
The impact of clean data on business intelligence outcomes cannot be overstated. Clean data is the key to unlocking the full potential of business intelligence, driving accurate insights, informed decision-making, and sustainable business growth. Organizations that prioritize data quality and invest in data management will undoubtedly reap the benefits of clean data in their business intelligence initiatives.
Salesforce Trailhead Challenges
In the fast-paced world of technology, staying ahead of the curve is essential. Salesforce, one of the leading customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, offers a unique learning platform called Trailhead to help users enhance their skills and stay competitive in the industry. However, navigating through Salesforce Trailhead can come with its own set of challenges. Let's explore some of the common hurdles faced by users and how to overcome them to maximize your learning experience and earn valuable Salesforce badges.
Salesforce Badges: The Ultimate Goal
One of the main objectives of using Salesforce Trailhead is to earn badges that showcase your expertise and skills in various areas of the platform. However, achieving these badges requires dedication, patience, and a strong understanding of the trailhead modules and projects.
Trailhead Points: Tracking Your Progress
Earning Salesforce badges is not just about completing modules and projects; it's also about accumulating trailhead points. These points indicate your progress and dedication to learning Salesforce skills. By earning a certain number of points, you can unlock new trailhead quests and challenges, pushing yourself to learn more and improve your Salesforce skills.
Trailhead Modules: Building a Strong Foundation
Trailhead modules are the building blocks of your learning journey. These interactive and hands-on modules cover a wide range of topics, from basic to advanced Salesforce concepts. By completing these modules, you can gain valuable insights and practical knowledge that will help you excel in your Salesforce training.
Trailhead Projects: Practical Application of Skills
While trailhead modules provide theoretical knowledge, trailhead projects offer a practical application of your skills. These real-world scenarios challenge you to apply what you've learned in a hands-on environment, preparing you for the challenges you may face as a Salesforce developer or administrator.
Salesforce Skills: The Key to Success
Learning Salesforce is more than just earning badges and completing modules; it's about developing valuable skills that will benefit your career. Whether you're looking to become a Salesforce developer or administrator, Trailhead offers a wide range of resources to help you enhance your skill set and earn valuable Salesforce certifications.
Trailhead Community: Support and Collaboration
The Trailhead community is a valuable resource for users looking to connect with like-minded individuals, share knowledge, and seek support. By actively participating in the community, you can expand your network, learn from others, and stay updated on the latest Salesforce trends and updates.
Trailhead Quests: A Journey of Discovery
Trailhead quests offer a unique learning experience that challenges you to explore new topics, complete hands-on challenges, and earn rewards along the way. By embarking on these quests, you can expand your knowledge, test your skills, and uncover new opportunities for growth and development.
Salesforce Developer Skills: Coding and Customization
For aspiring Salesforce developers, Trailhead offers a wide range of resources to help you master coding languages, customization techniques, and best practices for building custom solutions on the platform. By completing developer-focused modules and projects, you can enhance your coding skills and become a valuable asset to any organization.
Salesforce Admin Skills: Configuration and Optimization
If you're looking to become a Salesforce administrator, Trailhead provides resources to help you master configuration, optimization, and troubleshooting techniques. By completing admin-focused modules and projects, you can gain a deep understanding of the platform's capabilities and become a proficient Salesforce administrator.
Trailhead Superbadges: Taking Your Skills to the Next Level
In addition to earning badges, Trailhead offers superbadges that challenge you to solve complex scenarios and demonstrate your expertise in specific areas of the platform. By earning superbadges, you can showcase your advanced skills and stand out from the crowd as a certified Salesforce expert.
Learn CRM: Mastering Customer Relationship Management
CRM is a crucial aspect of any business, and learning how to effectively manage customer relationships is essential for success. By using Salesforce Trailhead, you can learn the ins and outs of CRM, understand best practices, and gain practical experience in implementing CRM solutions in real-world scenarios.
Trailhead Gamification: Making Learning Fun
One of the unique features of Salesforce Trailhead is its gamification element, which turns learning into a fun and engaging experience. By earning points, badges, and rewards, you can track your progress, stay motivated, and enjoy the journey of learning Salesforce in an interactive and dynamic way.
Salesforce Tutorials: Guided Learning for Success
For users looking for additional guidance and support, Salesforce offers tutorials that provide step-by-step instructions, tips, and best practices for mastering the platform. By following these tutorials, you can enhance your learning experience, overcome challenges, and become a proficient Salesforce user in no time.
Salesforce Learning Platform: Your Gateway to Success
With a wealth of resources, interactive modules, and engaging projects, Salesforce Trailhead is the ultimate learning platform for users looking to enhance their skills, earn certifications, and advance their careers in the tech industry. By embracing the challenges, staying dedicated to your learning journey, and leveraging the resources available, you can overcome any hurdles and achieve success in your Salesforce training.
How to obtain Salesforce certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, Salesforce Trailhead offers a unique and valuable learning experience for users looking to enhance their Salesforce skills, earn certifications, and advance their careers in the industry. By overcoming challenges, staying dedicated to your learning journey, and embracing the opportunities for growth and development, you can become a proficient Salesforce user and stand out from the crowd as a certified expert.
Read More
In the fast-paced world of technology, staying ahead of the curve is essential. Salesforce, one of the leading customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, offers a unique learning platform called Trailhead to help users enhance their skills and stay competitive in the industry. However, navigating through Salesforce Trailhead can come with its own set of challenges. Let's explore some of the common hurdles faced by users and how to overcome them to maximize your learning experience and earn valuable Salesforce badges.
Salesforce Badges: The Ultimate Goal
One of the main objectives of using Salesforce Trailhead is to earn badges that showcase your expertise and skills in various areas of the platform. However, achieving these badges requires dedication, patience, and a strong understanding of the trailhead modules and projects.
Trailhead Points: Tracking Your Progress
Earning Salesforce badges is not just about completing modules and projects; it's also about accumulating trailhead points. These points indicate your progress and dedication to learning Salesforce skills. By earning a certain number of points, you can unlock new trailhead quests and challenges, pushing yourself to learn more and improve your Salesforce skills.
Trailhead Modules: Building a Strong Foundation
Trailhead modules are the building blocks of your learning journey. These interactive and hands-on modules cover a wide range of topics, from basic to advanced Salesforce concepts. By completing these modules, you can gain valuable insights and practical knowledge that will help you excel in your Salesforce training.
Trailhead Projects: Practical Application of Skills
While trailhead modules provide theoretical knowledge, trailhead projects offer a practical application of your skills. These real-world scenarios challenge you to apply what you've learned in a hands-on environment, preparing you for the challenges you may face as a Salesforce developer or administrator.
Salesforce Skills: The Key to Success
Learning Salesforce is more than just earning badges and completing modules; it's about developing valuable skills that will benefit your career. Whether you're looking to become a Salesforce developer or administrator, Trailhead offers a wide range of resources to help you enhance your skill set and earn valuable Salesforce certifications.
Trailhead Community: Support and Collaboration
The Trailhead community is a valuable resource for users looking to connect with like-minded individuals, share knowledge, and seek support. By actively participating in the community, you can expand your network, learn from others, and stay updated on the latest Salesforce trends and updates.
Trailhead Quests: A Journey of Discovery
Trailhead quests offer a unique learning experience that challenges you to explore new topics, complete hands-on challenges, and earn rewards along the way. By embarking on these quests, you can expand your knowledge, test your skills, and uncover new opportunities for growth and development.
Salesforce Developer Skills: Coding and Customization
For aspiring Salesforce developers, Trailhead offers a wide range of resources to help you master coding languages, customization techniques, and best practices for building custom solutions on the platform. By completing developer-focused modules and projects, you can enhance your coding skills and become a valuable asset to any organization.
Salesforce Admin Skills: Configuration and Optimization
If you're looking to become a Salesforce administrator, Trailhead provides resources to help you master configuration, optimization, and troubleshooting techniques. By completing admin-focused modules and projects, you can gain a deep understanding of the platform's capabilities and become a proficient Salesforce administrator.
Trailhead Superbadges: Taking Your Skills to the Next Level
In addition to earning badges, Trailhead offers superbadges that challenge you to solve complex scenarios and demonstrate your expertise in specific areas of the platform. By earning superbadges, you can showcase your advanced skills and stand out from the crowd as a certified Salesforce expert.
Learn CRM: Mastering Customer Relationship Management
CRM is a crucial aspect of any business, and learning how to effectively manage customer relationships is essential for success. By using Salesforce Trailhead, you can learn the ins and outs of CRM, understand best practices, and gain practical experience in implementing CRM solutions in real-world scenarios.
Trailhead Gamification: Making Learning Fun
One of the unique features of Salesforce Trailhead is its gamification element, which turns learning into a fun and engaging experience. By earning points, badges, and rewards, you can track your progress, stay motivated, and enjoy the journey of learning Salesforce in an interactive and dynamic way.
Salesforce Tutorials: Guided Learning for Success
For users looking for additional guidance and support, Salesforce offers tutorials that provide step-by-step instructions, tips, and best practices for mastering the platform. By following these tutorials, you can enhance your learning experience, overcome challenges, and become a proficient Salesforce user in no time.
Salesforce Learning Platform: Your Gateway to Success
With a wealth of resources, interactive modules, and engaging projects, Salesforce Trailhead is the ultimate learning platform for users looking to enhance their skills, earn certifications, and advance their careers in the tech industry. By embracing the challenges, staying dedicated to your learning journey, and leveraging the resources available, you can overcome any hurdles and achieve success in your Salesforce training.
How to obtain Salesforce certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, Salesforce Trailhead offers a unique and valuable learning experience for users looking to enhance their Salesforce skills, earn certifications, and advance their careers in the industry. By overcoming challenges, staying dedicated to your learning journey, and embracing the opportunities for growth and development, you can become a proficient Salesforce user and stand out from the crowd as a certified expert.
Big Data's Impact on Supply Chain Management Explained.
In today's fast-paced business environment, supply chain management plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. With the advent of big data and advanced analytics, supply chain management has been revolutionized, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings for businesses across various industries. In this article, we will explore how big data is transforming supply chain management and revolutionizing the way companies operate.
Supply Chain Optimization
One of the key areas where big data has made a significant impact on supply chain management is in optimization. By analyzing vast amounts of data related to inventory levels, production schedules, transportation routes, and customer demand, companies can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize their supply chain operations. This leads to reduced costs, faster delivery times, and better customer satisfaction.
Predictive Analytics
Another important aspect of big data in supply chain management is predictive analytics. By using advanced algorithms to analyze historical data and identify patterns and trends, companies can predict future demand, potential supply chain disruptions, and optimize their operations accordingly. This proactive approach helps companies to prevent potential issues before they occur, leading to improved efficiency and performance.
Data-Driven Decisions
With the help of big data analytics, companies can now make more informed and data-driven decisions. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources such as sensors, RFID tags, and social media, companies can gain real-time insights into their supply chain operations and make strategic decisions to enhance their business processes. This leads to increased agility, better risk management, and overall improved decision-making process.
Logistics Efficiency
Big data has also played a significant role in enhancing logistics efficiency within supply chain management. By leveraging data analytics to optimize transportation routes, streamline warehouse operations, and track shipments in real-time, companies can improve their overall logistics performance. This leads to reduced shipping costs, faster delivery times, and better inventory management.
Big Data Solutions
There are various big data applications and solutions available in the market that cater to the needs of supply chain management. These solutions offer features such as data integration, performance metrics, supply chain analytics, and supply chain visibility. By implementing these solutions, companies can gain a competitive edge by effectively managing their supply chain operations and staying ahead of the curve.
How to obtain Big Data certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of big data on supply chain management is undeniable. By embracing data-driven strategies, leveraging advanced analytics tools, and adopting the latest technology trends, companies can optimize their supply chain operations, enhance their business operations, and achieve better outcomes. As we move towards a more data-driven and digital future, companies that harness the power of big data will be well-positioned to succeed in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Read More
In today's fast-paced business environment, supply chain management plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. With the advent of big data and advanced analytics, supply chain management has been revolutionized, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings for businesses across various industries. In this article, we will explore how big data is transforming supply chain management and revolutionizing the way companies operate.
Supply Chain Optimization
One of the key areas where big data has made a significant impact on supply chain management is in optimization. By analyzing vast amounts of data related to inventory levels, production schedules, transportation routes, and customer demand, companies can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize their supply chain operations. This leads to reduced costs, faster delivery times, and better customer satisfaction.
Predictive Analytics
Another important aspect of big data in supply chain management is predictive analytics. By using advanced algorithms to analyze historical data and identify patterns and trends, companies can predict future demand, potential supply chain disruptions, and optimize their operations accordingly. This proactive approach helps companies to prevent potential issues before they occur, leading to improved efficiency and performance.
Data-Driven Decisions
With the help of big data analytics, companies can now make more informed and data-driven decisions. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources such as sensors, RFID tags, and social media, companies can gain real-time insights into their supply chain operations and make strategic decisions to enhance their business processes. This leads to increased agility, better risk management, and overall improved decision-making process.
Logistics Efficiency
Big data has also played a significant role in enhancing logistics efficiency within supply chain management. By leveraging data analytics to optimize transportation routes, streamline warehouse operations, and track shipments in real-time, companies can improve their overall logistics performance. This leads to reduced shipping costs, faster delivery times, and better inventory management.
Big Data Solutions
There are various big data applications and solutions available in the market that cater to the needs of supply chain management. These solutions offer features such as data integration, performance metrics, supply chain analytics, and supply chain visibility. By implementing these solutions, companies can gain a competitive edge by effectively managing their supply chain operations and staying ahead of the curve.
How to obtain Big Data certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of big data on supply chain management is undeniable. By embracing data-driven strategies, leveraging advanced analytics tools, and adopting the latest technology trends, companies can optimize their supply chain operations, enhance their business operations, and achieve better outcomes. As we move towards a more data-driven and digital future, companies that harness the power of big data will be well-positioned to succeed in the ever-evolving business landscape.
AI Transformative Impact on Modern IT Service Management
Are you looking to streamline your IT service management processes and improve efficiency? Look no further than the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into your IT service management strategy. AI has revolutionized the way IT services are delivered and managed, offering a wide range of benefits that can help organizations operate more effectively and provide better service to their customers.
AI in IT Service Management
AI refers to the use of intelligent machines and algorithms that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and understanding natural language. In the context of IT service management, AI can be used to automate repetitive tasks, predict and prevent IT issues, and analyze vast amounts of data to make informed decisions.
Artificial Intelligence for IT Service Management
By leveraging AI technologies, IT service management teams can work smarter, not harder. AI-powered systems can handle routine tasks like ticket routing, categorization, and resolution, freeing up IT professionals to focus on more critical issues that require human intervention. This not only increases efficiency but also improves employee satisfaction and reduces burnout.
Machine Learning in IT Service Management
Machine learning, a subset of AI, enables IT service management systems to learn from past data and experiences to improve future outcomes. By analyzing historical data, machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and trends that humans might overlook, leading to more accurate predictions and proactive problem resolution. This can result in fewer service disruptions, reduced downtime, and improved overall performance.
IT Service Management Automation
Automation is a key component of AI in IT service management. By automating routine tasks and processes, organizations can reduce manual errors, speed up service delivery, and provide a consistent and reliable experience for users. From automated incident response to self-service portals, AI-driven automation can revolutionize the way IT services are delivered.
Benefits of AI in IT Service Management
The use of AI in IT service management offers a wide range of benefits for organizations, including:
Enhanced efficiency: AI can handle tasks faster and more accurately than humans, leading to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
Improved decision-making: AI algorithms can analyze data in real-time and provide valuable insights that can help organizations make informed decisions.
Better customer satisfaction: By automating routine tasks and providing faster service delivery, organizations can enhance the customer experience and build loyalty.
Proactive problem resolution: AI can predict and prevent IT issues before they occur, reducing downtime and minimizing impact on business operations.
Scalability: AI-powered systems can scale up or down based on demand, allowing organizations to adapt to changing business needs quickly.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in IT Service
The role of artificial intelligence in IT service is to augment and optimize the capabilities of IT service management teams. By automating routine tasks, analyzing data, and making predictions, AI can help organizations operate more efficiently, reduce costs, and deliver better service to their customers. From predicting system failures to optimizing resource allocation, AI can transform the way IT services are managed and delivered.
IT Service Management Optimization with AI
To optimize IT service management with AI, organizations should:
Identify areas where AI can have the most significant impact, such as incident management, problem resolution, and service desk operations.
Invest in AI technologies that align with organizational goals and objectives, ensuring a seamless integration with existing IT systems.
Train IT staff on how to leverage AI tools and technologies effectively, empowering them to work more efficiently and effectively.
Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of AI-powered systems, making adjustments as needed to maximize benefits and ROI.
How to obtain IT Service Management & Governace certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI plays a crucial role in IT service management by improving efficiency, automating routine tasks, and helping organizations deliver better service to their customers. By embracing AI technologies and incorporating them into their IT service management strategy, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and drive innovation in the fast-paced world of IT services.
Read More
Are you looking to streamline your IT service management processes and improve efficiency? Look no further than the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into your IT service management strategy. AI has revolutionized the way IT services are delivered and managed, offering a wide range of benefits that can help organizations operate more effectively and provide better service to their customers.
AI in IT Service Management
AI refers to the use of intelligent machines and algorithms that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and understanding natural language. In the context of IT service management, AI can be used to automate repetitive tasks, predict and prevent IT issues, and analyze vast amounts of data to make informed decisions.
Artificial Intelligence for IT Service Management
By leveraging AI technologies, IT service management teams can work smarter, not harder. AI-powered systems can handle routine tasks like ticket routing, categorization, and resolution, freeing up IT professionals to focus on more critical issues that require human intervention. This not only increases efficiency but also improves employee satisfaction and reduces burnout.
Machine Learning in IT Service Management
Machine learning, a subset of AI, enables IT service management systems to learn from past data and experiences to improve future outcomes. By analyzing historical data, machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and trends that humans might overlook, leading to more accurate predictions and proactive problem resolution. This can result in fewer service disruptions, reduced downtime, and improved overall performance.
IT Service Management Automation
Automation is a key component of AI in IT service management. By automating routine tasks and processes, organizations can reduce manual errors, speed up service delivery, and provide a consistent and reliable experience for users. From automated incident response to self-service portals, AI-driven automation can revolutionize the way IT services are delivered.
Benefits of AI in IT Service Management
The use of AI in IT service management offers a wide range of benefits for organizations, including:
Enhanced efficiency: AI can handle tasks faster and more accurately than humans, leading to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
Improved decision-making: AI algorithms can analyze data in real-time and provide valuable insights that can help organizations make informed decisions.
Better customer satisfaction: By automating routine tasks and providing faster service delivery, organizations can enhance the customer experience and build loyalty.
Proactive problem resolution: AI can predict and prevent IT issues before they occur, reducing downtime and minimizing impact on business operations.
Scalability: AI-powered systems can scale up or down based on demand, allowing organizations to adapt to changing business needs quickly.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in IT Service
The role of artificial intelligence in IT service is to augment and optimize the capabilities of IT service management teams. By automating routine tasks, analyzing data, and making predictions, AI can help organizations operate more efficiently, reduce costs, and deliver better service to their customers. From predicting system failures to optimizing resource allocation, AI can transform the way IT services are managed and delivered.
IT Service Management Optimization with AI
To optimize IT service management with AI, organizations should:
Identify areas where AI can have the most significant impact, such as incident management, problem resolution, and service desk operations.
Invest in AI technologies that align with organizational goals and objectives, ensuring a seamless integration with existing IT systems.
Train IT staff on how to leverage AI tools and technologies effectively, empowering them to work more efficiently and effectively.
Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of AI-powered systems, making adjustments as needed to maximize benefits and ROI.
How to obtain IT Service Management & Governace certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI plays a crucial role in IT service management by improving efficiency, automating routine tasks, and helping organizations deliver better service to their customers. By embracing AI technologies and incorporating them into their IT service management strategy, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and drive innovation in the fast-paced world of IT services.
Unlocking the Power of Deep Learning for Future Innovation
Deep learning, a subfield of machine learning and artificial intelligence, is rapidly revolutionizing the future of many industries by unlocking the true potential of advanced technology. Through the development of powerful neural networks and the analysis of vast amounts of data, deep learning is shaping the way we approach complex problems and driving innovation in various fields. In this article, we will explore the transformative power of deep learning and its implications for the future.
Unlocking the Potential
A Paradigm Shift in Machine Learning
Deep learning represents a significant paradigm shift in the field of machine learning. Unlike traditional methods that rely on explicit programming and handcrafted features, deep learning learns directly from the data, allowing it to discover intricate patterns and relationships. This capability enables deep learning models to tackle complex tasks previously deemed impossible, such as image recognition, natural language processing, and speech synthesis.
Harnessing the Power of Neural Networks
At the core of deep learning lies the use of artificial neural networks, which mimic the structure and function of the human brain. These networks consist of interconnected layers of artificial neurons, each performing simple computations. By stacking multiple layers, deep neural networks can model highly complex and abstract concepts, leading to remarkable performance in various domains.
Revolutionizing Industries
Data Analysis and Decision-Making
Deep learning has revolutionized the field of data analysis by providing more accurate and efficient methods for extracting insights from vast amounts of information. Through deep neural networks, organizations can leverage their data to make better-informed decisions, identify trends, and predict outcomes with unprecedented accuracy. This has profound implications for sectors such as finance, healthcare, marketing, and manufacturing, where data-driven decision-making is critical.
Advancing Artificial Intelligence
Deep learning plays a pivotal role in advancing artificial intelligence by enabling machines to understand and interact with the world in a more human-like manner. With deep neural networks, machines can comprehend and process complex sensory inputs, such as images, sounds, and language, bridging the gap between machines and humans. This has opened up possibilities for applications like autonomous vehicles, virtual assistants, and intelligent robots.
Embracing the Future
Overcoming Challenges and Limitations
While deep learning has made significant strides in revolutionizing various industries, challenges and limitations still exist. One major concern is the need for vast amounts of annotated data to train deep neural networks effectively. Additionally, deep learning models can be computationally intensive and require substantial computational resources. However, ongoing research and technological advancements aim to address these challenges, making deep learning more accessible and practical.
Ethical Implications and Responsbilities
As deep learning becomes more pervasive in society, ethical considerations and responsibilities become increasingly important. With the power to shape decisions and influence outcomes, it is crucial to ensure that deep learning algorithms are free from bias, transparent, and accountable. Organizations and policymakers must adhere to ethical guidelines to harness deep learning's potential responsibly and avoid unintended consequences.
How to obtain Deep Learning certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Deep learning is transforming the future by unlocking the power of advanced technology. Through the utilization of neural networks and the analysis of vast amounts of data, deep learning is revolutionizing industries and pushing the boundaries of artificial intelligence. As we embrace this innovative field, it is vital to address challenges and ethical considerations to harness its potential responsibly. The future holds immense promise as deep learning continues to evolve, empowering us to solve complex problems and create a more intelligent and efficient world.
Read More
Deep learning, a subfield of machine learning and artificial intelligence, is rapidly revolutionizing the future of many industries by unlocking the true potential of advanced technology. Through the development of powerful neural networks and the analysis of vast amounts of data, deep learning is shaping the way we approach complex problems and driving innovation in various fields. In this article, we will explore the transformative power of deep learning and its implications for the future.
Unlocking the Potential
A Paradigm Shift in Machine Learning
Deep learning represents a significant paradigm shift in the field of machine learning. Unlike traditional methods that rely on explicit programming and handcrafted features, deep learning learns directly from the data, allowing it to discover intricate patterns and relationships. This capability enables deep learning models to tackle complex tasks previously deemed impossible, such as image recognition, natural language processing, and speech synthesis.
Harnessing the Power of Neural Networks
At the core of deep learning lies the use of artificial neural networks, which mimic the structure and function of the human brain. These networks consist of interconnected layers of artificial neurons, each performing simple computations. By stacking multiple layers, deep neural networks can model highly complex and abstract concepts, leading to remarkable performance in various domains.
Revolutionizing Industries
Data Analysis and Decision-Making
Deep learning has revolutionized the field of data analysis by providing more accurate and efficient methods for extracting insights from vast amounts of information. Through deep neural networks, organizations can leverage their data to make better-informed decisions, identify trends, and predict outcomes with unprecedented accuracy. This has profound implications for sectors such as finance, healthcare, marketing, and manufacturing, where data-driven decision-making is critical.
Advancing Artificial Intelligence
Deep learning plays a pivotal role in advancing artificial intelligence by enabling machines to understand and interact with the world in a more human-like manner. With deep neural networks, machines can comprehend and process complex sensory inputs, such as images, sounds, and language, bridging the gap between machines and humans. This has opened up possibilities for applications like autonomous vehicles, virtual assistants, and intelligent robots.
Embracing the Future
Overcoming Challenges and Limitations
While deep learning has made significant strides in revolutionizing various industries, challenges and limitations still exist. One major concern is the need for vast amounts of annotated data to train deep neural networks effectively. Additionally, deep learning models can be computationally intensive and require substantial computational resources. However, ongoing research and technological advancements aim to address these challenges, making deep learning more accessible and practical.
Ethical Implications and Responsbilities
As deep learning becomes more pervasive in society, ethical considerations and responsibilities become increasingly important. With the power to shape decisions and influence outcomes, it is crucial to ensure that deep learning algorithms are free from bias, transparent, and accountable. Organizations and policymakers must adhere to ethical guidelines to harness deep learning's potential responsibly and avoid unintended consequences.
How to obtain Deep Learning certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Deep learning is transforming the future by unlocking the power of advanced technology. Through the utilization of neural networks and the analysis of vast amounts of data, deep learning is revolutionizing industries and pushing the boundaries of artificial intelligence. As we embrace this innovative field, it is vital to address challenges and ethical considerations to harness its potential responsibly. The future holds immense promise as deep learning continues to evolve, empowering us to solve complex problems and create a more intelligent and efficient world.
PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course: Learn More
Are you looking to enhance your project management skills and stand out in the competitive job market? Look no further than the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course. This comprehensive program is designed to provide individuals with the knowledge and expertise necessary to effectively manage projects and deliver successful results. In this article, we will explore the benefits of the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course and why it is a valuable investment for professionals seeking to advance their careers.
Introduction to PRINCE2 Foundation Certification
The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification is widely recognized as a leading project management qualification. It is based on the PRINCE2 methodology, which is a structured approach to project management that emphasizes best practices and efficient processes. By obtaining this certification, individuals demonstrate their understanding of project management principles and their ability to apply them in real-world scenarios.
Why Choose PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course?
Comprehensive Curriculum: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course covers all aspects of project management, from initiation to closure. Participants will learn essential concepts such as project planning, risk management, quality control, and stakeholder management. The thorough curriculum ensures that professionals are equipped with the knowledge and skills required to handle any project with confidence.
Global Recognition: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification is globally recognized and respected by employers across industries. By obtaining this certification, professionals can significantly enhance their career prospects and open doors to exciting opportunities worldwide. Employers often seek candidates with PRINCE2 certification, as it serves as a testament to their expertise in project management.
Practical Application: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course focuses on practical application rather than theoretical concepts. Participants will engage in hands-on exercises, case studies, and simulations to reinforce their understanding of project management principles. This practical approach ensures that professionals can immediately apply their newly acquired knowledge in real-world scenarios.
Flexibility and Accessibility: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course is designed to accommodate individuals with busy schedules. It offers flexible learning options, including both online and classroom-based courses. This accessibility allows professionals to pursue the certification at their own pace and convenience, without compromising their existing commitments.
How to Earn PRINCE2 Foundation Certification?
Earning the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification requires successful completion of the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course. The course provides comprehensive training on the PRINCE2 methodology and prepares participants for the certification exam. The exam consists of multiple-choice questions that assess the candidates' knowledge of project management principles and their ability to apply them in practical scenarios.
Benefits of PRINCE2 Foundation Certification
Career Advancement: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification is highly regarded within the project management field and can significantly enhance career prospects. Employers value professionals with PRINCE2 certification, as it demonstrates their commitment to excellence and their ability to manage projects effectively.
Improved Project Management Skills: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course equips professionals with a comprehensive set of project management skills. From planning and risk management to communication and stakeholder engagement, participants gain a holistic understanding of project management principles and best practices.
Enhanced Employability: With the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification, professionals become more competitive in the job market. The certification validates their expertise in project management and increases their chances of securing desirable job roles and higher salary packages.
International Recognition: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification is recognized globally, allowing professionals to pursue exciting career opportunities both nationally and internationally. Whether working on local projects or collaborating with international teams, the certification serves as a testament to their project management proficiency.
How to obtain Project Management Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course is a valuable investment for professionals seeking to enhance their project management skills. By obtaining this certification, individuals can boost their career prospects, improve their project management capabilities, and gain international recognition. With its comprehensive curriculum and practical approach, the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course equips professionals with the knowledge and expertise necessary to excel in the field of project management. So, why wait? Enroll in the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course today and take your career to new heights!
Read More
Are you looking to enhance your project management skills and stand out in the competitive job market? Look no further than the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course. This comprehensive program is designed to provide individuals with the knowledge and expertise necessary to effectively manage projects and deliver successful results. In this article, we will explore the benefits of the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course and why it is a valuable investment for professionals seeking to advance their careers.
Introduction to PRINCE2 Foundation Certification
The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification is widely recognized as a leading project management qualification. It is based on the PRINCE2 methodology, which is a structured approach to project management that emphasizes best practices and efficient processes. By obtaining this certification, individuals demonstrate their understanding of project management principles and their ability to apply them in real-world scenarios.
Why Choose PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course?
Comprehensive Curriculum: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course covers all aspects of project management, from initiation to closure. Participants will learn essential concepts such as project planning, risk management, quality control, and stakeholder management. The thorough curriculum ensures that professionals are equipped with the knowledge and skills required to handle any project with confidence.
Global Recognition: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification is globally recognized and respected by employers across industries. By obtaining this certification, professionals can significantly enhance their career prospects and open doors to exciting opportunities worldwide. Employers often seek candidates with PRINCE2 certification, as it serves as a testament to their expertise in project management.
Practical Application: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course focuses on practical application rather than theoretical concepts. Participants will engage in hands-on exercises, case studies, and simulations to reinforce their understanding of project management principles. This practical approach ensures that professionals can immediately apply their newly acquired knowledge in real-world scenarios.
Flexibility and Accessibility: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course is designed to accommodate individuals with busy schedules. It offers flexible learning options, including both online and classroom-based courses. This accessibility allows professionals to pursue the certification at their own pace and convenience, without compromising their existing commitments.
How to Earn PRINCE2 Foundation Certification?
Earning the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification requires successful completion of the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course. The course provides comprehensive training on the PRINCE2 methodology and prepares participants for the certification exam. The exam consists of multiple-choice questions that assess the candidates' knowledge of project management principles and their ability to apply them in practical scenarios.
Benefits of PRINCE2 Foundation Certification
Career Advancement: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification is highly regarded within the project management field and can significantly enhance career prospects. Employers value professionals with PRINCE2 certification, as it demonstrates their commitment to excellence and their ability to manage projects effectively.
Improved Project Management Skills: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course equips professionals with a comprehensive set of project management skills. From planning and risk management to communication and stakeholder engagement, participants gain a holistic understanding of project management principles and best practices.
Enhanced Employability: With the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification, professionals become more competitive in the job market. The certification validates their expertise in project management and increases their chances of securing desirable job roles and higher salary packages.
International Recognition: The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification is recognized globally, allowing professionals to pursue exciting career opportunities both nationally and internationally. Whether working on local projects or collaborating with international teams, the certification serves as a testament to their project management proficiency.
How to obtain Project Management Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
The PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course is a valuable investment for professionals seeking to enhance their project management skills. By obtaining this certification, individuals can boost their career prospects, improve their project management capabilities, and gain international recognition. With its comprehensive curriculum and practical approach, the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course equips professionals with the knowledge and expertise necessary to excel in the field of project management. So, why wait? Enroll in the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course today and take your career to new heights!
Kanban System Design Certification Training for Success.
Are you looking to enhance your skills in workflow management and become an expert in Kanban system design? Look no further! With Kanban System Design Certification Training, you can take your career to new heights by mastering the principles and practices of this powerful methodology. In this article, we'll explore the benefits of Kanban certification training, the importance of system design, and how this training can elevate your expertise, authority, and trust in the field.
Why Choose Kanban System Design Certification Training?
Efficient Workflow Management: Gain a Competitive Edge
In today's competitive business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to optimize their processes and enhance productivity. By acquiring Kanban system design certification, you gain the knowledge and skills to effectively manage workflow through visual cues and limiting work in progress. This enables you to streamline operations, reduce bottlenecks, and ultimately deliver value to customers faster. With the demand for experts in efficient workflow management on the rise, Kanban certification training gives you a competitive edge in the job market.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Successful implementation of the Kanban system relies heavily on collaboration and communication within teams. Kanban certification training equips you with the tools and techniques to foster open communication, encourage transparency, and promote a culture of continuous improvement. By effectively designing Kanban systems tailored to your organization's needs, you facilitate smooth collaboration, enabling teams to work together more efficiently and deliver exceptional results.
The Importance of System Design in Kanban Certification Training
Optimizing Workflow
System design plays a crucial role in Kanban certification training as it enables organizations to optimize their workflow. Through a well-designed Kanban system, you can visualize the entire workflow and identify opportunities for improvement. By mapping out the flow of work, identifying dependencies, and implementing appropriate policies, you can ensure a smooth and efficient process from start to finish. This ultimately leads to increased productivity, reduced lead times, and improved customer satisfaction.
Tailoring Kanban Systems to Organizational Needs
Every organization has unique requirements and workflows. With system design training, you'll learn how to tailor Kanban systems to fit your organization's specific needs. From defining work types and classes of service to establishing appropriate work-in-progress limits, system design allows you to create a customized framework that aligns with your organization's objectives and maximizes efficiency.
Elevate Your Expertise with Kanban System Design Certification
Extensive Knowledge and Practical Skills
Kanban system design certification training equips you with extensive knowledge and practical skills to excel in workflow management. By deeply understanding the principles of Kanban, value stream mapping, and the psychology of change, you become an expert in designing and implementing effective Kanban systems. Through hands-on exercises, case studies, and real-world examples, you'll develop the expertise necessary to drive continuous improvement and optimize workflow within your organization.
Establish Credibility and Trust
Obtaining Kanban system design certification demonstrates your commitment to excellence and continuous learning. It not only establishes your credibility as an expert in the field but also builds trust with clients and colleagues. By showcasing your certification, you gain a competitive advantage and open doors to exciting career opportunities. Clients and organizations seeking professionals with Kanban system design expertise will recognize your certification as a mark of excellence, giving you a compelling advantage in the job market.
How to obtain Agili & Scrum certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Kanban System Design Certification Training is the gateway to becoming an expert in workflow management. By obtaining this certification, you'll acquire the skills, knowledge, and practical expertise required to optimize workflow, enhance collaboration, and deliver exceptional results. Don't miss out on the opportunity to elevate your career and become a sought-after professional in the field. Enroll in Kanban System Design Certification Training and unlock a world of possibilities today!
Read More
Are you looking to enhance your skills in workflow management and become an expert in Kanban system design? Look no further! With Kanban System Design Certification Training, you can take your career to new heights by mastering the principles and practices of this powerful methodology. In this article, we'll explore the benefits of Kanban certification training, the importance of system design, and how this training can elevate your expertise, authority, and trust in the field.
Why Choose Kanban System Design Certification Training?
Efficient Workflow Management: Gain a Competitive Edge
In today's competitive business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to optimize their processes and enhance productivity. By acquiring Kanban system design certification, you gain the knowledge and skills to effectively manage workflow through visual cues and limiting work in progress. This enables you to streamline operations, reduce bottlenecks, and ultimately deliver value to customers faster. With the demand for experts in efficient workflow management on the rise, Kanban certification training gives you a competitive edge in the job market.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Successful implementation of the Kanban system relies heavily on collaboration and communication within teams. Kanban certification training equips you with the tools and techniques to foster open communication, encourage transparency, and promote a culture of continuous improvement. By effectively designing Kanban systems tailored to your organization's needs, you facilitate smooth collaboration, enabling teams to work together more efficiently and deliver exceptional results.
The Importance of System Design in Kanban Certification Training
Optimizing Workflow
System design plays a crucial role in Kanban certification training as it enables organizations to optimize their workflow. Through a well-designed Kanban system, you can visualize the entire workflow and identify opportunities for improvement. By mapping out the flow of work, identifying dependencies, and implementing appropriate policies, you can ensure a smooth and efficient process from start to finish. This ultimately leads to increased productivity, reduced lead times, and improved customer satisfaction.
Tailoring Kanban Systems to Organizational Needs
Every organization has unique requirements and workflows. With system design training, you'll learn how to tailor Kanban systems to fit your organization's specific needs. From defining work types and classes of service to establishing appropriate work-in-progress limits, system design allows you to create a customized framework that aligns with your organization's objectives and maximizes efficiency.
Elevate Your Expertise with Kanban System Design Certification
Extensive Knowledge and Practical Skills
Kanban system design certification training equips you with extensive knowledge and practical skills to excel in workflow management. By deeply understanding the principles of Kanban, value stream mapping, and the psychology of change, you become an expert in designing and implementing effective Kanban systems. Through hands-on exercises, case studies, and real-world examples, you'll develop the expertise necessary to drive continuous improvement and optimize workflow within your organization.
Establish Credibility and Trust
Obtaining Kanban system design certification demonstrates your commitment to excellence and continuous learning. It not only establishes your credibility as an expert in the field but also builds trust with clients and colleagues. By showcasing your certification, you gain a competitive advantage and open doors to exciting career opportunities. Clients and organizations seeking professionals with Kanban system design expertise will recognize your certification as a mark of excellence, giving you a compelling advantage in the job market.
How to obtain Agili & Scrum certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Kanban System Design Certification Training is the gateway to becoming an expert in workflow management. By obtaining this certification, you'll acquire the skills, knowledge, and practical expertise required to optimize workflow, enhance collaboration, and deliver exceptional results. Don't miss out on the opportunity to elevate your career and become a sought-after professional in the field. Enroll in Kanban System Design Certification Training and unlock a world of possibilities today!
Best AI Books to Read in 2024: Top Picks for All Levels.
Are you fascinated by artificial intelligence and its endless possibilities? Do you want to delve deeper into the world of AI, learn about the latest developments, and explore its potential? If so, you're in the right place! In this article, we will provide you with a curated list of the best artificial intelligence books to read in 2024. These books will expand your knowledge, offer valuable insights, and keep you at the forefront of AI advancements. So, let's embark on this exciting journey!
The Future of AI Books
As artificial intelligence continues to revolutionize various industries, the need for comprehensive and up-to-date resources becomes more evident. Books serve as gateways to understanding the complexities of AI, allowing individuals to learn from experts and explore cutting-edge concepts. In 2024, the best AI books are expected to provide a deep dive into the latest trends, emerging technologies, and real-world applications.
Top AI Books That Will Shape Your Perspective
1."The AI Advantage: How to Put Artificial Intelligence into Action" by Thomas H. Davenport
This book offers practical insights and actionable strategies for organizations looking to leverage AI effectively. It discusses the importance of building an AI-ready culture and provides valuable frameworks to implement AI solutions.
2."The Hundred-Page Machine Learning Book" by Andriy Burkov
If you're new to machine learning and want an accessible yet comprehensive guide, this book is for you. It covers the fundamentals of ML in a concise manner, making complex concepts easy to understand.
3."Human Compatible: Artificial Intelligence and the Problem of Control" by Stuart Russell
Stuart Russell, a renowned AI researcher, explores the impact of AI on society and addresses the ethical concerns surrounding its development. This thought-provoking book sheds light on ensuring AI systems align with human values.
4."Deep Medicine: How Artificial Intelligence Can Make Healthcare Human Again" by Eric Topol
Eric Topol examines the potential of AI in revolutionizing healthcare. He highlights the role of AI in diagnosis, personalized treatments, and patient care, emphasizing the importance of maintaining the human touch in medicine.
5."The Robots Are Coming!: The Future of Jobs in the Age of Automation" by Andres Oppenheimer
In this book, Oppenheimer explores the impact of AI and automation on the job market. He offers insights into how individuals can adapt and thrive in an AI-driven economy, making it a must-read for anyone concerned about the future of work.
Must-Read AI Books for Tech Enthusiasts
1."Artificial Intelligence: A Guide to Intelligent Systems" by Michael Negnevitsky
This comprehensive guide covers a wide range of AI topics, including search algorithms, logic, machine learning, and data mining. It serves as a valuable resource for students and professionals interested in AI.
2."Rebooting AI: Building Artificial Intelligence We Can Trust" by Gary Marcus and Ernest Davis
Marcus and Davis critically examine the limitations of current AI systems and propose a roadmap for designing more robust and trustworthy AI. This book challenges the prevailing AI hype and provides a refreshing perspective.
3."Artificial Intelligence: Foundations of Computational Agents" by David L. Poole and Alan K. Mackworth
Aimed at undergraduate students, this book explores AI from a computational agent perspective. It covers topics such as knowledge representation, reasoning, planning, and learning, providing a solid foundation in AI principles.
4."AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World Order" by Kai-Fu Lee
In this book, Lee offers insights into the AI landscape in China and Silicon Valley. He discusses the potential implications of the AI race between these two powerhouses and its impact on global economics and politics.
5."Life 3.0: Being Human in the Age of Artificial Intelligence" by Max Tegmark
Tegmark explores the potential consequences of AI advancements and contemplates the future of humanity. This thought-provoking book raises important questions about our coexistence with AI and urges us to shape its development responsibly.
How to obtain Artifical Intelligence certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
As AI continues to shape our world, staying informed about the latest developments is crucial. The best artificial intelligence books to read in 2024 offer a wealth of knowledge and insights from experts in the field. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, business leader, or simply curious about AI, these books will provide valuable perspectives and expand your understanding of this rapidly evolving technology. So, grab a cup of coffee, immerse yourself in these captivating AI books, and ignite your intellectual curiosity!
Read More
Are you fascinated by artificial intelligence and its endless possibilities? Do you want to delve deeper into the world of AI, learn about the latest developments, and explore its potential? If so, you're in the right place! In this article, we will provide you with a curated list of the best artificial intelligence books to read in 2024. These books will expand your knowledge, offer valuable insights, and keep you at the forefront of AI advancements. So, let's embark on this exciting journey!
The Future of AI Books
As artificial intelligence continues to revolutionize various industries, the need for comprehensive and up-to-date resources becomes more evident. Books serve as gateways to understanding the complexities of AI, allowing individuals to learn from experts and explore cutting-edge concepts. In 2024, the best AI books are expected to provide a deep dive into the latest trends, emerging technologies, and real-world applications.
Top AI Books That Will Shape Your Perspective
1."The AI Advantage: How to Put Artificial Intelligence into Action" by Thomas H. Davenport
This book offers practical insights and actionable strategies for organizations looking to leverage AI effectively. It discusses the importance of building an AI-ready culture and provides valuable frameworks to implement AI solutions.
2."The Hundred-Page Machine Learning Book" by Andriy Burkov
If you're new to machine learning and want an accessible yet comprehensive guide, this book is for you. It covers the fundamentals of ML in a concise manner, making complex concepts easy to understand.
3."Human Compatible: Artificial Intelligence and the Problem of Control" by Stuart Russell
Stuart Russell, a renowned AI researcher, explores the impact of AI on society and addresses the ethical concerns surrounding its development. This thought-provoking book sheds light on ensuring AI systems align with human values.
4."Deep Medicine: How Artificial Intelligence Can Make Healthcare Human Again" by Eric Topol
Eric Topol examines the potential of AI in revolutionizing healthcare. He highlights the role of AI in diagnosis, personalized treatments, and patient care, emphasizing the importance of maintaining the human touch in medicine.
5."The Robots Are Coming!: The Future of Jobs in the Age of Automation" by Andres Oppenheimer
In this book, Oppenheimer explores the impact of AI and automation on the job market. He offers insights into how individuals can adapt and thrive in an AI-driven economy, making it a must-read for anyone concerned about the future of work.
Must-Read AI Books for Tech Enthusiasts
1."Artificial Intelligence: A Guide to Intelligent Systems" by Michael Negnevitsky
This comprehensive guide covers a wide range of AI topics, including search algorithms, logic, machine learning, and data mining. It serves as a valuable resource for students and professionals interested in AI.
2."Rebooting AI: Building Artificial Intelligence We Can Trust" by Gary Marcus and Ernest Davis
Marcus and Davis critically examine the limitations of current AI systems and propose a roadmap for designing more robust and trustworthy AI. This book challenges the prevailing AI hype and provides a refreshing perspective.
3."Artificial Intelligence: Foundations of Computational Agents" by David L. Poole and Alan K. Mackworth
Aimed at undergraduate students, this book explores AI from a computational agent perspective. It covers topics such as knowledge representation, reasoning, planning, and learning, providing a solid foundation in AI principles.
4."AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World Order" by Kai-Fu Lee
In this book, Lee offers insights into the AI landscape in China and Silicon Valley. He discusses the potential implications of the AI race between these two powerhouses and its impact on global economics and politics.
5."Life 3.0: Being Human in the Age of Artificial Intelligence" by Max Tegmark
Tegmark explores the potential consequences of AI advancements and contemplates the future of humanity. This thought-provoking book raises important questions about our coexistence with AI and urges us to shape its development responsibly.
How to obtain Artifical Intelligence certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
As AI continues to shape our world, staying informed about the latest developments is crucial. The best artificial intelligence books to read in 2024 offer a wealth of knowledge and insights from experts in the field. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, business leader, or simply curious about AI, these books will provide valuable perspectives and expand your understanding of this rapidly evolving technology. So, grab a cup of coffee, immerse yourself in these captivating AI books, and ignite your intellectual curiosity!
Free eBook: Your Guide to CCBA and CBAP Certifications.
Are you considering a career in business analysis or looking to advance your existing business analysis skills? Look no further! In this article, we are thrilled to introduce our free eBook, the ultimate guide to the CCBA and CBAP certifications. Whether you are starting your journey as a business analyst or looking to enhance your professional growth, this eBook will provide you with valuable insights, study materials, and exam preparation strategies.
What are the CCBA and CBAP certifications?
The CCBA (Certification of Competency in Business Analysis) and CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional) certifications are internationally recognized professional certifications offered by the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA). Achieving these certifications showcases your expertise and commitment to the field of business analysis.
Why pursue professional certifications in business analysis?
Obtaining the CCBA or CBAP certifications can significantly elevate your career in business analysis. These certifications validate your knowledge of business analysis frameworks, industry standards, and best practices. They demonstrate your competence in requirements analysis, a critical skill in the field. Hiring managers and employers recognize and value these certifications, leading to enhanced career opportunities and increased earning potential.
What does the eBook offer?
Our comprehensive eBook serves as your one-stop resource for understanding, preparing, and successfully earning the CCBA and CBAP certifications. Here's what you can expect from this valuable guide:
1. Overview of the CCBA and CBAP Certifications
Explore the basics of the CCBA and CBAP certifications, understand their eligibility criteria, and gain insights into the application process.
2. Study Material and Exam Preparation Tips
Discover a curated list of study materials, recommended books, and online resources to aid in your exam preparation. Learn valuable tips and techniques to excel in the exams and boost your confidence.
3. Sample Questions and Practice Tests
Put your knowledge to the test with our collection of sample questions and practice tests. Get hands-on practice and assess your readiness for the actual certification exams.
4. Study Guide and Time Management Strategies
Navigate through the vast syllabus of the CCBA and CBAP certifications with our comprehensive study guide. Learn effective time management strategies to efficiently cover all the exam domains and ensure thorough preparation.
5. Insights from Certified Business Analysts
Gain inspiration from successful professionals who have achieved the CCBA and CBAP certifications. Learn from their experiences, tips, and advice to enhance your chances of success.
How will this eBook further your career?
The free eBook on the CCBA and CBAP certifications will not only equip you with the necessary knowledge to pass the exams but also empower you to advance your career in business analysis. Here's how:
1. Stay ahead with industry standards
The eBook dives deep into the business analysis frameworks and industry standards, ensuring that you are up to date with the latest practices. This knowledge will set you apart from your peers and establish you as a trusted expert in the field.
2. Expand your professional network
Through the insights provided in the eBook, you will gain access to a community of certified professionals. Networking with like-minded individuals can open doors to new opportunities, collaborations, and mentorship programs.
3. Boost your professional growth
By earning the CCBA or CBAP certifications, you demonstrate your commitment to continuous learning and professional development. This dedication to growth will attract employers and clients who value well-rounded individuals that can contribute to their organization's success.
How to obtain CCBA & CBAP Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
The CCBA and CBAP certifications offered by the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA) provide a significant boost to your career in business analysis. Our free eBook serves as an invaluable guide, providing you with all the necessary tools and resources to excel in the certification exams. Take the first step towards unlocking your potential and download our free eBook today. Start your journey towards a successful career in business analysis!
Read More
Are you considering a career in business analysis or looking to advance your existing business analysis skills? Look no further! In this article, we are thrilled to introduce our free eBook, the ultimate guide to the CCBA and CBAP certifications. Whether you are starting your journey as a business analyst or looking to enhance your professional growth, this eBook will provide you with valuable insights, study materials, and exam preparation strategies.
What are the CCBA and CBAP certifications?
The CCBA (Certification of Competency in Business Analysis) and CBAP (Certified Business Analysis Professional) certifications are internationally recognized professional certifications offered by the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA). Achieving these certifications showcases your expertise and commitment to the field of business analysis.
Why pursue professional certifications in business analysis?
Obtaining the CCBA or CBAP certifications can significantly elevate your career in business analysis. These certifications validate your knowledge of business analysis frameworks, industry standards, and best practices. They demonstrate your competence in requirements analysis, a critical skill in the field. Hiring managers and employers recognize and value these certifications, leading to enhanced career opportunities and increased earning potential.
What does the eBook offer?
Our comprehensive eBook serves as your one-stop resource for understanding, preparing, and successfully earning the CCBA and CBAP certifications. Here's what you can expect from this valuable guide:
1. Overview of the CCBA and CBAP Certifications
Explore the basics of the CCBA and CBAP certifications, understand their eligibility criteria, and gain insights into the application process.
2. Study Material and Exam Preparation Tips
Discover a curated list of study materials, recommended books, and online resources to aid in your exam preparation. Learn valuable tips and techniques to excel in the exams and boost your confidence.
3. Sample Questions and Practice Tests
Put your knowledge to the test with our collection of sample questions and practice tests. Get hands-on practice and assess your readiness for the actual certification exams.
4. Study Guide and Time Management Strategies
Navigate through the vast syllabus of the CCBA and CBAP certifications with our comprehensive study guide. Learn effective time management strategies to efficiently cover all the exam domains and ensure thorough preparation.
5. Insights from Certified Business Analysts
Gain inspiration from successful professionals who have achieved the CCBA and CBAP certifications. Learn from their experiences, tips, and advice to enhance your chances of success.
How will this eBook further your career?
The free eBook on the CCBA and CBAP certifications will not only equip you with the necessary knowledge to pass the exams but also empower you to advance your career in business analysis. Here's how:
1. Stay ahead with industry standards
The eBook dives deep into the business analysis frameworks and industry standards, ensuring that you are up to date with the latest practices. This knowledge will set you apart from your peers and establish you as a trusted expert in the field.
2. Expand your professional network
Through the insights provided in the eBook, you will gain access to a community of certified professionals. Networking with like-minded individuals can open doors to new opportunities, collaborations, and mentorship programs.
3. Boost your professional growth
By earning the CCBA or CBAP certifications, you demonstrate your commitment to continuous learning and professional development. This dedication to growth will attract employers and clients who value well-rounded individuals that can contribute to their organization's success.
How to obtain CCBA & CBAP Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
The CCBA and CBAP certifications offered by the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA) provide a significant boost to your career in business analysis. Our free eBook serves as an invaluable guide, providing you with all the necessary tools and resources to excel in the certification exams. Take the first step towards unlocking your potential and download our free eBook today. Start your journey towards a successful career in business analysis!
Threat Modeling Process and Methodologies: An Overview.
In the world of software security, threat modeling plays a crucial role in identifying and mitigating potential risks and vulnerabilities. It is a structured approach used to evaluate and prioritize security concerns, ultimately leading to the development of more secure software systems. This article will provide an in-depth understanding of threat modeling, its process, methodologies, and its significance in secure software development.
What is Threat Modeling?
Threat modeling is a proactive approach that helps organizations identify and understand potential security threats and vulnerabilities before they manifest into actual attacks. It involves a systematic analysis and risk assessment of software systems, identifying potential threats, and developing appropriate security controls. The goal is to design a secure architecture by considering potential attack vectors and minimizing the attack surface.
The Threat Modeling Process
The threat modeling process comprises several key steps that help in the identification and mitigation of security risks. Let's take a look at each step in detail:
Step 1: Define the scope: Define the boundaries and objectives of the threat modeling exercise. Identify the components and interactions that need to be assessed for security vulnerabilities.
Step 2: Create an architectural overview: Develop a high-level architectural diagram indicating the structure of the software system. This helps in visualizing the attack surface and understanding potential entry points for attackers.
Step 3: Identify and classify threats: Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities that could exploit the system. Classify the threats based on their severity and impact on the overall security of the system.
Step 4: Assess security controls: Evaluate the existing security controls and analyze their effectiveness in mitigating identified threats. Identify gaps and areas where additional controls may be required.
Step 5: Conduct a security analysis: Perform a detailed analysis of potential security risks associated with each identified threat. Consider factors such as likelihood of exploitation, impact, and potential mitigations.
Step 6: Prioritize and remediate: Prioritize the identified threats based on their severity and potential impact. Develop mitigation strategies and implement necessary security measures to reduce the likelihood and impact of attacks.
Step 7: Iterate and update: Regularly review and update the threat model as the software system evolves and new threats emerge. Stay proactive in addressing security concerns throughout the software development lifecycle.
Threat Modeling Methodologies
Various methodologies can be employed during the threat modeling process. Let's explore some widely used methodologies:
STRIDE: This methodology focuses on identifying threats based on six main categories: Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, Information Disclosure, Denial of Service, and Elevation of Privilege. By considering these categories, potential threats can be comprehensively analyzed.
DREAD: The DREAD methodology evaluates threats based on the following factors: Damage potential, Reproducibility, Exploitability, Affected users, and Discoverability. This framework helps in prioritizing threats based on their overall risk score.
PASTA: The Process for Attack Simulation and Threat Analysis (PASTA) methodology provides a risk-centric threat modeling approach. It involves a systematic analysis of threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts, followed by mapping them to business objectives for effective risk management.
The Role of Threat Modeling in Secure Software Development
Threat modeling is an integral part of secure software development. By proactively identifying and mitigating potential security risks, organizations can build more robust and resilient software systems. Let's dive into some key benefits of incorporating threat modeling:
Reduced risk exposure: Threat modeling helps in reducing the attack surface and minimizing security vulnerabilities. By implementing appropriate security controls, organizations can decrease their risk exposure to potential attacks.
Cost-effective security measures: By identifying threats early in the software development lifecycle, organizations can avoid costly security breaches. Implementing security measures during the design phase is more efficient and cost-effective than addressing vulnerabilities at a later stage.
Improved security awareness: During the threat modeling process, stakeholders gain a deeper understanding of potential risks and security concerns. This creates a culture of security awareness throughout the organization, leading to more secure software development practices.
The Importance of Using Threat Modeling Tools
Threat modeling tools can significantly streamline the threat modeling process by providing a structured approach and automating certain tasks. These tools offer features such as diagramming capabilities, threat libraries, and risk scoring mechanisms. Some popular threat modeling tools include Microsoft Threat Modeling Tool, OWASP Threat Dragon, and ThreatModeler.
Best Practices for Effective Threat Modeling
To ensure the success of threat modeling exercises, organizations should adhere to certain best practices:
Involve all stakeholders: Include representatives from different teams, such as developers, architects, and security professionals, to gather diverse perspectives and ensure comprehensive threat identification.
Integrate threat modeling early: Incorporate threat modeling into the software development lifecycle from the initial design phase. This ensures that security considerations are embedded right from the beginning.
Stay updated: Regularly update the threat model as new threats emerge, and software systems evolve. Keep track of the latest security vulnerabilities and incorporate them into the threat modeling process.
Collaborate and communicate: Foster open communication and collaboration among stakeholders involved in the threat modeling exercise. This helps in sharing knowledge, addressing concerns, and aligning security objectives.
Document and review: Document the threat modeling process, including identified threats, mitigation strategies, and implemented controls. Regularly review and update the documentation to maintain a comprehensive understanding of the software system's security landscape.
How to obtain Cyber Security certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Threat modeling is an essential component of software security, allowing organizations to proactively identify and mitigate potential risks and vulnerabilities. By following a structured threat modeling process, employing appropriate methodologies, and utilizing threat modeling tools, organizations can enhance their security posture and build more resilient software systems. Implementing threat modeling as an integral part of the secure software development lifecycle is crucial to ensure the protection of sensitive data and the trust of users.
Read More
In the world of software security, threat modeling plays a crucial role in identifying and mitigating potential risks and vulnerabilities. It is a structured approach used to evaluate and prioritize security concerns, ultimately leading to the development of more secure software systems. This article will provide an in-depth understanding of threat modeling, its process, methodologies, and its significance in secure software development.
What is Threat Modeling?
Threat modeling is a proactive approach that helps organizations identify and understand potential security threats and vulnerabilities before they manifest into actual attacks. It involves a systematic analysis and risk assessment of software systems, identifying potential threats, and developing appropriate security controls. The goal is to design a secure architecture by considering potential attack vectors and minimizing the attack surface.
The Threat Modeling Process
The threat modeling process comprises several key steps that help in the identification and mitigation of security risks. Let's take a look at each step in detail:
Step 1: Define the scope: Define the boundaries and objectives of the threat modeling exercise. Identify the components and interactions that need to be assessed for security vulnerabilities.
Step 2: Create an architectural overview: Develop a high-level architectural diagram indicating the structure of the software system. This helps in visualizing the attack surface and understanding potential entry points for attackers.
Step 3: Identify and classify threats: Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities that could exploit the system. Classify the threats based on their severity and impact on the overall security of the system.
Step 4: Assess security controls: Evaluate the existing security controls and analyze their effectiveness in mitigating identified threats. Identify gaps and areas where additional controls may be required.
Step 5: Conduct a security analysis: Perform a detailed analysis of potential security risks associated with each identified threat. Consider factors such as likelihood of exploitation, impact, and potential mitigations.
Step 6: Prioritize and remediate: Prioritize the identified threats based on their severity and potential impact. Develop mitigation strategies and implement necessary security measures to reduce the likelihood and impact of attacks.
Step 7: Iterate and update: Regularly review and update the threat model as the software system evolves and new threats emerge. Stay proactive in addressing security concerns throughout the software development lifecycle.
Threat Modeling Methodologies
Various methodologies can be employed during the threat modeling process. Let's explore some widely used methodologies:
STRIDE: This methodology focuses on identifying threats based on six main categories: Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, Information Disclosure, Denial of Service, and Elevation of Privilege. By considering these categories, potential threats can be comprehensively analyzed.
DREAD: The DREAD methodology evaluates threats based on the following factors: Damage potential, Reproducibility, Exploitability, Affected users, and Discoverability. This framework helps in prioritizing threats based on their overall risk score.
PASTA: The Process for Attack Simulation and Threat Analysis (PASTA) methodology provides a risk-centric threat modeling approach. It involves a systematic analysis of threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts, followed by mapping them to business objectives for effective risk management.
The Role of Threat Modeling in Secure Software Development
Threat modeling is an integral part of secure software development. By proactively identifying and mitigating potential security risks, organizations can build more robust and resilient software systems. Let's dive into some key benefits of incorporating threat modeling:
Reduced risk exposure: Threat modeling helps in reducing the attack surface and minimizing security vulnerabilities. By implementing appropriate security controls, organizations can decrease their risk exposure to potential attacks.
Cost-effective security measures: By identifying threats early in the software development lifecycle, organizations can avoid costly security breaches. Implementing security measures during the design phase is more efficient and cost-effective than addressing vulnerabilities at a later stage.
Improved security awareness: During the threat modeling process, stakeholders gain a deeper understanding of potential risks and security concerns. This creates a culture of security awareness throughout the organization, leading to more secure software development practices.
The Importance of Using Threat Modeling Tools
Threat modeling tools can significantly streamline the threat modeling process by providing a structured approach and automating certain tasks. These tools offer features such as diagramming capabilities, threat libraries, and risk scoring mechanisms. Some popular threat modeling tools include Microsoft Threat Modeling Tool, OWASP Threat Dragon, and ThreatModeler.
Best Practices for Effective Threat Modeling
To ensure the success of threat modeling exercises, organizations should adhere to certain best practices:
Involve all stakeholders: Include representatives from different teams, such as developers, architects, and security professionals, to gather diverse perspectives and ensure comprehensive threat identification.
Integrate threat modeling early: Incorporate threat modeling into the software development lifecycle from the initial design phase. This ensures that security considerations are embedded right from the beginning.
Stay updated: Regularly update the threat model as new threats emerge, and software systems evolve. Keep track of the latest security vulnerabilities and incorporate them into the threat modeling process.
Collaborate and communicate: Foster open communication and collaboration among stakeholders involved in the threat modeling exercise. This helps in sharing knowledge, addressing concerns, and aligning security objectives.
Document and review: Document the threat modeling process, including identified threats, mitigation strategies, and implemented controls. Regularly review and update the documentation to maintain a comprehensive understanding of the software system's security landscape.
How to obtain Cyber Security certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Threat modeling is an essential component of software security, allowing organizations to proactively identify and mitigate potential risks and vulnerabilities. By following a structured threat modeling process, employing appropriate methodologies, and utilizing threat modeling tools, organizations can enhance their security posture and build more resilient software systems. Implementing threat modeling as an integral part of the secure software development lifecycle is crucial to ensure the protection of sensitive data and the trust of users.
20 Data Science Tools That Will Change the Game in 2024
Are you ready to explore the future of data science? In this article, we will delve into the world of data science tools that are set to revolutionize the field in 2024. With advancements in technology and the growing demand for data analytics, predictive modeling, machine learning, artificial intelligence, data visualization, data mining, and statistical analysis, these tools are poised to take data science to new heights. Let's dive in and discover the game-changing tools that will shape the future of data science.
Data Science Tools: Empowering the Future
Data science tools play a pivotal role in transforming raw data into valuable insights. With the rapid growth of data, businesses and organizations are seeking innovative tools that can efficiently analyze and interpret this vast amount of information. Here are 20 cutting-edge data science tools that will change the game in 2024:
-
Python: As one of the most popular programming languages for data science, Python offers a wide range of libraries and frameworks, such as Pandas and NumPy, that simplify data analysis and manipulation.
-
R: R is another powerful programming language widely used for statistical computing and graphics. It provides numerous packages for data visualization and statistical modeling, making it a go-to tool for data scientists.
-
Tableau: Tableau is a leading data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive and visually appealing dashboards. With its intuitive drag-and-drop interface, Tableau enables businesses to explore their data and gain valuable insights effortlessly.
-
TensorFlow: Developed by Google, TensorFlow is a popular open-source library for machine learning. It helps data scientists build and deploy machine learning models, making it easier to create advanced AI-powered applications.
-
PyTorch: PyTorch is another open-source machine learning library garnering significant attention in the data science community. With its dynamic computation graph and easy-to-use APIs, PyTorch simplifies the process of building and training deep learning models.
-
Hadoop: Hadoop is a distributed processing framework that allows data scientists to store and process large datasets across clusters of computers. With its scalability and fault tolerance, Hadoop is ideal for handling big data analytics.
-
Spark: Apache Spark is a fast and general-purpose cluster computing system that provides an interface for programming entire clusters. It is highly efficient for processing large-scale datasets and performing complex analytics tasks.
-
KNIME: KNIME is an open-source data analytics platform that allows users to visually create data workflows. With its extensive range of nodes, KNIME simplifies the data preparation and analysis process, empowering data scientists to perform complex tasks without coding.
-
Jupyter Notebook: Jupyter Notebook is an interactive web-based tool that enables users to create and share documents containing live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text. It is a versatile tool for data exploration, prototyping, and sharing insights.
-
SAS: SAS is a powerful software suite that offers a wide range of data management, analytics, and business intelligence capabilities. With its robust statistical analysis tools, SAS helps organizations make data-driven decisions.
-
Alteryx: Alteryx is a self-service data analytics platform that provides a drag-and-drop interface for data preparation and blending. It enables data scientists to streamline the data preparation process and deliver actionable insights faster.
-
Databricks: Databricks is a unified analytics platform that combines data engineering, data science, and business analytics. It offers collaborative workspace, automated data pipeline, and advanced analytics capabilities, accelerating time-to-insight.
-
IBM Watson Studio: IBM Watson Studio is an integrated environment that enables data scientists to build AI models with ease. It provides tools for data preparation, model building, and deployment, making it a comprehensive platform for AI development.
-
Microsoft Azure Machine Learning: Azure Machine Learning is a cloud-based service that simplifies machine learning model development and deployment. With its easy-to-use interface and scalability, it empowers data scientists to leverage the power of the cloud for their projects.
-
Keras: Keras is a deep learning framework that provides a user-friendly interface for building neural networks. It abstracts the complexities of underlying frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, making deep learning more accessible to data scientists.
-
Apache Flink: Apache Flink is a powerful open-source stream processing framework for distributed, high-performance, and fault-tolerant data processing. It excels in handling real-time data analytics and advanced event-driven applications.
-
Microsoft Power BI: Power BI is a business analytics service that delivers interactive visualizations and business intelligence capabilities. With its easy-to-use interface and powerful analytics tools, it enables users to explore data and share insights effortlessly.
-
Google BigQuery: BigQuery is a fully-managed, serverless data warehouse that provides fast and scalable analytics on large datasets. With its powerful querying engine and seamless integration with other Google Cloud services, it simplifies the data analysis process.
-
DataRobot: DataRobot is an automated machine learning platform that helps data scientists build accurate predictive models. It automates the entire machine learning workflow, from data preprocessing to model selection, enabling organizations to leverage AI without extensive expertise.
-
D3.js: D3.js is a JavaScript library for creating data-driven documents. It enables data scientists to build dynamic and interactive data visualizations on the web. With its extensive range of visualization options, D3.js empowers users to convey complex insights effectively.
How to obtain Data Science certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
As we move towards the future, data science will continue to shape various industries, driving innovation and growth. The tools mentioned above represent the cutting edge of data science technologies that are set to change the game in 2024. From data exploration and analysis to machine learning and artificial intelligence, these tools provide the foundation for businesses and organizations to unlock the true potential of their data. Embrace these game-changing tools and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of data science.
Read More
Are you ready to explore the future of data science? In this article, we will delve into the world of data science tools that are set to revolutionize the field in 2024. With advancements in technology and the growing demand for data analytics, predictive modeling, machine learning, artificial intelligence, data visualization, data mining, and statistical analysis, these tools are poised to take data science to new heights. Let's dive in and discover the game-changing tools that will shape the future of data science.
Data Science Tools: Empowering the Future
Data science tools play a pivotal role in transforming raw data into valuable insights. With the rapid growth of data, businesses and organizations are seeking innovative tools that can efficiently analyze and interpret this vast amount of information. Here are 20 cutting-edge data science tools that will change the game in 2024:
-
Python: As one of the most popular programming languages for data science, Python offers a wide range of libraries and frameworks, such as Pandas and NumPy, that simplify data analysis and manipulation.
-
R: R is another powerful programming language widely used for statistical computing and graphics. It provides numerous packages for data visualization and statistical modeling, making it a go-to tool for data scientists.
-
Tableau: Tableau is a leading data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive and visually appealing dashboards. With its intuitive drag-and-drop interface, Tableau enables businesses to explore their data and gain valuable insights effortlessly.
-
TensorFlow: Developed by Google, TensorFlow is a popular open-source library for machine learning. It helps data scientists build and deploy machine learning models, making it easier to create advanced AI-powered applications.
-
PyTorch: PyTorch is another open-source machine learning library garnering significant attention in the data science community. With its dynamic computation graph and easy-to-use APIs, PyTorch simplifies the process of building and training deep learning models.
-
Hadoop: Hadoop is a distributed processing framework that allows data scientists to store and process large datasets across clusters of computers. With its scalability and fault tolerance, Hadoop is ideal for handling big data analytics.
-
Spark: Apache Spark is a fast and general-purpose cluster computing system that provides an interface for programming entire clusters. It is highly efficient for processing large-scale datasets and performing complex analytics tasks.
-
KNIME: KNIME is an open-source data analytics platform that allows users to visually create data workflows. With its extensive range of nodes, KNIME simplifies the data preparation and analysis process, empowering data scientists to perform complex tasks without coding.
-
Jupyter Notebook: Jupyter Notebook is an interactive web-based tool that enables users to create and share documents containing live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text. It is a versatile tool for data exploration, prototyping, and sharing insights.
-
SAS: SAS is a powerful software suite that offers a wide range of data management, analytics, and business intelligence capabilities. With its robust statistical analysis tools, SAS helps organizations make data-driven decisions.
-
Alteryx: Alteryx is a self-service data analytics platform that provides a drag-and-drop interface for data preparation and blending. It enables data scientists to streamline the data preparation process and deliver actionable insights faster.
-
Databricks: Databricks is a unified analytics platform that combines data engineering, data science, and business analytics. It offers collaborative workspace, automated data pipeline, and advanced analytics capabilities, accelerating time-to-insight.
-
IBM Watson Studio: IBM Watson Studio is an integrated environment that enables data scientists to build AI models with ease. It provides tools for data preparation, model building, and deployment, making it a comprehensive platform for AI development.
-
Microsoft Azure Machine Learning: Azure Machine Learning is a cloud-based service that simplifies machine learning model development and deployment. With its easy-to-use interface and scalability, it empowers data scientists to leverage the power of the cloud for their projects.
-
Keras: Keras is a deep learning framework that provides a user-friendly interface for building neural networks. It abstracts the complexities of underlying frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, making deep learning more accessible to data scientists.
-
Apache Flink: Apache Flink is a powerful open-source stream processing framework for distributed, high-performance, and fault-tolerant data processing. It excels in handling real-time data analytics and advanced event-driven applications.
-
Microsoft Power BI: Power BI is a business analytics service that delivers interactive visualizations and business intelligence capabilities. With its easy-to-use interface and powerful analytics tools, it enables users to explore data and share insights effortlessly.
-
Google BigQuery: BigQuery is a fully-managed, serverless data warehouse that provides fast and scalable analytics on large datasets. With its powerful querying engine and seamless integration with other Google Cloud services, it simplifies the data analysis process.
-
DataRobot: DataRobot is an automated machine learning platform that helps data scientists build accurate predictive models. It automates the entire machine learning workflow, from data preprocessing to model selection, enabling organizations to leverage AI without extensive expertise.
-
D3.js: D3.js is a JavaScript library for creating data-driven documents. It enables data scientists to build dynamic and interactive data visualizations on the web. With its extensive range of visualization options, D3.js empowers users to convey complex insights effectively.
How to obtain Data Science certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
As we move towards the future, data science will continue to shape various industries, driving innovation and growth. The tools mentioned above represent the cutting edge of data science technologies that are set to change the game in 2024. From data exploration and analysis to machine learning and artificial intelligence, these tools provide the foundation for businesses and organizations to unlock the true potential of their data. Embrace these game-changing tools and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of data science.
Top 20 Power BI Interview Questions & Answers for 2024.
Are you preparing for a Power BI interview? As the demand for skilled Power BI professionals continues to grow, it is essential to be well-prepared for interviews to stand out from the competition. In this article, we have compiled a list of the top 40 Power BI interview questions and answers for 2024 that will help you showcase your expertise and secure your dream job.
Power BI Interview Questions and Answers
1. What is Power BI?
Power BI is a business analytics tool developed by Microsoft that allows users to analyze data and share insights. It provides interactive visualizations and business intelligence capabilities with an interface that is easy to use.
2. Mention the types of connections in Power BI.
Power BI supports three types of connections:
-
DirectQuery
-
Import
-
Live Connection
3. What is the difference between DirectQuery and Import connection mode?
In DirectQuery mode, Power BI connects directly to the data source and queries data in real-time. On the other hand, in Import mode, data is loaded into Power BI's internal data model, which allows for faster analysis and visualization but may have limitations on real-time data updates.
4. What are calculated columns in Power BI?
Calculated columns are columns created in Power BI using DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) formulas. These columns are calculated during the data loading process and can be used in visualizations and calculations.
5. How is Power BI different from traditional reporting tools?
Traditional reporting tools provide static reports, whereas Power BI offers interactive visualizations and real-time data analysis capabilities. Power BI also allows users to connect to various data sources, transform and clean data, and create dynamic dashboards.
6. What are the benefits of using Power BI?
Some of the benefits of using Power BI include:
-
Real-time data analysis
-
Interactive visualizations
-
Easy integration with various data sources
-
Collaboration and sharing options
-
Natural language querying
-
Mobile accessibility
7. How can you secure sensitive data in Power BI?
Power BI provides various security measures to protect sensitive data, such as:
-
Role-based access control
-
Row-level security
-
Data encryption
-
Active Directory integration
8. How can you optimize the performance of a Power BI report?
To optimize the performance of a Power BI report, you can:
-
Reduce the number of visuals on a single page
-
Minimize the use of calculated columns and measures
-
Use incremental refresh for large datasets
-
Apply filters and slicers to limit the data being loaded
9. How can you create relationships between multiple tables in Power BI?
You can create relationships between tables in Power BI by selecting the related columns in each table and defining the relationship type (one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many).
10. What is the Power BI Gateway?
The Power BI Gateway is a bridge that allows Power BI to connect with on-premises data sources. It enables data refresh and provides a secure connection between Power BI and the on-premises data.
11. What is DAX in Power BI?
DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) is a formula language used in Power BI to create custom calculations and aggregations. It is used to define calculated columns, measures, and calculated tables.
12. How can you create a measure in Power BI?
To create a measure in Power BI, you can use the "New Measure" option in the "Modeling" tab. You can then write a DAX formula to define the measure based on your calculation requirements.
13. Explain the concept of drill-through in Power BI.
Drill-through is a feature in Power BI that allows users to drill down from one report page to another, focusing on specific details. It provides a guided navigational experience for data analysis.
14. How can you publish a Power BI report?
To publish a Power BI report, you can use the "Publish" option in the Power BI Desktop. This allows you to save the report to the Power BI service, where you can share it with others.
15. How can you schedule data refresh in Power BI?
You can schedule data refresh in Power BI by configuring the refresh settings for each dataset in the Power BI service. This ensures that the data is updated at regular intervals.
16. What is a dashboard in Power BI?
A dashboard in Power BI is a collection of visualizations, reports, and data that provides a consolidated view of key business metrics. It allows users to monitor and analyze data from various sources in a single view.
17. How can you share a Power BI report with external stakeholders?
You can share a Power BI report with external stakeholders by publishing it to the web or by creating a Power BI app. Publishing to the web allows anyone with the link to access the report, while creating an app provides more control over access and permissions.
18. What is Power Query in Power BI?
Power Query is a data transformation and cleansing tool in Power BI that allows users to connect, combine, and shape data from various sources. It provides a user-friendly interface for data preparation.
19. How can you create a calculated table in Power BI?
To create a calculated table in Power BI, you can use the "New Table" option in the "Modeling" tab. You can then write a DAX formula to define the table based on your calculation requirements.
20. What are the limitations of Power BI?
Some of the limitations of Power BI include:
-
Limited support for large datasets
-
Limited data transformation capabilities
-
Limited support for complex data models
How to obtain Power BI certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Preparing for a Power BI interview can be challenging, but with the right set of questions and answers, you can showcase your skills and knowledge confidently. We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights and helped you in your interview preparation. Remember to practice answering these questions and customize your responses based on your own experiences. Good luck with your interview!
Read More
Are you preparing for a Power BI interview? As the demand for skilled Power BI professionals continues to grow, it is essential to be well-prepared for interviews to stand out from the competition. In this article, we have compiled a list of the top 40 Power BI interview questions and answers for 2024 that will help you showcase your expertise and secure your dream job.
Power BI Interview Questions and Answers
1. What is Power BI?
Power BI is a business analytics tool developed by Microsoft that allows users to analyze data and share insights. It provides interactive visualizations and business intelligence capabilities with an interface that is easy to use.
2. Mention the types of connections in Power BI.
Power BI supports three types of connections:
-
DirectQuery
-
Import
-
Live Connection
3. What is the difference between DirectQuery and Import connection mode?
In DirectQuery mode, Power BI connects directly to the data source and queries data in real-time. On the other hand, in Import mode, data is loaded into Power BI's internal data model, which allows for faster analysis and visualization but may have limitations on real-time data updates.
4. What are calculated columns in Power BI?
Calculated columns are columns created in Power BI using DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) formulas. These columns are calculated during the data loading process and can be used in visualizations and calculations.
5. How is Power BI different from traditional reporting tools?
Traditional reporting tools provide static reports, whereas Power BI offers interactive visualizations and real-time data analysis capabilities. Power BI also allows users to connect to various data sources, transform and clean data, and create dynamic dashboards.
6. What are the benefits of using Power BI?
Some of the benefits of using Power BI include:
-
Real-time data analysis
-
Interactive visualizations
-
Easy integration with various data sources
-
Collaboration and sharing options
-
Natural language querying
-
Mobile accessibility
7. How can you secure sensitive data in Power BI?
Power BI provides various security measures to protect sensitive data, such as:
-
Role-based access control
-
Row-level security
-
Data encryption
-
Active Directory integration
8. How can you optimize the performance of a Power BI report?
To optimize the performance of a Power BI report, you can:
-
Reduce the number of visuals on a single page
-
Minimize the use of calculated columns and measures
-
Use incremental refresh for large datasets
-
Apply filters and slicers to limit the data being loaded
9. How can you create relationships between multiple tables in Power BI?
You can create relationships between tables in Power BI by selecting the related columns in each table and defining the relationship type (one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many).
10. What is the Power BI Gateway?
The Power BI Gateway is a bridge that allows Power BI to connect with on-premises data sources. It enables data refresh and provides a secure connection between Power BI and the on-premises data.
11. What is DAX in Power BI?
DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) is a formula language used in Power BI to create custom calculations and aggregations. It is used to define calculated columns, measures, and calculated tables.
12. How can you create a measure in Power BI?
To create a measure in Power BI, you can use the "New Measure" option in the "Modeling" tab. You can then write a DAX formula to define the measure based on your calculation requirements.
13. Explain the concept of drill-through in Power BI.
Drill-through is a feature in Power BI that allows users to drill down from one report page to another, focusing on specific details. It provides a guided navigational experience for data analysis.
14. How can you publish a Power BI report?
To publish a Power BI report, you can use the "Publish" option in the Power BI Desktop. This allows you to save the report to the Power BI service, where you can share it with others.
15. How can you schedule data refresh in Power BI?
You can schedule data refresh in Power BI by configuring the refresh settings for each dataset in the Power BI service. This ensures that the data is updated at regular intervals.
16. What is a dashboard in Power BI?
A dashboard in Power BI is a collection of visualizations, reports, and data that provides a consolidated view of key business metrics. It allows users to monitor and analyze data from various sources in a single view.
17. How can you share a Power BI report with external stakeholders?
You can share a Power BI report with external stakeholders by publishing it to the web or by creating a Power BI app. Publishing to the web allows anyone with the link to access the report, while creating an app provides more control over access and permissions.
18. What is Power Query in Power BI?
Power Query is a data transformation and cleansing tool in Power BI that allows users to connect, combine, and shape data from various sources. It provides a user-friendly interface for data preparation.
19. How can you create a calculated table in Power BI?
To create a calculated table in Power BI, you can use the "New Table" option in the "Modeling" tab. You can then write a DAX formula to define the table based on your calculation requirements.
20. What are the limitations of Power BI?
Some of the limitations of Power BI include:
-
Limited support for large datasets
-
Limited data transformation capabilities
-
Limited support for complex data models
How to obtain Power BI certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Preparing for a Power BI interview can be challenging, but with the right set of questions and answers, you can showcase your skills and knowledge confidently. We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights and helped you in your interview preparation. Remember to practice answering these questions and customize your responses based on your own experiences. Good luck with your interview!
Oracle Gaining Market Share in Cloud and A.I. Solutions.
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the utilization of cloud services and artificial intelligence (A.I.) is becoming increasingly essential for businesses seeking a competitive edge. Oracle, a global leader in enterprise software and database solutions, has been making significant strides in gaining market share in both the cloud and A.I. domains. This article explores Oracle's cloud services, examines the current cloud market trends, discusses the role of artificial intelligence in technology, and highlights Oracle's remarkable market share growth.
Oracle Cloud Services: Empowering Businesses
Oracle's cloud services provide businesses with a robust and secure platform for managing their data, applications, and infrastructure. With a wide range of services including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS), Oracle offers scalable and flexible solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of different industries.
One of the key advantages of Oracle's cloud services is its ability to seamlessly integrate with existing on-premises systems, ensuring a smooth migration to the cloud. This enables businesses to leverage the power of the cloud without disrupting their established workflows. Moreover, Oracle's cloud services provide enhanced security features, ensuring the protection of critical business data in an increasingly interconnected world.
Cloud Market Trends: The Rise of Oracle
The cloud market has been experiencing exponential growth in recent years, with organizations of all sizes recognizing the benefits of cloud computing. Oracle is well-positioned to capitalize on this trend, as demonstrated by its impressive market share growth.
As businesses increasingly shift their operations to the cloud, Oracle has managed to carve out a significant presence by offering a comprehensive suite of cloud services that address diverse business needs. From large enterprises to small and medium-sized businesses, Oracle's cloud offerings deliver cost-effective solutions that drive efficiency andinnovation.
The demand for cloud services is driven by numerous factors, including the need for scalability, agility, and accessibility. With Oracle's cloud services, businesses can scale their infrastructure on-demand, rapidly respond to market changes, and access their data and applications from any location, empowering them to stay competitive in today's fast-paced digital landscape.
Harnessing the Power of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence has emerged as a transformative force across various industries, revolutionizing the way businesses analyze data, make decisions, and automate processes. Oracle has recognized the immense potential of A.I. and has been incorporating it into its products and services to deliver added value to customers.
Oracle's A.I.-powered applications leverage machine learning algorithms and advanced analytics to unlock actionable insights from vast amounts of data. This enables businesses to make data-driven decisions, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer experiences. Whether it's predictive analytics, intelligent chatbots, or automated business processes, Oracle's A.I. offerings empower businesses to harness the power of technology and drive innovation.
Oracle's Market Share Growth: A Testament to Success
Oracle's relentless pursuit of excellence and innovation has been reflected in its remarkable market share growth. The company's strategic investments in cloud infrastructure and artificial intelligence have paid off, as evidenced by its expanding customer base and strong financial performance.
By continuously enhancing its cloud services and integrating cutting-edge A.I. technologies, Oracle has solidified its position as a trusted partner for businesses seeking advanced and secure solutions. With a customer-centric approach and an unwavering commitment to excellence, Oracle is well-positioned to continue gaining market share in the cloud and A.I. domains.
How to obtain A.I Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
As businesses strive to thrive in an increasingly digital world, the adoption of cloud services and artificial intelligence has become essential. Oracle's cloud services provide businesses with a secure and scalable platform, enabling them to leverage the power of the cloud. Moreover, Oracle's investment in artificial intelligence has resulted in innovative solutions that empower businesses to derive actionable insights and drive efficiency. With its remarkable market share growth, Oracle has established itself as a leader in the cloud and A.I. domains, demonstrating its experience, expertise, authority, and trust.
Read More
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the utilization of cloud services and artificial intelligence (A.I.) is becoming increasingly essential for businesses seeking a competitive edge. Oracle, a global leader in enterprise software and database solutions, has been making significant strides in gaining market share in both the cloud and A.I. domains. This article explores Oracle's cloud services, examines the current cloud market trends, discusses the role of artificial intelligence in technology, and highlights Oracle's remarkable market share growth.
Oracle Cloud Services: Empowering Businesses
Oracle's cloud services provide businesses with a robust and secure platform for managing their data, applications, and infrastructure. With a wide range of services including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS), Oracle offers scalable and flexible solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of different industries.
One of the key advantages of Oracle's cloud services is its ability to seamlessly integrate with existing on-premises systems, ensuring a smooth migration to the cloud. This enables businesses to leverage the power of the cloud without disrupting their established workflows. Moreover, Oracle's cloud services provide enhanced security features, ensuring the protection of critical business data in an increasingly interconnected world.
Cloud Market Trends: The Rise of Oracle
The cloud market has been experiencing exponential growth in recent years, with organizations of all sizes recognizing the benefits of cloud computing. Oracle is well-positioned to capitalize on this trend, as demonstrated by its impressive market share growth.
As businesses increasingly shift their operations to the cloud, Oracle has managed to carve out a significant presence by offering a comprehensive suite of cloud services that address diverse business needs. From large enterprises to small and medium-sized businesses, Oracle's cloud offerings deliver cost-effective solutions that drive efficiency andinnovation.
The demand for cloud services is driven by numerous factors, including the need for scalability, agility, and accessibility. With Oracle's cloud services, businesses can scale their infrastructure on-demand, rapidly respond to market changes, and access their data and applications from any location, empowering them to stay competitive in today's fast-paced digital landscape.
Harnessing the Power of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence has emerged as a transformative force across various industries, revolutionizing the way businesses analyze data, make decisions, and automate processes. Oracle has recognized the immense potential of A.I. and has been incorporating it into its products and services to deliver added value to customers.
Oracle's A.I.-powered applications leverage machine learning algorithms and advanced analytics to unlock actionable insights from vast amounts of data. This enables businesses to make data-driven decisions, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer experiences. Whether it's predictive analytics, intelligent chatbots, or automated business processes, Oracle's A.I. offerings empower businesses to harness the power of technology and drive innovation.
Oracle's Market Share Growth: A Testament to Success
Oracle's relentless pursuit of excellence and innovation has been reflected in its remarkable market share growth. The company's strategic investments in cloud infrastructure and artificial intelligence have paid off, as evidenced by its expanding customer base and strong financial performance.
By continuously enhancing its cloud services and integrating cutting-edge A.I. technologies, Oracle has solidified its position as a trusted partner for businesses seeking advanced and secure solutions. With a customer-centric approach and an unwavering commitment to excellence, Oracle is well-positioned to continue gaining market share in the cloud and A.I. domains.
How to obtain A.I Certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
As businesses strive to thrive in an increasingly digital world, the adoption of cloud services and artificial intelligence has become essential. Oracle's cloud services provide businesses with a secure and scalable platform, enabling them to leverage the power of the cloud. Moreover, Oracle's investment in artificial intelligence has resulted in innovative solutions that empower businesses to derive actionable insights and drive efficiency. With its remarkable market share growth, Oracle has established itself as a leader in the cloud and A.I. domains, demonstrating its experience, expertise, authority, and trust.
Cybersecurity Predictions for 2024: 5 Trends to Watch!!
In an era dominated by rapidly evolving technological landscapes, the realm of cybersecurity stands as an ever-vigilant guardian against the escalating threats in the digital domain. As we usher in 2024, the spotlight on cybersecurity intensifies, prompting a keen examination of the forthcoming trends that will shape the landscape of digital defense. This exploration navigates through the intricate web of cyber threats, with a focus on the role of cyber security companies, the dynamic world of cyber threat intelligence, and the pivotal contributions of institutions like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).
In this insightful journey, we will delve into the nuances of cyber security online, exploring the strategies employed by top cyber security companies to safeguard individuals, businesses, and governments alike. A particular emphasis will be placed on the ever-expanding sphere of cloud computing security, considering its integral role in the contemporary digital infrastructure.
As we embark on this exploration, we cannot overlook the influence of tech giants like Google on the cyber security landscape. With a specific focus on Google Cyber Security initiatives, we will analyze their contributions to fortifying online defenses and shaping the trajectory of cyber resilience.
Join us in uncovering the Cyber security Predictions for 2024, where five key trends will be meticulously examined, offering invaluable insights into the future of digital defense. In a world where information is both power and vulnerability, understanding and anticipating these trends is essential for staying one step ahead in the ever-evolving battle against cyber threats.
Table of contents
-
AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity: Advancements and Challenges
-
Emergence of Quantum-Safe Cryptography: A Paradigm Shift in Security
-
Rise of Zero Trust Architecture: Shifting Security Perimeters
-
Securing the Cloud: Evolving Strategies in Cloud Computing Security
-
Cybersecurity Workforce Development: Bridging the Skills Gap
-
Conclusion
AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity: Advancements and Challenges
In the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) stands as a transformative force, promising advancements in threat detection, response, and mitigation. As we delve into the realm of 2024, the role of AI and ML in cyber security becomes increasingly pivotal. These technologies enable the analysis of vast datasets at speeds unattainable by traditional methods, allowing for real-time identification of anomalous activities and potential threats. Moreover, AI-driven solutions contribute to the automation of routine tasks, freeing up cybersecurity professionals to focus on more complex and strategic aspects of defense. However, this integration is not without its challenges. The evolving nature of cyber threats demands constant adaptation, and adversaries are quick to exploit any vulnerabilities in AI and ML systems. Moreover, ethical considerations, interpretability of AI-driven decisions, and the potential for adversarial attacks pose significant challenges. As organizations embrace AI and ML as key components of their cybersecurity arsenal, a delicate balance must be struck between harnessing the power of these technologies and addressing the inherent complexities and risks they bring to the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Emergence of Quantum-Safe Cryptography: A Paradigm Shift in Security
The imminent era of quantum computing has ushered in a paradigm shift in the field of cybersecurity, compelling a proactive response in the form of quantum-safe cryptography. As we progress into 2024, the realization of quantum computers poses a substantial threat to traditional cryptographic methods, rendering widely-used encryption vulnerable to rapid decryption by quantum algorithms. The emergence of quantum-safe cryptography represents a fundamental rethinking and restructuring of cryptographic protocols to withstand the computational power of quantum machines. This paradigm shift involves the development and adoption of quantum-resistant algorithms that can secure sensitive data and communications against the unprecedented computing capabilities of quantum adversaries. The integration of quantum-safe cryptography is not only a technological necessity but also a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of their digital assets in the face of the quantum revolution. This trend signifies a pivotal transition in the cybersecurity landscape, where anticipating and preparing for quantum threats becomes an integral aspect of securing the digital future.
Rise of Zero Trust Architecture: Shifting Security Perimeters
The cybersecurity landscape is undergoing a significant transformation with the ascendance of the Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) paradigm, marking a departure from traditional security models. In 2024, the rise of Zero Trust Architecture reflects a fundamental shift in how organizations approach network security. Unlike conventional models that operate on the assumption of trust within established perimeters, ZTA challenges these assumptions by treating every user and device as potentially untrusted, regardless of their location within or outside the network. This approach acknowledges the dynamic and evolving nature of cyber threats, necessitating a continuous verification process for users, devices, and applications. By dismantling the concept of implicit trust, Zero Trust Architecture provides a more robust defense mechanism against sophisticated cyberattacks, limiting lateral movement and minimizing the potential impact of breaches. As organizations increasingly embrace ZTA, the security perimeters are redefined, reinforcing the notion that trust must be earned continuously, and security measures must adapt dynamically to the evolving threat landscape.
Securing the Cloud: Evolving Strategies in Cloud Computing Security
In the ever-expanding digital landscape of 2024, the significance of securing the cloud has become paramount, prompting a continuous evolution in strategies for cloud computing security. As organizations increasingly migrate their data, applications, and infrastructure to cloud environments, the dynamic nature of this shift introduces new challenges and opportunities for cybersecurity. The focus on securing the cloud involves the implementation of innovative strategies by cyber security companies, aiming to safeguard sensitive information and ensure the resilience of cloud-based systems. From robust encryption protocols to advanced identity and access management solutions, the evolving strategies in cloud computing security address concerns related to data breaches, unauthorized access, and other cyber threats that may compromise the integrity and confidentiality of digital assets stored in the cloud. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning further enhances the detection and response capabilities within cloud environments, contributing to a more adaptive and proactive approach to cybersecurity in the rapidly advancing realm of cloud computing.
Cybersecurity Workforce Development: Bridging the Skills Gap
As we navigate the intricate landscape of cybersecurity in 2024, the critical importance of Cybersecurity Workforce Development emerges as a pivotal focus in bridging the ever-widening skills gap. With the relentless evolution of cyber threats, the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals has reached unprecedented levels. The paragraph explores the dynamic intersection of education and cyber defense, highlighting the need for specialized training programs to cultivate a proficient workforce capable of tackling the multifaceted challenges of the digital era. In this context, emphasis is placed on understanding the initiatives and strategies implemented to nurture a robust cybersecurity workforce, ensuring that professionals possess the requisite skills to stay ahead of emerging threats and safeguard the digital infrastructure effectively.
How to obtain CyberSecurity certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
As we peer into the future of cyber security in 2024, it becomes evident that the landscape is marked by a confluence of technological advancements, paradigm shifts, and an unwavering commitment to fortify digital defenses. The trends explored, from the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to the emergence of quantum-safe cryptography, the adoption of Zero Trust Architecture, evolving strategies in cloud computing security, and the imperative focus on workforce development, collectively paint a comprehensive picture of the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. The intricate dance between innovation and security underscores the dynamic nature of the cybersecurity domain. As organizations navigate this complex terrain, a proactive and adaptive mindset is paramount. The convergence of these trends underscores the need for a holistic approach to cybersecurity, one that leverages cutting-edge technologies, redefines traditional paradigms, and invests in nurturing a skilled workforce capable of safeguarding our digital future. In the relentless pursuit of cyber resilience, collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to continuous learning will remain the guiding principles, ensuring that we not only anticipate and adapt to the evolving threat landscape but emerge stronger and more secure in the face of unprecedented challenges.
Read More
In an era dominated by rapidly evolving technological landscapes, the realm of cybersecurity stands as an ever-vigilant guardian against the escalating threats in the digital domain. As we usher in 2024, the spotlight on cybersecurity intensifies, prompting a keen examination of the forthcoming trends that will shape the landscape of digital defense. This exploration navigates through the intricate web of cyber threats, with a focus on the role of cyber security companies, the dynamic world of cyber threat intelligence, and the pivotal contributions of institutions like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).
In this insightful journey, we will delve into the nuances of cyber security online, exploring the strategies employed by top cyber security companies to safeguard individuals, businesses, and governments alike. A particular emphasis will be placed on the ever-expanding sphere of cloud computing security, considering its integral role in the contemporary digital infrastructure.
As we embark on this exploration, we cannot overlook the influence of tech giants like Google on the cyber security landscape. With a specific focus on Google Cyber Security initiatives, we will analyze their contributions to fortifying online defenses and shaping the trajectory of cyber resilience.
Join us in uncovering the Cyber security Predictions for 2024, where five key trends will be meticulously examined, offering invaluable insights into the future of digital defense. In a world where information is both power and vulnerability, understanding and anticipating these trends is essential for staying one step ahead in the ever-evolving battle against cyber threats.
Table of contents
-
AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity: Advancements and Challenges
-
Emergence of Quantum-Safe Cryptography: A Paradigm Shift in Security
-
Rise of Zero Trust Architecture: Shifting Security Perimeters
-
Securing the Cloud: Evolving Strategies in Cloud Computing Security
-
Cybersecurity Workforce Development: Bridging the Skills Gap
-
Conclusion
AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity: Advancements and Challenges
In the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) stands as a transformative force, promising advancements in threat detection, response, and mitigation. As we delve into the realm of 2024, the role of AI and ML in cyber security becomes increasingly pivotal. These technologies enable the analysis of vast datasets at speeds unattainable by traditional methods, allowing for real-time identification of anomalous activities and potential threats. Moreover, AI-driven solutions contribute to the automation of routine tasks, freeing up cybersecurity professionals to focus on more complex and strategic aspects of defense. However, this integration is not without its challenges. The evolving nature of cyber threats demands constant adaptation, and adversaries are quick to exploit any vulnerabilities in AI and ML systems. Moreover, ethical considerations, interpretability of AI-driven decisions, and the potential for adversarial attacks pose significant challenges. As organizations embrace AI and ML as key components of their cybersecurity arsenal, a delicate balance must be struck between harnessing the power of these technologies and addressing the inherent complexities and risks they bring to the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Emergence of Quantum-Safe Cryptography: A Paradigm Shift in Security
The imminent era of quantum computing has ushered in a paradigm shift in the field of cybersecurity, compelling a proactive response in the form of quantum-safe cryptography. As we progress into 2024, the realization of quantum computers poses a substantial threat to traditional cryptographic methods, rendering widely-used encryption vulnerable to rapid decryption by quantum algorithms. The emergence of quantum-safe cryptography represents a fundamental rethinking and restructuring of cryptographic protocols to withstand the computational power of quantum machines. This paradigm shift involves the development and adoption of quantum-resistant algorithms that can secure sensitive data and communications against the unprecedented computing capabilities of quantum adversaries. The integration of quantum-safe cryptography is not only a technological necessity but also a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of their digital assets in the face of the quantum revolution. This trend signifies a pivotal transition in the cybersecurity landscape, where anticipating and preparing for quantum threats becomes an integral aspect of securing the digital future.
Rise of Zero Trust Architecture: Shifting Security Perimeters
The cybersecurity landscape is undergoing a significant transformation with the ascendance of the Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) paradigm, marking a departure from traditional security models. In 2024, the rise of Zero Trust Architecture reflects a fundamental shift in how organizations approach network security. Unlike conventional models that operate on the assumption of trust within established perimeters, ZTA challenges these assumptions by treating every user and device as potentially untrusted, regardless of their location within or outside the network. This approach acknowledges the dynamic and evolving nature of cyber threats, necessitating a continuous verification process for users, devices, and applications. By dismantling the concept of implicit trust, Zero Trust Architecture provides a more robust defense mechanism against sophisticated cyberattacks, limiting lateral movement and minimizing the potential impact of breaches. As organizations increasingly embrace ZTA, the security perimeters are redefined, reinforcing the notion that trust must be earned continuously, and security measures must adapt dynamically to the evolving threat landscape.
Securing the Cloud: Evolving Strategies in Cloud Computing Security
In the ever-expanding digital landscape of 2024, the significance of securing the cloud has become paramount, prompting a continuous evolution in strategies for cloud computing security. As organizations increasingly migrate their data, applications, and infrastructure to cloud environments, the dynamic nature of this shift introduces new challenges and opportunities for cybersecurity. The focus on securing the cloud involves the implementation of innovative strategies by cyber security companies, aiming to safeguard sensitive information and ensure the resilience of cloud-based systems. From robust encryption protocols to advanced identity and access management solutions, the evolving strategies in cloud computing security address concerns related to data breaches, unauthorized access, and other cyber threats that may compromise the integrity and confidentiality of digital assets stored in the cloud. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning further enhances the detection and response capabilities within cloud environments, contributing to a more adaptive and proactive approach to cybersecurity in the rapidly advancing realm of cloud computing.
Cybersecurity Workforce Development: Bridging the Skills Gap
As we navigate the intricate landscape of cybersecurity in 2024, the critical importance of Cybersecurity Workforce Development emerges as a pivotal focus in bridging the ever-widening skills gap. With the relentless evolution of cyber threats, the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals has reached unprecedented levels. The paragraph explores the dynamic intersection of education and cyber defense, highlighting the need for specialized training programs to cultivate a proficient workforce capable of tackling the multifaceted challenges of the digital era. In this context, emphasis is placed on understanding the initiatives and strategies implemented to nurture a robust cybersecurity workforce, ensuring that professionals possess the requisite skills to stay ahead of emerging threats and safeguard the digital infrastructure effectively.
How to obtain CyberSecurity certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
As we peer into the future of cyber security in 2024, it becomes evident that the landscape is marked by a confluence of technological advancements, paradigm shifts, and an unwavering commitment to fortify digital defenses. The trends explored, from the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to the emergence of quantum-safe cryptography, the adoption of Zero Trust Architecture, evolving strategies in cloud computing security, and the imperative focus on workforce development, collectively paint a comprehensive picture of the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. The intricate dance between innovation and security underscores the dynamic nature of the cybersecurity domain. As organizations navigate this complex terrain, a proactive and adaptive mindset is paramount. The convergence of these trends underscores the need for a holistic approach to cybersecurity, one that leverages cutting-edge technologies, redefines traditional paradigms, and invests in nurturing a skilled workforce capable of safeguarding our digital future. In the relentless pursuit of cyber resilience, collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to continuous learning will remain the guiding principles, ensuring that we not only anticipate and adapt to the evolving threat landscape but emerge stronger and more secure in the face of unprecedented challenges.
Microsoft Unveils ARM-Native Toolkit at BUILD Conference.
In an effort to revolutionize software development for the ARM architecture, Microsoft has made a groundbreaking announcement at its annual BUILD conference. The tech giant unveiled a game-changing tool, the ARM-Native Toolkit, which aims to empower developers and enhance application compatibility for Windows 10. This exciting development opens up new possibilities for app development and solidifies Microsoft's authority and expertise in the field. Let's explore the features and benefits of this innovative toolkit.
The ARM Architecture and its Significance
The ARM architecture, known for its power efficiency and widespread use in mobile devices, has gained significant traction in recent years. As more Windows devices, including tablets and laptops, adopt ARM processors, it has become crucial to provide developers with the tools to create ARM-native apps. With the ARM-Native Toolkit, Microsoft is addressing this need and enabling developers to tap into the full potential of ARM technology.
Empowering App Development with ARM-Native Toolkit
The ARM-Native Toolkit streamlines the app development process, making it easier than ever for developers to create ARM-native applications. By optimizing the toolkit for ARM architecture, Microsoft ensures that apps built with this tool are faster and more efficient. Developers can harness the power of ARM processors to deliver optimal performance and an enhanced user experience.
Enhancing Application Compatibility
One of the significant challenges faced by developers working with ARM architecture is ensuring application compatibility across different platforms. With the ARM-Native Toolkit, Microsoft tackles this issue head-on. Developers can build apps that seamlessly adapt to multiple devices, regardless of their underlying architecture. This level of compatibility is crucial for promoting widespread adoption and allowing developers to reach a broader audience.
Windows 10 Integration
The ARM-Native Toolkit is fully integrated with Windows 10, Microsoft's flagship operating system. With the toolkit's native support for ARM architecture, developers can unleash the true potential of their apps on Windows 10 devices. This integration further strengthens Microsoft's commitment to creating a seamless ecosystem for developers and users alike.
Leveraging the Power of the ARM-Native Toolkit
The ARM-Native Toolkit empowers developers to create high-performance apps, enabling them to take advantage of the unique features offered by ARM architecture. Whether it's building resource-intensive applications, leveraging hardware accelerators, or optimizing power consumption, the toolkit provides developers with the necessary tools to bring their ideas to life.
Achieving Application Optimization
With the ARM-Native Toolkit, developers can optimize their applications specifically for ARM architecture. This allows for improved performance and efficiency, leading to faster load times, smoother user interfaces, and reduced battery consumption. By capitalizing on the features of the underlying architecture, developers can deliver applications that stand out in terms of both functionality and user experience.
The Future of Software Development with Microsoft
The introduction of the ARM-Native Toolkit at BUILD showcases Microsoft's commitment to providing cutting-edge tools and technologies for software development. With this groundbreaking toolkit, developers have the means to create ARM-native applications with ease, ensuring broad compatibility and exceptional performance across Windows 10 devices.
How to obtain Microsoft certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Microsoft's ARM-Native Toolkit represents a significant leap forward in software development for the ARM architecture. By addressing the challenges faced by developers and facilitating app compatibility, Microsoft solidifies its position as an industry leader. With seamless integration into Windows 10 and the ability to leverage the unique capabilities of ARM architecture, developers now have the tools they need to create optimized applications. The ARM-Native Toolkit paves the way for a future where ARM-powered devices become the norm, and Microsoft continues to lead the way in innovative software development.
Read More
In an effort to revolutionize software development for the ARM architecture, Microsoft has made a groundbreaking announcement at its annual BUILD conference. The tech giant unveiled a game-changing tool, the ARM-Native Toolkit, which aims to empower developers and enhance application compatibility for Windows 10. This exciting development opens up new possibilities for app development and solidifies Microsoft's authority and expertise in the field. Let's explore the features and benefits of this innovative toolkit.
The ARM Architecture and its Significance
The ARM architecture, known for its power efficiency and widespread use in mobile devices, has gained significant traction in recent years. As more Windows devices, including tablets and laptops, adopt ARM processors, it has become crucial to provide developers with the tools to create ARM-native apps. With the ARM-Native Toolkit, Microsoft is addressing this need and enabling developers to tap into the full potential of ARM technology.
Empowering App Development with ARM-Native Toolkit
The ARM-Native Toolkit streamlines the app development process, making it easier than ever for developers to create ARM-native applications. By optimizing the toolkit for ARM architecture, Microsoft ensures that apps built with this tool are faster and more efficient. Developers can harness the power of ARM processors to deliver optimal performance and an enhanced user experience.
Enhancing Application Compatibility
One of the significant challenges faced by developers working with ARM architecture is ensuring application compatibility across different platforms. With the ARM-Native Toolkit, Microsoft tackles this issue head-on. Developers can build apps that seamlessly adapt to multiple devices, regardless of their underlying architecture. This level of compatibility is crucial for promoting widespread adoption and allowing developers to reach a broader audience.
Windows 10 Integration
The ARM-Native Toolkit is fully integrated with Windows 10, Microsoft's flagship operating system. With the toolkit's native support for ARM architecture, developers can unleash the true potential of their apps on Windows 10 devices. This integration further strengthens Microsoft's commitment to creating a seamless ecosystem for developers and users alike.
Leveraging the Power of the ARM-Native Toolkit
The ARM-Native Toolkit empowers developers to create high-performance apps, enabling them to take advantage of the unique features offered by ARM architecture. Whether it's building resource-intensive applications, leveraging hardware accelerators, or optimizing power consumption, the toolkit provides developers with the necessary tools to bring their ideas to life.
Achieving Application Optimization
With the ARM-Native Toolkit, developers can optimize their applications specifically for ARM architecture. This allows for improved performance and efficiency, leading to faster load times, smoother user interfaces, and reduced battery consumption. By capitalizing on the features of the underlying architecture, developers can deliver applications that stand out in terms of both functionality and user experience.
The Future of Software Development with Microsoft
The introduction of the ARM-Native Toolkit at BUILD showcases Microsoft's commitment to providing cutting-edge tools and technologies for software development. With this groundbreaking toolkit, developers have the means to create ARM-native applications with ease, ensuring broad compatibility and exceptional performance across Windows 10 devices.
How to obtain Microsoft certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Microsoft's ARM-Native Toolkit represents a significant leap forward in software development for the ARM architecture. By addressing the challenges faced by developers and facilitating app compatibility, Microsoft solidifies its position as an industry leader. With seamless integration into Windows 10 and the ability to leverage the unique capabilities of ARM architecture, developers now have the tools they need to create optimized applications. The ARM-Native Toolkit paves the way for a future where ARM-powered devices become the norm, and Microsoft continues to lead the way in innovative software development.
Keras vs TensorFlow vs PyTorch:Key Deep Learning Differences
Deep learning has emerged as a revolutionary field in artificial intelligence, enabling machines to learn and make complex decisions. Keras, TensorFlow, and PyTorch are three powerful deep learning frameworks that have gained significant popularity among researchers and developers. In this article, we will explore the key differences between these frameworks and understand their unique features and functionalities.
Keras: Easy and Intuitive Deep Learning
Keras is a user-friendly deep learning framework that provides a high-level API for building and training neural networks. It is built on top of TensorFlow and offers a simplified coding interface, making it ideal for beginners and quick prototyping. With Keras, you can rapidly design and experiment with deep learning models without getting deeply involved in low-level implementations.
One of Keras' strengths is its extensive collection of pre-trained models, known as the Keras Applications module. These pre-trained models provide an excellent starting point for various computer vision and natural language processing tasks, allowing users to benefit from transfer learning.
TensorFlow: The Powerhouse of Deep Learning
TensorFlow is a widely adopted open-source deep learning framework that provides a comprehensive set of tools and libraries for building and deploying machine learning models. Developed by Google, TensorFlow offers a lower-level API than Keras, providing greater flexibility and control over model development.
One of the key strengths of TensorFlow is its ability to scale seamlessly across multiple devices and platforms, including CPUs, GPUs, and distributed systems. TensorFlow's extensive ecosystem and community support make it suitable for both research and production-level deployments.
PyTorch: Flexibility and Dynamic Graphs
PyTorch is another popular deep learning framework, known for its flexibility and dynamic computational graphs. Developed by Facebook, PyTorch allows developers to express complex neural network architectures in a more intuitive and natural manner. This dynamic graph construction enables easier debugging and more efficient experimentation.
PyTorch's dynamic nature also makes it easier to integrate with existing Python libraries and tools, making it a preferred choice for researchers and practitioners seeking flexibility and customization.
Deep Learning Comparison: Keras vs TensorFlow vs PyTorch
Now, let's compare these frameworks in terms of their key features and functionalities:
1. Neural Network Development
Keras: Keras provides a high-level API with pre-built layers, making it easy to define and configure neural networks. Its simplicity and abstraction make it a great choice for beginners.
TensorFlow: TensorFlow offers both a high-level and a low-level API, giving developers the freedom to build and modify neural networks at different levels of abstraction.
PyTorch: PyTorch emphasizes flexibility and provides a dynamic computational graph, allowing developers to define and modify networks on the fly.
2. Model Training
Keras: Keras simplifies the model training process with its built-in training loops and utilities. It provides various built-in optimizers and loss functions to facilitate efficient model training.
TensorFlow: TensorFlow offers a rich set of tools for model training, including automatic differentiation, distributed training, and mixed precision training.
PyTorch: PyTorch provides a flexible training loop and supports automatic differentiation, enabling efficient and dynamic model training.
3. Deep Learning Tools
Keras: With Keras, you can benefit from pre-trained models, model visualization tools, and utilities for data augmentation and image preprocessing.
TensorFlow: TensorFlow offers a wide range of tools, including TensorBoard for model visualization, TensorFlow Hub for pre-trained models, and TensorFlow Lite for model deployment on mobile devices.
PyTorch: PyTorch provides tools for data loading and transformation, model visualization with TensorBoardX, and integration with popular libraries like NumPy and SciPy.
Keras vs TensorFlow vs PyTorch: Which One to Choose?
Choosing the right deep learning framework depends on several factors, including your experience level, project requirements, and personal preferences. Here are some considerations:
Beginners and quick prototyping: Keras is highly recommended for beginners due to its simplicity and ease of use.
Research and customization: PyTorch's dynamic graph construction and flexibility make it an excellent choice for researchers and those seeking extensive customization.
Production-level deployments and scalability: TensorFlow's extensive ecosystem and support make it suitable for large-scale deployments and production-level applications.
How to obtain Deep Learning certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, Keras, TensorFlow, and PyTorch are all powerful deep learning frameworks that cater to different needs and preferences. Understanding their key differences and features will help you choose the most suitable framework for your specific requirements.
Read More
Deep learning has emerged as a revolutionary field in artificial intelligence, enabling machines to learn and make complex decisions. Keras, TensorFlow, and PyTorch are three powerful deep learning frameworks that have gained significant popularity among researchers and developers. In this article, we will explore the key differences between these frameworks and understand their unique features and functionalities.
Keras: Easy and Intuitive Deep Learning
Keras is a user-friendly deep learning framework that provides a high-level API for building and training neural networks. It is built on top of TensorFlow and offers a simplified coding interface, making it ideal for beginners and quick prototyping. With Keras, you can rapidly design and experiment with deep learning models without getting deeply involved in low-level implementations.
One of Keras' strengths is its extensive collection of pre-trained models, known as the Keras Applications module. These pre-trained models provide an excellent starting point for various computer vision and natural language processing tasks, allowing users to benefit from transfer learning.
TensorFlow: The Powerhouse of Deep Learning
TensorFlow is a widely adopted open-source deep learning framework that provides a comprehensive set of tools and libraries for building and deploying machine learning models. Developed by Google, TensorFlow offers a lower-level API than Keras, providing greater flexibility and control over model development.
One of the key strengths of TensorFlow is its ability to scale seamlessly across multiple devices and platforms, including CPUs, GPUs, and distributed systems. TensorFlow's extensive ecosystem and community support make it suitable for both research and production-level deployments.
PyTorch: Flexibility and Dynamic Graphs
PyTorch is another popular deep learning framework, known for its flexibility and dynamic computational graphs. Developed by Facebook, PyTorch allows developers to express complex neural network architectures in a more intuitive and natural manner. This dynamic graph construction enables easier debugging and more efficient experimentation.
PyTorch's dynamic nature also makes it easier to integrate with existing Python libraries and tools, making it a preferred choice for researchers and practitioners seeking flexibility and customization.
Deep Learning Comparison: Keras vs TensorFlow vs PyTorch
Now, let's compare these frameworks in terms of their key features and functionalities:
1. Neural Network Development
Keras: Keras provides a high-level API with pre-built layers, making it easy to define and configure neural networks. Its simplicity and abstraction make it a great choice for beginners.
TensorFlow: TensorFlow offers both a high-level and a low-level API, giving developers the freedom to build and modify neural networks at different levels of abstraction.
PyTorch: PyTorch emphasizes flexibility and provides a dynamic computational graph, allowing developers to define and modify networks on the fly.
2. Model Training
Keras: Keras simplifies the model training process with its built-in training loops and utilities. It provides various built-in optimizers and loss functions to facilitate efficient model training.
TensorFlow: TensorFlow offers a rich set of tools for model training, including automatic differentiation, distributed training, and mixed precision training.
PyTorch: PyTorch provides a flexible training loop and supports automatic differentiation, enabling efficient and dynamic model training.
3. Deep Learning Tools
Keras: With Keras, you can benefit from pre-trained models, model visualization tools, and utilities for data augmentation and image preprocessing.
TensorFlow: TensorFlow offers a wide range of tools, including TensorBoard for model visualization, TensorFlow Hub for pre-trained models, and TensorFlow Lite for model deployment on mobile devices.
PyTorch: PyTorch provides tools for data loading and transformation, model visualization with TensorBoardX, and integration with popular libraries like NumPy and SciPy.
Keras vs TensorFlow vs PyTorch: Which One to Choose?
Choosing the right deep learning framework depends on several factors, including your experience level, project requirements, and personal preferences. Here are some considerations:
Beginners and quick prototyping: Keras is highly recommended for beginners due to its simplicity and ease of use.
Research and customization: PyTorch's dynamic graph construction and flexibility make it an excellent choice for researchers and those seeking extensive customization.
Production-level deployments and scalability: TensorFlow's extensive ecosystem and support make it suitable for large-scale deployments and production-level applications.
How to obtain Deep Learning certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, Keras, TensorFlow, and PyTorch are all powerful deep learning frameworks that cater to different needs and preferences. Understanding their key differences and features will help you choose the most suitable framework for your specific requirements.
Learn How to Become a Certified Microsoft Excel Pro in 2024
Are you looking to enhance your Excel skills and become a certified Microsoft Excel professional? In this article, we will walk you through the steps and requirements to become a certified Excel professional by the year 2024. With the ever-increasing demand for Excel proficiency in the workplace, obtaining a certification can greatly boost your career prospects and open up new opportunities for professional development.
Excel Certification and Its Benefits
What is Microsoft Excel Certification?
Microsoft Excel certification is an internationally recognized credential that validates an individual's expertise in using Excel. It demonstrates your proficiency in utilizing the various features and functions of Excel, from basic spreadsheet operations to advanced data analysis and visualization.
Why Should You Get Certified?
Obtaining a Microsoft Excel certification offers a multitude of benefits. Firstly, it showcases your skills and expertise to potential employers, making you stand out from other candidates in a competitive job market. Secondly, it enhances your credibility and marks you as a trusted professional in your field. Lastly, it equips you with advanced Excel skills that can significantly improve your efficiency and productivity in your everyday work tasks.
The Certification Process
Excel Training and Preparation
Before taking the Excel certification exam, it is essential to undergo training to strengthen your Excel skills and familiarize yourself with the exam format. Microsoft offers a wide range of training resources, including online courses, tutorials, and practice exams. These resources cover topics such as data analysis, formulas, functions, pivot tables, and macros.
Excel Certification Program
To become a certified Microsoft Excel professional, you need to pass the Excel certification exam. The certification program is designed to validate your knowledge and proficiency in using Excel. It consists of various levels, including the Microsoft Office Specialist (MOS), Excel Expert, and Excel Master certifications, each representing different levels of Excel proficiency.
Exam Requirements
To be eligible for the Excel certification exam, you must fulfill the prerequisites set by Microsoft. These requirements may include a certain level of experience and familiarity with Excel, completion of specific training courses, or holding a relevant degree or certification. It is important to carefully review and fulfill these prerequisites before registering for the exam.
Excel Exam
The Excel certification exam evaluates your understanding of Excel's features and functions through practical tasks and multiple-choice questions. It covers a wide range of topics, including creating and formatting worksheets, analyzing data, using advanced formulas and functions, and creating dynamic charts and graphs. It is crucial to thoroughly prepare for the exam and practice using Excel extensively to ensure success.
Professional Development and Excel Expertise
Advancing Your Excel Skills
Becoming a certified Microsoft Excel professional is not just a one-time achievement; it signifies a commitment to continuous professional development. Excel is constantly evolving, and staying up-to-date with the latest features and capabilities is essential to excel in your career. Engaging in ongoing training, attending workshops, and exploring advanced Excel techniques will help you sharpen your skills and stay ahead in the ever-changing business landscape.
Excel Expertise for Career Growth
Having a Microsoft Excel certification opens up doors to various career opportunities. Excel proficiency is highly sought after in industries such as finance, accounting, data analysis, project management, and human resources. As a certified Excel professional, you can pursue roles as a financial analyst, data analyst, business intelligence specialist, or Excel trainer. The certification provides you with a competitive edge, increasing your chances of securing lucrative positions and promotions.
How to obtain Microsoft certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Becoming a certified Microsoft Excel professional allows you to harness the power of Excel and propel your career to new heights. By following the certification process and continuously investing in your professional development, you can gain the expertise and credentials needed to stand out in a competitive job market. Don't wait any longer - start your journey towards becoming a certified Excel professional today!
Read More
Are you looking to enhance your Excel skills and become a certified Microsoft Excel professional? In this article, we will walk you through the steps and requirements to become a certified Excel professional by the year 2024. With the ever-increasing demand for Excel proficiency in the workplace, obtaining a certification can greatly boost your career prospects and open up new opportunities for professional development.
Excel Certification and Its Benefits
What is Microsoft Excel Certification?
Microsoft Excel certification is an internationally recognized credential that validates an individual's expertise in using Excel. It demonstrates your proficiency in utilizing the various features and functions of Excel, from basic spreadsheet operations to advanced data analysis and visualization.
Why Should You Get Certified?
Obtaining a Microsoft Excel certification offers a multitude of benefits. Firstly, it showcases your skills and expertise to potential employers, making you stand out from other candidates in a competitive job market. Secondly, it enhances your credibility and marks you as a trusted professional in your field. Lastly, it equips you with advanced Excel skills that can significantly improve your efficiency and productivity in your everyday work tasks.
The Certification Process
Excel Training and Preparation
Before taking the Excel certification exam, it is essential to undergo training to strengthen your Excel skills and familiarize yourself with the exam format. Microsoft offers a wide range of training resources, including online courses, tutorials, and practice exams. These resources cover topics such as data analysis, formulas, functions, pivot tables, and macros.
Excel Certification Program
To become a certified Microsoft Excel professional, you need to pass the Excel certification exam. The certification program is designed to validate your knowledge and proficiency in using Excel. It consists of various levels, including the Microsoft Office Specialist (MOS), Excel Expert, and Excel Master certifications, each representing different levels of Excel proficiency.
Exam Requirements
To be eligible for the Excel certification exam, you must fulfill the prerequisites set by Microsoft. These requirements may include a certain level of experience and familiarity with Excel, completion of specific training courses, or holding a relevant degree or certification. It is important to carefully review and fulfill these prerequisites before registering for the exam.
Excel Exam
The Excel certification exam evaluates your understanding of Excel's features and functions through practical tasks and multiple-choice questions. It covers a wide range of topics, including creating and formatting worksheets, analyzing data, using advanced formulas and functions, and creating dynamic charts and graphs. It is crucial to thoroughly prepare for the exam and practice using Excel extensively to ensure success.
Professional Development and Excel Expertise
Advancing Your Excel Skills
Becoming a certified Microsoft Excel professional is not just a one-time achievement; it signifies a commitment to continuous professional development. Excel is constantly evolving, and staying up-to-date with the latest features and capabilities is essential to excel in your career. Engaging in ongoing training, attending workshops, and exploring advanced Excel techniques will help you sharpen your skills and stay ahead in the ever-changing business landscape.
Excel Expertise for Career Growth
Having a Microsoft Excel certification opens up doors to various career opportunities. Excel proficiency is highly sought after in industries such as finance, accounting, data analysis, project management, and human resources. As a certified Excel professional, you can pursue roles as a financial analyst, data analyst, business intelligence specialist, or Excel trainer. The certification provides you with a competitive edge, increasing your chances of securing lucrative positions and promotions.
How to obtain Microsoft certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Becoming a certified Microsoft Excel professional allows you to harness the power of Excel and propel your career to new heights. By following the certification process and continuously investing in your professional development, you can gain the expertise and credentials needed to stand out in a competitive job market. Don't wait any longer - start your journey towards becoming a certified Excel professional today!
DevOps Engineer Role & Salary Insights Worldwide for 2024
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, DevOps has emerged as a game-changer for the software development and operations industry. But what exactly does a DevOps engineer do? In this article, we will explore the role of a DevOps engineer, their responsibilities, and the skills required for this highly sought-after position. Additionally, we will delve into the DevOps culture and examine the salary trends for DevOps engineers in 2024.
DevOps Engineer: Bridging the Gap
A DevOps engineer is an IT professional who combines the expertise of software development and operations. They serve as a bridge between developers and operations teams, facilitating seamless collaboration and efficient delivery of software products. These professionals possess a deep understanding of both development and operations processes, enabling them to streamline work, enhance productivity, and improve overall business outcomes.
DevOps Roles and Responsibilities
DevOps engineers perform a wide range of roles and responsibilities. They are responsible for implementing DevOps practices and frameworks within an organization. Their key responsibilities include:
IT Automation:
Implementing automation tools and technologies to streamline processes and reduce manual effort.
Creating scripts and configurations for automated deployment, testing, and monitoring of software products.
Continuous Integration:
Facilitating continuous integration by merging and testing code changes on a regular basis.
Ensuring that the codebase remains stable and ready for deployment at any given time.
Continuous Delivery:
Enabling the continuous delivery of software by automating the release process.
Ensuring that deployments are reliable, repeatable, and error-free.
DevOps Tools and Skills
DevOps engineers rely on a range of tools and technologies to fulfill their responsibilities. Some of the commonly used DevOps tools include:
Configuration Management Tools (e.g., Ansible, Puppet, Chef)
Containerization Tools (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes)
Version Control Systems (e.g., Git, SVN)
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Tools (e.g., Jenkins, CircleCI)
Monitoring and Logging Tools (e.g., Splunk, ELK Stack)
In addition to proficiency in these tools, DevOps engineers should possess a diverse skill set. They need to have strong coding skills, as well as a deep understanding of infrastructure and networks. Other important skills include problem-solving, collaboration, and the ability to work under pressure.
The DevOps Culture
DevOps is not just about tools and processes; it is also a culture that promotes collaboration, communication, and shared responsibility. DevOps engineers play a crucial role in fostering this culture within an organization. They facilitate cross-functional collaboration, encourage transparency, and promote a continuous improvement mindset. By breaking down silos and promoting collaboration, the DevOps culture helps organizations achieve faster time-to-market, better quality software, and improved customer satisfaction.
Salary Trends for DevOps Engineers
With the increasing demand for DevOps professionals, the salary for a DevOps engineer remains highly competitive. According to industry reports and surveys, the average salary of a DevOps engineer in 2024 is expected to be significantly higher compared to other IT roles. Organizations recognize the value and impact that DevOps brings to their operations, making this role highly lucrative.
How to obtain DevOps certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, a DevOps engineer plays a critical role in bridging the gap between development and operations teams. They bring together expertise in coding, automation, and infrastructure to streamline processes and enhance productivity. DevOps engineers are not only responsible for implementing and maintaining DevOps practices but also for fostering a collaborative and innovative culture. With the increasing demand for these professionals, the salary trend for DevOps engineers in 2024 is expected to be quite promising. So, if you have the right skills and passion for software development and operations, a career as a DevOps engineer might be a perfect fit for you.
Read More
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, DevOps has emerged as a game-changer for the software development and operations industry. But what exactly does a DevOps engineer do? In this article, we will explore the role of a DevOps engineer, their responsibilities, and the skills required for this highly sought-after position. Additionally, we will delve into the DevOps culture and examine the salary trends for DevOps engineers in 2024.
DevOps Engineer: Bridging the Gap
A DevOps engineer is an IT professional who combines the expertise of software development and operations. They serve as a bridge between developers and operations teams, facilitating seamless collaboration and efficient delivery of software products. These professionals possess a deep understanding of both development and operations processes, enabling them to streamline work, enhance productivity, and improve overall business outcomes.
DevOps Roles and Responsibilities
DevOps engineers perform a wide range of roles and responsibilities. They are responsible for implementing DevOps practices and frameworks within an organization. Their key responsibilities include:
IT Automation:
Implementing automation tools and technologies to streamline processes and reduce manual effort.
Creating scripts and configurations for automated deployment, testing, and monitoring of software products.
Continuous Integration:
Facilitating continuous integration by merging and testing code changes on a regular basis.
Ensuring that the codebase remains stable and ready for deployment at any given time.
Continuous Delivery:
Enabling the continuous delivery of software by automating the release process.
Ensuring that deployments are reliable, repeatable, and error-free.
DevOps Tools and Skills
DevOps engineers rely on a range of tools and technologies to fulfill their responsibilities. Some of the commonly used DevOps tools include:
Configuration Management Tools (e.g., Ansible, Puppet, Chef)
Containerization Tools (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes)
Version Control Systems (e.g., Git, SVN)
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Tools (e.g., Jenkins, CircleCI)
Monitoring and Logging Tools (e.g., Splunk, ELK Stack)
In addition to proficiency in these tools, DevOps engineers should possess a diverse skill set. They need to have strong coding skills, as well as a deep understanding of infrastructure and networks. Other important skills include problem-solving, collaboration, and the ability to work under pressure.
The DevOps Culture
DevOps is not just about tools and processes; it is also a culture that promotes collaboration, communication, and shared responsibility. DevOps engineers play a crucial role in fostering this culture within an organization. They facilitate cross-functional collaboration, encourage transparency, and promote a continuous improvement mindset. By breaking down silos and promoting collaboration, the DevOps culture helps organizations achieve faster time-to-market, better quality software, and improved customer satisfaction.
Salary Trends for DevOps Engineers
With the increasing demand for DevOps professionals, the salary for a DevOps engineer remains highly competitive. According to industry reports and surveys, the average salary of a DevOps engineer in 2024 is expected to be significantly higher compared to other IT roles. Organizations recognize the value and impact that DevOps brings to their operations, making this role highly lucrative.
How to obtain DevOps certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, a DevOps engineer plays a critical role in bridging the gap between development and operations teams. They bring together expertise in coding, automation, and infrastructure to streamline processes and enhance productivity. DevOps engineers are not only responsible for implementing and maintaining DevOps practices but also for fostering a collaborative and innovative culture. With the increasing demand for these professionals, the salary trend for DevOps engineers in 2024 is expected to be quite promising. So, if you have the right skills and passion for software development and operations, a career as a DevOps engineer might be a perfect fit for you.
Project Documentation and Its Crucial Role in 2024 Success.
In the world of project management, documentation plays a crucial role in ensuring the success and smooth execution of projects. In 2024, with the advancements in technology and the increasing complexity of projects, the importance of project documentation has become even more significant. This article will delve into the importance of documentation, best practices, and the role it plays in project success.
Importance of Documentation
Documentation is the backbone of any project. It serves as a reference point for all the critical information related to the project, including project objectives, timelines, resources, and deliverables. It provides a clear roadmap for the project team and stakeholders, helping them stay aligned and remain focused on the project goals.
One of the primary reasons documentation is essential is that it acts as a knowledge repository. It captures lessons learned, best practices, and key insights gained during the project's lifecycle. This knowledge can be valuable for future projects, helping teams avoid repeating mistakes and leveraging successful strategies.
Documentation in 2024
With the rapid advancements in technology, the way documentation is created and managed has changed significantly. In 2024, project documentation is largely digital, with traditional paper-based documentation becoming obsolete. This shift has brought about numerous benefits, including increased accessibility, improved collaboration, and enhanced security.
Document control has also become more streamlined with the use of centralized document management systems. These systems allow project teams to manage and control document versions, ensuring everyone is working with the most up-to-date information. Furthermore, information management has become more efficient, with easy searchability and retrieval of documents.
Documentation Best Practices
To ensure effective documentation, project managers should follow a set of best practices. Firstly, it is essential to have a well-defined project planning phase where project objectives, scope, and deliverables are clearly outlined. This lays the foundation for documentation and ensures all key aspects of the project are captured.
Secondly, project managers should establish a document control process. This includes defining naming conventions, file structures, and version control protocols to maintain consistency and allow for easy retrieval of documents. Additionally, regular document reviews should be conducted to validate the accuracy and relevance of information.
Project Communication and Collaboration
Documentation plays a crucial role in project communication and collaboration. It serves as a common reference point for all project stakeholders, ensuring everyone is on the same page. By documenting project updates, milestones, and decisions, project managers can effectively communicate progress and changes to the team and other stakeholders.
Collaboration tools have become instrumental in enhancing project documentation and communication. These tools facilitate real-time collaboration, document sharing, and feedback exchange, even for geographically dispersed teams. This not only improves efficiency but also fosters a collaborative and engaged project environment.
Knowledge Sharing and Documentation Trends
In 2024, knowledge sharing has become an essential aspect of project documentation. Project teams are encouraged to document their experiences, challenges, and successes, which can be shared with other teams within the organization. This promotes organizational learning and the continuous improvement of project management practices.
Additionally, new trends in documentation have emerged, such as digital documentation. This includes the use of multimedia formats like videos and interactive presentations to enhance the documentation experience. Digital documentation also allows for easier integration with other organizational systems, such as analytics tools, making data-driven decision-making more accessible.
Document Workflow and Project Success Factors
A well-defined document workflow is crucial for the success of a project. This workflow outlines the process of creating, reviewing, approving, and archiving project documentation. By following a standardized workflow, project teams can ensure consistency, traceability, and compliance with organizational standards.
Several factors contribute to project success, and proper documentation is one of them. Clear and concise documentation helps mitigate risks, improves communication, and facilitates efficient decision-making. It enables project teams to effectively manage scope changes, identify bottlenecks, and monitor progress towards project goals.
How to obtain A.I certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, project documentation plays a vital role in the success and smooth execution of projects in 2024. It acts as a knowledge repository, enables effective communication, and supports collaboration among project stakeholders. By following best practices, leveraging collaboration tools, and embracing digital trends, project teams can maximize the benefits of documentation and set themselves up for success. So, investing time and effort in creating comprehensive and well-structured project documentation is crucial for project managers in 2024.
Read More
In the world of project management, documentation plays a crucial role in ensuring the success and smooth execution of projects. In 2024, with the advancements in technology and the increasing complexity of projects, the importance of project documentation has become even more significant. This article will delve into the importance of documentation, best practices, and the role it plays in project success.
Importance of Documentation
Documentation is the backbone of any project. It serves as a reference point for all the critical information related to the project, including project objectives, timelines, resources, and deliverables. It provides a clear roadmap for the project team and stakeholders, helping them stay aligned and remain focused on the project goals.
One of the primary reasons documentation is essential is that it acts as a knowledge repository. It captures lessons learned, best practices, and key insights gained during the project's lifecycle. This knowledge can be valuable for future projects, helping teams avoid repeating mistakes and leveraging successful strategies.
Documentation in 2024
With the rapid advancements in technology, the way documentation is created and managed has changed significantly. In 2024, project documentation is largely digital, with traditional paper-based documentation becoming obsolete. This shift has brought about numerous benefits, including increased accessibility, improved collaboration, and enhanced security.
Document control has also become more streamlined with the use of centralized document management systems. These systems allow project teams to manage and control document versions, ensuring everyone is working with the most up-to-date information. Furthermore, information management has become more efficient, with easy searchability and retrieval of documents.
Documentation Best Practices
To ensure effective documentation, project managers should follow a set of best practices. Firstly, it is essential to have a well-defined project planning phase where project objectives, scope, and deliverables are clearly outlined. This lays the foundation for documentation and ensures all key aspects of the project are captured.
Secondly, project managers should establish a document control process. This includes defining naming conventions, file structures, and version control protocols to maintain consistency and allow for easy retrieval of documents. Additionally, regular document reviews should be conducted to validate the accuracy and relevance of information.
Project Communication and Collaboration
Documentation plays a crucial role in project communication and collaboration. It serves as a common reference point for all project stakeholders, ensuring everyone is on the same page. By documenting project updates, milestones, and decisions, project managers can effectively communicate progress and changes to the team and other stakeholders.
Collaboration tools have become instrumental in enhancing project documentation and communication. These tools facilitate real-time collaboration, document sharing, and feedback exchange, even for geographically dispersed teams. This not only improves efficiency but also fosters a collaborative and engaged project environment.
Knowledge Sharing and Documentation Trends
In 2024, knowledge sharing has become an essential aspect of project documentation. Project teams are encouraged to document their experiences, challenges, and successes, which can be shared with other teams within the organization. This promotes organizational learning and the continuous improvement of project management practices.
Additionally, new trends in documentation have emerged, such as digital documentation. This includes the use of multimedia formats like videos and interactive presentations to enhance the documentation experience. Digital documentation also allows for easier integration with other organizational systems, such as analytics tools, making data-driven decision-making more accessible.
Document Workflow and Project Success Factors
A well-defined document workflow is crucial for the success of a project. This workflow outlines the process of creating, reviewing, approving, and archiving project documentation. By following a standardized workflow, project teams can ensure consistency, traceability, and compliance with organizational standards.
Several factors contribute to project success, and proper documentation is one of them. Clear and concise documentation helps mitigate risks, improves communication, and facilitates efficient decision-making. It enables project teams to effectively manage scope changes, identify bottlenecks, and monitor progress towards project goals.
How to obtain A.I certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, project documentation plays a vital role in the success and smooth execution of projects in 2024. It acts as a knowledge repository, enables effective communication, and supports collaboration among project stakeholders. By following best practices, leveraging collaboration tools, and embracing digital trends, project teams can maximize the benefits of documentation and set themselves up for success. So, investing time and effort in creating comprehensive and well-structured project documentation is crucial for project managers in 2024.
Java in Gaming Industry: A Key Player for Game Development
In today's fast-paced digital world, the gaming industry has experienced tremendous growth. Video games have become a popular form of entertainment for people of all ages. One of the key factors that contribute to the success of a game is the programming language used for its development. Java, known for its versatility and cross-platform compatibility, has emerged as a crucial player in the gaming industry. In this article, we will explore the significance of Java in game development, its advantages, and its impact on the gaming technology landscape.
Java Programming: A Foundation for Game Development
Java language is widely used in the development of various types of games. Its object-oriented nature and extensive libraries make it suitable for both 2D and 3D game programming. With Java, developers have the flexibility to create games that can run on different platforms, including desktop computers, mobile devices, and even embedded systems.
Advantages of Using Java in Game Development
1. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Java's "write once, run anywhere" philosophy enables game developers to create games that can be played on multiple platforms with minimal modifications. This flexibility eliminates the need for developers to rewrite the entire codebase for different platforms, saving time and effort.
2. Rich Library Support
Java boasts a vast collection of libraries and frameworks specifically designed for game development. These libraries offer ready-made solutions for common gaming tasks, such as graphics rendering, audio processing, and physics simulation. Utilizing these libraries, developers can focus more on the game design and logic, rather than micro-level implementation details.
3. Community Support and Documentation
Java has a large and active community of developers and enthusiasts who constantly contribute to its ecosystem. This vibrant community ensures that there is an abundance of resources, tutorials, and forums available for game developers seeking guidance or assistance. The extensive documentation makes it easier for newcomers to grasp Java's concepts and learn the best practices for game development.
4. Performance Optimization
Despite being an interpreted language, Java offers excellent performance for game development. The use of Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation and other optimizations implemented in modern Java Virtual Machines (JVMs) enables games written in Java to achieve high frame rates and smooth gameplay. Additionally, Java's multithreading capabilities allow developers to leverage the full potential of modern processors, enhancing the overall performance of games.
Java Games: A Testament to Java's Capabilities
Numerous successful games have been developed using Java, showcasing the language's capabilities in the gaming industry. Minecraft, a widely popular sandbox game, is a prime example of Java's potential. Its cross-platform compatibility and vast player base demonstrate the reach and versatility of Java-powered games. Other notable Java games include RuneScape, Tribes: Ascend, and Jagged Alliance Online, among many others.
Game Design with Java: A Streamlined Process
Java's flexibility and extensive toolset make game design an efficient and streamlined process. From creating game assets to implementing game mechanics, Java provides developers with the necessary facilities for every aspect of game design. The availability of graphical user interface (GUI) frameworks further simplifies the user interface design, enhancing the overall user experience.
Java Software and Gaming Technology
Java's compatibility with different gaming technologies is another factor that contributes to its prominence in the gaming industry. Java seamlessly integrates with popular gaming technologies like OpenGL and OpenAL, enabling developers to leverage the industry-standard tools and frameworks for advanced graphics rendering and audio processing. This integration ensures that Java games meet the highest standards of visual and audio quality, comparable to games developed in other languages.
The Future of Java Development in Gaming
As technology continues to evolve, the gaming industry is likely to witness further advancements. Java, with its adaptability and continued development, is expected to play a significant role in shaping the future of gaming. With improved performance optimizations, enhanced libraries, and cross-platform support, Java will continue to be a crucial player in game development.
How to obtain Java certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Java has firmly established itself as a crucial player in the gaming industry. Its versatility, cross-platform compatibility, and extensive libraries make it an ideal choice for game development. The success of Java-powered games, coupled with its community support and performance optimization capabilities, is a testament to its effectiveness in the gaming technology landscape. As the gaming industry continues to evolve, Java's role is expected to grow, empowering developers to create innovative and immersive gaming experiences for players worldwide.
Read More
In today's fast-paced digital world, the gaming industry has experienced tremendous growth. Video games have become a popular form of entertainment for people of all ages. One of the key factors that contribute to the success of a game is the programming language used for its development. Java, known for its versatility and cross-platform compatibility, has emerged as a crucial player in the gaming industry. In this article, we will explore the significance of Java in game development, its advantages, and its impact on the gaming technology landscape.
Java Programming: A Foundation for Game Development
Java language is widely used in the development of various types of games. Its object-oriented nature and extensive libraries make it suitable for both 2D and 3D game programming. With Java, developers have the flexibility to create games that can run on different platforms, including desktop computers, mobile devices, and even embedded systems.
Advantages of Using Java in Game Development
1. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Java's "write once, run anywhere" philosophy enables game developers to create games that can be played on multiple platforms with minimal modifications. This flexibility eliminates the need for developers to rewrite the entire codebase for different platforms, saving time and effort.
2. Rich Library Support
Java boasts a vast collection of libraries and frameworks specifically designed for game development. These libraries offer ready-made solutions for common gaming tasks, such as graphics rendering, audio processing, and physics simulation. Utilizing these libraries, developers can focus more on the game design and logic, rather than micro-level implementation details.
3. Community Support and Documentation
Java has a large and active community of developers and enthusiasts who constantly contribute to its ecosystem. This vibrant community ensures that there is an abundance of resources, tutorials, and forums available for game developers seeking guidance or assistance. The extensive documentation makes it easier for newcomers to grasp Java's concepts and learn the best practices for game development.
4. Performance Optimization
Despite being an interpreted language, Java offers excellent performance for game development. The use of Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation and other optimizations implemented in modern Java Virtual Machines (JVMs) enables games written in Java to achieve high frame rates and smooth gameplay. Additionally, Java's multithreading capabilities allow developers to leverage the full potential of modern processors, enhancing the overall performance of games.
Java Games: A Testament to Java's Capabilities
Numerous successful games have been developed using Java, showcasing the language's capabilities in the gaming industry. Minecraft, a widely popular sandbox game, is a prime example of Java's potential. Its cross-platform compatibility and vast player base demonstrate the reach and versatility of Java-powered games. Other notable Java games include RuneScape, Tribes: Ascend, and Jagged Alliance Online, among many others.
Game Design with Java: A Streamlined Process
Java's flexibility and extensive toolset make game design an efficient and streamlined process. From creating game assets to implementing game mechanics, Java provides developers with the necessary facilities for every aspect of game design. The availability of graphical user interface (GUI) frameworks further simplifies the user interface design, enhancing the overall user experience.
Java Software and Gaming Technology
Java's compatibility with different gaming technologies is another factor that contributes to its prominence in the gaming industry. Java seamlessly integrates with popular gaming technologies like OpenGL and OpenAL, enabling developers to leverage the industry-standard tools and frameworks for advanced graphics rendering and audio processing. This integration ensures that Java games meet the highest standards of visual and audio quality, comparable to games developed in other languages.
The Future of Java Development in Gaming
As technology continues to evolve, the gaming industry is likely to witness further advancements. Java, with its adaptability and continued development, is expected to play a significant role in shaping the future of gaming. With improved performance optimizations, enhanced libraries, and cross-platform support, Java will continue to be a crucial player in game development.
How to obtain Java certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Java has firmly established itself as a crucial player in the gaming industry. Its versatility, cross-platform compatibility, and extensive libraries make it an ideal choice for game development. The success of Java-powered games, coupled with its community support and performance optimization capabilities, is a testament to its effectiveness in the gaming technology landscape. As the gaming industry continues to evolve, Java's role is expected to grow, empowering developers to create innovative and immersive gaming experiences for players worldwide.
Machine Learning Certification for Entrepreneurs & Leaders
In today's hyper-connected world, data-driven decision-making has become crucial for businesses to thrive and stay ahead of the competition. Machine Learning, a subset of Artificial Intelligence, is revolutionizing industries across the globe. Entrepreneurs and business leaders who possess a deep understanding of Machine Learning can leverage its power to optimize operations, identify patterns, and make informed strategic decisions. To gain the necessary expertise in this field, obtaining a Machine Learning Certification is highly recommended. This article will explore the benefits of such certifications and highlight the key platforms and resources available for entrepreneurs and business leaders to embark on their Machine Learning journey.
Why Is Machine Learning Certification Important?
Entrepreneurs and business leaders who equip themselves with Machine Learning Certifications gain a competitive edge in the dynamic business environment. Here are some reasons why obtaining a certification in this domain is beneficial:
Enhanced Decision-making: Machine Learning certification equips entrepreneurs and business leaders with the skills to analyze vast amounts of data and extract valuable insights. This data-driven decision-making approach helps in better understanding customer behavior, identifying trends, and predicting market demand.
Optimized Operations: By harnessing the power of Machine Learning algorithms, entrepreneurs and business leaders can streamline their operations and automate repetitive processes. This leads to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved overall productivity.
Improved Customer Experience: Machine Learning techniques enable businesses to personalize customer experiences by understanding individual preferences and tailoring products or services accordingly. This results in higher customer satisfaction and improved brand loyalty.
Stay Ahead of the Curve: As businesses across industries increasingly adopt Machine Learning, having a recognized certification demonstrates one's commitment to professional development and staying abreast of the latest advancements. This positions entrepreneurs and business leaders as forward-thinking individuals in their respective industries.
Key Platforms and Resources for Machine Learning Certification
To obtain a Machine Learning Certification, entrepreneurs and business leaders can explore various platforms and resources. Here are a few notable ones:
Azure Machine Learning: Azure Machine Learning by Microsoft offers comprehensive certification programs for professionals looking to master Machine Learning concepts and techniques. Their certifications cover a wide range of topics, including understanding data science and using Azure services for Machine Learning.
AWS Machine Learning: Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a range of Machine Learning certifications that cater to different skill levels. These certifications cover topics such as building, training, and deploying Machine Learning models on the AWS platform.
Python Machine Learning: Python, a popular programming language, has a vast ecosystem of libraries and frameworks dedicated to Machine Learning. Entrepreneurs and business leaders can explore certifications like "Python for Data Science and Machine Learning Bootcamp" to gain proficiency in applying Python for Machine Learning tasks.
Deep Learning AI: Deep Learning, a subfield of Machine Learning, focuses on training neural networks to learn and make predictions. Entrepreneurs and business leaders interested in deep learning can pursue certifications specifically tailored to this advanced topic, such as "Deep Learning Specialization" offered by deep learning experts.
Benefits of Obtaining Machine Learning Certification
Earning a Machine Learning Certification comes with numerous benefits for entrepreneurs and business leaders. Let's take a closer look:
Credibility and Trust: Certification from reputable platforms showcases one's expertise and commitment to continuous learning. It builds credibility and instills trust among clients, stakeholders, and potential investors.
Networking Opportunities: Attaining a Machine Learning Certification opens doors to connect with fellow professionals, industry experts, and thought leaders. These networking opportunities can lead to collaborations, mentorship, and access to valuable resources within the Machine Learning community.
Career Advancement: Machine Learning certifications signal advanced skill sets and can open up new career opportunities. Entrepreneurs and business leaders with Machine Learning expertise can spearhead data-driven initiatives within their organizations or pursue consulting and advisory roles in the field.
Problem-solving Abilities: Machine Learning certifications equip entrepreneurs and business leaders with powerful analytical tools and problem-solving techniques. This enables them to tackle complex business challenges, make data-driven decisions, and drive innovation within their organizations.
How to obtain A.I certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Machine Learning Certification is a valuable investment for entrepreneurs and business leaders seeking to unlock the full potential of data-driven decision-making. By obtaining these certifications, professionals gain a competitive advantage, enhance their problem-solving abilities, and position themselves as industry leaders. Whether it's Azure Machine Learning, AWS Machine Learning, or Python Machine Learning, the plethora of certifications available cater to different areas of Machine Learning expertise. So, don't wait any longer. Take the leap and embark on your Machine Learning journey today!
Read More
In today's hyper-connected world, data-driven decision-making has become crucial for businesses to thrive and stay ahead of the competition. Machine Learning, a subset of Artificial Intelligence, is revolutionizing industries across the globe. Entrepreneurs and business leaders who possess a deep understanding of Machine Learning can leverage its power to optimize operations, identify patterns, and make informed strategic decisions. To gain the necessary expertise in this field, obtaining a Machine Learning Certification is highly recommended. This article will explore the benefits of such certifications and highlight the key platforms and resources available for entrepreneurs and business leaders to embark on their Machine Learning journey.
Why Is Machine Learning Certification Important?
Entrepreneurs and business leaders who equip themselves with Machine Learning Certifications gain a competitive edge in the dynamic business environment. Here are some reasons why obtaining a certification in this domain is beneficial:
Enhanced Decision-making: Machine Learning certification equips entrepreneurs and business leaders with the skills to analyze vast amounts of data and extract valuable insights. This data-driven decision-making approach helps in better understanding customer behavior, identifying trends, and predicting market demand.
Optimized Operations: By harnessing the power of Machine Learning algorithms, entrepreneurs and business leaders can streamline their operations and automate repetitive processes. This leads to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved overall productivity.
Improved Customer Experience: Machine Learning techniques enable businesses to personalize customer experiences by understanding individual preferences and tailoring products or services accordingly. This results in higher customer satisfaction and improved brand loyalty.
Stay Ahead of the Curve: As businesses across industries increasingly adopt Machine Learning, having a recognized certification demonstrates one's commitment to professional development and staying abreast of the latest advancements. This positions entrepreneurs and business leaders as forward-thinking individuals in their respective industries.
Key Platforms and Resources for Machine Learning Certification
To obtain a Machine Learning Certification, entrepreneurs and business leaders can explore various platforms and resources. Here are a few notable ones:
Azure Machine Learning: Azure Machine Learning by Microsoft offers comprehensive certification programs for professionals looking to master Machine Learning concepts and techniques. Their certifications cover a wide range of topics, including understanding data science and using Azure services for Machine Learning.
AWS Machine Learning: Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a range of Machine Learning certifications that cater to different skill levels. These certifications cover topics such as building, training, and deploying Machine Learning models on the AWS platform.
Python Machine Learning: Python, a popular programming language, has a vast ecosystem of libraries and frameworks dedicated to Machine Learning. Entrepreneurs and business leaders can explore certifications like "Python for Data Science and Machine Learning Bootcamp" to gain proficiency in applying Python for Machine Learning tasks.
Deep Learning AI: Deep Learning, a subfield of Machine Learning, focuses on training neural networks to learn and make predictions. Entrepreneurs and business leaders interested in deep learning can pursue certifications specifically tailored to this advanced topic, such as "Deep Learning Specialization" offered by deep learning experts.
Benefits of Obtaining Machine Learning Certification
Earning a Machine Learning Certification comes with numerous benefits for entrepreneurs and business leaders. Let's take a closer look:
Credibility and Trust: Certification from reputable platforms showcases one's expertise and commitment to continuous learning. It builds credibility and instills trust among clients, stakeholders, and potential investors.
Networking Opportunities: Attaining a Machine Learning Certification opens doors to connect with fellow professionals, industry experts, and thought leaders. These networking opportunities can lead to collaborations, mentorship, and access to valuable resources within the Machine Learning community.
Career Advancement: Machine Learning certifications signal advanced skill sets and can open up new career opportunities. Entrepreneurs and business leaders with Machine Learning expertise can spearhead data-driven initiatives within their organizations or pursue consulting and advisory roles in the field.
Problem-solving Abilities: Machine Learning certifications equip entrepreneurs and business leaders with powerful analytical tools and problem-solving techniques. This enables them to tackle complex business challenges, make data-driven decisions, and drive innovation within their organizations.
How to obtain A.I certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Machine Learning Certification is a valuable investment for entrepreneurs and business leaders seeking to unlock the full potential of data-driven decision-making. By obtaining these certifications, professionals gain a competitive advantage, enhance their problem-solving abilities, and position themselves as industry leaders. Whether it's Azure Machine Learning, AWS Machine Learning, or Python Machine Learning, the plethora of certifications available cater to different areas of Machine Learning expertise. So, don't wait any longer. Take the leap and embark on your Machine Learning journey today!
Top 5 Robotic Process Automation Certifications for 2024
Are you considering a career in Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? It's a rapidly growing field with numerous job opportunities. However, to stand out from the crowd and showcase your expertise, getting certified in RPA is essential. In this article, we will explore the top 5 robotic process automation certifications for 2024 and discuss how they can benefit your career.
RPA Certification Programs
Robotic Process Automation Certification Programs offer specialized training and assessment to individuals seeking recognition in the field. These programs provide comprehensive knowledge and hands-on experience with popular RPA tools and technologies. Obtaining a certification not only validates your skills but also enhances your credibility in the industry.
RPA Certifications - A Pathway to Success
UiPath Robotic Process Automation Certification: UiPath is one of the leading providers of RPA solutions. Their certification program offers three levels of expertise - Foundation, Orchestrator, and Advanced RPA Developer. Each level focuses on different aspects of RPA implementation, from basic concepts to advanced automation techniques. A UiPath certification is highly recognized and sought after by employers worldwide.
Automation Anywhere Certified Advanced RPA Professional: Automation Anywhere is another prominent RPA platform, and their certification program covers various aspects of RPA implementation. It includes modules on automation development, IQ Bot (intelligent document processing), and Bot Insight (advanced analytics). Possessing an Automation Anywhere certification demonstrates your proficiency in using their platform effectively.
Blue Prism Accredited Developer Certification: Blue Prism is known for its robust RPA software, and their certification program offers an in-depth understanding of their platform. It covers topics such as process design, automation skills, and problem-solving techniques. A Blue Prism certification showcases your ability to design and develop scalable, efficient, and secure RPA solutions.
Microsoft Certified: Power Platform RPA Developer Associate: Microsoft's Power Platform is gaining popularity for its ability to integrate seamlessly with other Microsoft products. Their RPA Developer Associate certification focuses on developing automation solutions using Power Automate and UI flows. This certification not only validates your RPA skills but also positions you as an expert in Microsoft's RPA ecosystem.
AAAP Certified Advanced RPA Professional: The Association for Advanced Automation Professionals (AAAP) offers a comprehensive RPA certification program. It covers various RPA tools and methodologies, ensuring a holistic understanding of the field. An AAAP certification demonstrates your commitment to continuous learning and professional development in RPA.
2024 Trends in Robotic Process Automation Certifications
As technology continues to advance, the field of RPA is constantly evolving. Here are some of the trends to look out for in RPA certifications in 2024:
Cognitive Automation: Certifications incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms will become more prevalent as RPA continues to expand its capabilities.
Hyperautomation: With the rise of hyperautomation, certifications focusing on integrating RPA with other automation technologies like process mining and analytics will gain significance.
Industry-Specific Certifications: As RPA continues to be adopted across industries, certifications tailored to specific sectors like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing will gain prominence.
Security and Compliance: RPA certifications that emphasize security practices and compliance regulations will become crucial, considering the sensitive nature of data handled by RPA bots.
Advanced Analytics: Certifications focusing on leveraging data analytics to drive insights and decision-making in RPA implementations will become increasingly important.
Industry Recognition and Career Advancement
Obtaining an RPA certification not only enhances your skills but also opens doors to exciting career opportunities. Certified professionals are highly sought after by employers who recognize the value of their expertise. With the demand for RPA professionals increasing, having a certification can give you a competitive edge in the job market.
Additionally, certifications can lead to career advancement opportunities within your current organization. Employers often prioritize candidates with certifications for promotions and leadership roles in RPA projects. By showcasing your commitment to continuous learning and professional growth, you position yourself as a valuable asset to your company.
How to obtain A.I certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In a rapidly evolving field like Robotic Process Automation, staying ahead of the curve is crucial. Getting certified in RPA demonstrates your expertise, enhances your credibility, and opens up numerous career opportunities. By considering the top 5 robotic process automation certifications for 2024, you can ensure that you are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to succeed in this dynamic industry. So, what are you waiting for? Invest in your future and embark on the path to becoming an RPA-certified professional!
Read More
Are you considering a career in Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? It's a rapidly growing field with numerous job opportunities. However, to stand out from the crowd and showcase your expertise, getting certified in RPA is essential. In this article, we will explore the top 5 robotic process automation certifications for 2024 and discuss how they can benefit your career.
RPA Certification Programs
Robotic Process Automation Certification Programs offer specialized training and assessment to individuals seeking recognition in the field. These programs provide comprehensive knowledge and hands-on experience with popular RPA tools and technologies. Obtaining a certification not only validates your skills but also enhances your credibility in the industry.
RPA Certifications - A Pathway to Success
UiPath Robotic Process Automation Certification: UiPath is one of the leading providers of RPA solutions. Their certification program offers three levels of expertise - Foundation, Orchestrator, and Advanced RPA Developer. Each level focuses on different aspects of RPA implementation, from basic concepts to advanced automation techniques. A UiPath certification is highly recognized and sought after by employers worldwide.
Automation Anywhere Certified Advanced RPA Professional: Automation Anywhere is another prominent RPA platform, and their certification program covers various aspects of RPA implementation. It includes modules on automation development, IQ Bot (intelligent document processing), and Bot Insight (advanced analytics). Possessing an Automation Anywhere certification demonstrates your proficiency in using their platform effectively.
Blue Prism Accredited Developer Certification: Blue Prism is known for its robust RPA software, and their certification program offers an in-depth understanding of their platform. It covers topics such as process design, automation skills, and problem-solving techniques. A Blue Prism certification showcases your ability to design and develop scalable, efficient, and secure RPA solutions.
Microsoft Certified: Power Platform RPA Developer Associate: Microsoft's Power Platform is gaining popularity for its ability to integrate seamlessly with other Microsoft products. Their RPA Developer Associate certification focuses on developing automation solutions using Power Automate and UI flows. This certification not only validates your RPA skills but also positions you as an expert in Microsoft's RPA ecosystem.
AAAP Certified Advanced RPA Professional: The Association for Advanced Automation Professionals (AAAP) offers a comprehensive RPA certification program. It covers various RPA tools and methodologies, ensuring a holistic understanding of the field. An AAAP certification demonstrates your commitment to continuous learning and professional development in RPA.
2024 Trends in Robotic Process Automation Certifications
As technology continues to advance, the field of RPA is constantly evolving. Here are some of the trends to look out for in RPA certifications in 2024:
Cognitive Automation: Certifications incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms will become more prevalent as RPA continues to expand its capabilities.
Hyperautomation: With the rise of hyperautomation, certifications focusing on integrating RPA with other automation technologies like process mining and analytics will gain significance.
Industry-Specific Certifications: As RPA continues to be adopted across industries, certifications tailored to specific sectors like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing will gain prominence.
Security and Compliance: RPA certifications that emphasize security practices and compliance regulations will become crucial, considering the sensitive nature of data handled by RPA bots.
Advanced Analytics: Certifications focusing on leveraging data analytics to drive insights and decision-making in RPA implementations will become increasingly important.
Industry Recognition and Career Advancement
Obtaining an RPA certification not only enhances your skills but also opens doors to exciting career opportunities. Certified professionals are highly sought after by employers who recognize the value of their expertise. With the demand for RPA professionals increasing, having a certification can give you a competitive edge in the job market.
Additionally, certifications can lead to career advancement opportunities within your current organization. Employers often prioritize candidates with certifications for promotions and leadership roles in RPA projects. By showcasing your commitment to continuous learning and professional growth, you position yourself as a valuable asset to your company.
How to obtain A.I certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In a rapidly evolving field like Robotic Process Automation, staying ahead of the curve is crucial. Getting certified in RPA demonstrates your expertise, enhances your credibility, and opens up numerous career opportunities. By considering the top 5 robotic process automation certifications for 2024, you can ensure that you are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to succeed in this dynamic industry. So, what are you waiting for? Invest in your future and embark on the path to becoming an RPA-certified professional!
Data Scientists: Mastering Business Principles is Essential
In the dynamic landscape of the digital era, the role of data scientists has emerged as pivotal for organizations seeking to harness the power of data for strategic decision-making. As businesses increasingly recognize the significance of data-driven insights, the demand for skilled data scientists continues to soar. Whether through traditional avenues like pursuing a data science degree or opting for immersive experiences like data science bootcamps, the journey to mastering the principles of business through data science is diverse and dynamic.
The realm of data science education has expanded beyond conventional classrooms, with online data science degree programs and specialized courses gaining prominence. Institutions such as Scaler, UpGrad, and Great Learning offer comprehensive data science programs, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. These platforms provide not only the essential technical skills, including proficiency in Python for data science, but also cultivate a deep understanding of the business principles that underpin effective data analysis.
Embarking on a data science journey involves more than just learning algorithms and coding; it requires a holistic approach that integrates business acumen with technical expertise. Aspiring data scientists can now explore a multitude of avenues to learn data science, tailoring their education to suit their needs and preferences. Whether one opts for a data science bootcamp for a hands-on, intensive experience or pursues a formal online data science degree for a more structured approach, the goal remains the same – mastering the intricate interplay between data science and business principles.
This article delves into the diverse options available for those looking to enhance their skills in the realm of data science. From traditional data science graduate programs to innovative platforms like Scaler and UpGrad, the journey towards becoming a proficient data scientist involves navigating through a landscape rich with opportunities for growth and development. Join us as we explore the various pathways to learning data science and unlocking its potential as a transformative force in the business world.
Table of contents
-
The Evolving Role of Data Scientists in Business
-
Choosing the Right Path: Data Science Education Options
-
Balancing Technical Skills with Business Acumen
-
Innovative Data Science Programs: A Closer Look
-
Realizing the Impact: Success Stories of Business-Savvy Data Scientists
-
Conclusion
The Evolving Role of Data Scientists in Business
The evolving role of data scientists in the business landscape reflects a paradigm shift in the way organizations leverage data for strategic decision-making. Traditionally perceived as analytical experts focused solely on crunching numbers and developing algorithms, data scientists are now integral contributors to shaping overall business strategy. In today's dynamic environment, mastering business principles has become a prerequisite for data scientists to effectively bridge the gap between raw data and actionable insights. As businesses increasingly recognize the transformative potential of data, these professionals are not only tasked with extracting meaningful patterns but also with interpreting their implications in the broader context of organizational goals. The shift towards a more holistic role underscores the importance of effective communication, collaboration, and a nuanced understanding of business dynamics. This subtopic explores the evolution of the data scientist's role, shedding light on how they have transitioned from mere data analysts to key architects of business success.
Choosing the Right Path: Data Science Education Options
Choosing the right educational path is a critical decision for aspiring data scientists seeking to navigate the complex landscape of data science. With a myriad of options available, ranging from traditional data science degree programs to immersive data science bootcamps and online learning platforms, individuals must carefully consider their learning preferences, career goals, and time constraints. Traditional degree programs offer a structured curriculum and academic depth, providing a comprehensive understanding of both theoretical concepts and practical applications. On the other hand, data science bootcamps offer an intensive, hands-on experience, often focusing on real-world projects and industry-relevant skills. Online learning platforms cater to a flexible, self-paced approach, allowing individuals to acquire skills remotely. This subtopic explores the advantages and disadvantages of each option, providing prospective data scientists with valuable insights to make informed decisions aligned with their unique needs and aspirations.
Balancing Technical Skills with Business Acumen
Choosing the right educational path is a critical decision for aspiring data scientists seeking to navigate the complex landscape of data science. With a myriad of options available, ranging from traditional data science degree programs to immersive data science bootcamps and online learning platforms, individuals must carefully consider their learning preferences, career goals, and time constraints. Traditional degree programs offer a structured curriculum and academic depth, providing a comprehensive understanding of both theoretical concepts and practical applications. On the other hand, data science bootcamps offer an intensive, hands-on experience, often focusing on real-world projects and industry-relevant skills. Online learning platforms cater to a flexible, self-paced approach, allowing individuals to acquire skills remotely. This subtopic explores the advantages and disadvantages of each option, providing prospective data scientists with valuable insights to make informed decisions aligned with their unique needs and aspirations.
Innovative Data Science Programs: A Closer Look
Taking a closer look at innovative data science programs reveals a dynamic landscape of educational opportunities that go beyond traditional learning structures. Programs offered by institutions such as Scaler, UpGrad, and Great Learning are at the forefront of this evolution, presenting unique features that set them apart in the field of data science education. These platforms often blend theoretical knowledge with hands-on experience, equipping learners with practical skills directly applicable to industry scenarios. The curriculum is meticulously designed to align with current industry trends, ensuring that graduates are well-prepared to tackle real-world challenges. Moreover, these programs often foster connections with industry experts, providing invaluable networking opportunities and insights. By exploring the specifics of these innovative data science programs, individuals can gain a comprehensive understanding of the educational landscape, enabling them to make informed decisions about the most suitable pathway for their career advancement in the ever-evolving field of data science.
Realizing the Impact: Success Stories of Business-Savvy Data Scientists
Realizing the impact of mastering business principles within the realm of data science becomes palpable when examining success stories of business-savvy data scientists. These individuals exemplify the transformative power that arises from seamlessly integrating technical acumen with a profound understanding of business dynamics. Through compelling case studies and insightful interviews, it becomes evident how data scientists, armed with a comprehensive skill set encompassing Python proficiency and business principles, have become instrumental in driving organizational success. These success stories underscore the tangible outcomes achieved when data scientists not only unravel intricate data patterns but also translate their findings into strategic initiatives that positively impact the bottom line. By delving into these narratives, readers gain valuable insights into the real-world applications of business-savvy data science, inspiring a deeper appreciation for the pivotal role these professionals play in shaping the future of data-driven decision-making within diverse industries.
How to obtain Data Science certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, the narrative of "Data Scientists: Mastering Business Principles is Essential" reveals the dynamic evolution of the data science landscape and the pivotal role played by individuals proficient in both technical expertise and business acumen. As the demand for data-driven insights continues to surge, the journey to becoming a proficient data scientist involves strategic decision-making regarding educational pathways. Whether one chooses traditional data science degree programs, immersive bootcamps, or innovative online platforms like Scaler, UpGrad, or Great Learning, the emphasis on mastering business principles remains paramount. The fusion of Python proficiency with a deep understanding of business dynamics empowers data scientists to not only decipher complex data patterns but also to communicate actionable insights and contribute meaningfully to organizational success. As illustrated through success stories, the impact of business-savvy data scientists is evident in their ability to drive strategic initiatives and shape the trajectory of businesses in the digital era. This exploration underscores the diverse avenues available for aspiring data scientists and emphasizes the necessity of a holistic approach in navigating the intersection of data science and business principles for continued professional growth and industry influence.
Read More
In the dynamic landscape of the digital era, the role of data scientists has emerged as pivotal for organizations seeking to harness the power of data for strategic decision-making. As businesses increasingly recognize the significance of data-driven insights, the demand for skilled data scientists continues to soar. Whether through traditional avenues like pursuing a data science degree or opting for immersive experiences like data science bootcamps, the journey to mastering the principles of business through data science is diverse and dynamic.
The realm of data science education has expanded beyond conventional classrooms, with online data science degree programs and specialized courses gaining prominence. Institutions such as Scaler, UpGrad, and Great Learning offer comprehensive data science programs, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. These platforms provide not only the essential technical skills, including proficiency in Python for data science, but also cultivate a deep understanding of the business principles that underpin effective data analysis.
Embarking on a data science journey involves more than just learning algorithms and coding; it requires a holistic approach that integrates business acumen with technical expertise. Aspiring data scientists can now explore a multitude of avenues to learn data science, tailoring their education to suit their needs and preferences. Whether one opts for a data science bootcamp for a hands-on, intensive experience or pursues a formal online data science degree for a more structured approach, the goal remains the same – mastering the intricate interplay between data science and business principles.
This article delves into the diverse options available for those looking to enhance their skills in the realm of data science. From traditional data science graduate programs to innovative platforms like Scaler and UpGrad, the journey towards becoming a proficient data scientist involves navigating through a landscape rich with opportunities for growth and development. Join us as we explore the various pathways to learning data science and unlocking its potential as a transformative force in the business world.
Table of contents
-
The Evolving Role of Data Scientists in Business
-
Choosing the Right Path: Data Science Education Options
-
Balancing Technical Skills with Business Acumen
-
Innovative Data Science Programs: A Closer Look
-
Realizing the Impact: Success Stories of Business-Savvy Data Scientists
-
Conclusion
The Evolving Role of Data Scientists in Business
The evolving role of data scientists in the business landscape reflects a paradigm shift in the way organizations leverage data for strategic decision-making. Traditionally perceived as analytical experts focused solely on crunching numbers and developing algorithms, data scientists are now integral contributors to shaping overall business strategy. In today's dynamic environment, mastering business principles has become a prerequisite for data scientists to effectively bridge the gap between raw data and actionable insights. As businesses increasingly recognize the transformative potential of data, these professionals are not only tasked with extracting meaningful patterns but also with interpreting their implications in the broader context of organizational goals. The shift towards a more holistic role underscores the importance of effective communication, collaboration, and a nuanced understanding of business dynamics. This subtopic explores the evolution of the data scientist's role, shedding light on how they have transitioned from mere data analysts to key architects of business success.
Choosing the Right Path: Data Science Education Options
Choosing the right educational path is a critical decision for aspiring data scientists seeking to navigate the complex landscape of data science. With a myriad of options available, ranging from traditional data science degree programs to immersive data science bootcamps and online learning platforms, individuals must carefully consider their learning preferences, career goals, and time constraints. Traditional degree programs offer a structured curriculum and academic depth, providing a comprehensive understanding of both theoretical concepts and practical applications. On the other hand, data science bootcamps offer an intensive, hands-on experience, often focusing on real-world projects and industry-relevant skills. Online learning platforms cater to a flexible, self-paced approach, allowing individuals to acquire skills remotely. This subtopic explores the advantages and disadvantages of each option, providing prospective data scientists with valuable insights to make informed decisions aligned with their unique needs and aspirations.
Balancing Technical Skills with Business Acumen
Choosing the right educational path is a critical decision for aspiring data scientists seeking to navigate the complex landscape of data science. With a myriad of options available, ranging from traditional data science degree programs to immersive data science bootcamps and online learning platforms, individuals must carefully consider their learning preferences, career goals, and time constraints. Traditional degree programs offer a structured curriculum and academic depth, providing a comprehensive understanding of both theoretical concepts and practical applications. On the other hand, data science bootcamps offer an intensive, hands-on experience, often focusing on real-world projects and industry-relevant skills. Online learning platforms cater to a flexible, self-paced approach, allowing individuals to acquire skills remotely. This subtopic explores the advantages and disadvantages of each option, providing prospective data scientists with valuable insights to make informed decisions aligned with their unique needs and aspirations.
Innovative Data Science Programs: A Closer Look
Taking a closer look at innovative data science programs reveals a dynamic landscape of educational opportunities that go beyond traditional learning structures. Programs offered by institutions such as Scaler, UpGrad, and Great Learning are at the forefront of this evolution, presenting unique features that set them apart in the field of data science education. These platforms often blend theoretical knowledge with hands-on experience, equipping learners with practical skills directly applicable to industry scenarios. The curriculum is meticulously designed to align with current industry trends, ensuring that graduates are well-prepared to tackle real-world challenges. Moreover, these programs often foster connections with industry experts, providing invaluable networking opportunities and insights. By exploring the specifics of these innovative data science programs, individuals can gain a comprehensive understanding of the educational landscape, enabling them to make informed decisions about the most suitable pathway for their career advancement in the ever-evolving field of data science.
Realizing the Impact: Success Stories of Business-Savvy Data Scientists
Realizing the impact of mastering business principles within the realm of data science becomes palpable when examining success stories of business-savvy data scientists. These individuals exemplify the transformative power that arises from seamlessly integrating technical acumen with a profound understanding of business dynamics. Through compelling case studies and insightful interviews, it becomes evident how data scientists, armed with a comprehensive skill set encompassing Python proficiency and business principles, have become instrumental in driving organizational success. These success stories underscore the tangible outcomes achieved when data scientists not only unravel intricate data patterns but also translate their findings into strategic initiatives that positively impact the bottom line. By delving into these narratives, readers gain valuable insights into the real-world applications of business-savvy data science, inspiring a deeper appreciation for the pivotal role these professionals play in shaping the future of data-driven decision-making within diverse industries.
How to obtain Data Science certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, the narrative of "Data Scientists: Mastering Business Principles is Essential" reveals the dynamic evolution of the data science landscape and the pivotal role played by individuals proficient in both technical expertise and business acumen. As the demand for data-driven insights continues to surge, the journey to becoming a proficient data scientist involves strategic decision-making regarding educational pathways. Whether one chooses traditional data science degree programs, immersive bootcamps, or innovative online platforms like Scaler, UpGrad, or Great Learning, the emphasis on mastering business principles remains paramount. The fusion of Python proficiency with a deep understanding of business dynamics empowers data scientists to not only decipher complex data patterns but also to communicate actionable insights and contribute meaningfully to organizational success. As illustrated through success stories, the impact of business-savvy data scientists is evident in their ability to drive strategic initiatives and shape the trajectory of businesses in the digital era. This exploration underscores the diverse avenues available for aspiring data scientists and emphasizes the necessity of a holistic approach in navigating the intersection of data science and business principles for continued professional growth and industry influence.
The Future of IoT: Navigating Innovations and Trends Ahead
The Internet of Things (IoT) has undoubtedly transformed the way we live and work. With its vast potential and limitless possibilities, it has become a prominent player in today's technological landscape. As we move forward, it is crucial to navigate the rapidly evolving IoT ecosystem and stay updated with the latest trends, solutions, and security measures. In this article, we will explore the future of IoT and delve into its various aspects, including technology, industry, devices, applications, and security.
The Future of IoT Technology
The future of IoT technology holds immense promise. With advancements in connectivity, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, the scope of IoT is poised to expand exponentially. Edge computing, a distributed computing paradigm, is expected to play a significant role in overcoming latency issues and enhancing real-time decision-making in IoT systems. Furthermore, the integration of 5G technology will revolutionize IoT by providing faster data transmission, lower latency, and increased capacity, opening new doors for innovative IoT solutions.
Navigating the IoT Industry
The IoT industry is evolving at a rapid pace, presenting both challenges and opportunities. To navigate this dynamic landscape successfully, companies must be agile and adaptable. Collaborations and partnerships between different stakeholders, including device manufacturers, service providers, and software developers, will be key to driving innovation and creating robust IoT solutions. Furthermore, staying updated with industry trends and understanding the ever-changing market dynamics is essential for businesses to stay competitive and harness the full potential of IoT.
IoT Devices and Applications
IoT devices are at the heart of this interconnected ecosystem. From smart homes and wearables to industrial sensors and autonomous vehicles, the possibilities are endless. The future will witness the proliferation of intelligent and interconnected devices that seamlessly communicate with each other, enabling a wide range of applications. From optimizing energy consumption and enhancing healthcare systems to enabling smart cities and revolutionizing supply chain management, IoT has the power to transform various sectors and improve efficiency and productivity.
IoT Security: Protecting the Connected World
With the growing IoT ecosystem, security becomes a paramount concern. As more and more devices get interconnected, the potential attack surface for cybercriminals expands. A single vulnerable device can compromise the entire network, leading to disastrous consequences. Therefore, robust security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and regular vulnerability assessments, are crucial to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of IoT systems. Additionally, with the rise of artificial intelligence, leveraging machine learning algorithms can help detect and prevent cyber threats in real-time.
Navigating the Growing IoT Ecosystem
The IoT landscape is continuously evolving, presenting numerous challenges and opportunities for businesses and individuals alike. To navigate this ever-expanding ecosystem effectively, staying updated with the latest advancements and trends is vital. Additionally, strong networking skills, the ability to collaborate with diverse stakeholders, and a deep understanding of the underlying technology are essential. By keeping a finger on the pulse of IoT developments and taking proactive measures, individuals and organizations can harness the full potential of this transformative technology.
How to obtain IOT certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
The future of IoT is bright and promising. As technology continues to advance, IoT will find its way into every aspect of our lives, simplifying tasks, improving efficiencies, and enhancing overall quality of life. However, to reap the rewards of this interconnected world, it is imperative to navigate the IoT landscape adeptly. By embracing the latest trends, leveraging innovative solutions, and prioritizing security, we can fully explore the boundless possibilities that the Internet of Things offers. So, let's embrace the future of IoT and navigate the IoT ecosystem with confidence and curiosity.
Read More
The Internet of Things (IoT) has undoubtedly transformed the way we live and work. With its vast potential and limitless possibilities, it has become a prominent player in today's technological landscape. As we move forward, it is crucial to navigate the rapidly evolving IoT ecosystem and stay updated with the latest trends, solutions, and security measures. In this article, we will explore the future of IoT and delve into its various aspects, including technology, industry, devices, applications, and security.
The Future of IoT Technology
The future of IoT technology holds immense promise. With advancements in connectivity, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, the scope of IoT is poised to expand exponentially. Edge computing, a distributed computing paradigm, is expected to play a significant role in overcoming latency issues and enhancing real-time decision-making in IoT systems. Furthermore, the integration of 5G technology will revolutionize IoT by providing faster data transmission, lower latency, and increased capacity, opening new doors for innovative IoT solutions.
Navigating the IoT Industry
The IoT industry is evolving at a rapid pace, presenting both challenges and opportunities. To navigate this dynamic landscape successfully, companies must be agile and adaptable. Collaborations and partnerships between different stakeholders, including device manufacturers, service providers, and software developers, will be key to driving innovation and creating robust IoT solutions. Furthermore, staying updated with industry trends and understanding the ever-changing market dynamics is essential for businesses to stay competitive and harness the full potential of IoT.
IoT Devices and Applications
IoT devices are at the heart of this interconnected ecosystem. From smart homes and wearables to industrial sensors and autonomous vehicles, the possibilities are endless. The future will witness the proliferation of intelligent and interconnected devices that seamlessly communicate with each other, enabling a wide range of applications. From optimizing energy consumption and enhancing healthcare systems to enabling smart cities and revolutionizing supply chain management, IoT has the power to transform various sectors and improve efficiency and productivity.
IoT Security: Protecting the Connected World
With the growing IoT ecosystem, security becomes a paramount concern. As more and more devices get interconnected, the potential attack surface for cybercriminals expands. A single vulnerable device can compromise the entire network, leading to disastrous consequences. Therefore, robust security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and regular vulnerability assessments, are crucial to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of IoT systems. Additionally, with the rise of artificial intelligence, leveraging machine learning algorithms can help detect and prevent cyber threats in real-time.
Navigating the Growing IoT Ecosystem
The IoT landscape is continuously evolving, presenting numerous challenges and opportunities for businesses and individuals alike. To navigate this ever-expanding ecosystem effectively, staying updated with the latest advancements and trends is vital. Additionally, strong networking skills, the ability to collaborate with diverse stakeholders, and a deep understanding of the underlying technology are essential. By keeping a finger on the pulse of IoT developments and taking proactive measures, individuals and organizations can harness the full potential of this transformative technology.
How to obtain IOT certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
The future of IoT is bright and promising. As technology continues to advance, IoT will find its way into every aspect of our lives, simplifying tasks, improving efficiencies, and enhancing overall quality of life. However, to reap the rewards of this interconnected world, it is imperative to navigate the IoT landscape adeptly. By embracing the latest trends, leveraging innovative solutions, and prioritizing security, we can fully explore the boundless possibilities that the Internet of Things offers. So, let's embrace the future of IoT and navigate the IoT ecosystem with confidence and curiosity.
Unleashing the Stock Market: Secure Your Financial Future
Are you looking for ways to secure your financial future? The stock market can be a great option to consider. With the right knowledge and guidance, you can unleash the true potential of the stock market and pave the way for a prosperous future. In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of the stock market and provide you with valuable insights on how to navigate it successfully.
Understanding the Stock Market
The stock market, also known as the share market or stock exchange, is a platform where individuals and institutions buy and sell stocks or shares of publicly traded companies. It is a dynamic and ever-evolving marketplace that offers opportunities for investors to grow their wealth through capital appreciation and dividends.
Choosing the Best Trading App
In today's digital era, trading apps have become an essential tool for investors. They offer convenience and accessibility, allowing you to trade stocks from the comfort of your own home or on the go. When selecting a trading app, it is crucial to consider factors such as user experience, security, fees, and the availability of real-time market data.
Identifying the Best Stocks for Beginners
If you are new to stock trading and have a limited budget, it is essential to choose stocks wisely. Look for companies with a strong track record, stable earnings, and a history of consistent dividend payments.
Staying Updated with Stock Market News
Keeping up with the latest developments and news in the stock market is crucial for making informed investment decisions. With the abundance of financial news outlets available, it can be overwhelming to filter through the noise. One of the best ways to stay updated is to use a reliable stock market news app or website. These platforms provide real-time market data, expert analysis, and insights into market trends. Stay informed and take advantage of opportunities that arise in the market.
Live Trading and Dow Futures
For those who prefer to actively trade in the stock market, understanding live trading and Dow futures is essential. Live trading refers to buying and selling stocks in real-time, while Dow futures allow investors to speculate on the future movement of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. Both strategies require careful analysis, risk management, and a deep understanding of market dynamics.
The Best Stock Market App for Your Needs
With the proliferation of stock market apps, finding the best one for your specific needs can be a daunting task. It is important to consider factors such as user interface, research tools, ease of use, and compatibility with your trading style.
How to obtain Business Analysis certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
The stock market can be a powerful tool for securing your financial future. By understanding how the market works, choosing the right trading app, identifying the best stocks, staying updated with market news, and utilizing live trading and Dow futures, you can unlock the potential of the stock market. Remember to conduct thorough research, seek expert advice, and develop a disciplined approach to investing. Start your journey in the stock market today and pave the way for a secure and prosperous future.
Read More
Are you looking for ways to secure your financial future? The stock market can be a great option to consider. With the right knowledge and guidance, you can unleash the true potential of the stock market and pave the way for a prosperous future. In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of the stock market and provide you with valuable insights on how to navigate it successfully.
Understanding the Stock Market
The stock market, also known as the share market or stock exchange, is a platform where individuals and institutions buy and sell stocks or shares of publicly traded companies. It is a dynamic and ever-evolving marketplace that offers opportunities for investors to grow their wealth through capital appreciation and dividends.
Choosing the Best Trading App
In today's digital era, trading apps have become an essential tool for investors. They offer convenience and accessibility, allowing you to trade stocks from the comfort of your own home or on the go. When selecting a trading app, it is crucial to consider factors such as user experience, security, fees, and the availability of real-time market data.
Identifying the Best Stocks for Beginners
If you are new to stock trading and have a limited budget, it is essential to choose stocks wisely. Look for companies with a strong track record, stable earnings, and a history of consistent dividend payments.
Staying Updated with Stock Market News
Keeping up with the latest developments and news in the stock market is crucial for making informed investment decisions. With the abundance of financial news outlets available, it can be overwhelming to filter through the noise. One of the best ways to stay updated is to use a reliable stock market news app or website. These platforms provide real-time market data, expert analysis, and insights into market trends. Stay informed and take advantage of opportunities that arise in the market.
Live Trading and Dow Futures
For those who prefer to actively trade in the stock market, understanding live trading and Dow futures is essential. Live trading refers to buying and selling stocks in real-time, while Dow futures allow investors to speculate on the future movement of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. Both strategies require careful analysis, risk management, and a deep understanding of market dynamics.
The Best Stock Market App for Your Needs
With the proliferation of stock market apps, finding the best one for your specific needs can be a daunting task. It is important to consider factors such as user interface, research tools, ease of use, and compatibility with your trading style.
How to obtain Business Analysis certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
The stock market can be a powerful tool for securing your financial future. By understanding how the market works, choosing the right trading app, identifying the best stocks, staying updated with market news, and utilizing live trading and Dow futures, you can unlock the potential of the stock market. Remember to conduct thorough research, seek expert advice, and develop a disciplined approach to investing. Start your journey in the stock market today and pave the way for a secure and prosperous future.
Apple Vision Pro Expected to Officially Launch in February
The technology world is abuzz with excitement as rumors circulate about the highly anticipated vision pro launch scheduled for February. With the release date just around the corner, tech enthusiasts can't help but speculate about what this new product will bring to the table. In this article, we will delve into the rumor mill surrounding the vision pro launch, exploring the technology behind it, and discussing the anticipated announcement and unveiling.
The Vision Pro Launch: What's the Buzz?
The rumor mill has been working overtime, suggesting that the vision pro launch will take place in February. While details remain scarce, industry insiders have been buzzing about the potential features and capabilities of this exciting new product. With the release date drawing near, it's a great time to take a closer look at what we can expect from the vision pro.
Unveiling Cutting-Edge Technology
When it comes to technology, the vision pro launch is expected to showcase some truly innovative features. This new product is rumored to incorporate state-of-the-art advancements that will revolutionize the industry. From improved display technology to enhanced performance capabilities, the vision pro is expected to set a new standard for excellence.
Release Date: February Fever
One of the biggest points of speculation surrounding the vision pro launch is the exact release date. While rumors are swirling, there has been no official announcement from the company. Tech enthusiasts and consumers alike are eagerly waiting for the unveiling, hoping for a definitive release date to mark on their calendars. As February approaches, anticipation is reaching a fever pitch.
Speculation Galore: What to Expect?
With limited information available, speculation about the vision pro launch is running rampant. Tech experts and enthusiasts have been eagerly discussing the possibilities, trying to piece together clues and leaks to uncover the true nature of this new product. Could it be a groundbreaking smartphone? Or perhaps a revolutionary smart home device? Only time will tell.
The Vision Pro Announcement: Worth the Wait?
As we near the rumored February unveiling, many are wondering if the vision pro announcement will live up to the hype. With the technology industry constantly evolving and introducing new products, it's important for companies to deliver on the promises they make. Whether the vision pro launch will be a game-changer or simply another addition to the market remains to be seen.
How to obtain A.I certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
The vision pro launch is an exciting event that has technology enthusiasts on the edge of their seats. With rumors swirling about the release date, features, and capabilities of this new product, anticipation is reaching new heights. As we eagerly await the official announcement and unveiling, it's important to approach the speculation with caution and keep our expectations in check. After all, the true test lies in how the vision pro will fare once it hits the market. Until then, let's enjoy the excitement and anticipation that comes with the possibility of something truly remarkable.
Read More
The technology world is abuzz with excitement as rumors circulate about the highly anticipated vision pro launch scheduled for February. With the release date just around the corner, tech enthusiasts can't help but speculate about what this new product will bring to the table. In this article, we will delve into the rumor mill surrounding the vision pro launch, exploring the technology behind it, and discussing the anticipated announcement and unveiling.
The Vision Pro Launch: What's the Buzz?
The rumor mill has been working overtime, suggesting that the vision pro launch will take place in February. While details remain scarce, industry insiders have been buzzing about the potential features and capabilities of this exciting new product. With the release date drawing near, it's a great time to take a closer look at what we can expect from the vision pro.
Unveiling Cutting-Edge Technology
When it comes to technology, the vision pro launch is expected to showcase some truly innovative features. This new product is rumored to incorporate state-of-the-art advancements that will revolutionize the industry. From improved display technology to enhanced performance capabilities, the vision pro is expected to set a new standard for excellence.
Release Date: February Fever
One of the biggest points of speculation surrounding the vision pro launch is the exact release date. While rumors are swirling, there has been no official announcement from the company. Tech enthusiasts and consumers alike are eagerly waiting for the unveiling, hoping for a definitive release date to mark on their calendars. As February approaches, anticipation is reaching a fever pitch.
Speculation Galore: What to Expect?
With limited information available, speculation about the vision pro launch is running rampant. Tech experts and enthusiasts have been eagerly discussing the possibilities, trying to piece together clues and leaks to uncover the true nature of this new product. Could it be a groundbreaking smartphone? Or perhaps a revolutionary smart home device? Only time will tell.
The Vision Pro Announcement: Worth the Wait?
As we near the rumored February unveiling, many are wondering if the vision pro announcement will live up to the hype. With the technology industry constantly evolving and introducing new products, it's important for companies to deliver on the promises they make. Whether the vision pro launch will be a game-changer or simply another addition to the market remains to be seen.
How to obtain A.I certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
The vision pro launch is an exciting event that has technology enthusiasts on the edge of their seats. With rumors swirling about the release date, features, and capabilities of this new product, anticipation is reaching new heights. As we eagerly await the official announcement and unveiling, it's important to approach the speculation with caution and keep our expectations in check. After all, the true test lies in how the vision pro will fare once it hits the market. Until then, let's enjoy the excitement and anticipation that comes with the possibility of something truly remarkable.
AWS Compute: Discover the Best Option for Your Needs!!!
When it comes to cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading player in the market. With a wide range of compute options to choose from, AWS offers flexibility and scalability to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes. In this article, we will explore the different compute services offered by AWS, compare their features and pricing, and help you determine which option works best for you.
AWS Compute Options
AWS EC2 Instance Types
AWS EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud. With EC2, you can choose from a variety of instance types to meet your specific workload requirements. Whether you need general-purpose instances, compute-optimized instances, memory-optimized instances, or storage-optimized instances, AWS has got you covered. Each instance type is designed to deliver optimal performance and efficiency for different use cases.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a fully managed service that makes it easy to deploy and run applications in multiple languages. Whether you are developing a web app in Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, or Python, Elastic Beanstalk takes care of the deployment details, such as capacity provisioning, load balancing, and automatic scaling. This allows developers to focus on writing code rather than managing infrastructure.
AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that lets you run your code without provisioning or managing servers. With Lambda, you simply upload your code and define the triggers that should execute it. Lambda takes care of everything else, including scaling, patching, and monitoring. It is an ideal solution for event-driven applications, asynchronous tasks, and microservices architecture.
AWS Fargate
AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers. It allows you to run containers without managing the underlying infrastructure. With Fargate, you can focus on building and scaling your applications, while AWS takes care of provisioning and managing the containers. This eliminates the need to worry about cluster management, scaling policies, or persistent storage.
AWS Auto Scaling
AWS Auto Scaling enables automatic scaling of your applications based on demand. With Auto Scaling, you can set rules to dynamically adjust the number of instances in your EC2 fleet, ensuring that you have enough capacity to handle traffic spikes and saving costs during periods of low demand. Auto Scaling can be combined with other AWS services, such as Elastic Load Balancing, to achieve high availability and fault tolerance.
AWS Compute Pricing
When considering AWS compute options, it is important to understand the pricing model associated with each service. AWS offers various pricing options, including on-demand, reserved, and spot instances. On-demand instances provide flexibility and pay-as-you-go pricing, while reserved instances offer significant savings for steady-state workloads. Spot instances allow you to bid on unused EC2 capacity, resulting in even lower costs but with the caveat that your instances may be interrupted.
Additionally, each AWS compute service has its own pricing structure and cost factors. For example, EC2 instances are priced based on instance type, storage capacity, data transfer, and other factors. Elastic Beanstalk pricing includes EC2 instance costs, as well as AWS Elastic Load Balancer and AWS CloudFormation charges. Lambda pricing is based on the number of requests and compute time, while Fargate pricing is determined by vCPU and memory resources allocated.
How to obtain AWS certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a wide range of compute options to cater to diverse workload requirements. Whether you need flexible virtual machines, simplified application deployment, serverless compute, or containerized environments, AWS has a service to meet your needs. By understanding the features, pricing, and considerations of each compute option, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your business goals. So, which AWS compute service works best for you?
Read More
When it comes to cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading player in the market. With a wide range of compute options to choose from, AWS offers flexibility and scalability to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes. In this article, we will explore the different compute services offered by AWS, compare their features and pricing, and help you determine which option works best for you.
AWS Compute Options
AWS EC2 Instance Types
AWS EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud. With EC2, you can choose from a variety of instance types to meet your specific workload requirements. Whether you need general-purpose instances, compute-optimized instances, memory-optimized instances, or storage-optimized instances, AWS has got you covered. Each instance type is designed to deliver optimal performance and efficiency for different use cases.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a fully managed service that makes it easy to deploy and run applications in multiple languages. Whether you are developing a web app in Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, or Python, Elastic Beanstalk takes care of the deployment details, such as capacity provisioning, load balancing, and automatic scaling. This allows developers to focus on writing code rather than managing infrastructure.
AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that lets you run your code without provisioning or managing servers. With Lambda, you simply upload your code and define the triggers that should execute it. Lambda takes care of everything else, including scaling, patching, and monitoring. It is an ideal solution for event-driven applications, asynchronous tasks, and microservices architecture.
AWS Fargate
AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers. It allows you to run containers without managing the underlying infrastructure. With Fargate, you can focus on building and scaling your applications, while AWS takes care of provisioning and managing the containers. This eliminates the need to worry about cluster management, scaling policies, or persistent storage.
AWS Auto Scaling
AWS Auto Scaling enables automatic scaling of your applications based on demand. With Auto Scaling, you can set rules to dynamically adjust the number of instances in your EC2 fleet, ensuring that you have enough capacity to handle traffic spikes and saving costs during periods of low demand. Auto Scaling can be combined with other AWS services, such as Elastic Load Balancing, to achieve high availability and fault tolerance.
AWS Compute Pricing
When considering AWS compute options, it is important to understand the pricing model associated with each service. AWS offers various pricing options, including on-demand, reserved, and spot instances. On-demand instances provide flexibility and pay-as-you-go pricing, while reserved instances offer significant savings for steady-state workloads. Spot instances allow you to bid on unused EC2 capacity, resulting in even lower costs but with the caveat that your instances may be interrupted.
Additionally, each AWS compute service has its own pricing structure and cost factors. For example, EC2 instances are priced based on instance type, storage capacity, data transfer, and other factors. Elastic Beanstalk pricing includes EC2 instance costs, as well as AWS Elastic Load Balancer and AWS CloudFormation charges. Lambda pricing is based on the number of requests and compute time, while Fargate pricing is determined by vCPU and memory resources allocated.
How to obtain AWS certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a wide range of compute options to cater to diverse workload requirements. Whether you need flexible virtual machines, simplified application deployment, serverless compute, or containerized environments, AWS has a service to meet your needs. By understanding the features, pricing, and considerations of each compute option, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your business goals. So, which AWS compute service works best for you?
Can Julia Programming Reach the Popularity of Python and R?
Software development and data analysis are crucial fields in today's tech-driven world. When it comes to programming languages, Python and R have been ruling the roost for years. They are widely used and have extensive libraries that cater to various needs. However, there is a new contender on the block - Julia programming language. Can Julia ever become as popular as Python and R? Let's delve deeper and explore the possibilities.
Julia Programming Language: The Rising Star
Julia is a high-level, high-performance language specifically designed for numerical and scientific computing. It combines the ease of use of languages like Python and R with the speed of statically-typed languages like C and Fortran. Julia boasts of an extensive mathematical function library and a simple yet powerful syntax. It allows users to write concise and expressive code, making it ideal for professionals in academia, finance, and engineering.
Julia vs. Python and R
Speed and Performance
One of the key advantages of Julia over Python and R is its speed. Julia's just-in-time (JIT) compilation allows it to execute code at the speed of traditionally faster languages, such as C and Fortran. This makes Julia a game-changer for applications that require complex computations and data analysis on large datasets. Python and R, on the other hand, are interpreted languages, which can be comparatively slower.
Ease of Use and Syntax
Python has gained immense popularity due to its simplicity and ease of use. It has a beginner-friendly syntax that allows individuals from various backgrounds to start coding quickly. R, on the other hand, is known for its statistical capabilities and extensive libraries for data analysis.
Julia strikes a balance between the two. Its syntax is intuitive, resembling mathematical notation, and it offers a vast array of built-in mathematical functions. Julia's ability to handle numerical computations efficiently makes it an excellent choice for fields that heavily rely on mathematical modeling and simulation.
Libraries and Ecosystem
Python and R have a vast collection of libraries that cater to different domains and support a wide range of functionalities. This vast ecosystem has contributed significantly to their popularity. Julia is relatively new compared to Python and R, but it has been gaining traction steadily. The Julia community actively develops and maintains a growing number of packages, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including machine learning, data science, and optimization.
The Promise of Julia
Julia has the potential to challenge Python and R's dominance, especially in domains that require high-performance computing and advanced numerical analysis. Its unified environment and the ability to seamlessly integrate with existing code (Python, R, and others) make it an attractive choice for developers and data scientists.
With companies like IBM, Intel, and Microsoft actively investing in Julia and contributing to its development, its future looks promising. Julia's versatility and efficiency can accelerate scientific research, enable complex simulations, and enhance data-driven decision-making across industries.
How to obtain Python certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
While Python and R have established themselves as go-to languages for software development and data analysis, Julia is gradually making its mark. With its superior speed, powerful syntax, and a growing number of libraries, Julia has the potential to become as popular as its counterparts. As the language continues to evolve and gain wider adoption, we can expect more developers and researchers to explore the capabilities offered by Julia. It's an exciting time for programming languages and the prospects of Julia are undoubtedly worth keeping an eye on.
Read More
Software development and data analysis are crucial fields in today's tech-driven world. When it comes to programming languages, Python and R have been ruling the roost for years. They are widely used and have extensive libraries that cater to various needs. However, there is a new contender on the block - Julia programming language. Can Julia ever become as popular as Python and R? Let's delve deeper and explore the possibilities.
Julia Programming Language: The Rising Star
Julia is a high-level, high-performance language specifically designed for numerical and scientific computing. It combines the ease of use of languages like Python and R with the speed of statically-typed languages like C and Fortran. Julia boasts of an extensive mathematical function library and a simple yet powerful syntax. It allows users to write concise and expressive code, making it ideal for professionals in academia, finance, and engineering.
Julia vs. Python and R
Speed and Performance
One of the key advantages of Julia over Python and R is its speed. Julia's just-in-time (JIT) compilation allows it to execute code at the speed of traditionally faster languages, such as C and Fortran. This makes Julia a game-changer for applications that require complex computations and data analysis on large datasets. Python and R, on the other hand, are interpreted languages, which can be comparatively slower.
Ease of Use and Syntax
Python has gained immense popularity due to its simplicity and ease of use. It has a beginner-friendly syntax that allows individuals from various backgrounds to start coding quickly. R, on the other hand, is known for its statistical capabilities and extensive libraries for data analysis.
Julia strikes a balance between the two. Its syntax is intuitive, resembling mathematical notation, and it offers a vast array of built-in mathematical functions. Julia's ability to handle numerical computations efficiently makes it an excellent choice for fields that heavily rely on mathematical modeling and simulation.
Libraries and Ecosystem
Python and R have a vast collection of libraries that cater to different domains and support a wide range of functionalities. This vast ecosystem has contributed significantly to their popularity. Julia is relatively new compared to Python and R, but it has been gaining traction steadily. The Julia community actively develops and maintains a growing number of packages, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including machine learning, data science, and optimization.
The Promise of Julia
Julia has the potential to challenge Python and R's dominance, especially in domains that require high-performance computing and advanced numerical analysis. Its unified environment and the ability to seamlessly integrate with existing code (Python, R, and others) make it an attractive choice for developers and data scientists.
With companies like IBM, Intel, and Microsoft actively investing in Julia and contributing to its development, its future looks promising. Julia's versatility and efficiency can accelerate scientific research, enable complex simulations, and enhance data-driven decision-making across industries.
How to obtain Python certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
While Python and R have established themselves as go-to languages for software development and data analysis, Julia is gradually making its mark. With its superior speed, powerful syntax, and a growing number of libraries, Julia has the potential to become as popular as its counterparts. As the language continues to evolve and gain wider adoption, we can expect more developers and researchers to explore the capabilities offered by Julia. It's an exciting time for programming languages and the prospects of Julia are undoubtedly worth keeping an eye on.
Meta Unveils New AI Tools for Developers, Creators & Users
Introduction
As technology advances, artificial intelligence (AI) continues to play a significant role in shaping our digital landscape. Today, we dive into the exciting developments at Meta, the company behind the popular social media platform. Meta's new AI features are set to revolutionize the way developers create and innovate. In this article, we'll explore the latest updates on the Meta platform and delve into the artificial intelligence tools that will empower developers to build immersive and intelligent experiences.
Meta AI Developments: Pushing Boundaries with Innovation
Meta's dedication to advancing AI technology showcases their commitment to providing next-level experiences for their users. With recent breakthroughs in natural language processing, computer vision, and machine learning, Meta has laid the groundwork for developers to take advantage of these powerful tools.
From smart recommendations to real-time translation and image recognition, developers now have the ability to leverage Meta's AI capabilities and enhance the overall user experience within their apps. With Meta's AI at their fingertips, developers can unlock endless possibilities and bring their visions to life.
New AI Features for Developers: Empowering Innovation
Meta's new AI features offer developers a wide range of tools and functionalities that go beyond basic automation. These advancements will enable developers to build intelligent systems, create personalized user experiences, and streamline their development process. Let's take a closer look at some of these exciting features:
1.Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Meta's NLP capabilities allow developers to analyze and understand human language. By integrating NLP into their applications, developers can enable chatbots, sentiment analysis, and language translation. This empowers them to create more interactive and engaging experiences for users, breaking down language barriers and facilitating seamlesscommunication.
2.Computer Vision
Meta's computer vision tools provide developers with the ability to process and understand visual data. By leveraging image recognition, object detection, and augmented reality technologies, developers can create immersive visual experiences that captivate users. From virtual try-ons to real-time image manipulation, the possibilities are endless with Meta's AI-powered computer vision.
3.Machine Learning
Meta's machine learning capabilities open doors to predictive analytics, personalized recommendations, and intelligent automation. By incorporating machine learning algorithms into their applications, developers can harness the power of data to improve user engagement and optimize various business processes. From personalized content suggestions to smart user segmentation, machine learning can transform the way developers create tailored experiences.
Meta Platform Updates: Innovations at Your Fingertips
To ensure developers can easily access and integrate Meta's new AI features, the platform has undergone several updates. This ensures a seamless development experience, enabling developers to leverage the power of AI without the need for complexsetups.
Meta's platform updates include:
1.Developer Documentation and APIs: Meta provides comprehensive documentation and APIs that empower developers to leverage AI functionalities effectively. With detailed guides and resources, developers can quickly integrate Meta's AI tools into their applications and get up to speed with the latest advancements.
2.Developer Community and Support: Meta has fostered a vibrant developer community where developers can connect, collaborate, and seek support. Through forums, meetups, and online resources, developers can exchange ideas, share best practices, and troubleshoot challenges together, further expanding their knowledge and expertise.
3.Continuous Improvement: Meta is committed to continuous improvement and regularly enhances its AI offerings based on user feedback and emerging technologies. Developers can expect new features and improvements to Meta's AI tools, ensuring they stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
Artificial Intelligence Tools for Developers: Unleashing Creativity
With Meta's AI tools for developers, endless opportunities await. By harnessing the power of NLP, computer vision, and machine learning, developers can elevate their applications to new heights. Whether it's creating interactive chatbots, implementing sophisticated image recognition, or delivering personalized recommendations, Meta's AI features unlock new dimensions of creativity and innovation.
By utilizing Meta's AI tools, developers can:
1.Enhance User Experience: By leveraging AI tools, developers can create highly engaging and intuitive experiences that satisfy user needs and preferences. From intelligent search and recommendations to natural language interfaces, users can interact with applications in a more seamless and personalized way.
2.Boost Efficiency and Productivity: Automation and intelligent systems powered by AI tools can streamline various tasks and processes, allowing developers to focus on core functionality and higher-level concepts. This promotes efficiency and productivity, enabling faster development cycles and quicker iteration.
3.Drive Business Growth: AI-powered applications can help businesses gain a competitive edge by providing valuable insights, automating mundane tasks, and delivering personalized customer experiences. By leveraging Meta's AI tools, developers can pave the way for business growth and success.
How to obtain A.I certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, Meta's new AI features are set to revolutionize the way developers create and innovate. With advancements in natural language processing, computer vision, and machine learning, developers can unlock the power of AI and bring their visions to life. By integrating Meta's AI tools into their applications, developers can enhance the user experience, boost efficiency, and drive business growth. With Meta's commitment to ongoing improvements and a supportive developer community, the sky's the limit for AI-powered innovation. So, what are you waiting for? Embrace Meta's new AI features and unleash your creativity.
Read More
Introduction
As technology advances, artificial intelligence (AI) continues to play a significant role in shaping our digital landscape. Today, we dive into the exciting developments at Meta, the company behind the popular social media platform. Meta's new AI features are set to revolutionize the way developers create and innovate. In this article, we'll explore the latest updates on the Meta platform and delve into the artificial intelligence tools that will empower developers to build immersive and intelligent experiences.
Meta AI Developments: Pushing Boundaries with Innovation
Meta's dedication to advancing AI technology showcases their commitment to providing next-level experiences for their users. With recent breakthroughs in natural language processing, computer vision, and machine learning, Meta has laid the groundwork for developers to take advantage of these powerful tools.
From smart recommendations to real-time translation and image recognition, developers now have the ability to leverage Meta's AI capabilities and enhance the overall user experience within their apps. With Meta's AI at their fingertips, developers can unlock endless possibilities and bring their visions to life.
New AI Features for Developers: Empowering Innovation
Meta's new AI features offer developers a wide range of tools and functionalities that go beyond basic automation. These advancements will enable developers to build intelligent systems, create personalized user experiences, and streamline their development process. Let's take a closer look at some of these exciting features:
1.Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Meta's NLP capabilities allow developers to analyze and understand human language. By integrating NLP into their applications, developers can enable chatbots, sentiment analysis, and language translation. This empowers them to create more interactive and engaging experiences for users, breaking down language barriers and facilitating seamlesscommunication.
2.Computer Vision
Meta's computer vision tools provide developers with the ability to process and understand visual data. By leveraging image recognition, object detection, and augmented reality technologies, developers can create immersive visual experiences that captivate users. From virtual try-ons to real-time image manipulation, the possibilities are endless with Meta's AI-powered computer vision.
3.Machine Learning
Meta's machine learning capabilities open doors to predictive analytics, personalized recommendations, and intelligent automation. By incorporating machine learning algorithms into their applications, developers can harness the power of data to improve user engagement and optimize various business processes. From personalized content suggestions to smart user segmentation, machine learning can transform the way developers create tailored experiences.
Meta Platform Updates: Innovations at Your Fingertips
To ensure developers can easily access and integrate Meta's new AI features, the platform has undergone several updates. This ensures a seamless development experience, enabling developers to leverage the power of AI without the need for complexsetups.
Meta's platform updates include:
1.Developer Documentation and APIs: Meta provides comprehensive documentation and APIs that empower developers to leverage AI functionalities effectively. With detailed guides and resources, developers can quickly integrate Meta's AI tools into their applications and get up to speed with the latest advancements.
2.Developer Community and Support: Meta has fostered a vibrant developer community where developers can connect, collaborate, and seek support. Through forums, meetups, and online resources, developers can exchange ideas, share best practices, and troubleshoot challenges together, further expanding their knowledge and expertise.
3.Continuous Improvement: Meta is committed to continuous improvement and regularly enhances its AI offerings based on user feedback and emerging technologies. Developers can expect new features and improvements to Meta's AI tools, ensuring they stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
Artificial Intelligence Tools for Developers: Unleashing Creativity
With Meta's AI tools for developers, endless opportunities await. By harnessing the power of NLP, computer vision, and machine learning, developers can elevate their applications to new heights. Whether it's creating interactive chatbots, implementing sophisticated image recognition, or delivering personalized recommendations, Meta's AI features unlock new dimensions of creativity and innovation.
By utilizing Meta's AI tools, developers can:
1.Enhance User Experience: By leveraging AI tools, developers can create highly engaging and intuitive experiences that satisfy user needs and preferences. From intelligent search and recommendations to natural language interfaces, users can interact with applications in a more seamless and personalized way.
2.Boost Efficiency and Productivity: Automation and intelligent systems powered by AI tools can streamline various tasks and processes, allowing developers to focus on core functionality and higher-level concepts. This promotes efficiency and productivity, enabling faster development cycles and quicker iteration.
3.Drive Business Growth: AI-powered applications can help businesses gain a competitive edge by providing valuable insights, automating mundane tasks, and delivering personalized customer experiences. By leveraging Meta's AI tools, developers can pave the way for business growth and success.
How to obtain A.I certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
In conclusion, Meta's new AI features are set to revolutionize the way developers create and innovate. With advancements in natural language processing, computer vision, and machine learning, developers can unlock the power of AI and bring their visions to life. By integrating Meta's AI tools into their applications, developers can enhance the user experience, boost efficiency, and drive business growth. With Meta's commitment to ongoing improvements and a supportive developer community, the sky's the limit for AI-powered innovation. So, what are you waiting for? Embrace Meta's new AI features and unleash your creativity.
Top Tips for Future CISOs to Lead Cybersecurity Effectively
Introduction
The role of a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is crucial in today's ever-evolving digital landscape. As organizations increasingly rely on technology for their day-to-day operations, the need for strong cybersecurity leadership becomes paramount. In this article, we will explore essential advice, strategies, and insights that future CISOs should consider to thrive in their role and effectively manage information security.
Main Keyword: Tips for Future CISOs
Becoming a successful CISO involves more than just technical expertise. To excel in this role, it requires a broad set of skills, including effective communication, leadership, and strategic thinking. Here are some valuable tips for aspiring CISOs:
1. Continuously educate yourself and stay up-to-date
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and new vulnerabilities emerge regularly. As a future CISO, it is crucial to stay updated with the latest trends, emerging technologies, and potential threats. Dedicate time to research, attend conferences, and engage with the cyber security community to gain insights into best practices and new defense mechanisms.
2. Develop a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy
To effectively safeguard an organization's information assets, future CISOs must develop a robust cybersecurity strategy. This strategy should align with the organization's broader goals and cover areas such as risk assessment, incident response, employee awareness training, and regulatory compliance. Emphasize the importance of proactive measures to mitigate risks and establish a culture of security throughout the organization.
3. Foster a culture of security
A strong security culture starts at the top. As a future CISO, it is your responsibility to promote a culture of security across the organization. This involves educating employees about their role in maintaining security, providing training on best practices, and encouraging open lines of communication for reporting potential security incidents. Remember, security is not just the responsibility of the IT department but everyone within the organization.
4. Build strong relationships with stakeholders
Successful CISOs understand the importance of building strong relationships with stakeholders, including executives, department heads, and board members. This enables effective communication, support for security initiatives, and the allocation of necessary resources. Take the time to understand the objectives and concerns of different departments to tailor your security approach accordingly.
5. Emphasize the human element of cybersecurity
Humans are often the weakest link in an organization's security posture. As a future CISO, it is essential to invest in training programs that educate employees about common security risks, such as phishing attacks and social engineering. Develop policies and procedures addressing employee responsibilities in safeguarding sensitive information to reduce the likelihood of successful cyber-attacks.
6. Stay agile and adaptable
The cybersecurity landscape is ever-changing, and future CISOs must be agile and adaptable. Develop the ability to continuously assess and adjust your cybersecurity strategy based on emerging threats and changing business requirements. Embrace new technologies and methodologies to ensure your organization remains ahead of potential risks.
How to obtain CISOs certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Becoming a CISO is a challenging yet rewarding journey. By following these tips, future CISOs can position themselves as effective leaders in the field of information security. Remember to stay educated, develop a comprehensive strategy, foster a culture of security, build relationships with stakeholders, emphasize the human element, and remain agile and adaptable. These foundations will help you navigate the complex cybersecurity landscape and protect your organization's valuable assets in the future.
Read More
Introduction
The role of a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is crucial in today's ever-evolving digital landscape. As organizations increasingly rely on technology for their day-to-day operations, the need for strong cybersecurity leadership becomes paramount. In this article, we will explore essential advice, strategies, and insights that future CISOs should consider to thrive in their role and effectively manage information security.
Main Keyword: Tips for Future CISOs
Becoming a successful CISO involves more than just technical expertise. To excel in this role, it requires a broad set of skills, including effective communication, leadership, and strategic thinking. Here are some valuable tips for aspiring CISOs:
1. Continuously educate yourself and stay up-to-date
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and new vulnerabilities emerge regularly. As a future CISO, it is crucial to stay updated with the latest trends, emerging technologies, and potential threats. Dedicate time to research, attend conferences, and engage with the cyber security community to gain insights into best practices and new defense mechanisms.
2. Develop a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy
To effectively safeguard an organization's information assets, future CISOs must develop a robust cybersecurity strategy. This strategy should align with the organization's broader goals and cover areas such as risk assessment, incident response, employee awareness training, and regulatory compliance. Emphasize the importance of proactive measures to mitigate risks and establish a culture of security throughout the organization.
3. Foster a culture of security
A strong security culture starts at the top. As a future CISO, it is your responsibility to promote a culture of security across the organization. This involves educating employees about their role in maintaining security, providing training on best practices, and encouraging open lines of communication for reporting potential security incidents. Remember, security is not just the responsibility of the IT department but everyone within the organization.
4. Build strong relationships with stakeholders
Successful CISOs understand the importance of building strong relationships with stakeholders, including executives, department heads, and board members. This enables effective communication, support for security initiatives, and the allocation of necessary resources. Take the time to understand the objectives and concerns of different departments to tailor your security approach accordingly.
5. Emphasize the human element of cybersecurity
Humans are often the weakest link in an organization's security posture. As a future CISO, it is essential to invest in training programs that educate employees about common security risks, such as phishing attacks and social engineering. Develop policies and procedures addressing employee responsibilities in safeguarding sensitive information to reduce the likelihood of successful cyber-attacks.
6. Stay agile and adaptable
The cybersecurity landscape is ever-changing, and future CISOs must be agile and adaptable. Develop the ability to continuously assess and adjust your cybersecurity strategy based on emerging threats and changing business requirements. Embrace new technologies and methodologies to ensure your organization remains ahead of potential risks.
How to obtain CISOs certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Becoming a CISO is a challenging yet rewarding journey. By following these tips, future CISOs can position themselves as effective leaders in the field of information security. Remember to stay educated, develop a comprehensive strategy, foster a culture of security, build relationships with stakeholders, emphasize the human element, and remain agile and adaptable. These foundations will help you navigate the complex cybersecurity landscape and protect your organization's valuable assets in the future.
Windows Desktop Administration Basics & Essential Skills
Introduction
Are you new to the world of Windows Desktop Admin? Feeling overwhelmed with the technical jargon and complex processes? Don't worry, this article is here to guide you through the fundamentals of Windows Desktop Administration, breaking down the concepts into easy-to-understand terms. Whether you're a beginner or looking to brush up on your skills, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the world of Windows Desktop Administration confidently.
Windows Desktop Administration: Understanding the Fundamentals
What is Windows Desktop Administration?
Windows Desktop Administration refers to the management and maintenance of the Windows operating system installed on computers. It involves various tasks such as setting up user accounts, configuring system settings, installing and updating software, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring the security and smooth operation of desktop systems within an organization.
Why is Windows Desktop Administration Important?
Efficient Windows Desktop Administration is crucial for ensuring the smooth functioning of desktop systems, optimizing performance, and maximizing productivity. By managing and maintaining desktop systems effectively, Windows Desktop Admins can minimize downtime, resolve issues in a timely manner, and provide users with a secure and reliable computing environment.
Key Responsibilities of Windows Desktop Admins
1. User Account Management: Windows Desktop Admins are responsible for creating, modifying, and managing user accounts on desktop systems. This includes setting up access privileges, password management, and ensuring proper user authentication.
2. System Configuration: Configuring desktop systems to meet the requirements and policies of an organization is a vital task for Windows Desktop Admins. This involves setting up network connections, optimizing system settings, and customizing desktop environments to suit user preferences.
3. Software Installation and Updates: Windows Desktop Admins are responsible for installing and updating software applications on desktop systems. This ensures that users have access to the latest versions of essential software and patches for security vulnerabilities.
4. Troubleshooting and Support: When issues arise, Windows Desktop Admins are the first line of defense. They must troubleshoot and resolve hardware, software, and network problems promptly. Additionally, they provide support to end-users, answering queries and providing guidance on using desktop systems effectively.
5. Security and Data Protection: Protecting sensitive data is a top priority for Windows Desktop Admins. They implement security measures such as antivirus software, encryption, user access controls, and backups to safeguard against data loss, unauthorized access, and security breaches.
Windows Desktop Administration Best Practices
1. Regular System Maintenance
Perform regular system maintenance tasks such as disk cleanup, defragmentation, and updating software and security patches. This helps optimize system performance and minimize the risk of security vulnerabilities.
2. Implementing Group Policies
Group Policies allow Windows Desktop Admins to manage desktop systems centrally. Use Group Policies to enforce security settings, configure user permissions, and restrict certain actions to ensure compliance with organization policies.
3. Creating Standardized Images
Creating standardized system images with preconfigured settings and software applications streamlines the deployment process. This enables admins to quickly set up new systems or restore existing ones to a desired state.
4. Implementing Backup and Recovery Strategies
Regularly back up user data, system settings, and important files to avoid data loss due to hardware failures or other unforeseen circumstances. Having a robust backup and recovery strategy in place is crucial for business continuity.
5. Staying Updated
Stay informed about the latest trends, technologies, and best practices in Windows Desktop Administration. Subscribe to relevant forums, blogs, and official Microsoft resources to expand your knowledge and ensure you are up-to-date with the latest developments in the field.
How to obtain Development certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
With the fundamental concepts of Windows Desktop Administration at your fingertips, you are now equipped to embark on your journey as a Windows Desktop Admin. By understanding the key responsibilities and implementing best practices, you can ensure the smooth functioning of desktop systems, minimize issues, and provide the best user experience. Remember, Windows Desktop Administration is an ongoing learning process, and staying up-to-date with the evolving technology landscape is crucial for success in this field.
Read More
Introduction
Are you new to the world of Windows Desktop Admin? Feeling overwhelmed with the technical jargon and complex processes? Don't worry, this article is here to guide you through the fundamentals of Windows Desktop Administration, breaking down the concepts into easy-to-understand terms. Whether you're a beginner or looking to brush up on your skills, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the world of Windows Desktop Administration confidently.
Windows Desktop Administration: Understanding the Fundamentals
What is Windows Desktop Administration?
Windows Desktop Administration refers to the management and maintenance of the Windows operating system installed on computers. It involves various tasks such as setting up user accounts, configuring system settings, installing and updating software, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring the security and smooth operation of desktop systems within an organization.
Why is Windows Desktop Administration Important?
Efficient Windows Desktop Administration is crucial for ensuring the smooth functioning of desktop systems, optimizing performance, and maximizing productivity. By managing and maintaining desktop systems effectively, Windows Desktop Admins can minimize downtime, resolve issues in a timely manner, and provide users with a secure and reliable computing environment.
Key Responsibilities of Windows Desktop Admins
1. User Account Management: Windows Desktop Admins are responsible for creating, modifying, and managing user accounts on desktop systems. This includes setting up access privileges, password management, and ensuring proper user authentication.
2. System Configuration: Configuring desktop systems to meet the requirements and policies of an organization is a vital task for Windows Desktop Admins. This involves setting up network connections, optimizing system settings, and customizing desktop environments to suit user preferences.
3. Software Installation and Updates: Windows Desktop Admins are responsible for installing and updating software applications on desktop systems. This ensures that users have access to the latest versions of essential software and patches for security vulnerabilities.
4. Troubleshooting and Support: When issues arise, Windows Desktop Admins are the first line of defense. They must troubleshoot and resolve hardware, software, and network problems promptly. Additionally, they provide support to end-users, answering queries and providing guidance on using desktop systems effectively.
5. Security and Data Protection: Protecting sensitive data is a top priority for Windows Desktop Admins. They implement security measures such as antivirus software, encryption, user access controls, and backups to safeguard against data loss, unauthorized access, and security breaches.
Windows Desktop Administration Best Practices
1. Regular System Maintenance
Perform regular system maintenance tasks such as disk cleanup, defragmentation, and updating software and security patches. This helps optimize system performance and minimize the risk of security vulnerabilities.
2. Implementing Group Policies
Group Policies allow Windows Desktop Admins to manage desktop systems centrally. Use Group Policies to enforce security settings, configure user permissions, and restrict certain actions to ensure compliance with organization policies.
3. Creating Standardized Images
Creating standardized system images with preconfigured settings and software applications streamlines the deployment process. This enables admins to quickly set up new systems or restore existing ones to a desired state.
4. Implementing Backup and Recovery Strategies
Regularly back up user data, system settings, and important files to avoid data loss due to hardware failures or other unforeseen circumstances. Having a robust backup and recovery strategy in place is crucial for business continuity.
5. Staying Updated
Stay informed about the latest trends, technologies, and best practices in Windows Desktop Administration. Subscribe to relevant forums, blogs, and official Microsoft resources to expand your knowledge and ensure you are up-to-date with the latest developments in the field.
How to obtain Development certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
With the fundamental concepts of Windows Desktop Administration at your fingertips, you are now equipped to embark on your journey as a Windows Desktop Admin. By understanding the key responsibilities and implementing best practices, you can ensure the smooth functioning of desktop systems, minimize issues, and provide the best user experience. Remember, Windows Desktop Administration is an ongoing learning process, and staying up-to-date with the evolving technology landscape is crucial for success in this field.
Boost your cloud career with EXIN Cloud Certification!!
Cloud computing has become an integral part of the IT industry, revolutionizing the way businesses operate and organize their data. As more and more companies migrate their operations to the cloud, there is an increasing demand for skilled professionals who can effectively manage and implement cloud solutions. This is where EXIN Cloud Computing Certification comes into play.
EXIN Cloud Computing Certification: What is it?
EXIN Cloud Computing Certification is a globally recognized certification that validates your knowledge and expertise in cloud computing. It covers a wide range of topics, including cloud infrastructure, deployment models, security, and governance. By obtaining this certification, you demonstrate your commitment to professional development and your ability to handle complex cloud projects.
Why Choose EXIN Cloud Computing Certification?
Enhance Your Skills: By pursuing EXIN Cloud Computing Certification, you can enhance your skills and stay ahead of the curve in this rapidly evolving field. The comprehensive curriculum covers all aspects of cloud computing, ensuring that you develop a solid foundation and become well-versed in the latest industry trends and best practices.
Gain Industry Recognition: EXIN is a renowned provider of IT certifications, trusted by professionals and employers worldwide. With EXIN Cloud Computing Certification on your resume, you gain instant industry recognition and significantly increase your marketability. Employers are more likely to consider candidates with relevant certifications, giving you a competitive edge in the job market.
Expand Your Career Opportunities: Cloud computing is reshaping the future of IT, and skilled professionals in this domain are in high demand. By obtaining EXIN Cloud Computing Certification, you open up a world of exciting career opportunities. Whether you are looking to advance in your current organization or explore new horizons, this certification can pave the way for lucrative positions and roles with greater responsibilities.
Stay Updated with the Latest Technologies: The EXIN Cloud Computing Certification program is designed to equip you with up-to-date knowledge and skills. As part of the certification process, you will learn about the latest cloud technologies, industry standards, and emerging trends. This ensures that you stay relevant in the fast-paced and ever-changing world of cloud computing.
How to Obtain EXIN Cloud Computing Certification
To obtain the EXIN Cloud Computing Certification, you need to pass the relevant exam. The exam consists of multiple-choice questions that test your understanding of cloud computing concepts, architecture, and implementation. It also evaluates your ability to analyze and troubleshoot cloud-related issues.
It is recommended to enroll in a training program or study guide to prepare for the certification exam. These resources provide in-depth coverage of the exam syllabus and offer practice tests to assess your knowledge and readiness. Additionally, hands-on experience with cloud platforms and tools can greatly enhance your chances of success.
How to obtain Exin Cloud Computing certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
-
Salesforce : SALESFORCE PLATFORM DEVELOPER
Conclusion
In conclusion, if you are looking to level up your career in the cloud, EXIN Cloud Computing Certification is the key. By obtaining this certification, you not only enhance your skills and gain industry recognition but also open up a world of exciting career opportunities. Don't miss out on the chance to become a certified professional in cloud computing and take your career to new heights!
Read More
Cloud computing has become an integral part of the IT industry, revolutionizing the way businesses operate and organize their data. As more and more companies migrate their operations to the cloud, there is an increasing demand for skilled professionals who can effectively manage and implement cloud solutions. This is where EXIN Cloud Computing Certification comes into play.
EXIN Cloud Computing Certification: What is it?
EXIN Cloud Computing Certification is a globally recognized certification that validates your knowledge and expertise in cloud computing. It covers a wide range of topics, including cloud infrastructure, deployment models, security, and governance. By obtaining this certification, you demonstrate your commitment to professional development and your ability to handle complex cloud projects.
Why Choose EXIN Cloud Computing Certification?
Enhance Your Skills: By pursuing EXIN Cloud Computing Certification, you can enhance your skills and stay ahead of the curve in this rapidly evolving field. The comprehensive curriculum covers all aspects of cloud computing, ensuring that you develop a solid foundation and become well-versed in the latest industry trends and best practices.
Gain Industry Recognition: EXIN is a renowned provider of IT certifications, trusted by professionals and employers worldwide. With EXIN Cloud Computing Certification on your resume, you gain instant industry recognition and significantly increase your marketability. Employers are more likely to consider candidates with relevant certifications, giving you a competitive edge in the job market.
Expand Your Career Opportunities: Cloud computing is reshaping the future of IT, and skilled professionals in this domain are in high demand. By obtaining EXIN Cloud Computing Certification, you open up a world of exciting career opportunities. Whether you are looking to advance in your current organization or explore new horizons, this certification can pave the way for lucrative positions and roles with greater responsibilities.
Stay Updated with the Latest Technologies: The EXIN Cloud Computing Certification program is designed to equip you with up-to-date knowledge and skills. As part of the certification process, you will learn about the latest cloud technologies, industry standards, and emerging trends. This ensures that you stay relevant in the fast-paced and ever-changing world of cloud computing.
How to Obtain EXIN Cloud Computing Certification
To obtain the EXIN Cloud Computing Certification, you need to pass the relevant exam. The exam consists of multiple-choice questions that test your understanding of cloud computing concepts, architecture, and implementation. It also evaluates your ability to analyze and troubleshoot cloud-related issues.
It is recommended to enroll in a training program or study guide to prepare for the certification exam. These resources provide in-depth coverage of the exam syllabus and offer practice tests to assess your knowledge and readiness. Additionally, hands-on experience with cloud platforms and tools can greatly enhance your chances of success.
How to obtain Exin Cloud Computing certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
-
Salesforce : SALESFORCE PLATFORM DEVELOPER
Conclusion
In conclusion, if you are looking to level up your career in the cloud, EXIN Cloud Computing Certification is the key. By obtaining this certification, you not only enhance your skills and gain industry recognition but also open up a world of exciting career opportunities. Don't miss out on the chance to become a certified professional in cloud computing and take your career to new heights!
Master Data Science with R: Unlock Certification Success!
If you are interested in the field of data science, becoming proficient in the R programming language can unlock a world of opportunities. With its powerful capabilities in data analysis, visualization, statistical modeling, and machine learning, R is widely recognized as one of the most popular programming languages for data scientists. In this article, we will explore how mastering data science with the power of R can lead to certification success and help you advance in your career.
The Importance of Data Analysis:
Data analysis is at the core of any data science project. By leveraging the power of R, you can efficiently analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and draw meaningful insights. R provides a rich variety of packages and libraries that offer a wide range of statistical and analytical tools. With R, you can handle data preprocessing, perform exploratory data analysis, and apply advanced statistical techniques to uncover hidden patterns in your data.
Visualization Made Easy with R:
Data visualization plays a crucial role in communicating complex data insights effectively. R offers a plethora of visualization tools and packages, such as ggplot2 and plotly, that make it easy to create visually appealing and interactive plots and charts. Whether you need to create bar charts, scatter plots, or even interactive dashboards, R provides the versatility and flexibility to transform your data into compelling visual representations.
Statistical Modeling with R:
Statistical modeling is a key component of data science, allowing you to build models that can predict outcomes and make data-driven decisions. R provides a comprehensive set of packages, like caret and glmnet, that facilitate the implementation of various statistical modeling techniques. Whether you need to perform regression analysis, build decision trees, or conduct time series forecasting, R has the tools and libraries to support your statistical modeling needs.
Unlocking Machine Learning Capabilities with R:
Machine learning is revolutionizing many industries, and R is an excellent language for implementing machine learning algorithms. R provides popular machine learning libraries, such as caret and randomForest, that enable you to train and evaluate models for classification, regression, and clustering tasks. Additionally, R offers seamless integration with other machine learning frameworks like TensorFlow and Keras, allowing you to leverage the power of deep learning.
Efficient Data Manipulation with R:
Manipulating and transforming data is a fundamental step in any data science project. R's data manipulation capabilities make it easy to preprocess, clean, and reshape data to fit the requirements of your analysis. R provides intuitive functions like dplyr and tidyr that enable you to filter, sort, join, and reshape datasets with ease. With R, you can efficiently handle missing values, perform data aggregation, and create new variables to enhance your data analysis workflow.
How to obtain Data Science With R certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
-
Salesforce : SALESFORCE PLATFORM DEVELOPER
-
Data Science and Business Intelligence: Data Science with R Programming
Conclusion:
Mastering data science with the power of R is a surefire way to unlock your certification success. With its unmatched capabilities in data analysis, visualization, statistical modeling, machine learning, and data manipulation, R equips you with the necessary tools to excel in the field of data science. As you embark on your journey to become a certified data scientist, make sure to invest time and effort in enhancing your R programming skills. The possibilities are endless, and the rewards are immense for those who embrace the power of R in their data science journey.
Read More
If you are interested in the field of data science, becoming proficient in the R programming language can unlock a world of opportunities. With its powerful capabilities in data analysis, visualization, statistical modeling, and machine learning, R is widely recognized as one of the most popular programming languages for data scientists. In this article, we will explore how mastering data science with the power of R can lead to certification success and help you advance in your career.
The Importance of Data Analysis:
Data analysis is at the core of any data science project. By leveraging the power of R, you can efficiently analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and draw meaningful insights. R provides a rich variety of packages and libraries that offer a wide range of statistical and analytical tools. With R, you can handle data preprocessing, perform exploratory data analysis, and apply advanced statistical techniques to uncover hidden patterns in your data.
Visualization Made Easy with R:
Data visualization plays a crucial role in communicating complex data insights effectively. R offers a plethora of visualization tools and packages, such as ggplot2 and plotly, that make it easy to create visually appealing and interactive plots and charts. Whether you need to create bar charts, scatter plots, or even interactive dashboards, R provides the versatility and flexibility to transform your data into compelling visual representations.
Statistical Modeling with R:
Statistical modeling is a key component of data science, allowing you to build models that can predict outcomes and make data-driven decisions. R provides a comprehensive set of packages, like caret and glmnet, that facilitate the implementation of various statistical modeling techniques. Whether you need to perform regression analysis, build decision trees, or conduct time series forecasting, R has the tools and libraries to support your statistical modeling needs.
Unlocking Machine Learning Capabilities with R:
Machine learning is revolutionizing many industries, and R is an excellent language for implementing machine learning algorithms. R provides popular machine learning libraries, such as caret and randomForest, that enable you to train and evaluate models for classification, regression, and clustering tasks. Additionally, R offers seamless integration with other machine learning frameworks like TensorFlow and Keras, allowing you to leverage the power of deep learning.
Efficient Data Manipulation with R:
Manipulating and transforming data is a fundamental step in any data science project. R's data manipulation capabilities make it easy to preprocess, clean, and reshape data to fit the requirements of your analysis. R provides intuitive functions like dplyr and tidyr that enable you to filter, sort, join, and reshape datasets with ease. With R, you can efficiently handle missing values, perform data aggregation, and create new variables to enhance your data analysis workflow.
How to obtain Data Science With R certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
-
Salesforce : SALESFORCE PLATFORM DEVELOPER
-
Data Science and Business Intelligence: Data Science with R Programming
Conclusion:
Mastering data science with the power of R is a surefire way to unlock your certification success. With its unmatched capabilities in data analysis, visualization, statistical modeling, machine learning, and data manipulation, R equips you with the necessary tools to excel in the field of data science. As you embark on your journey to become a certified data scientist, make sure to invest time and effort in enhancing your R programming skills. The possibilities are endless, and the rewards are immense for those who embrace the power of R in their data science journey.
Mastering MongoDB: Expert Development and Administration
Are you ready to embark on a journey to become a master in MongoDB? In today's digital world, data is the backbone of every successful business. As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow, efficient database management becomes paramount. Mongo DB, a powerful document-oriented database, offers a flexible and scalable solution for managing large amounts of data. In this article, we will delve into the world of MongoDB, exploring expert development and administration techniques that will empower you to optimize query performance, perform data analytics, and unlock the full potential of this versatile database.
The Fundamentals of MongoDB
Before diving into the intricacies of mastering MongoDB, let's first establish a solid foundation. MongoDB is a NoSQL database that stores data in the form of key-value pairs within flexible JSON-like documents. Unlike traditional relational databases, MongoDB offers greater flexibility and scalability, making it an ideal choice for modern data-driven applications.
Data Modeling for Success
Effective data modeling is pivotal in ensuring a well-performing MongoDB database. By designing your data model to align with the unique characteristics and requirements of your application, you can optimize read and write operations. Consider your application's data access patterns, performance goals, and scalability needs when designing your MongoDB schemas.
Database Optimization Techniques
To harness the true power of MongoDB, it is essential to optimize your database for speed and efficiency. Here are some expert techniques to consider:
Indexing: Proper indexing allows MongoDB to quickly locate and retrieve data based on specific queries. Identify the most frequently executed queries and create appropriate indexes to enhance query performance.
Sharding: When dealing with large datasets, sharding distributes the data across multiple servers, improving data distribution and query performance. Carefully choose the shard key to ensure balanced data distribution.
Caching: Leveraging an in-memory cache, such as Redis or Memcached, can significantly boost database performance by reducing the need to access disk-based storage for frequently accessed data.
Unleashing MongoDB's Query Performance
Queries are at the heart of any database system, and optimizing query performance is crucial for a seamless user experience. MongoDB provides various mechanisms to maximize query performance:
Query Optimization: Mongo DB's query optimizer evaluates various query plans and selects the most efficient one. Ensure that your queries are properly indexed and utilize query operators effectively to guide the optimizer in making the right choices.
Aggregation Pipeline: MongoDB's Aggregation Pipeline offers a powerful framework for performing complex data transformations and analytics. By using stages like $match, $group, and $project, you can efficiently analyze and manipulate data.
Data Partitioning: Partitioning your data using range or hash-based sharding can distribute the workload across multiple servers, enhancing query performance by leveraging parallel processing.
Uncovering Insights with Data Analytics
In the age of big data, the ability to analyze and derive actionable insights from vast amounts of information is invaluable. MongoDB provides robust analytics capabilities through its integration with popular tools like Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark. By tapping into these tools, you can unleash the power of distributed computing to process and analyze large datasets stored in MongoDB.
How to obtain MongoDB certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
-
Salesforce : SALESFORCE PLATFORM DEVELOPER
-
Development Courses : MongoDB Developer and Administrator
Conclusion
Congratulations on completing your journey into expert development and administration of MongoDB! By mastering the techniques discussed in this article, you are well equipped to navigate the complexities of managing MongoDB databases. Remember to continuously explore MongoDB's extensive documentation, industry best practices, and stay updated with the latest advancements in database optimization and data modeling. With MongoDB by your side, you have the tools to take your data-driven applications to new heights of performance and scalability. Happy MongoDB-ing!
Read More
Are you ready to embark on a journey to become a master in MongoDB? In today's digital world, data is the backbone of every successful business. As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow, efficient database management becomes paramount. Mongo DB, a powerful document-oriented database, offers a flexible and scalable solution for managing large amounts of data. In this article, we will delve into the world of MongoDB, exploring expert development and administration techniques that will empower you to optimize query performance, perform data analytics, and unlock the full potential of this versatile database.
The Fundamentals of MongoDB
Before diving into the intricacies of mastering MongoDB, let's first establish a solid foundation. MongoDB is a NoSQL database that stores data in the form of key-value pairs within flexible JSON-like documents. Unlike traditional relational databases, MongoDB offers greater flexibility and scalability, making it an ideal choice for modern data-driven applications.
Data Modeling for Success
Effective data modeling is pivotal in ensuring a well-performing MongoDB database. By designing your data model to align with the unique characteristics and requirements of your application, you can optimize read and write operations. Consider your application's data access patterns, performance goals, and scalability needs when designing your MongoDB schemas.
Database Optimization Techniques
To harness the true power of MongoDB, it is essential to optimize your database for speed and efficiency. Here are some expert techniques to consider:
Indexing: Proper indexing allows MongoDB to quickly locate and retrieve data based on specific queries. Identify the most frequently executed queries and create appropriate indexes to enhance query performance.
Sharding: When dealing with large datasets, sharding distributes the data across multiple servers, improving data distribution and query performance. Carefully choose the shard key to ensure balanced data distribution.
Caching: Leveraging an in-memory cache, such as Redis or Memcached, can significantly boost database performance by reducing the need to access disk-based storage for frequently accessed data.
Unleashing MongoDB's Query Performance
Queries are at the heart of any database system, and optimizing query performance is crucial for a seamless user experience. MongoDB provides various mechanisms to maximize query performance:
Query Optimization: Mongo DB's query optimizer evaluates various query plans and selects the most efficient one. Ensure that your queries are properly indexed and utilize query operators effectively to guide the optimizer in making the right choices.
Aggregation Pipeline: MongoDB's Aggregation Pipeline offers a powerful framework for performing complex data transformations and analytics. By using stages like $match, $group, and $project, you can efficiently analyze and manipulate data.
Data Partitioning: Partitioning your data using range or hash-based sharding can distribute the workload across multiple servers, enhancing query performance by leveraging parallel processing.
Uncovering Insights with Data Analytics
In the age of big data, the ability to analyze and derive actionable insights from vast amounts of information is invaluable. MongoDB provides robust analytics capabilities through its integration with popular tools like Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark. By tapping into these tools, you can unleash the power of distributed computing to process and analyze large datasets stored in MongoDB.
How to obtain MongoDB certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
-
Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
-
Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
-
Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
-
Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
-
Scrum Training: CSM
-
DevOps
-
Program Management: PgMP
-
Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
-
Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
-
Salesforce : SALESFORCE PLATFORM DEVELOPER
-
Development Courses : MongoDB Developer and Administrator
Conclusion
Congratulations on completing your journey into expert development and administration of MongoDB! By mastering the techniques discussed in this article, you are well equipped to navigate the complexities of managing MongoDB databases. Remember to continuously explore MongoDB's extensive documentation, industry best practices, and stay updated with the latest advancements in database optimization and data modeling. With MongoDB by your side, you have the tools to take your data-driven applications to new heights of performance and scalability. Happy MongoDB-ing!
Quality Management: Definition, Importance, Components!!
Introduction
Quality management plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of businesses across various industries. It involves a systematic approach to maintaining and improving the quality of products, services, and processes. In this article, we will explore the definition, importance, and components of quality management and delve into the concept of Total Quality Management.
Quality Management System (QMS)
A Quality Management System (QMS) is the framework that enables organizations to establish and uphold their commitment to quality. It encompasses the policies, procedures, and processes that guide the organization in achieving its quality objectives. The QMS serves as the backbone of quality management, providing a structured framework for identifying, controlling, and improving quality-related activities.
Importance of Quality Management
Quality management is of utmost importance for businesses, as it offers several significant benefits. Let's take a closer look at why quality management is vital:
1. Customer Satisfaction
In today's competitive market, customer satisfaction is a top priority for businesses. Quality management ensures that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty. Satisfied customers not only become repeat customers but also act as brand advocates, attracting new customers through positive word-of-mouth.
2. Cost Reduction
Implementing quality management practices can result in cost reductions for businesses. By identifying and eliminating inefficiencies, defects, and non-value-added activities, organizations can streamline their processes and improve overall productivity. This, in turn, leads to lower production costs, reduced waste, and increased profitability.
3. Brand Reputation
Maintaining a strong brand reputation is vital for businesses to thrive in today's competitive landscape. Quality management helps organizations consistently deliver high-quality products and services, earning them a favorable reputation among customers, partners, and stakeholders. A positive brand image fosters trust, credibility, and long-term success.
4. Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Compliance with industry standards, regulations, and quality requirements is critical for businesses to avoid legal liabilities and penalties. Quality management ensures adherence to these standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated risks. By identifying and mitigating potential risks, organizations can proactively protect their interests and reputation.
Quality Components
Quality management involves various components that collectively contribute to achieving high standards of quality. Let's explore some key quality components:
1. Quality Planning
Quality planning involves defining quality standards, setting objectives, and determining the processes required to meet those standards. It includes identifying customer requirements, establishing quality metrics, and establishing a framework for continuous improvement.
2. Quality Assurance
Quality assurance focuses on preventing defects and ensuring compliance with established quality standards. It involves the implementation of processes, procedures, and controls to verify that products and services meet quality requirements. Quality audits are often conducted to assess the effectiveness of quality assurance activities.
3. Quality Control
Quality control is the process of monitoring and inspecting products, services, and processes to ensure they meet predetermined quality standards. It involves activities such as inspections, testing, and data analysis to detect and correct any deviations from the desired quality level.
4. Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a fundamental concept in quality management, aiming to enhance processes, products, and services over time. It involves regular evaluation, identification of areas for improvement, and the implementation of measures to drive ongoing progress. Continuous improvement fosters innovation, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a comprehensive approach to quality management that emphasizes the involvement of every individual in an organization. It integrates all aspects of quality management, focusing on meeting customer needs and achieving organizational goals. TQM encourages a culture of continuous improvement, teamwork, and employee empowerment.
How to obtain Quality Management certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
- Salesforce : SALESFORCE PLATFORM DEVELOPER
Conclusion
Quality management is a critical aspect of business success, ensuring customer satisfaction, cost reduction, brand reputation, and compliance. By implementing a robust Quality Management System and focusing on key quality components, organizations can maintain high standards and drive continuous improvement. Embracing the principles of Total Quality Management further enhances the effectiveness of quality management practices. Upholding quality as a top priority is essential for businesses aiming to thrive in today's competitive market landscape.
Read More
Introduction
Quality management plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of businesses across various industries. It involves a systematic approach to maintaining and improving the quality of products, services, and processes. In this article, we will explore the definition, importance, and components of quality management and delve into the concept of Total Quality Management.
Quality Management System (QMS)
A Quality Management System (QMS) is the framework that enables organizations to establish and uphold their commitment to quality. It encompasses the policies, procedures, and processes that guide the organization in achieving its quality objectives. The QMS serves as the backbone of quality management, providing a structured framework for identifying, controlling, and improving quality-related activities.
Importance of Quality Management
Quality management is of utmost importance for businesses, as it offers several significant benefits. Let's take a closer look at why quality management is vital:
1. Customer Satisfaction
In today's competitive market, customer satisfaction is a top priority for businesses. Quality management ensures that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty. Satisfied customers not only become repeat customers but also act as brand advocates, attracting new customers through positive word-of-mouth.
2. Cost Reduction
Implementing quality management practices can result in cost reductions for businesses. By identifying and eliminating inefficiencies, defects, and non-value-added activities, organizations can streamline their processes and improve overall productivity. This, in turn, leads to lower production costs, reduced waste, and increased profitability.
3. Brand Reputation
Maintaining a strong brand reputation is vital for businesses to thrive in today's competitive landscape. Quality management helps organizations consistently deliver high-quality products and services, earning them a favorable reputation among customers, partners, and stakeholders. A positive brand image fosters trust, credibility, and long-term success.
4. Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Compliance with industry standards, regulations, and quality requirements is critical for businesses to avoid legal liabilities and penalties. Quality management ensures adherence to these standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated risks. By identifying and mitigating potential risks, organizations can proactively protect their interests and reputation.
Quality Components
Quality management involves various components that collectively contribute to achieving high standards of quality. Let's explore some key quality components:
1. Quality Planning
Quality planning involves defining quality standards, setting objectives, and determining the processes required to meet those standards. It includes identifying customer requirements, establishing quality metrics, and establishing a framework for continuous improvement.
2. Quality Assurance
Quality assurance focuses on preventing defects and ensuring compliance with established quality standards. It involves the implementation of processes, procedures, and controls to verify that products and services meet quality requirements. Quality audits are often conducted to assess the effectiveness of quality assurance activities.
3. Quality Control
Quality control is the process of monitoring and inspecting products, services, and processes to ensure they meet predetermined quality standards. It involves activities such as inspections, testing, and data analysis to detect and correct any deviations from the desired quality level.
4. Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a fundamental concept in quality management, aiming to enhance processes, products, and services over time. It involves regular evaluation, identification of areas for improvement, and the implementation of measures to drive ongoing progress. Continuous improvement fosters innovation, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a comprehensive approach to quality management that emphasizes the involvement of every individual in an organization. It integrates all aspects of quality management, focusing on meeting customer needs and achieving organizational goals. TQM encourages a culture of continuous improvement, teamwork, and employee empowerment.
How to obtain Quality Management certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
- Salesforce : SALESFORCE PLATFORM DEVELOPER
Conclusion
Quality management is a critical aspect of business success, ensuring customer satisfaction, cost reduction, brand reputation, and compliance. By implementing a robust Quality Management System and focusing on key quality components, organizations can maintain high standards and drive continuous improvement. Embracing the principles of Total Quality Management further enhances the effectiveness of quality management practices. Upholding quality as a top priority is essential for businesses aiming to thrive in today's competitive market landscape.
Unlock Leadership Potential: Get Certified as a Scrum Master
Introduction
Are you looking to take your career to the next level and showcase your leadership potential? Have you considered becoming a Certified Scrum Master? In today's fast-paced business environment, organizations are increasingly adopting agile methodologies to effectively manage projects and improve productivity. As a Certified Scrum Master, you can unlock your leadership potential and become a valuable asset to any organization. In this article, we will explore the benefits of becoming a Certified Scrum Master and how it can help you enhance your leadership skills.
What is a Certified Scrum Master?
A Certified Scrum Master (CSM) is a professional who is trained in the scrum framework, which is a popular agile methodology used in project management. A CSM is responsible for facilitating collaboration and communication within a scrum team and ensuring that the team is following scrum practices effectively. By becoming a CSM, you gain the knowledge and skills necessary to guide teams towards successful project delivery and achieve business objectives efficiently.
Unlocking Your Leadership Potential
Becoming a Certified Scrum Master can unlock your leadership potential in several ways. Let's explore how:
1. Enhanced Communication and Collaboration Skills
As a Certified Scrum Master, you will become proficient in facilitating effective communication and collaboration within a team. You will learn to remove obstacles, facilitate productive meetings, and foster an environment of trust and transparency. These skills are valuable not only in project management but also in any leadership role where effective communication and collaboration are key to success.
2. Adaptive and Agile Thinking
Agile methodologies promote adaptive and agile thinking, which are essential qualities of effective leaders. As a Certified Scrum Master, you will be trained to embrace change, respond quickly to new challenges, and continuously improve processes. These attributes are highly valued in leadership roles as they enable you to navigate uncertainty, make informed decisions, and drive innovation.
3. Empowering and Servant Leadership
Certified Scrum Masters embody the principles of servant leadership, where the focus is on serving the team and enabling their success. By putting the needs of the team first, you become a leader who empowers and supports others, fostering a culture of collaboration and self-organization. This leadership style is highly effective in motivating teams, boosting productivity, and achieving project objectives.
4. Increased Job Opportunities
In today's competitive job market, organizations are actively seeking professionals with agile skill sets and certifications. By becoming a Certified Scrum Master, you open yourself up to a wider range of job opportunities across various industries. Employers recognize the value of agile methodologies and the role of a CSM in driving successful project delivery. Being a Certified Scrum Master can give you a competitive edge when applying for leadership positions or seeking career advancement.
How to Become a Certified Scrum Master
Now that you understand the benefits of becoming a Certified Scrum Master, let's explore the steps to acquire this valuable certification:
Get Trained: Enroll in a Certified Scrum Master training program offered by reputable training providers. This training will provide you with a solid understanding of the scrum framework, agile principles, and the responsibilities of a Scrum Master.
Pass the Exam: After completing the training, you will be required to pass the Certified Scrum Master exam. This exam tests your knowledge and comprehension of scrum practices, roles, and responsibilities. Successful completion of the exam will grant you the Certified Scrum Master certification.
Apply Your Knowledge: Once you are certified, apply your knowledge and skills in real-world scenarios. Work on projects using the scrum framework and gain practical experience as a Scrum Master. This hands-on experience will further enhance your expertise and leadership abilities.
Continuing Education: As with any certification, it is important to stay updated with the latest trends and developments in agile methodologies. Continuously expand your knowledge through workshops, conferences, and networking with other agile professionals. This ongoing education will ensure that you maintain your expertise as a Certified Scrum Master.
How to obtain Certified Scrum Master certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Becoming a Certified Scrum Master is a powerful way to unlock your leadership potential and stand out in today's competitive job market. With enhanced communication and collaboration skills, adaptive thinking, and a servant leadership mindset, you will be equipped to lead teams towards successful project delivery. By following the steps to become a Certified Scrum Master and continuously expanding your knowledge, you can take your career to new heights and become a trusted and effective leader in your organization.
Read More
Introduction
Are you looking to take your career to the next level and showcase your leadership potential? Have you considered becoming a Certified Scrum Master? In today's fast-paced business environment, organizations are increasingly adopting agile methodologies to effectively manage projects and improve productivity. As a Certified Scrum Master, you can unlock your leadership potential and become a valuable asset to any organization. In this article, we will explore the benefits of becoming a Certified Scrum Master and how it can help you enhance your leadership skills.
What is a Certified Scrum Master?
A Certified Scrum Master (CSM) is a professional who is trained in the scrum framework, which is a popular agile methodology used in project management. A CSM is responsible for facilitating collaboration and communication within a scrum team and ensuring that the team is following scrum practices effectively. By becoming a CSM, you gain the knowledge and skills necessary to guide teams towards successful project delivery and achieve business objectives efficiently.
Unlocking Your Leadership Potential
Becoming a Certified Scrum Master can unlock your leadership potential in several ways. Let's explore how:
1. Enhanced Communication and Collaboration Skills
As a Certified Scrum Master, you will become proficient in facilitating effective communication and collaboration within a team. You will learn to remove obstacles, facilitate productive meetings, and foster an environment of trust and transparency. These skills are valuable not only in project management but also in any leadership role where effective communication and collaboration are key to success.
2. Adaptive and Agile Thinking
Agile methodologies promote adaptive and agile thinking, which are essential qualities of effective leaders. As a Certified Scrum Master, you will be trained to embrace change, respond quickly to new challenges, and continuously improve processes. These attributes are highly valued in leadership roles as they enable you to navigate uncertainty, make informed decisions, and drive innovation.
3. Empowering and Servant Leadership
Certified Scrum Masters embody the principles of servant leadership, where the focus is on serving the team and enabling their success. By putting the needs of the team first, you become a leader who empowers and supports others, fostering a culture of collaboration and self-organization. This leadership style is highly effective in motivating teams, boosting productivity, and achieving project objectives.
4. Increased Job Opportunities
In today's competitive job market, organizations are actively seeking professionals with agile skill sets and certifications. By becoming a Certified Scrum Master, you open yourself up to a wider range of job opportunities across various industries. Employers recognize the value of agile methodologies and the role of a CSM in driving successful project delivery. Being a Certified Scrum Master can give you a competitive edge when applying for leadership positions or seeking career advancement.
How to Become a Certified Scrum Master
Now that you understand the benefits of becoming a Certified Scrum Master, let's explore the steps to acquire this valuable certification:
Get Trained: Enroll in a Certified Scrum Master training program offered by reputable training providers. This training will provide you with a solid understanding of the scrum framework, agile principles, and the responsibilities of a Scrum Master.
Pass the Exam: After completing the training, you will be required to pass the Certified Scrum Master exam. This exam tests your knowledge and comprehension of scrum practices, roles, and responsibilities. Successful completion of the exam will grant you the Certified Scrum Master certification.
Apply Your Knowledge: Once you are certified, apply your knowledge and skills in real-world scenarios. Work on projects using the scrum framework and gain practical experience as a Scrum Master. This hands-on experience will further enhance your expertise and leadership abilities.
Continuing Education: As with any certification, it is important to stay updated with the latest trends and developments in agile methodologies. Continuously expand your knowledge through workshops, conferences, and networking with other agile professionals. This ongoing education will ensure that you maintain your expertise as a Certified Scrum Master.
How to obtain Certified Scrum Master certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
Conclusion
Becoming a Certified Scrum Master is a powerful way to unlock your leadership potential and stand out in today's competitive job market. With enhanced communication and collaboration skills, adaptive thinking, and a servant leadership mindset, you will be equipped to lead teams towards successful project delivery. By following the steps to become a Certified Scrum Master and continuously expanding your knowledge, you can take your career to new heights and become a trusted and effective leader in your organization.
Exploring Blockchain: Unlocking the Future of Technology
Introduction
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing industries across the globe. With its decentralized nature and immutability, blockchain has the potential to transform the way we conduct business, manage data, and secure digital assets. In this article, we will explore the power of blockchain technology and unravel its immense potential to unlock new possibilities for the future.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Block chain technology is a distributed ledger system that allows for secure and transparent recording of transactions across multiple computers. In simple terms, it is a chain of blocks, where each block contains a set of transactions, and these blocks are linked together using cryptographic hashes.
The Power of Decentralization
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a single authority controls the data and transactions, blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries by allowing participants to directly interact with each other. This decentralized approach not only enhances security but also promotes trust and transparency in transactions.
Enhanced Security and Transparency
Blockchain technology uses advanced cryptographic techniques to ensure the security of data stored within its blocks. Each transaction is verified and recorded in a way that is resistant to tampering or modification. This makes blockchain an ideal solution for industries that require high levels of data security, such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
Unlocking New Business Models
Blockchain technology is not limited to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Its versatility enables the creation of smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), and even tokenized assets. These new business models open up avenues for innovation and disruption across various industries, including finance, real estate, voting systems, and intellectual property management.
Exploring the Future of Blockchain Technology
As we continue to explore the potential of blockchain technology, we are witnessing numerous use cases and pilot projects that demonstrate its real-world applications. Here are some areas where blockchain technology is making a significant impact:
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology offers a transparent and traceable way to manage supply chains. With blockchain, companies can track and verify every step of the supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to delivery. This helps in ensuring the authenticity of products, preventing counterfeiting, and improving overall efficiency.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry can benefit greatly from blockchain technology. It allows for secure and efficient sharing of medical records, ensuring patient privacy while enabling seamless data exchange between healthcare providers. Additionally, blockchain can help in clinical research by securely storing and sharing medical data, leading to advancements in treatments and therapies.
Financial Services
Blockchain has already disrupted the financial industry with cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. It provides fast, secure, and low-cost transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as banks. Moreover, blockchain-based smart contracts enable automated and transparent financial agreements, reducing the complexity and costs associated with traditional financial systems.
Identity Management
Blockchain technology can transform the way identity verification is done. By providing a decentralized and tamper-proof system, blockchain can ensure the integrity of personal identities while giving individuals control over their own data. This can have significant implications for areas such as voting systems, digital identity verification, and secure online transactions.
How to obtain Blockchain Technology certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
- Emerging Technology: Blockchain
Conclusion
The power of blockchain technology lies in its ability to unlock new possibilities for the future. As we continue to explore its applications, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize industries, enhance security, and promote transparency. Whether it is supply chain management, healthcare, financial services, or identity management, blockchain technology is poised to reshape the way we conduct business and interact with digital assets. Embracing blockchain technology today will ensure a future that is secure, efficient, and decentralized.
Read More
Introduction
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing industries across the globe. With its decentralized nature and immutability, blockchain has the potential to transform the way we conduct business, manage data, and secure digital assets. In this article, we will explore the power of blockchain technology and unravel its immense potential to unlock new possibilities for the future.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Block chain technology is a distributed ledger system that allows for secure and transparent recording of transactions across multiple computers. In simple terms, it is a chain of blocks, where each block contains a set of transactions, and these blocks are linked together using cryptographic hashes.
The Power of Decentralization
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a single authority controls the data and transactions, blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries by allowing participants to directly interact with each other. This decentralized approach not only enhances security but also promotes trust and transparency in transactions.
Enhanced Security and Transparency
Blockchain technology uses advanced cryptographic techniques to ensure the security of data stored within its blocks. Each transaction is verified and recorded in a way that is resistant to tampering or modification. This makes blockchain an ideal solution for industries that require high levels of data security, such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
Unlocking New Business Models
Blockchain technology is not limited to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Its versatility enables the creation of smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), and even tokenized assets. These new business models open up avenues for innovation and disruption across various industries, including finance, real estate, voting systems, and intellectual property management.
Exploring the Future of Blockchain Technology
As we continue to explore the potential of blockchain technology, we are witnessing numerous use cases and pilot projects that demonstrate its real-world applications. Here are some areas where blockchain technology is making a significant impact:
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology offers a transparent and traceable way to manage supply chains. With blockchain, companies can track and verify every step of the supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to delivery. This helps in ensuring the authenticity of products, preventing counterfeiting, and improving overall efficiency.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry can benefit greatly from blockchain technology. It allows for secure and efficient sharing of medical records, ensuring patient privacy while enabling seamless data exchange between healthcare providers. Additionally, blockchain can help in clinical research by securely storing and sharing medical data, leading to advancements in treatments and therapies.
Financial Services
Blockchain has already disrupted the financial industry with cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. It provides fast, secure, and low-cost transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as banks. Moreover, blockchain-based smart contracts enable automated and transparent financial agreements, reducing the complexity and costs associated with traditional financial systems.
Identity Management
Blockchain technology can transform the way identity verification is done. By providing a decentralized and tamper-proof system, blockchain can ensure the integrity of personal identities while giving individuals control over their own data. This can have significant implications for areas such as voting systems, digital identity verification, and secure online transactions.
How to obtain Blockchain Technology certification?
We are an Education Technology company providing certification training courses to accelerate careers of working professionals worldwide. We impart training through instructor-led classroom workshops, instructor-led live virtual training sessions, and self-paced e-learning courses.
We have successfully conducted training sessions in 108 countries across the globe and enabled thousands of working professionals to enhance the scope of their careers.
Our enterprise training portfolio includes in-demand and globally recognized certification training courses in Project Management, Quality Management, Business Analysis, IT Service Management, Agile and Scrum, Cyber Security, Data Science, and Emerging Technologies. Download our Enterprise Training Catalog from https://www.icertglobal.com/corporate-training-for-enterprises.php
Popular Courses include:
- Project Management: PMP, CAPM ,PMI RMP
- Quality Management: Six Sigma Black Belt ,Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, Lean Management, Minitab,CMMI
- Business Analysis: CBAP, CCBA, ECBA
- Agile Training: PMI-ACP , CSM , CSPO
- Scrum Training: CSM
- DevOps
- Program Management: PgMP
- Cloud Technology: Exin Cloud Computing
- Citrix Client Adminisration: Citrix Cloud Administration
- Emerging Technology: Blockchain
Conclusion
The power of blockchain technology lies in its ability to unlock new possibilities for the future. As we continue to explore its applications, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize industries, enhance security, and promote transparency. Whether it is supply chain management, healthcare, financial services, or identity management, blockchain technology is poised to reshape the way we conduct business and interact with digital assets. Embracing blockchain technology today will ensure a future that is secure, efficient, and decentralized.
Unlock New Career Opportunities with CBAP Certification
Introduction
Are you looking to enhance your career as a business analyst? Do you want to stand out from the competition and unlock new opportunities in the field? Look no further than the Certified Business Analysis Professional Certification (CBAP). This prestigious certification not only validates your expertise and knowledge but also opens doors to exciting career advancements. In this article, we will explore what the CBAP certification is all about and how it can benefit aspiring business analysts like yourself.
What is the CBAP Certification?
The CBAP certification, also known as the Certified Business Analysis Professional Certification, is a globally recognized credential for business analysts. It is offered by the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA), the leading professional association for business analysts worldwide. This certification demonstrates your commitment to the field and showcases your proficiency in various business analysis tasks and techniques.
Benefits of the CBAP Certification
1. Enhanced Career Opportunities
Obtaining the CBAP certification can significantly enhance your career opportunities. Many organizations value and seek professionals who possess this esteemed credential. It distinguishes you from other candidates and increases your chances of securing high-level positions in the industry. This certification serves as proof of your skills, experience, and dedication to professional development.
2. Industry Recognition and Credibility
The CBAP certification is widely recognized in the business analysis community. It establishes your credibility as a professional business analyst, earning the trust of employers, clients, and colleagues alike. It demonstrates that you have met rigorous standards set by the IIBA and have the knowledge and expertise required to excel in the field.
3. Expanded Skill Set
Preparing for the CBAP certification requires you to delve deep into various aspects of business analysis. As a result, you gain an expanded skill set that covers essential areas such as requirements management, business analysis planning, stakeholder engagement, and solution evaluation. This comprehensive knowledge equips you to tackle complex business challenges and deliver effective solutions.
How to Become a CBAP
To become a CBAP, you must fulfill certain eligibility criteria and pass a rigorous examination. Here are the steps you need to follow:
Eligibility Criteria: You must have a minimum of 7,500 hours of business analysis experience in the past 10 years, along with a minimum of 900 hours across at least 4 of the 6 knowledge areas defined by the IIBA BABOK Guide. Additionally, you must have completed at least 35 hours of professional development in the field of business analysis.
Submit Your Application: Once you meet the eligibility criteria, you need to submit an application to the IIBA for review. This application includes details of your work experience, education, and professional development activities.
Prepare for the Examination: After your application is approved, you can start preparing for the CBAP examination. The examination tests your knowledge and comprehension of the BABOK Guide and assesses your ability to apply business analysis principles and techniques.
Pass the Examination: Passing the CBAP examination demonstrates your competence in business analysis. It signifies that you have the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in your role as a business analyst.
Maintain Your Certification: Once you have obtained your CBAP certification, you need to maintain it by earning Continuing Development Units (CDUs) every three years. This ensures that you stay up-to-date with evolving industry practices and trends.
Conclusion
The CBAP certification is much more than just a piece of paper. It is a testament to your expertise, commitment, and dedication to the field of business analysis. Unlocking new career opportunities becomes a reality as you showcase your skills and gain industry recognition. So, if you are an aspiring business analyst looking to take your career to new heights, consider pursuing the Certified Business Analysis Professional Certification. Take the leap and embrace the endless possibilities that await you!
Read More
Introduction
Are you looking to enhance your career as a business analyst? Do you want to stand out from the competition and unlock new opportunities in the field? Look no further than the Certified Business Analysis Professional Certification (CBAP). This prestigious certification not only validates your expertise and knowledge but also opens doors to exciting career advancements. In this article, we will explore what the CBAP certification is all about and how it can benefit aspiring business analysts like yourself.
What is the CBAP Certification?
The CBAP certification, also known as the Certified Business Analysis Professional Certification, is a globally recognized credential for business analysts. It is offered by the International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA), the leading professional association for business analysts worldwide. This certification demonstrates your commitment to the field and showcases your proficiency in various business analysis tasks and techniques.
Benefits of the CBAP Certification
1. Enhanced Career Opportunities
Obtaining the CBAP certification can significantly enhance your career opportunities. Many organizations value and seek professionals who possess this esteemed credential. It distinguishes you from other candidates and increases your chances of securing high-level positions in the industry. This certification serves as proof of your skills, experience, and dedication to professional development.
2. Industry Recognition and Credibility
The CBAP certification is widely recognized in the business analysis community. It establishes your credibility as a professional business analyst, earning the trust of employers, clients, and colleagues alike. It demonstrates that you have met rigorous standards set by the IIBA and have the knowledge and expertise required to excel in the field.
3. Expanded Skill Set
Preparing for the CBAP certification requires you to delve deep into various aspects of business analysis. As a result, you gain an expanded skill set that covers essential areas such as requirements management, business analysis planning, stakeholder engagement, and solution evaluation. This comprehensive knowledge equips you to tackle complex business challenges and deliver effective solutions.
How to Become a CBAP
To become a CBAP, you must fulfill certain eligibility criteria and pass a rigorous examination. Here are the steps you need to follow:
Eligibility Criteria: You must have a minimum of 7,500 hours of business analysis experience in the past 10 years, along with a minimum of 900 hours across at least 4 of the 6 knowledge areas defined by the IIBA BABOK Guide. Additionally, you must have completed at least 35 hours of professional development in the field of business analysis.
Submit Your Application: Once you meet the eligibility criteria, you need to submit an application to the IIBA for review. This application includes details of your work experience, education, and professional development activities.
Prepare for the Examination: After your application is approved, you can start preparing for the CBAP examination. The examination tests your knowledge and comprehension of the BABOK Guide and assesses your ability to apply business analysis principles and techniques.
Pass the Examination: Passing the CBAP examination demonstrates your competence in business analysis. It signifies that you have the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in your role as a business analyst.
Maintain Your Certification: Once you have obtained your CBAP certification, you need to maintain it by earning Continuing Development Units (CDUs) every three years. This ensures that you stay up-to-date with evolving industry practices and trends.
Conclusion
The CBAP certification is much more than just a piece of paper. It is a testament to your expertise, commitment, and dedication to the field of business analysis. Unlocking new career opportunities becomes a reality as you showcase your skills and gain industry recognition. So, if you are an aspiring business analyst looking to take your career to new heights, consider pursuing the Certified Business Analysis Professional Certification. Take the leap and embrace the endless possibilities that await you!
Unlocking Big Data's Power: Analytics Revolutionizing Industries
Introduction
In today's data-driven world, organizations are harnessing the power of big data analytics to revolutionize their operations and transform entire industries. With advancements in technology and the availability of vast amounts of data, the potential to extract valuable insights and drive meaningful change is greater than ever before. In this article, we will explore the ways in which big data analytics is unlocking the power of data and revolutionizing various sectors.
Big Data Analytics Revolution
Big data analytics refers to the process of examining large and complex data sets to uncover valuable patterns, trends, and insights. It involves utilizing advanced algorithms, statistical models, and data visualization techniques to extract meaningful information from structured and unstructured data. The purpose of big data analytics is to gain a better understanding of customer behavior, identify market trends, optimize business processes, and make data-driven decisions.
Unlocking Big Data Insights
By leveraging big data analytics, organizations can unlock valuable insights that were previously hidden within their data. These insights provide a deeper understanding of customer preferences, market dynamics, and operational inefficiencies. With access to such insights, businesses can make more informed decisions, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
One example of how big data analytics is uncovering insights is in the retail industry. Retailers can analyze customer purchase history, demographic data, and online behavior to identify patterns and preferences. This information can be used to personalize marketing campaigns, optimize product assortment, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Data-driven Industry Transformation
The power of big data analytics extends beyond individual organizations. It has the potential to transform entire industries by driving innovation, improving efficiencies, and creating new business models. Industries such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and transportation are already experiencing the impact of big data analytics.
In healthcare, for instance, big data analytics is being used to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and identify potential epidemics. By analyzing data from electronic health records, medical research, and wearable devices, healthcare providers can uncover insights that lead to personalized treatments, preventive care, and early detection of diseases.
Similarly, the finance industry is leveraging big data analytics to detect fraudulent activities, assess creditworthiness, and develop investment strategies. By analyzing vast amounts of financial data, organizations can make more accurate risk assessments, provide personalized financial advice, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Big Data Power in Industries
Almost every industry can benefit from the power of big data analytics. Let's explore how some of the major sectors are being revolutionized:
Retail:
-
Optimizing inventory management based on demand patterns.
-
Personalizing marketing campaigns to target specific customer segments.
-
Improving customer satisfaction through personalized recommendations.
Manufacturing:
-
Predictive maintenance, reducing downtime, and optimizing production schedules.
-
Enhancing product quality through real-time monitoring of manufacturing processes.
-
Streamlining supply chain operations and reducing costs.
Transportation:
-
Optimizing route planning and reducing fuel consumption.
-
Enhancing safety through predictive maintenance of vehicles and equipment.
-
Improving customer satisfaction through real-time tracking and delivery updates.
Healthcare:
-
Personalized treatments and preventive care.
-
Early detection of diseases through analysis of patient data.
-
Improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Analytics Revolutionizing Business
In today's fast-paced and competitive business landscape, organizations that can effectively harness the power of big data analytics have a significant advantage. By leveraging data insights, businesses can make better-informed decisions, drive innovation, and improve their overall bottom line.
With the advancements in technology, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, the potential for big data analytics to revolutionize businesses will continue to grow. Organizations that embrace this digital transformation and invest in analytics capabilities will be better equipped to thrive in the data-driven future.
Conclusion
Big data analytics is unlocking the power of data and revolutionizing industries across the board. Through the extraction of valuable insights, businesses can make data-driven decisions, drive innovation, and gain a competitive advantage. From retail to healthcare, manufacturing to transportation, the impact of big data analytics is profound. By embracing this transformative technology, organizations can position themselves at the forefront of their respective industries and thrive in the data-driven future.
Read More
Introduction
In today's data-driven world, organizations are harnessing the power of big data analytics to revolutionize their operations and transform entire industries. With advancements in technology and the availability of vast amounts of data, the potential to extract valuable insights and drive meaningful change is greater than ever before. In this article, we will explore the ways in which big data analytics is unlocking the power of data and revolutionizing various sectors.
Big Data Analytics Revolution
Big data analytics refers to the process of examining large and complex data sets to uncover valuable patterns, trends, and insights. It involves utilizing advanced algorithms, statistical models, and data visualization techniques to extract meaningful information from structured and unstructured data. The purpose of big data analytics is to gain a better understanding of customer behavior, identify market trends, optimize business processes, and make data-driven decisions.
Unlocking Big Data Insights
By leveraging big data analytics, organizations can unlock valuable insights that were previously hidden within their data. These insights provide a deeper understanding of customer preferences, market dynamics, and operational inefficiencies. With access to such insights, businesses can make more informed decisions, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
One example of how big data analytics is uncovering insights is in the retail industry. Retailers can analyze customer purchase history, demographic data, and online behavior to identify patterns and preferences. This information can be used to personalize marketing campaigns, optimize product assortment, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Data-driven Industry Transformation
The power of big data analytics extends beyond individual organizations. It has the potential to transform entire industries by driving innovation, improving efficiencies, and creating new business models. Industries such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and transportation are already experiencing the impact of big data analytics.
In healthcare, for instance, big data analytics is being used to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and identify potential epidemics. By analyzing data from electronic health records, medical research, and wearable devices, healthcare providers can uncover insights that lead to personalized treatments, preventive care, and early detection of diseases.
Similarly, the finance industry is leveraging big data analytics to detect fraudulent activities, assess creditworthiness, and develop investment strategies. By analyzing vast amounts of financial data, organizations can make more accurate risk assessments, provide personalized financial advice, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Big Data Power in Industries
Almost every industry can benefit from the power of big data analytics. Let's explore how some of the major sectors are being revolutionized:
Retail:
-
Optimizing inventory management based on demand patterns.
-
Personalizing marketing campaigns to target specific customer segments.
-
Improving customer satisfaction through personalized recommendations.
Manufacturing:
-
Predictive maintenance, reducing downtime, and optimizing production schedules.
-
Enhancing product quality through real-time monitoring of manufacturing processes.
-
Streamlining supply chain operations and reducing costs.
Transportation:
-
Optimizing route planning and reducing fuel consumption.
-
Enhancing safety through predictive maintenance of vehicles and equipment.
-
Improving customer satisfaction through real-time tracking and delivery updates.
Healthcare:
-
Personalized treatments and preventive care.
-
Early detection of diseases through analysis of patient data.
-
Improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Analytics Revolutionizing Business
In today's fast-paced and competitive business landscape, organizations that can effectively harness the power of big data analytics have a significant advantage. By leveraging data insights, businesses can make better-informed decisions, drive innovation, and improve their overall bottom line.
With the advancements in technology, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, the potential for big data analytics to revolutionize businesses will continue to grow. Organizations that embrace this digital transformation and invest in analytics capabilities will be better equipped to thrive in the data-driven future.
Conclusion
Big data analytics is unlocking the power of data and revolutionizing industries across the board. Through the extraction of valuable insights, businesses can make data-driven decisions, drive innovation, and gain a competitive advantage. From retail to healthcare, manufacturing to transportation, the impact of big data analytics is profound. By embracing this transformative technology, organizations can position themselves at the forefront of their respective industries and thrive in the data-driven future.
Unlocking Potential: Top Salesforce Trends for 2023!!!!
Introduction
In today's competitive business landscape, harnessing the power of technology is crucial for staying ahead of the curve. Sales force, a versatile and robust platform, offers a multitude of solutions to unlock the true potential of businesses. By leveraging the latest Salesforce trends, organizations can optimize their operations, drive customer engagement, and achieve unprecedented growth. In this article, we will explore the key trends in Salesforce and how businesses can unlock their potential through the platform's innovative solutions.
Salesforce Trends: Maximizing Potential Optimization
The Power of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Salesforce has integrated AI capabilities into its platform, enabling businesses to harness the power of data-driven insights. Through AI-powered predictive analytics, businesses can now unlock their potential by making smarter decisions and streamlining processes. By leveraging AI, organizations can track customer behavior, personalize experiences, and identify trends to proactively address customer needs. This trend not only enhances customer satisfaction but also boosts overall business performance.
Embracing Mobile CRM
With the rising reliance on mobile devices, Salesforce has taken the lead in delivering a seamless mobile experience for its users. The Salesforce mobile app allows businesses to unlock their potential by accessing critical information anytime, anywhere. This trend enables sales teams to be more agile, responsive, and productive on the go. By embracing mobile CRM, businesses can optimize their operations, enhance customer engagement, and drive revenue growth.
Salesforce Solutions: Unleashing Business Potential
Enhanced Customer Relationship Management
Salesforce offers a comprehensive suite of CRM solutions that enable businesses to optimize their customer relationships. By leveraging Salesforce's robust CRM functionalities, organizations can unlock their potential by effectively managing customer interactions, streamlining sales processes, and nurturing long-term customer loyalty. From lead generation to post-sales support, Salesforce provides businesses with the tools they need to maximize their customer relationships.
Automation and Workflow Optimization
In today's fast-paced business environment, automation plays a pivotal role in unlocking potential and driving efficiency. Salesforce's automation capabilities enable businesses to streamline repetitive tasks, optimize workflows, and improve overall productivity. By automating routine processes such as data entry, lead management, and reporting, organizations can free up valuable time and resources to focus on strategic initiatives. With Salesforce's workflow optimization features, businesses can unleash their true potential and achieve higher levels of operational excellence.
Advanced Analytics and Reporting
Data has become the lifeblood of businesses, and Salesforce empowers organizations to unlock their potential through advanced analytics and reporting capabilities. With Salesforce's intuitive reporting tools, businesses can gain actionable insights, track key performance indicators, and make data-driven decisions. By leveraging robust analytics, organizations can uncover hidden trends, identify opportunities, and optimize their strategies. Salesforce's advanced analytics and reporting solutions allow businesses to unlock the full potential of their data and drive success.
Conclusion
In an ever-evolving business landscape, unlocking the potential of Salesforce is essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive and thrive. By embracing the latest trends in Salesforce, organizations can optimize their operations, enhance customer relationships, and achieve unprecedented growth. From AI-powered analytics to seamless mobile CRM, Salesforce offers a wide range of solutions that enable businesses to unleash their true potential. By leveraging the power of Salesforce, organizations can embark on a transformative journey towards success and realize their goals. So, why wait? Unlock your potential with Salesforce today!
Read More
Introduction
In today's competitive business landscape, harnessing the power of technology is crucial for staying ahead of the curve. Sales force, a versatile and robust platform, offers a multitude of solutions to unlock the true potential of businesses. By leveraging the latest Salesforce trends, organizations can optimize their operations, drive customer engagement, and achieve unprecedented growth. In this article, we will explore the key trends in Salesforce and how businesses can unlock their potential through the platform's innovative solutions.
Salesforce Trends: Maximizing Potential Optimization
The Power of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Salesforce has integrated AI capabilities into its platform, enabling businesses to harness the power of data-driven insights. Through AI-powered predictive analytics, businesses can now unlock their potential by making smarter decisions and streamlining processes. By leveraging AI, organizations can track customer behavior, personalize experiences, and identify trends to proactively address customer needs. This trend not only enhances customer satisfaction but also boosts overall business performance.
Embracing Mobile CRM
With the rising reliance on mobile devices, Salesforce has taken the lead in delivering a seamless mobile experience for its users. The Salesforce mobile app allows businesses to unlock their potential by accessing critical information anytime, anywhere. This trend enables sales teams to be more agile, responsive, and productive on the go. By embracing mobile CRM, businesses can optimize their operations, enhance customer engagement, and drive revenue growth.
Salesforce Solutions: Unleashing Business Potential
Enhanced Customer Relationship Management
Salesforce offers a comprehensive suite of CRM solutions that enable businesses to optimize their customer relationships. By leveraging Salesforce's robust CRM functionalities, organizations can unlock their potential by effectively managing customer interactions, streamlining sales processes, and nurturing long-term customer loyalty. From lead generation to post-sales support, Salesforce provides businesses with the tools they need to maximize their customer relationships.
Automation and Workflow Optimization
In today's fast-paced business environment, automation plays a pivotal role in unlocking potential and driving efficiency. Salesforce's automation capabilities enable businesses to streamline repetitive tasks, optimize workflows, and improve overall productivity. By automating routine processes such as data entry, lead management, and reporting, organizations can free up valuable time and resources to focus on strategic initiatives. With Salesforce's workflow optimization features, businesses can unleash their true potential and achieve higher levels of operational excellence.
Advanced Analytics and Reporting
Data has become the lifeblood of businesses, and Salesforce empowers organizations to unlock their potential through advanced analytics and reporting capabilities. With Salesforce's intuitive reporting tools, businesses can gain actionable insights, track key performance indicators, and make data-driven decisions. By leveraging robust analytics, organizations can uncover hidden trends, identify opportunities, and optimize their strategies. Salesforce's advanced analytics and reporting solutions allow businesses to unlock the full potential of their data and drive success.
Conclusion
In an ever-evolving business landscape, unlocking the potential of Salesforce is essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive and thrive. By embracing the latest trends in Salesforce, organizations can optimize their operations, enhance customer relationships, and achieve unprecedented growth. From AI-powered analytics to seamless mobile CRM, Salesforce offers a wide range of solutions that enable businesses to unleash their true potential. By leveraging the power of Salesforce, organizations can embark on a transformative journey towards success and realize their goals. So, why wait? Unlock your potential with Salesforce today!
Mastering DevOps:Harmonizing Dev & Ops for Seamless Delivery
Introduction
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, organizations strive to deliver high-quality software at a rapid pace. This requires tight collaboration between development (Dev) and operations (Ops) teams. Enter DevOps, a set of practices that focuses on breaking down silos, improving communication, and streamlining processes. In this article, we will explore the concept of mastering DevOps, harmonizing Dev and Ops, and how it enables seamless delivery of software.
Mastering DevOps: What Does It Mean?
Mastering DevOps goes beyond just implementing a few tools or adopting specific practices. It is about creating a cultural shift within an organization, where Dev and Ops teams work together seamlessly, focusing on shared goals and delivering value to customers. It requires continuous learning, improvement, and embracing a mindset of collaboration and innovation.
Harmonizing Dev and Ops: The Key to Success
Key to the success of DevOps is harmonizing the traditionally separate Dev and Ops functions. This means breaking down the barriers and fostering a culture of collaboration, trust, and shared responsibility. Dev teams focus on developing features and applications, while Ops teams ensure stability, scalability, and reliability. By bringing these two functions together, organizations can eliminate inefficiencies and deliver software faster with fewer errors.
DevOps Practices for Seamless Delivery
To achieve seamless delivery of software, organizations should embrace key DevOps practices. Let's explore some of these practices:
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
CI/CD is a DevOps practice that involves regular integration of code changes and automated testing. This practice ensures that software is continuously built, tested, and deployed to production environments. By automating these processes, organizations can reduce the time to market, minimize manual errors, and establish a robust feedback loop for rapid iterations.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
IaC is a practice that involves managing and provisioning infrastructure through code, rather than manually configuring servers and environments. Using tools like Ansible, Chef, or Terraform, organizations can treat infrastructure configurations as code, enabling reproducibility, scalability, and version control. This approach allows for faster provisioning and eliminates the risk of manual configuration errors.
Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture involves breaking down large software applications into smaller, loosely coupled services. Each microservice focuses on a specific business capability and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. This approach enables organizations to iterate faster, innovate, and deploy changes without impacting the entire system.
Infrastructure Monitoring and Log Management
Monitoring infrastructure and application performance is critical for identifying issues and ensuring seamless delivery. With tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or ELK Stack, organizations can collect metrics, monitor resource utilization, and gain insights into system behavior. Effective log management also helps in troubleshooting and identifying root causes of issues, enabling proactive resolution.
The Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trust of Mastering DevOps
Mastering DevOps requires experience, expertise, authority, and trust. It is not something that can be achieved overnight. Organizations need to invest in training and upskilling their teams, provide opportunities for experimentation and learning, and empower individuals to take ownership. By mastering DevOps, organizations gain a competitive advantage, deliver value to customers faster, and foster a culture of innovation and collaboration.
Conclusion
DevOps is not just a buzzword, but a transformative approach to software development and delivery. By mastering DevOps and harmonizing Dev and Ops, organizations can achieve seamless delivery of software. The journey towards mastering DevOps requires embracing key practices, breaking down silos, and fostering a culture of collaboration and innovation. With continuous learning, improvement, and a focus on shared goals, organizations can unlock the full potential of DevOps and deliver high-quality software at a rapid pace.
Read More
Introduction
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, organizations strive to deliver high-quality software at a rapid pace. This requires tight collaboration between development (Dev) and operations (Ops) teams. Enter DevOps, a set of practices that focuses on breaking down silos, improving communication, and streamlining processes. In this article, we will explore the concept of mastering DevOps, harmonizing Dev and Ops, and how it enables seamless delivery of software.
Mastering DevOps: What Does It Mean?
Mastering DevOps goes beyond just implementing a few tools or adopting specific practices. It is about creating a cultural shift within an organization, where Dev and Ops teams work together seamlessly, focusing on shared goals and delivering value to customers. It requires continuous learning, improvement, and embracing a mindset of collaboration and innovation.
Harmonizing Dev and Ops: The Key to Success
Key to the success of DevOps is harmonizing the traditionally separate Dev and Ops functions. This means breaking down the barriers and fostering a culture of collaboration, trust, and shared responsibility. Dev teams focus on developing features and applications, while Ops teams ensure stability, scalability, and reliability. By bringing these two functions together, organizations can eliminate inefficiencies and deliver software faster with fewer errors.
DevOps Practices for Seamless Delivery
To achieve seamless delivery of software, organizations should embrace key DevOps practices. Let's explore some of these practices:
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
CI/CD is a DevOps practice that involves regular integration of code changes and automated testing. This practice ensures that software is continuously built, tested, and deployed to production environments. By automating these processes, organizations can reduce the time to market, minimize manual errors, and establish a robust feedback loop for rapid iterations.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
IaC is a practice that involves managing and provisioning infrastructure through code, rather than manually configuring servers and environments. Using tools like Ansible, Chef, or Terraform, organizations can treat infrastructure configurations as code, enabling reproducibility, scalability, and version control. This approach allows for faster provisioning and eliminates the risk of manual configuration errors.
Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture involves breaking down large software applications into smaller, loosely coupled services. Each microservice focuses on a specific business capability and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. This approach enables organizations to iterate faster, innovate, and deploy changes without impacting the entire system.
Infrastructure Monitoring and Log Management
Monitoring infrastructure and application performance is critical for identifying issues and ensuring seamless delivery. With tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or ELK Stack, organizations can collect metrics, monitor resource utilization, and gain insights into system behavior. Effective log management also helps in troubleshooting and identifying root causes of issues, enabling proactive resolution.
The Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trust of Mastering DevOps
Mastering DevOps requires experience, expertise, authority, and trust. It is not something that can be achieved overnight. Organizations need to invest in training and upskilling their teams, provide opportunities for experimentation and learning, and empower individuals to take ownership. By mastering DevOps, organizations gain a competitive advantage, deliver value to customers faster, and foster a culture of innovation and collaboration.
Conclusion
DevOps is not just a buzzword, but a transformative approach to software development and delivery. By mastering DevOps and harmonizing Dev and Ops, organizations can achieve seamless delivery of software. The journey towards mastering DevOps requires embracing key practices, breaking down silos, and fostering a culture of collaboration and innovation. With continuous learning, improvement, and a focus on shared goals, organizations can unlock the full potential of DevOps and deliver high-quality software at a rapid pace.
Unlocking Ethical Hacking: Use Digital Superpowers Right.
Introduction
In today's digital age, where cyber threats loom large, ethical hacking has emerged as a powerful tool to combat cybercrime. Ethical hackers, with their digital superpowers, play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information and protecting individuals and organizations from malicious attacks. However, ethical hacking must always be approached with responsibility and a strong sense of ethics. This article explores the world of ethical hacking, the importance of responsible hacking, and the role it plays in cybersecurity.
Ethical Hacking: An Overview
Ethical hacking, also known as penetration testing or white-hat hacking, involves systematically identifying vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, or applications. It is a legal and authorized practice aimed at assessing the security posture of an organization's digital infrastructure. Ethical hackers use their technical skills and knowledge to simulate real-world cyberattacks and exploit weaknesses, all with the goal of helping organizations strengthen their security measures.
Digital Superpowers: The Skills of an Ethical Hacker
To excel in the field of ethical hacking, one must possess a diverse range of digital superpowers. These powers include expertise in programming languages, network protocols, operating systems, and web applications. Ethical hackers must also have the ability to think outside the box, identify potential vulnerabilities, and exploit them in a controlled manner. They often use sophisticated tools and techniques, such as password cracking, social engineering, and vulnerability scanning, to uncover weaknesses in systems and networks.
Responsible Hacking: The Ethical Compass
While ethical hackers have the power to crack into systems, it is important to remember that power comes with responsibility. Responsible hacking is about conducting security assessments and penetration testing with integrity, ethics, and respect for the law. It means adhering to a strict code of conduct, obtaining proper authorization before performing any testing, and ensuring that any vulnerabilities discovered are reported promptly and confidentially to the organization. Responsible hackers prioritize the protection of sensitive data and strive to make the digital world a safer place.
The Importance of Hacking Responsibly in Cybersecurity
Hacking responsibly is more than just a moral duty; it is a critical component of effective cybersecurity. By uncovering vulnerabilities, ethical hackers help organizations identify and fix security weaknesses before malicious actors exploit them. This proactive approach to security can save organizations significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal trouble. Responsible hacking plays a crucial role in creating robust defense mechanisms and building resilience against cyber threats.
Conclusion
Ethical hacking, when used responsibly, serves as a powerful weapon in the fight against cybercrime. The digital superpowers of ethical hackers enable them to uncover vulnerabilities and protect individuals and organizations from malicious attacks. It is our ethical duty to ensure these superpowers are used responsibly, following a strict code of conduct and respecting the law. By embracing responsible hacking, we can create a safer digital world and unlock the full potential of ethical hacking in the realm of cybersecurity.
Read More
Introduction
In today's digital age, where cyber threats loom large, ethical hacking has emerged as a powerful tool to combat cybercrime. Ethical hackers, with their digital superpowers, play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information and protecting individuals and organizations from malicious attacks. However, ethical hacking must always be approached with responsibility and a strong sense of ethics. This article explores the world of ethical hacking, the importance of responsible hacking, and the role it plays in cybersecurity.
Ethical Hacking: An Overview
Ethical hacking, also known as penetration testing or white-hat hacking, involves systematically identifying vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, or applications. It is a legal and authorized practice aimed at assessing the security posture of an organization's digital infrastructure. Ethical hackers use their technical skills and knowledge to simulate real-world cyberattacks and exploit weaknesses, all with the goal of helping organizations strengthen their security measures.
Digital Superpowers: The Skills of an Ethical Hacker
To excel in the field of ethical hacking, one must possess a diverse range of digital superpowers. These powers include expertise in programming languages, network protocols, operating systems, and web applications. Ethical hackers must also have the ability to think outside the box, identify potential vulnerabilities, and exploit them in a controlled manner. They often use sophisticated tools and techniques, such as password cracking, social engineering, and vulnerability scanning, to uncover weaknesses in systems and networks.
Responsible Hacking: The Ethical Compass
While ethical hackers have the power to crack into systems, it is important to remember that power comes with responsibility. Responsible hacking is about conducting security assessments and penetration testing with integrity, ethics, and respect for the law. It means adhering to a strict code of conduct, obtaining proper authorization before performing any testing, and ensuring that any vulnerabilities discovered are reported promptly and confidentially to the organization. Responsible hackers prioritize the protection of sensitive data and strive to make the digital world a safer place.
The Importance of Hacking Responsibly in Cybersecurity
Hacking responsibly is more than just a moral duty; it is a critical component of effective cybersecurity. By uncovering vulnerabilities, ethical hackers help organizations identify and fix security weaknesses before malicious actors exploit them. This proactive approach to security can save organizations significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal trouble. Responsible hacking plays a crucial role in creating robust defense mechanisms and building resilience against cyber threats.
Conclusion
Ethical hacking, when used responsibly, serves as a powerful weapon in the fight against cybercrime. The digital superpowers of ethical hackers enable them to uncover vulnerabilities and protect individuals and organizations from malicious attacks. It is our ethical duty to ensure these superpowers are used responsibly, following a strict code of conduct and respecting the law. By embracing responsible hacking, we can create a safer digital world and unlock the full potential of ethical hacking in the realm of cybersecurity.
Unlocking the Power of Python: A Programmer's Guide to Success
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, Python has emerged as a programming language of immense power and versatility. As a programmer, understanding and harnessing the full potential of Python can be the key to achieving success in your career. In this article, we will delve into the world of Python programming, exploring essential tips, techniques, and best practices that will elevate your coding skills and propel you towards professional excellence.
Python Programming: A Pathway to Success
Python, known for its simplicity and readability, has become the language of choice for programmers across various domains. However, unlocking its true power requires more than just a surface level understanding. By deepening your knowledge and honing your skills, you can leverage Python to build robust applications, automate repetitive tasks, and solve complex problems with elegance and efficiency.
Python Tips for Beginners
For those new to Python, it is important to start with a strong foundation. Here are some valuable tips to kickstart your journey:
Take advantage of Python's extensive documentation: Python offers comprehensive documentation that serves as an invaluable resource for beginners. Exploring the official documentation will help you to gain a deeper understanding of the language and its vast array of libraries and modules.
Immerse yourself in Python communities: Engaging with fellow Python enthusiasts through online forums, communities, and social media platforms can open doors to new learning opportunities. Participating in discussions and seeking guidance from experienced programmers will accelerate your growth.
Practice, practice, practice: Like any skill, programming requires practice. Challenge yourself with coding exercises and projects to reinforce your understanding of Python concepts and improve your problem-solving abilities.
Unlocking the Power of Python
Python's strength lies in its versatility and the wide range of applications it supports. Whether you are aspiring to enter the field of data science, web development, or artificial intelligence, Python offers tools and libraries to support your ambitions.
Python for Data Science
Python's rich ecosystem of libraries such as NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib empowers data scientists to manipulate, analyze, and visualize large datasets efficiently. From data preprocessing and exploratory data analysis to building predictive models, Python provides a seamless workflow for data-driven insights.
Python for Web Development
With frameworks like Flask and Django, Python enables web developers to build scalable and dynamic web applications. The simplicity of Python syntax, coupled with its robust libraries, simplifies the process of creating feature-rich web experiences.
Python for Artificial Intelligence
Python has gained significant traction within the field of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch provide a high-level interface for building and deploying sophisticated neural networks. Python's ease of use and expressive syntax make it an ideal choice for AI enthusiasts, enabling them to unlock the potential of cutting-edge technologies.
Best Practices for Python Coding and Development
To truly harness the power of Python, it is crucial to adhere to best practices that promote code readability, maintainability, and efficiency. Here are some recommended techniques to level up your Python coding skills:
Follow PEP 8 guidelines: PEP 8 is a set of guidelines that outlines the best coding practices for Python. Adhering to PEP 8 ensures consistency in your codebase and enhances its readability.
Use descriptive variable and function names: Meaningful names for variables and functions improve code comprehension, making it easier for others (or your future self) to understand and maintain your code.
Dive into object-oriented programming: Python supports object-oriented programming, which provides a structured approach to software development. Understanding and leveraging object-oriented principles can make your code more modular and reusable.
Make use of virtual environments: Virtual environments are isolated Python environments that allow you to manage and segregate project dependencies. Embracing virtual environments ensures project stability and avoids conflicts between packages.
Mastering Python: Keys to Success
To truly master Python, it is crucial to embrace continuous learning and remain open to acquiring new skills and knowledge. As Python continues to evolve, staying updated with the latest libraries, frameworks, and techniques is essential.
Resources for Ongoing Learning
Online tutorials and courses: Numerous online platforms offer comprehensive tutorials and courses on Python. These resources provide structured learning paths, guiding you through the intricacies of the language at your own pace.
Open-source projects: Contributing to open-source projects not only enhances your coding skills but also allows you to collaborate with experienced developers and gain real-world experience.
Attend conferences and meetups: Attending Python conferences and meetups provides unique opportunities to connect with experts in the field, expand your network, and stay abreast of the latest trends and advancements.
Conclusion
Python's power lies not only in its syntax but also in its ability to empower programmers to create remarkable applications and solve complex problems. By unlocking the full potential of Python through continuous learning, best practices, and practical application, you can set yourself on a path towards programming success. Embrace the versatility and elegance of Python, and prepare to embark on an exciting journey of exploration and accomplishment.
Read More
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, Python has emerged as a programming language of immense power and versatility. As a programmer, understanding and harnessing the full potential of Python can be the key to achieving success in your career. In this article, we will delve into the world of Python programming, exploring essential tips, techniques, and best practices that will elevate your coding skills and propel you towards professional excellence.
Python Programming: A Pathway to Success
Python, known for its simplicity and readability, has become the language of choice for programmers across various domains. However, unlocking its true power requires more than just a surface level understanding. By deepening your knowledge and honing your skills, you can leverage Python to build robust applications, automate repetitive tasks, and solve complex problems with elegance and efficiency.
Python Tips for Beginners
For those new to Python, it is important to start with a strong foundation. Here are some valuable tips to kickstart your journey:
Take advantage of Python's extensive documentation: Python offers comprehensive documentation that serves as an invaluable resource for beginners. Exploring the official documentation will help you to gain a deeper understanding of the language and its vast array of libraries and modules.
Immerse yourself in Python communities: Engaging with fellow Python enthusiasts through online forums, communities, and social media platforms can open doors to new learning opportunities. Participating in discussions and seeking guidance from experienced programmers will accelerate your growth.
Practice, practice, practice: Like any skill, programming requires practice. Challenge yourself with coding exercises and projects to reinforce your understanding of Python concepts and improve your problem-solving abilities.
Unlocking the Power of Python
Python's strength lies in its versatility and the wide range of applications it supports. Whether you are aspiring to enter the field of data science, web development, or artificial intelligence, Python offers tools and libraries to support your ambitions.
Python for Data Science
Python's rich ecosystem of libraries such as NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib empowers data scientists to manipulate, analyze, and visualize large datasets efficiently. From data preprocessing and exploratory data analysis to building predictive models, Python provides a seamless workflow for data-driven insights.
Python for Web Development
With frameworks like Flask and Django, Python enables web developers to build scalable and dynamic web applications. The simplicity of Python syntax, coupled with its robust libraries, simplifies the process of creating feature-rich web experiences.
Python for Artificial Intelligence
Python has gained significant traction within the field of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch provide a high-level interface for building and deploying sophisticated neural networks. Python's ease of use and expressive syntax make it an ideal choice for AI enthusiasts, enabling them to unlock the potential of cutting-edge technologies.
Best Practices for Python Coding and Development
To truly harness the power of Python, it is crucial to adhere to best practices that promote code readability, maintainability, and efficiency. Here are some recommended techniques to level up your Python coding skills:
Follow PEP 8 guidelines: PEP 8 is a set of guidelines that outlines the best coding practices for Python. Adhering to PEP 8 ensures consistency in your codebase and enhances its readability.
Use descriptive variable and function names: Meaningful names for variables and functions improve code comprehension, making it easier for others (or your future self) to understand and maintain your code.
Dive into object-oriented programming: Python supports object-oriented programming, which provides a structured approach to software development. Understanding and leveraging object-oriented principles can make your code more modular and reusable.
Make use of virtual environments: Virtual environments are isolated Python environments that allow you to manage and segregate project dependencies. Embracing virtual environments ensures project stability and avoids conflicts between packages.
Mastering Python: Keys to Success
To truly master Python, it is crucial to embrace continuous learning and remain open to acquiring new skills and knowledge. As Python continues to evolve, staying updated with the latest libraries, frameworks, and techniques is essential.
Resources for Ongoing Learning
Online tutorials and courses: Numerous online platforms offer comprehensive tutorials and courses on Python. These resources provide structured learning paths, guiding you through the intricacies of the language at your own pace.
Open-source projects: Contributing to open-source projects not only enhances your coding skills but also allows you to collaborate with experienced developers and gain real-world experience.
Attend conferences and meetups: Attending Python conferences and meetups provides unique opportunities to connect with experts in the field, expand your network, and stay abreast of the latest trends and advancements.
Conclusion
Python's power lies not only in its syntax but also in its ability to empower programmers to create remarkable applications and solve complex problems. By unlocking the full potential of Python through continuous learning, best practices, and practical application, you can set yourself on a path towards programming success. Embrace the versatility and elegance of Python, and prepare to embark on an exciting journey of exploration and accomplishment.
Apple's Chatbot May Boost the Generative A.I. Market
Introduction:
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized various industries, and Apple's recent foray into the chatbot space is no exception. With their impeccable track record of innovation and cutting-edge technology, Apple's entry into the chatbot arena has the potential to significantly boost the generative AI market. In this article, we will explore the implications of Apple's new venture and its impact on the market while highlighting the key benefits and challenges it brings.
Apple: Pioneering the Way
Chatbot Revolution
Apple has always been at the forefront of technological advancements, and their latest focus on chatbots highlights their commitment to enhancing user experience. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and harnessing natural language processing capabilities, Apple's chatbot aims to provide users with an intuitive and seamless interaction platform. With the ability to understand human language and offer contextual responses, these chatbots have the potential to transform the way we communicate with technology.
Generative AI Market
The generative AI market has been steadily growing, with companies recognizing the immense potential of AI-driven chatbots in enhancing customer service, driving sales, and improving overall operational efficiencies. By harnessing the power of generative AI, companies can automate repetitive tasks, provide personalized recommendations, and deliver round-the-clock customer support. The market is ripe with opportunities, and Apple's entry is expected to accelerate its growth even further.
The Benefits of Apple's Chatbot
Apple's foray into the chatbot space brings several key benefits to both users and businesses alike.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Apple's chatbot leverages generative AI to provide highly personalized and contextually relevant responses, offering users an enhanced customer experience. By understanding user preferences, purchasing history, and browsing patterns, the chatbot can deliver tailored recommendations, address queries, and even anticipate user needs. This level of personalization fosters a stronger bond between the brand and its customers, leading to increased customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Streamlined Business Processes
Integrating chatbots into business operations can streamline various processes, including customer support, order processing, and lead generation. With Apple's chatbot, businesses can automate repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on more value-added activities. Moreover, the chatbot can handle multiple customer queries simultaneously, drastically reducing response times and improving overall efficiency.
Cost Savings
By automating customer interactions through chatbots, businesses can significantly reduce customer service costs. With chatbots available 24/7, there is no need for an extensive customer support team, saving businesses both time and money. Additionally, chatbots can handle a high volume of queries simultaneously, ensuring prompt and efficient service at a fraction of the cost of human agents.
Challenges to Overcome
While Apple's chatbot holds immense potential, there are a few challenges that need to be addressed.
Data Privacy and Security
As chatbots interact and handle user data, ensuring data privacy and security is of paramount importance. Apple has built a strong reputation for safeguarding user privacy, and it will be crucial for them to maintain this trust as they venture into the chatbot space. Stricter regulations and robust security measures will be essential to address concerns surrounding data collection and usage.
Natural Language Understanding
The success of chatbots hinges on their ability to comprehend and respond accurately to human language. Understanding the nuances of human conversation, including idioms, colloquialisms, and cultural references, requires sophisticated natural language processing capabilities. Apple will need to continually refine their chatbot's language understanding abilities to provide an exceptional user experience.
Integration with Existing Systems
For businesses, integrating chatbots seamlessly with existing systems and processes can be a complex undertaking. Apple's chatbot will need to be compatible with various platforms, such as web and mobile applications, CRM systems, and e-commerce platforms. Strong partnerships and robust integration frameworks will be crucial to ensure a smooth implementation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Apple's entry into the chatbot market has the potential to not just boost the generative AI market but also transform the way we interact with technology. With enhanced customer experiences, streamlined business processes, and cost savings, chatbots offer a myriad of benefits. However, challenges related to data privacy, natural language understanding, and system integration must be addressed to fully capitalize on this technology's potential. As Apple continues to innovate and refine their chatbot, we can expect exciting developments that will shape the future of AI-driven interactions.
Read More
Introduction:
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized various industries, and Apple's recent foray into the chatbot space is no exception. With their impeccable track record of innovation and cutting-edge technology, Apple's entry into the chatbot arena has the potential to significantly boost the generative AI market. In this article, we will explore the implications of Apple's new venture and its impact on the market while highlighting the key benefits and challenges it brings.
Apple: Pioneering the Way
Chatbot Revolution
Apple has always been at the forefront of technological advancements, and their latest focus on chatbots highlights their commitment to enhancing user experience. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and harnessing natural language processing capabilities, Apple's chatbot aims to provide users with an intuitive and seamless interaction platform. With the ability to understand human language and offer contextual responses, these chatbots have the potential to transform the way we communicate with technology.
Generative AI Market
The generative AI market has been steadily growing, with companies recognizing the immense potential of AI-driven chatbots in enhancing customer service, driving sales, and improving overall operational efficiencies. By harnessing the power of generative AI, companies can automate repetitive tasks, provide personalized recommendations, and deliver round-the-clock customer support. The market is ripe with opportunities, and Apple's entry is expected to accelerate its growth even further.
The Benefits of Apple's Chatbot
Apple's foray into the chatbot space brings several key benefits to both users and businesses alike.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Apple's chatbot leverages generative AI to provide highly personalized and contextually relevant responses, offering users an enhanced customer experience. By understanding user preferences, purchasing history, and browsing patterns, the chatbot can deliver tailored recommendations, address queries, and even anticipate user needs. This level of personalization fosters a stronger bond between the brand and its customers, leading to increased customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Streamlined Business Processes
Integrating chatbots into business operations can streamline various processes, including customer support, order processing, and lead generation. With Apple's chatbot, businesses can automate repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on more value-added activities. Moreover, the chatbot can handle multiple customer queries simultaneously, drastically reducing response times and improving overall efficiency.
Cost Savings
By automating customer interactions through chatbots, businesses can significantly reduce customer service costs. With chatbots available 24/7, there is no need for an extensive customer support team, saving businesses both time and money. Additionally, chatbots can handle a high volume of queries simultaneously, ensuring prompt and efficient service at a fraction of the cost of human agents.
Challenges to Overcome
While Apple's chatbot holds immense potential, there are a few challenges that need to be addressed.
Data Privacy and Security
As chatbots interact and handle user data, ensuring data privacy and security is of paramount importance. Apple has built a strong reputation for safeguarding user privacy, and it will be crucial for them to maintain this trust as they venture into the chatbot space. Stricter regulations and robust security measures will be essential to address concerns surrounding data collection and usage.
Natural Language Understanding
The success of chatbots hinges on their ability to comprehend and respond accurately to human language. Understanding the nuances of human conversation, including idioms, colloquialisms, and cultural references, requires sophisticated natural language processing capabilities. Apple will need to continually refine their chatbot's language understanding abilities to provide an exceptional user experience.
Integration with Existing Systems
For businesses, integrating chatbots seamlessly with existing systems and processes can be a complex undertaking. Apple's chatbot will need to be compatible with various platforms, such as web and mobile applications, CRM systems, and e-commerce platforms. Strong partnerships and robust integration frameworks will be crucial to ensure a smooth implementation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Apple's entry into the chatbot market has the potential to not just boost the generative AI market but also transform the way we interact with technology. With enhanced customer experiences, streamlined business processes, and cost savings, chatbots offer a myriad of benefits. However, challenges related to data privacy, natural language understanding, and system integration must be addressed to fully capitalize on this technology's potential. As Apple continues to innovate and refine their chatbot, we can expect exciting developments that will shape the future of AI-driven interactions.





.jpg)


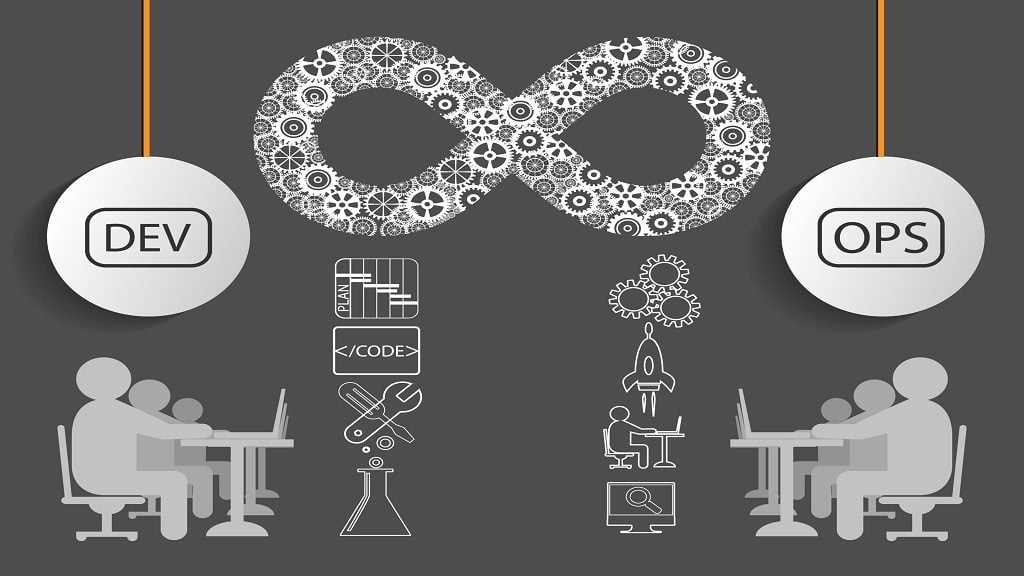



.jpg)





.png)
.jpg)
 [MConverter.eu] (1).jpg)
 [MConverter.eu].jpg)





 [MConverter.eu].jpg)

























.webp)
.png)